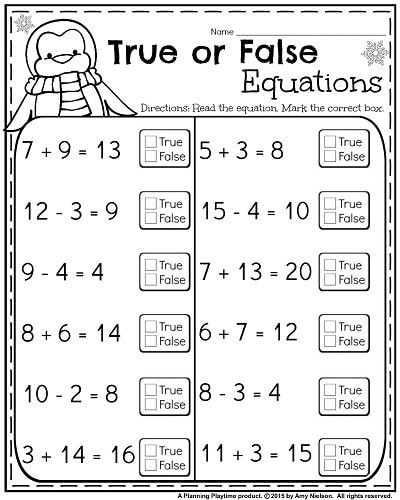
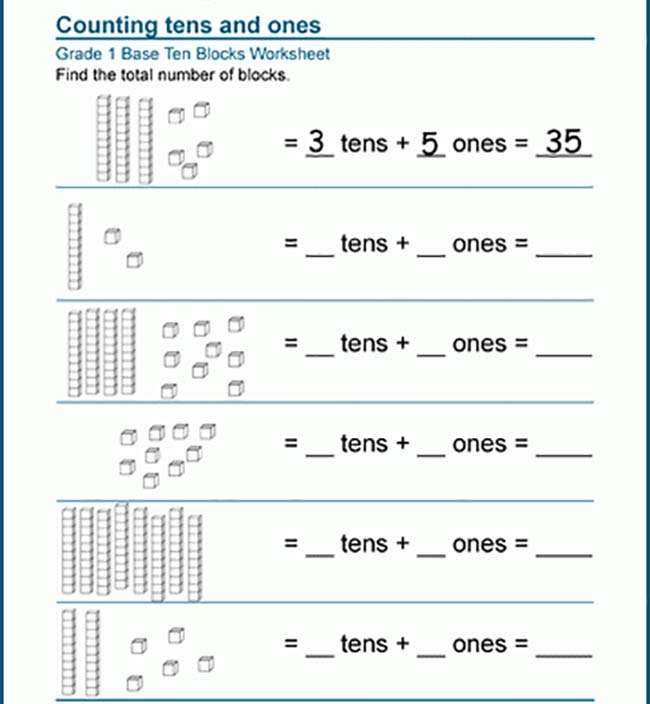
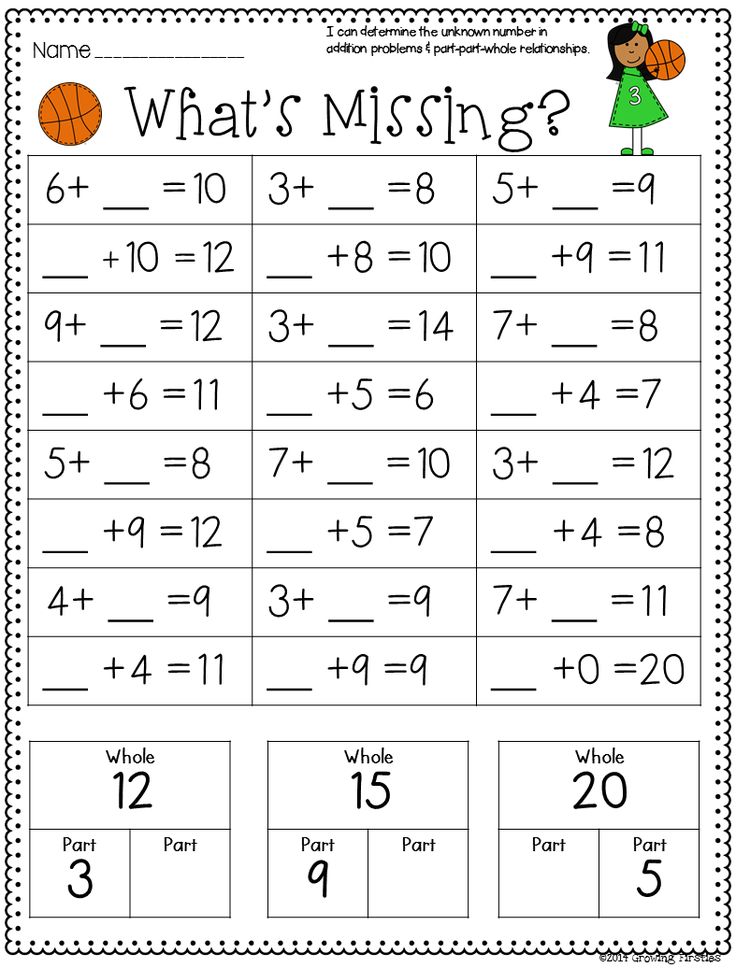
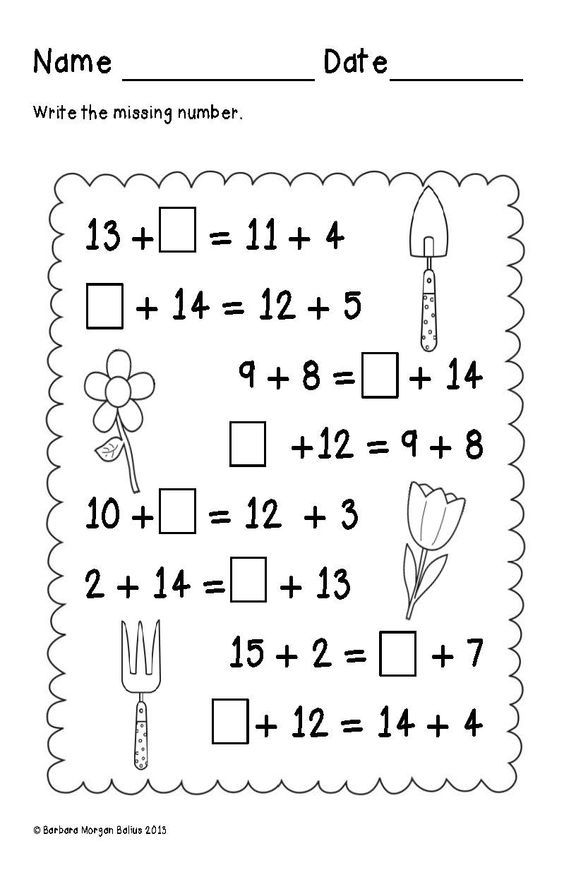
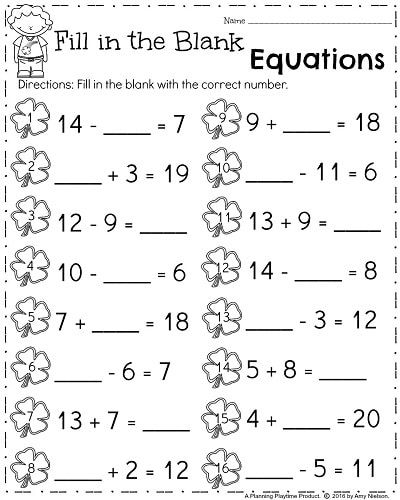
Math equations for first graders
1st Grade Math Worksheets
Rich with scads of practice, the CCSS aligned printable 1st grade math worksheets with answer keys help kids solve addition and subtraction problems within 20, extend their counting sequence, understand place value and number systems, measure length and compare sizes, tell time, count money, represent and interpret data, and know the attributes of 2D and 3D shapes in geometry. Our free math worksheets for grade 1 kids give you a peek into what's in store!
All
Addition
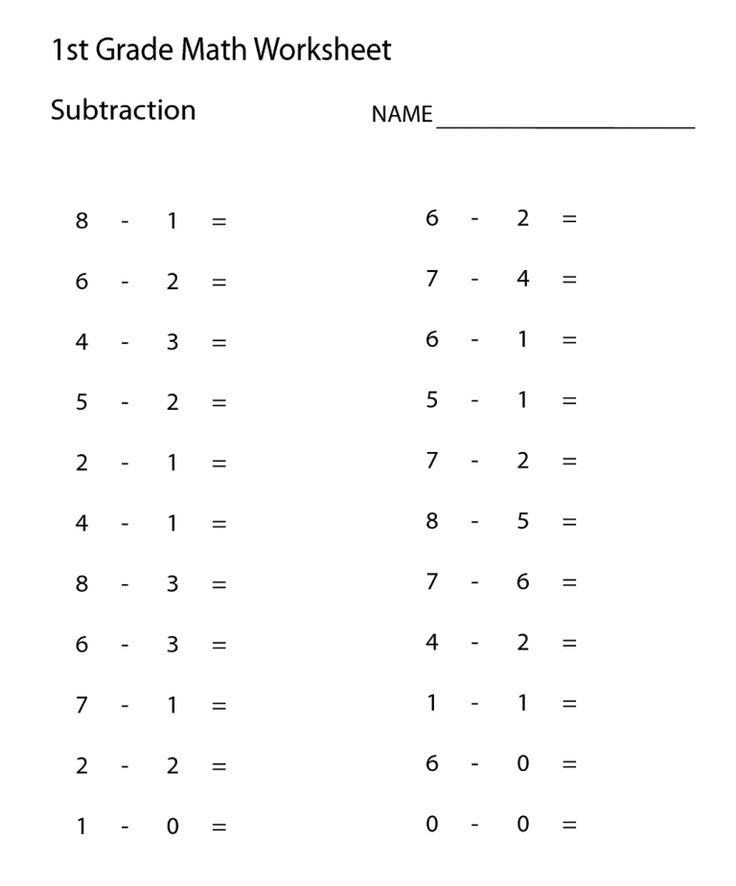
Subtraction
Patterns
Counting
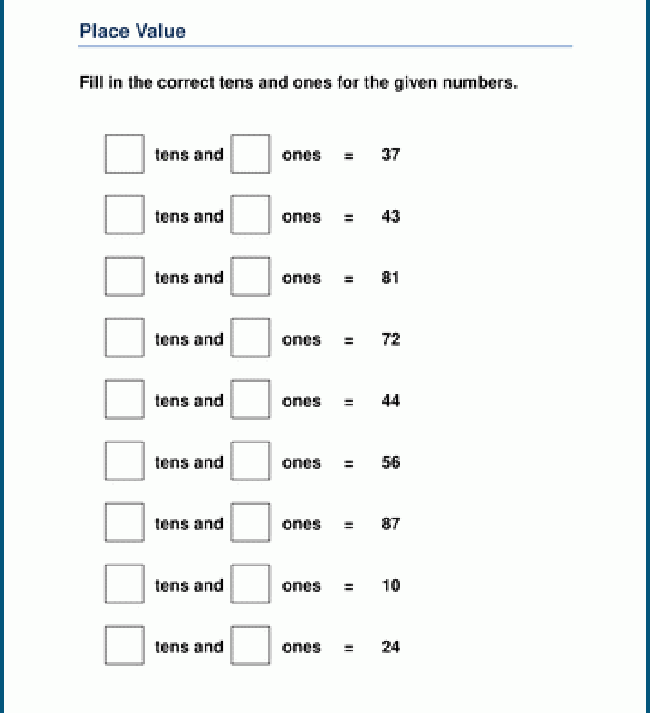
Place Value
Number System
Measurement
Time
Money
Data & Graphs
Geometry
Explore 2,200+ First Grade Math Worksheets
Counting and Adding Pictures
The pictures in two groups present a fascinating array of addition equations for 1st grade kids. Count the pictures in the two groups separately, and then combine the two to find the total number.
Subtracting on Number Lines | 0 to 10
Get the little hoppers to draw hops on the number lines in these printable grade 1 math worksheets and complete the subtraction equations involving numbers up to 10.
Identifying the Next Picture in a Repeating Pattern
Develop pattern awareness in kids with this set of pdf worksheets. Study the pattern, identify the pattern's core or terms that repeat in the same order and make a logical prediction of what comes next.
Reading and Writing Numbers from 1 to 25
Fluency with numbers is vital in first grade math. Task kids to look at the top of this printable chart, identify and read the numbers from 1 to 25 repeatedly, and copy them to complete the table.
Base Ten Blocks | Tens and Ones
Visualizing numbers is easy with place value blocks or base-10 blocks. Get kids to count the units and rods in the base-10 blocks and write the base-10 numerals.
Identifying Greater and Smaller 2-Digit Numbers
Cracking these 1st grade math worksheet pdfs is a true measure of your place value skills.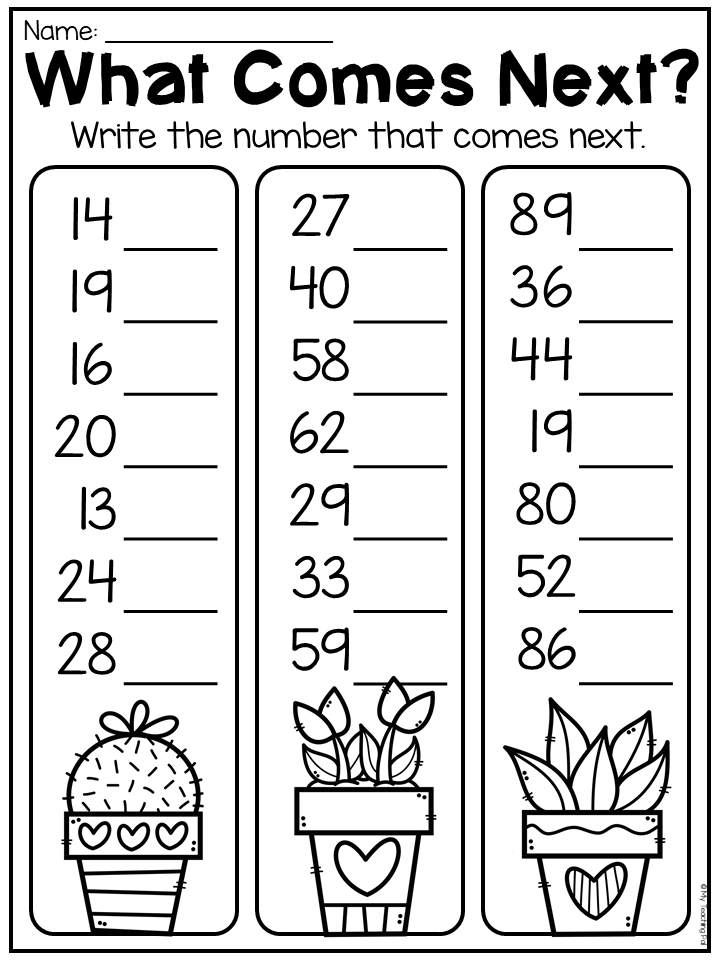 Compare 2-digit numbers using symbols in Part A. Circle the greater number in Part B, and the smaller number in Part C.
Compare 2-digit numbers using symbols in Part A. Circle the greater number in Part B, and the smaller number in Part C.
Ordering Objects from the Shortest to the Longest
Arranging objects of three different sizes from the shortest to the longest, numbering them 1, 2, and 3 respectively, is all that is expected of grade 1 kids.
Telling Time | Hourly Increment
With these pdf math worksheets for grade 1 kids at your disposal, the time is ripe to practice reading clocks to tell the time in whole hours, and choosing the clock face that depicts the specified time.
Counting Dimes
Develop skills in counting the dimes and expressing the amount in dollars, trading dimes for dollars, and converting between them in word problems with this compilation of first grade math worksheet pdfs.
Counting Tally Marks
Let's travel back in time and practice counting using tally marks.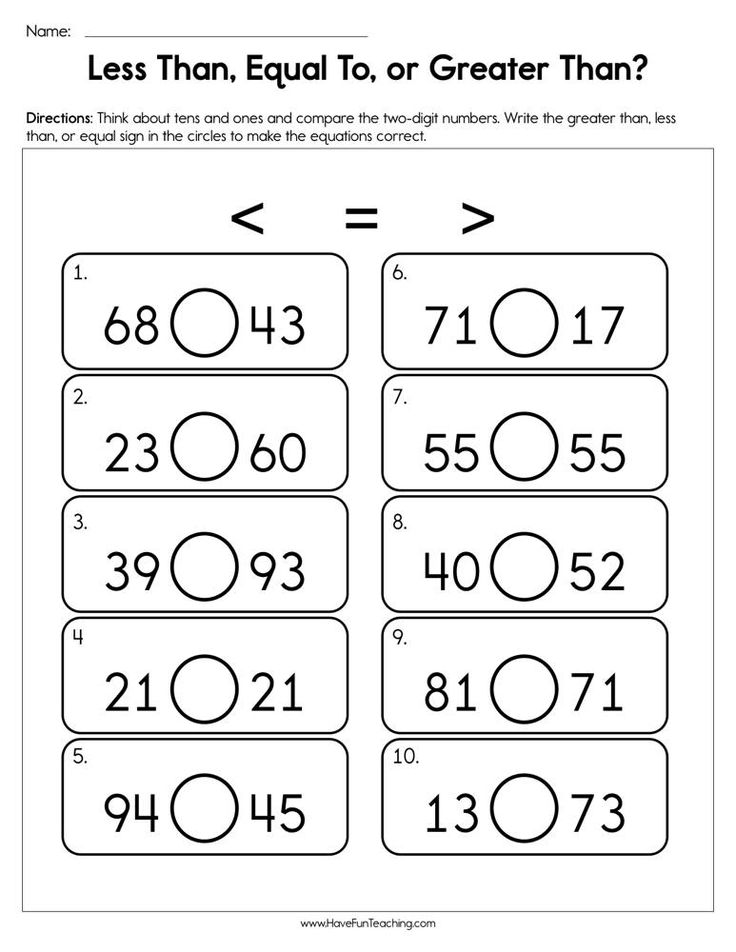 First grade kids have a blast reading and counting each set of tally marks and writing the value it represents.
First grade kids have a blast reading and counting each set of tally marks and writing the value it represents.
Identifying 2D Shapes | MCQ
Can the little architects of grade 1 distinguish between a rectangle and a square? Watch them recognize the two-dimensional figures and check the appropriate option that best describes each.
Number Line Addition | 0 to 10
This stack of 1st grade math worksheets has pre-drawn hops on the number lines. The starting-point of the hops, and the number of hops are the two addends and the endpoint is the sum.
Writing Subtraction Equations from Number Lines | 0 to 10
Examine the hops on the number line; identify the minuend, subtrahend, and the difference. Once this is done, completing the subtraction sentence is not a hard nut to crack!
Repeating Patterns | Cut and Glue Activity
Add a spark of fun with repeating picture patterns in this bundle of printable math worksheets for 1st grade kids.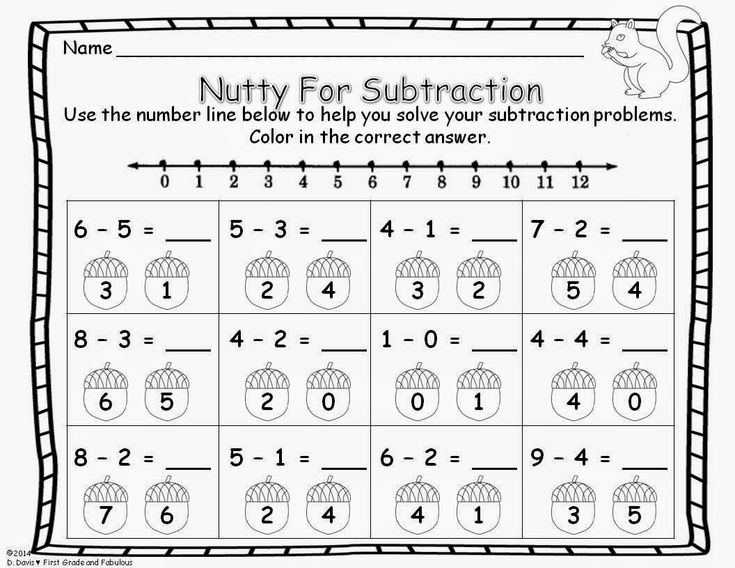 Comprehend the pattern, cut out the graphics and glue the one that comes next in order.
Comprehend the pattern, cut out the graphics and glue the one that comes next in order.
Display Chart - Numbers 1 to 25 | Theme based
The crawling number snails get kids to instantly memorize numerals from 1 to 25. This show-and-tell chart comprising snails-shells inscribed with numbers is a compulsive-print.
Next »
1st Grade Math Worksheets
Share to PinterestPinterestShare to FacebookFacebookShare to PocketPocketShare to TwitterTwitterShare to EmailEmailShare to FlipboardFlipboardWorksheets
Printables
PuzzlesT-Shirts
Math Worksheets
Go Ad Free!
Core Math Worksheets
Fraction Worksheets
Word Problems
Algebra
Other Worksheets
Measurement & Conversions
Patterns and Puzzles
Color by Number
Holiday & Seasonal
Early Learning
Printables
Calculators
Math Worksheets by Grade
Worksheet News
Base 10 Blocks
Base ten blocks worksheets that teach basic addition, subtraction, number sense and place value using visual representations of quantity.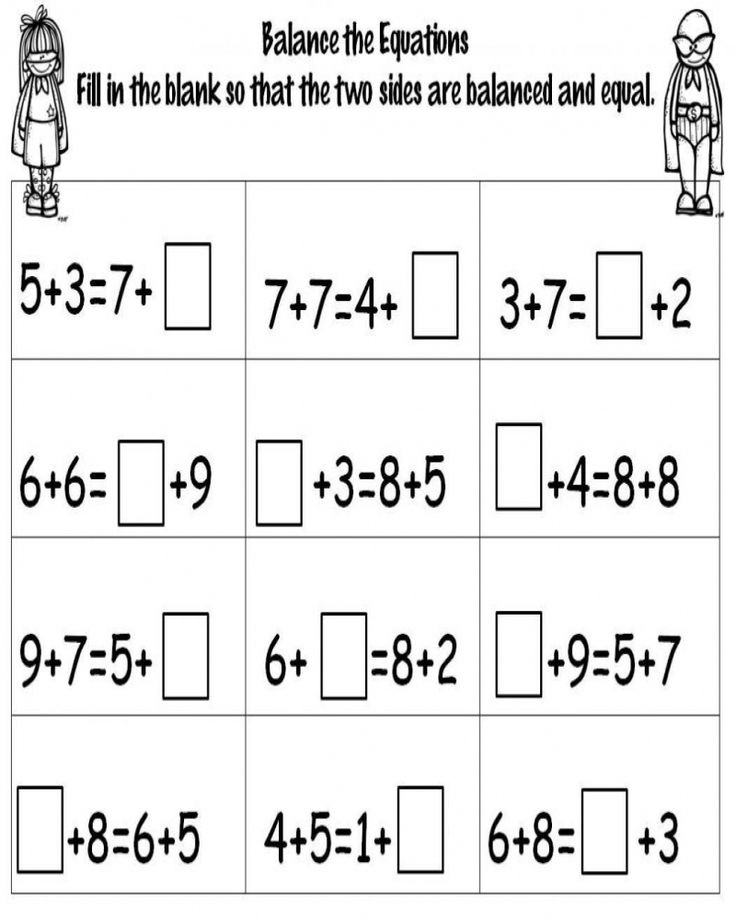 Get your first grade student started with these basic math skill worksheets!
Get your first grade student started with these basic math skill worksheets!
Base 10 Blocks
Addition Worksheets
This is the main page for the addition worksheets. Follow the links for Spaceship Math Addition worksheets, multiple digit addition worksheets, no-carrying addition worksheets and other addition topics. These addition worksheets are free for personal or classroom use.
Addition Worksheets
Subtraction Worksheets
This is the main page for the subtraction worksheets. Follow the links for Spaceship Math Subtraction worksheets, timed subtraction tests, multiple digit subtraction worksheets, simple borrowing and regrouping worksheets, and math worksheets with mixed addition and subtraction problems
Subtraction Worksheets
Fact Family Worksheets
Fact family worksheets focus on sets of related math facts, not specific operations. Teach your kids addition and subtraction at the same time, and reinforce the relationships in a fact family! Two fact families are introduced at each level and allow for progressive practice, or just use the worksheets at the end for comprehensive fact family review.
Teach your kids addition and subtraction at the same time, and reinforce the relationships in a fact family! Two fact families are introduced at each level and allow for progressive practice, or just use the worksheets at the end for comprehensive fact family review.
Fact Family Worksheets
Ordering Numbers
Practice ordering numbers worksheets for with multiple numbers in ascending (greatest to least) and descending (least to greatest) orders. Includes whole numbers, decimal numbers and negative numbers. Similar sets of ordering numbers worksheets are presented in both horizontal and vertical formats.
Ordering Numbers
Printable Flash Cards
This page contains free printable flash cards for each math operation. Print the 'worksheet' on the front, then turn the page over and print the 'answer key' version on the back. Some sets have duplicate facts for the more difficult problems near the end so that the sets end up on a multiple of pages. Those cards are clearly marked as duplicates... use them for extra practice on the harder problems, or put them aside if you want a set with only one flash card for each math fact.
Those cards are clearly marked as duplicates... use them for extra practice on the harder problems, or put them aside if you want a set with only one flash card for each math fact.
Printable Flash Cards
Hundreds Chart
Every hundreds chart you could imagine! If you're teaching basic counting, number sense, rounding or the basics of arithmetic, you can use a number chart like one of these to speed up building math skills.
Hundreds Chart
Place Value Chart
This page has printable place value charts. In the decimal numbering system, the position (or 'place') of an individual digit in a number determines its value relative to other digits. When a number is written in standard form with groups of three place values separated by commas, each of those groups is called a period. Building number sense by understanding place values is an important early math skill, and these place value charts provide a way to break numbers down to better understand the significane of each digit. There are place value chart variations for whole numbers only, decimal numbers, and very large numbers. There are different place value chart layouts that reinforce just the place value as well as the period value.
There are place value chart variations for whole numbers only, decimal numbers, and very large numbers. There are different place value chart layouts that reinforce just the place value as well as the period value.
Place Value Chart
Telling Analog Time
Practice worksheets for telling analog clock time, including both reading time and drawing clock faces.
Telling Analog Time
Handwriting Paper
Printable hand writing paper templates in a variety of line heights, including 3-line practice paper in both normal and wide layouts, blank story paper, and regular lined paper for older grade students. Check out the numbered blank spelling test templates!
Handwriting Paper
Graph Paper
Free printable graph paper, grid paper and dot paper for math problems, crafts, zentangling, landscape design, architecture or just simple doodling. All graph paper styles include inch and centimeter variations..gif) All of these PDF files are designed to print on 8.5 x 11 inch paper.
All of these PDF files are designed to print on 8.5 x 11 inch paper.
Graph Paper
Picture Math Addition
These printable worksheets use pictures and grouping to build a conceptual understanding of addition. These worksheets start out with simple addition picture problems where only basic counting skills are required to come up with addition number sentences, but later worksheets require students to produce a similar grid illustration to demonstrate their understanding of addition concepts. These are a perfect first instruction to addition for students in preschool, kindergarten or first grade.
Picture Math Addition
Picture Math Subtraction
These printable worksheets use pictures and grouping to build a conceptual understanding of subtraction. These worksheets start out with simple subtraction picture problems where only basic counting skills are required to come up with subtraction number sentences, but later worksheets require students to produce a similar grid illustration to demonstrate their understanding of subtraction concepts. These are a perfect first introduction to subtraction for students in kindergarten or first grade.
These are a perfect first introduction to subtraction for students in kindergarten or first grade.
Picture Math Subtraction
Picture Math Multiplication
These printable worksheets use pictures and grouping to build a conceptual understanding of multiplication. These worksheets start out with simple multiplication picture problems where only basic counting skills are required to come up with subtraction number sentences, but later worksheets require students to produce a similar grid illustration to demonstrate their understanding of multiplication concepts. These are a perfect first introduction to multiplication for students in second grade, third grade or fourth grade.
Picture Math Multiplication
Money
These printable money worksheets feature realistic coins and bills in problems for identifying coins, making change, counting coins, comparing amounts of money. They build foundational recognition and counting skills in Kindergarten and first grade to prepare for full money practice necessary to pass second grade.
Money
Spaceship Math Check-Off
Spaceship check-off pages (complete with the Spaceship ship!) for tracking progress on the Spaceship Math or Rocket Math worksheets for each of the four basic operations.
Spaceship Math Check-Off
Color By Number
These coloring worksheets feature simple color by number instructions for young students who are either just learning their numbers or as a reward activity for older kids. You'll find a growing set of holiday and seasonal themes that I'll be adding to over time... Please check back often for updates, or if you have a suggestion send me a note at the contact link below!
Color By Number
Valentine's Day
Looking for worksheets to make learning math on Valentine's Day a bit more fun? This page has a collection of color by number worksheets appropriate for kindergarten through fourth grade, covering addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations. There are also a collection of simple math exercises with fun Valentine's Day themes.
There are also a collection of simple math exercises with fun Valentine's Day themes.
Valentine's Day
Earth Day
Looking for worksheets to make learning math on Earth Day a bit more fun? This page has a collection of color by number worksheets appropriate for kindergarten through fourth grade, covering addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations. There are also a collection of simple math exercises with fun Earth Day themes.
Earth Day
St. Patrick's Day
You can't really solely on the luck of the Irish when it comes to math, but these St. Patrick's Day do make it a bit more fun! This page has a collection of color by number worksheets appropriate for kindergarten through fourth grade, covering addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations. There are also a collection of simple math exercises with fun St. Patrick's Day shamrock themes.
St. Patrick's Day
Patrick's Day
Spring
What better time of year to start growing some new math skills than Spring! This page has a collection of color by number worksheets appropriate for kindergarten through fourth grade, covering addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations. There is also a collection of simple spring math worksheets with fun spring flower themes, along with a multiplication chart, hundreds chart, graph paper and coordinate plane!
Spring
Word Search Puzzles
Use these math word search puzzles to introduce vocabulary and terms to grade school students as they are introduced to new math concepts! These word search puzzles include sets for various Common Core aligned grade levels, along with specific topics for geometry, algebra and more!
Word Search Puzzles
First Grade Math Worksheets
1st grade math is the start of learning math operations, and 1st grade addition worksheets are a great place to start the habit of regular math practice. The math worksheets in this section are selected especially for first graders and working with them will build a solid foundation for math topics as students move on to higher grades. Students who master addition in first grade might get an early jump on subtraction math fact practice, and may even learn a few early multiplication facts. This is an exciting time for students learning math, and keeping the challenge and enthusiasm for math at a high level is a worthwhile endeavor for parents and teachers. The selection of 1st grade math worksheets here should be an excellent map for that journey and should provide a great headstart to 2nd grade math as well!
The math worksheets in this section are selected especially for first graders and working with them will build a solid foundation for math topics as students move on to higher grades. Students who master addition in first grade might get an early jump on subtraction math fact practice, and may even learn a few early multiplication facts. This is an exciting time for students learning math, and keeping the challenge and enthusiasm for math at a high level is a worthwhile endeavor for parents and teachers. The selection of 1st grade math worksheets here should be an excellent map for that journey and should provide a great headstart to 2nd grade math as well!
Mathematics lesson in the 1st grade "Solving equations"
Lesson type: R.
Lesson goal:
- To form the ability to correct mistakes made based on reflection own activities.
- Train the ability to solve equations all studied types.
- Consolidation of counting skills within 10.
Lesson 9 progress0005
- Self-determination for learning activities. (1 -2 min.)
Purpose of the step:
- Motivation of students for learning activities;
- Determining the content of the lesson.
Organization of the educational process at stage 1:
Spring is rich in water, and man is rich in knowledge. (word “spring” closed)
- What is our lesson?
- What is written on the blackboard?
- Can you read?
- Guess what it is?
- How do you understand “a person is rich in knowledge”.
- How does a person accumulate knowledge?
- What knowledge do we accumulate in the lessons mathematics?
- But the offer is not fully open. Do you want find out which word is closed?
-To open it, you need to complete tasks.
- What kind of knowledge do we discover in the lessons? nine0005
2. Updating knowledge and fixing difficulties in own activities.
Updating knowledge and fixing difficulties in own activities.
Purpose of the stage:
- Update learning content: finding the whole and the part, addition and subtraction in within 10, solving simple problems of finding whole and part;
- actualize mental operations: analysis, synthesis, analogy;
- fix repeatable concepts and algorithms with the help of standards; nine0012
- organize self-execution works No. 1;
- organize a self-examination of work on the model with students recording their results.
Organization of the educational process at stage 2:
Mathematical dictation (on readings).
- subsequent number 9 ( 10)
- previous number 6 (5)
- how much is 5 less than 8 (3)
- how much is 10 greater than 3 (7)
- what number is between 5 and 7 (6)
- minuend 10, subtract 6.
 What is the difference? (4)
What is the difference? (4) - First term 4, second term 5. What is the amount equal? (9)
- I thought of a number. Subtract 3 from it and get 5. What number did I think? (8)
- Arrange the numbers in descending order.
- Choose three numbers like this. So that each the next one was 3 more than the previous one.
- Insert the numbers so that they are correct equality.
- What interesting things did you notice? (In equalities each column has the same parts and the whole, there are unknown numbers).
- What is unknown in each equality - part or whole?
- How to find the part?
- Which entry is superfluous?
9 - 2 ... 8 - 4
10 - 3 = 7
X + 5 = 8
- Decipher the word.
10 6 4 2 7 B E C H A nine0172
- x + 3= 7
- x - 4 = 6
- 6 + x = 8
- 9 - x = 3
- x - 5 = 2
When solving equations, students make comments.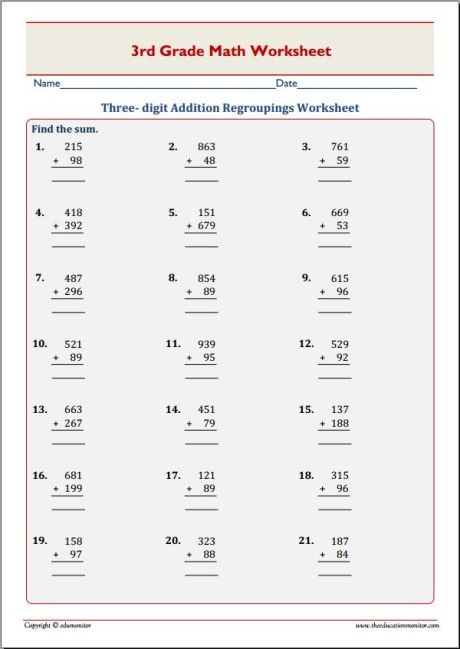
- how to find the part?
- how to find the integer?
Open the word and read the proverb.
Spring is rich in water, and man is rich in knowledge.
- What knowledge is needed to solve equations?
Posting cards. nine0005
- Finding the whole and the part.
- Application of the rules.
- Addition and subtraction within 10.
- Composition of numbers .
- How to understand that we have learned to solve equations?
(Need to do independent work and test yourself)
- What is your goal?
(Let's check how we learned to solve equations. We will train the ability to find and correct mistakes). nine0005
The teacher hangs out a card: Practice.
- What does it mean to “find and fix a mistake”?
(This is to determine WHERE? - place and WHY? - reason errors).
The teacher hangs out goal-setting cards.
We repeated the procedures. Which of listed on the board is necessary when solving equations?
You will solve independent work.
Self-study #1. nine0008
Check according to the sample and put a “+” sign next to a correctly completed task, and a sign “?” next to an incorrectly completed task.
- After checking the work, you should have found out if there is are you having difficulty?
3. Localization of difficulties.
Purpose of the step:
- Train the ability to perform actions according to the error correction algorithm, to form ability to identify location and cause difficulties in their own activities; nine0012
- Clarify individual lesson objectives.
- Who got the same answer in the first equation?
- In the second?
- Who has everything right, what will you do? (Check standard solution).
- And when you make sure that everything is done correctly than can you get busy? (Let's make an additional task and check it according to a detailed sample).
- What to do to someone whose answer did not match? (Check against the standard)
- What is the further goal of your work? (Find place and cause of the error, correct it. To find out, why there is a problem).
- You still need to check if you wrote it down correctly the equation.
4. Building a project to get out of the difficulty.
Purpose of the stage:
- To form the ability to correct own activities; nine0012
- Organize the children to build an exit project out of difficulty (correcting one's mistakes).
Organization of the educational process at this stage:
- Who has already identified the location and cause of the error?
- Who could not determine the location and cause of the error?
- How to be? (check against the standard)
- In application, what course of action are you did you fix the error? nine0005
- How will we correct our mistakes?
- How else to train to prevent mistakes?
5. Independent work No. 2.
Independent work No. 2.
Purpose of the stage:
- Interiorization of ways of doing things, causing trouble;
- Recording the achievement of an individual goal.
Organization of work at stage No. 5.
Students who made no mistakes check correct completion of additional tasks according to the detailed pattern.
The teacher addresses children who have made mistakes:
Why will we do the tasks in independent work No. 2?
(To practice again and not make mistakes)
- When you complete the tasks, how will you check yourself?
(detailed)
Children do the work.
- Who managed to complete an independent job number 2 without errors? nine0005
- Tell us about your successes.
- What should I pay attention to next?
6. Inclusion in the knowledge system and repetition.
Organization of the educational process at stage 6.
Completion of tasks of increased difficulty.
7. Reflection of activity.
Purpose of the stage:
- Performance self-assessment; nine0011 Awareness of the method of overcoming difficulties (error correction algorithm), fix correct methods of action in tasks where they were mistakes have been made.
- What is the purpose of our lesson? (learned to find and correct mistakes).
- Who reached the goal?
- Give an analysis of your activities.
Self-study No. 1.
Solve the equations and check.
x + 20 = 90
x - 30 = 50
Standard of independent work No. 1.
To find a part, you need to subtract from the whole part.
If x + a = b, then x = b - a
X + 20 = 90
X = 90 - 20
X \u003d 70
70 + 20 \u003d 90
90 \u003d 90
To find the whole, you need to add the parts.
If x - a = b, then x = a + b
X - 30 = 50
X = 30 + 50
X = 80
80 - 30 = 50
50 = 50
Self-study No. 2.
Solve the equations and check.
x + 50 = 70
x - 20 = 30
Self-study benchmark No. 2.
To find a part, you need to subtract from the whole part.
If x + a = b, then x = b - a
X + 50 = 70
X = 70 - 50
X \u003d 20
20 + 50 \u003d 70
70 \u003d 70
To find the whole, you need to add the parts.
If x - a = b, then x = a + b
X - 20 = 30
X = 20 + 30
X = 50
50 - 20 = 30
30 = 30
Additional task.
1. Solve the problem. nine0520
First can contains 4 liters of milk and second can contains 2 liters more milk.
How many liters of milk are in two cans?
1)
2)
Answer:
2. Compare, put signs <, >, =.
Compare, put signs <, >, =.
6 cm + 3 cm ... 4 cm + 3 cm
9 cm - 5 cm ... 8 cm - 2 cm
4 cm + 3 cm ... 3 cm + 4 cm
3. Solve the examples.
30 + 50 =
90 - 70 =
80 - 60 =
80 - 40 =
40 + 20 =
20 + 60 =
An example of completing an additional task.
1. Solve the problem.
First can contains 4 liters of milk, second can contains 2 liters more milk.
How many liters of milk are in two cans?
1) 4 + 2 = 6 (l)
2) 4 + 6 = 10 (l)
Answer: 10 liters.
2. Compare, put signs <, >, =.
6 cm + 3 cm > 4 cm + 3 cm
9 cm - 5 cm < 8 cm - 2 cm
4 cm + 3 cm = 3 cm + 4 cm
3. Solve the examples.
30 + 50 = 80
90 - 70 = 20
80 - 60 = 20
80 - 40 = 40
40 + 20 = 60
20 + 60 = 80
| nine0163 | Stage I. Motivation for activity | ||||||||||
| Purpose Motivate students to study the topic "Equation" This stage involves a conscious transition of the student from life to the space of learning activities. For this purpose: 1) conditions are created for the student to have an internal need to be included in educational activities (“I want”). 2) the requirements for the student in terms of learning activities are updated and thematic frameworks are established (“should”, “can”). |
(Various sources of information) Slide #1. - What mathematical notation do we know? Name them. 4 + 5, 6 - 3 (expressions) - How to read these expressions? (sum of numbers ..., first term ..., second term ...; difference of numbers ..., reduced ..., subtracted ...) 3 < 9, 10 > 6 (correct inequalities) -Why? Prove it. 3 + 7 = 9 (equality) - Is this equality correct? (No) - Why? Prove it. ( Using a number beam, counting material, addition table ) front. work - Turn this equality into true. How to do it? (3 + 7 = 10 - placed on the card on the board ) - How to check the correctness of the solution? ( With the help of a number beam, counting material, addition table ) - What other mathematical equations are there, you know? nine0618 - Do you want to know? | ||||||||||
| Purpose To form an idea of the main features of equations This stage involves: 1) actualization of the studied methods of action sufficient to build new knowledge, and their generalization; 2) training of appropriate mental operations; 3) motivating students to a trial educational action (“must” - “can” - “want”) and its independent implementation; nine0618 4) fixation by students of difficulties in the individual performance of a trial educational activity or its justification. 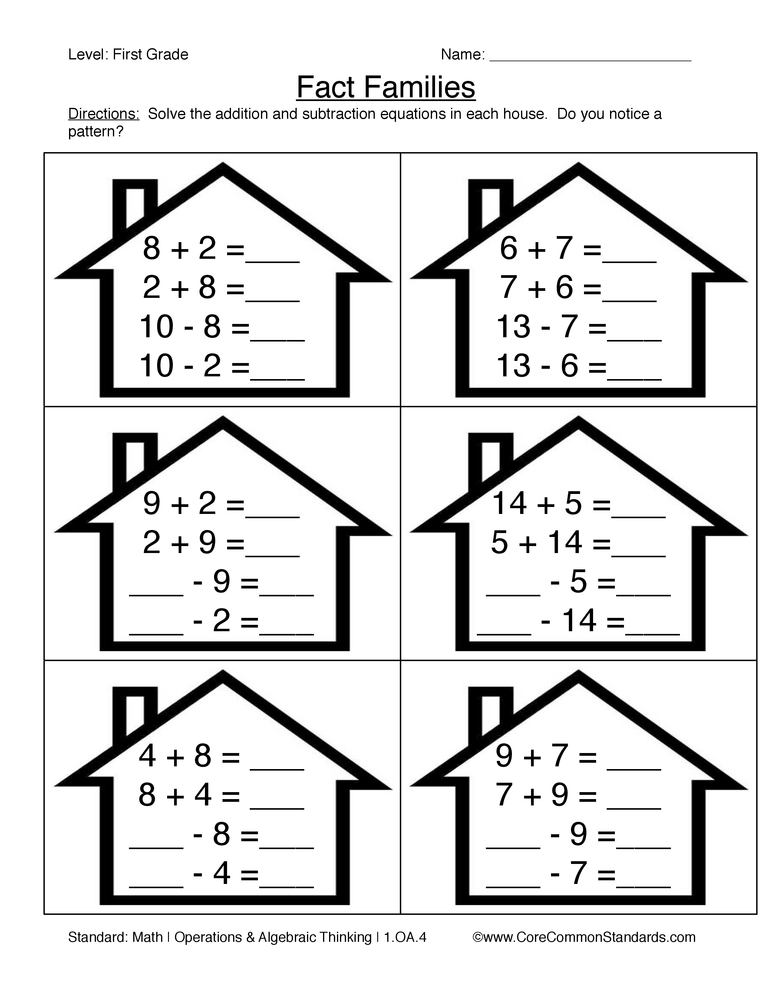 | Stage 2. Actualization of knowledge and individual difficulty in trial action. Open your textbooks on page 60, read task number 1 and complete it. Slide number 2: examples with "windows". Textbook Part 2, p. 60, #13 += 10 - 3 = 7 Left example for girls, right example for boys. Who wants to go out and show their solution on the interactive whiteboard? Thank you. What knowledge helped you to complete this task correctly? Let's remember the solution algorithm. (Students have already met this algorithm more than once, so you can count on them to reproduce it exactly.) Slide No. 3. Repetition of the solution algorithm:
| examples with windows. Textbook Part 2, p. 60 | |||||||||
| 1) the reconstruction of the performed operations is carried out and fixation in the language (verbally and symbolically) of the step, the operation where the difficulty arose; 2) students correlate their actions with the method of action used (algorithm, concept, etc. 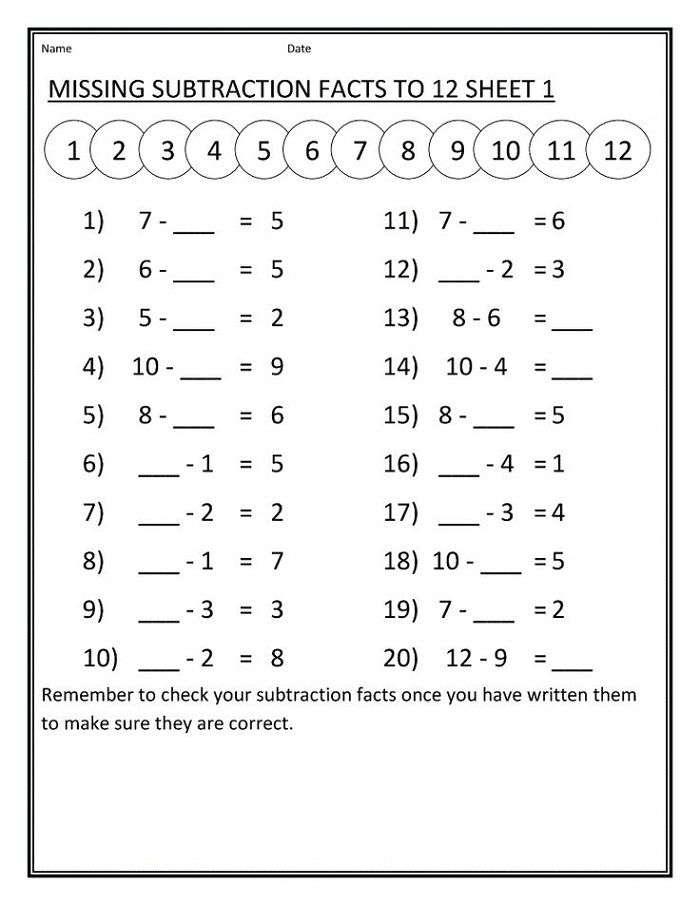 ), and on this basis identify and fix the cause of the difficulty in external speech - those specific knowledge, skills or abilities that are not enough to solve the original problem and problems of this class or type in general. nine0618 ), and on this basis identify and fix the cause of the difficulty in external speech - those specific knowledge, skills or abilities that are not enough to solve the original problem and problems of this class or type in general. nine0618 | Stage 3. Construction of the project of an exit from difficulty. — What is our goal? (Find out what these mathematical records are called.) - What will be the topic of the lesson? (Introduction to new mathematical expressions. Their solution) Slide number 4: - Let's outline our action plan (children say): 1. Let's try to complete the task ourselves: find out what these records are called.2. Let's compare our assumptions with the textbook, ask the teacher.3. Eliminate the difficulty.4. Let's apply the new knowledge. (Before you have a possible answer for the children) - What will help us? (own experience, textbook, dictionary (meaning of the word "equation"), teacher) | ||||||||||
Various options proposed by students are discussed, and the best option is chosen, which is fixed in the language verbally and symbolically.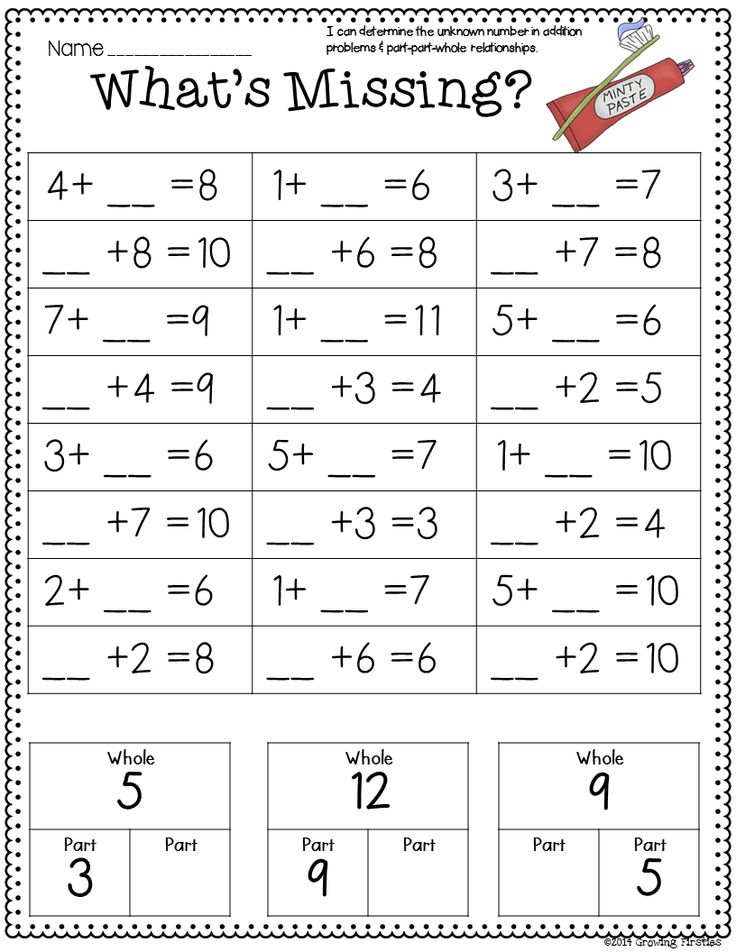 The constructed method of action is used to solve the original problem that caused difficulty. In conclusion, the overcoming of the difficulty that arose earlier is fixed. The constructed method of action is used to solve the original problem that caused difficulty. In conclusion, the overcoming of the difficulty that arose earlier is fixed. | Stage 4. Implementation of the constructed project. - Look again at these equalities. Write on the board: 3 + x = 10 y - 3 = 7 - What is unusual here? (Some foreign letters). - What do these letters replace? (Probably some numbers). - Do you know what numbers you need to substitute instead of letters to get the correct equality? - Let's find out from the textbook what these mathematical records are called. Working with the textbook, p. 60. (Read the rule. What do mathematicians call the new entries? Say the word "equation" aloud. What do you hear? Correct. Equal, the same. I suggest you read the article in the Explanatory Dictionary at home and find out all the meanings of the word "equation." "equalizes", is made "equal" in this notation? - Mathematical expression and number // Left and right parts of the expression. 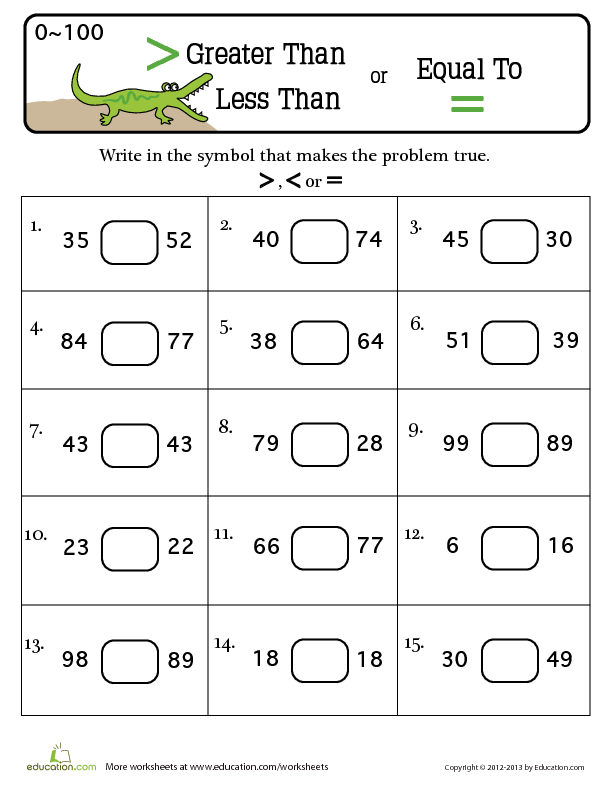 Work with handouts in pairs. Underline the equations in blue. Slide No. 5. Work with handouts in pairs. Underline the equations in blue. Slide No. 5.
| Work in pairs: Underline the equations in blue (different types of numerical expressions are given, among which there are equations | |||||||||
| Solving typical tasks for a new way of acting with speaking the solution algorithm aloud. | Stage 5. Primary consolidation in external speech. Fixing new knowledge in speech and signs: p.60 No. 2. Let's go back to task No. 2 on page 60-What does it mean to solve an equation? (children's answers, based on the meaning of the word) -Let's compare our assumptions with the textbook.  (S. 60 - reading the rule). -Let's make an algorithm for solving the equation. Slide number 6 (S. 60 - reading the rule). -Let's make an algorithm for solving the equation. Slide number 6
- Choose such a number instead of x to get the correct equality. (10) -How can this be done? - In the notebook we will write as follows: x = 6 + 4; x=10 - How to solve the equation? (children's answers).  - Compare with textbook answer p.60. - Well done! Slide No. 7 y - 4 = 6 y=6+4 y=10 Answer: 10A similar frontal work is carried out with the equation 8-y=5. | ||||||||||
| Students independently perform tasks of a new type and carry out their self-test, step by step comparing with the standard. At the end, a performing reflection of the implementation of the constructed project of educational activities and control procedures is organized. | Stage 6. Independent work with self-test according to the standard . (individual work) each student solves and pronounces an algorithm for solving the equation. Page 60 No. 3 (1 column). Option 1 starts with the 1st equation. Option 2 - from the second. At this point in the lesson, two options can be considered. Slide No. 8 1. An algorithm for solving an equation using a technique (solving an equation based on the relationship between the components and the result of the action).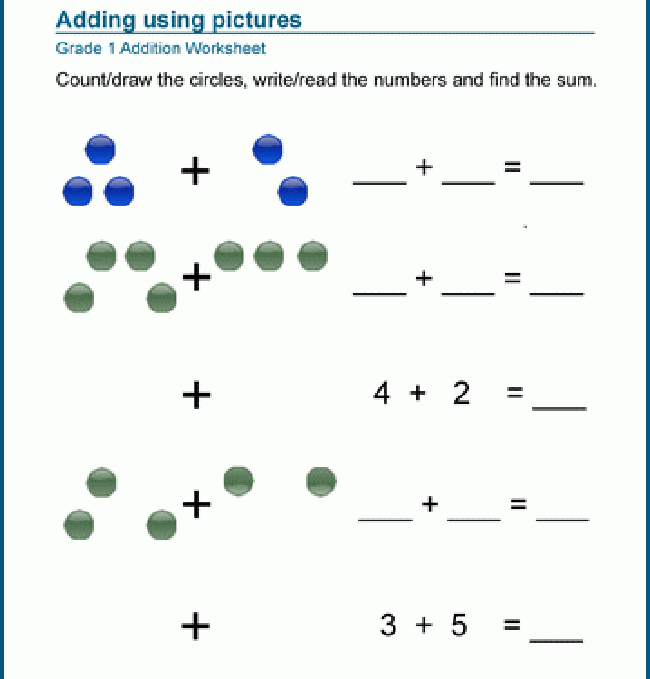 1. I am reading the entry.2. I analyze the meaning of the action sign.3. I define the components of actions.4. I remember how to find an unknown component.5. I make a calculation.6. I check the correctness of the selection based on the knowledge of the composition of the number or with the help of a numerical beam, counting material, addition table. Slide No. 92. Algorithm for solving an equation using technology (solving an equation based on the relationship between part and whole) 1. I am reading the entry.2. I analyze the meaning of the action sign.3. I define the components of actions.4. I remember how to find an unknown component.5. I make a calculation.6. I check the correctness of the selection based on the knowledge of the composition of the number or with the help of a numerical beam, counting material, addition table. Slide No. 92. Algorithm for solving an equation using technology (solving an equation based on the relationship between part and whole)
Here it is expedient to show already solved equations as a standard. 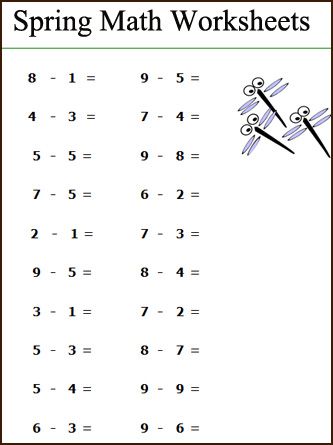 - Who's got it right? Why? - Who has mistakes? Why? - What is the reason? | ||||||||||
| At this stage, the limits of applicability of new knowledge are identified and tasks are performed in which a new way of acting is provided as an intermediate step. | Stage 7. Inclusion in the system of knowledge and repetition. nine0618 — What skills do you develop when you solve equations? (We made an algorithm for solving equations. We learned to apply this algorithm depending on the unknown component and the sign of the action, to count correctly ...) - When performing what tasks do you also learn to think, count? (When solving problems). Solving the problem in groups: (p. 60 No. 5 (2)) I suggest that you unite in teams, make a choice and solve the problem in the most interesting way for you. Slide No. 11 1 team - Commander Carlson - Decision on text. 2 team - commander Mermaid - Decision according to the scheme.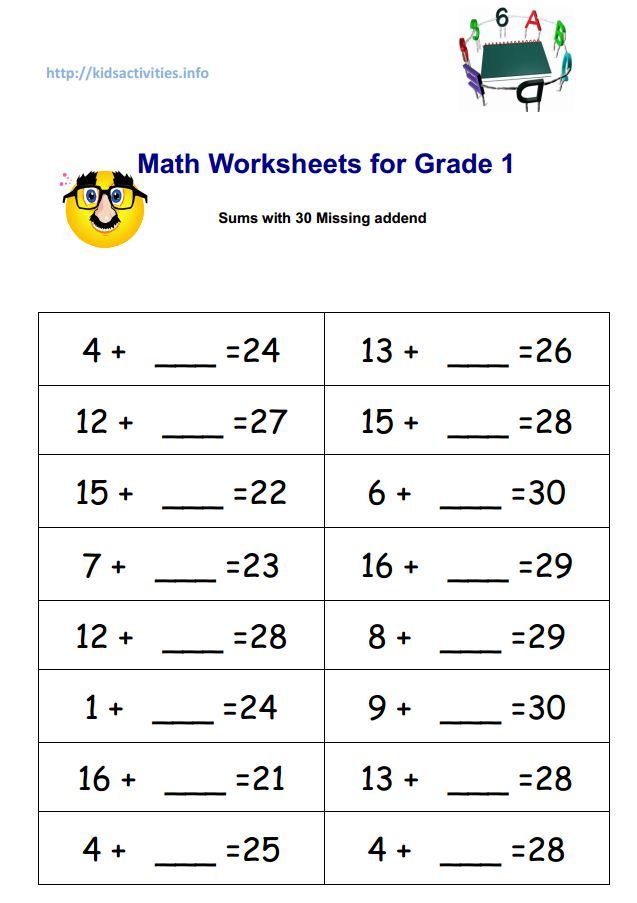 3 team - commander Wise Owl - Decision using new knowledge (equation) Slides No. 12-14 Let's check the work of the teams. Complete the diagram, choose an action and solve .1. Make a short note and solve by action.2. Solve the problem with an equation. Each option is analyzed and positively evaluated. nine0163 3 team - commander Wise Owl - Decision using new knowledge (equation) Slides No. 12-14 Let's check the work of the teams. Complete the diagram, choose an action and solve .1. Make a short note and solve by action.2. Solve the problem with an equation. Each option is analyzed and positively evaluated. nine0163 | ||||||||||
| Purpose To fix the new content of the lesson. To organize reflection and self-assessment by students of their own learning activities. | Stage 8. Reflection of learning activity in the lesson — What was the purpose of today's lesson ? - Have you reached your goals? Prove it. (students can use the rule in the textbook. scheme (whole and parts) - What helped us learn how to solve equations by the selection method. ( Algorithm) - Where can we use the ability to draw up an algorithm or action plan outside the lessons ? - Draw a ladder of success in your notebooks and evaluate your activity in the lesson.  | ||||||||||

 primary school teacher MBOU secondary school No. 5 of the resort city of Gelendzhik, Krasnodar Territory
primary school teacher MBOU secondary school No. 5 of the resort city of Gelendzhik, Krasnodar Territory