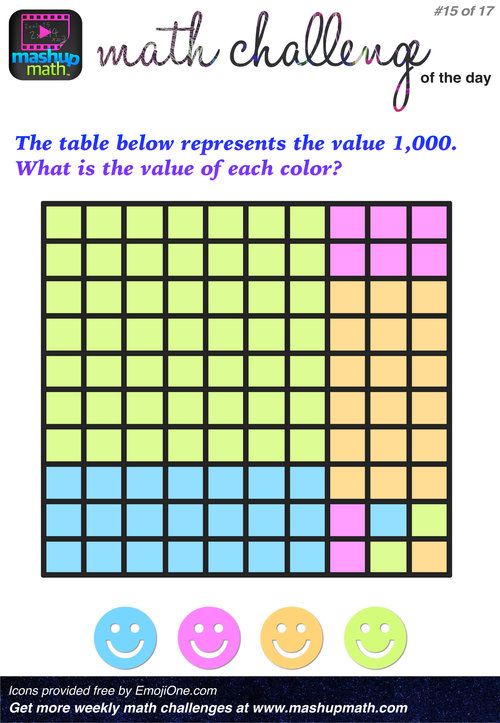
Math game for elementary
Logic Games | Fun Games for Kids
Kindergarten
1st Grade
2nd Grade
3rd Grade
4th Grade
5th Grade
6th Grade
Fun Games for Kids
Logic Games and Puzzles
New Blog: A Tale of Two Playgrounds
Category Spotlight: Skill Games
Advertisement
Featured Games
Advertisement
Code Panda
Red Block Returns
Zero Squares
Cookie Trail
Liquid Bubble Sort
Drop It
Find the Differences
Zero Numbers
Find the Pug
Globehopper
Monkey Bubbles
Happy Cups
NEW! Fun Logic Games at Puzzle Playground
Sokogem
Snake Falls
Reach the Flag
Kitty Gram
Sokonumber
Get the Stars
Give Your Brain a Workout
Mazes and Keys
Robot Islands PLUS
Color Maze
Drop the Number
Wind and Solar
One Liner
Jelly Doods
Dots and Boxes
Arty Agent
Paint the House Blue
Rescue Yellow
Chef Slash
Connect the Roads
Block the Pig
Logic Steps
Lightybulb 3
Car Park Puzzle
Cross the Bridge
Puzzle Ball
Double Up
Sudoku
Logic Tail
Robot Islands
The Parking Lot
Four Colors
Logic Magnets
Feed That Thing
3D Memory
Number Snake
Laser Trap
Trap the Mouse
Hex Blocks
Monsterland 4
Lightybulb
2048
Gnomy Night
Sorting Spheres
Andy's Golf
Red Block Returns
2Red Block Returns
3Islands Of Creatures
Maze Collapse
Maze Collapse
2Maze Collapse
3Gems Glow
Tic Tac Toe
Chess
Ghostie Loners
Animalines
Pin Cracker
Lightybulb 2
Scratch and Sniff
Fox Adventurer
Purple Mole
Brain Workouts
Monsterland 5
Green Mission
Reverse the Discs
Candy Pool
Code Builder
Follow the Code
Monsta Munchies
Fox Journey
Piece of Pie
Connect
Fluffy Cuddlies
Color Fill
Liquid Sort
Push Pull Blocks
Spot the Difference
Lost Joe
Blue Turn
Checkers
Flowers
Jewel Routes
Klocki
Number Path
Spatial Rescue
Adventure Tom
Aqua Thief
8 Square
Box Rotate
Laser Maker
Animal Memory
Monsterjong
Rainbow Tower
Bloxorz
Electrio
Red
Me and the Key
Me and the Key 2
Doggnation
Duck Think!
Full Moon
A Bark in the Dark
Factory Balls
Factory Balls 2
Factory Balls 3
Space is Key
Space is Key 2
Layer Maze
Layer Maze 2
Layer Maze 3
Layer Maze 4
Layer Maze 5
Veggi Rabbit
Robotion
Shift the Block
Brixx
Jon Lightning
Zippy Boxes
ClickPLAY Time 6
Hook
Froggy's Pond
Boxed
Jelly Collapse
Tube Master
Light Rays
Sum Blocks
Overlap Sums
Sum Stacks
Number Sequence
Snoring Pirates
Jelly Slice
Reflector
Brain Trainer
Block Turns
Crazy Balls
Golden Scarabaeus
Break the Code
Sum Links 2
Peg Jumper
Pet Party
Tetra Squares
Mancala
Tip Tap Tile
One Clown Standing
The Warehouse
Stones of the Pharoahs
Tangrams
Four in a Row
Piggy in the Puddle 2
Brain Patterns
Capture and Turn
Red Swap Blue
Memory Artist
How to Feed Animals
Draw in Code
Bubble Blaster
2nd Grade Math | Free, Online Math Games
Kindergarten
1st Grade
2nd Grade
3rd Grade
4th Grade
5th Grade
6th Grade
Fun Games for Kids
2nd Grade Math Games
Game Spotlight: Canoe Puppies
Advertisement
Multiplayer Math Games
Advertisement
Jet Ski Addition
Money
Time
Tug Addition
Ducky Race Subtraction
Sailboat Subtraction
Island Subtraction
Skateboard Pups
Kitten Match
Shape Names
Time
Money
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
Skateboard Pups
Thinking Blocks Jr
Thinking Blocks
Monster Stroll
Bridge Builder
Code Sums
Kitten Match
Alien Addition
Galaxy Pals 20
Math Monster Subtraction
Addition Facts
Math Racer Addition
Missing Digits Subtraction
Ducky Race Subtraction
Sailboat Subtraction
Math Surpass Compare
Take the Cake Addition
Galaxy Pals 100
Monster Mischief
Addition Blocks
Magic Triangle
Number Trails Addition
Addition Snake
Missing Digits Addition
Island Chase Subtraction
One Sum
Jet Ski Addition
Number Bonds II
Math Monster Addition
Minus Mission
Tug Team Addition
Subtraction Facts
Zogs and Monsters +
Math Word Problems
Skip Counting Video
Multiplication Video
Bridge Builder X
Number Bonds 10 to 20
Number and Operations in Base Ten
Tandem Turtles Rounding
Bingo Tens
Space Jaunt Rounding
Find the Bus Stop
Superhero Subtraction
Bingo Hundreds
Place Value Game
Number Patterns
SumBots
Treasure Quest Numbers
Addition Chart
Place Value Party
Untamed Number Names
Bingo 3 Numbers
Treasure Quest Addition
Hundreds Chart
Bingo Number Pairs
Chain Sums
Addition
Amusement Park Addition
Subtraction
Bingo Rounding
Canoe Puppies
Whole Numbers
Math Bars
Place Value Video
Subtraction Video
Addition Video
Advanced Addition Video
Measurement and Data
Clocks
Time
Time Video
Picture Graphs Video
Time
Money
Money
Money
Money
Candy Cashier
Bar Graphs Video
Bar Graphs Video 2
Geometry
Pattern Blocks
Geoboard
Shape Names
Tangrams
Shapes
Where are the Aliens?
Find the Point
Reflection Painter
Rotation Painter
Super Math Puzzles
Triangle
Triangle Pro
Undercover
Undercover Pro
Pyramid
Pyramid Pro
Pyramid Double
Number Chart
Number Chart Pro
Grid Junior
Grid Junior
Grid Pro
Grid X
Function Machine
Logic and Problem Solving Games
Squirrel Hop
Pingu and Friends
Cake Topping
Katana Fruit
Mila's Magic Shop
Pac Rat
Playful Kitty
Piggy Bank Adventure
Jumpy Kangaroo
Icy Super Slide
Arcade Golf
Rabbit Samurai 2
Duck Life 4
Icy Purple Head 2
Duck Life Space
Doctor Acorn 3
Doctor Acorn 2
Arty Agent
Block the Pig
Car Park Puzzle
Red Block Returns
Connect the Roads
Cross the Bridge
Mazes and Keys
Mini Golf World
Sophia's World
Aqua Thief
Monsterland 4
Monsterland 5
Find the Robot
Robot Maze
Chef Slash
One Liner
Puzzle Ball
Double Up
Logic Tail
Robot Islands
The Parking Lot
Feed That Thing
Trap the Mouse
Hex Blocks
2048
Dots and Boxes
Sorting Spheres
Andy's Golf
Islands Of Creatures
Maze Collapse
Gems Glow
Tic Tac Toe
Chess
Ghostie Loners
Animalines
Scratch and Sniff
Reverse the Discs
Candy Pool
Code Builder
Follow the Code
Monsta Munchies
Fluffy Cuddlies
Spot the Difference
Checkers
Flowers
Zippy Boxes
Jelly Collapse
Tube Master
Filltracks
Number Sequence
Snoring Pirates
Jelly Slice
Brixx
8 Square
Paint the House Blue
Number Path
Find the Differences
Liquid Sort
Animal Memory
Monsterjong
Rainbow Tower
Peg Jumper
Tetra Squares
Mancala
Tangrams
Four in a Row
Piggy in the Puddle 2
Capture and Turn
Memory Artist
Rabbit Samurai
Unpuzzle 2
Temple Crossing
Unpuzzle
Color Match
Dot 2 Dot
Puzzle Blocks
Puzzle Slide
Word Games
Letter Recognition
Word Recognition
Typing Jets
Spelling Bees
Double Vowels
Spelling Words
Math games for elementary school.
Home » Extracurricular activities
Extracurricular activities
Of the numerous types of extracurricular activities with younger students (grades I - II), mainly episodic activities are held : mathematical games, fun and entertainment. These classes are given from 5 to 10 minutes at the beginning of the lesson, and later during extracurricular time. Title mathematical games and their distribution by class can be seen from the table below.
| Grades | Program | Games in class | Extracurricular games | ||
| Outdoor | 1 | Ten | , Silent guessing game, thinking and guessing numbers, adding up to 10, who is faster, the best counter, cunning star. fun count | Object bingo, digital bingo, counting bingo, cubes, splinter, fun matches, building material, mathematical top | Living numbers, numerical figures in the form of live pictures, rhythmic movements |
| 1 - 2 | |||||
| Games indicated for the first ten, chain, circular count, addition to 100, game in halves, quarters and eighths, forbidden number, counting game without words, digital cipher game, labyrinths, entertaining simple and complex squares, number guessing tables, lightning mathematician, phenomenal memory, math fan, funny count | Flying caps, ricochet, sniper, lotto in various variations, multiplication lotto, fun squares, arithmetic puzzles | Arithmetic run, goal game: throwing in a circle. Ladder Throwing, Ball Throwing, Ring Throwing, Dice Throwing Ladder Throwing, Ball Throwing, Ring Throwing, Dice Throwing | |||
| 2 -3 | Thousand | Games indicated for the second ten and first hundred, arithmetic puzzles, living numbers | Flying caps, Japanese billiard, game of 15 , phenomenal memory | Mobile Abak | |
| 3 - 4 | any values | games indicated for thousands, guessing numbers, name, date, digits, pages of the book | Arithmetic puzzles, arithmetic puzzles | Culti - | Culti -volume. |
| 3 – 4 | Geometric material material | In one stroke, which is more | Archers, match games, the secret of the triangle, colored tangrams, geometric dominoes | Games with sticks, construction of geometric figures, measuring work on the ground, determining the height of objects, the width of rivers, etc. |
Competently, a fun game instills in students a taste for learning mathematics. Familiarity with games and the ability to conduct them on your own can be used to organize evenings or matinees. So, in Moscow schools No. 525, 554, 628, matinees were held for students of three or four first grades. The matinee was held according to the following program:
Familiarity with games and the ability to conduct them on your own can be used to organize evenings or matinees. So, in Moscow schools No. 525, 554, 628, matinees were held for students of three or four first grades. The matinee was held according to the following program:
- Solving coded examples that determine the purpose of the lesson (count, solve, guess).
- Games on the topic "Who is more correct, who is faster?".
- Live Case Solution.
- Problem solving in verse.
- Guessing riddles.
- "Funny score" (within 20).
For any section of the program, 3-5 students from each class were interviewed, the points for the answer were summed up and at the end the winner classes were announced.
The same matinees, such as competitions, were also held with fourth-grade students.
Here is the program of one such matinee.
- Guessing the leader of the intended multi-digit number.
- Solving problems where terms are given, taken in pairs.
- Solution of examples written on the board: answer sheets are served on the table to the facilitator.
- Solving examples with erased (missing) digits.
- Joking tasks.
- "Funny score" (within 100).
Program numbers that require movement (Live examples, Live numbering, Arithmetic run, etc.) bring a lot of animation.
At matinees, there may be a presentation with a short message from the host (pre-prepared student) on the topics: How did people learn to count? to measure? Phenomenal counters, children and young mathematicians, etc.
Mathematical excursions in grades I and II are devoted to outdoor games or in the gym (throwing in a circle and ladder with a cube, ring, ball, etc.). Possible mathematical excursions to the forest, park or garden to collect counting material. With grades III-IV, there are also excursions to the forest to determine the number of trees per 1 a, to the river to find its width, to an open meadow to build models of geometric shapes and bodies from meter-long sticks; in the same clearing it is convenient to carry out hanging lines, determining distances by eye, checking straight lines by hanging and other methods.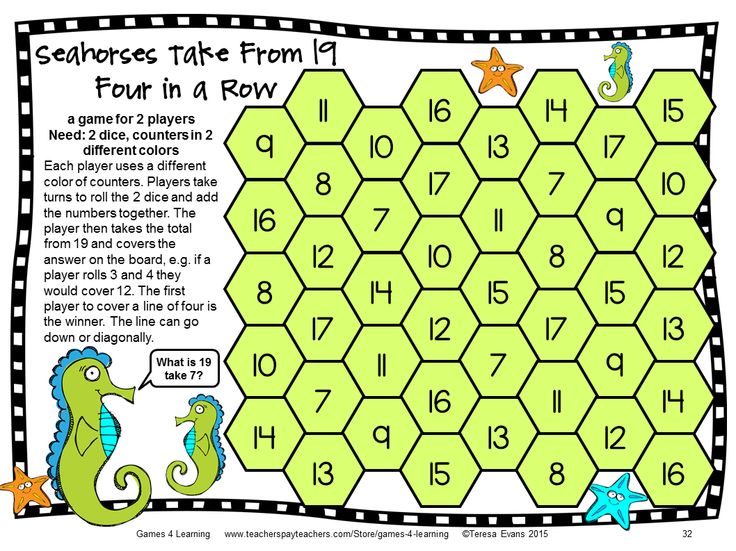 Depending on the environment of the school, other excursions are also possible: to the construction of a house to determine the volume of building materials (boards, logs, etc.), to the railway to calculate the volume of wagons, the dimensions of the rail, sleepers, etc.
Depending on the environment of the school, other excursions are also possible: to the construction of a house to determine the volume of building materials (boards, logs, etc.), to the railway to calculate the volume of wagons, the dimensions of the rail, sleepers, etc.
After the math excursion, the students describe the work done and write down the numerical data found.
Math mugs . A mathematical circle is organized by a teacher, he can be assisted by members of the pioneer and Komsomol organizations of the school, as well as parents. When organizing a circle, it is necessary to take into account the interests of students in solving problems, in computer technology, in measuring practice and drawing, in making manuals. In multi-complete schools, a circle can unite students from several classes. Each circle pursues a specific goal in its work. Members of the circle assume obligations: regularly attend classes, complete assignments, etc. The circle works according to a plan drawn up by the teacher and adopted by the circle.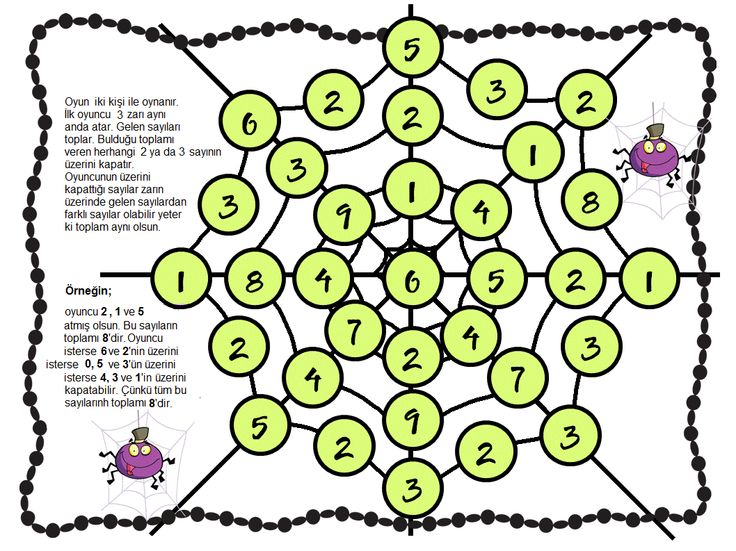 The teacher and members of the circle report on the work done to the school administration and the group of students (pioneer and Komsomol organizations).
The teacher and members of the circle report on the work done to the school administration and the group of students (pioneer and Komsomol organizations).
Games in mathematics lessons in elementary school / Kharkiv Central Educational School of I-III Stages No. 58 Kharkiv city for the sake of Kharkiv region
“ Game is a special form of children's life, developed or created by society to control the development of children, in this sense, it is special pedagogical creation. Shchedrovitsky G.P.
⭐Goals: to determine the most effective methods of using didactic games in mathematics lessons in elementary school.
Tasks:
✅ give an idea of the didactic game;
✅ give an idea of the types of didactic games;
✅choose the most methodically effective didactic games for mastering the material.
Play is of great importance in a child's life. After all, the game is activity, work and creativity.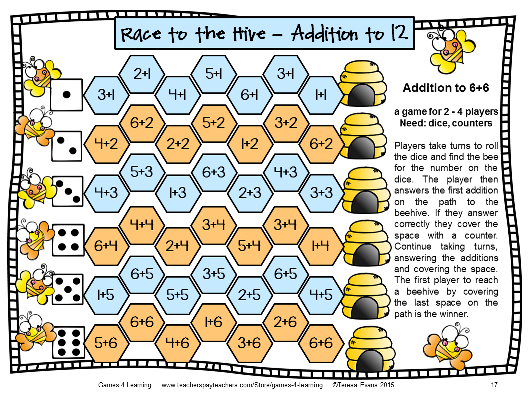 Children play and develop. Develop the mind and human qualities. In the lessons of mathematics, we actively use games and game moments. The most important thing is that the goal of the game coincides with the educational task that you set for the lesson. Younger students have visual-figurative thinking, so there is a lot of visualization in the lessons. These are both fairy tale characters and heroes of children's cartoons. They create the right mood. And in order to maintain interest in mathematics and increase activity in the lesson, we use games.
Children play and develop. Develop the mind and human qualities. In the lessons of mathematics, we actively use games and game moments. The most important thing is that the goal of the game coincides with the educational task that you set for the lesson. Younger students have visual-figurative thinking, so there is a lot of visualization in the lessons. These are both fairy tale characters and heroes of children's cartoons. They create the right mood. And in order to maintain interest in mathematics and increase activity in the lesson, we use games.
Didactic games can be divided into:
1) games according to the model;
2) games for developing computational skills;
3) games that change;
4) games containing elements of search and creativity.
Each game has a structure:
1) the goal is what we check, what we fix, what we study;
2) rules - the condition of the game and how to comply;
3) game actions.
The use of games takes place at different stages of the lesson. When explaining new material, in part - search tasks, when generalizing and consolidating.
Games:
1. Butterflies
Didactic goal: to consolidate the methods of addition and subtraction. Equipment: drawings of butterflies and flowers. Content: flowers with a number on the board, butterflies in a group on another part of the board. Children are asked to guess which flower the butterfly will land on. To do this, they read the examples on the back of the butterfly drawings and count it, then put the butterflies on the flowers.
2. Logical endings
Didactic goal: to develop logical thinking. Content: arm yourself with logical thinking, students must complete the phrases: If the table is higher than the chair, then the chair ... (below the table). If 2 is more than one, then one ... (less than two). If the sister is older than the brother, then the brother ... (younger than the sister). If the right hand is on the right, then the left ... (on the left). If the river is deeper than the brook, then the brook ... (smaller than the river). If water pours from a bucket, then the bucket ... (leaky).
If the right hand is on the right, then the left ... (on the left). If the river is deeper than the brook, then the brook ... (smaller than the river). If water pours from a bucket, then the bucket ... (leaky).
3. Mathematical football
Didactic goal: to develop skills of addition and subtraction within 20, 100, 1000 or multiplication and division. Equipment: pictures of goals, balls with examples. They run out in turn, take the ball, an example is written on the reverse side, if they decide correctly, then they score a goal. The winner is the one who counts without errors and scores more goals.
4. In numerical order
Didactic purpose: to consolidate the ordinal value of a number. Equipment: two sets of cards of different colors with numbers from 5 to 15. Content: for the game you need two teams of ten players. Two teams of 10 people line up facing the class. The host has two sets of cards of different colors with numbers from 5 to 15. Before the start of the game, the host shuffles the cards of each set and attaches one to the backs of the players. None of the players knows what number is on their card. Everyone can learn this only from his neighbor. On a signal, the players of the teams must line up so that the numbers on their cards are in order. The team that completes the task faster and more accurately wins.
None of the players knows what number is on their card. Everyone can learn this only from his neighbor. On a signal, the players of the teams must line up so that the numbers on their cards are in order. The team that completes the task faster and more accurately wins.
5. Mathematical fishing
Didactic goal: to form and consolidate oral counting skills.
Equipment: fish and fisherman.
Content: teams play, take turns taking a fish and solving an example. I made the right choice and caught a fish. Who will catch more. You can write examples on the back of the fish.
6. Christmas tree
Purpose: to develop and test counting skills. Equipment: Christmas tree, pictures of Santa Claus and Snow Maiden, Christmas decorations. Content: the student of the Snow Maiden helps to decorate the Christmas tree if he correctly solves the example written on the back of the toy.
7. Train.
Didactic goal: fix the ordinal value of the number. Equipment: pictures of trains, wagons, cards with numbers from 10 to 20. Content: train on the board, wagons are arranged in disorder. The children are told that the numbers have gone astray. Children arrange the numbers indicating the numbers of the second ten.
Equipment: pictures of trains, wagons, cards with numbers from 10 to 20. Content: train on the board, wagons are arranged in disorder. The children are told that the numbers have gone astray. Children arrange the numbers indicating the numbers of the second ten.
8. Guess
Didactic goal: to consolidate knowledge of the composition of the first ten numbers. Content: the teacher says that she thought of 2 numbers, added them up, it turned out 5. What numbers did she add up? Children: 0 and 5, 5 and 0, 4 and 1, 1 and 4, 2 and 3, 3 and 2. At the first stage, children illustrate the composition of numbers on sticks, in geometric shapes.
9. Mathematical tricks
Didactic goal: practicing and testing counting skills.
Contents:
1. The teacher asks someone to guess any number, then subtract 1 from it, multiply the result by 2, subtract the intended number from the product and tell you the result. By adding the number 2 to it, you will guess what was intended.
2. Multiply your birth date by 2, add 5, multiply by 50, and add the number of the month. From the number that turned out, subtract 250 and get the birthday and month. 3. Someone thought of a number. You ask to multiply it by 2, then add 12 to the product, divide the sum in half and subtract the intended number from it. Whatever number is intended, the result will always be 6.
10. Vice versa
Didactic goal: to develop children's speech, reinforce the concepts of thick, thin, wide, narrow, etc.
Content: the teacher says the word, and the child says the opposite. The teacher does not name names, but throws the ball.
Supplement.
Didactic goal: Develop children's speech, include mathematical terms in the active dictionary.
Equipment: drawings of a rocket, an airplane, a helicopter, a bird, a butterfly.
Content: The teacher places pictures on the board from top to bottom. Explains to the children that it is necessary to continue the sentence (Flies high in the sky .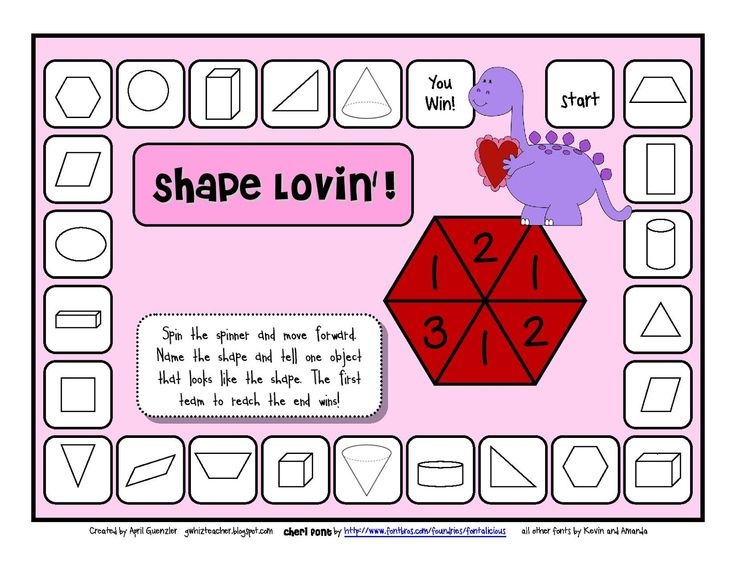 .., flies below the rocket .... The plane flies higher, flies below the helicopter ...)
.., flies below the rocket .... The plane flies higher, flies below the helicopter ...)
11. Let's make a flower
Didactic goal: fixing the composition of the first ten numbers. Equipment: petals with examples; stem with a leaf on which is a number.
Contents: Stems with a leaf are attached to the board. The petals are on the table. The student comes out and takes a petal, reads the example in different ways, decides verbally and attaches it to the desired stem. Children play in teams: how many colors, so many teams.
12. Logic games-tasks
Didactic goal: to develop logical thinking. Equipment: chocolate, stones, chessboard.
Content: the teacher announces the problems:
Problem 1. Two people take turns breaking a 6 x 8 chocolate bar. During a turn, it is allowed to make a straight break of any of the pieces along the depression. The one who cannot make a move loses. Solution. The main consideration: after each move, the number of pieces increases by exactly 1. First there was one piece. At the end of the game, when no moves can be made, the chocolate bar is broken into small pieces. And there are 48 of them! Thus, the game will last exactly 47 moves. The last, 47th move (as well as all other odd-numbered moves) will be made by the first player. Therefore, he wins this game, regardless of how he plays.
First there was one piece. At the end of the game, when no moves can be made, the chocolate bar is broken into small pieces. And there are 48 of them! Thus, the game will last exactly 47 moves. The last, 47th move (as well as all other odd-numbered moves) will be made by the first player. Therefore, he wins this game, regardless of how he plays.
Problem 2. There are three heaps of stones: in the first - 10, in the second - 15, in the third - 20. It is allowed to split any heap into two smaller ones during a turn; whoever loses. can't make a move. Solution. After each move, the number of heaps increases by 1. At first there were 3 of them, at the end - 45. Thus, 42 moves will be made in total. The last winning 42nd move will be made by the second player.
Problem 3. Numbers from 1 to 20 are written in a line. Players take turns placing pluses and minuses between them. After all places are filled, the result is calculated. If it is even, then the first player wins, if it is odd, then the second. Decision. The parity of the result does not depend on the arrangement of pluses and minuses, but depends only on the number of odd numbers in the initial set. Since in this case there are 10 of them (i.e. an even number), the first player wins.
Decision. The parity of the result does not depend on the arrangement of pluses and minuses, but depends only on the number of odd numbers in the initial set. Since in this case there are 10 of them (i.e. an even number), the first player wins.
Problem 4. Two people take turns placing rooks on the chessboard so that the rooks do not attack each other. The one who cannot make a move loses. Decision. After each move, both the number of files and the number of rows on which rooks can be placed are reduced by 1. Therefore, the game will continue for exactly 8 moves. The last, winning move will be made by the second player.
13. Chain
Didactic goal: to teach how to transform one example into another.
Equipment: pictures of tumblers, cars, leaves.
Contents: pictures are placed in groups, in each group there are pictures of two colors.
For example: 2 green and 3 blue tumblers. One student makes an example for addition 2 + 3 from this picture, the other uses the commutative property 3 + 2, the third makes an example for the composition of numbers 5 = 3 + 2, the fourth makes an example for subtracting one of the terms 5–3=2, the fifth makes another subtraction example, the sixth compares the number of green tumblers and blue ones. Then also with another group of pictures.
Then also with another group of pictures.
14. Let's play a problem
Didactic goal: to check the assimilation of the concept of a task. Equipment: cards "task", "condition", "question", "solution", "answer". Content: the child receives a card and must find his place .
15. Cosmonauts
Didactic goal: to consolidate counting skills within 10, 20.
Equipment: 3 cards with the image of rockets (examples in the windows).
Content: the class is divided into 3 crews according to the number of rows.
On the 1st desk of each row is a rocket with expressions. Their number corresponds to the number of crew members and is the same for each row. The teacher says, “We are going on a space journey. The first rocket to take off is the one whose crew is the first to correctly find the values of all expressions. On a signal, students begin to solve examples in turn, one example at a time. The last one decides to raise the rocket. The solution is checked and, if everything is correct, the crew goes into space.