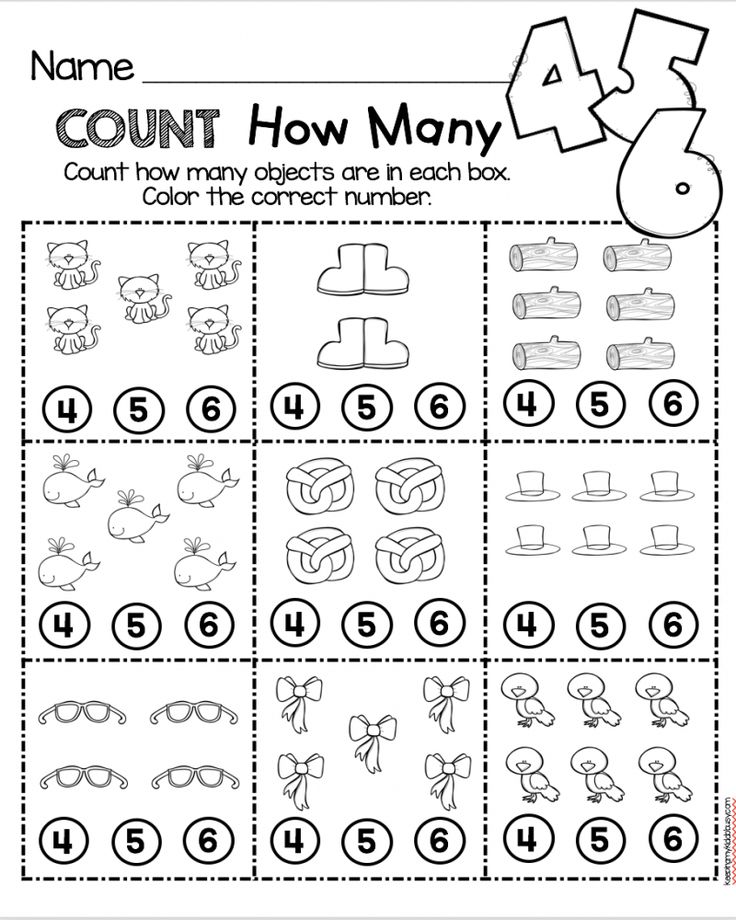
Math lessons for first graders
First Grade Online Lesson Plans
View Our Lesson Demos!
A first grade math curriculum should teach students the fundamentals in a way that is not just effective, but also fun. In addition to giving students a solid foundation, first grade math fluency also arms students with the tools and confidence they need to learn more advanced concepts down the road.
If a child can’t keep up with a first grade math curriculum, not only will they fall behind and, in turn, lose confidence, but they’ll also lose interest in the subject. Additionally, the skills and concepts that students learn in first grade math aren’t just limited to use in their academic studies. First grade math fluency also helps students become better problem solvers and logical thinkers.
What Math Should a 1st Grader Know
Students will acquire tons of new math skills in first grade. This knowledge will serve as a foundation for what they will learn in second grade math and also expand on what they learned in kindergarten. As they go into first grade, students should be familiar with a number of concepts in order for them to be successful and learn more advanced topics and math strategies. These include, but are not limited to:
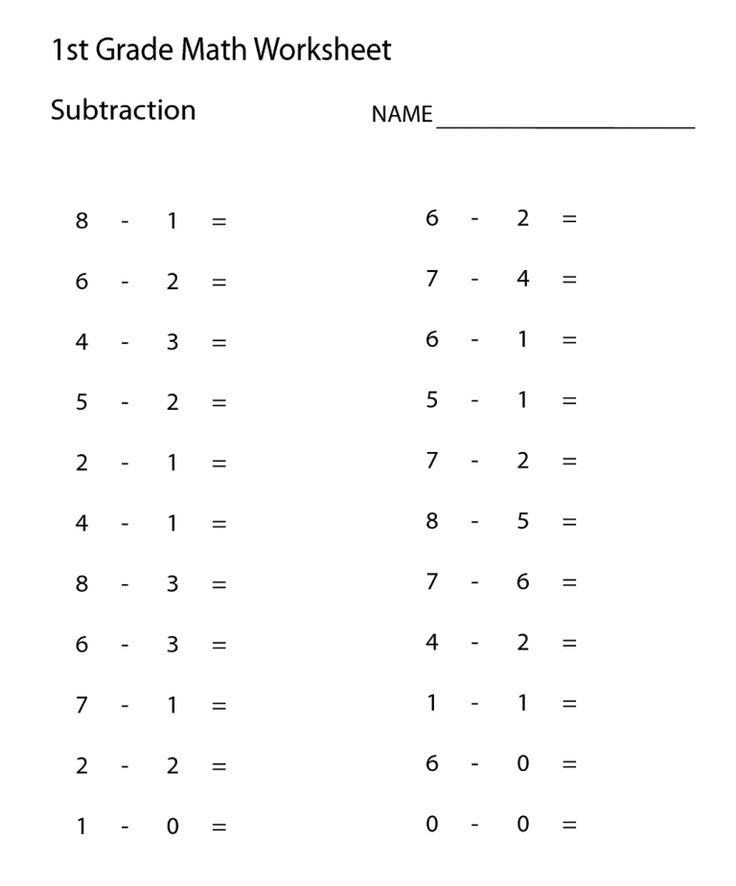
- Be able to count, identify and write numbers
- Perform one-digit addition and subtraction
- Have an understanding of quantity (more and less)
- Familiarity with patterns and shapes
- Knowledge of place value (ones, tens, etc.)
The ideal math curriculum for first grade should not only build on these skills and ensure mastery of new concepts, but also make learning fun by engaging and motivating students.
Math Objectives for 1st Grade
Once you’ve selected the ideal math curriculum, it is important to set some attainable goals. Below is a sample of what some of these math goals should be:
- Count to 100; county by 5s and 10s to 100; count by 2s to 40
- Represent numbers on a number line
- Add and subtract 2-digit numbers
- Write the date; tell time; read a calendar
- Count and create coin combinations; add and subtract money
- Identify, sort and classify 2-dimensional shapes
- Understanding the value of money
Towards the end of the year, if your child has already achieved most of their first grade math goals you can give them a head start for the next year by having them practice math facts. This will solidify what they learned in first grade and prepare them for their second grade math learning targets.
This will solidify what they learned in first grade and prepare them for their second grade math learning targets.
1st Grade Math Scope & Sequence
Chapter 1: “Number Sense”
Lesson 1: Read Numbers –
2 ActivitiesRead whole numbers up to 100. Use one-to-one correspondence to count objects up to 100.
Lesson 2: Compare Numbers –
2 ActivitiesCompare and order whole numbers up to 100 by understanding the concepts of greater than, less than, and equality.
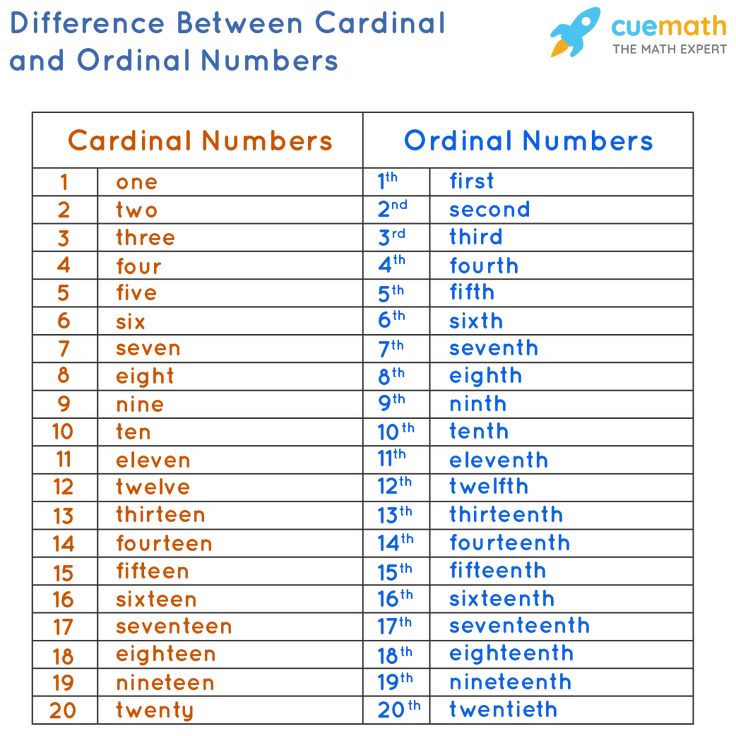
Lesson 3: Ordinal Numbers –
2 ActivitiesMatch ordinal numbers with an ordered set of up to ten items. Identify first, second, and third by name.
Lesson 4: Count Numbers –
2 ActivitiesCount forward and backward by ones and count forward by tens from any number less than 100.
Lesson 5: Place Value –
2 ActivitiesIdentify the place value of a digit in whole numbers to 100. Identify the value of digits up to the hundreds place.
Identify the value of digits up to the hundreds place.
Lesson 6: Compare with Place Value –
2 ActivitiesGroup objects by tens and ones. Compare and order whole numbers up to 100 using place value.
Lesson 7: Count by Twos and Fives –
2 ActivitiesCount forward by twos and fives up to 50.
Lesson 8: Odd and Even Numbers –
2 ActivitiesModel and identify even and odd numbers.
Chapter Test: Number Sense
Chapter 2: “Fractions”
Lesson 1: Equal and Unequal Parts –
2 ActivitiesIdentify equal and unequal parts of wholes.
Lesson 2: Halves and Fourths –
2 ActivitiesIdentify and demonstrate fractions (1/2, 1/4) as parts of whole and parts of a set using concrete materials and drawings.
Lesson 3: Thirds –
2 ActivitiesIdentify and demonstrate thirds and 1/3 of wholes using concrete materials and objects.
Lesson 4: Equal Fractions –
2 ActivitiesIdentify equivalent fractional parts as a whole.
Chapter Test: Fractions
Chapter 3: “Operations”
Lesson 1: Adding and Subtracting –
4 ActivitiesDemonstrate understanding of the meaning of addition and subtraction by using language such as put together, take away, increase, decrease, compare, and find the difference. Relate informal language to mathematical language and symbols.
Lesson 2: Place Value –
2 ActivitiesWhen given any number up to 100, identify one more than, one less than, 10 more than, and 10 less than.
Lesson 3: Equal Numbers –
2 ActivitiesUsing diagrams and/or numerical expressions, represent equivalent forms of the same number up to 12.
Lesson 4: One-digit Addition –
2 ActivitiesSolve one-digit addition problems.
Lesson 5: One-digit Subtraction –
2 ActivitiesSolve one-digit subtraction problems.
Lesson 6: Sum of Three Addends –
6 ActivitiesFind the sum of three one-digit numbers.
Lesson 7: Two-digit Addition –
6 ActivitiesSolve two-digit addition problems.
Lesson 8: Zero as a Placeholder –
2 ActivitiesExplain the meaning of zero and its function as a placeholder. Explore adding and subtracting zero.
Lesson 9: Addition and Subtraction Strategies –
7 ActivitiesSolve for basic addition and subtraction facts by using strategies such as counting on, counting back, doubling, doubling plus one, and making ten.
Lesson 10: One-Digit Word Problems –
2 ActivitiesSolve addition and subtraction one-digit word problems by selecting the proper operation.
Lesson 11: Problem Solving Strategies –
2 ActivitiesChoose an appropriate method, such as using concrete materials, mental math, or paper and pencil to solve real-world addition and subtraction problems.
Lesson 12: Estimation Language –
2 ActivitiesUse the appropriate language of estimation such as about, near, closer to, and between to identify and describe numbers in real-world situations.
Lesson 13: Estimate –
3 ActivitiesEstimate reasonable answers to compare amounts, count objects, and solve basic facts.
Chapter Test: Operations
Chapter 4: “Money”
Lesson 1: Coin Values –
2 ActivitiesIdentify and name the values of coins (penny, nickel, dime) and show different combinations of coins that equal the same value, up to 75¢. Recognize and use the cents sign.
Lesson 2: Count Money –
2 ActivitiesIdentify and count money to equal an amount using the fewest coins.
Lesson 3: Model Money Amounts –
2 ActivitiesIdentify and count money to equal an amount using the fewest coins.
Lesson 4: Add and Subtract Money –
3 ActivitiesSolve simple addition and subtraction problems involving the use of pennies, nickels, and dimes up to 50¢.
Chapter Test: Money
Chapter 5: “Patterns”
Lesson 1: Sort Using One Attribute –
2 ActivitiesSort and classify objects by one attribute.
Lesson 2: Sort Using Two Attributes –
2 ActivitiesSort and classify objects by two or more attributes.
Lesson 3: Rules for Sorting –
2 ActivitiesJustify rules for sorting and classifying.
Lesson 4: Build Patterns –
2 ActivitiesUse one attribute to create a pattern. Identify errors in repeating patterns.
Lesson 5: Classify Patterns –
2 ActivitiesClassify, describe, and extend patterns of objects using a wide variety of attributes (i.e., size, shape, color).
Lesson 6: Picture and Number Patterns –
2 ActivitiesPredict and extend pictorial patterns. Identify and generate patterns in number pairs by adding to a T-chart.
Lesson 7: Repeating and Growing Patterns –
2 ActivitiesExplore and create repeating patterns and growing patterns and generate rule for such patterns.
Lesson 8: Patterns on a Hundreds Chart –
2 ActivitiesExplore patterns of numbers on a hundreds chart.
Lesson 9: Skip Counting –
2 ActivitiesUse patterns to skip count by 2s, 5s, and 10s to 100. Understand and identify odd and even numbers.
Lesson 10: Extend Number Patterns –
2 ActivitiesPredict and extend existing numerical patterns using addition.
Chapter Test: Patterns
Chapter 6: “Algebra”
Lesson 1: Order Property –
2 ActivitiesUse the Commutative Property of Addition in solving problems.
Lesson 2: Add and Subtract Numbers –
2 ActivitiesUsing objects and pictures, model situations that involve the addition and subtraction of whole numbers.
Lesson 3: Fact Families –
2 ActivitiesIdentify fact families by understanding the patterns in related addition and subtraction sentences.
Lesson 4: Number Sentences –
2 ActivitiesUsing objects, create models that represent a variety of number sentences including the missing addend.
Lesson 5: Equal and Unequal –
2 ActivitiesUse concrete objects and pictorial representations to explore equalities and inequalities.
Lesson 6: Greater Than and Less Than –
2 ActivitiesUse concrete objects to solve number sentences with equalities and inequalities using the symbols <, =, >.
Lesson 7: Solve for Unknown Numbers –
3 ActivitiesSolve addition and subtraction problems with an unknown number represented by a geometric shape.
Chapter Test: Algebra
Chapter 7: “Shapes”
Lesson 1: Straight and Curved Lines –
2 ActivitiesCompare plane figures based on their straight and curved lines.
Lesson 2: Open and Closed Shapes –
2 ActivitiesIdentify open and closed figures.
Lesson 3: Plane and Solid Shapes –
4 ActivitiesIdentify circles, triangles, and rectangles (including squares), and describe the shape of balls, boxes, cans, and cones. Sort shapes by attributes (sides, curves, corners).
Lesson 4: Special Plane Shapes –
2 ActivitiesRecognize plane shapes such as hexagons, trapezoids, and rhombi.
Lesson 5: Attributes of Plane Shapes –
2 ActivitiesDescribe and compare attributes (sides, vertices, angles) of two-dimensional shapes.
Lesson 6: Name Solid Shapes –
2 ActivitiesRecognize solid shapes such as spheres, cylinders, cones, and cubes.
Lesson 7: Attributes of Solid Shapes –
2 ActivitiesDescribe and compare attributes (edges, vertices, faces) of three-dimensional shapes.
Lesson 8: Congruent Shapes –
3 ActivitiesIdentify congruent two- and three-dimensional shapes.
Chapter Test: Shapes
Chapter 8: “Positions”
Lesson 1: Positions of Objects –
2 ActivitiesDescribe relative positions of objects or shapes using words such as top, middle, on, inside, and outside.
Lesson 2: Direction Words –
2 ActivitiesInterpret directional words such as left, right, up, and down.
Lesson 3: Position Words –
2 ActivitiesIdentify, locate, and move objects according to positional words such as to the left, above, and behind.
Lesson 4: The Number Line –
2 ActivitiesLocate, plot, and identify known and unknown numbers on a number line from 0 to 20 by ones and from 1 to 100 by tens.
Chapter Test: Positions
Chapter 9: “Using Shapes”
Lesson 1: Slides and Turns –
2 ActivitiesIdentify slides and turns with objects.
Lesson 2: Congruent Shapes –
2 ActivitiesIdentify matching pairs of congruent figures that have been turned or flipped.
Lesson 3: Symmetry –
2 ActivitiesIdentify lines of symmetry in two-dimensional shapes.
Chapter Test: Using Shapes
Chapter 10: “Spatial Sense”
Lesson 1: Build Shapes –
6 ActivitiesCreate two-dimensional and three-dimensional shapes using other shapes (e. g., two squares make a rectangle).
g., two squares make a rectangle).
Lesson 2: Plane and Solid Shapes –
2 ActivitiesRecognize two- and three-dimensional shapes from various perspectives.
Lesson 3: Perimeter and Area –
2 ActivitiesCompare perimeter and area of two-dimensional shapes in terms of less than, equal to, or greater than.
Lesson 4: Shapes Around Us –
2 ActivitiesRecognize geometric shapes in the environment.
Lesson 5: Pattern Blocks –
2 ActivitiesUse pattern blocks to form shapes. Identify combined shapes in nature, art, and architecture.
Chapter Test: Spatial Sense
Chapter 11: “Time”
Lesson 1: Calendar –
2 ActivitiesIdentify the names of the week and months of the year using a calendar.
Lesson 2: Passage of Time –
2 ActivitiesIdentify the keywords that name the passage of time such as yesterday, afternoon, night, and day.
Lesson 3: Tools for Telling Time –
2 ActivitiesIdentify tools for measuring time such as clocks and calendars and name parts of each tool.
Lesson 4: Time to the Hour and Half-hour –
2 ActivitiesTell time on analog and digital clocks to hour and half hour, and relate time events using shorter/longer.
Lesson 5: Time to the Hour and Half-hour –
2 ActivitiesTell time on analog and digital clocks to hour and half hour, and relate time events using shorter/longer.
Lesson 6: Elapsed Time –
2 ActivitiesSolve simple real-world problems involving elapsed time to the hour and half hour and minutes.
Chapter Test: Time
Chapter 12: “Length”
Lesson 1: Non-standard Units –
2 ActivitiesUse nonstandard units to estimate and measure lengths.
Lesson 2: Compare Lengths –
2 ActivitiesCompare the length of two or more objects by using direct comparison or by using nonstandard units.
Lesson 3: Customary Units –
2 ActivitiesUse customary units to measure, compare, and order objects according to lengths, in inches and feet.
Lesson 4: Tools and Units –
2 ActivitiesChoose the appropriate unit and tool to measure length.
Lesson 5: Metric Units –
2 ActivitiesUse metric units to measure, compare, and order objects according to lengths.
Chapter Test: Length
Chapter 13: “Weight”
Lesson 1: Non-standard Units –
2 ActivitiesUse nonstandard units to estimate and measure weights.
Lesson 2: Compare Weights –
2 ActivitiesCompare the weight of two or more objects by using direct comparison or by using nonstandard units.
Lesson 3: Customary Units –
3 ActivitiesCompare the weight of two or more objects using customary units and identify the tools for measuring weight.
Lesson 4: Metric Units –
2 ActivitiesUse metric units to measure, compare, and order objects according to weights.
Chapter Test: Weight
Chapter 14: “Capacity”
Lesson 1: Non-standard Units –
2 ActivitiesUse nonstandard units to estimate and measure capacity.
Lesson 2: Compare Capacity –
2 ActivitiesCompare the capacity of two or more containers using direct comparison.
Lesson 3: Customary Units –
2 ActivitiesCompare the capacity (in cups, pints, and quarts) of two or more containers. Identify the tools for measuring capacity.
Lesson 4: Metric Units –
2 ActivitiesUse metric units to measure, compare, and order objects according to capacity.
Chapter Test: Capacity
Chapter 15: “Temperature”
Lesson 1: Measure Temperature –
2 ActivitiesUsing a Fahrenheit thermometer, tell temperature to the nearest 10 degrees. Match temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to the feeling outside of a warm or cold day.
Lesson 2: Compare Temperature –
2 ActivitiesCompare temperatures in degrees Fahrenheit of two or more objects. Identify tools for measuring temperature.
Chapter Test: Temperature
Chapter 16: “Graphing”
Lesson 1: Tally Table –
2 ActivitiesSort objects into categories and create a tally table.
Lesson 2: Pictographs –
2 ActivitiesOrganize and record data in pictographs.
Lesson 3: Bar Graphs –
2 ActivitiesOrganize and record data in bar graphs.
Chapter Test: Graphing
Chapter 17: “Using Data”
Lesson 1: Compare Data –
2 ActivitiesInterpret data and explore range and mode in simple graphs.
Lesson 2: Make Predictions –
2 ActivitiesUse data to make predictions about events or situations.
Chapter Test: Using Data
Chapter 18: “Probability”
Lesson 1: Certain or Impossible –
2 ActivitiesIdentify whether an event is certain, possible, or impossible.
Lesson 2: Most and Least Likely –
2 ActivitiesIdentify the likelihood of a given event.
Chapter Test: Probability
Why Choose Time4Learning First Grade Math Homeschool Curriculum
Without a thorough understanding of foundational math skills, students will find it difficult to keep up with a first grade math curriculum. As we all know, in order to keep a young child engaged and to instill a lifelong love of learning they need to enjoy the lessons.
Time4Learning makes learning fun for first graders through interactive, multimedia-based lessons that feature colorful animations, funny characters, and catchy songs — all of which help children learn, retain information, and have fun. With a simple-to-follow format that builds on previous material, students are able to expand their knowledge and build their first grade math fluency in order to master concepts in number sense, addition, subtraction, estimation, money, patterns, and more.
In addition to providing an award-winning curriculum for students, Time4Learning can help your student achieve all their first grade math goals and objectives with our flexible, student-paced curriculum. It also offers convenient tools for parents that help you save time and homeschool with confidence. Learn more about our online first grade homeschool curriculum, designed to help your child learn and master their fundamental concepts.
First Grade Math Games That Will Really Engage Your Students
Early elementary teachers have a chance to instill in their students a love of math right from the start. One great way to do that is to make math fun! These first grade math games cover all the standard skills firsties need to know, in ways that make learning engaging and enjoyable for all.
(Just a heads up, WeAreTeachers may collect a share of sales from the links on this page. We only recommend items our team loves!)
1. Assemble a domino puzzle
Print the free puzzles at the link below. Then grab some dominoes and start filling in the puzzle one piece at a time by placing a domino that adds up to the number shown in each rectangle. The trick is that regular domino rules still apply, so each number must touch another domino with the same number on that end.
Then grab some dominoes and start filling in the puzzle one piece at a time by placing a domino that adds up to the number shown in each rectangle. The trick is that regular domino rules still apply, so each number must touch another domino with the same number on that end.
Learn more: Games 4 Gains
2. Play tic-tac-toe with addition problems
Work out the answer to each problem in the grid, and dot or circle the ones that add up to 10. First to get three in a row wins!
Learn more: 123Homeschool4Me—Tic-Tac-Toe Math Game
ADVERTISEMENT
3. Face off in Dice War
Dice games are fantastic in the classroom! With this one, kids practice their addition facts and get a little work with subitizing too. The concept is so simple: Each player rolls the dice and adds up their numbers. The highest sum wins that round. This is one of those first grade math games that can be expanded by adding a third die. (You can also use playing cards. )
)
Learn more: Miss Giraffe’s Class
4. Use sticky notes to make 10
Sticky notes have so many uses in the classroom. In this case, challenge students to put together the numbered notes that “make 10.” They’ll practice adding to 10 with multiple numbers. You can also do this with subtraction, starting at 10, to make zero.
Learn more: Life Over C’s
5. Play Shut the Box
This game has been played for hundreds of years, but it’s a fun and sneaky way to practice addition facts fluency. The goal is to “close” each of the numbers in the box from one to nine by rolling the dice. For instance, if a player rolls 11, they may close 1, 2, 3, and 5, as these add up to 11. If no numbers are available to add up to the dice total, play passes to the next player and continues until someone finally “shuts the box” by closing the last available number. You can play this game with a specially designed box, as it has been played for years. You don’t need the box, though; simply have kids write out the numbers 1 through 9 and cross them out as they play.
6. Assemble some addition grab bags
Fill a variety of bags with collections of small objects. Kids grab a handful from two different bags, then count and add up the results. Be sure they write it all down to get practice at setting up equations. First grade math games like this one work for subtraction too.
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching—Grab Bags
7. Face Off to find the difference
Each player rolls the dice (try polyhedral dice for higher numbers, or roll several dice and add them together) and builds a stack of math cubes. Then they “face off” and find the difference between their two stacks.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls
8. Plant flowers and count on
Pick up some artificial flowers at the dollar store for this springtime garden game. Roll the die and add that number of flowers to your pot. Then roll again and add more, counting on from where you left off. Easy and fun!
Learn more: Fun-a-Day
9.
 Build and count on
Build and count onHere’s a fun hands-on way to practice counting on and addition. You can use any type of building blocks for this one. Get free printables at the link.
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching—Building On
10. Print a hundreds chart to play Battleship
Help students master numbers up to 100 by playing Battleship, using a standard hundreds chart. They’ll enjoy the strategy (and the fun of crying “boom!” when they sink a ship) while they develop number sense and practice number words.
Learn more: 123Homeschool4Me—Hundreds Chart Battleship
11. Fill in a number grid puzzle
These hundreds chart puzzles encourage kids to use a variety of first grade math skills to fill in the missing numbers. They’ll practice counting on, numbers to 100, skip counting, and more. Grab these 10 free printable puzzles at the link.
Learn more: Helping With Math
12. Try nuts and bolts for place-value practice
Mastering the concepts of tens and ones is more fun with hands-on activities.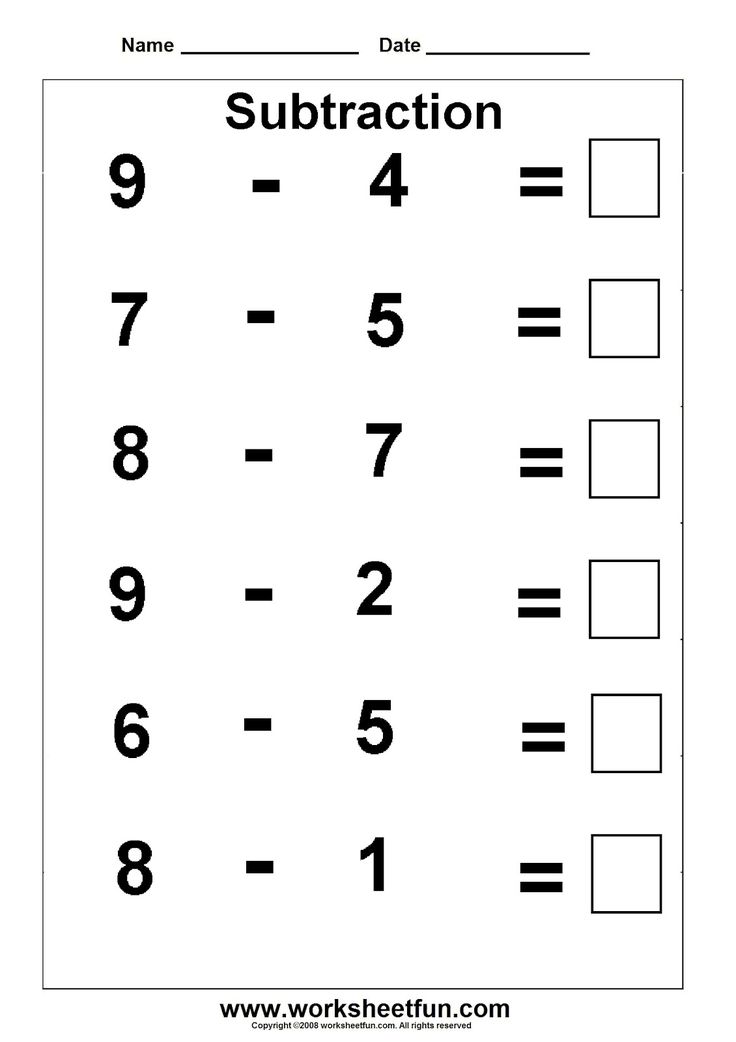 We love these DIY math manipulatives that use inexpensive nuts and bolts from the hardware store to drive home the idea of place value. (Bonus: Kids also practice fine motor skills!) Get free printable mats to use with this activity at the link.
We love these DIY math manipulatives that use inexpensive nuts and bolts from the hardware store to drive home the idea of place value. (Bonus: Kids also practice fine motor skills!) Get free printable mats to use with this activity at the link.
Learn more: The Measured Mom
13. Have a place-value scavenger hunt
Grab a stack of old magazines and use it for a place-value scavenger hunt! You can do this one at school or send it home for homework. Get free printables to use for this first grade math game at the link.
Learn more: Primary Theme Park—Place Value Scavenger Hunt
14. Practice tens and ones with I Have, Who Has
As first graders work with the concepts of tens and ones, play this simple game to give them confidence. Using the free printable cards at the link, the first player calls out “I have …” followed by the number shown on their card in blocks. Then they call out the number on the bottom, and the player who has that number takes over.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato—I Have, Who Has
15. Deal Uno cards to compare numbers
Some first grade math games are just slightly harder versions of kindergarten ones. Make a greater than/less than mat with paper scraps and a brad, as shown. Lay out two Uno cards on each side, since first graders work on comparing two-digit numbers. Swing the arms of the signs around to the correct direction to indicate which is greater.
Learn more: The Kindergarten Smorgasboard
16. Knock down the pins with dot arrangement bowling
Take an inexpensive toy bowling set (or make your own with plastic bottles) and add sticky dots arranged in patterns. Students roll the ball and then have to quickly subitize to determine how many dots are on each pin they knocked down. If they get it right, they get the points!
Learn more: The First Grade Parade
17. Navigate a time-telling maze
Start with the first clock and color in the line that shows the correct time.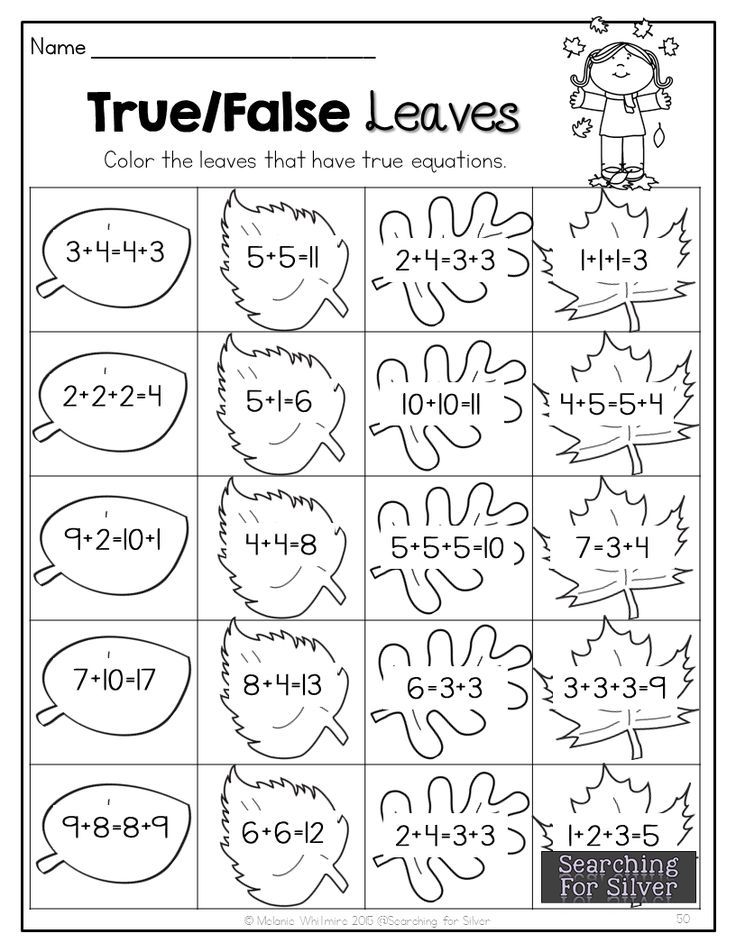 That leads you to the next clock, and so on, until you’re done!
That leads you to the next clock, and so on, until you’re done!
Learn more: 123Homeschool4Me—Time-Telling Maze
18. Assemble time-telling puzzles
Firsties should be mastering time to the hour and half hour. These free printable puzzles help them match up analog and digital clock times. Have them say the times out loud as they match them up too.
Learn more: 123Homeschool4Me—Time-Telling Puzzles
19. Match up plastic eggs
This is always a popular way to practice telling time. Draw clocks on one half of the eggs, and write out the times in numbers or words on the other half. For even more fun, hide the halves around the room and go on an egg hunt before you match them up!
Learn more: The STEM Laboratory
20. Put together shapes to make other shapes
Use pattern blocks with the free printable cards at the link to get kids playing around with simple geometry. They’ll practice recognizing basic shapes and learn they can use some shapes to make new ones.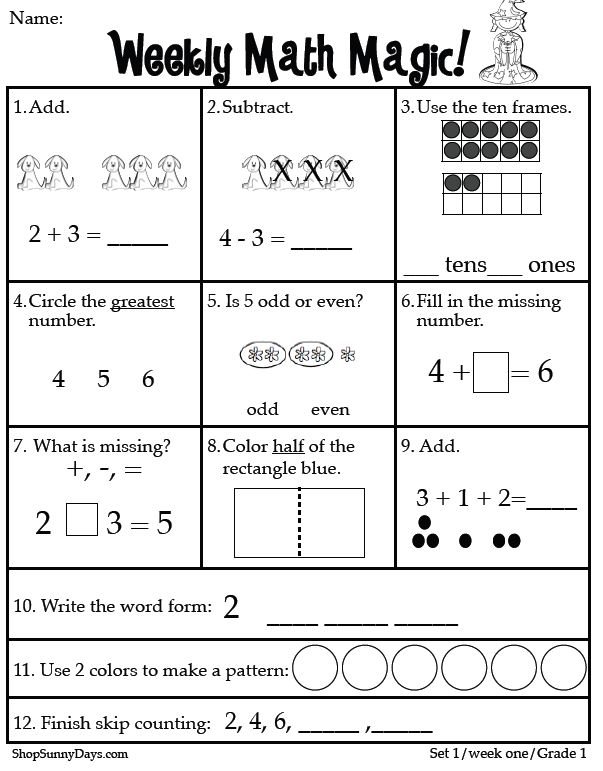
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching—Pattern Blocks
21. Partition and sort shapes
Gather up sticky notes in a variety of shapes and sizes. Draw lines on them to partition them equally or unequally. Then, have kids sort them based on type.
Learn more: Smitten With First
22. Build and measure with LEGO bricks
Everything is more fun with LEGO! Pull out a pile of square bricks and use them for these fun and free activities that incorporate estimating, measuring, and comparing length.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato—LEGO Math
23. Race and measure with toy cars
First, kids get a little STEM practice by figuring out how to build a ramp. Then, they race toy cars down the ramp, marking where they land. Finally, they compare distances using any kind of non-standard measurement they like.
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching—Non-Standard Measurement
24. Sort out your classroom toys
First graders work on sorting by attribute in as many as three categories. Put out a variety of building blocks, beads, or other classroom toys and lay out some Hula-Hoops. Ask kids to define the categories and start sorting! You can even overlap the hoops into Venn diagrams for items that meet more than one criteria.
Put out a variety of building blocks, beads, or other classroom toys and lay out some Hula-Hoops. Ask kids to define the categories and start sorting! You can even overlap the hoops into Venn diagrams for items that meet more than one criteria.
Learn more: BSM Year 2
25. Go on a bug hunt
Grab the free printable game at the link, then have kids graph their insects as they play. When they’re done, ask questions to ensure they understand the data they’ve collected.
Learn more: Primary Theme Park—Bug Hunt
Like these first grade math games? Don’t miss these 50 First Grade Math Word Problems of the Day!
Teachers deserve a strong support system. Find yours on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
100 math lessons for kids
Course lessons
All coursesAbout the course 1–4. Introduction
1. Numbers, Symbols, Shapes 2. Commensurability and incommensurability of segments 3. Visual representation of Newton's binomial 4. Infinite sums
Numbers, Symbols, Shapes 2. Commensurability and incommensurability of segments 3. Visual representation of Newton's binomial 4. Infinite sums
5–10. Movements of a straight line and a circle
5. Initial ideas about movement 6. Classification of straight line movements 7. Table of compositions of straight movements 8. Circle movements 9. Multiplication table of circle movements 10. Finite subgroups of motions of a straight line and a circle
Classification of straight line movements 7. Table of compositions of straight movements 8. Circle movements 9. Multiplication table of circle movements 10. Finite subgroups of motions of a straight line and a circle
11–20. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic and corollaries from it
Fundamental theorem of arithmetic and corollaries from it
11. Introduction to remainder arithmetic 12. Multiplication tables of residues 13. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic. Part 1 14. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic. Part 2 15. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic. Consequences 16. Solution of linear equations in integers. Part 1 17. Solution of linear equations in integers. Part 2 18. Continued fraction method 19. Results of arithmetic studies.
Fundamental theorem of arithmetic. Consequences 16. Solution of linear equations in integers. Part 1 17. Solution of linear equations in integers. Part 2 18. Continued fraction method 19. Results of arithmetic studies. Part 1 20. Results of arithmetic studies. Part 2
Part 1 20. Results of arithmetic studies. Part 2
21–30. Permutations
21. Introduction to permutations 22. Compositions of permutations 23. Cycles and order of permutations 24. Even permutation. Homomorphism 25. Game "Fifteen" and other tasks 26. Conjugation and conjugacy classes 27. Homomorphisms and Kernels 28. Normal subgroup 29.
Klein group 30. Generating subset
31–35. Plane movements
31. Introduction to plane movements 32. Classification of plane movements 33. Sliding Symmetry 34. Table of compositions of plane movements. Part 1 35. Table of compositions of plane movements. Part 2
Table of compositions of plane movements. Part 1 35. Table of compositions of plane movements. Part 2
36-50. Complex numbers
36. Number systems 37. The appearance of complex numbers 38. Addition, subtraction and multiplication of complex numbers 39.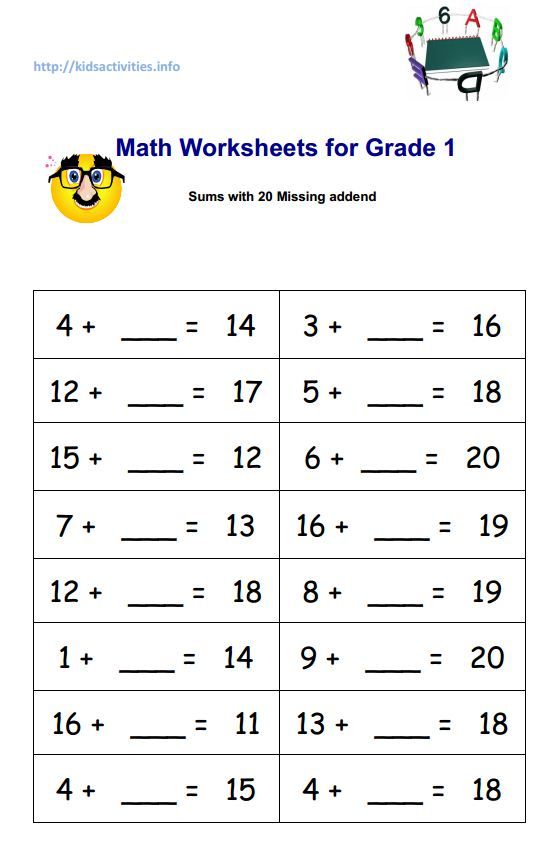 Complex numbers: conjugation, modulus, norm, division 40. Geometric meaning of multiplication of complex numbers 41. Degrees and Roots 42. Introduction to Gaussian numbers 43. Divisibility Arithmetic in Gaussian Numbers 44.
Complex numbers: conjugation, modulus, norm, division 40. Geometric meaning of multiplication of complex numbers 41. Degrees and Roots 42. Introduction to Gaussian numbers 43. Divisibility Arithmetic in Gaussian Numbers 44. Sums of squares 45. On the Approaches to Fermat's Christmas Theorem (RTF) 46. Geometry ℤ[i]. Division with remainder. Ideals 47. Completion of Fermat's Christmas Theorem 48. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic in Gaussian numbers 49.
Sums of squares 45. On the Approaches to Fermat's Christmas Theorem (RTF) 46. Geometry ℤ[i]. Division with remainder. Ideals 47. Completion of Fermat's Christmas Theorem 48. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic in Gaussian numbers 49.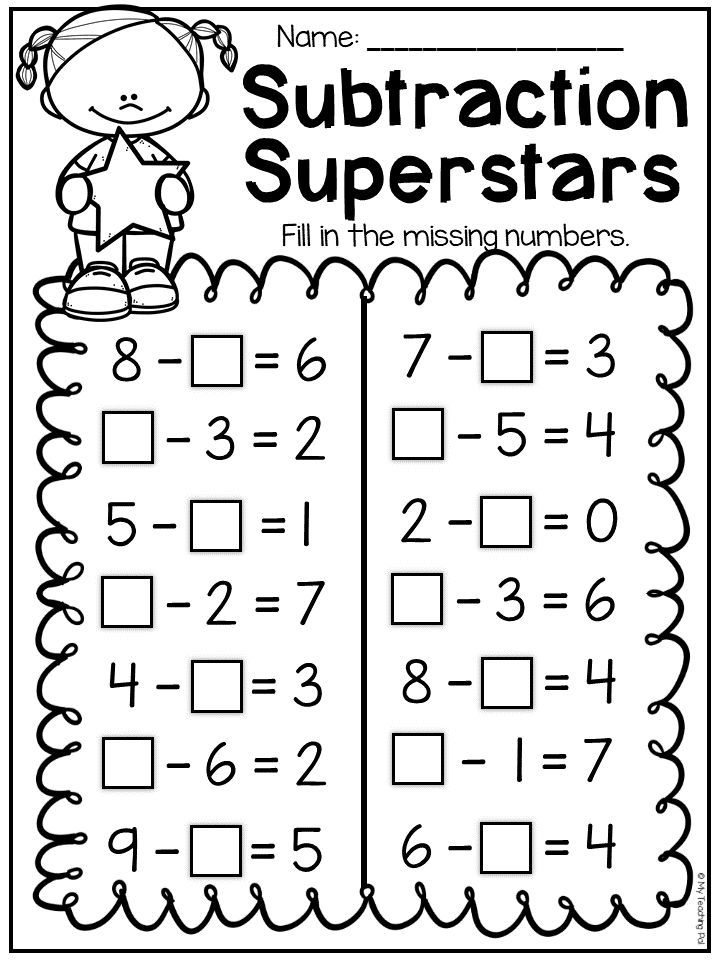 Pythagorean triplets. Start 50. Pythagorean triples. End
Pythagorean triplets. Start 50. Pythagorean triples. End
51-58. Polynomials and fields
51. Introduction to polynomials 52. Bezu and around
Game theory (lectures in Intellectual)
Lecture 1. Introduction to game theory Lecture 2. Mixed strategies Lecture 3.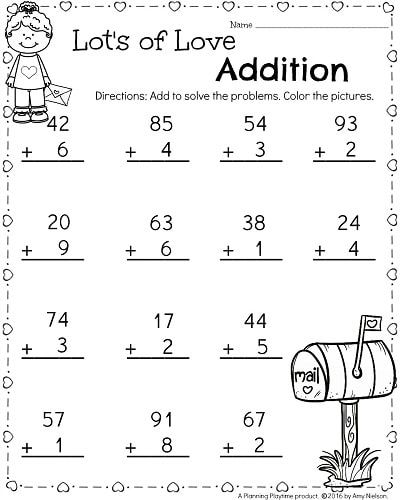 Dynamic game theory
Dynamic game theory
Mathematics
Alexey Vladimirovich Savvateev
Grade 5-11
This course was supported by:
courses, lessons for schoolchildren in the online school Amakids.ru
How to choose mathematics courses for a child
skills that the child will acquire. A correct and effective technique forms in children a cognitive interest in mathematics and other exact sciences, develops intelligence in many ways, teaches them to apply their abilities in practice, that is, both in school and in everyday life. Amamatika is a program for the development of mathematical abilities from the AMAKids Academy, which was developed by professional methodologists and meets all modern requirements and educational standards.
Benefits of the AMAKids Mathematics Teaching Method
Amamatika is a comprehensive program that combines all areas of mathematics required for younger students. The course allows you to learn the basics of arithmetic and geometry, acquire basic knowledge in the field of programming and financial literacy. This technique will teach you how to solve logical and complex non-standard tasks, form a child's spatial and analytical thinking. All this makes Amamatika one of the best methods of teaching mathematics for children in elementary school. Didactic materials and teaching aids of the course are filled with bright content that makes the learning process interesting and exciting.
The course allows you to learn the basics of arithmetic and geometry, acquire basic knowledge in the field of programming and financial literacy. This technique will teach you how to solve logical and complex non-standard tasks, form a child's spatial and analytical thinking. All this makes Amamatika one of the best methods of teaching mathematics for children in elementary school. Didactic materials and teaching aids of the course are filled with bright content that makes the learning process interesting and exciting.
Fundamentals of teaching mathematics in grades 1-4
Amamatika is a unique technique that will not only help students improve mathematics in grades 1-2 and 3-4, but will also increase their interest in this subject and in learning in general. The course is based on a large number of practical tasks - they will help to realize the importance of mathematics and related areas. When a child understands how this or that subject is useful to him, he makes more efforts to study it. In addition, it is in practice that it is best to consolidate knowledge and learn how to apply it.
In addition, it is in practice that it is best to consolidate knowledge and learn how to apply it.
What is better - a math tutor or an effective method?
Amamatika is aimed not only at studying the basics of mathematics, but also at inculcating knowledge in related areas to the student. This contributes to the expansion of the horizons of the child and the more harmonious development of his intellect. Even if you find a good tutor in mathematics, this effect will not be achieved because the tutor, preparing for classes, collects extracts from various methods and textbooks. This approach does not allow to make classes holistic and consistent. The Amamatika method works more comprehensively, which is especially important when teaching children in elementary school.
How to make teaching mathematics effective and simple?
If the child is not interested in learning, then the effectiveness of the educational process is reduced. Classes that are conducted in a playful way will help to change the attitude towards learning.