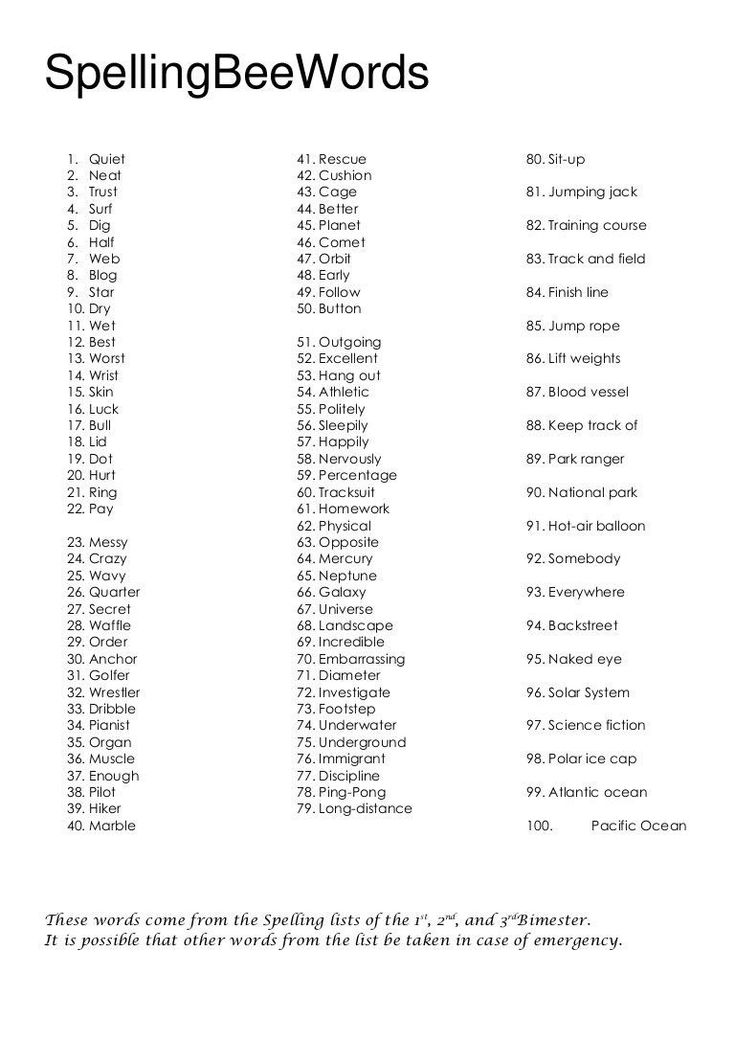
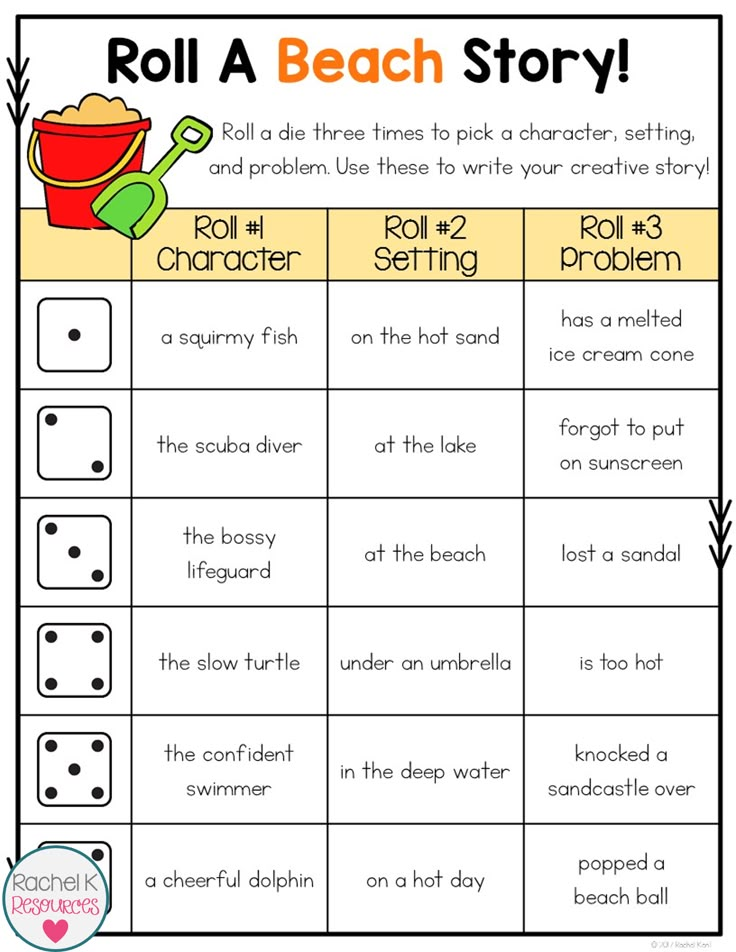
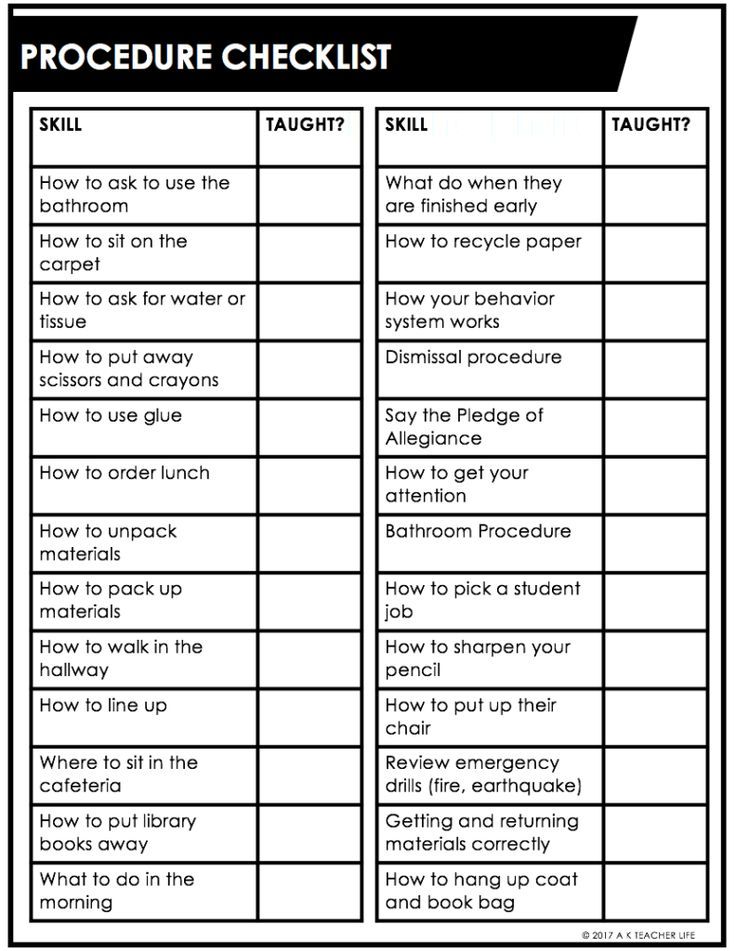
Math projects for kindergarteners
7 Kindergarten Math Activities To Make Learning Fun
Young children are often eager to learn new skills and concepts. That’s why introducing kindergarten math activities can be so effective.
One thing to always remember, though, is to make learning at home fun and engaging because children learn best through play. And, luckily for you, our experts at HOMER know a thing or two about that!
This article will give you a detailed guideline to help your child get a solid mathematical foundation. These easy at-home activities are fun, engaging, and offer lots of learning opportunities.
Without further ado, let’s get started.
Kindergarten Math Concepts
Before we dive in, it’s important to understand which concepts your young learner will be tackling in kindergarten. That way, it’s easier to know which activities and math skills to focus on at home.
The following are the key math principles your child may know by the end of their kindergarten year:
- Counting and cardinality
- Recognizing numbers beyond 10
- Adding and subtracting single-digit numbers
- Recognizing shapes
- Classifying objects by size
With the principles above in mind, we’ve compiled a list of activities that will help your child develop these essential skills.
7 Fun Kindergarten Math Activities
1) Shape Hunt
What You’ll Need:
- Notebook
- Crayons
What To Do:
Start by selecting any two objects around your house that look different but have the same shape. Then, give your child clues about one of the objects. For example, you might say, “It has a round shape.”
Your child will need to act as a detective and solve this shape mystery! When they are confident that they know what this object is, encourage them to take their detective notebook and draw the item.
Repeat this process for the second object.
Once your little detective has found and drawn the two objects, you can evaluate them and discuss other items with the same shape. So, for something that’s round, this can be plates, pizza, door handles, and so on.
Once you’re confident they understand the properties of the shape, you can play the game again with another shape (triangle, square, etc.).
You don’t have to limit yourselves to your indoor space. You can also head outside and search for many interesting shapes in your garden, local park, or neighborhood if you’d like.
You can also head outside and search for many interesting shapes in your garden, local park, or neighborhood if you’d like.
Find out more about this interesting game from our blog.
2) Count The Beans
What You’ll Need:
- Spoon
- Dried kidney beans
What To Do:
For this fun activity, you will need to take a spoon and hold it outstretched. Your child will then proceed to put one dried kidney bean at a time onto the spoon.
When the first one falls off, you then count how many beans you managed to get on the spoon.
You can play this game with a larger spoon as well. For this, the numbers will get higher, so your child will need to be familiar with higher numbers before they’re ready for this one.
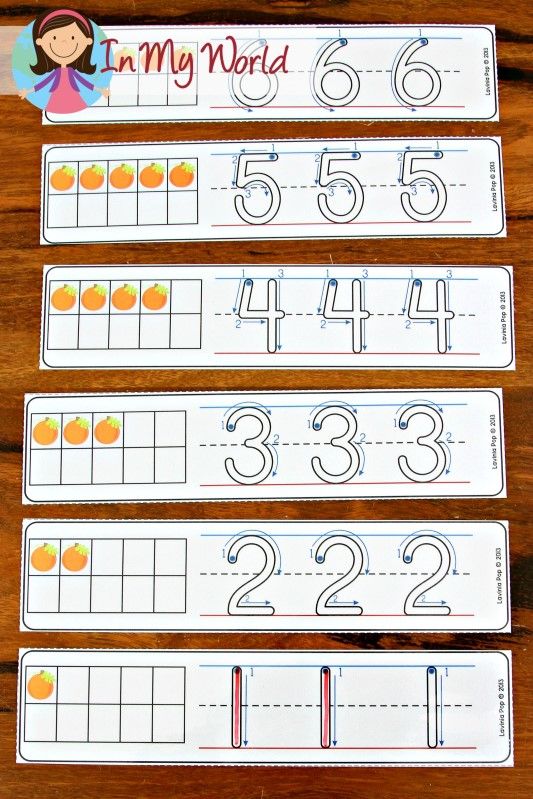
To help, a simple 10 frame should do the trick (a 10 frame is basically a rectangle with 10 equal spaces (five on top and five on the bottom).
If, when counting the beans, you end up with more than 10, you can put each set of 10 in a small paper cup, allocate the cups to each frame, and then add everything for the final tally.
This activity helps kindergarteners continue practicing their counting and gain an understanding of number sense.
3) Building Sets With Blocks
What You’ll Need:
- Building blocks
What To Do:
This activity requires you to ask your young learner to build a color tower with a specific number of blocks. For example, “Build a blue tower with 10 blocks, a red tower with eight blocks, and a yellow tower with eleven blocks.”
All this information will need to be remembered by your child, so this can be a great way to help build memory. Children will also continue practicing colors and counting skills with this activity.
4) Number Guessing
What You’ll Need:
Magnetic numbers (0 – 9)
What To Do:
For this activity, your child will need to put their hands behind their back. You will then place one of the magnetic numbers in their hands for them to feel. Can they guess the number?
If this is a little challenging at first, it can help to have another set of magnetic numbers that they can see as they feel.
This is a great sensory activity that can help familiarize children with each number’s interesting shape and unique qualities.
5) Shape Hopscotch
What You’ll Need:
- Different colored paper
- Scissors
- Painter’s tape
What To Do:
Hopscotch is one of our favorite games here at HOMER. If you’re looking to play the traditional game, you can check out this link, which includes other fun math-related activities in addition to Hopscotch.
For this article, we decided to switch things up a bit with shape hopscotch. All you need to do is cut out six different (but easily recognizable) shapes and give each shape its own color (for example, red circles, yellow triangles, blue squares, purple stars, etc.).
Once you have your shapes, tape them to the floor with painter’s tape. While taping, ensure that the spacing works for your child (the shapes aren’t too far apart).
You can encourage your child to jump, hop, or wiggle through the shapes. Here are a few ways they can make it through their shape maze:
Here are a few ways they can make it through their shape maze:
- Call out colors or shapes for your child to race and find
- Have them hop from one side to the other side by only touching one shape or color
- Give them directions as they go, and ask what they’ve landed on. For example, “Jump three shapes to the left, one shape up, and two shapes right. What color and shape are you on?”
This is an excellent and fun way for kids to continue working on their gross motor skills while incorporating shape and color recognition. Children will also work on the important skill of following directions.
6) Make A Number Line
What You’ll Need:
- Chalk
- Paved area outside
- Deck of cards
What To Do:
On your paved area outside, draw a large number line with chalk. You can write numbers up to 10, 20, or even 30 as your child becomes familiar with those numbers.
Next, take five red playing cards (numbers 1 – 5) and five black playing cards (numbers 1 – 5). Then, you each get a token which you’ll place in the middle of the number line. Mix the cards and put them face down.
Then, you each get a token which you’ll place in the middle of the number line. Mix the cards and put them face down.
Next, take turns picking cards. A red card means you go up the number line based on the card’s value (for example, if you pull a red five of hearts, you move up five spaces). A black card, on the other hand, means you go down on the number line (red four of clubs = down four spaces).
If you end up below the number one or above the top number on the line, you’ll stay put until all players have had their turn.
After each player has picked four cards, whoever is highest on the number line wins!
7) Snowball Battle
What You’ll Need:
- Paper
- 3 small buckets
What To Do:
Crumble your paper to make “snowballs.” Then, place your buckets at the end of the room. Challenge your child to toss the snowballs into any of the buckets until they reach a target number (e.g., 10).
If you have multiple kids, this can turn into some friendly competition with a timer. How many can you land in five minutes?
How many can you land in five minutes?
You can also vary the game a bit for older kids by having them toss all 10 snowballs into the three buckets and then write down how they got to 10 (for example, with 3 balls in one bucket, 4 balls in the next, and 3 balls in the last). How many ways can it be done?
Gross motor and counting skills come into play when engaging in this activity.
Tips For Helping Kindergarteners With Math
The above activities should help your child practice and understand their math skills. Additionally, here are a few key points to keep in mind.
Incorporate Math Into Everyday Life
Math is all around us! It is in the shapes of objects and buildings, the measurements we take when baking, and the sorting of patterns. This makes it easy to incorporate math into everyday activities.
Remember that the more practice your child gets, the easier it will be to grasp these foundational concepts.
Make It Enjoyable
When something seems too challenging, kids can quickly become overwhelmed and give up before starting. Help your child understand how much fun math is by regularly introducing them to math activities in a fun, relaxed way.
Help your child understand how much fun math is by regularly introducing them to math activities in a fun, relaxed way.
We recommend checking out the HOMER blog to see what other entertaining learning games your child can play to build their math skills.
Practice Positive Reinforcement
Positive feedback is one of the key components for your child to continue having a healthy relationship with mathematics. So, when they finally grasp a concept they’ve been struggling with, make a big deal out of it by praising them.
And, if there’s a math skill they haven’t grasped yet, be patient and continue practicing. Soon enough, they’ll get it!
Lay A Solid Foundation With Kindergarten Math Activities
Sometimes children (and adults) view math negatively. You’ll often hear them express how challenging it is. But kindergarten math activities can help build positivity and confidence!
While it can be a challenge, math is still one of the most important subjects children learn and can benefit them for the rest of their lives.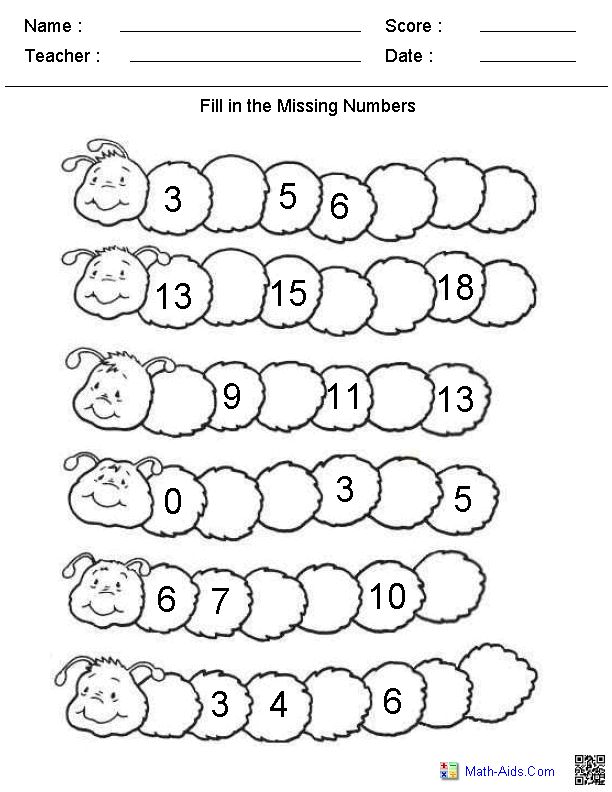 That’s why building math skills early on matters.
That’s why building math skills early on matters.
Engaging in fun, entertaining, and educational kindergarten math activities can help children achieve just that. And our list above offers great ways to practice.
Check out the HOMER Learn & Grow app for even more math activities and to discover how we can help your young learner thrive!
Author
Kindergarten Math Games That Make Learning Fun from the Start
Looking for ways to make math fun for young learners? Check out these kindergarten math games! They teach all the basic math skills kindergartners need to master and are sure to engage every kid in the learning process.
(Just a heads up, WeAreTeachers may collect a share of sales from the links on this page. We only recommend items our team loves!)
1. Conquer cardinality with penguin dominoes
Kindergarten math students work to master cardinality, understanding that written numerals correspond to the number of items pictured. These free printable penguin dominoes make the concept fun to practice.
These free printable penguin dominoes make the concept fun to practice.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
2. Put together puzzles to gain number sense
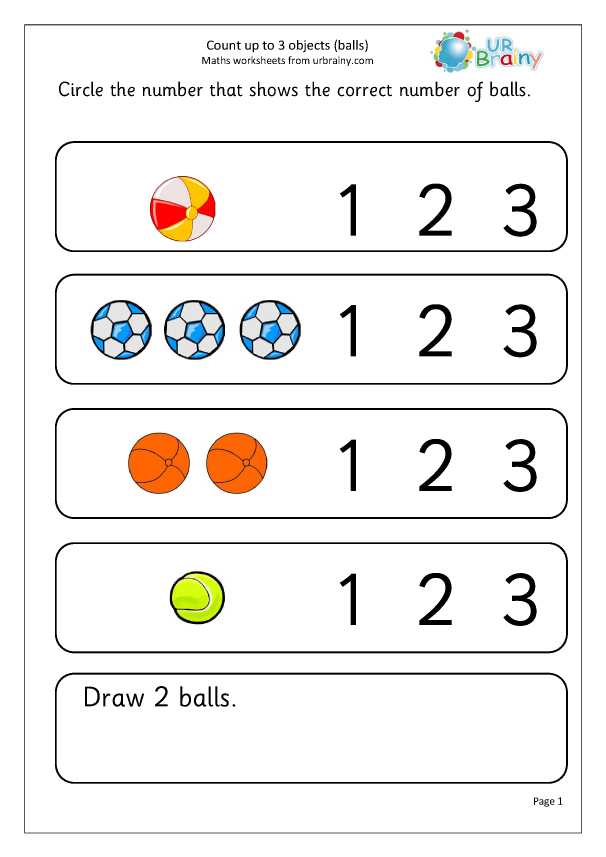
Kindergarten math students learn to understand that numbers can be represented in a variety of ways. These free printable puzzles help them practice those skills.
Learn more: Tickled Pink in Primary
ADVERTISEMENT
3. Play teen-number bingo
This free printable game helps little ones master their numbers from 11 to 20, both as numerals and represented on ten-frames.
Learn more: The Measured Mom
4. Stack cups and count to 100
Kids love stacking things, so they’ll get a kick out of kindergarten math games that make use of stackable cups. This one has them doing it with 100 cups while they count! Turn it into a competition by putting them in teams and timing them to see who can finish the task the fastest.
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard/100 Cups
5.
 Visit the skip-counting store
Visit the skip-counting storeHow fun is this? Grab some toys and label them with price tags in increments of 10 cents. Give kids a handful of plastic dimes, and have them count out the amount needed for each “purchase.”
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Skip Counting Store
6. Have a rubber duck race
In this game, kids race to see who can be the first to get their rubber duckies to 10 (or any number you choose). They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
Learn more: Happy Toddler Playtime
7. Practice counting on with cards and dice
Remove the face cards from a deck of playing cards and grab a pair of dice. The first player turns over a card and then rolls the dice. The number on the dice indicates how far they “count on” from the card. (For example, a player turns over a three and rolls a four. They say, “Three: four, five, six, seven.”) If the player gets it right, they keep the card, and the other player(s) get a turn.
(For example, a player turns over a three and rolls a four. They say, “Three: four, five, six, seven.”) If the player gets it right, they keep the card, and the other player(s) get a turn.
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Counting On
8. Skip-count with craft sticks
There are endless ways to use craft sticks in the classroom. For this game, number a series of colorful sticks by fives, as shown. Kids can practice by putting them in order first. Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Learn more: Simply Kinder
9. Match teen numbers
Once they’ve mastered the numbers 1 to 10, it’s time to understand how those numerals add up to make bigger numbers. These free printable cards show numerals and matching bundles of sticks that deconstruct each teen number into tens and ones.
Learn more: The Kindergarten Connection
10. Compare numbers with dominoes
Kindergartners learn to compare numbers to determine which is larger and which smaller. Stacking math cubes based on the numbers on dominoes is a fun, hands-on way to compare the two numbers side by side, making it easier to see the difference.
Learn more: My Fabulous Class
11. Face off and compare numbers
You’ll need some small toys for this game, as well as polyhedral dice. Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Learn more: Natalie Lynn Kindergarten
12. Make 10 with two-sided chips
You’ll need counting chips that are a different color on each side for this activity. Kids shake up 10 chips in a cup and pour them out on the table. Then they see how many they have of each color and write that number bond to make 10.
Learn more: First Grade Fairytales
13. Throw snowballs to make 10
Make “snowballs” from paper (or any way you like), then place them in a bucket at one end of the room. Start kids out by having them toss snowballs into another bucket until they reach 10 (or any target number). Then, up the challenge by placing some snowballs in each bucket and have kids figure out how many more they need to toss in to make 10.
Start kids out by having them toss snowballs into another bucket until they reach 10 (or any target number). Then, up the challenge by placing some snowballs in each bucket and have kids figure out how many more they need to toss in to make 10.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Snowball Math Games
14. Use Uno cards to play addition war
In the card game War, players each flip an Uno card, and the one whose card is greatest takes them both. In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Addition Game
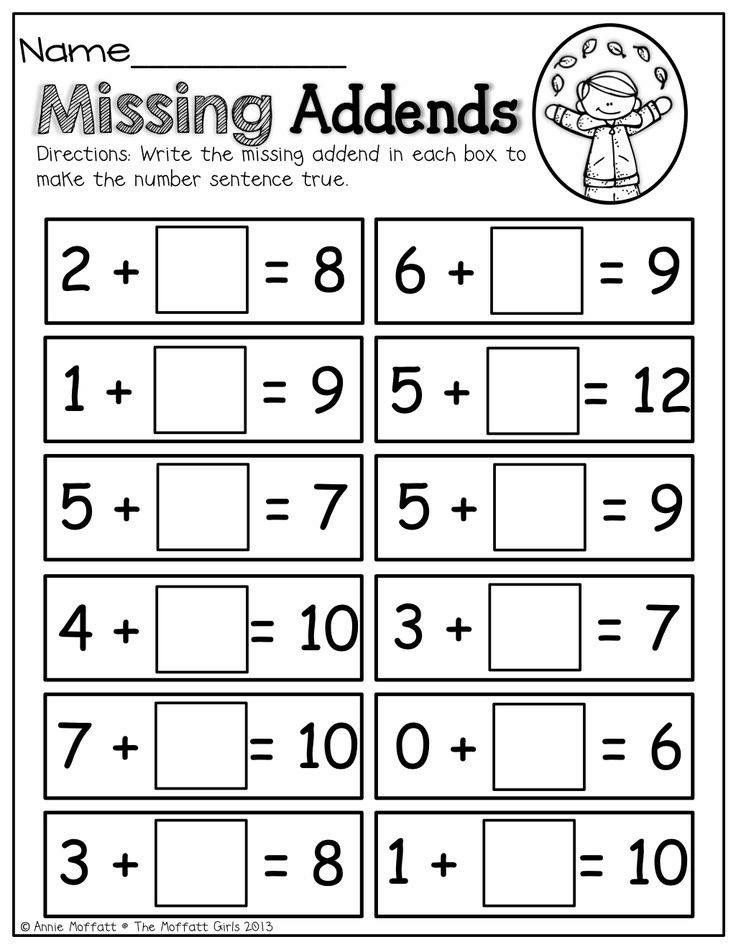
15. Roll and add for fluency within 5
Kindergarten math students work to become fluent in adding and subtracting within 5. This free printable board game makes it fun!
Learn more: Liz’s Early Learning Spot
16.
 Get four in a row and learn place value
Get four in a row and learn place valueThis customizable game helps teach the early place-value concept of tens plus ones. Get it for free at the link.
Learn more: Two Boys and a Dad
17. Bowl and subtract within 10
Set up a toy bowling pin set (or make one from plastic bottles or toilet-paper tubes). Kids bowl and see how many pins they knock down, subtracting that number from 10. Then they repeat, this time subtracting from the previous answer. First to get to zero wins!
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Subtraction Worksheets
18. Get off my boat!
So simple, so engaging, so fun! Use tape to outline a boat shape on the floor (or try this outside with sidewalk chalk). Let some kids board the “boat,” then make some get off. Use those numbers to write a subtraction number sentence and solve the equation!
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard—Get Off My Boat!
19. Drive and compare numbers to music
Prep for this game by using dot markers on paper plates as shown (visit the link below for more examples). Each kid takes a plate then uses it to “drive” around the room as you play music. When the music stops, they find a nearby partner and compare what they see on each other’s plates (e.g., “8 dots is more than 4 dots. 1 green dot is less than 4 green dots.” Then start the music up and repeat!
Each kid takes a plate then uses it to “drive” around the room as you play music. When the music stops, they find a nearby partner and compare what they see on each other’s plates (e.g., “8 dots is more than 4 dots. 1 green dot is less than 4 green dots.” Then start the music up and repeat!
20. Build a weigh station
Use a hanger and plastic cups to build a super-simple weigh station. Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
21. Battle it out in ribbon war
Looking for kindergarten math games that teach non-standard measurement? This idea is fun and easy. Cut colorful ribbons into a variety of lengths and place them in a bag. Each student pulls a ribbon from the bag. Then, put students in pairs and have them compare their ribbons to identify the longer one. The student with the longer ribbon keeps both, and the game continues.
22. Hold a shape scavenger hunt
Kindergarten math students are learning to recognize shapes in their environment and also to categorize and sort. This scavenger hunt does it all! Send them out to find objects in the room that match the shapes. Then count and compare to see how many you have in each category.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Shape Scavenger Hunt
23. Hop along a shapes maze
Use sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun—Shape Maze
24. Make a match to learn shapes
Grab these free printable memory cards at the link. Then play and learn the basic shapes.
Learn more: Life Over C’s
25. Guess the mystery shapes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing 3D shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like “The shape in this bag has 4 sides.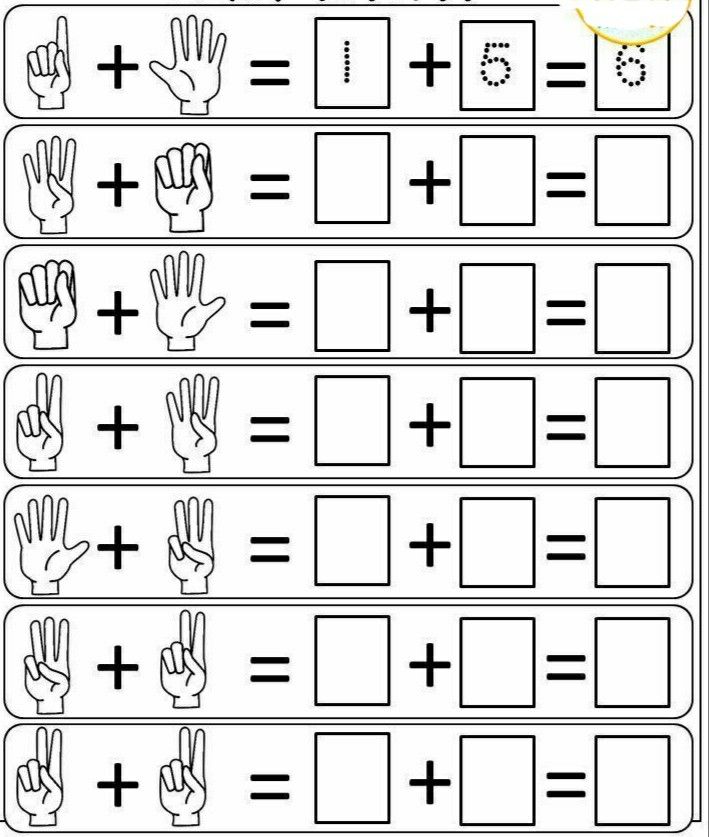 What could it be?”
What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
Love these kindergarten math games? You’ll also enjoy these 50 Kindergarten Math Word Problems of the Day!
Want more articles like this? Subscribe to our newsletters!
Entertaining Mathematics Project | Project in mathematics (senior group):
Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution Kindergarten "Berezka"
Cognitive project on the topic:
"Entertaining Mathematics"
.N.
Igrim, 2017
Relevance.
Mathematics is one of the most difficult subjects in the school cycle, therefore, in order to successfully teach a child at school already in kindergarten, it is necessary to promote the mathematical development of a preschooler, expand their mathematical horizons, and improve the quality of mathematical preparation for school. This will allow children to more confidently navigate the simplest patterns of the reality around them and actively use mathematical knowledge in everyday life.
Mathematical representations should be mastered by a preschooler consistently, evenly and systematically. To this end, it is necessary to organize educational activities carried out both in the process of organizing various types of activities (game, communication, labor, cognitive research, productive, musical and artistic, reading fiction), and during regime moments; as well as independent activities of children using a variety of gaming tools. Also, the mathematical development of children will be more effective when interacting with the families of children.
Didactic game and game exercises using visual material (using diagrams, cards, models, objects) arouse interest in children, facilitate and speed up the process of memorization, form techniques for working with memory and thinking, which in a visual and accessible form help children remember complex material.
Entertaining mathematical material is given by game elements contained in each task, logical exercise, entertainment, be it checkers or the most elementary puzzle. The inclusion of entertaining material in the GCD for FEMP allows you to keep children's interest in the lesson, and this creates the conditions for increasing the emotional attitude to the content of the educational material, ensures its accessibility and awareness. The mathematical techniques used, the combination of practical and gaming activities, the solution of problem-playing and search situations contribute to the development of elementary mathematical concepts in children.
The inclusion of entertaining material in the GCD for FEMP allows you to keep children's interest in the lesson, and this creates the conditions for increasing the emotional attitude to the content of the educational material, ensures its accessibility and awareness. The mathematical techniques used, the combination of practical and gaming activities, the solution of problem-playing and search situations contribute to the development of elementary mathematical concepts in children.
In order to teach preschool children to love mathematics, to maintain interest in intellectual activity, to encourage them to solve search problems, it is necessary to approach the organization of the learning process creatively and with interest, use the variety and variability of educational games with mathematical content.
Type of project: cognitive-playing.
Implementation period: short-term (1 month).
Composition of participants: group (teacher, children of the older group, parents).
The purpose of the project: the formation of elementary mathematical concepts in children of senior preschool age through entertaining material in the organized and independent activities of children.
Tasks:
- To create conditions for the assimilation of mathematical concepts by preschoolers, to ensure the successful development of children's abilities and thinking.
- To promote the development of the ability to count forward and backward within 10, to use ordinal and cardinal numbers correctly.
- Help to consolidate the ability to recognize and name geometric shapes.
- To help improve the ability to identify sets of objects or figures that have a common property.
- To promote the development of mental operations: logical thinking, ingenuity, visual memory, imagination, the ability to compare and analyze.
- Promote the development of interest in games that require mental effort, intellectual effort.
- To promote independence, the ability to understand the learning task and perform it independently.

- Help improve the readiness of preschool children for schooling.
- Encourage parents to participate in the project and work with children at home.
Expected results:
- Raising the level of mathematical concepts in children of senior preschool age.
- Children have developed an interest in the very process of learning mathematics.
- Children independently find ways to solve cognitive problems, strive to achieve the set goal, overcome difficulties, and are able to transfer the acquired experience to new situations.
- Activation of parents' interest in the use of mathematical games and exercises.
- Parents' awareness of the importance of forming elementary mathematical concepts in children with the help of entertaining material, expanding parents' knowledge of entertaining material.
Preparatory phase:
- Definition of the project topic.
- Setting goals and objectives of the project.

- Selection of methodical, fiction literature on the topic of the project.
- Selection of didactic, outdoor games, physical education sessions on the topic of the project.
- Production of educational games in mathematics.
- Drawing up a plan for the main stage of the project.
- Development of summaries of proposed educational activities, quizzes.
- Involving parents in joint work on the project:
- creative task: pick up mathematical riddles, tasks, rebuses and colorfully arrange this material;
- help of parents in making didactic games on FEMP.
- Parent survey.
- Making a folder - sliding "Mathematics for preschoolers".
- Conversation with parents "How to organize children's games at home using entertaining material"
Main stage:
- GCD according to the calendar-forward planning in the senior group:
- GCD for FEMP "Letters of the Queen of Mathematics", "Cities of the Queen of Mathematics" mathematics";
- GCD for fine arts: drawing "Funny Figures", pea appliqué "Magic Numbers", modeling "Funny Figures".
- Reading mathematical fairy tales, fairy tales with counting elements: "Three Bears", "Two Bear Cubs", "Twelve Months" by S. Marshak, "Flower - Seven-Colored" by V. Kataev; K. Ushinsky's story "Four Desires".
- Learning poems about numbers, counting rhymes, riddles about geometric shapes and numbers.
- Viewing a computer presentation "Flight to the planet Mathematics", "Funny figures".
- Mathematical coloring, number drawing.
- Design.
- Working with counting sticks.
- Drawing geometric figures on a semolina
- Didactic games with mathematical content: "Tic-tac-toe", "Mathematical loto", "Ladybugs and daisies", "Labyrinths", "What numbers are lost", "Funny numbers", "Mathematical houses”, “Mosaic from caps”, “Tangram”, “Mathematical tablet “Geometric”, “Magic circles”, “Domino”, “Wonderful bag”, “simulator “Ladybugs”.
- Guessing riddles, entertaining questions, comic puzzles, puzzles.
- Outdoor games: "Make a figure", "The sea is worried.
 "
" - Finger exercises.
- Physical education minutes "Exercise", "Make a figure".
Final stage:
- Exhibition of educational games made together with children and parents.
- Conversation "Why I'm interested in mathematical games."
- Exhibition of baby books with mathematical tasks.
- Independent activity of children in the mathematical corner.
- Use of didactic games on FEMP at GCD.
- The final event - the quiz "Clever and clever".
- Processing and design of project materials.
Project progress.
The work on the project took place in several stages. At the preparatory stage, a plan for the implementation of the main stage of the project was drawn up, methodological and fiction literature, illustrative material, computer presentations "Flight to the Planet Mathematics", "Funny Figures", didactic games, physical exercises, finger gymnastics were selected. Developing games of mathematical content were made.
Parents were involved in the preparation of the project implementation: a survey was conducted with them, a folder was made for them - the “Mathematics for Preschoolers” movement. Parents also helped in the production of educational games in mathematics. Parents were given a task: to pick up entertaining mathematical material (problems, riddles, puzzles, rebuses) and colorfully arrange it.
At the main stage of the project, many lessons were related to the topic of the project. In the classes on the development of speech and reading fiction, we with children:
- read mathematical stories and fairy tales with mathematical content: "Three Bears", "Two Bear Cubs", "Twelve Months" by S. Marshak, "Flower - Seven-Flower" by V. Kataev; K. Ushinsky's story "Four Desires";
- memorized poems about numbers, counting rhymes, mathematical riddles.
During the art classes, children created drawings using geometric shapes, made “magic” numbers from peas and plasticine.
During math classes and during free activities, children worked with mathematical prescriptions - coloring pages, made constructions from construction kits, mosaics, Gyönysh blocks. The children also worked with counting sticks: they assembled figures according to the model and according to the plan. The children really enjoyed drawing geometric shapes on the semolina.
We played a lot of homemade didactic games of mathematical content:
- Tic Tac Toe. Tasks: to promote the development of attention, memory, the ability to focus on a particular subject for a long time, to promote the development of the ability to distinguish between concepts such as "diagonally", "vertically", "horizontally".
- "Mathematical Lotto". Tasks: to promote the assimilation of the sequence of numbers from 1 to 9; consolidate knowledge of geometric shapes.
- Ladybugs and Daisies. Purpose: the formation of the ability to compare, compare numbers and figures, arrange them in forward and reverse order.

- "Labyrinths". Tasks: to promote the development of logical and spatial thinking, multivariance, the ability to achieve goals, to promote the development of perseverance and patience.
- "Which numbers are missing?". Purpose: development of the ability to determine the place of a particular number in a series and the relationship to the previous and subsequent number.
- Math Houses. Purpose: the formation of knowledge about the composition of the number of two smaller ones.
- Tangram puzzle. Purpose: to develop the ability of children to analyze images, to highlight geometric shapes in them, to break the whole object into parts, and vice versa - to compose a given model from elements.
- Mathematical tablet Geometric. Purpose: formation of the ability to create images, development of figurative thinking, concentration,
- "Magic Circles". Purpose: development of counting skills and consolidation of the composition of the number.
- Ladybug Trainer.
 Purpose: formation of the ability to navigate the playing field with cells, move the ladybug in the indicated direction, determine the spatial arrangement of objects: “above”, “below”, “right - left”, “left - right”.
Purpose: formation of the ability to navigate the playing field with cells, move the ladybug in the indicated direction, determine the spatial arrangement of objects: “above”, “below”, “right - left”, “left - right”. - "Funny numbers". Purpose: the formation of the ability to lay out numbers from various materials at hand, the development of fine motor skills.
Solved comic problems, puzzles, guessed mathematical riddles. In this work, we used baby books made by parents. Together with the children, we learned and mastered new outdoor games, physical exercises and finger gymnastics of mathematical content.
At the final stage of the project, the following were arranged: a corner of entertaining mathematics, an exhibition of joint creative works of parents and children. A mathematical quiz "Clever and smart" was also held. Project materials were processed and designed, a presentation was created.
Project results.
The project proposes a system of work with children and parents on the introduction of educational games with mathematical content into the educational process in order to develop logical thinking and creative abilities in children of senior preschool age. The formation of mathematical representations and elements of logical thinking requires constant, systematic and systematic work, both in the joint activity of an adult and a child, and in independent activity. Developing games of a mathematical orientation contribute to the successful learning of the basics of mathematics, the formation of mathematical thinking, stimulates the development of creative imagination, the education of perseverance, will, perseverance, and determination.
The formation of mathematical representations and elements of logical thinking requires constant, systematic and systematic work, both in the joint activity of an adult and a child, and in independent activity. Developing games of a mathematical orientation contribute to the successful learning of the basics of mathematics, the formation of mathematical thinking, stimulates the development of creative imagination, the education of perseverance, will, perseverance, and determination.
Math in Motion Project
Math in Motion Project
Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution kindergarten No. 10 Dubravushka Gryazinsky municipal district of the Lipetsk region
Educational area: Cognition. FEMP.
The project was prepared by: Pitaeva Natalya Anatolyevna. 2021
"Learning can only be fun"
French novelist Anatole France.
Project type: educational.
Project duration: long-term: two years.
Project participants: children of the senior and preparatory groups, educators, parents.
Relevance of the topic: In the modern world, children suffer from physical inactivity. The dominance of gadgets makes children inactive, which negatively affects their physical and psychological health. But health is the main condition for the success of everyone. A healthy nation is the prosperity of the state. Therefore, in modern education, concern for the preservation of the health of children is in the first place. Everyone knows that in order to maintain health, it is necessary to conduct active motor activity. And for children, movement is vital, movement is the essence of a child's growing organism.
Download abstract
If a child stays in a static position for a long time during classes, it tires him, reduces his attention, reduces susceptibility, and therefore worsens the quality and quantity of information received. Boredom, which at the same time begins to overcome the child, strengthens his dislike for classes, and everything connected with them.
Boredom, which at the same time begins to overcome the child, strengthens his dislike for classes, and everything connected with them.
How to make sure that children learn knowledge and skills in an easy and natural way?
This project aims to combine children's education with active physical activity. It was decided to combine movement with mathematics. Why?
Everyone knows that mathematics is a serious, difficult, boring science. But at the same time, it is mathematics that contributes to the development of systems thinking, one of the important skills of modern society. How to make sure that the formation of mathematical ideas takes place in a relaxed atmosphere, so that each child has the opportunity to comprehend the basics of mathematics at the pace of their individual development, while none of the children feel lagging behind? But at the same time, everyone felt successful so that children could easily and easily learn from each other?
Game! The mobile game will help us with this! Outdoor games are the kind of games in which children can get a charge of physical and emotional vigor, while training their dexterity, speed, reaction, broadening their horizons and consolidating their knowledge. Therefore, the introduction of mathematical concepts into outdoor games will make outdoor games more cognitive and purposeful, and mathematics lessons more exciting. Children will not only learn to count, they will learn to see mathematics around them, which will contribute to the formation of a holistic picture of the world.
Therefore, the introduction of mathematical concepts into outdoor games will make outdoor games more cognitive and purposeful, and mathematics lessons more exciting. Children will not only learn to count, they will learn to see mathematics around them, which will contribute to the formation of a holistic picture of the world.
New
The novelty of the project lies in the search for and mastery of outdoor games in which children will not only actively move physically, but also master elementary mathematical and sensory representations at the same time. These classes will also be aimed at developing the cognitive abilities of children (memory, attention, logic, thinking) , at developing personal qualities (self-confidence) , at developing the work of both hemispheres of the brain.
Purpose:
Search for effective methods of cognitive development of the child's personality and the formation of his mathematical representations through the activation of motor activity.
Tasks:
to form thinking and logic skills;
to form the ability to control one's own actions, to get the result and evaluate it;
to join mathematics in a playful and entertaining way;
familiarization with active forms of cognition;
activation of motor activity of children;
education of independence, the ability to negotiate and work collectively.
Planned results:
children will become more independent, able to occupy themselves with useful and interesting play;
their cognitive activity is activated;
expanding your cognitive abilities (memory, attention, thinking, logic) , children will learn to take the initiative, become more self-confident;
children will not only acquire elementary mathematical concepts, they will develop an interest in mathematics, children will learn how to use it in everyday life;
active physical activity and a relaxed atmosphere will contribute to a good mood and the preservation of children's health.
Work plan:
- development of outdoor games with mathematical content;
- creation of a card index of mathematical games;
- production of attributes for mobile mathematical games;
- introduction of mobile mathematical games into the educational process;
- creation of a file of kinesiology exercises and their introduction into the educational process;
- development of class notes for FEMP using outdoor games with a mathematical bias;
- involvement of parents in the work.
Parent Plan:
1. Visual and information work:
- sliding folder Math is fun
- booklet "Mathematics around"
2. Consultation for parents "Cognitive abilities - their role in the education of children" .
3. Competition "Games of my family" Stage 1: video library;
4. Competition "Games of my family" Stage 2: making mathematical games with your own hands.
Competition "Games of my family" Stage 2: making mathematical games with your own hands.
Product of the project activity: design of a mathematics corner, leisure "Merry Mathematicians" .
Project presentation: "Mathematics in motion" .
Applications.
Card file of games.
Outdoor game "Find the same"
Purpose: to form an idea of the number and quantity, learning to count.
Option 1. On the floor or table, the cards are laid out in a circle, face down. Objects are drawn on the cards in different quantities (on one card there is one object, on the other two objects, etc.) Children run in single file around the table to the music, when the music stops, the children stop, everyone takes the card near which they stopped, counts the number of objects and searches in the group for the place where the same number of objects are laid out (caregiver prepares this in advance) and runs to that place.
Option 2. Numbers can be shown on the cards.
Variant 3. On the cards, as in the first variant, the image of objects, having counted the objects on their card, the children look for the image of the corresponding number in the group and run to it.
Relay Quick Count .
Purpose: to form an idea of the number and quantity, we train the ability to quickly count.
Option 1. Children can be divided into two teams; beforehand, children are given cards with a different number of depicted objects. Players take turns running on a signal to their table, where the toys are. Each player must take the number of toys that is shown on his card, run or jump back to his team and put the items in basket (each team has its own basket) , whose team will finish collecting their basket faster.
Option 2. Cards can have numbers.
Option 3. Each player leaves in his hands the number of toys he took, so we check the correctness of the task by each child.
Option 4. After counting the number of items on their card, the players run to the table in turn and take the corresponding number, return to their team's place. Whose team will gather faster.
Outdoor game Do the same
Purpose:
Option 1. The leader says to each player a number from 1 to 5 (senior group) or from 1 to 10 (preparatory group) , the player performs this number of exercises, the children count in chorus, thus guessing the number that the leader with guessed as a child.
Option 2. “Do one less (more) ”
Relay Plant a Garden
Two teams, two fields 1.5 by 1.5 m, lined with 9squares with numbers.
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Option 1. On a signal, the players run in turn to their field and put the number of toys corresponding to the number in one of the squares.
Option 2. The toys are already laid out in the cells, but the number of toys does not correspond to the desired number, the players count the toys in one of the cells, compare with the number and perform the action to remove or add a toy.
Option 3. Instead of numbers, there can be geometric objects, the child takes one of the geometric shapes from the basket and puts it on one of the cells. Whose team will collect their field faster.
Outdoor game Harvest or Purpose: development of auditory attention, the ability to count the number of sounds, the development of sensory perception. The teacher knocks with a hammer, the children count, then they go around the group and each picks up the same number of objects. The task can be complicated by typing objects of a certain shape or color. You can use this game when working with handouts. Make sure that there are as many objects as the hammer knocks, or one less or one more. Ball game Names of my neighbors Purpose: development of attentiveness, memory, orientation in space (right-left) Option 1. Children stand in a circle and pass the ball to each other. The one who received the ball in his hands calls his name and the names of his neighbors. Option 2. Having received the ball, the child names only the one on the right or only the one on the left. Game "Who left" Purpose: development of memory, teaching ordinal counting. 10 children form a line, the rest count them in order and memorize the order of formation. Then they close their eyes. One of the line leaves. Children guess who left and where he was standing. Relay Schemes Purpose: development of attention, development of sensory perception, development of thinking, consolidation of knowledge of geometric shapes. Option 1. Each child has a card diagram with geometric shapes, each of them must lay out the same diagram on their table. Option 2. According to the given scheme on the card, we supplement the large scheme on the table with the missing figures. Recommendation: diagrams can be arranged both in the table and horizontally. Children can complete tasks both individually and competing in the relay race. Game Live Week Purpose: Teaching the days of the week. For children, cards with a different number of buttons (from 1 to 7) , by the number of buttons on their card, children determine their day of the week, move to the music, when the melody stops, line up in accordance with the days of the week. Game Scheme Journey Purpose: acquaintance with the cell, development of the ability to navigate according to the scheme and in space, development of thinking, learning the ability to count one's movements. Option 1. Scheme on a sheet in a cell, where one cell corresponds to one step, the child moves according to the scheme and lays out a card with the image of the object shown in the diagram. Option 2. Children line up. We throw a large dice with dots, how many fell on the upper face, so many steps are taken by the child who threw the dice. Game "Who will build the figure faster" Purpose: to consolidate the ability to build according to the model, independently select building material; Recommendations: the game can be individual or team relay; the game can be desktop (counting sticks, flat desktop geometric figures) or floor (gymnastic sticks, floor geometric figures) , Nikitin or Tangram cubes can be used. Each child or team is given a diagram. Mobile game Make no mistake Purpose: to develop perception, the ability to highlight the properties of objects, compare them and group them. Children are divided into three teams. In the center is a basket with geometric shapes. Each team has a hoop, each performs its own task: one collects figures of a certain color, the other forms, the third selects figures in size (all large or all small) . It is possible for the fourth team to collect all the figures made from a certain material. Game "Merry circle" or ( "Where does the bell ring?" ) Purpose: improving the ability to determine the spatial direction relative to oneself. Children stand in a circle and close their eyes. The teacher walks in a circle, stops near the child and rings a bell. The child determines where the bell rings (in front, behind, left, right, top) . Game Who stands where Purpose: to teach to determine the location of people and objects relative to oneself and designate it with the words ahead, behind, left, right. Children stand in a circle, one in the center, children go in a round dance to the music, at the word “stop” children stop, the child in the center determines which of the children is in front of him, who is behind him, who is on the right, who is on the left. Game Labyrinth Purpose: 2-3 labyrinths on the floor of colored long cords, 2-3 teams of 3-4 children advance in a chain. Holding hands through the mazes, each in their own way. Game Happy Caterpillar Purpose: training in quantitative and ordinal counting, quick reaction and teamwork skills. Children are given cards with a different number of objects (for example, a card with the image of two objects, a card with three objects, etc.) . Children dance to the music, with the end of the music they should line up in order, the first child with a card, where there is one object, etc. Ball game "Name the next number" (previous) Purpose: to fix the ordinal score. Children stand in a circle. The leader throws and calls the number, the child calls the next or previous one and returns the ball to the leader. Games for the formation of spatial representations: left, right, above, below, in front, behind, far, close. Game "What's on the right" . Children sit along the edge of the carpet. On all sides of the carpet there are 5-6 toys. Option 1. The facilitator asks the children to remember where their right hand is. Then one of the children is invited to stand in the center on the carpet and name which toys are located to his right. In this case, each next child is turned in a different direction compared to the previous one. Option 2. Option 3. The host asks one of the children to stand so that the toys sitting on one side of the carpet (name them) are to his right. Game On the Raft . Purpose: to develop spatial orientation. Children stand on the carpet at the same distance from each other. Everyone stands on an imaginary raft. The facilitator asks the children individually questions, while constantly asking them to change direction. For example, “Peter, who is standing on your left; Masha, who is standing behind you; Seryozha, who is standing in front of you; everyone turned to the left; Tanya, who is standing to your left” , etc. Game Say the opposite . Purpose: to consolidate spatial concepts. This game can be played with all children or with 1-2 children. Games for the formation of skills to navigate in motion. Game Where will you go and what will you find . Before the game, all children sit in a semicircle in front of the shelves with toys. One of the children turns to face all the children, but does not see where the leader has hidden the toy. Then the facilitator gives instructions to this child. For example, take 2 steps forward, 3 steps to the left, 1 more step forward, look on the bottom shelf. At first, the teacher acts as the leader, then it can be a child who correctly followed the instructions. Game New Walk . This game can be played with 1-2 children on a walk. We agree that now we will walk not like all people, but in a special way. Card file of kinesiology exercises Kinesiology is the science of developing mental abilities and physical health through certain motor exercises. Kinesiology is the science of brain development through movement. It has been around for two hundred years and is used all over the world. Kinesiology exercise is a complex of movements allowing to activate interhemispheric influence. Kinesiology movements were used by Hippocrates and Aristotle. The main goal of kinesology is the development of interhemispheric interaction, which contributes to the activation of mental activity. Tasks of kinesiology: synchronization of the work of the hemispheres; development of fine motor skills; ability development; development of memory, attention, speech; development of thinking. The development of the child's brain begins in utero and continues actively after birth. The human brain is a "commonwealth" functionally asymmetric left and right hemispheres. Each of them is not a mirror image of the other, but a necessary addition. In order to think creatively about any problem, both hemispheres are needed: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. According to the studies of physiologists, the right hemisphere of the brain - humanitarian, figurative, creative - is responsible for the body, coordination of movements, spatial visual and kinesthetic perception. The left hemisphere of the brain - mathematical, symbolic, speech, logical, analytical - is responsible for the perception of auditory information, setting goals and building programs. The unity of the brain consists of the activity of the two hemispheres, closely interconnected by a system of nerve fibers (corpus callosum) . Under the influence of kinesiology training, positive structural changes occur in the body. Moreover, the more intense the load, the more significant these changes. This technique allows you to reveal the hidden abilities of the child and expand the boundaries of the capabilities of his brain. Exercise should be done daily. First, we teach young children to perform finger games from simple to complex. All exercises should be carried out with the use of musical accompaniment. Calm, melodic music creates a certain mood in children. Card file of kinesiology exercises. Ear-nose exercise. Left hand - take hold of the tip of the nose, right hand - take hold of the right ear. On command, release the ear-nose, clap your hands and change the position of the hands "exactly the opposite." Exercise "Snake". Cross your arms with your palms facing each other, clasp your fingers, turn your arms towards you. Option 1: with closed eyes, the child names the finger and hand touched by the teacher. Option 2: accurately and clearly move the finger that the teacher calls. Make sure that the rest of the fingers do not participate in the movement. Exercise Ring . Alternately and as quickly as possible go over the fingers, connecting the index, middle, etc. into a ring with the thumb. The exercise is performed in the forward and reverse (from the little finger to the index finger) order. Exercises Fist-Rib-Palm . Three positions of the hand on the plane of the table, successively replace each other. Palm on the plane, palm clenched into a fist, palm edge on the plane of the table, straightened palm on the plane of the table. It is performed first with the right hand, then with the left, then with two hands together 8-10 times. You can give yourself commands: fist-rib-palm. Exercise "Mill" . The arm and the opposite leg rotate in a circular motion, first forward, then backward, simultaneously with the rotation of the eyes to the right, left, up, down. Runtime 1-2 minutes. Breathing is arbitrary. Exercise "Engine" . Put the right hand under the left collarbone, while doing 10 circles with the left arm bent at the elbow joint and shoulder forward, then the same number back. Exercise Robot . Stand facing the wall, feet shoulder-width apart, palms resting on the wall at eye level. Move along the wall to the right and then to the left with side steps, arms and legs should move in parallel, and then move using opposite arms and legs. Exercise Pick apples . Starting position - standing. Imagine that in front of each of you grows an apple tree with wonderful big apples. Apples hang directly overhead, but it is not possible to get them without difficulty. Look at the apple tree, see a big apple hanging at the top right. Stretch your right arm as high as you can, rise on your tiptoes and take a sharp breath. Now pick the apple. Bend over and place the apple in a small basket on the ground. Now exhale slowly. Straighten up and look up to the left. There are two wonderful apples hanging there. First, reach there with your right hand, rise on your tiptoes, inhale and pick one apple. Abstract of a lesson in mathematics in the senior group. Purpose: through outdoor games to consolidate the mathematical knowledge of children. Tasks. educational: to consolidate the spatial concept on the right, counting skills, knowledge of numbers, the ability to correlate number and quantity, sensory knowledge (color, geometric shapes) ; developing: develop memory, attention, thinking, development of fine motor skills of hands, development of interhemispheric interaction; educational: we instill a sense of responsiveness, the ability to act according to the rules. Game situation “Children receive a distress signal, where the inhabitants of a fairy-tale land ask children for help. 1. Organizational moment. Educator: “Guys, before we hit the road, we need to determine the exact place, who will sit where. Ball game Names of my neighbors Children stand in a circle and pass the ball, at the signal of the teacher “stop” the passing of the ball stops, the child in whose hands the ball is located calls the name of his neighbor on the right or left, or on both sides. Children must answer in full: "I have on the right..." . Then the children sit on chairs. 2. Educator: "Guys, our car is unusual, fabulous and starts in an unusual way" . Kinesiology exercises Fist-rib-palm . Three positions of the hand on the plane of the table, successively replacing each other. 3. Educator: “Guys, the inhabitants of a fairy-tale land are multi-colored - blue men like to play with blue toys, yellow men play with yellow toys, etc. What do you think, what kind of toys do red men like to play with? And the green men? But during the storm, the fairy-tale little men lost all their toys. Can we help them?" Game Quick Score . Children receive cards with numbers (numbers of different colors) , according to the color of their card, children look for toys of their color in the playroom and each collects as many toys as the number on the card shows. 4. Educator: “Guys, in order to defeat the evil wizard, you need to get into the magic door, unfortunately the key to this door is broken. The guys are offered to find the details of the key and fix it. Game Find Your Shape Each child receives their own card - a diagram with symbols and, in accordance with the symbols, find their geometric figure (flat, floor figures) . The number of diagrams and figures corresponds to the number of children. Circuit example: Y The diagram shows that you need to find a small, red triangle. Y The diagram shows that you need to find a large, red square. Y The diagram shows that you need to find a small, green triangle. 5. Game "Fold the key" . A chain diagram of geometric shapes is displayed on the screen. Children all together, according to the scheme given to them, make up a chain of figures that were found in the previous game. On the screen, children see that the door opens and funny fairy-tale characters appear. Leisure "Merry Mathematicians" . Purpose: to awaken and consolidate children's interest in mathematics through fun outdoor games. Tasks: Educational: consolidate knowledge of numbers, ordinal counting, knowledge of primary colors; to consolidate the skills of spatial orientation relative to oneself (right-left) , to consolidate knowledge of geometric shapes. Developing: to develop phonemic hearing, to develop the ability to correlate the score with movements, to develop the ability to build according to the model, to independently select building material; development of mindfulness, memory, thinking. Educational: we instill a sense of solidarity, friendship, moderation to work in a team. Stroke: Children enter the hall to the music and sit on chairs. Znayka: “Hello, we are arguing about mathematics. Znayka and Romashka argue that mathematics is the queen of sciences. I think it's boring and unnecessary. I don't want to learn math! . Educator: “Do not quarrel, our dear guests. Tell me, Dunno, do you like to run, jump and have fun? - Yes. - Then we invite you and your friends to our fun competitions. 1. The teacher asks children riddles about numbers, the children answer in unison. Each child has his own number on his chest (three children have each number, only of a different color) , having heard his number, the child goes to his color guide. So three teams line up, the children stand in a line in order. Guests - heroes join the guys, become members of their teams and help them. 2. The teacher offers to check whose team is faster. To do this, they play with the ball "The names of my neighbors" . Children stand in a circle and pass the ball to each other. The one who received the ball in his hands calls his name and the names of his neighbors. Fairy-tale heroes control the correctness of the task. 3. Task for team captains. The teacher gives the captain a card with a number so that others do not see. The child performs some exercise as many times as the number on the card shows. The captains of the other teams call the number. The task can be made more difficult. The captain who guesses the number must hit the drum the same number of times. 4. Relay Schemes . Each team receives its own large canvas-scheme, the canvas depicts geometric shapes and must be filled in. Large flat geometric figures are located in the hall on the floor, the children as a whole team look for the necessary figures to the music and fill in their canvas, which is spread on the floor. 5. Game "Who will build the figure faster" . For this game we use Nikitin cubes or tangrams. The team is given a scheme to reproduce using large Nikitin floor cubes or a large floor tangram. Whose team will complete the task faster. 6. Dance minute. At the end of their leisure time, the heroes offer the guys to dance. All teams line up in one big circle, in the center of Dunno, he has large cards with numbers in his hands, which he will show, the guys who have the corresponding numbers on their chests go to the center of the circle to dance with him. At the end they all dance together. At the end of leisure, the teacher asks Dunno if he liked the competition, if he noticed that they were mathematical, if Dunno agrees that mathematics is a fun science.

 You can arrange a team competition, whose caterpillar will gather faster. Number cards can be used.
You can arrange a team competition, whose caterpillar will gather faster. Number cards can be used.  The host or one of the children names toys located in the same row and asks the child in the center of the carpet to name which side they are on.
The host or one of the children names toys located in the same row and asks the child in the center of the carpet to name which side they are on.  The leader names spatial landmarks, and the child who received the sign (ball, arrow, chip, etc.) calls the landmark that is opposite in meaning. For example: left - right, top - bottom, etc.
The leader names spatial landmarks, and the child who received the sign (ball, arrow, chip, etc.) calls the landmark that is opposite in meaning. For example: left - right, top - bottom, etc.  For example, two steps forward, one step to the right, or a step back, two steps forward. When the game becomes more difficult, the child must not only control his "gait" , but also turn his body in such a way as to reach a certain goal.
For example, two steps forward, one step to the right, or a step back, two steps forward. When the game becomes more difficult, the child must not only control his "gait" , but also turn his body in such a way as to reach a certain goal. 

 It calms, directs to the rhythm of the exercises in accordance with changes in the melody.
It calms, directs to the rhythm of the exercises in accordance with changes in the melody.  At the beginning, the exercise is performed with each hand separately, then with both hands at the same time.
At the beginning, the exercise is performed with each hand separately, then with both hands at the same time.  Change the position of the hands and repeat the exercise.
Change the position of the hands and repeat the exercise.  Then raise your left hand as high as you can and pick the other apple hanging there. Now lean forward, put both apples in the basket in front of you and exhale. Now you know what you need to do. Use both hands alternately to pick up the lovely big apples hanging from your left and right and put them in the basket.
Then raise your left hand as high as you can and pick the other apple hanging there. Now lean forward, put both apples in the basket in front of you and exhale. Now you know what you need to do. Use both hands alternately to pick up the lovely big apples hanging from your left and right and put them in the basket. 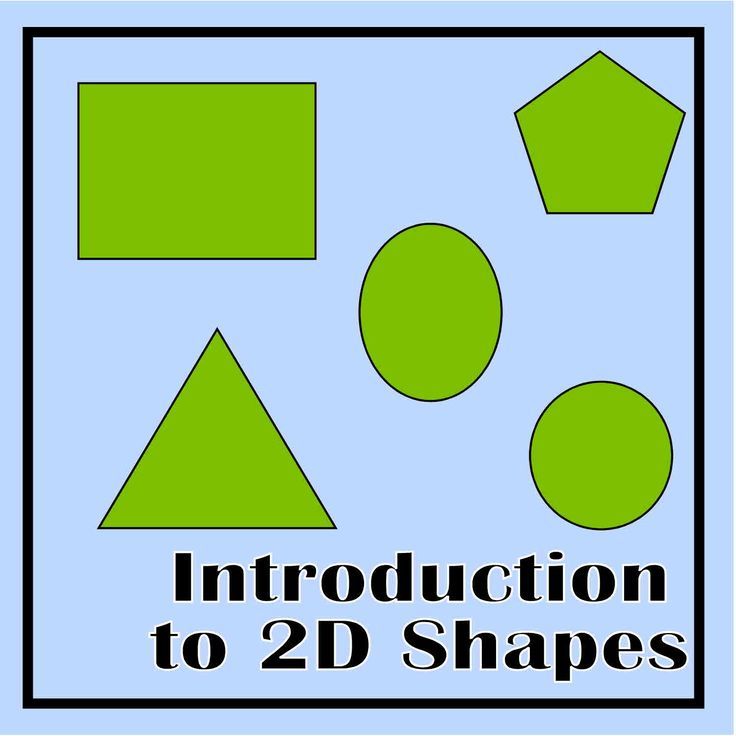 The educator offers to go to the aid of the fairy-tale inhabitants” .
The educator offers to go to the aid of the fairy-tale inhabitants” .  Palm on the plane, palm clenched into a fist, palm edge on the plane of the table, straightened palm on the plane of the table. It is performed first with the right hand, then with the left, then with two hands together 8-10 times. You can give yourself commands: fist-rib-palm.
Palm on the plane, palm clenched into a fist, palm edge on the plane of the table, straightened palm on the plane of the table. It is performed first with the right hand, then with the left, then with two hands together 8-10 times. You can give yourself commands: fist-rib-palm.  What do we do?"
What do we do?"  They thank the children for their release, and the children return home the same way they came.
They thank the children for their release, and the children return home the same way they came.  Suddenly, the children hear a noise, the heroes enter the hall: Dunno, Znayka and Chamomile, they are arguing loudly. Children recognize the heroes, the teacher asks the heroes: “Hello, guests, why are you arguing?”
Suddenly, the children hear a noise, the heroes enter the hall: Dunno, Znayka and Chamomile, they are arguing loudly. Children recognize the heroes, the teacher asks the heroes: “Hello, guests, why are you arguing?” 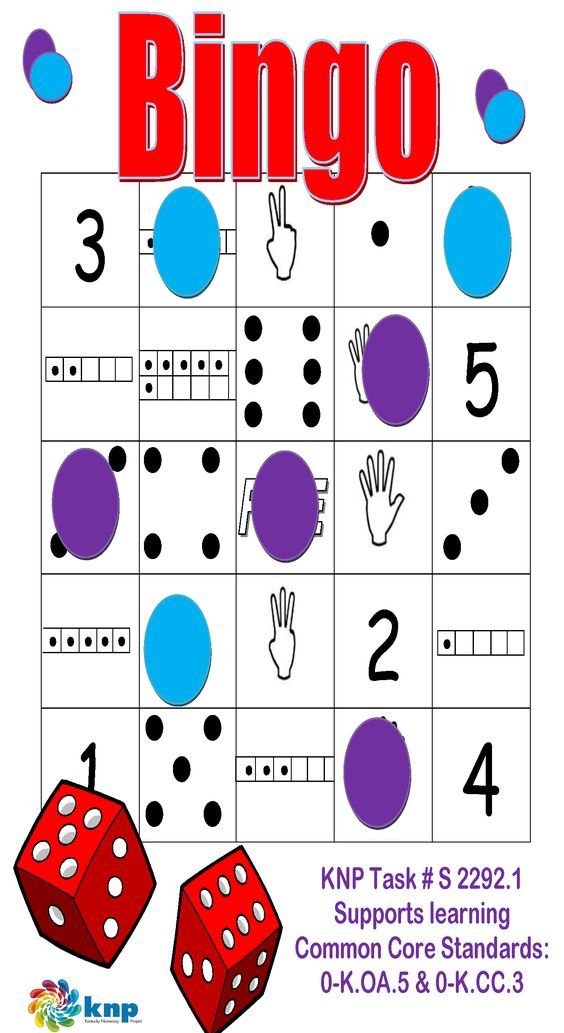
 The task can be complicated, on the canvas of each team there will be one window not filled, because such a figure will not be available. The team must name the missing piece.
The task can be complicated, on the canvas of each team there will be one window not filled, because such a figure will not be available. The team must name the missing piece. 
Learn more