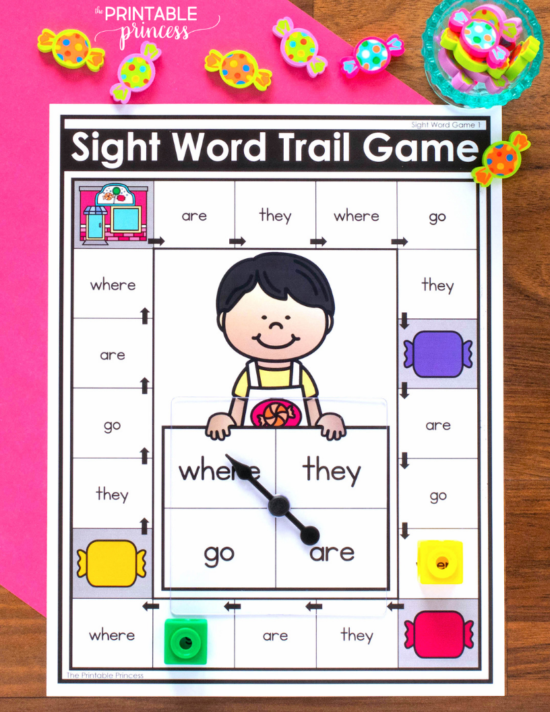
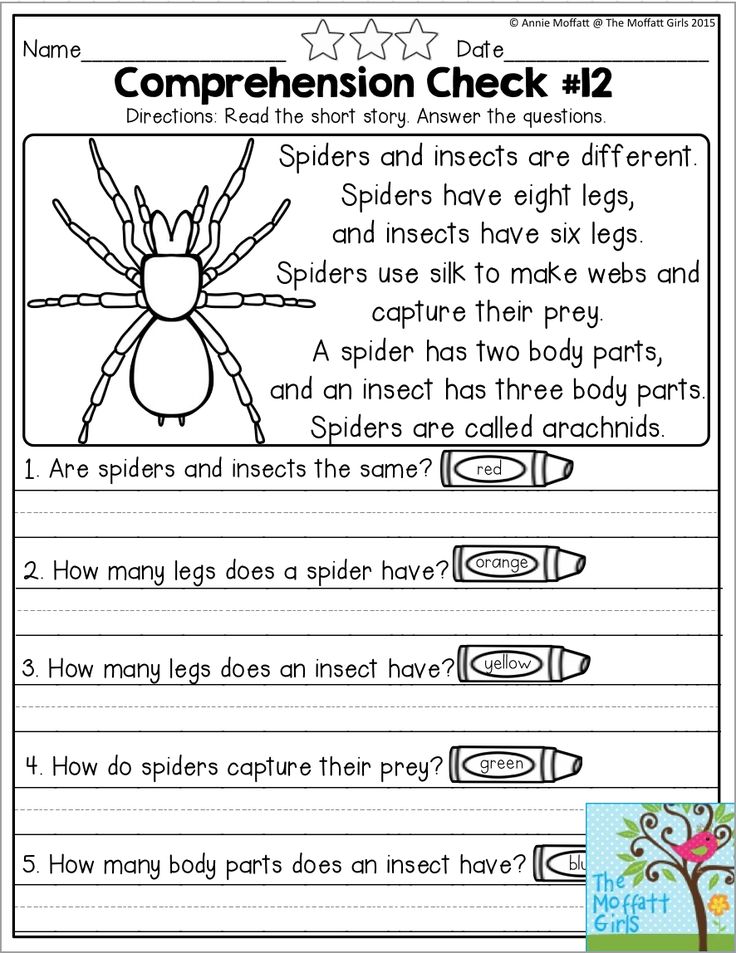
Reading level for 2nd graders
How to Overcome the 2nd Grade Reading Stumble | Scholastic
Learning to read involves a long journey, beginning with the ABCs and ending with (we hope) a lifelong love and interest in books. But many children experience a few bumps along the road as they develop into skilled readers, and often a problem arises in 2nd grade reading, when children are faced with more challenging material.
Some kids have trouble now because (1) they are still having decoding difficulties, (2) they have weak reading fluency (speed), or (3) the text is just too difficult. Here's what you need to know about each issue:
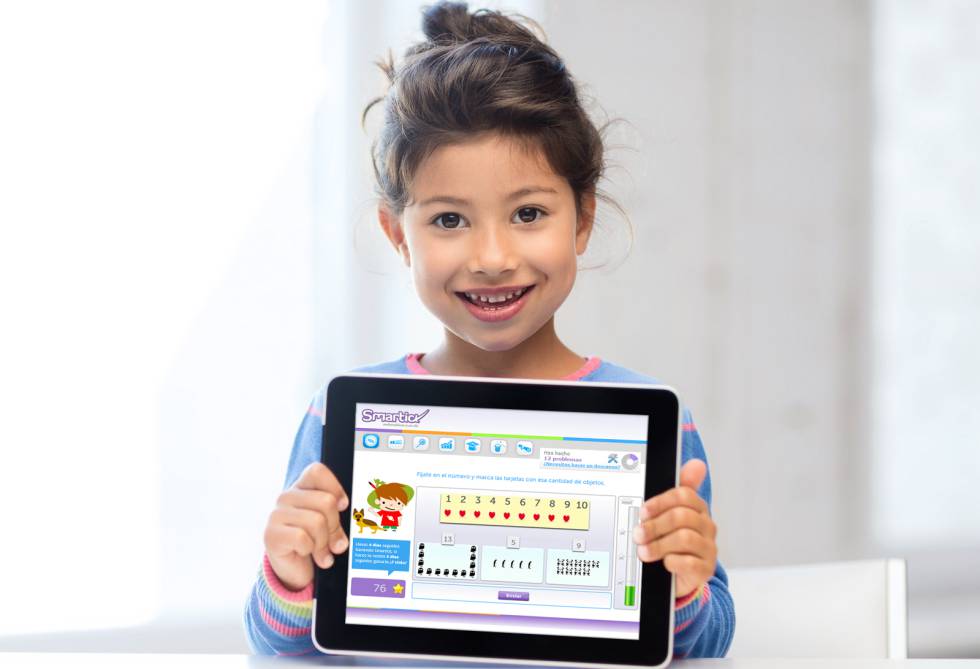
1. Weak Decoding. In 1st grade, some children do well by memorizing most words by sight rather than sounding them out. This strategy begins to break down in 2nd grade reading when the number of words increases and there is less repetition, making it more difficult to learn words by sight. One of the quickest ways to determine if your child is over-relying on reading words by sight is the Nonsense Word Test below.
These words are made up, but can be sounded out with early phonics skills. If he can sound them out, then decoding isn't the issue. If he uses one or two letters of the word to guess another word, decoding issues exist. More phonics work, including learning basic phonics skills and reading lots of simple phonics books, will help. A few great examples for the 2nd grade level are Pete the Cat Phonics Box Set, Pokemon Phonics Boxed Set, and Disney Learning: Toy Story Phonics Box which incorproates well-loved characters to make your child's learning journey a fun one!
Nonsense Word Test
Tell your child that these words are made-up words, and ask him to read them to you.
1. lat (rhymes with "cat")
2. rud (rhymes with "mud")
3. chab (rhymes with "grab")
4. stot (rhymes with "hot")
5. mabe (rhymes with "babe")
6. glay (rhymes with "play")
7. weam (rhymes with "team")
8. jern (rhymes with "fern")
9. froom (rhymes with "broom")
10.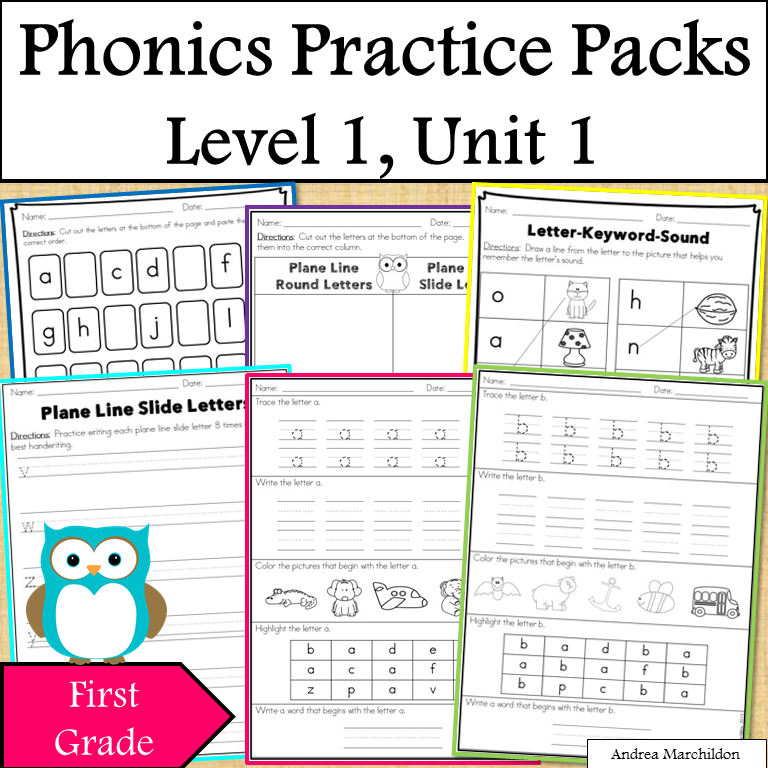 prouch (rhymes with "couch")
prouch (rhymes with "couch")
2. Weak Fluency. In order to understand what we read, we have to read at a speed appropriate for making meaning from the text (comprehension). In 2nd grade reading, your child should be reading 50 to 60 words a minute at the beginning of the school year and 90 words per minute by the end of the year. To test this, give your child a story from her reading list that she has not read, but will pique her interest. If it's below the speed levels noted above, then fluency is a problem. Make sure she has lots of experiences reading simple books. (One Scholastic Parents fan discovered that having her boys read the Elephant & Piggie Series aloud helped her boys improve reading fluency.) Repeated readings of stories she's already read in class will help, by providing the multiple exposures and decoding opportunities she needs.
MORE: How the Elephant & Piggie Series Helped My Kids Become Fluent Readers
3. Text Difficulty.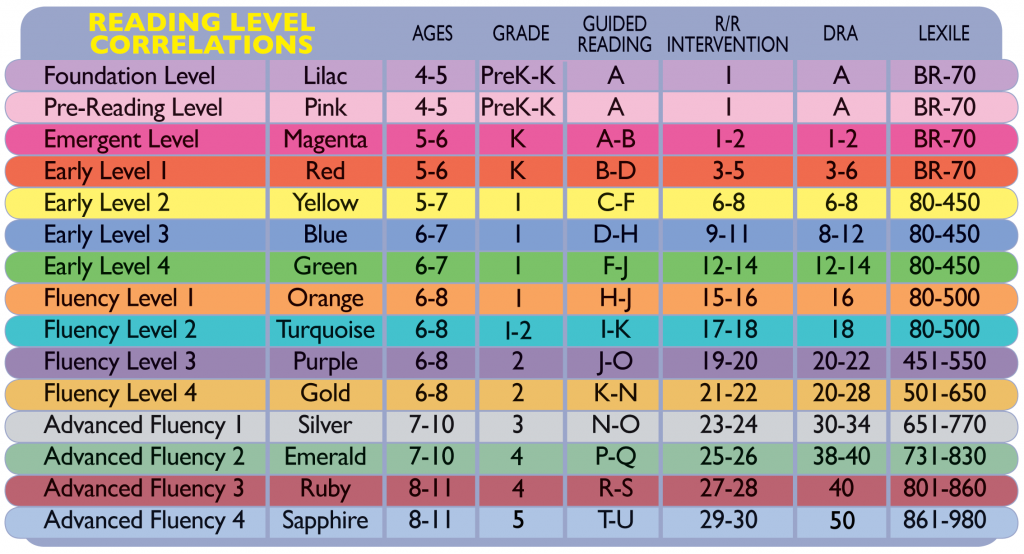 Your child needs lots of reading practice in stories that are not too hard. That is, he should be able to recognize over 90 percent of the words in his 2nd-grade reading books without your help. If you need to assist your child more frequently, then the story is too tough for him. Stories at this level — his frustration level — do not advance his reading skills. They make comprehension difficult because he is stopping so frequently to figure out words. These constant stops break the flow of reading and don't allow him to focus on the meaning of the story. Give
Scholastic Success With Grade 2: Reading Comprehension a try to better determine his level of reading difficulty and practice common skills he's learning in school.
Your child needs lots of reading practice in stories that are not too hard. That is, he should be able to recognize over 90 percent of the words in his 2nd-grade reading books without your help. If you need to assist your child more frequently, then the story is too tough for him. Stories at this level — his frustration level — do not advance his reading skills. They make comprehension difficult because he is stopping so frequently to figure out words. These constant stops break the flow of reading and don't allow him to focus on the meaning of the story. Give
Scholastic Success With Grade 2: Reading Comprehension a try to better determine his level of reading difficulty and practice common skills he's learning in school.
©Ridofranz/iStockphoto
Raise a reader by getting the best book recommendations, reading tips, and discounts delivered straight to your inbox.
PLEASE ENTER A VALID EMAIL ADDRESS.
PLEASE SELECT A NEWSLETTER OPTION.
Preschool View Sample
Elementary School View Sample
Privacy Policy
<div><h3>Thanks for signing up! Look out for a confirmation email from us.</h3><h4>Want to connect now? Find us on social media!</h4><h3><a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.facebook.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/facebook. svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
What Reading Level Should a Second Grader Be At?Making English Fun
Both learning to read and reading to learn are an essential developmental skill and assessment tool at all levels of education from second grader to university level. Reading levels are an integral educational tool
to not just assess progress of students but also give information to help teachers, parents and educators plan to improve students reading levels.
A second grader reading level will range between 6 to 20 on RR and Pm Reading levels. There will be outlying numbers depending on the situation of individual students. Reading levels allow teachers to choose appropriate reading materials to effectively develop students reading and comprehension skills.
This what reading level should a second grader be at article will also cover the following information:
- What are reading levels and how they can be used to help your 2nd graders to improve their reading skills.
- What you can do to support your students, 2nd grade and others, to progress.
- Reading skills and concepts that students will learn in second grade.
- Links to our 2nd grade reading resources ( and other resources)
If you are looking for worksheets for grade 2 we have a large collection here in the article below.
What Is a Reading Level?
There are multiple different programs and tools to assess students reading levels. The majority of these reading level assessments all share common indicators. They assess the comprehension, pronunciation, decoding and fluency ability of a student of English while they are reading a short leveled text.
Second graders are highly unlikely to be reading at a seventh grader level and it would not be useful or effective to have them reading the same materials. At this stage, in second grade, there is still more emphasis on reading skills and the actual mechanics of reading.
Reading comprehension is included in 2nd grader lessons but it is introduced as their hard reading skills become more developed. It is impossible for them to understand something they cant actually read!
Scholastic, have detailed information on the different reading level assessments and programs which, as highlighted above, all have commonalities.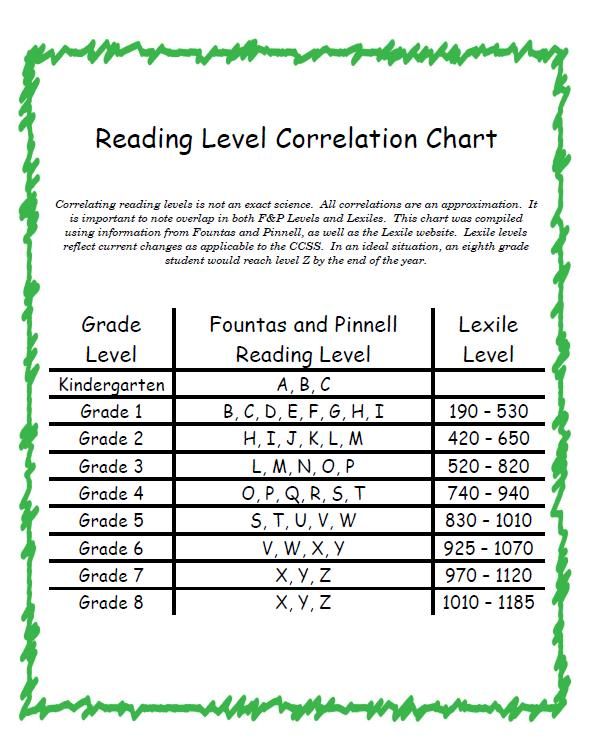 They do of course have difference as well, with some like Lexile concentrating on word count or difficultly of words and others like the PM benchmark looking at simplicity of both words and sentence construction.
They do of course have difference as well, with some like Lexile concentrating on word count or difficultly of words and others like the PM benchmark looking at simplicity of both words and sentence construction.
Different schools, regions and educational systems will use different reading assessment tools, but the chart below offers a handy comparison to help both teachers and parents when it comes to choosing reading materials.
The different systems can be confusing at first and when choosing what reading levels books to choose for 2nd grade classrooms it is definitely of use to spend some time with both your reading resources and the chart to make sure they fit the reading level of your students.
We use this chart in all our reading level articles.
Many Guided reading publishers have developed their own systems as well.
- Scholastic Guided Level Reading Program
- CCSS Lexile Recommendations
- DRA Level
- PM Benchmark
For both ease and continuity, ( as we have used this Reading level assesment tool in our other reading level articles) we will use the DRA reading level today.
The DRA ( Developmental Reading Assessment) is a reading skill assessment tool that aims to evaluate students reading levels to enable teachers and parents to assess students reading skills including fluency, comprehension and phonics. They aim to discover the independent and instructional reading level of students.
What is an Instructional Reading Level?
Instructional Reading level is the reading level directly below independent. Students should be able to comprehend and decode upwards of 80% of the text at an instructional level. This level can vary between students and also between subjects as students have interest and motivators that differ.
What is an Independent Reading Level?
An independent reading level is a level of reading ability that allows students to read texts without assistance from teachers or parents. When reading this level of text students will be able to decode over 90% of words and answer increasingly complex comprehension questions independently.
What is a Frustration Reading Level?
Frustration level reading can be defined as text that are to complex for a students current reading level. Texts at this level will not help progress students to higher levels, conversely attempting to read at this level will demotivate students and hinder their development of reading skills.
In 2nd grade, as well as other grades, classrooms and homes teachers and parents should aim at using an instructional reading level. This enables students to comprehend and therefore engage with texts with minimal assistance, and gives them the motivation to see they are doing well, but still have the support and guidance of teachers and parents.
Guided reading, for which we have many articles and resources, is an excellent way of introducing text at this levels to small groups of 2nd graders. In fact is it more beneficial to introduce guided reading at this stage as students have matured and are becoming more independent. Check out the links to know more. We have an article here on what age you can start teaching guided reading.
Check out the links to know more. We have an article here on what age you can start teaching guided reading.
What 2nd Graders Learn Throughout the Year.
As we mentioned above a second grader can be reading from about reading level 6 to level 20. However please don’t worry if your students or children are below this, or be to confident if they are above this.
As time progresses so will your students reading levels. Just aim to to the best job you can, and provide them with appropriate leveled 2nd grade materials and the time to cover them.
The next section covers what skills they will learn to help them improve their reading levels through out the second grade.
Note: Children develop at very different speeds, and different learning environments will impact. If English is a second language, or if there are other demands on students or parents time will all play a part. Be assured that in the vast majority of cases, with a little planning, all students progress and develop their reading skills.
What Reading Skills They Will Learn in Second Grade
Although we mentioned in our What level should a first grader be at article, that an essential part of learning and reading in first grade is comprehension, this is not just a face value statement. In First grade there is a focus on shared reading or story telling which is undertaken in whole class or larger groups. This asks students to read together more than in small groups.
They have to retell stories and predict outcomes and books will be fairly formulaic story books with similar phonic and sentence structures. In Second grade, as mentioned above, emphasis can be moved on to guided reading sessions.
According to Reading Rockets, a second grader will be focusing on the following English and reading skills. We have put this information in a table to provide resources for FREE download to help you as well.
Vowels and long vowels will be introduced in greater detail in second grade including Silent E, and some alternative spellings like diphthongs and vowel digraphs. The teaching of these will help students increase their decoding skills and improve their vocabulary.
The teaching of these will help students increase their decoding skills and improve their vocabulary.
Punctuation is another essential part of the second grade year. Exclamation points, question marks, periods might be introduced in some grade one classrooms, but will certainly make an appearance in second grade classrooms.
Semicolons and colons might be introduced in more advanced lessons or towards the end of the year. you can find some punctuation worksheets here and on the link in the table above.
Reading and writing skills such and conjunctions, pronouns will be built on and by now capitalization will have been covered so revising that may be necessary if you notice your children or students forgetting or not using this. We have some worksheets here and in the table above if you need. Pronouns are likely to be expanded on as well.
- 10%
Amazon.com
Phonics Flash Cards - Learn to Read in 20 Phonic Stages - Digraphs CVC Blends. ..
..
$17.99 $19.99
BUY NOW
- 31%
Amazon.com
Learning Resources Sight Word Swat a Sight Words Game - 114 Pieces, Ages 5+...
$12.25 $17.99
BUY NOW
Amazon.com
Sight Words Level 2 Bingo Game
$13.99
BUY NOW
Sentences and constructing sentence will become more important in second grade. Reading materials will include more complex versions and teachers and parents can use reading levels to gain appropriate levels of text for their students and children. We have some on the site for free, and in addition we also have sentence making and sentence scramble worksheets as well (link)
However some of the best ways to engage 2nd graders is through online games. By this time they will have become aware of tablets and phones being help in parents and siblings hands. We have articles on some of the best online games, and have a page that has all the ones we make as well. These are free to play and very popular and certainly add motivation to your lessons!
These are free to play and very popular and certainly add motivation to your lessons!
What Can Teachers Do to Improve Reading Levels at 2nd Grade.
Teachers can develop a love of reading in classrooms and encourage students to take control of their own learning as well.
- Have a selection of levelled suitable for 2nd graders covering fiction and NON fiction texts.
- Make sure there is a mix of text types and text subjects.
- Try to have a corner in the classroom for quiet reading.
- Mix up ways of presenting resources, online games, worksheets readers etc.
- Read stories and continue doing story time, many children don’t get chance to experience this enough.
- Display reading strategies and phonics strategies on walls for students to reference. ( also put in their day books or on desks)
- Run Guided reading lessons. ( you can get information on this here)
What Language Will Books at Grade Two Reading Levels Contain?
During students second grade year, Language contained in reading resources will move from three to four letter words and start to include fairly familiar longer words and two or three syllable words.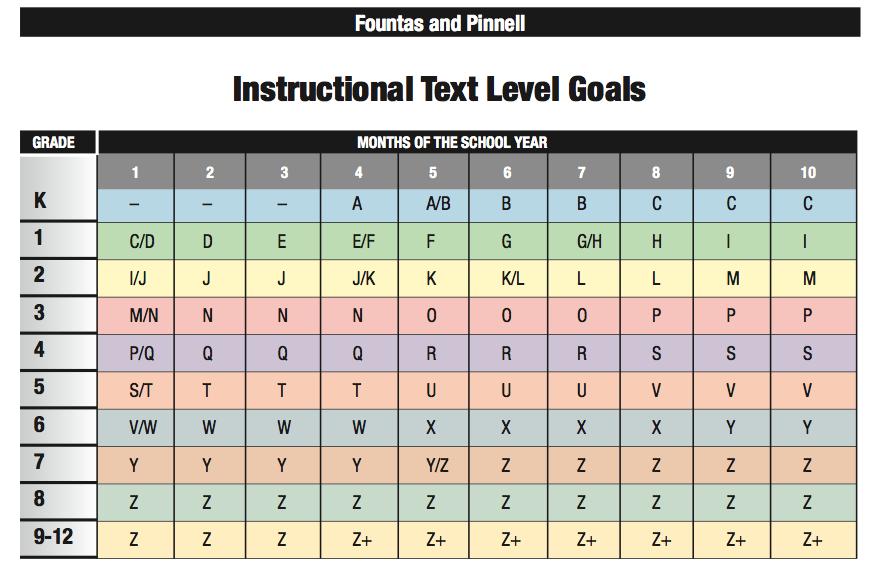 Common words will be used like days of the week, hobbies, weather and more o help increase vocabulary.
Common words will be used like days of the week, hobbies, weather and more o help increase vocabulary.
Parents.com suggests asking your child questions about books, stories, and sentences that they’re reading. This allows them to process information as they are reading and to move from just learning words to attaching meaning to them. Our reading materials include 3 to 5 questions to help with this. These can be asked verbally or they can complete them as a worksheet post reading.
This is taken from our Reading for first grade article but applies across all grades.
- Break down every word into individual letters. If there’s a combination (sh, th, ough), separate it into its own chunk. This starts to introduce syllables to students.
- Focus on words that they already know how to say. If they’re familiar with the word, they’ll be able to use contextual clues to figure out how to read it.
- Don’t study for too long. Short 15-minute study sessions hold their interest long enough to prevent reading from becoming a boring chore. Little and often is better.
- Use the resources from school and online to supplement these skills. you can access using the following links the 1000s of reading resources on our site for free and premium downloads.
How Can Parents Help Their Second Grader Develop a Love for Reading?
Parents, especially at first and second grade, play a vital role in helping your child become interested in reading. Story telling, appropriate reading resources and books in the house will all help. However we have a list below to help you gather some ideas as well.
Here’s a list of ways that you can help your second grader develop a love for reading:
- Find reading material that they’re interested in. For example, if they love animals or nature , choose those books over anything else.
 Also allow them to choose as well. It’s not the concept that matters; It’s the words found throughout the reading that makes a big difference. We have some leveled reading material aimed at young learners here. However sites like Starfall offer online stories that may help as well.
Also allow them to choose as well. It’s not the concept that matters; It’s the words found throughout the reading that makes a big difference. We have some leveled reading material aimed at young learners here. However sites like Starfall offer online stories that may help as well. - Offer incentives for their reading. Although the aim is to have them choose to read for fun all things start slowly and build momentum. If you can associate reading with enjoyment and reward (extrinsic in the first place) then they will start to enjoy reading and learning for its own merits.
- Picture books can keep your child’s interest . If you stop reading after 15 to 20 minutes, they’ll be begging to jump back into the material. Its great bonding time as well
- Use alternative texts, screen magazines etc. Children can be introduced to different text types to show there are reading opportunities everywhere.

- Ask what your children are covering in school. If you ask their teachers they will be happy to share and offer advice on how to help your second grader progress as well as they can.
- Take a look at using online games to diversify how you introduce learning and reading.
Children are always seeking out new opportunities to learn. Parents can simply guide them to make sure there is a little structure to their learning. Using their interests to guide their reading means they are learning about topics they like and improving their reading. As they progress so with their reading levels.
Finally
We have covered the average reading levels for second graders in native classrooms, of course there will be some difference in ESL or other classrooms. They key takeaway from all of this is that children will progress at their own speed. you can help them on their reading journey but you shouldn’t force them
Reading should be a joy not a chore.
Here’s a quick recap of the post:
- Second graders typically fall between a 6 to 20 reading level.
- Focus on reading for fun, decoding skills, and comprehension.
- Follow their interests, it helps motivate them to read
- Use additional resources and activities to engage and inspire them
if you are looking for other grades reading levels then we have these in the table below.
Other Grades Average Reading Levels.
We have a selection of articles on reading level expectations for different grades below.
Sources
- Scholastic – Learn About Leveled Reading
- Reading A to Z – Levelled Books
- Amazon Second Grade Reading.
Hi I’m Marc. A teacher of over 15 years, English, General Studies and Outdoor Education. Thought it was about time to sharing both what I have learnt during that time and the resources I have put together. On this site we aim to teach the theory and share our thoughts, but also go that one step further and give you access to the hard resources you need for your class or for you children
On this site we aim to teach the theory and share our thoughts, but also go that one step further and give you access to the hard resources you need for your class or for you children
Like this:
Like Loading...
Making English Fun!
I have been a teacher of English for over 15 years, in that time i made hundreds and thousands of resources and learnt so much i think its worth sharing. Hopefully to help teachers and parents around the world.
standards for grades and quarters
Reading is a key skill that opens the gate to the land of knowledge for a child. Thanks to this skill, children learn about the phenomena and events of the world around them, get acquainted with the characters and actions of people, meet new problems and ideas. This skill helps them to expand their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
To understand how well a child develops this skill, it helps to check the reading technique. Reading technique is a multifactorial test that characterizes the development of a skill from different angles. In the technique of reading are evaluated:
- reading speed,
- reading method,
- reading awareness,
- correct reading,
- expressiveness of reading.
A difficult reading skill consists of both a technical and a semantic component and is aimed at achieving the main goal - understanding and assimilation of the information read.
Reading technique parameters
Let's consider all the components of reading technique in more detail.
- Reading speed - the number of words read in a certain period of time. Often, parents focus on the formation of fluent reading, while the child makes many mistakes, does not understand and does not remember what he read. It is not necessary to force only speed, slower conscious reading and a gradual increase in tempo are better than fast mechanical reading with errors and inaccuracies.

- Way of reading — syllabic reading or reading the whole word, smoothly. With the development of the skill, the child has a gradual transition from syllabic reading to smooth reading in whole words.
- The correct reading of is characterized by the absence of errors and hesitation. Inattention, diction problems lead to inaccurate reading, indistinct articulation and, as a result, to a distortion of meaning. Pay attention to the correct reading - this will be the key to competent writing.
- Reading awareness involves reading comprehension, awareness of the idea and meaning of the text, and in the future - this is the ability to catch the subtext, humor, irony, the attitude of the author. Interfering with reading comprehension can be low reading speed, distorted reproduction - guessing words, changing the shape of words, not reading endings.
- Reading expressiveness - the use of pauses, finding the right intonation, the correct placement of stresses.
 The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
Reading speed standards for elementary school
GEF standards determine the desired reading speed for a child by a certain point in learning, help to understand whether the development of a skill is successful or whether additional attention is required. Standards - indicative values; it is important to take into account the individual psychophysiological characteristics of each child and evaluate the growth of his personal indicators.
Grade 1 reading speed standards
Reading speed standards in grade 2
Reading speed standards in grade 3
Reading speeds in grade 4,
Reading speed, to which it is necessary schools, is reading at the speed of conversational speech, 110-120 words per minute. The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
Other parameters of reading technique
Grade 1
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading is smooth syllabic, conscious and correct, with a clear pronunciation of syllables and words.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading is conscious, correct, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable.
Grade 2
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Compound words can be read syllable by syllable.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading meaningful, correct, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable.
Grade 3
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, with the help of which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
4th grade
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With the help of observed pauses and intonations, the child not only expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read, but is able to express his attitude to what he has read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read.
How can I test my child's reading skills on my own?
Have your child see how well they read already. Children usually love to know how many centimeters they have grown, and they may also be interested in knowing their progress in reading. Warn about the upcoming test and ask the child to read quickly.
The control of reading technique in sensitive children who, due to their temperament, can hardly tolerate various tests, can be carried out imperceptibly or in the form of a game. Do not create unnecessary excitement around the upcoming test, do not arrange a test in the form of an exam. If the child is worried, stutters, transfer control to another time.
Verification process:
- Prepare a clock with a second hand or use the stopwatch on your phone, and choose the appropriate text.
- Ask the child to take a seat.
- Show him the text and ask him to read it aloud.
- Track the time from the moment your child starts reading.
 Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results.
Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results. - Usually, one minute is noted for checking, but some experts recommend taking 2 minutes for monitoring, since not all children are equally quickly included in the work. Divide the result obtained in 2 minutes in half.
- Do not correct or interrupt while reading. It is better to discuss the mistakes made after the child has finished reading.
- Assess the speed, correctness, awareness and expressiveness of reading.
- Retest and compare results. Reading technique may differ depending on the child's fatigue, health status and mood.
Which text is suitable for verification?
Both fiction and non-fiction texts appropriate for the child's age are suitable for this purpose. The text should be unfamiliar, but understandable to the child, have educational and educational value. The texts of V. Bianchi, L. Tolstoy, N. Nosov, B. Zhitkov, K. Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
You should find the text that is located on the spread of the book so that the child does not have to waste time turning pages. Choose text without an abundance of punctuation marks and distracting illustrations. It is not desirable that the passage contains common complex sentences and dialogues. The font must be large enough and legible. The text should not have a technical focus and contain terms incomprehensible to the child.
Test score
Speed score
Count how many words the child read in one minute. When counting words, pay attention:
- prepositions, conjunctions, particles of 1-2 letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, the word is counted as 2 words;
- if the word is written with a hyphen, look at how many letters are on both sides of the hyphen: if there are more than three, we count it as 2 words, for example, “long-long”, if less than three, for example, “somehow”, - as one .

Compare your score with the recommended range and your child's previous performance.
Comprehension score
Determine how well the child understood what they read. If the student reads slowly and has read only a couple of sentences, let him read the passage to the end. Ask your child a few questions about the text. Ask what or who he read about. Ask the child to identify the main idea of what they read and retell the text.
For a deeper check of the meaning of the reading and learning, use special teaching kits.
Correctness assessment
Pay attention to whether the child reads what is written correctly, whether he pronounces words clearly, whether there are hesitations and corrections, whether he alters words, whether he changes endings, whether he places stresses correctly. Discuss the mistakes with the student.
Evaluation of expressiveness
To assess the expressiveness of reading, the child is offered a familiar text. Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Improving reading technique
Poor results in reading technique are not a reason to be upset, but only a signal that additional efforts need to be made to improve the skill. You can work with the child on your own or contact a specialist who will analyze the weak points and select the appropriate exercises. Conduct additional activities with the child in the mode of "sparing reading" without pressure. It is more important to observe the regularity and frequency of classes: 10-20 minutes daily.
How can you motivate your child to read:
- Reward your efforts with stickers, stars.
- Mark progress visually - create a success board so your child can visually see their progress
- Conduct activities in the form of a game, such as "going to the library" or "reading to your favorite toys.
 "
" - Choose books and texts that are interesting for your child.
- Let the child read to pets, they are grateful and accepting listeners. Reading to them, the child is not afraid to make a mistake, he relaxes and overcomes the fear of failure.
- Have a reading competition between peers and siblings.
To improve the speed of reading will help:
- Reading by syllabic tables.
- Multiple reading. Read the same text several times, increasing the pace. From the second time the child will be able to read faster.
- "Tug". An adult leads a finger along the line, setting the pace. The child tries to read at a given pace.
- Tops and roots. The child reads the words, covering the upper or lower half of the letters with a ruler.
- Reading in a book turned upside down.
- Lightning. Alternating reading at a comfortable pace with reading at the highest possible speed for 20 seconds on the command "Lightning!".

- "Sprint". Reading speed competition between classmates.
- Work on expanding the field of view according to Schulte tables.
- Reading with a window to eliminate "regression" - recurrent eye movements that lead to repeated reading.
For correct reading:
- Work on clear diction, do articulation exercises.
- Read tongue twisters and tongue twisters.
- Invite the child to correct the deformed sentences: "The weather is good on the street."
- "Imaginary word". When reading, the wrong word is pronounced, the child must correct it.
Reading comprehension
- Wave Reading. First, the child reads aloud, then retells what he read.
- Drawing up a plan for reading.
- The student reads to himself at a comfortable pace, tells what he understood and felt, what he thought about
- Discuss unfamiliar words and expressions.
- Invite the child to draw a picture of the passage they read.

- Ask them to tell you what they liked about the text, what they remember.
For expressive reading
- Role-playing, staging.
- Put on a "radio show".
- Expressive recitation of poems.
- Voice flexibility training. The ability to speak quieter-louder, higher-lower.
- Conducting reading indicating the tone or strength of the voice.
- Live Picture. One reads, the other reacts with facial expressions.
Improving reading skills in elementary school is very important. It is fluent and meaningful reading that activates the processes of thinking, attention, memory and is the basis for a child's successful learning in the future. This detailed instruction on reading technique control will help you track and improve your child's skill development. 93 times a year: at the beginning of the school year, at the end of the first half of the year and at the end of the fourth quarter. But sometimes the teacher prefers to check the reading technique at the end of each quarter.
The reading technique test includes not only reading speed, but also reading accuracy, comprehension and expressiveness. I wrote about this in more detail in article "How to test a child's reading technique."
- Special texts are selected to test the reading technique.
- The text should be unfamiliar to the child, but understandable.
- Sentences should be short, without any complicating constructions or signs.
- It is better if the text for checking reading is without illustrations and dialogues, so that children do not get distracted while reading.
- Text must be placed on one page.
- While reading the text, you can not interrupt the child, correct mistakes. After completing the reading, you need to return to those words that caused difficulty or were read incorrectly and ask the child to read them again. In the process of reading, a first grader can follow the text with his finger so as not to lose the line.
- To test reading comprehension, you need to ask a few questions about the text.
Norm of reading technique in grade 2
1st half year
Reading is correct, conscious, in whole words. There is a logical emphasis.
Reading speed - 40-50 words per minute.
2 semester
Meaningful, correct reading of whole words, observing pauses, intonations and logical stresses.
Reading speed - 50-60 words per minute.
These texts can be used not only to test the child's reading technique, but also for retelling. How to teach a child to retell can be found in the article “Teaching a child to retell”.
2nd Grade Reading Test
Sparrow Thermometer
My birds are not idle. Sparrows show my temperature like thermometers.
In the morning I just look out the window at the feeder and I already know whether it is warm or cold outside. If the sparrows are smooth and lean, it means that it is warm outside, and if they are plump and disheveled, like inflated balls, it means that the frost is crackling, take care of your ears and nose!
If the sparrows are smooth and lean, it means that it is warm outside, and if they are plump and disheveled, like inflated balls, it means that the frost is crackling, take care of your ears and nose!
If only the sparrows let me down. (According to N. Sladkov)
(58 words)
Questions:
- How does the author recognize the weather from sparrows?
- What do sparrows look like when it's warm outside?
- In what weather do sparrows fluff their feathers?
Flower clock
The children made a flower clock at the camp. Poppies were planted along the edge of the flower bed. They wake up first. A carnation was placed nearby. She opens the petals after the poppy. Behind the carnation are marigolds. They bloom during the day. The last thing in the flowerbed was fragrant tobacco. It shows evening time.
Sunflowers were planted in the center of the flower bed.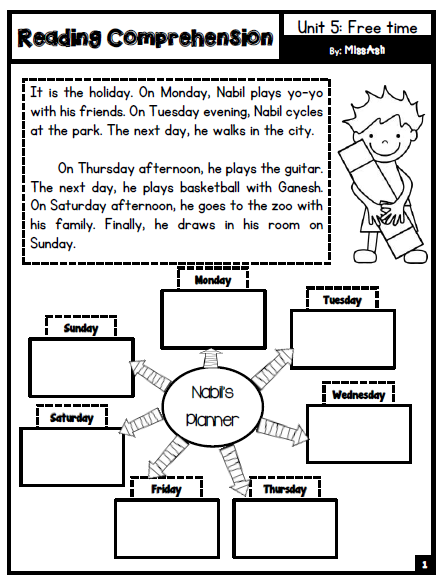 Their golden heads face the sun all day long. Sunflowers will be the hands of the clock. (According to V. Vetlipa)
Their golden heads face the sun all day long. Sunflowers will be the hands of the clock. (According to V. Vetlipa)
(60 words)
Questions:
- Which flower wakes up first?
- Where did sunflowers grow and why?
Hedgehog
A gray hedgehog went for a walk in the forest on a dark night. I saw a red cranberry and pricked it on a gray needle. I saw a yellow fox and also pricked it.
Finally noticed a blue star in a blue puddle. I also wanted to prick - but nothing happened. The hedgehog thought, thought, and covered it with a burlap: let it lie down until morning.
And in the morning, instead of a blue star, I found a red sun under the burlap. Here the hedgehog laughed. (G. Tsiferov)
(61 words)
Questions:
- When did the hedgehog go for a walk?
- What did the hedgehog find?
- What has the blue star turned into in the morning?
Beavers
A big beaver came out on the shore. The tail is thick and flat, like a shovel. The front legs are shorter than the hind legs.
The tail is thick and flat, like a shovel. The front legs are shorter than the hind legs.
He examined a young aspen, grabbed the trunk with his front paws, and began to gnaw. The beaver worked quickly. The tree collapsed.
The beaver bit the branches and dragged them to the water. He moved quickly, deftly. Soon the beaver appeared again and went to the tree.
Hills rose on the shore. The beavers covered the branches of the trees with mud. These were the dwellings of the beavers. (According to Yu. Dmitriev)
(61 words)
Questions:
- What does a beaver's tail look like?
- What tree was the beaver eating?
- What do beaver dwellings look like?
The eagle
The eagle built his nest on the high road, far from the sea, and brought out the children.
Once people were working near a tree, and an eagle flew up to the nest with a big fish in its claws. People saw the fish, surrounded the tree, shouted and threw stones at the eagle.
People saw the fish, surrounded the tree, shouted and threw stones at the eagle.
The eagle dropped the fish, and the people picked it up and left.
The eagle sat on the edge of the nest, and the eaglets raised their heads and began to squeak: they asked for food.
(65 words)
Questions:
- Where did the eagle make his nest?
- For whom did the eagle catch the fish?
- How did the people act?
Ducklings and a dragonfly
Every morning the hostess brought a plate full of chopped eggs to the ducklings. She put the plate near the bush, and she left.
As soon as the ducklings ran to the plate, a large dragonfly flew out of the garden. She chirped terribly. The ducklings ran away and hid in the grass. They were afraid that the dragonfly would bite them all.
And the evil dragonfly sat on the plate, tasted the food and then flew away.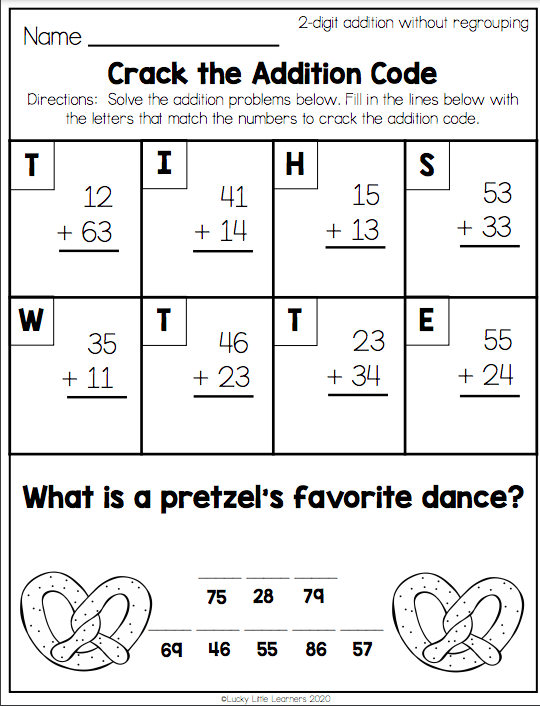 After that, the ducklings did not approach the plate for a whole day. (According to E. Zhitkov)
After that, the ducklings did not approach the plate for a whole day. (According to E. Zhitkov)
(68 words)
Questions:
- What did the hostess feed the ducklings with?
- Who scared the kids?
- What did the ducklings do when the dragonfly flew away?
Mole
In a forest clearing, heaps of loose earth, like small beds. But who is digging the earth here?
Suddenly the grass began to stir up ahead. I froze, and the earth began to rise in a mound.
Two wide paws with claws appeared, a wet nose. Well, of course it's a mole.
Looked out into the white light and again dived into the depths. And in the clearing there was a fresh pile of earth, like a small garden bed. Seeds fly from the trees, fall on the plowed land. A birch or pine will grow here. (According to E. Shim)
Shim)
(70 words)
Questions:
- What did the mole look like?
- What did the animal do?
- What are the benefits of moles?
Squirrel
A squirrel built a nest on a tall pine tree in the forest. Everything is round, closed, and on one side a loophole is left so that you can climb inside.
The squirrel is a clever animal. All day long, from knot to knot, from tree to tree, he jumps - where he picks a berry, where a fir cone. And autumn will come - then the squirrel will begin to prepare supplies for the winter. Either he will hang the mushrooms to dry, or he will hide the nuts in a hollow. It's cold, hungry in winter, so supplies will come in handy for the squirrel. (At V. Chaplin)
(70 words)
Questions:
- Where did the squirrel make a nest?
- What shape is the squirrel's nest?
- What stores does a squirrel make for the winter?
Morning rays
A wonderful sun came up to the sky. It began to scatter its golden rays.
It began to scatter its golden rays.
The first beam hit the lark's nest. The lark fluttered out of its nest. He rose into the sky and sang a wonderful song.
The second beam hit the bunny. The bunny ran to get dewy grass for breakfast.
The third beam hit the chicken coop. The rooster flapped its wings and woke up the hens. They started looking for worms.
The fourth ray hit the hive. A bee buzzed, crawled out of the hive and flew off to collect honey from fragrant flowers. (According to K. Ushinsky)
(72 words)
Questions:
- What did the lark do?
- Who was hit by the second ray of sun?
- Who was awakened by the third ray?
- What did the bee do?
Hands
Look at your hands. Look at them with respect.
Here is the table. You are sitting at the table. Here is the desk. You are learning at the desk. Here is the window. Through it you look at the street.
You are sitting at the table. Here is the desk. You are learning at the desk. Here is the window. Through it you look at the street.
A book, a house, bread, a dress, a coat - all this was made by human hands. They can grow bread, build a house, write a book, throw a ball into a net, send a spaceship to the moon. Everything can be done, everything can be done by human hands. And a person must respect the work of his own hands and the work of another person. (According to L. Kassil)
(75 words)
Questions:
- What can human hands do?
- How should one treat hands and work?
Frosty patterns
It got very cold during the night. It's a frosty morning. Patterns appeared on the glass. Rays of sunlight played on the glass with multi-colored lights.
Here is a long branch of a palm tree. Here is a wonderful flower. The snowy pattern is beautiful both in the brilliance of the morning sun and in the blue of the winter evening.
The snowy pattern is beautiful both in the brilliance of the morning sun and in the blue of the winter evening.
Where did the snow patterns come from? Moroz Ivanovich draws them. How does he draw them? Transparent steam, which is always in the air.
Warm water vapor settles on the cold glass of the window. They freeze. Other droplets stick to them. A garden of ice gradually grows on the window. The garden sparkles in the winter sun. (According to M. Gumilevskaya)
(82 words)
Questions:
- What do frost patterns look like?
- How are they formed?
Harvest festival
In autumn, the villagers held a harvest festival. Tables were placed from end to end of the main street. There are baskets with bulk apples, juicy pears, and various vegetables on the tables.
Heads of cabbage came from the gardens for the harvest festival. Forty clothes and all without fasteners. Behind them are carrots. Whoever eats carrots will get more blood. And here is the beetroot - a master of blushing cheeks. Cucumbers, turnips, radishes, potatoes - all vegetables in the collection.
Forty clothes and all without fasteners. Behind them are carrots. Whoever eats carrots will get more blood. And here is the beetroot - a master of blushing cheeks. Cucumbers, turnips, radishes, potatoes - all vegetables in the collection.
Each vegetable is good in its own way. Everyone stocked up for the winter with the summer sun, summer rains, and took from the earth a particle of its great strength. (According to I. Strelkova)
(88 words)
Questions:
- When did the residents organize a harvest festival?
- What vegetables did you bring to the holiday?
- What did vegetables stock up on over the summer?
Spring
In the morning a spring was born in the field. As soon as the sun has risen, the grass has not yet dried up, and the bee is already flying to work to collect juice from flowers. The bee says to the fontanel:
— Spring, spring, where did you come from?
— I don't know, I'm still small.
— Spring, spring, — says the bee, — give me some water to drink.
- Drink your fill, please.
The bee got drunk, thanked and flew away.
The fontanel got stronger, gurgled more cheerfully. The sun rose high above the horizon.
A titmouse flew by, she saw him and asked:
— Spring, spring, where did you come from?
- Drink your fill, please.
The titmouse bird drank water, thanked him and flew off on his own business. And the fontanel became bigger, brighter, stronger.
The sun rose above the horizon, it became very warm in the field. (According to V. Belov)
(107 words)
Questions:
- Who was the first to see the spring?
- What was the fontanel?
- How did the fontanel become?
If the child's reading technique is below the norm, then he will not be able to study well. It is necessary to improve the quality of reading and reading comprehension. To do this, you need to read a lot (which is very difficult with poor reading quality) or use special techniques and exercises, because. The reasons for bad reading can be different.
It is necessary to improve the quality of reading and reading comprehension. To do this, you need to read a lot (which is very difficult with poor reading quality) or use special techniques and exercises, because. The reasons for bad reading can be different.
Slow readers and children who are struggling to improve their reading speed can be helped by using syllabary reading or, much more effectively, by using an integrated approach that includes various professional techniques.
To do this, I suggest you use the books:
THE BIG BOOK OF SYLLING TABLES is
- a ready-made tool for training reading and speed reading skills;
- 200 syllabic tables of different levels of complexity;
- professional spreadsheet technique.
The most effective methods will allow each table to be used repeatedly several times, increasing the child's interest in reading.
Working with these syllabic tables the child will receive:
- improvement in reading skills;
- reading speed increase;
- improved diction;
- reading comprehension;
- development of thinking and attention;
- expansion of vocabulary;
- increased self-confidence.
The child will stop stumbling over difficult words while reading. The reading process will become natural and painless.
You can easily print the pages you need. All pages of the book can be used separately.
THE BIG BOOK OF SAYLING CHARTS is suitable for those who are just taking their first steps in reading, and for those who want to significantly improve the quality of reading.
Syllabaries help children develop their speed reading skills. But it often happens that a child gets stuck at a reading speed of 10-20 words per minute. It is important to track this moment in time and start immediately performing the necessary exercises.
But it often happens that a child gets stuck at a reading speed of 10-20 words per minute. It is important to track this moment in time and start immediately performing the necessary exercises.
I have created a training that will help you overcome this barrier without much difficulty. It is convenient to use both at home and when working with the whole class. A variety of tasks will not let children get bored, and parents and teachers will not have to select the necessary material for a long time and torment children with an exhausting, incredibly difficult process at this stage - reading.
Download TRAINING "Speed Reading and Speech Development"
Together with the training you will receive a small book as a gift - 20 syllabic tables for practicing reading skills (they do not repeat the tables of a large book).
O. Naumova "Noisy texts for reading and retelling"
The skill of high-quality reading and writing depends on the state of visual perception and attention of the child.
The better the child recognizes visual images, the better he reads and writes more competently.
Working with noisy texts engages the child's brain to the maximum and increases the productivity of classes many times over. At the same time, there is a development of figurative thinking, attention, memory, the ability to understand what is read.
In the book you will find:
- Noisy texts with questions;
- Texts with questions for reading, retelling, checking reading technique;
- Method of working with noisy texts;
- High productivity options;
- Exercises for the development of speech and reading comprehension.
As a result, the child:
- read speed increases;
- attention and memory develop;
- conscious reading skills are developed;
- self-control skills develop;
- speech develops;
- the number of writing errors decreases;
- the process of writing summaries and essays is facilitated;
- improving academic performance.