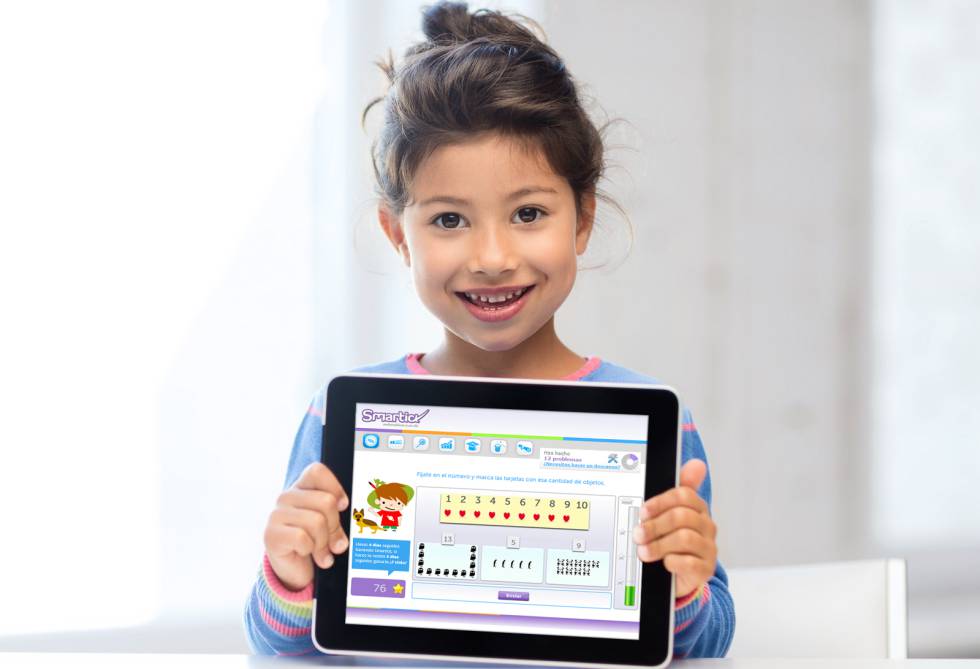
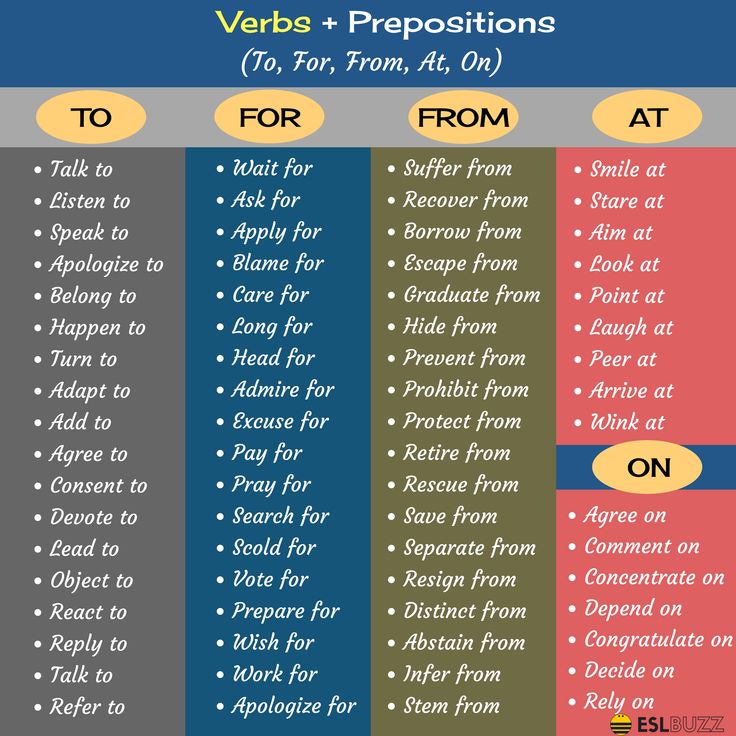
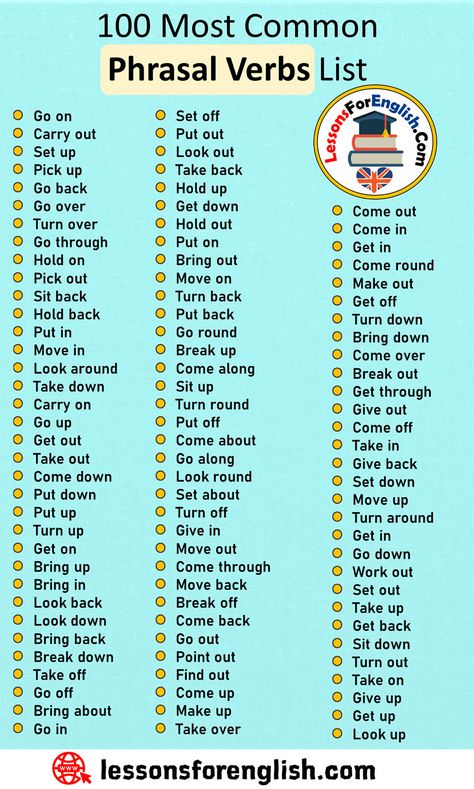
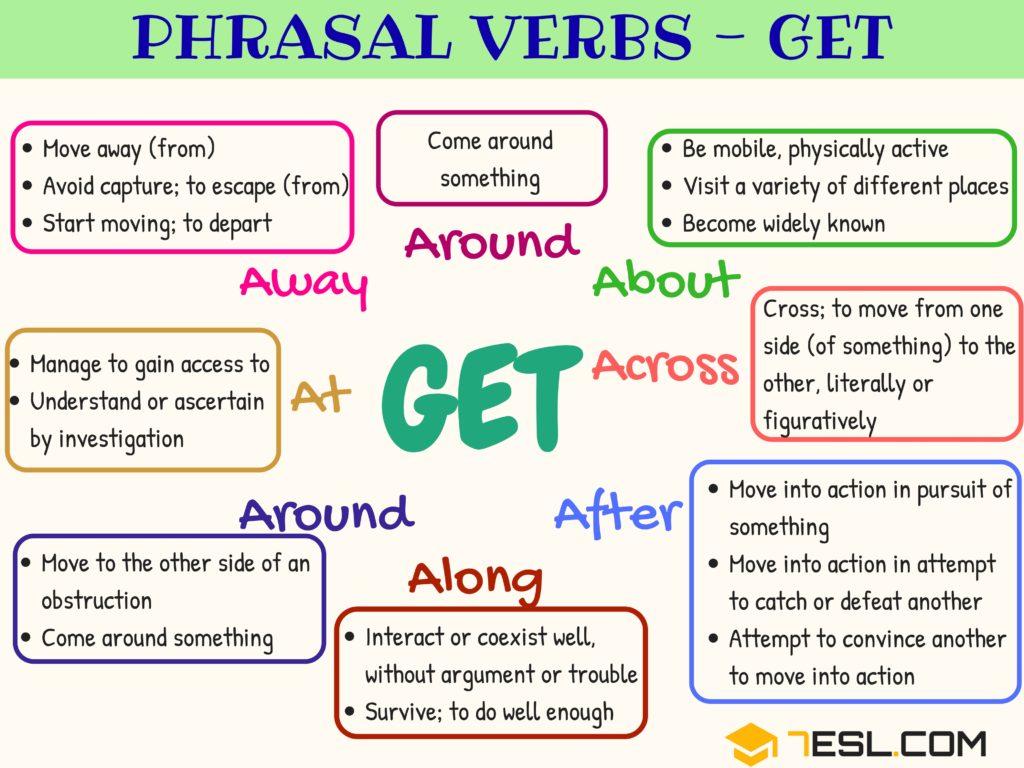
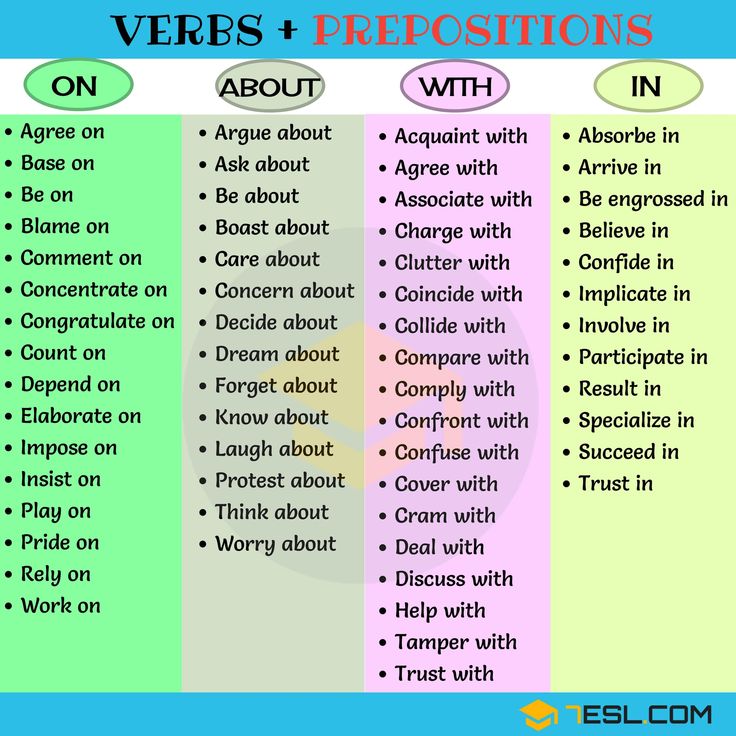
What are common verbs
100 Most Common English Verbs List
This is a list of the 100 most common verbs in English. If you are learning English it would be useful to learn these popular verbs first. Click though to see full conjugation tables of each verb.
Irregular verb forms are in red
Remove ads
| No. | Verb | Simple Past | Past Participle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | to be | were | been | Conjugate |
| 2 | to have | had | had | Conjugate |
| 3 | to do | did | done | Conjugate |
| 4 | to say | said | said | Conjugate |
| 5 | to go | went | gone | Conjugate |
| 6 | to get | got | got / gotten | Conjugate |
| 7 | to make | made | made | Conjugate |
| 8 | to know | knew | known | Conjugate |
| 9 | to think | thought | thought | Conjugate |
| 10 | to take | took | taken | Conjugate |
| 11 | to see | saw | seen | Conjugate |
| 12 | to come | came | come | Conjugate |
| 13 | to want | wanted | wanted | Conjugate |
| 14 | to look | looked | looked | Conjugate |
| 15 | to use | used | used | Conjugate |
| 16 | to find | found | found | Conjugate |
| 17 | to give | gave | given | Conjugate |
| 18 | to tell | told | told | Conjugate |
| 19 | to work | worked | worked | Conjugate |
| 20 | to call | called | called | Conjugate |
| 21 | to try | tried | tried | Conjugate |
| 22 | to ask | asked | asked | Conjugate |
| 23 | to need | needed | needed | Conjugate |
| 24 | to feel | felt | felt | Conjugate |
| 25 | to become | became | become | Conjugate |
Popular
- The top irregular verbs you need to know
- 100 Most common English verbs
- Most common nouns
- Vocabulary lists & games
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely.
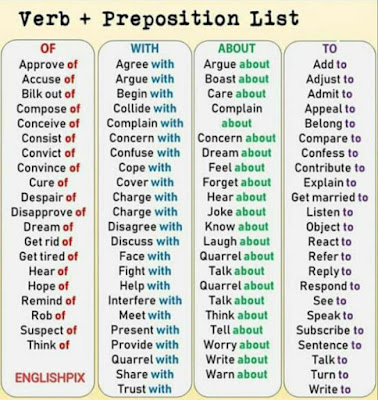
1000+ Most Common English Verbs List with Useful Examples • 7ESL
Are you looking for a comprehensive list of verbs in the English language? Here you will find 1000+ common verbs list with example sentences and ESL printable worksheets (in alphabetical order, by their grammatical functions, and by activity). One of the most important parts of a sentence when using the English language-or any language for that matter, is the verb. These words are used to tell the listener or reader what action is being performed by the subject of the sentence. There are a lot of verbs to learn and they fall into further subcategories.
Table of Contents
Verbs
What Are Verbs in English?
Verbs, in theory, are pretty straightforward.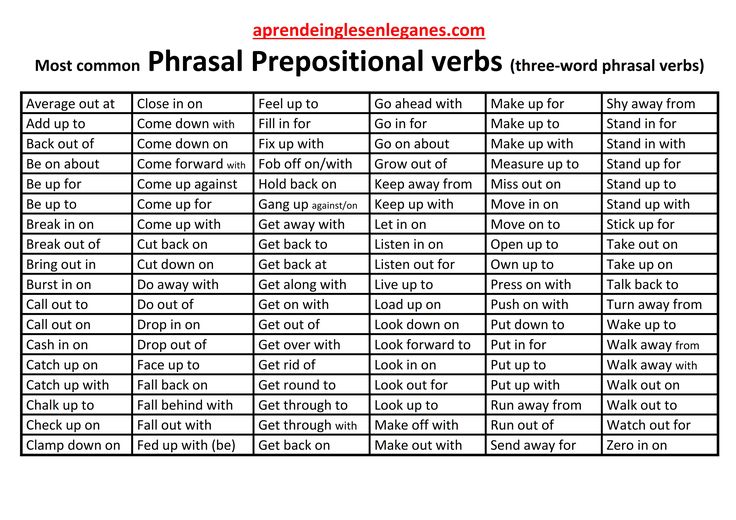 But, not everybody would be able to provide a definition, even if they know how to use them within a sentence. There’s also a tendency amongst people to stick to certain verbs that they know, and pushing themselves to use new ones becomes a bit of a challenge. In the interest of giving you some variety, we’ll take a look at what exactly a verb is, we’ll use some examples for you to see how they function as part of a sentence, and we’ll provide you with some lists of verbs by different categories so you can find some that might help you mix things up a little in your writing.
But, not everybody would be able to provide a definition, even if they know how to use them within a sentence. There’s also a tendency amongst people to stick to certain verbs that they know, and pushing themselves to use new ones becomes a bit of a challenge. In the interest of giving you some variety, we’ll take a look at what exactly a verb is, we’ll use some examples for you to see how they function as part of a sentence, and we’ll provide you with some lists of verbs by different categories so you can find some that might help you mix things up a little in your writing.
A verb is a word that shows action, occurrence, or a state of being. When written with the particle ‘to’ the verb is in its infinitive form. This is where you would write it like this:
- To bake
- To clean
- To cook
- To sing
There are many more verbs of course, but the above list shows you what a verb looks like in its infinitive form, making it slightly easier for you to identify whether or not a word in a sentence is a verb.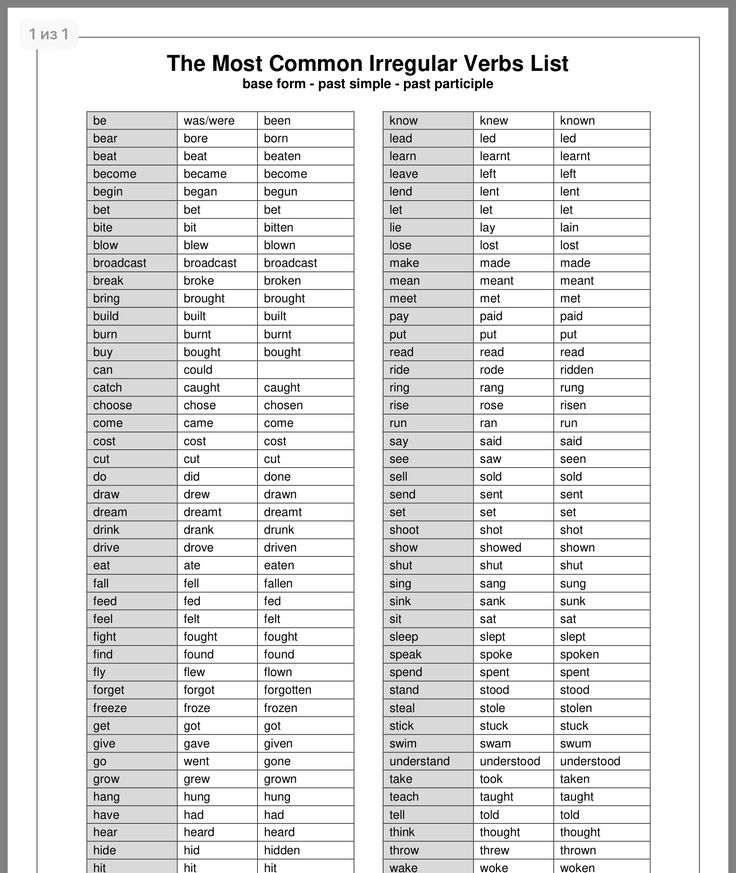 Remember, a verb should show that something is happening, because an action is taking place in some way or another. Many people when first learning about verbs simply refer to them as ‘doing words’, because they always show that something has been done, is being done, or will be done in the future (depending on the tense that you are writing in).
Remember, a verb should show that something is happening, because an action is taking place in some way or another. Many people when first learning about verbs simply refer to them as ‘doing words’, because they always show that something has been done, is being done, or will be done in the future (depending on the tense that you are writing in).
Verb Examples
Let’s look at the examples of the verbs above in a sentence so you can see how they might work. We’ll show them in different tenses too so you can see how they would need to be changed slightly to make sense.
Verb Examples in the Simple Tenses
- I bake everyday – here the sentence works as a simple present tense sentence. Let’s change it to past.
- I baked everyday – changing it to past simple tense means we say ‘baked’ not ‘bake’. This shows that ‘I’ used to bake everyday, but don’t any longer.
- I will bake everyday – again, changing to the future means you need the word ‘will’ between the subject ‘I’ and the verb ‘bake’.
 There are other tenses that aren’t simple, but we couldn’t possibly explain each one thoroughly here, but take a look at some more examples below and notice the changes that have been made for yourself. We’ll provide a brief explanation to help you slightly.
There are other tenses that aren’t simple, but we couldn’t possibly explain each one thoroughly here, but take a look at some more examples below and notice the changes that have been made for yourself. We’ll provide a brief explanation to help you slightly.
Examples of Verbs in the Continuous Tenses
Throughout each of these next three sections, the past tense version will be written on top, the middle will be present tense, and the future tense will be at the bottom. So that in this case, the top one is written in the past continuous tense, the middle in the present continuous tense, and the third in the future continuous tense. It will follow the same pattern in the following two sections, but continuous will be replaced with ‘perfect’ and ‘perfect continuous’ respectively.
The easiest way to remember continuous tense, is that it’s referring to a verb that was happening over time, is still happening now, or will be happening in the future. Take a look at the examples below and see how the sentences change to show what is happening and how the verb looks different from its infinitive form:
- I was cleaning when you arrived.
- I am cleaning right now.
- I will be cleaning when you get here.
Verb Examples in the Perfect Tenses
The best way to remember the perfect tense, is that it is referring to something that was completed, has just been completed, or will be completed in the future. Again notice how the verb looks different this time compared to its infinitive form, and how the surrounding words are different to accommodate the tense:
- I had cooked everything when you arrived.
- I have cooked everything.
- I will have cooked everything when you arrive.
Verbs Examples in the Perfect Continuous Tenses
The simplest way to remember the perfect continuous tense is that it’s the previous two combined. So, it refers to something that was happening but has recently been completed, something that is happening now but will soon stop, and something that will happen and then be completed.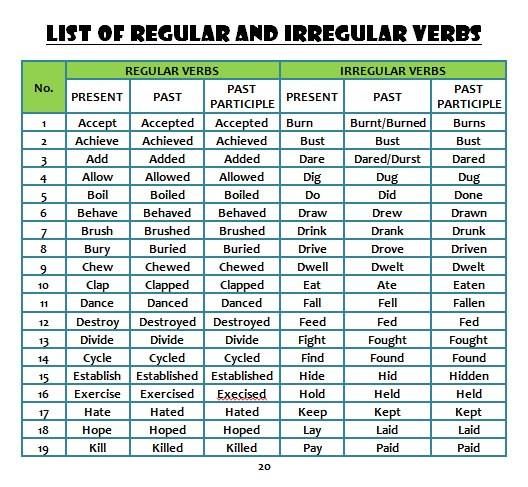 Take a look below:
Take a look below:
- I had been singing for an hour when you arrived.
- I have been singing for an hour.
- I will have been singing for an hour when you arrive.
List of Verbs
Now that we’ve taken a look at verbs, and all the possible tenses that you can write them in for you to think about, we’re going to provide you with some lists of verbs to help you vary your vocabulary a little bit.
In English grammar, verbs are one of the nine parts of speech. A verb is a word or group of words that describes an action, experience or expresses a state of being.
List of Verbs (in Alphabetical Order) / Examples of Verbs in Sentences
The following list of verbs will take you through various different verbs in alphabetical order for you to consider. See if you can spot one you would usually use and try to find one with the same meaning for you to try using in a sentence instead.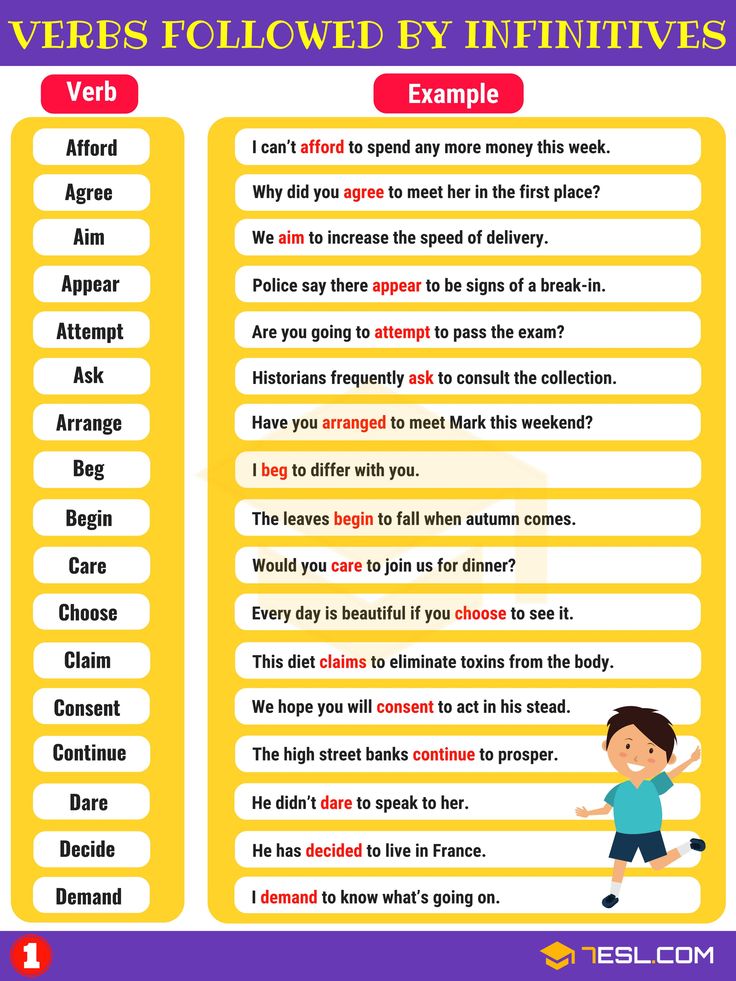
Verbs List (A)
List of verbs that start with A with verb examples.
- Accept: I accept your appolozy.
- Accuse: Tom accused me of lying.
- Achieve: She achieved remarkable results
- Acknowledge: She acknowledged receiving assistance.
- Acquire: Meg acquired many new friends.
- Adapt: He adapted himself to his new life.
- Add: I added a room to my house.
- Adjust: You will soon adjust to living in a dormitory.
- Admire: I admire your confidence.
- Admit: He was embarrassed to admit making a mistake.
- Adopt: I liked your idea and adopted it.
- Adore: He adores his grandfather.
- Advise: He advised applying at once.
- Afford: I can’t afford to spend any more money this week.

- Agree: Why did you agree to meet her in the first place?
- Aim: We aim to increase the speed of delivery.
- Allow: Swimming isn’t allowed here.
- Announce: She announced her intention to retire.
- Anticipate: I didn’t anticipate having to do the cooking myself!
- Apologize: You don’t have to apologize.
- Appear: Jack appears to be tired today.
- Apply: Tom applied for a leave of absence.
- Appreciate: I appreciate having a trouble with his supervisor.
- Approach: She approached him with a smile on her face.
- Approve: I don’t think Tom would approve.
- Argue: I don’t want to argue with you.
- Arise: The problem has arisen simply because you didn’t follow my instructions.
- Arrange: Have you arranged to meet Mark this weekend?
- Arrive: We arrived home late.
- Ask: Historians frequently ask to consult the collection.
- Assume: I assume Tom didn’t show up.
- Assure: I assure you Tom will be perfectly safe.
- Astonish: I was astonished by his ignorance.
- Attach: You need to attach your photo to the application form.
- Attempt: Are you going to attempt to pass the exam?
- Attend: She attends school at night.
- Attract: Tom certainly attracted a lot of attention.
- Avoid: She decided to be a nun in order to avoid meeting him.
- Awake: Tom awoke at daybreak.
Verbs List (B)
List of verbs that start with B with verb examples.
- Bake: Tom baked some muffins.
- Bathe: I bathe every day.
- Be: He is immature.
- Bear: I wish she wouldn’t eat so fast.
 I can’t bear watching her.
I can’t bear watching her. - Beat: You can’t beat me.
- Become: John became very sick.
- Beg: I beg to differ with you.
- Begin: The leaves begin to fall when autumn comes.
- Behave: Tom always behaves himself well. However, Mary does not.
- Believe: I believe you’re right.
- Belong: This bicycle belongs to me.
- Bend: Lie flat and let your knees bend.
- Bet: I bet you know French.
- Bind: Do you bind books?
- Bite: I got bitten by mosquitoes.
- Blow: Tom blew himself up accidentally.
- Boil: Please boil an egg for me.
- Borrow: I need to borrow your car.
- Bounce: Bounce the ball and try and hit it over the net.
- Bow: Every child bowed to the teacher.

- Break: We broke up.
- Breed: Rabbits breed quickly.
- Bring: I brought some dessert.
- Broadcast: We broadcast news on the hour.
- Build: We need to build a fire.
- Burn: The spy burned the papers.
- Burst: John burst into the room.
- Buy: I’ll buy a lot of candies for you.
Verbs List (C)
List of verbs that start with C with verb examples.
- Calculate: A computer can calculate very rapidly.
- Can/Could: Can you give me a ring at about 10?
- Care: Would you care to join us for dinner?
- Carry: I don’t carry cash anymore.
- Catch: Let’s catch a bite.
- Celebrate: We’re celebrating Tom’s birthday.
- Change: I changed my mind.

- Choose: Every day is beautiful if you choose to see it.
- Chop: Tom chopped down the tree that was in our front yard.
- Claim: This diet claims to eliminate toxins from the body.
- Climb: Carlos climbed the mountain.
- Cling: The mud clung to his shoes.
- Come: I’m coming today.
- Commit: David didn’t commit those crimes.
- Communicate: I can’t communicate with Anna like I used to.
- Compare: They compared the new car with the old one.
- Compete: I competed with him for the first prize.
- Complain: John complained about the weather.
- Complete: He completed drawing his pictures.
- Concern: I’m concerned for Anna’s safety.
- Confirm: The report has yet to be confirmed.

- Consent: We hope you will consent to act in his stead.
- Consider: Investors should consider putting some money into an annuity.
- Consist: A soccer team consists of eleven players.
- Consult: You’d better consult your doctor.
- Contain: This box contains five apples.
- Continue: The finance minister will continue to mastermind Poland’s economic reform.
- Convince: I’m not totally convinced of that.
- Cook: The pizza will then take about twenty minutes to cook.
- Cost: It’ll cost about 10,000 yen.
- Count: We’re counting on you.
- Crawl: Tom crawled into bed just before midnight.
- Create: I have to create a new website.
- Creep: We crept toward the enemy.
- Criticize: Tom criticized Mary for not doing the job correctly.
- Cry: The baby is crying.
- Cut: John cut his finger.
Verbs List (D)
List of verbs that start with D with verb examples.
- Dance: I want to dance.
- Dare: He didn’t dare to speak to her.
- Deal: I have to dealt with it.
- Decide: He has decided to live in France.
- Defer: She deferred writing my thesis.
- Delay: Big companies often delay paying their bills.
- Deliver: Letters are delivered every day.
- Demand: I demand to know what’s going on.
- Deny: She denied taking the money.
- Depend: I can’t depend on you anymore.
- Describe: John can’t describe how painful it was.
- Deserve: They didn’t deserve to win.
- Desire: We all desire success.

- Destroy: John’s house was destroyed by a hurricane.
- Determine: I am determined to carry out this plan.
- Develop: Swimming develops our muscles.
- Differ: My opinion differs from yours.
- Disagree: It pains me to disagree with your opinion.
- Discover: The miner discovered a valuable pocket of gold.
- Discuss: We briefly discussed buying a second car.
- Dislike: I dislike being the centre of attention.
- Distribute: The teacher distributed the leaflets.
- Dive: John learned to dive when he was five.
- Do: I don’t know.
- Doubt: I doubt if it’ll snow.
- Drag: I had to drag him out of bed.
- Dream: I dreamt about you.
- Drill: They intended to drill for oil.
- Drink: Can I have something to drink?
- Drive: He drives a truck.
- Drop: I dropped my sandwich.
- Dry: Raisins are dried grapes.
Verbs List (E)
List of verbs that start with E with verb examples.
- Earn: He earns three times more than me.
- Eat: You can’t eat your cake and have it.
- Emphasize: I want to emphasize this point in particular.
- Enable: His wealth enables him to do anything.
- Encourage: John encouraged Mary to learn how to speak French.
- Engage: We used to be engaged.
- Enhance: Can we enhance the image?
- Enjoy: I really enjoy talking to you.
- Ensure: This medicine will ensure you a good night’s sleep.
- Entail: This review procedure entails repeating the test.

- Enter: He entered the room.
- Establish: The school was established in 1650.
- Examine: The doctor examined the patients.
- Exist: I don’t believe such things to exist.
- Expand: The workers are expanding the road.
- Expect: What time do you expect to arrive home?
- Experiment: They’re experimenting with a new car.
- Explain: I can explain everything.
- Explore: He explored the Amazon jungle.
- Extend: We extended a hearty welcome to them.
Verbs List (F)
List of verbs that start with F with verb examples.
- Fail: I fail to comprehend their attitude.
- Fall: I fell in the pool.
- Feed: We just fed the baby.
- Feel: I feel that Mr. Peter is a good teacher.

- Fight: Don’t fight with me.
- Find: I can find them.
- Finish: He finished cleaning the kitchen.
- Fit: This coat doesn’t fit me.
- Fly: Tom wishes he could fly.
- Fold: Tom and Mary folded up the flag.
- Follow: We must follow the rules of the game.
- Forbid: I forbid you to smoke.
- Forget: I’ll never forget visiting them.
- Forgive: We have already forgiven you.
- Freeze: It’s freezing cold in this country.
- Fry: She fried fish in salad oil.
Verbs List (G)
List of verbs that start with G with verb examples.
- Generate: This machine generates electricity.
- Get: We’ve got to get the economy under control or it will literally eat us up.
- Give: The waiter gives me the menu.
- Go: Let’s go eat.
- Grind: We grind our coffee by hand.
- Grow: Apples grow on trees.
Verbs List (H)
List of verbs that start with H with verbs examples.
- Hang: Don’t you hang up on me.
- Happen: You made it happen.
- Hate: I hate getting to the theatre late.
- Have: I have a car.
- Hear: I will hear me.
- Hesitate: I hesitate to spend so much money on clothes.
- Hide: I’m hiding from Tim.
- Hit: I hit the jackpot.
- Hold: Hold the knife at an angle.
- Hop: I tried to hop on my good foot while holding onto Jim…
- Hope: I hope to see you again soon.
- Hug: I really need a hug.

- Hurry: It had to hurry to find a home because I was already on to something else.
- Hurt: I hurt my elbow.
Verbs List (I-J)
List of verbs that start with I & J with verbs examples.
- Identify: She identified him as the murderer.
- Ignore: He ignored her advice.
- Illustrate: The teacher will illustrate how to do it.
- Imagine: I can imagine how you felt.
- Imply: Silence implies consent.
- Impress: We’re not impressed.
- Improve: I need to improve my French.
- Include: Tom’s lunch includes a sandwich and an apple.
- Incorporate: Her business was incorporated.
- Indicate: The arrow indicates the way to go.
- Inform: I’ll inform John about our decision.

- Insist: She insisted on going there.
- Install: The man tried to install his own antenna.
- Intend: I heard they intend to marry.
- Introduce: I’ll introduce you to Tom.
- Invest: He invested his money in stocks.
- Investigate: I came here to investigate Tom’s death.
- Involve: This procedure involves testing each sample twice.
- Iron: I iron my clothes almost every day.
- Jog: I make it a rule to jog every morning.
- Jump: Can you jump over the river?
- Justify: My results justify taking drastic action.
Verbs List (K)
List of verbs that start with K with verbs examples.
- Keep: I keep thinking about Joe, all alone in that place.
- Kick: The kids love to kick a ball against my wall.

- Kiss: Did you kiss anybody?
- Kneel: Do not run, stand, kneel or spin in the slide.
- Knit: She knit him a sweater for his birthday.
- Know: We know him.
Verbs List (L)
List of verbs that start with L with verbs examples.
- Lack: Tom seems to lack energy.
- Laugh: Tom is laughing.
- Lay: He laid on his back.
- Lead: Tom leads a quiet life.
- Lean: He leaned on his elbows.
- Leap: Ken leapt over the wall.
- Learn: Children learn to creep ere they can go.
- Leave: Leave me alone!
- Lend: Tom lent Mary his camera.
- Lie (in bed): Lie back down.
- Lift: He couldn’t lift the table and no more could I.
- Light: Better to light one candle than to curse the darkness.

- Lie (not to tell the truth): He hated lying.
- Like: She likes playing tennis.
- Listen: Why won’t you listen?
- Look: It looks cold outside.
- Lose: She lost a book.
- Love: I love going out to restaurants.
Verbs List (M,N)
List of verbs that start with M & N with verbs examples.
- Maintain: Tom maintained eye contact with Mary.
- Make: I’m making tea.
- Manage: Did you manage to catch the post?
- Matter: It doesn’t matter, Tom.
- May: Each nurse may be responsible for up to twenty patients.
- Mean: I didn’t mean to hurt your feelings.
- Measure: The surfboard measures 2 meters by 55 centimeters.
- Meet: We’ve never met.
- Melt: The snow is melted.
- Mention: He mentioned going to that college.
- Might: Donna might be able to come tomorrow, but it’s very unlikely.
- Mind: Would you mind repeating what you just said?
- Miss: He had missed being elected by a single vote.
- Mix: If you mix blue and red, you get violet.
- Mow: I mowed Tom’s lawn.
- Must: I really must get some exercise.
- Need: You need to change your eating habits.
- Neglect: Don’t neglect to lock the door when you leave.
- Negotiate: The two countries negotiated a treaty.
Verbs List (O)
List of verbs that start with O with verbs examples.
- Observe: You must observe those rules.
- Obtain: I obtained the painting at an auction.
- Occur: The accident occurred yesterday morning
- Offer: She offered to help me move my things to my new house.
- Open: Open the windows.
- Operate: I can’t figure out how to operate this machine.
- Order: What do you suggest I order?
- Organize: They want me to organize the party.
- Ought to: You ought to get your watch repaired.
- Overcome: We have to overcome many difficulties.
- Overtake: Their car overtook ours.
- Owe: Tom owes me money.
- Own: I own a German car.
Verbs List (P)
List of verbs that start with P with verbs examples.
- Paint: She painted the wall pink.
- Participate: He participated in the debate.
- Pay: Can I pay by installment payment?
- Peel: Anna peeled the apple.
- Perform: Tom performs in a jazz club three nights a week.
- Persuade: I persuaded Tom to help me.
- Pinch: He pinched and scraped for many years to save money.
- Plan: Next year I plan to travel around the world.
- Play: I can play tennis.
- Point: Tom pointed to the sky.
- Possess: The old man possesses great wealth.
- Postpone: He postponed returning to Paris.
- Pour: She poured tea for me.
- Practice: Today we’re going to practice parking.
- Prefer: Chantal prefers travelling by train.
- Prepare: The doctor prepared to prescribe a receipt.
- Pretend: She was pretending to cry. I knew she was lying.
- Prevent: The rain prevented me from coming.
- Proceed: They will proceed to build another laboratory building.
- Promise: He promised to collect her from the airport.

- Propose: We propose to deal with this subject in the following chapter.
- Protect: We’re supposed to be protecting John.
- Prove: I’ll prove it to you.
- Pull: John pulled out a pen.
- Punch: You punch like a girl.
- Pursue: The police pursued the murderer.
- Push: We had to push our way through the crowd.
- Put: I put on my shoes.
Verbs List (Q,R)
List of verbs that start with Q & R with verbs examples.
- Qualify: He is qualified as an English teacher.
- Quit: She quits worrying about the problem.
- React: Tom reacted appropriately.
- Read: I read the book.
- Realize: I didn’t realise we were late.
- Recall: I don’t recall seeing any cars parked outside.
- Receive: We received a warm welcome.
- Recollect: I recollect seeing Ryder some years ago in Bonn.
- Recommend: I would never recommend using a sunbed on a regular basis.
- Reduce: I think we should reduce the price.
- Refer: I often refer to the dictionary.
- Reflect: She reflected on what she had done.
- Refuse: She refused to answer questions about her personal finances.
- Regret: I regret leaving school so young.
- Relate: She is related to him by marriage.
- Relax: We’re supposed to relax.
- Relieve: I was relieved to hear that he was alive.
- Rely: You can certainly rely on him.
- Remain: He remained poor all his life.
- Remember: He had remembered to bring a pair of gloves, unlike me.

- Remind: It reminds me of the good old days.
- Repair: He repaired his watch by himself.
- Replace: The car replaced the bicycle.
- Represent: He represented the labor union on the committee.
- Require: This task requires dexterity.
- Resent: Many conscripts resent having to do their military service.
- Resist: She can never resist buying new shoes.
- Retain: We had to retain a lawyer.
- Retire: I have decided to retire.
- Rid: You’ve got to get rid of it
- Ride: Life is a horse, and either you ride it or it rides you.
- Ring: The phone is ringing.
- Rise: The sun is about to rise.
- Risk: He risked being caught.
- Roast: He is roasting coffee beans.
- Run: Do not run too fast after gain.
Verbs List (S)
List of verbs that start with S with verbs examples.
- Sanction: They will not sanction copying without permission.
- Satisfy: He satisfied his thirst with a large glass of beer.
- Say: No one says that.
- Scrub: Tom asked Mary to scrub the toilet.
- See: Do you see that bird?
- Seem: I always seem to be unlucky at cards.
- Sell: I can’t sell you that.
- Send: They’re sending help.
- Serve: They serve good nosh in the cafeteria.
- Set: I’m going to set the table.
- Settle: The problem is not settled yet.
- Sew: Mary is sewing baby clothes.
- Shake: They shook hands when they met at the airport.
- Shall: Shall I add your name to the list?
- Shed: She tried not to shed a tear.
- Shine: Susan shined your father’s shoes.
- Shoot: I’ll shoot both of you.
- Should: The university should provide more sports facilities.
- Show: I’ll show you later.
- Shrink: My jeans shrank after I washed them.
- Shut: I shut my eyes again.
- Sing: Tom loves to sing.
- Sink: A ship sank near here yesterday.
- Sit: Sit on the floor, stretching your legs out in front of you.
- Ski: I like skiing very much.
- Sleep: I slept too much.
- Slice: It’s best to slice into a rich cake from the middle.
- Slide: He slid the money into my pocket.
- Slip: She slipped into her clothes.
- Smell: Something smells bad. What is this?
- Snore: Tom snored loudly with his mouth open.
- Solve: He solved the difficult problem.
- Sow: Farmers sow seeds in the spring.
- Speak: He speaks English.
- Specify: Tom didn’t specify how many pencils to buy.
- Spell: I don’t know how to spell the word.
- Spend: I spent some time in Boston.
- Spill: I’m afraid I spilled coffee on the tablecloth.
- Spit: I can’t put up with the way he spits.
- Spread: He spread some strawberry jam on his toast.
- Squat: Tom squatted down next to his dog.
- Stack: They are specially packaged so that they stack easily.
- Stand: Can you stand up?
- Start: He started tipping the pea pods into a pan.
- Steal: My watch was stolen.
- Stick: He stuck to his job.
- Sting: I was stung by a bee.
- Stink: It stinks in here.
- Stir: She stirred the soup with a spoon.
- Stop: I hoped he would stop asking awkward questions.
- Stretch: Breathe in through your nose as you stretch up.
- Strike: Tom struck the wall with his fist.
- Struggle: He struggled to keep his footing on the slippery floor.
- Study: She studies hard.
- Submit: I submitted the application myself.
- Succeed: He’ll succeed for sure.
- Suffer: We suffered a pretty big loss.
- Suggest: Tracey suggested meeting for a drink after work.
- Supply: I supplied Tom with everything he needed.

- Suppose: I suppose you’re hungry.
- Surprise: She surprised him when she arrived early.
- Survive: He survived the plane crash.
- Swear: Do you swear to tell the whole truth?
- Sweep: I will sweep out my room.
- Swell: The river swelled rapidly because of the heavy rain.
- Swim: She swims well.
- Swing: The lamp was swinging back and forth.
Verbs List (T)
List of verbs that start with T with verbs examples.
- Take: I took a walk.
- Talk: Tom talked a lot.
- Taste: The soup tastes salty.
- Teach: I’ll teach you how to swim.
- Tear: I tore the picture out of the album.
- Tell: I told him to come.
- Tend: She tends to be late for school.

- Think: I think that Mr. Peter is a good teacher.
- Threaten: They threatened to ban the book.
- Throw: I threw away my shoes.
- Tiptoe: Tom quietly tiptoed out of the room.
- Tolerate: We don’t tolerate smoking in the library.
- Translate: He translated the verse into English.
- Try: We tried to confuse the enemy.
Verbs List (U,V)
List of verbs that start with U & V with verbs examples.
- Understand: I knew you’d understand.
- Vacuum: Tom vacuumed his bedroom.
- Value: We value our customers.
- Vary: The boxes vary in size from small to large.
- Volunteer: They volunteer to teach introductory courses.
Verbs List (W)
List of verbs that start with W with verbs examples.
- Wait: I can’t wait to see you.
- Wake: I have to wake Tom up.
- Walk: Don’t try to walk before you can crawl.
- Want: I want to watch TV.
- Warn: We’ve got to warn Tom.
- Wash: Tom washed his hands.
- Watch: We watched a movie.
- Wave: She waved her hand to me.
- Wear: Tom wore black pants.
- Weep: She wept over her child’s death.
- Weigh: The suitcase weighs 20 pounds.
- Whip: She whipped out her pistol.
- Will: I don’t think Emma will get the job.
- Win: I can win this time.
- Wish: I wish to insert an advertisement in your newspaper.
- Would: If I lived on an island, I would know how to swim.
- Write: Write it down on a piece of paper.
List of Verbs (by Grammatical Functions)
Sometimes verbs don’t always behave the same in a sentence, so to make things easier for you to follow along, we’ve split these verbs up into their grammatical functions so you can see how they would be used in a sentence slightly differently.
A useful list of verbs classified by their grammatical functions. In this section, you will be learning about the different verbs in grammar and this will enable you to form much more concise and comprehensive sentences.
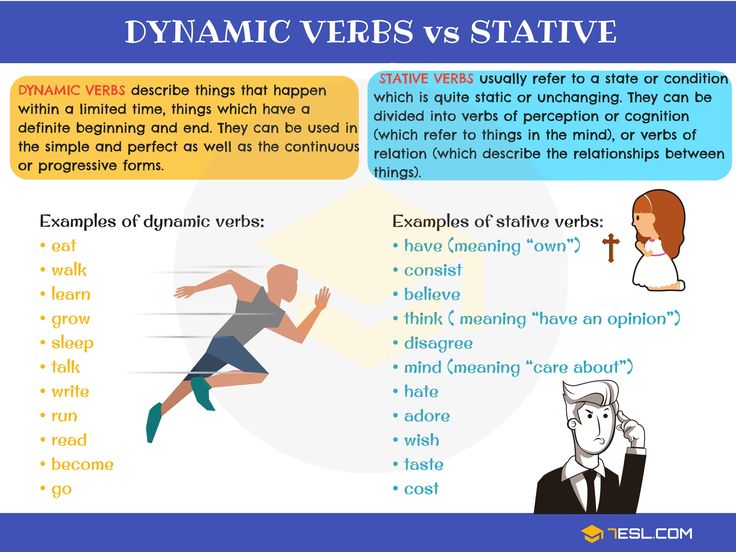
Stative Verbs List
List of common stative verbs in English
Mental State
- Know
- Believe
- Understand
- Doubt
- Think (have an opinion)
- Suppose
- Recognise
- Forget
- Remember
- Imagine
- Mean
- Agree
- Disagree
- Deny
- Promise
- Satisfy
- Realise
- Appear
- Astonish
- Please
- Impress
- Surprise
- Concern
Possession
- Have
- Own
- Possess
- Lack
- Consist
- Involve
- Include
- Contain
Emotions
- Love
- Like
- Dislike
- Hate
- Adore
- Prefer
- Care for
- Mind
- Want
- Need
- Desire
- Wish
- Hope
- Appreciate
- Value
Measure, cost, others
- Cost
- Measure
- Weigh
- Owe
- Seem
- Fit
- Depend
- Matter
Stative Verbs Examples in English | Image
Pin
Dynamic Verbs List
In English grammar, a “dynamic verb” means that the verb describes an action rather than a state. In contrast, a “stative verb” means that the verb describes a state rather than an action.
In contrast, a “stative verb” means that the verb describes a state rather than an action.
Dynamic verbs are sometimes known as “action verbs.”
List of Verbs Can be Both Stative and Dynamic Verbs
- Look
- Appear
- Think
- Feel
- Have
- See
- Taste
- Smell
- Be
- Weigh
- Measure
- Mind
Stative and Dynamic Verbs Examples | Image
Pin
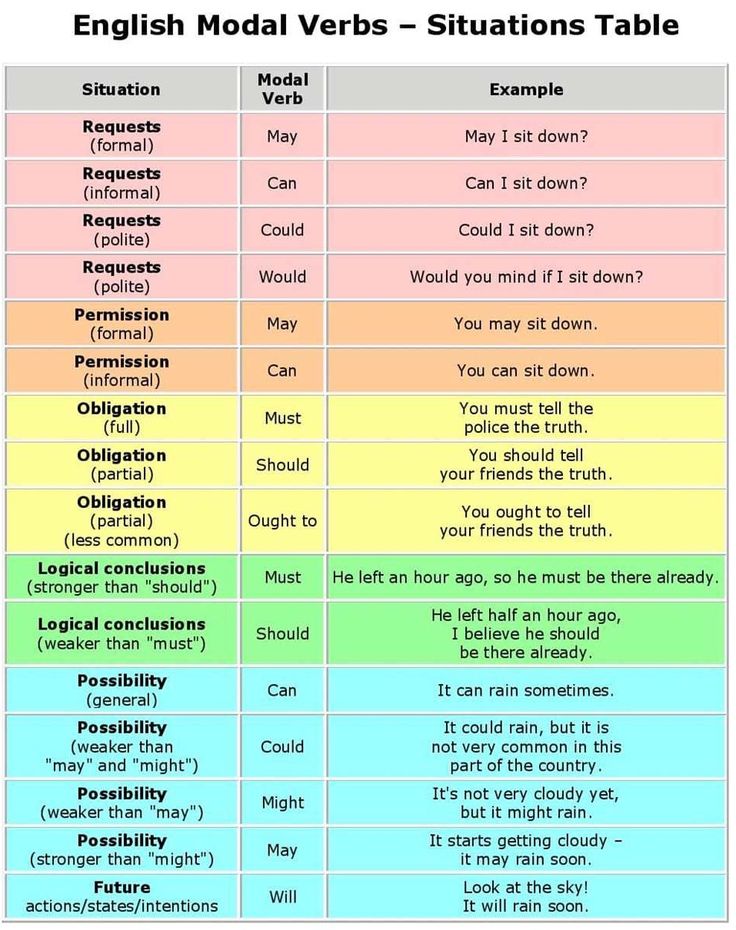
Modal Verbs List
List of modal verbs in English
- Will
- Shall
- Would
- Should
- Ought to
- Must
- Mustn’t
- May
- Might
- Can
- Could
- Have to/ Has to
- Don’t/ Doesn’t have to
Modal Verbs Examples in English | Image
Pin
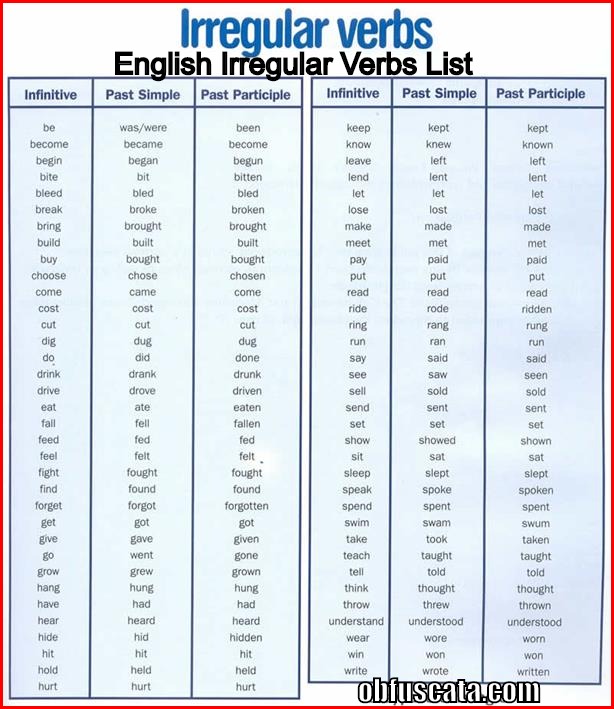
Irregular verbs List
Learn a useful list of Irregular Verbs in English
- Arise
- Awake
- Be
- Bear
- Beat
- Become
- Begin
- Bend
- Bet
- Bind
- Bite
- Bleed
- Blow
- Break
- Breed
- Bring
- Broadcast
- Build
- Burn
- Burst
- Buy
- Can
- Catch
- Choose
- Cling
- Come
- Cost
- Creep
- Cut
- Deal
- Dig
- Do
- Draw
- Dream
- Drink
- Drive
- Eat
- Fall
- Feed
- Feel
- Fight
- Find
- Fly
- Forbid
- Forget
- Forgive
- Freeze
- Get
- Give
- Go
- Grind
- Grow
- Hang
- Have
- Hear
- Hide
- Hit
- Hold
- Hurt
- Keep
- Kneel
- Know
- Lay
- Lead
- Lean
- Learn
- Leave
- Lent
- Lie (in bed)
- Lie (not to tell the truth)
- Light
- Lose
- Make
- May
- Mean
- Meet
- Mow
- Must
- Overtake
- Pay
- Put
- Read
- Ride
- Ring
- Rise
- Run
- Saw
- Say
- See
- Sell
- Send
- Set
- Sew
- Shake
- Shed
- Shine
- Shoot
- Show
- Shrink
- Shut
- Sing
- Sink
- Sit
- Sleep
- Slide
- Smell
- Sow
- Speak
- Spell
- Spend
- Spill
- Spit
- Spread
- Stand
- Steal
- Stick
- Sting
- Stink
- Strike
- Swear
- Sweep
- Swell
- Swim
- Swing
- Take
- Teach
- Tear
- Tell
- Think
- Throw
- Understand
- Wake
- Wear
- Weep
- Win
- Wind
- Write
Irregular Verbs Examples in English | Image
Pin
Participles, Gerunds & Infinitives
The three verbals— gerunds, infinitives, and participles—are formed from verbs, but are never used alone as action words in sentences.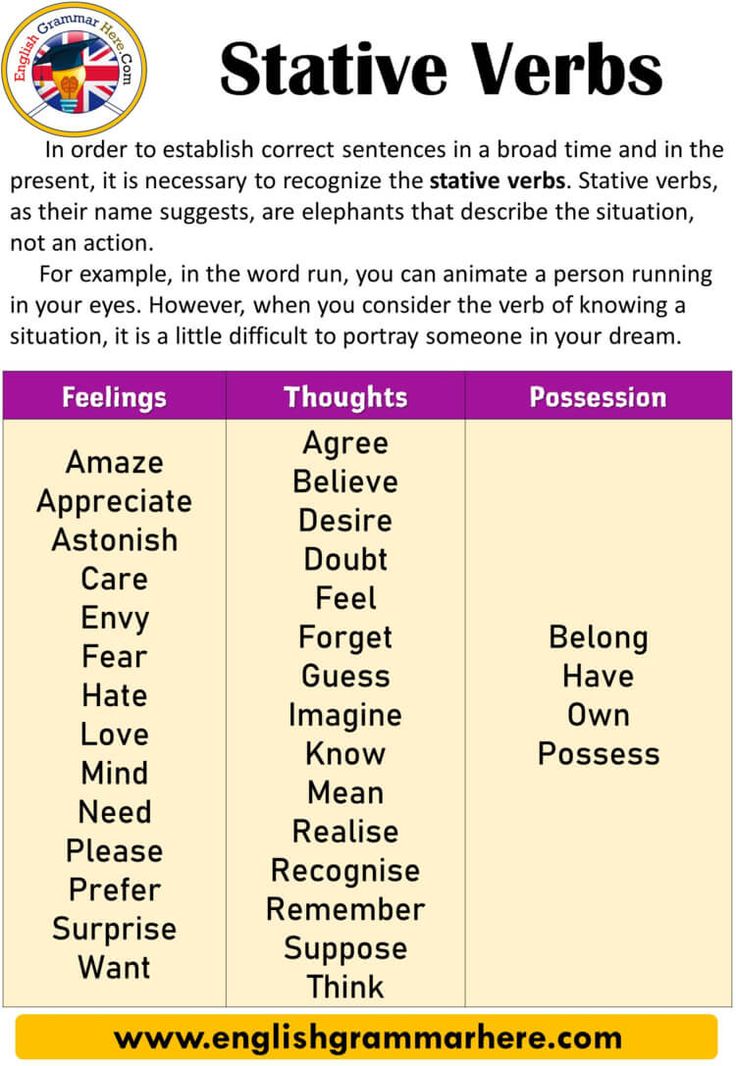 Instead, verbals function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. These verbals are important in phrases.
Instead, verbals function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. These verbals are important in phrases.
Participles
A participle is a verbal that is used as an adjective and most often ends in -ing or -ed. They function as adjectives, thus participles modify nouns or pronouns.
Learn more how to form Present and Past Participles in English.
Gerunds: List of Verbs Followed by Gerunds
Gerunds are verbals that function as nouns and have an –ing ending.
Useful list of Verbs Followed by Gerunds in English
- Admit
- Advise
- Anticipate
- Acknowledge
- Appreciate
- Avoid
- Bear
- Begin
- Complete
- Consider
- Defer
- Delay
- Deny
- Discuss
- Dislike
- Enjoy
- Entail
- Finish
- Forget
- Hate
- Intend
- Involve
- Justify
- Keep
- Like
- Love
- Mention
- Mind
- Miss
- Postpone
- Practice
- Prefer
- Quit
- Recall
- Recollect
- Recommend
- Regret
- Resent
- Resist
- Risk
- Sanction
- Start
- Stop
- Suggest
- Tolerate
- Try
List of Verbs Followed by Gerunds | Image
Pin
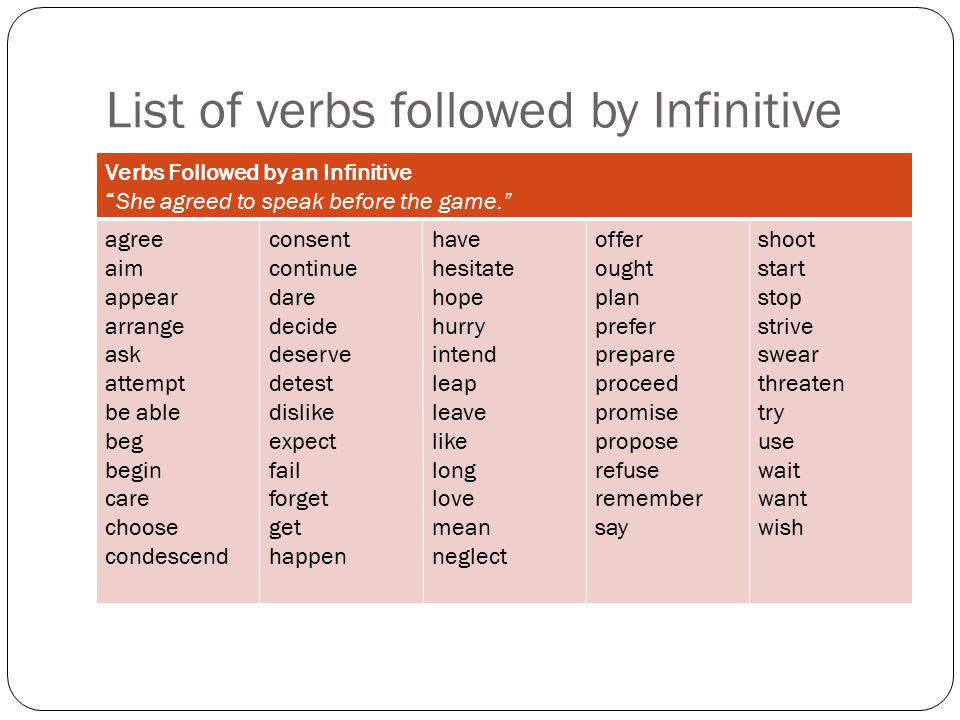
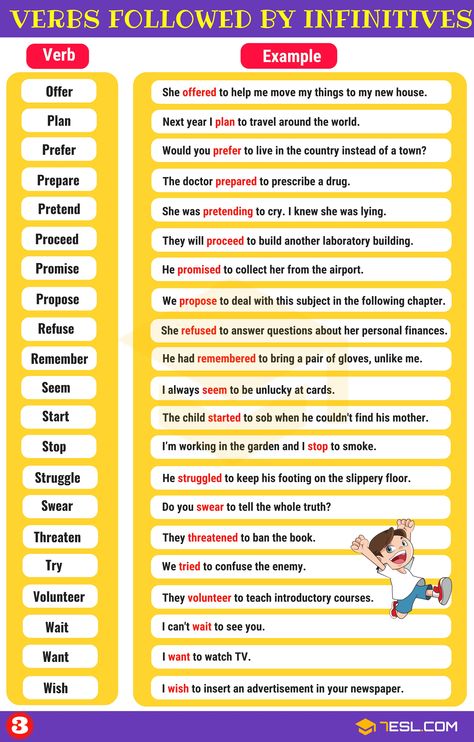
Infinitives: List of Verbs Followed by Infinitives
A to-infinitive is a verbal consisting of to + a verb, and it acts like a subject, direct object, subject complement, adjective, or adverb in a sentence.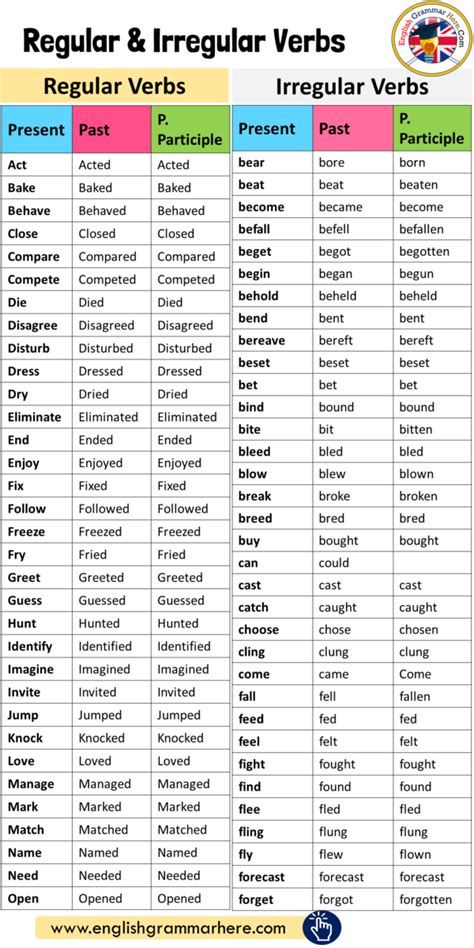 Infinitives are easy to identify because they’re written with to + a verb.
Infinitives are easy to identify because they’re written with to + a verb.
A useful list of commonly used Verbs Followed by Infinitives
- Afford
- Agree
- Aim
- Appear
- Attempt
- Ask
- Arrange
- Beg
- Begin
- Care
- Choose
- Claim
- Consent
- Continue
- Dare
- Decide
- Demand
- Deserve
- Dislike
- Expect
- Fail
- Forget
- Get
- Hesitate
- Hope
- Hurry
- Intend
- Learn
- Like
- Love
- Manage
- Mean
- Neglect
- Need
- Offer
- Plan
- Prefer
- Prepare
- Pretend
- Proceed
- Promise
- Propose
- Refuse
- Remember
- Seem
- Start
- Stop
- Struggle
- Swear
- Threaten
- Try
- Volunteer
- Wait
- Want
- Wish
List of Verbs Followed by Infinitives | Image
Pin
Auxiliary Verbs List
List of Auxiliary Verbs in English
- Do
- Have
- Be
- Will
Causative Verbs List
List of Causative Verbs in English
- Have
- Get
- Make
- Let
Causative Verbs Examples | Image
Pin
Verbs List (by Activity)
Finally, we’ve put together this list of verbs by activity. Whether it’s verbs associated with a restaurant, verbs associated with a sports event, or even verbs associated with body movements, we’ve categorized them all as best we can. Hopefully, you can look over them and understand different verbs that are more appropriate in some categories than in others.
Whether it’s verbs associated with a restaurant, verbs associated with a sports event, or even verbs associated with body movements, we’ve categorized them all as best we can. Hopefully, you can look over them and understand different verbs that are more appropriate in some categories than in others.
List of different types of verbs with pictures in English.
Action Verbs List
List of action verbs commonly used in English.
| Bathe | Eat | Sleep |
| Bow | Fight | Smell |
| Buy | Fly | Snore |
| Clap | Give | Stack |
| Climb | Hug | Stand up |
| Close | Jump | Talk |
| Cook | Kiss | Turn off |
| Crawl | Knit | Turn on |
| Cry | Laugh | Think |
| Cut | Listen | Throw away |
| Dance | Open | Wait |
| Dig | Paint | Wash |
| Dive | Play | Watch TV |
| Dream | Read | Win |
| Drink | Ride | Write |
| Shake | Sew | Sing |
Pin
Cooking Verb Examples with Pictures
| Add | Peel |
| Bake | Pinch |
| Barbecue | Pour |
| Boil | Roast |
| Break | Roll out |
| Cut | Saute |
| Chop | Slice |
| Fry | Spread |
| Grate | Steam |
| Layer | Stir |
| Melt | Taste |
| Mix | Weigh |
Pin
Restaurant Verbs List with Pictures
- Give
- Drink
- Serve
- Pay
- Eat
- Cook
- Hold
- Light
- Order
- Spread
- Lift
- Write
- Slice
- Stack
- Set (the table)
Pin
Sports Verbs List with Pictures
| Bend | Pass |
| Bounce | Ride |
| Catch | Run |
| Dribble | Serve |
| Hit | Shoot |
| Hop | Sit |
| Jump | Skip |
| Kick | Stretch |
| Kneel | Throw |
| Lie down | Walk |
Pin
Classroom Verb Examples
| Ask | Open |
| Calculate | Paint |
| Close | Play |
| Count | Read |
| Cut | Say |
| Draw | Show |
| Experiment | Sing |
| Explain | Spell |
| Give | Study |
| Listen | Teach |
| Observe | Think |
Pin
Body Movement Verbs List
| Bend | Push | Dance |
| Lift | Run | Break |
| Carry | Lean | Stand |
| Kneel | Squat | Jog |
| Hold | Throw | March |
| Sit | Tiptoe | Wave |
| Drag | Walk | Talk |
| Jump | Hit | Open |
| Leap | Catch | Cartwheel |
| Pick up | Kick | Put down |
| Punch | Kiss | Stretch |
| Pull | Clap | Drop |
| Dive | Laugh | Point |
| Look | Trip | Slip |
| Crawl | Pour | Cry |
Pin
English Verbs List | Pictures
Common English Verbs List | Image 1
Pin
English Verbs List | Image 2
Pin
Common English Verbs List | Image 3
Pin
English Verbs List | Image 4
Pin
List of Verbs Videos
Verbs are relatively easy to understand, but the key to using them successfully in sentences is being aware of the tense.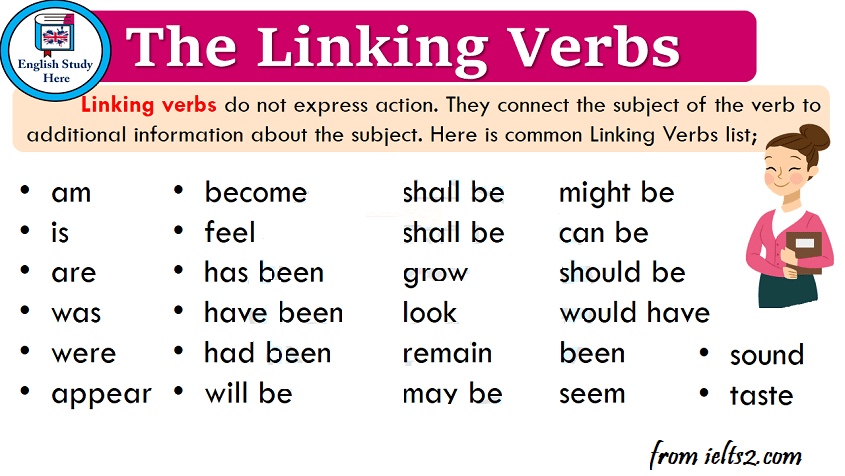 The best way to combat this is by reading the sentence aloud. It’s incredibly easy to pick up issues with tenses when you hear it rather than read it. Remember, you can always look back here for more information about how verbs change in tenses to give you an idea about what changes you might need to make to your sentence for it to make sense. And of course, our list of verbs will be here for you to look over for new ideas about which verbs to use in different contexts or for different grammatical functions.
The best way to combat this is by reading the sentence aloud. It’s incredibly easy to pick up issues with tenses when you hear it rather than read it. Remember, you can always look back here for more information about how verbs change in tenses to give you an idea about what changes you might need to make to your sentence for it to make sense. And of course, our list of verbs will be here for you to look over for new ideas about which verbs to use in different contexts or for different grammatical functions.
Learn 250+ verb examples with pictures and American English pronunciation.
Verb (general)
English
English Grammar
A verb is a part of speech that denotes an action or state of a person or object.
The main function of the verb in the sentence is the function of the predicate:
Not studies at the Institute. — He studies at the institute.
Yesterday I slept six hours. I slept six hours yesterday.
Forms of the English verb are divided into personal and impersonal.
Personal forms of the verb contain an indication of the person, number, aspect, mood, tense, voice. The verb in the personal form performs the function of a predicate and always agrees with the subject in person and number:
Nick lives in Moscow. — Nick lives in Moscow.
Not working at the library. — He works in the library.
These houses were built last year. These houses were built last year.
Non-finite forms of the verb (infinitive, gerund, participle I, II) express action without indication of person, number and mood. On their own, they cannot perform the function of a predicate. In combination with personal forms of the verb, they form a predicate:
I am reading a book. - I read a book.
- I read a book.
I want to read this book. - I want to read this book.
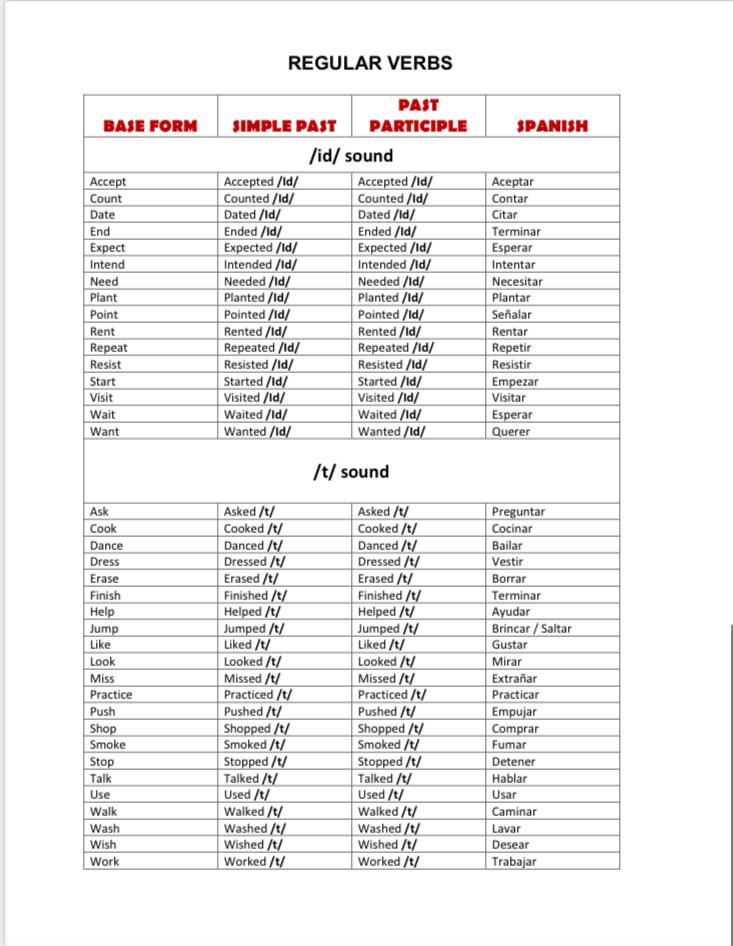
According to the way of formation of forms of the past indefinite tense and participle II, all verbs are divided into regular and irregular.
Most of the verbs belong to the regular verbs, which form the past indefinite tense and participle II by adding the suffix -ed to the verb stem.
to use - used - used Ending -ed is pronounced:
as [d] after voiced consonants and vowels:
lived - [livd]
distroyed - [dis'troid]
as [t] after voiceless consonants:
helped - [helpt]
as [id] after consonants d and t:
ended - ['endid]
wanted - ['wontid]
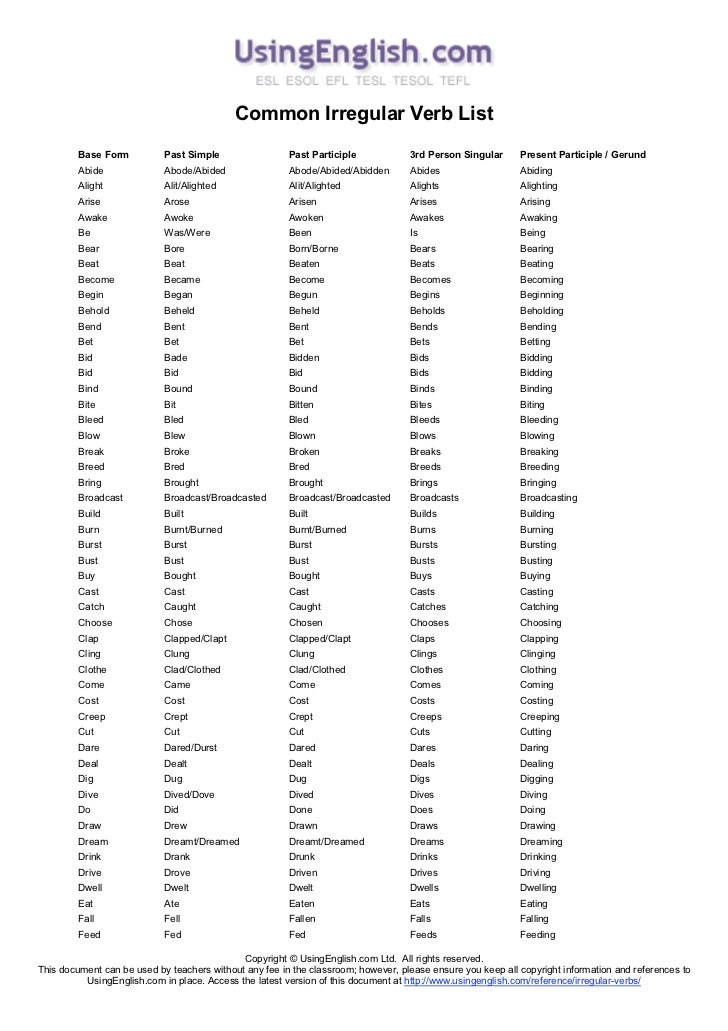
Irregular verbs form the past indefinite tense and participle II in special ways. The number of irregular verbs is small, but they include the most common verbs. Irregular verbs are recommended to be memorized in three or four basic forms according to the tables attached to dictionaries and textbooks. In dictionary entries, irregular verbs are given in three basic forms.
There are three moods in English:
indicative, showing that the speaker considers this action as a real fact:
Not reads newspapers in the evening. He reads newspapers in the evening.
I saw an interesting film yesterday. Yesterday I saw an interesting film.
My brother will graduate from the Institute next year. My brother will graduate from the institute next year.
subjunctive, showing that the speaker regards the action as intended or desired, and not as a real fact:
Not suggested that we (should) go to the country. - He suggested that we go out of town
imperative expressing an order, request or wish.
Go to the blackboard. - Go to the blackboard. Verbs have two voices:
the active voice indicates that the subject is the person or thing doing the action:
Not published his book at the age of twenty. He published his book at the age of 20.
passive voice indicates that the subject is a person or thing being acted upon by another person or thing:
The first book was published many years ago.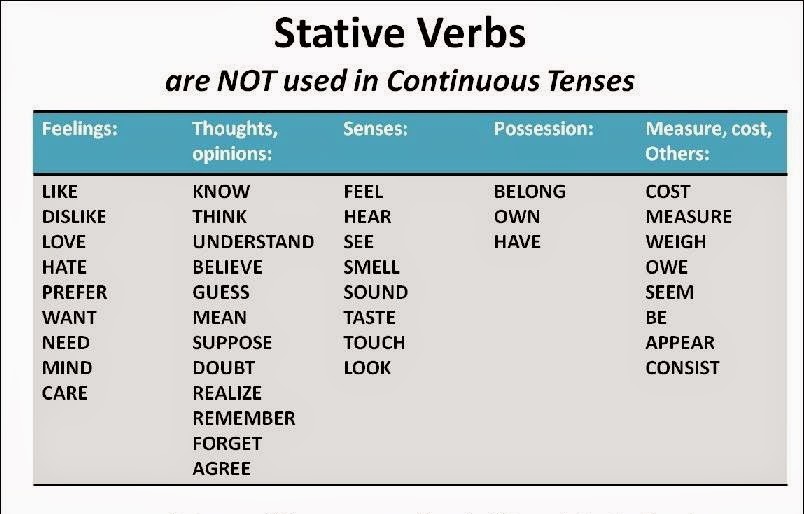 The first book was published many years ago.
The first book was published many years ago.
Various compound forms of the verb are formed using auxiliary verbs to be, to have, to do, shall (should), will (would).
Auxiliary verbs do not have an independent meaning, but are only indicators of time, person, number, voice, etc.
In the tables, the forms of verbs are presented in the following order: infinitive, i.e. the indefinite form of the verb (The Infinitive), the past indefinite tense (The Past Indefinite Tense), the past participle, i.e. participle II (The Past Participle, or Participle II) and sometimes a fourth form is given: the present participle, i.e. participle I, which is called -ing-form of the verb (The Present Participle, or Participle I).
Verbs to be, to have, to do are also used as semantic verbs with meanings: to be - to be; to have - to have; to do - do.
Verb to be
Conjugation of the verb to be in a real uncertain time:
The only number
I am
YOU ARE
She IS
9000
multiple
WE ARE
YOOU ARE
In the past indefinite tense, the verb to be has the forms was (singular) and were (plural). Participle forms: been, being, i.e. to be - was, were - Yeel - being.
Participle forms: been, being, i.e. to be - was, were - Yeel - being.
He was in St Petersburg last year. — He was in St. Petersburg last year.
They were in yesterday. They were at home yesterday.
In the present and past interrogative form, the verb is placed before the subject:
Are you an engineer? - You're an engineer?
The negative form of the present and past tense is formed by negating not, which is placed after the verb:
Not is not a student. - He's not a student.
All other verb tenses are formed according to the general rule.
In a sentence, the verb to be can be used:
as a semantic verb with the meaning "to be", "to be":
My friend was in Leningrad during the war. — My friend was in Leningrad during the war.
as an auxiliary verb for the formation of a group of continuous tenses:
Not is reading a book now. - Now he is reading a book, and for the formation of all tenses of the passive voice:
This house was built last year.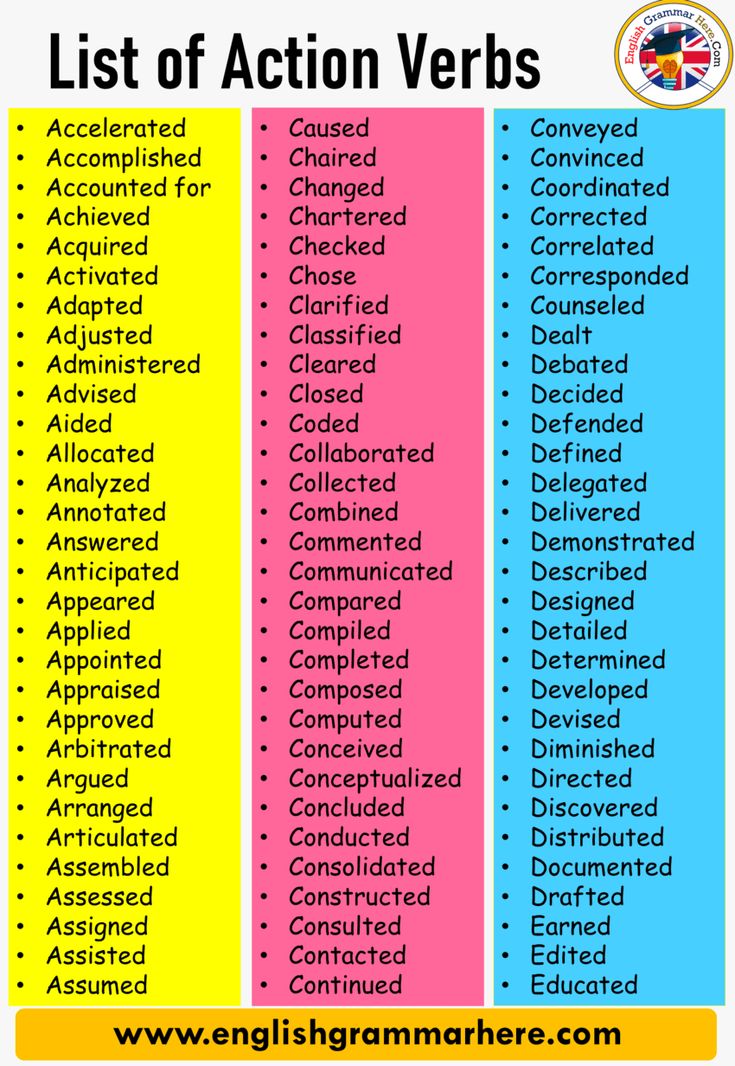 This house was built last year.
This house was built last year.
This house has already been built. This house has already been built.
as a linking verb:
She is a doctor. - She is a doctor,
to express an obligation:
We are to meet at 8. - We are to meet at 8.
Verb to have
Conjugation of the verb to have in the present indefinite tense:
Singular
I have
You have
Not has
She has
It has
Plural
We have
You have
They have
:
I was sure I hadn't met him before. I was sure I hadn't met him before.
Having been there before, I knew what to expect. “Having been here before, I knew what to expect.
Spoken English uses abbreviated forms of the verb to have when it is an auxiliary:
What've [av] you been doing? - What are you doing?
I've been reading. - I am reading.
As a semantic verb to have is used with the meaning "to have", "possess":
I have a new radio-set. — I have (I have) a new radio.
— I have (I have) a new radio.
Previously, auxiliary verbs were not required to form interrogative and negative sentences in such cases:
Have you any brothers or sisters? - Do you have any brothers or sisters?
I have no brothers or sisters. - I have no brothers or sisters. This is true for the literary style.
Do you have brothers or sisters?
Spoken English is characterized by two forms: have got or verb forms with an auxiliary verb do:
Have you got any brothers or sisters?
Do you have any brothers or sisters?
I haven't got you haven't got he/she/it has't got we haven't got they haven't got
I've got
you've got
He's/she's/it's got
we' ve got
they've got
Shapes to have got:
have I got? have you got? has he/she/it got? have we got? have they got?
In British English, have with an auxiliary do is used to indicate a habitual, repetitive action or state. Compare:
We don't usually have whiskey in the house. We don't usually have whiskey in the house.
We don't usually have whiskey in the house.
I haven't got any whiskey. — I don't have any whisky.
I've got toothache. - I have a toothache.
I often have a toothache. - I often have a toothache.
Under the influence of American English forms with auxiliary do are becoming more and more common in cases where we are not talking about habitual actions:
Sorry, I don't have any whiskey. Sorry, I don't have any whiskey.
In American English, the form of the verb have is simpler; as a rule, in all cases, the verb do is used for shaping:
I have a problem. — I have a problem
Do you have a problem? - Do you have a problem?
That have in these cases does not have continuous tense forms.
The verb to have is used in combination with a large number of nouns, losing its main meaning:
to have dinner / breakfast - to have lunch, breakfast;
to have tea/coffee
to have a bath / a wash - take a bath, wash;
to have a shave / a shower / a rest - shave, take a shower, relax;
to have a sleep / a dream - sleep, dream;
to have a holiday / a good time - relax, have a good time.
In these cases, the interrogative and negative forms of the verb GO have are formed using the auxiliary verb GO do:
Where do you have dinner? - Where do you have lunch?
To express obligation, the verb have to is used with the auxiliary verb do in the interrogative and negative forms to indicate a habitual, repetitive action:
How often do you have to travel on business? - How often do you have to go on business trips?
I don't usually have to work on Sundays. Usually I don't have to work on Sundays.
Do you often have to speak French in your job? Do you often have to speak French at work?
Use have got to indicate one-time actions
I haven't got to work tomorrow. I don't have to work tomorrow.
The verb to do
The verb to do is conjugated in all active and passive tenses according to the general rules for conjugation of verbs:
The verb to do can be used:
as a semantic verb with the meaning "to do":
I shall do it tomorrow. — I will do it tomorrow, as an auxiliary verb:
— I will do it tomorrow, as an auxiliary verb:
to form an interrogative and negative sentence of the present indefinite and past indefinite:
Do you speak English? - You speak English?
Didn't work here yesterday. - Yesterday he did not work here, for the formation of a negative form of the imperative mood:
Do not (don't) open the window. - Do not open the window, the day of increasing the value of the action:
But I do know him. But I (really) know him.
I did do it. I (really) did it.
- Back
- Forward
General information, types and classification of verbs in English
The verb is a part of speech denoting an action, state, feelings or mental processes.
to build, to go, to rest, to think
In English, many verbs in their form do not differ from nouns and are recognized only by their role in the sentence:
Dance - to dance; dance
Jump - jump; jump
Verbs in English can be divided into simple, derivative, complex and compound.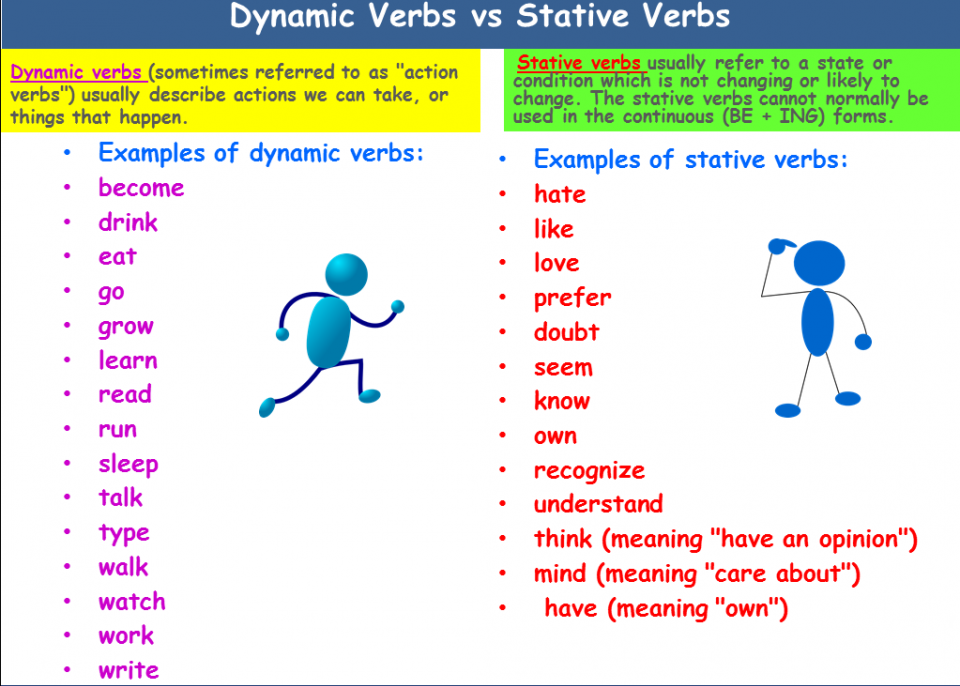
Simple verbs consist of one stem ( root ):
to speak, to run, to try
0060 Suffixes or Prefixes :
to Re Write, TO DIS Cover, To Organ Ize , To Modi FY are the most frequent evidence of 9000 . From adjectives: Red - RIDD EN Wide - WID EN –FY : SPECI FY , ELECTRI FY 9000 9000 9000 —Ize 900 -ize 900 --ize 9000 -ize 9000 –Ize0061: SPECIALI ZE , Util Ize , Activ Ize also use prefixes :
Dress- 9000 UNs- 9000 UNs- 9000 UNs- 9000 UNs- 9,0009 Dress- 9000 UN Cover - un cover
Tie - un tie
Dis- (also negative):
Like - dis kile
Approve1 90 90 Approve60008
Re- (meaning repetition):
Write - re write
Organize - re organize
separate from each other in other words:
to sit down - sit down
to put on - put on
to go away - leave
Compound verbs have two stems:
to browbeat - to intimidate
to machine-gun - to shell
According to their syntactic function and meaning, verbs are divided into semantic (national Verbs), auxiliary (Auxiliary Verbs) and semi-auxiliary (Suxiliary verbs) .
Semantic verbs - verbs that have an independent meaning and, accordingly, can perform the function of a simple verbal predicate in a sentence:
I hate this place - I hate this place
Service English verbs:
Auxiliary verbs - verbs that do not have an independent meaning and are used to form complex forms of the verb. Such verbs include: to do, to be, to have, to let, shall, should, will, would:
They told me she would come at six - they told me that she would come at six
Semi-auxiliary verbs - verbs that do not have a completely independent meaning and only in combination with other words can they be a predicate. These include:
- Linking verbs - used to form a compound nominal predicate: to be, to seem, to feel, to grow, etc.
- Modal verbs . They are also called insufficient verbs, since they do not have impersonal forms (infinitive, participle, gerund) and do not have all personal forms.
 These are verbs: can, may, must, need, should, ought, to have, to be.
These are verbs: can, may, must, need, should, ought, to have, to be.
I must get there before nine
Can you speak Spanish? - you can speak Spanish
You should start at once - you must start immediately
Important!!! We must remember that such verbs as:
ShOULD
to BE
To have
to 9000
TO Let type 9000. but also semantic or semi-auxiliaries!
The main forms of the English verb:
In English there are main forms of the verb, such as:
- Infinitive (To Sing, To Travel)
- Past indefinite time (Sang, TRAVELLELD) Past participle (second participle) (sung, travelled)
Sometimes they are called the first, second and third forms of the English verb respectively.