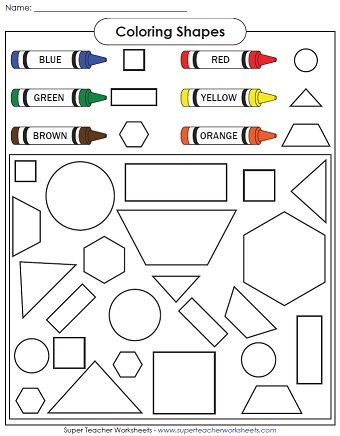
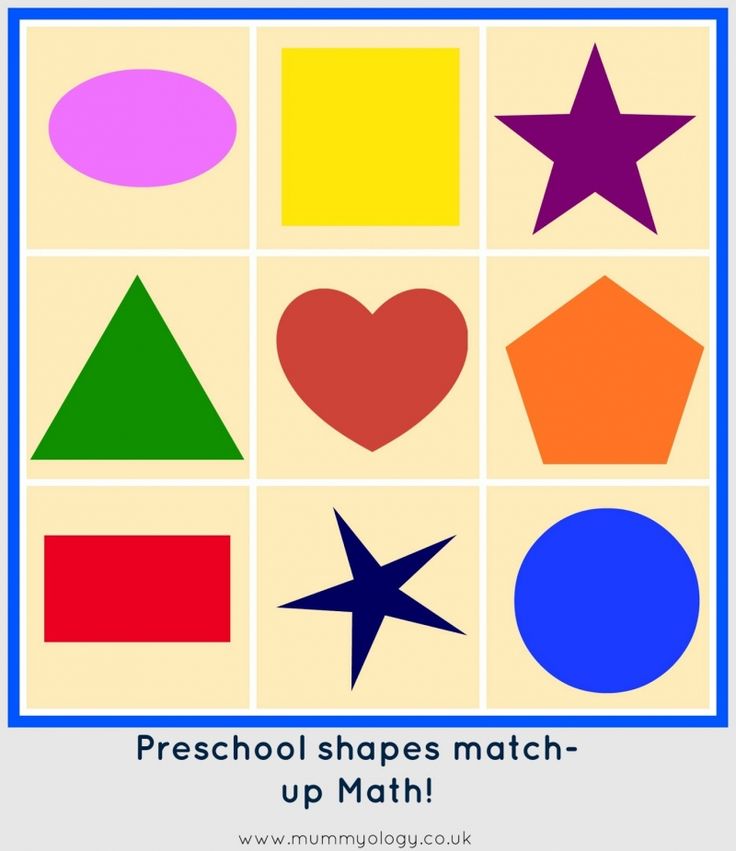
Shapes to teach preschoolers
Teaching Shapes in Preschool
Do you teach shapes in your preschool or pre-k classroom? If you’re looking for fun, hands-on activities for teaching shapes that will get your kids excited about learning, then you’re in the right place!
Teaching Shapes in Preschool
Learning about 2D shapes is an important early math skill. There are so many different ways to teach your little learners about shapes, but the most effective methods will be those that provide opportunities for hands-on learning.
2D Shape Activities
Shapes are a Skill
This might be a surprise to some, but shapes are a skill, not a unit of study. A skill develops over time and needs to be reviewed and reinforced throughout the year.
Teaching Shapes with Manipulatives
Your little learners will benefit the most from exploring and creating with shapes all over the classroom, not just in the math center.
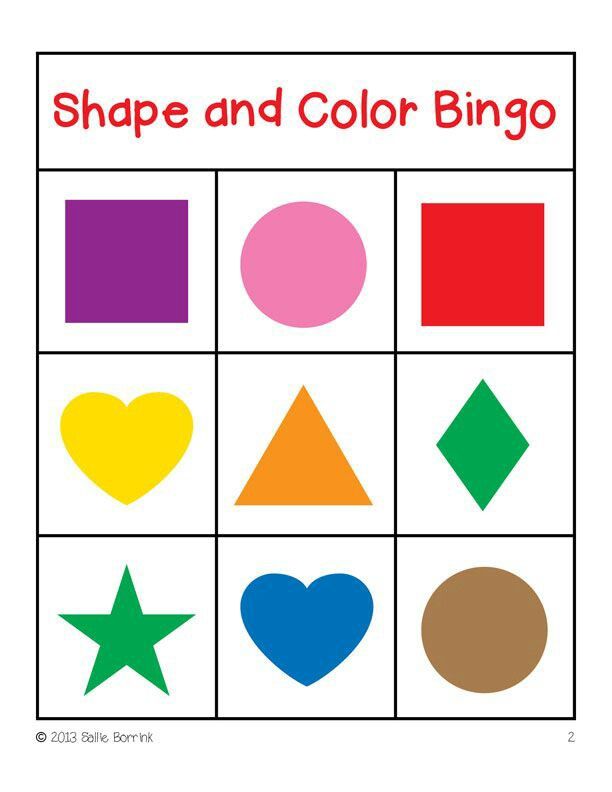
You can put shape manipulatives like pattern blocks, geoboards, and magnetic shapes in your classroom centers. I like to keep a color and shape bingo game in my puzzles and games center all year long.
Hands-On Learning
If you really want your students to learn shapes, you can provide them with hands-on activities for learning shapes all year long.
These road shape mats pictured above are a perfect example of a fun, hands-on learning activity your kids will love!
Embedding shapes into your units of study is a more effective approach because it will help your kids learn and remember the names of the shapes being taught.
Pattern Blocks
Another fun way for teaching shapes is to use pattern blocks. These pattern block mats are the perfect shapes activity.
Your little learners will be practicing shape matching, and they’ll also be flipping and turning the shapes on the mat. Matching, flipping, and turning shapes is the foundation of geometry.
Geoboard Shapes
These geoboard shapes task cards can be used all year long.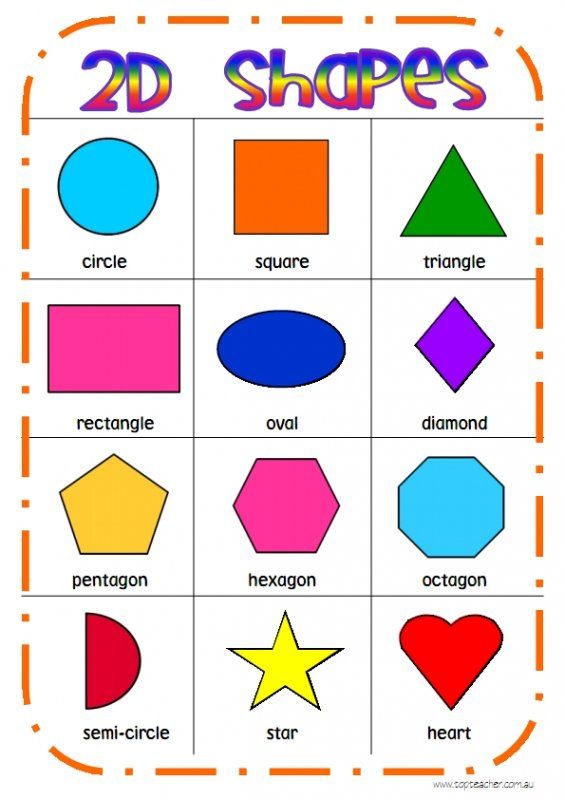 Not only are they fun for your kids to use, but they’re also great for developing those important fine motor skills.
Not only are they fun for your kids to use, but they’re also great for developing those important fine motor skills.
Craft Stick Shapes
Making shapes with craft sticks is a super fun and inexpensive way to learn shapes! Use these done-for-you craft stick shape cards to create a hands-on shape learning experience your kids will love!
Play Dough Shapes
Do your kids love playing with play dough? These play dough shape mats are a great way to introduce shapes to your little learners! They’ll love rolling “snakes” and making shapes on their mats. They’ll also be developing visual discrimination skills by searching for the picture that doesn’t belong and fine motor skills with tracing.
Teaching Shapes
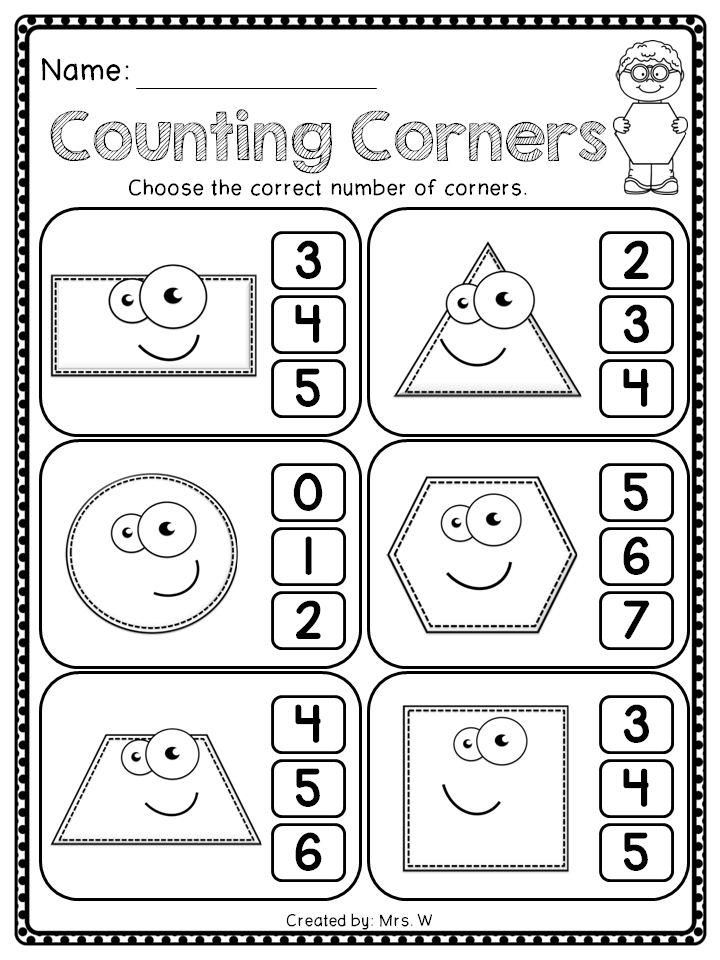
When teaching your little learners about shapes, remember to talk about how many sides each shape has. Don’t be afraid to use real math language, like sides and vertices. Using real math language will help your students develop important academic vocabulary.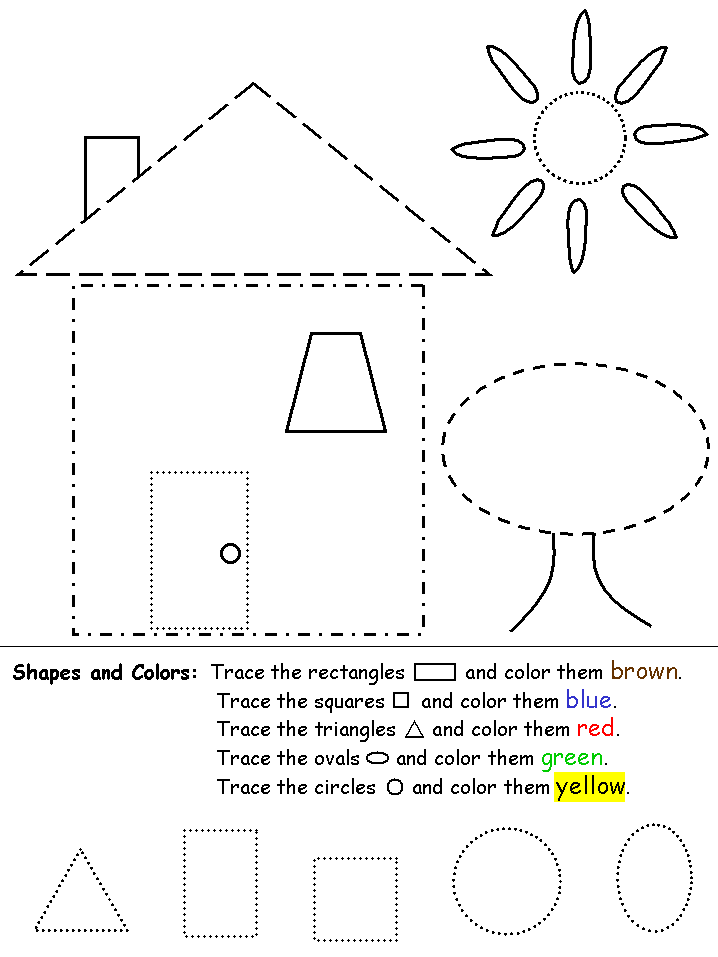
When you use shape manipulatives in your classroom, your little learners can feel, touch and count the number of sides and vertices each shape has. You can even talk about how a circle doesn’t have any sides or vertices!
Shapes in the Math Center
You can also incorporate shape activities into your math center throughout the year to reinforce shape recognition.
Shape Books
More Math Ideas from Pre-K Pages
Related Links
Prekinders
40 Easy And Fun Hands-On Shape Activities For Preschoolers
One of the first math concepts that preschoolers learn is identifying shapes. They begin to distinguish among the different shapes and categorize items according to shape. They learn the names of shapes and their characteristics. They find shapes in everyday items. This collection of shape activities for preschoolers can lead preschoolers to explore shapes in all kinds of ways.
Shapes Activities for Preschoolers
These activities will help your preschoolers learn their shapes. These shape activities for toddlers, will work in your preschool classroom and your kindergarten classroom.
These shape activities for toddlers, will work in your preschool classroom and your kindergarten classroom.
1. Road Shapes with Cars (Pre-K Pages) – 22 printable road shape mats to help your litte learners identify shapes.
2. Making Shapes with Play Dough (Pre-K Pages) – A fun, hands-on playful learning experience that uses play dough to teach shapes!
3. Pattern Block Shapes (Pre-K Pages) – Pattern blocks can actually help your little learners build a strong foundation for learning geometry later.
4. Making Shapes with Geoboards (Pre-K Pages) – If you haven’t tried geoboard activities in your classroom yet, your kids are going to love them!
5. Create a Shapes Photo Book (Pre-K Pages) – To introduce shape concepts to my son, I grabbed the book So Many Circles, So Many Squares from our library as the anchor to our learning ship. Using this book, we went on a shape scavenger hunt and made a fun shape keepsake.
6. Perfect Square Shapes Art (Pre-K Pages) – This Perfect Square art activity is so easy to set up and totally open-ended. It goes perfectly with the book and would be an excellent addition to a
shapes unit.
It goes perfectly with the book and would be an excellent addition to a
shapes unit.
7. Building Shapes with Craft Sticks (Pre-K Pages) – Pair this activity with the book Shapes, Shapes, Shapes by Tana Hoban and you’ve got the perfect low-prep shapes lesson!
8. Teaching 3D Shapes (Pre-K Pages) – Here are some of my favorite ideas for teaching 3D shapes to young children in pre-k or kindergarten. I also wrote some very simple 3D shape songs for you that incorporate hands on learning; keep reading to download the 3D shapes printable song charts.
9. Nature Shape Scavenger Hunt (Pre-K Pages) – A Star in My Orange is a great way to reinforce shape recognition with your preschoolers. They will also immediately want to run outside for their very own shapes scavenger hunt in nature!
10. The Shape of Things Chalk Drawings (Pre-K Pages) – Shapes are found, identified, and drawn in all preschool classrooms! Discovering just how often circles, squares, and triangles occur in our everyday life make them relevant to children.
11. Shape Wands (Pre-K Pages) – Make some shape wands and turn your home or classroom into the perfect place for kids to learn and identify shapes.
12. Shape Exploration (Pre-K Pages) – After reading the wonderful book Mouse Shapes by Ellen Walsh, I thought it would be fun to make a mouse that could be used in a shape game. The mice in the book explore shapes so, why shouldn’t we?
13. Make a Tortilla Shape Snack (Pre-K Pages) – We have the perfect recipe for exploring a math concept. Read aloud one great children’s book. Make a healthy and yummy treat. Combine the two together and you have a lesson on shapes.
14. Shapes Word Chart (Pre-K Pages) – This word chart focused on shapes but you can make a word chart for any topic.
15. “I Have Who Has” Shapes Game (Prekinders) – You may have seen the “I Have, Who Has” card games circulating the internet a lot lately, so this is a fun twist for Pre-K to teach shapes.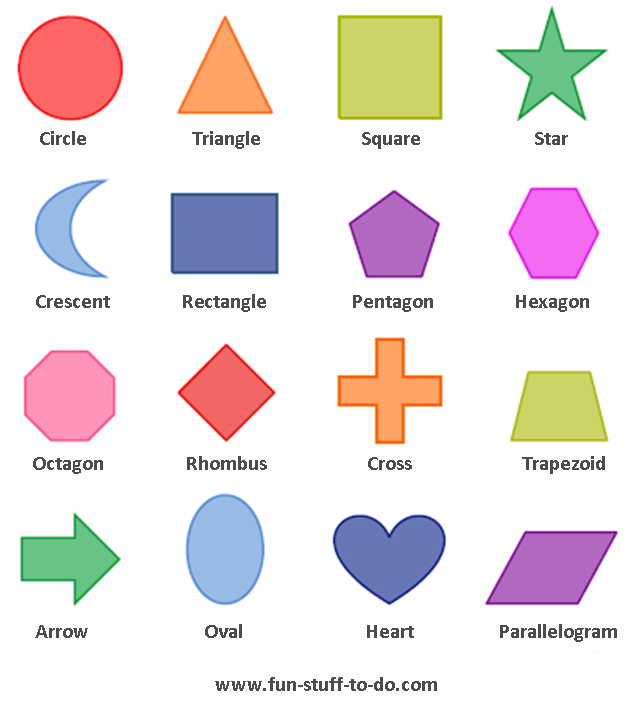
16. Games and Activities for Teaching Shapes (Prekinders) – Here are a fun few ways to teaching shapes, like shape bingo and a memory game.
17. Tracing Shapes on the Flannel Board (Teach Preschool) – A wonderful way to introduce letters and shapes while building pre-writing skills!
18. Hunting for Shapes (Teach Preschool) -Explore shapes with a fun and interactive game!
19. Exploring Shapes with Blocks on a Table Top (Teach Preschool) – A simple and engaging exploration of shapes and colors!
20. Learning Shapes by Rolling a Ball (Hands On As We Grow) – Try a fun hands on activity for toddlers for a creative twist to learn shapes!
21. Finding Shapes at the Playground (Buggy and Buddy)- Just print out the free shape hunt printable and go searching for shapes at the playground with this fun geometry activity for children!
22. Geometric Shapes Math Activity (Little Bins for Little Hands) – This simple geometric shapes activity for kids is easy to do at home or as a math center in school. It also makes a terrific STEAM project including a bit of art and design too.
It also makes a terrific STEAM project including a bit of art and design too.
23. Gruffalo Themed Shape Animals (Educators’ Spin on It) – Exploring shapes with young children can be such fun when you involve a few animal friends from The Gruffalo.
Shapes Activities for Preschoolers
24. Feed the Shape Monster Game (Imagination Tree) – Make a fun activity for preschoolers and school aged kids with this feed the hungry shape monsters sorting game!
25. Sticky Shape Bugs Activity (Mom Inspired Life) – This was a great way to develop fine motor skills and critical thinking skills while learning about shapes.
26. Learning Shapes with Spaghetti Noodles (Teaching Mama) – Looking for a fun way to teach shapes? Well here’s a very fun way using spaghetti noodles! This hands-on activity also is a great sensory activity.
27. Matching Shapes to Outlines (Busy Toddler) – Create this fun easy DIY shape mat to practice shapes with your preschoolers.
28. Chalk Shapes Jumping Game (Craftulate) – All you need for this shape activity is some sidewalk chalk!
Chalk Shapes Jumping Game (Craftulate) – All you need for this shape activity is some sidewalk chalk!
29. Open and Closed Polygons Game (JDaniel4’s Mom) Grab some LEGOs and have fun with these polygon games, like hockey!
30. Shape Sensory Squish Bag (Still Playing School) – Create this sensory squish bag with triangles, circles, and squares. It’s irresistible to touch and talk about in the window or on the table. It’s super easy to make, too!
31. DIY Shape Puzzles (Munchkins and Moms) – If you have some Jenga blocks and markers, then this easy DIY shape puzzle will be a fun engaging activity for your preschoolers.
32. Stamping Shapes in Kinetic Sand (Still Playing School) – Stamping shapes into kinetic sand is a great opportunity to work on shape identification, count the sides and corners, and compare and contrast the shapes.
33. Making Trucks from Shapes (Powerful Mothering) – Using your wooden blocks to draw and create trucks!
34. DIY Waldorf Square (Rhythms of Play) – An easy DIY toy for kids made with wooden blocks and liquid watercolor paints.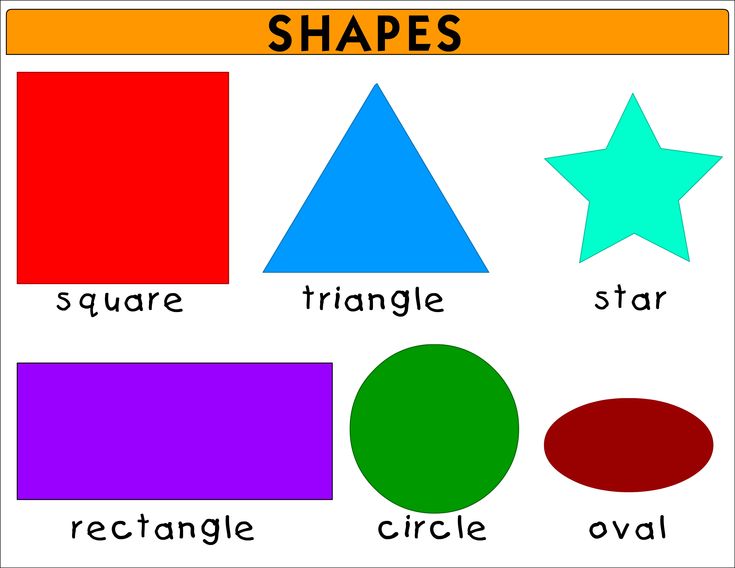
35. Magazine Shape Hunt and Sort (Mom Inspired Life) – This magazine shape hunt is jam-packed with learning! Kids will learn shapes while they practice cutting, gluing and sorting. It’s also an awesome way to work on critical thinking and observation skills.
36. Building Rockets with Shapes (Stir the Wonder) – Building rockets with shapes is a fun way to review shapes and colors with toddlers and preschoolers!
37. Build on Shape Outlines (Brick by Brick) – Use wooden blocks in a new fun way and work on shapes at the same time!
38. Shapes in Our Neighborhood Book (Munchkins and Moms) – Go for a walk and look for shapes in the neighborhood and then create a photo book after!
39. Sorting Shapes in the Sensory Bin (Learning 4 Kids) – Your preschoolers will practice their shapes and fine motor skills while having fun with this shape sensory bin.
40. I Spy Shape Hunt (Munchkins and Moms) – Create these fun easy spy glasses and go on a shape hunt!
Follow my Shapes Pinterest Board for more great ideas!
Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution Kindergarten No.
 16
16 Form of organization of education is a way of organizing education, which is carried out in a certain order and mode.
Forms differ:
- according to the number of participants;
- the nature of the interaction between them;
- ways of activity;
- venue.
Our kindergarten uses frontal, group, individual forms of organized education, development and training.
Individual form of organization of education allows individualization of education (content, methods, means), however, it requires a lot of nervous costs from the child; creates emotional discomfort; uneconomical training; limiting cooperation with other children.
Group form of organization of training (individual-collective). The group is divided into subgroups. The bases for a complete set: personal sympathy, common interests, but not on levels of development. At the same time, it is important for the teacher, first of all, to ensure the interaction of children in the process of development and learning.
Frontal form of organization of training . Work with the whole group, a clear schedule, a single content. At the same time, the content of training in frontal classes can be activities: both cognitive and speech in nature, and artistically productive. The advantages of this form of education are a clear organizational structure, simple management, the possibility of interaction between children, the cost-effectiveness of education; The disadvantage is the difficulty in individualizing learning.
The main form of organizing development and learning in our preschool educational institution is organized educational activities (OOE). Organized educational activities are organized and conducted by teachers in accordance with the main general educational program of the preschool educational institution and the recommendations of the Federal State Educational Standard. OOD are held with children of all age groups of the kindergarten. In the daily routine of each group, the time of the OOD is determined in accordance with the "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, content and organization of the working hours of preschool educational organizations".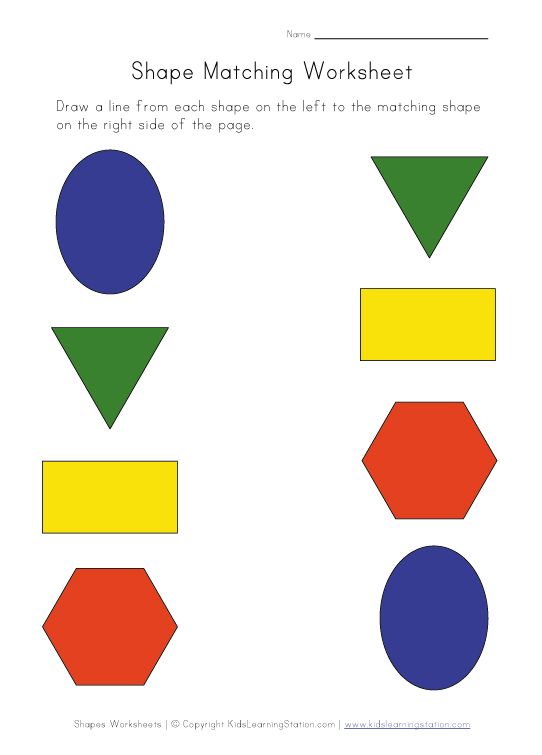
Organized educational activities are organized in all areas of educational work with children: familiarization with others, speech development, musical education, fine arts, design, the formation of elementary mathematical concepts, physical culture, etc.
educational activities stand out three main parts.
First part - introducing children to the topic of the lesson, setting goals, explaining what children should do.
The second part of is the independent activity of children to fulfill the task of the teacher or the plan of the child himself.
The third part of - analysis of the performance of the task and its evaluation.
Requirements for organizing organized educational activities
Hygiene requirements:
- directly educational activities are carried out in a clean, ventilated, well-lit room;
- educator, constantly monitors the correct posture of the child;
- does not allow overwork of children in the classroom;
- provides for the alternation of various types of children's activities not only in different classes, but also throughout one lesson.
Didactic requirements:
- precise definition of the educational tasks of GCD, its place in the general system of educational activities;
- creative use of all didactic principles in unity when conducting GCD;
- determine the optimal content of GCD in accordance with the program and the level of training of children;
- choose the most rational methods and techniques of teaching, depending on the didactic goal of GCD;
- ensure the cognitive activity of children and the developmental nature of GCD, rationally correlate verbal, visual and practical methods with the purpose of the lesson;
- use didactic games for the purpose of teaching (board-printed, games with objects, plot-didactic and dramatization games, verbal and game techniques, didactic material;
- systematically monitor the quality of children's assimilation of cognitive material (knowledge, skills and abilities).
Organizational requirements
- have a well-thought-out plan for conducting GCD;
- clearly define the purpose and didactic tasks of GCD;
- competently select and rationally use various teaching aids, including TCO, ICT;
- to maintain the necessary discipline and organization of children during the GCD.

- conduct GCD in a playful way, because in the game, the child to a greater extent masters the ways of communication, masters human relations.
- GCD in a preschool educational institution should not be carried out according to school technologies, but should be organized as a planned GCD in the morning and evening in a playful way, in regime moments, in the play and creative activities of children.
- GCD should be carried out in a certain system, connected with the daily life of children (knowledge gained in the classroom is used in free activities.).
- When organizing the learning process, the integration of content is useful, which allows you to make the learning process meaningful, interesting for children and contributes to the effectiveness of development. To this end, integrated and comprehensive classes are held.
Home
Methods, forms, means of educational activities
Model for describing forms, means,
File size: 377.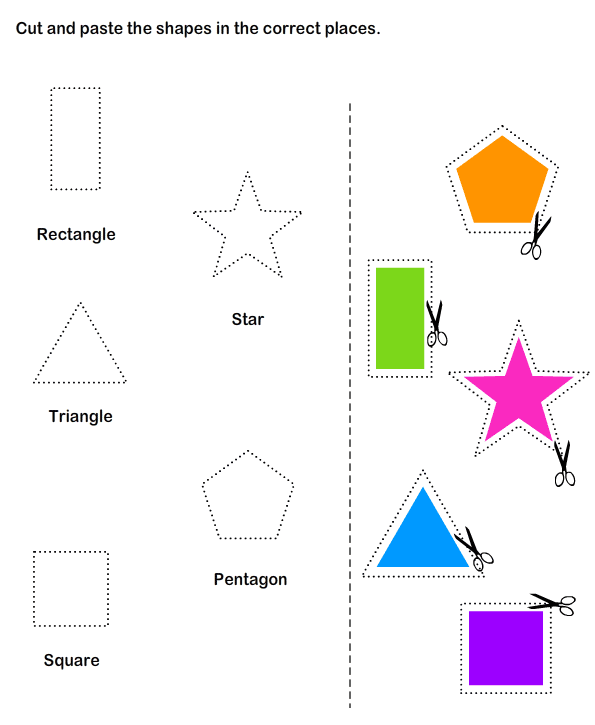 18 kb
18 kb
Download
Methods are cognizable. interest
File size: 209.87 kb
Methods and techniques for developing cognitive interests
Download
How is it expedient to describe the ways, methods, forms and means of implementing the program?
- In accordance with the objectives of the educational areas.
- In line with expected learning outcomes.
- Focused on the GEF targets.
Rules for describing the methods, methods, forms and means of program implementation:
1. In accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard DO:
- Implementation of the program in forms specific to children ..., primarily games, cognitive and research activities, creative activity.
- Age appropriateness.
- Combining education and upbringing into a single holistic educational process.
- Developing nature of education.
- Variation.
2. In accordance with the "Exemplary Basic Educational Program":
In accordance with the "Exemplary Basic Educational Program":
- All forms together and each separately can be implemented through a combination of organized by adults and independently initiated types of activities freely chosen by children.
- Must ensure the active participation of the child in the educational process in accordance with their abilities and interests, the personality-developing nature of interaction and communication, etc.
3. In accordance with the "Methodological recommendations for the use of POOP DL in the development of an educational program for DL in an educational organization."
- Versatility and variability.
- Usefulness of OOP for ECE: concreteness, orientation towards flexible planning of the educational process.
- Focus on the targets of the standard.
4. The rules established by the developers of the BEP, taking into account the author's comprehensive educational program "From Birth to School".
- Combination of principles of scientific validity and practical applicability.
- Compliance with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (solving the tasks set using a reasonable "minimum" content and methods).
DESIGN OF VARIATIVE FORMS, WAYS, METHODS AND MEANS OF IMPLEMENTING THE EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM OF PRESCHOOL EDUCATION
Koreneva-Leontieva L.V.
Kindergarten No. 25 of the Central District St. Petersburg
The task of designing an educational program for preschool education is relevant for all preschool educational organizations in the Russian Federation. At the same time, an unambiguous interpretation of the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education [1] to the content of the educational program of preschool education has not been developed to date. The question of determining the content and format of designing variable forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the educational program of preschool education remains significant. Participants in the process of designing educational programs of preschool education pose the following questions: education? What is the point of designing this part of the educational program? How specifically do you need to design ways, methods, means and forms of program implementation? Interpreting the conceptual series: forms, methods, methods, means, we came to the conclusion that the largest concept is the concept of "form". The concept of "form" can be considered as "organizational form of educational activity" [5]. With such a broad interpretation, the form can be defined as an external structure of the educational process, the nature of which is determined by a system of stable links between content, methods and means. The main forms of organizing educational activities in preschool education are: forms of independent activity of children, forms of joint activity of a teacher and children in regime moments, forms of joint activity of a teacher and children within the framework of continuous educational activities.
Participants in the process of designing educational programs of preschool education pose the following questions: education? What is the point of designing this part of the educational program? How specifically do you need to design ways, methods, means and forms of program implementation? Interpreting the conceptual series: forms, methods, methods, means, we came to the conclusion that the largest concept is the concept of "form". The concept of "form" can be considered as "organizational form of educational activity" [5]. With such a broad interpretation, the form can be defined as an external structure of the educational process, the nature of which is determined by a system of stable links between content, methods and means. The main forms of organizing educational activities in preschool education are: forms of independent activity of children, forms of joint activity of a teacher and children in regime moments, forms of joint activity of a teacher and children within the framework of continuous educational activities. Sometimes in pedagogical science the concepts of “form of education” and “form of organization of education” differ.
Sometimes in pedagogical science the concepts of “form of education” and “form of organization of education” differ.
For example, M.I. Makhmutov understands the form of education as the collective, frontal and individual work of students, and under the form of organization of education - a specific type of organization of this activity [2]. Thus, when describing the construction of time periods of the educational process, one can indicate the expected volume of “forms of education” characteristic of preschool education : collective, subgroup, frontal, network and individual work, build their hierarchy for the implementation of the educational program in each age group. But it is also possible to indicate specific forms of educational activity, for example, game situations, story-based didactic games, social and communicative trainings, communication situations, projects, TRIZ situations, etc. When describing specific forms of educational activities in order to increase the systemic nature of the description, program developers can build a description by educational areas, taking into account age groups, individual characteristics of the development of each children's team. All forms together and each separately can be implemented through a combination of organized by adults and independently initiated activities freely chosen by children. The method can be considered as a sequence of actions (work) aimed at obtaining a result.
All forms together and each separately can be implemented through a combination of organized by adults and independently initiated activities freely chosen by children. The method can be considered as a sequence of actions (work) aimed at obtaining a result.
Method (literally - the path of movement towards the goal) - a system of teacher actions aimed at organizing children's activities to solve an educational problem. The concepts of "method" and "method" can be combined into the following construction: method - the sequence of using methods. A tool is a material or ideal object that is used to achieve educational goals. Under the ideal object, it is customary to understand the established norms and rules of behavior and activities, communication, traditions of the organization. The means of implementing the educational program are materials of the subject-spatial developing educational environment that contribute to solving the problems of the educational program. Determining the relationship between forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the Program allows you to build ways to individualize the educational activities of children. Let's consider a possible scheme for linking these concepts. The forms of implementation of the Program include a set of forms with their tasks, methods are selected based on the tasks. The selection and hierarchy of methods in a specific form of implementation of the Program determines the way the Program is implemented. Based on the method of teaching, the subject-spatial developing educational environment changes. Suppose the following forms are used in the implementation of the Program: - forms of subgroup work; - forms of individual work; - forms of collective work; - forms of frontal work; - forms of network work. The form of network work is used to solve the following tasks: the development of the child's personal qualities, his oral communication competencies, the ability to adapt to a different educational environment, traditions and pedagogical approaches (socialization) [4].
Let's consider a possible scheme for linking these concepts. The forms of implementation of the Program include a set of forms with their tasks, methods are selected based on the tasks. The selection and hierarchy of methods in a specific form of implementation of the Program determines the way the Program is implemented. Based on the method of teaching, the subject-spatial developing educational environment changes. Suppose the following forms are used in the implementation of the Program: - forms of subgroup work; - forms of individual work; - forms of collective work; - forms of frontal work; - forms of network work. The form of network work is used to solve the following tasks: the development of the child's personal qualities, his oral communication competencies, the ability to adapt to a different educational environment, traditions and pedagogical approaches (socialization) [4].
Schools, museums, libraries, organizations of additional education are common network partners for preschool educational organizations. The most common form of networking is project activity. Depending on the choice of a network partner, elements due to network interaction will appear in the subject-spatial developing educational environment. For example, when interacting with a museum of fine arts, special attention is paid to the preparation of exhibitions, reproductions of familiar works of art appear, materials related to the life and work of the studied artists, the range of visual materials expands, thematic collections can appear, mini-museums are organized, etc.
The most common form of networking is project activity. Depending on the choice of a network partner, elements due to network interaction will appear in the subject-spatial developing educational environment. For example, when interacting with a museum of fine arts, special attention is paid to the preparation of exhibitions, reproductions of familiar works of art appear, materials related to the life and work of the studied artists, the range of visual materials expands, thematic collections can appear, mini-museums are organized, etc.
How is it expedient to describe the ways, methods, forms and means of implementing the program? Firstly, in accordance with the tasks of educational areas - this makes it possible to single out forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the educational program that are specific and universal for educational areas. Universal categories - will allow formulating trends towards the integration of educational areas, and unique categories - will show the individual nature of each area, most often unique categories - this is an indicator of the need to attract additional specialists or additional education of the teacher.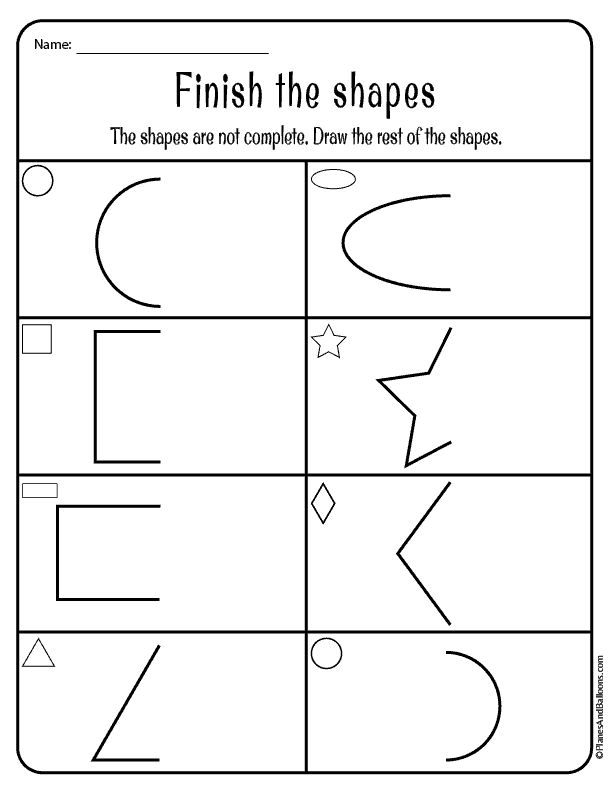 Secondly, in accordance with the expected educational results. This will allow you to adjust the content of the program depending on the level of development of children, their achievements. Thirdly, with a focus on the targets of GEF DO. The educational program should be focused on achieving targets, and when choosing one or another method, choosing the form of education, it is useful for the teacher to correlate his choice with the ultimate goal of educational activity [3]. Let's give an example of designing variable forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the educational field Social and communicative development” in the senior general developmental group. To do this, it is necessary to specify the objectives of educational activities. We will choose for designing the task: "Assimilation by the child of the norms and values accepted in society, including moral values." This task is focused on the following targets of the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education: “A child can follow social norms of behavior and rules in various activities, in relationships with adults and peers.
Secondly, in accordance with the expected educational results. This will allow you to adjust the content of the program depending on the level of development of children, their achievements. Thirdly, with a focus on the targets of GEF DO. The educational program should be focused on achieving targets, and when choosing one or another method, choosing the form of education, it is useful for the teacher to correlate his choice with the ultimate goal of educational activity [3]. Let's give an example of designing variable forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the educational field Social and communicative development” in the senior general developmental group. To do this, it is necessary to specify the objectives of educational activities. We will choose for designing the task: "Assimilation by the child of the norms and values accepted in society, including moral values." This task is focused on the following targets of the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education: “A child can follow social norms of behavior and rules in various activities, in relationships with adults and peers.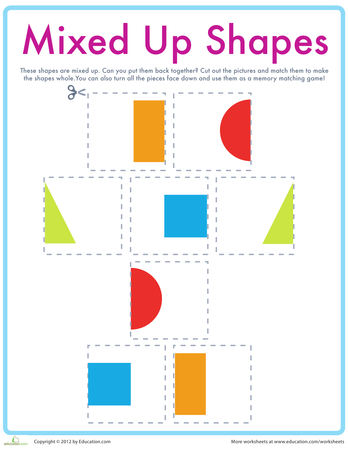 Adequately shows his feelings, tries to resolve conflicts. Designing methods for implementing the educational area is closely related to determining the results of solving the tasks (educational results). This is due to the focus of the methods on solving the problems of education or training, on achieving the expected result. Determining the result of solving a problem is connected with its translation into the language of the child's "action", his achievement, formulated diagnostically. This approach makes it possible to assess the degree of effectiveness of the application of the chosen methods and methods of organizing educational activities.
Adequately shows his feelings, tries to resolve conflicts. Designing methods for implementing the educational area is closely related to determining the results of solving the tasks (educational results). This is due to the focus of the methods on solving the problems of education or training, on achieving the expected result. Determining the result of solving a problem is connected with its translation into the language of the child's "action", his achievement, formulated diagnostically. This approach makes it possible to assess the degree of effectiveness of the application of the chosen methods and methods of organizing educational activities.
The task “Assimilation by a child of the norms and values accepted in society, including moral values” can be solved in the following way (using the following sequence of methods): 1. An example of an adult. 2. Presentation and explanation of new rules. 3. Accustoming to positive forms of behavior. 4. Game methods (game sketches, dramatization games, simulation games for reproducing behavioral options for children and adults, emotional states, plot-didactic games). 5. Method of free self-expression of thoughts, feelings, views. 6. The teacher's story, reading fiction. 7. Watching movies, cartoons. 8. Consideration of paintings and illustrations. 9.Ethical conversations. In other age groups, the sequence of using the methods will differ depending on the age characteristics of the children. In this case, the means of implementing the task will be used: - ideal: the rules of a culture of behavior; -material: card index of games, etudes, plot and didactic games; a selection of children's books, illustrations and cartoons. This will achieve the following educational result: it applies the rules of cultural behavior. Thus, a consistent description of the forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the PLO DL allows you to build an integral system of educational activities in the content section. Such a system enables teachers - users of the educational program of preschool education to consciously design work programs, keeping the relationship between the forms they choose, methods, methods and means of implementing the Program and the targets of the Federal State Educational Standard of preschool education, educational results
5. Method of free self-expression of thoughts, feelings, views. 6. The teacher's story, reading fiction. 7. Watching movies, cartoons. 8. Consideration of paintings and illustrations. 9.Ethical conversations. In other age groups, the sequence of using the methods will differ depending on the age characteristics of the children. In this case, the means of implementing the task will be used: - ideal: the rules of a culture of behavior; -material: card index of games, etudes, plot and didactic games; a selection of children's books, illustrations and cartoons. This will achieve the following educational result: it applies the rules of cultural behavior. Thus, a consistent description of the forms, methods, methods and means of implementing the PLO DL allows you to build an integral system of educational activities in the content section. Such a system enables teachers - users of the educational program of preschool education to consciously design work programs, keeping the relationship between the forms they choose, methods, methods and means of implementing the Program and the targets of the Federal State Educational Standard of preschool education, educational results
Literature:
1.