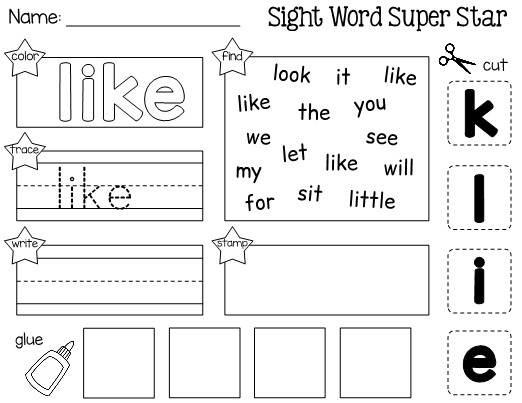
Sight word learning activities
48 Fun Sight Word Activities That Work
Teachers are always on the hunt for great sight word activities. Sight words are any words readers recognize automatically “by sight”—for fluent readers, that’s almost all words! High-frequency words, the most commonly occurring words in written English like those on the Dolch list, are often thought of as the most crucial sight words.
It’s a myth that blindly memorizing every letter in a sight word is the only way to learn it. The science of reading tells us that linking sounds and letters is the most effective way for kids’ brains to learn any word. Many common words are easy to tackle using beginning phonics skills (like “at,” “can,” “him,” etc.), so staying true to a strong phonics curriculum is one way to support kids’ sight word learning. Even irregularly spelled words have decodable parts, e.g., kids can use the sounds of “s” and “d” to help with “said,” even if the “ai” is unexpected. Experts often call these words “heart words” to call out for kids that they should learn the unexpected word parts “by heart.
” (If all this is unfamiliar to you, it can feel overwhelming, but you’ve got this! Check out teaching guru Jillian Starr’s explanation for more help.)
Check out these low-prep and engaging sight word activities for both teaching and practicing words.
1. Map it and drive it
This is a genius way to introduce words with appealing materials: Say the word, represent each sound with a LEGO brick, write letters for each sound, and “drive” to read it.
Source: @droppinknowledgewithheidi
2. Smush play dough for each sound
Set up a routine that works for any word. Play dough squishing for each sound is the ultimate multi-sensory component.
ADVERTISEMENT
Source: @playdough3plato
3. Map words with a magnet wand
It is so super-satisfying to drag those magnetic dots around! Watch the video below for lots of tips on introducing a word using this process.
Source: @warriorsforliteracy
4.
 Make a mini book
Make a mini book
Lots of handy info in one place for your little learners.
Source: @hughesheartforfirst
5. Tap it, pop it, learn it!
Hardwire those words in kids’ brains with this comprehensive word intro routine. (You had us with the pop its!)
Source: @hellojenjones
6. Find and swat words
An oldie but such a goodie. Find a word in an array and WHACK! Swat it with a fly swatter!
Source: @kids_play_learn_laugh
7. Flip word pancakes
Serve up sight word pancakes while practicing spelling them aloud.
Source: @bee_happy_teaching
8. Wear heart word bracelets
Make kids feel like sight word VIPs.
Source: @teachingmoore
9. Search for sight word balls
Write sight words on ball pit balls with a chalk marker or dry-erase marker. Kids can race around hunting for balls to read and toss in a basket, or hunt through a big tub of balls for a certain word.
Source: @preschoolforyou
10.
 Start a sight word band
Start a sight word bandLoud but oh-so-fun! Feel the rhythm while tapping and reading sight words stuck to homemade percussion instruments.
Source: @earlyyears_withmrsg
11. Drive on a sight word path
This is one of many fun ways to use magnetic tiles for learning! Kids love “knocking down” word tiles with a toy car as they read each one.
Source: @travisntyler
12. Use sticky notes to inspire sight word sentences
Have kids stick words on items that give them ideas for sentences. “My Mom said to wear a helmet!” = so good!
Source: @kinneypodlearning
13. Write words on a sensory bag
So easy: Fill a zip-top bag with a small amount of kid-safe paint, seal well, and have kids practice “writing” sight words with their finger or a cotton swab.
Source: @makeitmultisensory
14. Wear a sight word crown
Wear your word proudly and practice reading others’ words. Fun in person or virtually.
Source: @mrsjonescreationstation
15. Play a magnetic-tile board game
We love new ideas for ways to use magnetic tiles for sight word activities. Easy to set up and fun to play.
Source: @twotolove_bairantwins
16. Spell words to a familiar tune
Get sight words stuck in everyone’s head, in a good way. We’d add a line for chanting the sounds in the word!
Source: @saysbre
17. Feed a word monster
Nom, nom, nom.
Source: @ecplayandlearn
18. Search for the pom-pom under sight word cups
Read all the words as you try to find the cup that hides the prize.
Source: @la.la.learning
19. Play sight word KABOOM
This classroom classic is perfect for sight words. If you need a refresher on the rules, Jillian Starr covers them.
Source: @essentiallykinder
20. Roll and write words
Roll, write, repeat.
Source: @mylittlepandamonium
21. Write words with rainbow colors
Bonus points for aromatic markers.
Source: @mylittlepandamonium
22. Trace words with flashlights
Stock up on batteries because kids never get tired of this!
Source: @giggleswithgerg
23. Find words in plastic eggs
Give kids a checklist of words to find as they open each egg.
Source: @blooming_tots1
24. Spy words around the classroom
Just add a magnifying glass and clipboard to make kids feel like supersleuths!
Source: @readingcorneronline
25. Find words in the morning message
Don’t forget about old standbys! This is one of our favorite ways to get kids to recognize sight words in connected text.
Source: @tales_of_a_kinder_classroom
26. Build words with bricks
Such a great use of extra building bricks!
Source: @raysinkinder
27. Write words in sand
Easy-peasy to set up and keep neat if you use plastic pencil boxes.
Source: @teacherhacks
28. Spell words on a construction site
Bulldozing over each word to read it is the best part!
Source: @planningplaytime
29.
 Spell words with toy cars
Spell words with toy carsDrive on over!
Source: @lozlovesprep
30. Park in a sight word “parking lot”
This one is easy to modify based on whatever toys are available in the classroom or at home.
Source: @msbendersclassroom
31. “Plant” words in play dough
Watch those reading skills grow!
Source: @planningplaytime
32. Build words in a sensory tub
Because spelling is just more fun when your hands are covered in beans!
Source: @coffeeandspitup
33. Write words on a magnetic drawing board
That eraser track makes for a perfect word card holder!
Source: @moffattgirls
34. Or write words on the window!
Everyone wants a turn to write on the window!
Source: @kindergarten_matters
35. Shhh! Discover words written in invisible ink
Write words in white crayon and reveal them with watercolors on top!
Source: @teachstarter
36.
 Dot-paint words with a cotton swab
Dot-paint words with a cotton swabCalming and effective.
Source: @sightwordactivities
37. “Type” words on a keyboard
Busy day at the sight word office! Use a keyboard cover or any old keyboard.
Source: @lifebetweensummers
38. Read words before heading through the door
The line leader can double as the word pointer during transitions.
Source: @ms.rowekinder
39. Read the word the teacher’s wearing!
Wait, is there something on my shirt?
Source: @theprimarypartner
40. Take a sight word cakewalk
Choose a winning word when the music stops!
Source: @joyfulinkinder
41. Play sight word hopscotch
If you can’t get outdoors, tape on the floor works just as well.
Source: @wheretheliteracygrows
42. Play tic-tac-toe
I’ll be team “the.”
Source: @create_n_teach
43. Go sight word bowling
No bowling pins? Use half-filled plastic water bottles instead.
Source: @thecreativeteacher_
44. Ready, aim, read
Just throw a beanbag at a word target if foam darts are a no-go.
Source: @laurens_lil_learners
45. Play muffin tin ball toss
Toss and read. It’s easy to use colored muffin cups to prep different sets of words.
Source: @homeschooling_fun_with_lynda
46. DIY sentence flash cards
Authentic use of words in context for the win.
Source: @teachertipsandtales
47. Play sight word checkers
King me! If kids don’t have a partner available, they can “play” with a stuffed animal and get double practice.
Source: @sightwordactivities
48. Play sight word Guess Who?
Set up this game once and use it forever.
Source: @lessons_and_lattes
We’d love to hear—what are your favorite sight word activities? Share in the comments below.
Want more articles like this? Be sure to sign up for our newsletters.
Plus, what are sight words?
12 Hands on Sight Word Activities
You are here: Home / Activities / Learning / Literacy & ABCs / 12 Sight Word Activities with a Lot of Hands on Learning
19 Sep
Literacy & ABCsKindergartnersResources
Sight Words17 Comments
SHARE POST
Henry is a first grader this year and came home with a letter about their expectations for learning sight words.
Call me crazy, but I was so excited!
That means we get to do all these fun sight word activities to help him learn them!
Sight words are all about memorization and recognition. Not about the spelling or sounding them out.
Seeing the sight word and knowing what it is right off the bat. That’s the goal.
All throughout kindergarten we’ve been doing tons of sight word activities to practice, practice, practice. Henry loves it, so I just go with it!
These are twelve activities that we’ve done to learn sight words, with a few from around the web as well.
A wonderful bonus to any of these activities is that they can usually be adapted to letters. Check out the game on the stairs, or the magic paint.
So, if you have a preschooler that wants to play along, just switch out the sight words for letters of the alphabet.
I’ve done this so many times with Henry and George. Henry works on sight words and George works on letters. Its a wonderful combo for hands on learning.
Its a wonderful combo for hands on learning.
12 sight word activities using a lot of hands on learning:
- Make a sight word treasure hunt.
- Find matching pairs of sight words. Like the worksheets that you draw a line to the matching pair… but big.
- Jump and grab the sight words.
- Make an I spy sensory bag to spot the sight words.
- A spider web caught the sight words! Oh-no! Find the matching sight words on the web.
- Sight word practice, a game to get to the top of the stairs.
- Magic sight word learning. What sight word magically appears? Can you name it?
- Can you spot the sight word in the magazine? Circle it!
- Sight word cup crash from Coffee Cups and Crayons
- Sight word speed racer game from No Time for Flash Cards
- Sight word parking lot from Juggling with Kids
- Sight word scavenger hunt from No Time for Flashcards
Please share in the comments any of your favorite ways for your kids to learn sight words.
More homework? Check these out:
- 21 Crazy Fun Ways to Practice Spelling Words
- 24 Common Core Activities to Help Your Kindergartner Succeed
Products I recommend to practice sight words:
These product links are affiliate links to help provide you with easy ways to learn and practice sight words with your kids.
- BOB Books
- Melissa & Doug See & Spell
- Magnetic Sight Words
- 100 Super Sight Word Poems
SHARE POST
About Jamie Reimer
Jamie learned to be a hands on mom by creating activities, crafts and art projects for her three boys to do. Jamie needed the creative outlet that activities provided to get through the early years of parenting with a smile! Follow Jamie on Pinterest and Instagram!
Reader Interactions
| Navigation: home Random Page Feedback TOP Interesting to know Favorites Top: Dynamics and determinants of gas analysis indicators of young athletes in the recovery period after laboratory loads to failure . Characteristics of the ATP and the welding and tinsmith site: Transport is currently one of the most important sectors of the national economy ... nine0005 Medical and nursing team equipment. Interesting: Aura as an energy field: a multi-layered human aura can be imagined as... The impact of the business environment on the effective functioning of the enterprise: The business environment is a combination of external and internal factors that affect the functioning of the company... What to do with leukemia: sickness... Disciplines: Automation Anthropology Archeology Architecture Audit Biology Accounting Military science Genetics Geography Geology Demography Journalism Zoology Foreign languages Computer science Art History Cinematography Computerization Shipbuilding Culinary Culture Lexicology Linguistics Literature Logic Marketing Mathematics Mechanical Engineering Medicine Management Metallurgy Metrology Mechanics Musicology Engineering Law Entrepreneurship Education Industrial Security Programming Pedagogics Psychology Radio communication Religion Rhetoric Sociology Sport Standardization Statistics Building Theology Technology Trade Transport Pharmacology Physics Physiology Philosophy Finance Chemistry Economy Drafting Ecology Economics Electronics Energy Jurisprudence nine0005 | ⇐ PreviousPage 5 of 8Next ⇒
The content of the educational material is acquired by students in the process of learning activities. Study of psychological studies of educational activity, in particular E.I. Savanko, showed that in order for students to develop the right attitude towards it, it is necessary to build educational activities in a special way. It turned out that the study of each independent section or topic of the curriculum should consist of three main stages: motivational, operational-cognitive and reflective-evaluative. After analyzing the data of E.I. Savanko, we did not fully agree with her position, since the description of the stages often contains the wording: "... the teacher tells, the teacher clarifies, the teacher makes a conclusion . In order for the motivational side of learning to be in the teacher's field of vision, it is necessary that he single out three main stages in the learning activity of students in the school learning process, the description of which is given below.
At this stage, students should understand why and why they need to study this section of the program, what exactly they must do in order to successfully complete the main educational task. The motivational stage usually consists of the following learning activities:
a) setting a task for the student, the solution of which is possible only on the basis of studying this topic; b) a conversation about the theoretical and practical significance of the upcoming topic (section) of the program. c) discussion of children's versions and opinions about how the problem was solved in the history of science.
The learning task shows the students the benchmark on which they should direct their activities in the process of studying the topic. “No activity can arise without the presence of a goal and a task that sets this process in motion, giving it a direction,” wrote L.S. Vygodsky. An important condition for the organization of educational activities is to lead students to independently set and accept educational tasks.
After the main learning task is accepted by the students, they plan and discuss the plan for the upcoming work. The teacher reports the time allotted for the study of the topic, the approximate timing of its completion. This gives students a clear perspective of work. Then there is a discussion of what you need to know and be able to study the topic. Thus, students create an attitude to the need to prepare for the study of the material. The judgment ends with individual students giving a self-assessment of their ability to study the topic, indicating what material they are repeating, and what else they will do to prepare for the upcoming lessons. nine0005 This whole stage of studying the topic is very important for the development of students' motivation for learning activities. It is unlikely that those teachers who omit it completely or confine themselves to one phrase: “Today we are starting to study the topic . 2. Operational-cognitive stage. At this stage, students learn the content of the topic of the program and master the learning activities and operations included in this content. The role of this stage in the formation of the motivation of educational activity depends on whether the students will be clear about the need for the entire content and its individual parts, all educational actions and operations to solve the scientific main task set at the motivational stage. Do they realize the natural connection between all parts of the educational tasks and the basis, do all these tasks act for the student as a clearly visible system, a hierarchy of educational tasks. nine0005 With such a structure of the students' scientific activity, when the main content of the operational-cognitive stage becomes the modeling of objects and phenomena, the study of the constructed models, the students' activity acquires a theoretical character. . Reflective-evaluative stage. This stage is final in the process of studying the topic, when students learn to reflect (analyze) their own learning activities, evaluate it, comparing the results with the tasks set. The qualitative implementation of this stage is of great importance in the development of motivation for learning activities. The work on summarizing the study of the completed section must be organized so that students can experience a sense of emotional satisfaction from what they have done, the joy of victory over overcome difficulties, the happiness of learning new and interesting things. Thus, an orientation toward experiencing such feelings in the future will develop, which will lead to the emergence of needs for creativity, persistent independent study, that is, the development of a positive sustainable motivation for learning activities. In order to develop the ability of schoolchildren to evaluate their work, it is appropriate to give them the following homework: “Write a list of the main questions we covered in this topic, and mark next to how you learned this question: well or not very well, or didn't get it at all. On another piece of paper, list the skills that you planned to acquire while studying the topic, and indicate how you learned these skills: well, poorly, or not learned at all. This is useful for developing an adequate self-assessment of educational activities, for finding out the reasons for existing gaps and for encouraging students to close these gaps. nine0005 It is important that monitoring and evaluation not only establish the actual state of knowledge and skills of each student, but also be used to encourage him to further work, to create further prospects for this work. Particular emphasis should be placed on the role of problem-developing teaching methods in the development of learning motives. The fact is that the development of the needs and motives of activity occurs in the process of carrying out the activity itself. No matter how much the student hears about the need to study, about his duty and obligations, about the importance of learning activities for himself and his future life, and no matter how well he realizes the validity of these words, but if he does not get involved in this activity, then he has the appropriate motives. will not develop. In order for motives to be strengthened and developed, the student must begin to act. If the activity itself arouses interest in him, if in the process of its implementation he experiences bright positive emotions of satisfaction, then we can expect that he will gradually develop needs for this activity. nine0005 At the lesson, the teacher tells, shows to the students, but all this information is insignificant for some children: they listen and do not hear, look and do not see, they are engaged in completely different activities: they dream, think about their own. It is very effective, especially in the lower grades, to start creating educational problem situations not with a question, task or story, but with some kind of practical work. And if immediately after this a problematic question is posed, then such a problematic situation will undoubtedly be a powerful impetus to the beginning of intensive thinking. nine0005 Problem-based learning helps maintain a deep interest in the very content of the educational material, in general methods of cognitive actions, thereby forming positive motivation in children. psychological motivation student mathematics ⇐ Previous12345678Next ⇒ Individual and group drinkers: for animals. Schemes and designs ... Mechanical retention of earth masses: Mechanical retention of earth masses on a slope is provided by buttress structures of various designs . Mobile electrified feeder: scheme and operation of the device... Organization of surface water runoff: The largest amount of moisture on the globe evaporates from the surface of seas and oceans (88‰)... |
34_Bredikhina_Teaching Methods.cdr
%PDF-1.3 % 453 0 obj > endobj 452 0 obj >stream application/pdf

 ..
..  From what this activity is, what educational actions it consists of, how these parts relate to each other, what is the structure of educational activity - the result of training largely depends on all this. The attitude of children to their own activities is determined largely by how the teacher organizes learning activities, what is its structure and nature. nine0005
From what this activity is, what educational actions it consists of, how these parts relate to each other, what is the structure of educational activity - the result of training largely depends on all this. The attitude of children to their own activities is determined largely by how the teacher organizes learning activities, what is its structure and nature. nine0005  ..", and the opinion of the children, their experience is not taken into account, which, in our opinion, does not contribute to a productive learning and development of positive learning motivation. nine0005
..", and the opinion of the children, their experience is not taken into account, which, in our opinion, does not contribute to a productive learning and development of positive learning motivation. nine0005 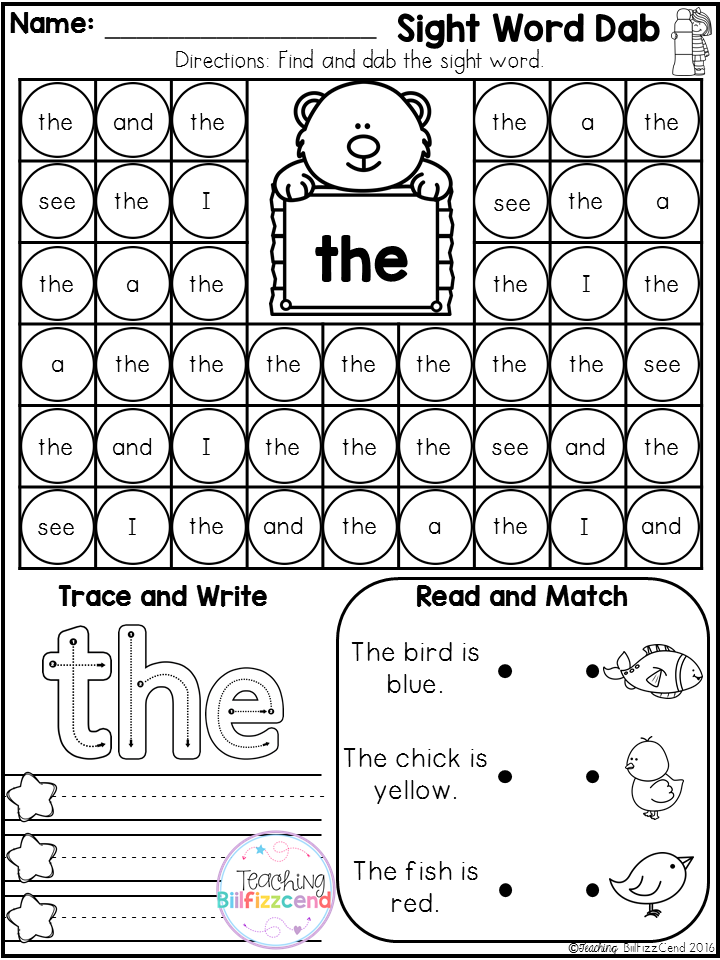 For example, before studying the topic “Suggestion”, the teacher says: “Imagine that you need to tell your comrades about an important matter so that everyone understands and starts acting on the basis of your story”; nine0005
For example, before studying the topic “Suggestion”, the teacher says: “Imagine that you need to tell your comrades about an important matter so that everyone understands and starts acting on the basis of your story”; nine0005  nine0005
nine0005  ..”, proceeding immediately to the presentation of new material, are hardly doing the right thing. This "saving of time" will have a painful effect on the entire nature of the students' learning activities.
..”, proceeding immediately to the presentation of new material, are hardly doing the right thing. This "saving of time" will have a painful effect on the entire nature of the students' learning activities. 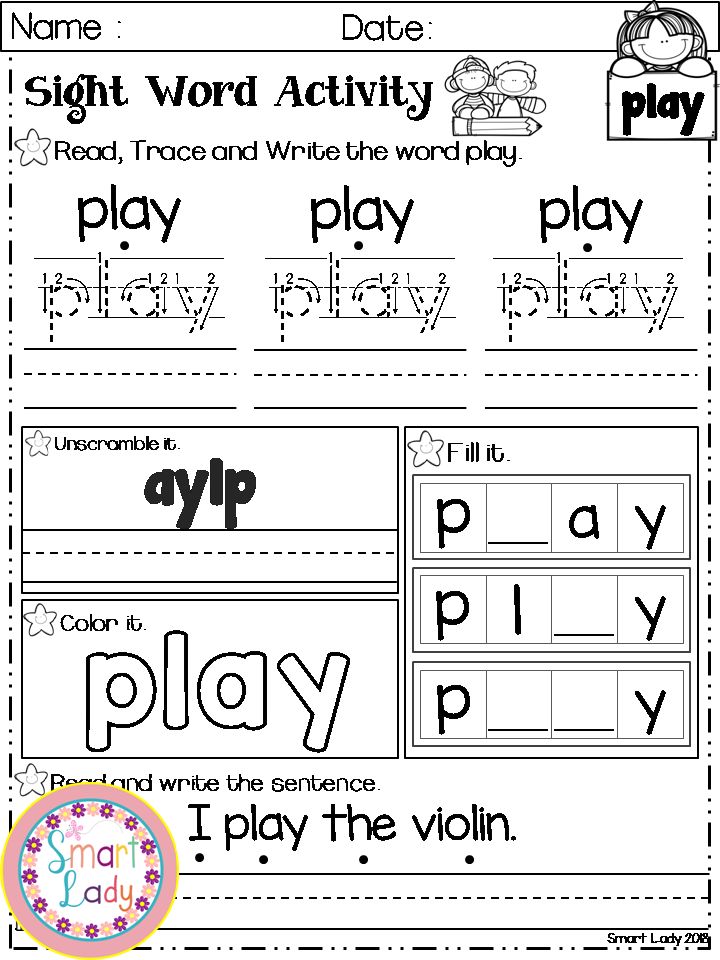 In this way, students are, as it were, introduced into the laboratory of thought of the relevant sciences, gaining experience in truly creative activity, creative thinking. All this is an extremely powerful tool that contributes to the development of the necessary motivation for the educational activity of students. nine0005
In this way, students are, as it were, introduced into the laboratory of thought of the relevant sciences, gaining experience in truly creative activity, creative thinking. All this is an extremely powerful tool that contributes to the development of the necessary motivation for the educational activity of students. nine0005  nine0005
nine0005  Let's consider some psychological aspects of knowledge and the role of problem-based learning for the formation and development of motivation.
Let's consider some psychological aspects of knowledge and the role of problem-based learning for the formation and development of motivation.  In order for these children to be involved in educational work, it is necessary to create an incentive for an enhanced thinking process. Such an example that stimulates thinking is the creation of educational problem situations.
In order for these children to be involved in educational work, it is necessary to create an incentive for an enhanced thinking process. Such an example that stimulates thinking is the creation of educational problem situations.  ..
..