Sounds of alphabets in english
Learn Pronunciation with Speak Method
The Sounds of the Alphabet: Learn Pronunciation with Speak Method| English Online with Speak Method |
|
| Online Classes | Pronunciation Facts | R, Th, T and other sounds | 500 Words Practice |
| Local Classes | Business Communication | TOEFL Prep | ESL Stories |
| Contact us | Vowel
Sounds |
Grammar and Idioms | For Young People |
With
this alphabet chart, understand how to say
the names of the letters and read about all the sounds of each letter
from the alphabet. These are the basic phonetic sounds for American English. To learn important sounds using free videos
online, go to Pronunciation in
English: 500 Words.
|
Letter |
Sound of Letter Name |
All sounds of letter |
Examples |
|
A, a |
ā-ee (long a to long e, also spell "ay") |
, ā, ah, ā-uh, uh |
cat, late, all, and, around |
|
B, b |
Bee |
buh |
bike |
|
C, c |
See |
kuh, suh |
cake, city |
|
D, d |
Dee |
duh |
did |
|
E, e |
Ee |
eh, ee, silent |
bed, free, late |
|
F, f |
Ef |
fuh |
fed |
|
G, g |
Jee |
guh, juh |
glad, large |
|
H, h |
ā-ch |
huh, silent |
hotel, what |
|
I, i |
ah-ee |
ah-ee, ĭ |
light, sit |
|
J, j |
Jay |
juh |
jump |
|
K, k |
Kay |
kuh |
kite |
|
L, l |
El |
luh, ul |
lot, full |
|
M, m |
Em |
muh |
mother |
|
N, n |
En |
nuh |
nest |
|
O, o |
ō (oh) |
ah, ō, uh, oo, ů |
hot, slow, computer, fool, good |
|
P, p |
Pee |
puh |
put |
|
Q, q |
Kyoo (kyū) |
kwuh |
quick |
|
R, r |
Ah-r |
ruh, ur |
race, stir |
|
S, s |
Es |
suh, zuh |
stick, is |
|
T, t |
Tee |
tuh, duh, N, silent, stopped tuh |
table, better, mountain, interview, hot |
|
U, u |
Yoo (yū) |
uh, yoo, oo, ů |
up, use, flute, full |
|
V, v |
Vee |
vuh |
very |
|
W, w |
Dubōyoo |
wuh, silent |
well, slow |
|
X, x |
Eks |
ks, zuh |
box, xylophone |
|
Y, y |
Wah-ee |
yuh, ee, ah-ee (i), ĭ |
yes, happy, try, cylinder |
|
Z, z |
Zee |
zuh |
zebra |
|
|
|
|
|
pronunciation English
pronunciation Learn More Sound American: Change Your Speech The 500 Common English Words What is a Vowel? English Free Online |
Speakmethod. com: English
Pronunciation, Seattle, WA
com: English
Pronunciation, Seattle, WA
English online with Speak Method
Best Tips to Help You Learn Easily
Are you beginning your journey into learning English? It’s always best to start from the beginning. And what better starting foundation is there than learning the English alphabet?Alphabets are everywhere. These sequential sets of symbols and letters represent the phonetics of any given language and form the foundation of many languages in the world.
In this article, you’ll learn about the importance of the alphabet, the pronunciation of English alphabet letters, and the English phonetic alphabet. We also cover a few fun (and useful!) songs and tips to help you master the alphabet.
Keep reading to gain some specific knowledge of the English alphabet, practical tips on how to learn the English alphabet and get the confidence to read, pronounce and write English letters. Let’s get started.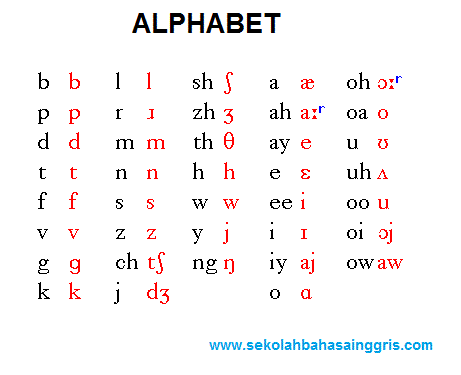
Why learn the English alphabet?
The English alphabet is the foundation of the spoken English language, giving learners the benefit of understanding how to pronounce words and letters, think, and spell in the language.
Three of the biggest reasons to learn the English alphabet include:
1. To learn how to pronounce words
Learning and mastering the alphabet will help you to speak like a fluent English speaker. This will be helpful to you or other learners in being able to pronounce complete words. It’s a great way to learn letter sounds and master them properly.
2. To think in the English language
When you think in the English language, you eliminate the need for translations from your first language. This will make it easy to communicate faster and speak more like a fluent English speaker.
Knowing the English alphabet and learning the sounds of each letter can help you read words as they’re spoken.
3. To learn how to spell
Learning the alphabet letters can help you master how to spell words in the English language and even form grammatically-correct sentences.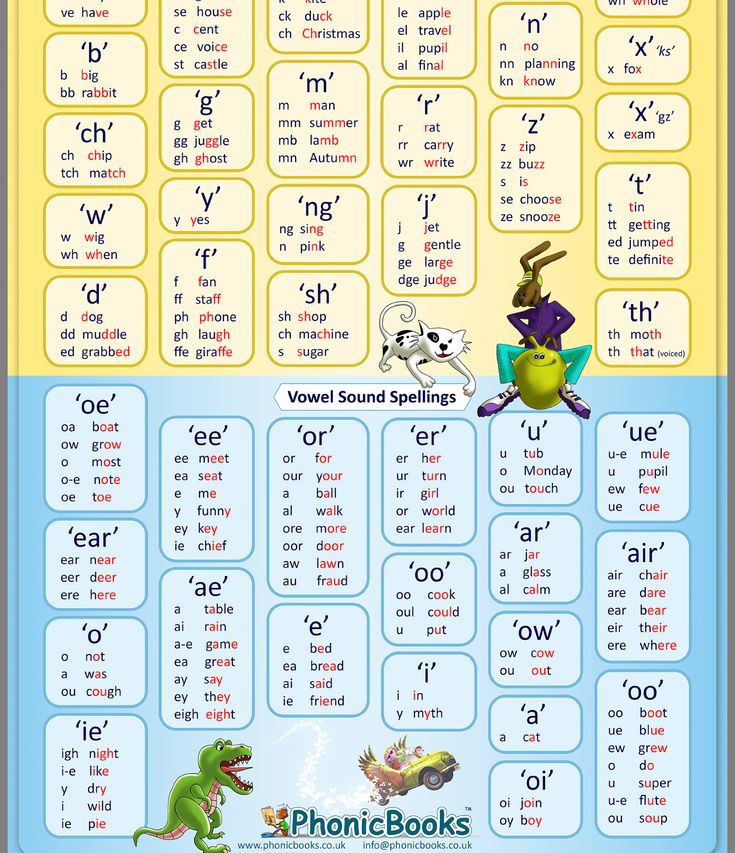
With knowledge of how to spell words in the English language, you can more easily communicate in it. You can also learn how to spell out useful words, like your name and address.
English alphabet pronunciation
Just as you learn to spell out words in English, you’ll also learn the pronunciation of each alphabet letter in the language. When letters are pronounced as part of a word, their pronunciation changes.
For example, the letter “y” is pronounced as /waɪ/. However, it’s pronounced as /i: / when part of a word, such as “family.”
The English phonetic spelling helps students learn to understand how to pronounce letters and words. It will help you learn how to pronounce letters of the alphabet faster and remember them easily. For example, /waɪ/ is the phonetic spelling for pronouncing the letter “y.”
English Phonetic Spelling for Each Alphabet Letter and Relevant Pronunciation
| Upper case letter | Lower case letter | English alphabet pronunciation |
| A | a | [eɪ] |
| B | b | [biː] |
| C | c | [siː] |
| D | d | [diː] |
| E | e | [iː] |
| F | f | [ɛf] |
| G | g | [dʒiː] |
| H | h | [eɪtʃ] |
| I | i | [aɪ] |
| J | j | [dʒeɪ] |
| K | k | [keɪ] |
| L | l | [ɛl] |
| M | m | [ɛm] |
| N | n | [ɛn] |
| O | o | [oʊ] |
| P | p | [piː] |
| Q | q | [kjuː] |
| R | r | [ɑr] |
| S | s | [ɛs] |
| T | t | [tiː] |
| U | u | [juː] |
| V | v | [viː] |
| W | w | [ˈdʌbəl juː] |
| X | x | [ɛks] |
| Y | y | [waɪ] |
| Z | z | [ziː] |
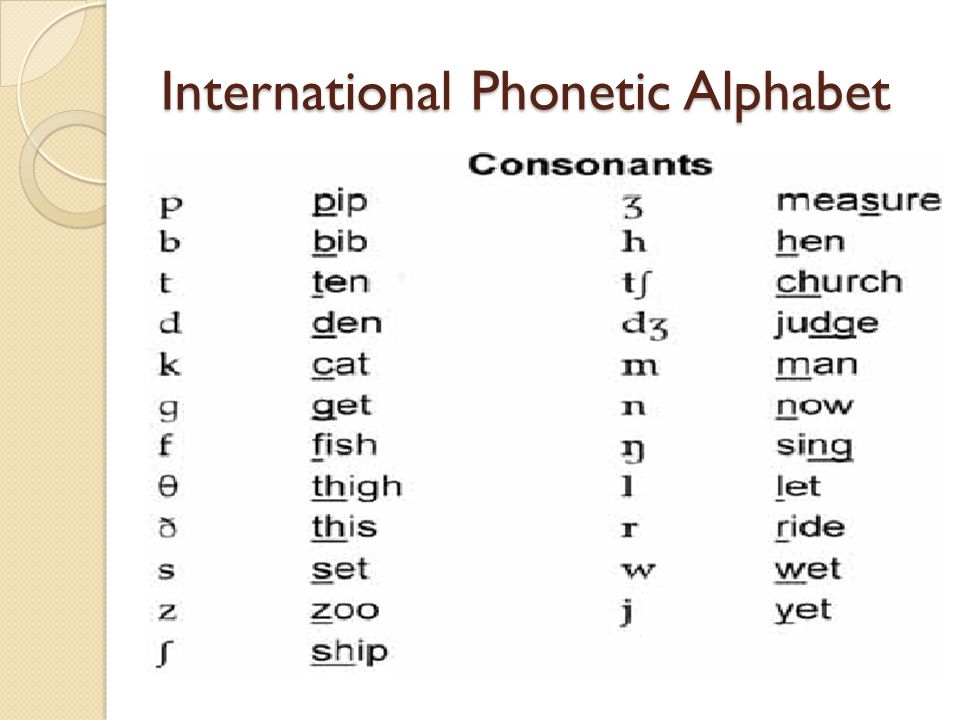
The phonetic alphabet
What is the phonetic alphabet?
The phonetic alphabet uses the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to give individual spelling of letters.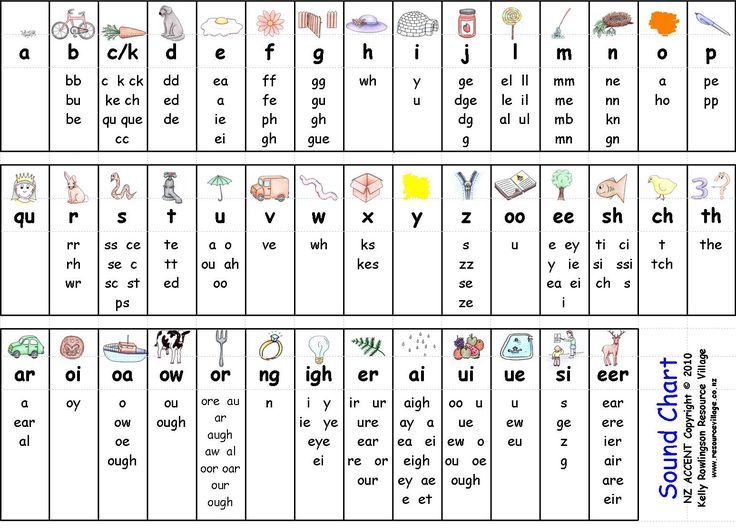 It enables learners to accurately represent the sounds of a language in written symbols and characters.
It enables learners to accurately represent the sounds of a language in written symbols and characters.
The spelling alphabet uses the NATO phonetic alphabet for communication. The set of words for oral communication utilizes a code word representing the initial alphabetic symbol or letter. The phonetic alphabet has 26 codewords assigned to the English alphabet from the first to the last letter.
| Symbol or letter | Codeword | Phonic pronunciation |
| A | Alfa/Alpha | Al Fah |
| B | Bravo | Brah Voh |
| C | Charlie | Char Lee |
| D | Delta | Dell Tah |
| E | Echo | Eck Oh |
| F | Foxtrot | Foks Trot |
| G | Golf | Golf |
| H | Hotel | Hoh Tell |
| I | India | In Dee Ah |
| J | Juliett | Jew Lee Ett |
| K | Kilo | Key Loh |
| L | Lima | Lee Mah |
| M | Mike | MIke |
| N | November | No Vember |
| O | Oscar | Oss Cah |
| P | Papa | Pah Pah |
| Q | Quebec | Keh Beck |
| R | Romeo | Row Me Oh |
| S | Sierra | See Airrah |
| T | Tango | Tang Oh |
| U | Uniform | You Nee Form |
| V | Victor | Vik Tah |
| W | Whiskey | Wiss Key |
| X | X-Ray | Ecks Ray |
| Y | Yankee | Yang Key |
| Z | Zulu | Zoo Loo |
English alphabet songs
Science suggests that music and language learning go hand in hand! With that in mind, English alphabet songs could be a practical way to get the English alphabetic letters cemented in your memory when learning the English alphabet.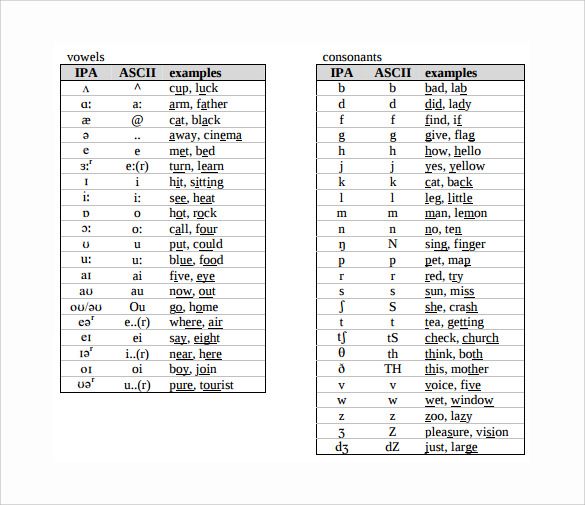
Some popular English alphabet songs include:
See It, Say It, Sign it by Jack Hartmann – Children’s Music
This English alphabet song teaches the sign language (the American Sign Language) of each letter of the English alphabet, including corresponding letter sounds.
The ABC Song – A Pop Music for Kids
This song helps kids to learn the English Alphabet with their corresponding phonics.
The ABC Song for Adult ESL Learners
With this English alphabet song, adult learners can master letters of the alphabet, such as ABC in English, including their sounds and phonics.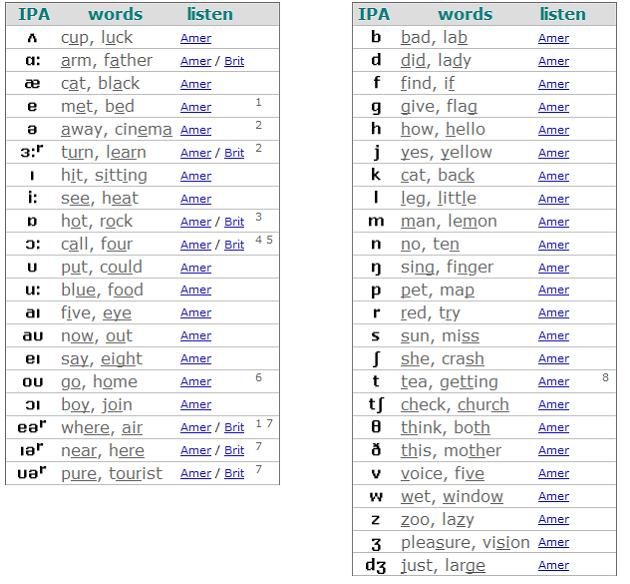
FAQs for the English alphabet
What are some English alphabet exercises I can do to help me learn?Some English alphabet exercises to help you learn include:
- vowels: listen and math;
- the alphabet: listen and write, listen: place the letters in order; and
- write the missing letters, among others.
Semitic-speaking people in the Middle East developed the alphabet at about 1700 B.C. before being spread by the Phoenicians about 700 years later. It was from this alphabet that the modern alphabet was developed.
How many letters are in the English alphabet?The English alphabet has 26 letters, including 21 consonants and 5 vowels.
How to learn the English alphabet: Tips and tricks
English is used widely across the world, and the pronunciation of letters and words can help you correct a heavy accent.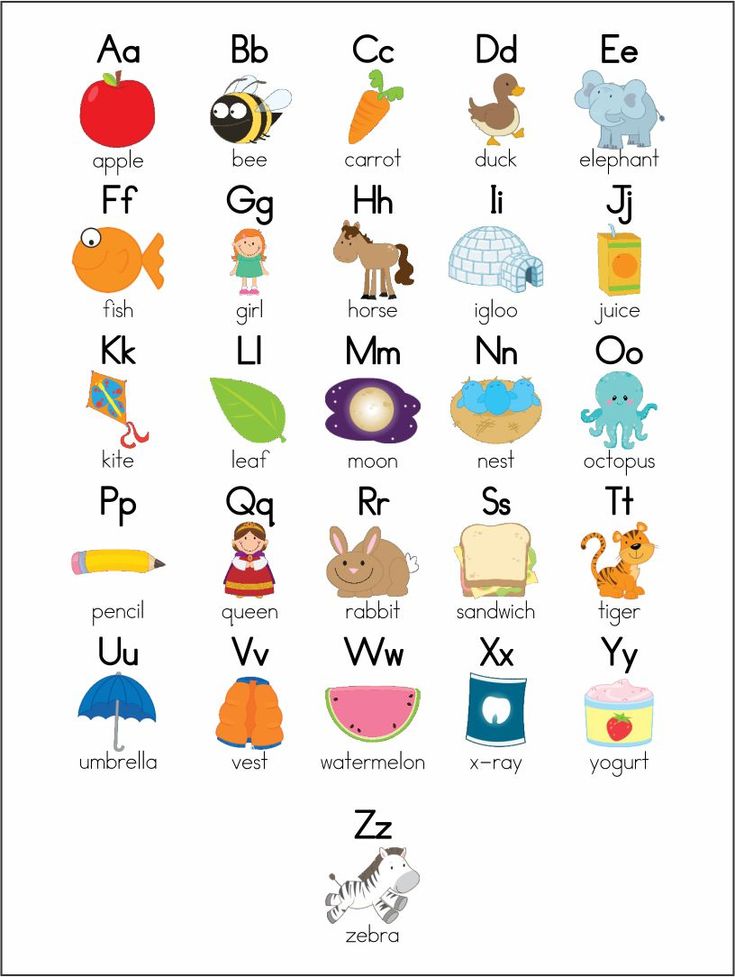
Also known as the modern Latin alphabet, the English alphabet provides a solid foundation for learning English as a first or second language.
Whether you want to learn English as a second language or you’re keen to become a polyglot with a different language alphabet, the following tips can help you master the basics of the English alphabet:
1. Gamify your alphabet learningFirstly, learn how to spell out your own name correctly - this is one of the most common words you will need to repeat and often.
Associate objects to the sounds of the first letter of words you already know in English to help you master the alphabet letters. For example, “c” for ‘car’ or “d” for ‘dog’.
Learn words and spelling in batches of 4 or 5 letters to prevent information overload.
Alphabet games can help you to learn the alphabet letters in fun ways, eliminating boredom and enhancing your morale for learning. Some fun games for memorable and enjoyable learning include:
- Alphabet puzzles
- Treasure hunts
- Object Match – uses random objects or pictures to help you learn the sound of the first letters in words or names.
 The game allows for competitive fun among learners.
The game allows for competitive fun among learners.
Visuals can help you memorize how letters are formed and written correctly, while audio helps you learn the sounds of each alphabet letter.
Although you can recite individual alphabet letters and memorize them, video technology has made the learning process easier. YouTube and other free online platforms are useful sources of videos for learning the English alphabet.
3. Spelling or reciting lettersSpell out words loudly and recite their letters to master the English language alphabet. You can also learn from the mistakes of other students when they recite letters and spellings of words.
As a result, you’ll master the letters of words you already know and even learn new ones. Use vocabulary and grammar at your learning level to master words easily.
4. Learn simple words firstThe English alphabet pronunciation, spelling, grammar, and vocabulary are the pillars of learning the English language.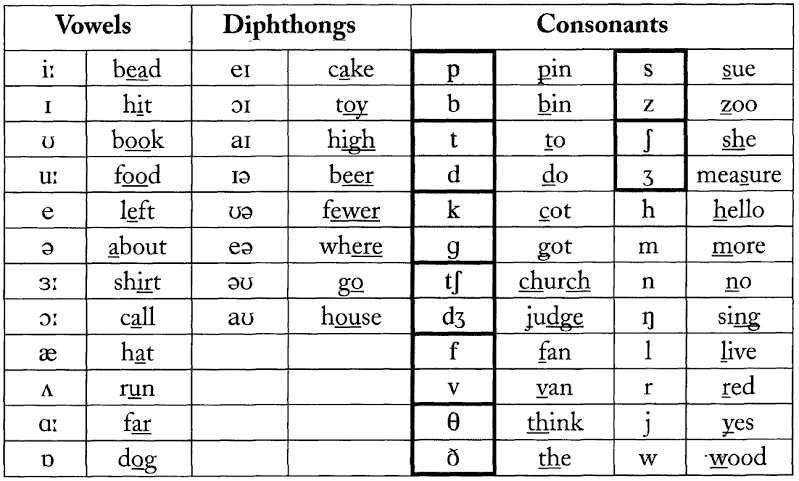 You can learn basic vocabulary, such as days of the week, as you master the alphabet to progress faster in your learning endeavor.
You can learn basic vocabulary, such as days of the week, as you master the alphabet to progress faster in your learning endeavor.
After mastering symbols and words, you can proceed to learn more advanced grammar. After learning how to spell out your name, focus on words that use common English alphabet letters A, B, D, N, and E.
You can use the letters to form various words, such as:
- Bad
- Den
- Bed
- Dan
- Ben, etc.
At this point, you can also learn how to produce sounds using consonants and vowels.
Learning the English alphabet is an excellent foundation
The English alphabet is the basis of learning the language as an ESL learner. Knowing these 26 letters will assist you in learning English online, including how to pronounce each letter and use them to create words.
So whether you’re looking to begin your own journey, are looking for some tips to help someone you know begin theirs, remember - practice makes perfect. Soon, you’ll be able to sing the ABCs better than the Jackson 5 and then progress to more advanced English topics - all the while having fun!
Soon, you’ll be able to sing the ABCs better than the Jackson 5 and then progress to more advanced English topics - all the while having fun!
English alphabet with pronunciation, transcription and translation (letters and sounds)
How many letters are in the English alphabet
The modern English alphabet contains 26 letters. English sounds were first recorded in the Anglo-Saxon runic alphabet as early as the 5th century. Christian missionaries brought to the island not only their religion, but also the Latin alphabet, which began to replace the runic alphabet around the 7th century. For a long time, these two alphabets existed in parallel.
The modern English alphabet (The English alphabet [ˈalfəbɛt]) is based on the Latin alphabet or "Latin". So what is the number in the English alphabet? Unlike the Russian language, which has 33 letters, the English alphabet consists of 26 letters:
- 6 letters can represent vowel sounds: "A", "E", "I", "O", "U", "Y";
- 21 letters can represent consonants: "B", "C", "D", "F", "G", "H", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N" ”, “P”, “Q”, “R”, “S”, “T”, “V”, “W”, “X”, “Y”, “Z”.
Below we have added a table where you can see the entire English alphabet with the numbering of letters in order.
| | ||
|---|---|---|
| Direct number | Letter | Reverse number |
| 1 | a | 26 |
| 2 | B b | 25 |
| 3 | C c | 24 |
| 4 | D | 23 |
| 5 | e | 22 |
| 6 | F f | 21 |
| 7 | G g | 20 |
| 8 | H h | 19 |
| 9 | I i | 18 |
| 9 | I i | 18 |
| 10 | J | 17 |
| 11 | K k | 16 |
| 12 | L l | 15 |
| 13 | M m | 14 |
| 14 | N n | 13 |
| 15 | O o | 12 |
| 16 | P | 11 |
| 17 | Q q | 10 |
| 18 | r | 9 |
| 19 | S s | 8 |
| 20 | T t | 7 |
| 21 | U u | 6 |
| 22 | V v | 5 |
| 23 | W w | 4 |
| 24 | x | 3 |
| 25 | Y y | 2 |
| 26 | Z z | 1 |
By the way, the letter Y can stand for both a vowel and a consonant, and therefore refers to both vowels and consonants.
Almost all letters of the English alphabet are pronounced the same by Americans and British, except for the last one. The American alphabet differs in that the letter Z is pronounced as "zi" [ziː], and in the British - "zed" [zed].
Demo lesson for free and without registration!
Take a lesson, learn about the school and get a promotional code for English classes
Pronunciation of the English alphabet with the names of letters in English and Russian:
Below is a table where we have outlined the English alphabet with translation - transcription and pronunciation in Russian.
| | ||
|---|---|---|
| Letter | Transcription | pronunciation of |
| a | [eɪ] | hey |
| B b | [biː] | bi |
| C c | [siː] | and |
| D d | [diː] | di |
| e | [iː] | and |
| F | [ɛf] | eff |
| G g | [dʒiː] | ji |
| h h | [eɪtʃ] | h |
| i | [aɪ] | ai |
| J | [dʒeɪ] | jay |
| K k | [keɪ] | key |
| L l | [ɛl] | el |
| M m | [ɛm] | em |
| N n | [ɛn] | en |
| O o | [əʊ] | ou |
| P p | [piː] | pi |
| Q q | [kjuː] | cue |
| R r | [ɑː] or [ɑɹ] | a:, ar |
| S s | [ɛs] | es |
| t | [tiː] | and |
| U u | [juː] | y |
| V v | [viː] | and |
| w w | [ˈdʌb(ə)l juː] | double |
| x | [ɛks] | ex |
| Y y | [waɪ] | wye |
| Z z | [zɛd], [ziː] | zed, zi |
Sounds of the English alphabet
We start learning English letters even before we encounter foreign language lessons. We know them even before we start learning English: we meet them at work, when we play computer games or surf the Internet. English words are found everywhere: on advertising posters, in the names of goods, in store signs.
Although the letters may be visually familiar to us, they are not always pronounced the way they are written. The alphabet of the English language for beginners with pronunciation, numbering and translation will help here, because even those who are fluent in foreign languages find it difficult to speak correctly. A typical situation is to spell an English word, for example, to give an email address, your name or street in English. This is where the difficulties begin, and we try to explain ourselves with images and associations: i - “like a stick with a dot”, H - “like a Russian n”, s - “like a dollar”, v - “like a tick.
From here it is better to memorize not only the letters, but also their pronunciation. The latter is written by transcription and enclosed in square brackets. At first, it will be easier for you to memorize transcription with Russian pronunciation, but gradually you need to give it up and focus only on English transcription.
At first, it will be easier for you to memorize transcription with Russian pronunciation, but gradually you need to give it up and focus only on English transcription.
How to Learn the English Alphabet
Learning the alphabet is not just memorizing the order of the alphabet in English, Russian or Spanish, or knowing how many non-letters there are. To know the alphabet is to be able to pronounce sounds, as well as to write lowercase and uppercase letters correctly. In order to learn the entire alphabet of the English language easily, quickly and forever, follow these rules:
- Memorize both uppercase and lowercase letters of the English alphabet at the same time, pay attention to how English letters are written.
- Learn both the name of the English letters and the correct pronunciation, use the alphabet with transcription. It is easier to remember this at the same time than to relearn it later.

- Use all available resources: use audio recordings, videos of examples of correct pronunciation, printed texts, Internet resources.
- Learn the English alphabet in order, as in the alphabet. Then change tactics: start studying the letters backwards, randomly, grouping.
- Exercise regularly, preferably every day for at least a few minutes. If you are tired of learning the same letters, take any children's book in English. Maybe you will not understand the meaning of what is written, but you will definitely be able to recognize and name this or that letter.
Another good way to learn the alphabet is to memorize a special rhyme. It is very short, but it will help to know every letter by heart:
Do you know your ABC?
You can learn along with me!
A, B, C, D, E, F, G,
H, I, J, K,
L, M, N, O, P U, V,
W, X, Y and Z
Now, I know my ABC's.
Next time won't you sing with me?
And the last piece of advice. Divide all letters into three large groups and learn them in three stages: the first group is 6 vowels: Aa, Her, Ii, Oo, Uu, Yy. Do not forget about transcription and remember that in English vowels can change their sound depending on the type of syllables, stress and other conditions; the second group of letters includes those that are written and pronounced similarly to Russian letters. They are easy to remember: Bb, Cc, Dd, Kk, Ll, Mm, Nn, Pp, Ss, Tt, Xx; the third group consists of those letters that sound and are written unfamiliar to native Russian speakers: Ff, Gg, Hh, Jj, Qq, Rr, Vv, Ww, Zz.
Methods and techniques for memorizing the English alphabet
There are many ways to learn the English alphabet from scratch that are suitable for both adults and children.
The most popular way to learn the English alphabet is through tables. You can print the English alphabet tables from this article or search for others: English alphabet by numbers; English alphabet with numbering of letters, etc. Hang them over your desk and browse and read aloud whenever you have a free moment. The main thing is to memorize the alphabet with the pronunciation of sounds.
You can print the English alphabet tables from this article or search for others: English alphabet by numbers; English alphabet with numbering of letters, etc. Hang them over your desk and browse and read aloud whenever you have a free moment. The main thing is to memorize the alphabet with the pronunciation of sounds.
One of the most effective ways is to make colored cards with the letters and words that begin with them and place them in a prominent place. These cards can be made by yourself or bought in the store. It is better to use well-known words, for example, the names of animals.
You can train with special exercises, for example, this one: get a special notebook and write down the letters in it several lines - both uppercase and lowercase letters of the English alphabet. And when writing, dictate to yourself aloud the name of the letter. This exercise includes all three main types of memory: auditory, visual and motor.
Don't forget about games that will help you learn the English alphabet. For example, Spell the word or “Spell the word” - whoever spells it wrong first loses. And you can also read the alphabet at speed, write letters correctly by ear, pronounce the letters written on the card, and so on. The audio alphabet of the English language with pronunciation has proven itself well. A student can independently master the letters and sounds just by listening to the recording. The main thing is to be systematic.
For example, Spell the word or “Spell the word” - whoever spells it wrong first loses. And you can also read the alphabet at speed, write letters correctly by ear, pronounce the letters written on the card, and so on. The audio alphabet of the English language with pronunciation has proven itself well. A student can independently master the letters and sounds just by listening to the recording. The main thing is to be systematic.
Interesting facts about the English alphabet
Learning the sounds and letters of the English language will be more fun if you know a few interesting facts about the alphabet:
- The English alphabet can be called by its first letters "ABC";
- The English word alphabet comes from the Latin alphabet, where alpha and beta were the first letters of the alphabet. But even before the Latin alphabet, they were the first letters of the Phoenician alphabet (alef and bet), which arose in 1050 BC.
 e.
e. - The article the is the most common word in English.
- The most common letter in the English alphabet is E, and the most common consonant is T. The letters S and T are most common at the beginning of English words. The rarest letters in the alphabet are Q and Z.
- In English there are only 5 vowels and as many as 20 vowel sounds! For example, the letters Y and W can be pronounced as vowels (try, my, cow, few). The same letter can be read in several ways, for example, in the words cat [kæt], place [pleis], dark [daːk], air [ɛə].
- All 26 letters of the English alphabet can be put into a sentence or pangram that shows how each letter of the font will look like: "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" (loosely translated: "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." English analogue - "Eat some more of these soft French rolls and drink tea").
Conclusion
English speakers remember their alphabet much more often than Russian speakers, because in English the pronunciation of a word often does not match its spelling.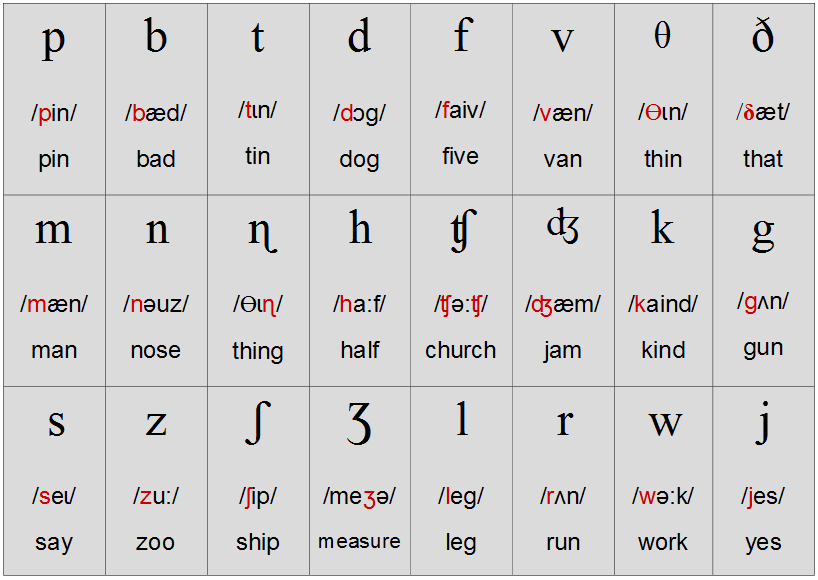 Especially in geographical names and surnames. Then they spell these words (to spell). Therefore, in order to learn the entire English alphabet with the correct pronunciation for an adult, to speak English well and understand native speakers, it is necessary to learn how to spell words. And the phrase "Please spell this word!" ("Please spell") to help you.
Especially in geographical names and surnames. Then they spell these words (to spell). Therefore, in order to learn the entire English alphabet with the correct pronunciation for an adult, to speak English well and understand native speakers, it is necessary to learn how to spell words. And the phrase "Please spell this word!" ("Please spell") to help you.
Check if you know the top 100 English words
The sounds and letters of the English language
The English alphabet
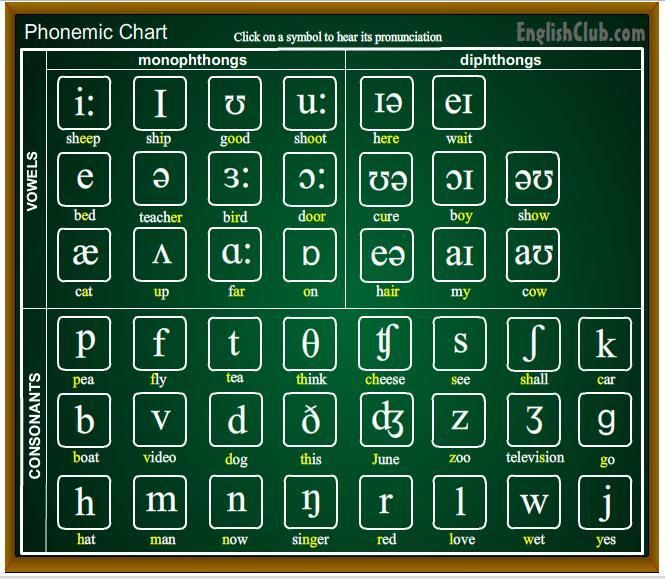
There are 26 letters in the English language. In different combinations and positions, they represent 44 sounds.
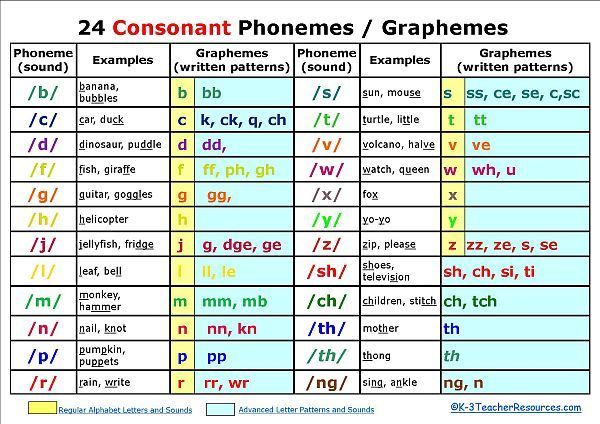
In English, 24 consonants are distinguished, and they are transmitted in writing by 20 letters: Bb; cc; Dd; ff; Gg ; hh; Jj; kk; LI; mm; Nn; pp; Qq; Rr; Ss; Tt; vv; ww; xx; Zz.
In English, 12 vowels and 8 diphthongs are distinguished, and they are transmitted in writing by 6 letters: Aa; ee; li; Oh; Uu; Yy. Russian alphabet. Use of the alphabet
Video: English lesson on the English alphabet
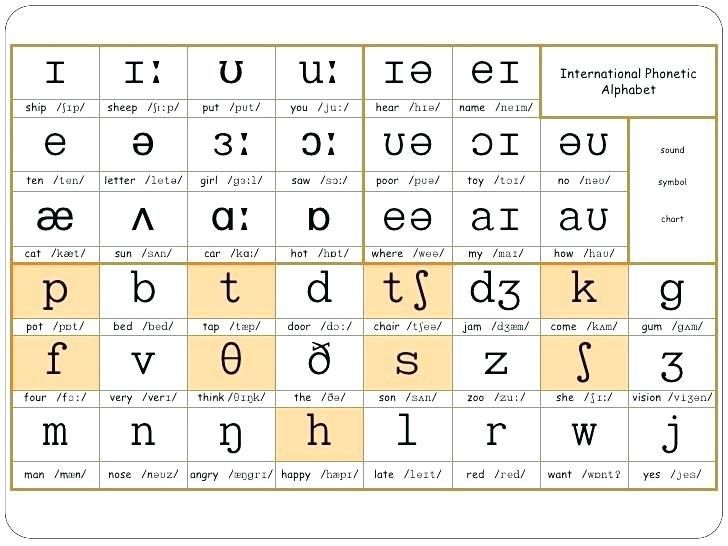
Transcription and stress
Phonetic transcription is an international system of signs used to show exactly how words should be pronounced. Each sound is displayed with a separate icon. These icons are always written in square brackets.
In transcription, verbal stress is indicated (on which syllable in the word the stress falls). The stress mark [‘] is placed before the stressed syllable.
English consonants
- Features of English consonants
- English consonants, transmitted by letters b, f, g, m, s, v, z, are close in pronunciation to the corresponding Russian consonants, but should sound more energetic and tense.
- English consonants are not softened.
- Voiced consonants are never stunned, neither before voiceless consonants nor at the end of a word.
- Double consonants, that is, two identical consonants side by side, are always pronounced as one sound.

- Some English consonants are aspirated: the tip of the tongue must be pressed firmly against the alveoli (the bumps where the teeth attach to the gum). Then the air between the tongue and teeth will pass with effort, and you will get a noise (explosion), that is, aspiration.
Rules for reading consonants in English: link 1, link 2
| Table of pronunciation of English consonants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Phonetic transcription | Examples | Approximate matches in Russian |
| [b] | b ad, b ox | voiced sound corresponding to Russian [b] in the word b rat |
| [p] | o p en, p et | a dull sound corresponding to the Russian [p] in the word p ero , but pronounced aspirated |
| [d] | d i d , d ay | voiced sound, similar to Russian [d] in the word d om , but more energetic, “sharper”; when pronouncing it, the tip of the tongue rests on the alveoli |
| [t] | t ea, t ake | a dull sound corresponding to the Russian [t] in the word t ermos , but pronounced with a breath, while the tip of the tongue rests on the alveoli |
| [v] | v oice, v isit | voiced sound corresponding to Russian [v] in the word in osk , but more energetic |
| [f] | f ind, f ine | a dull sound corresponding to Russian [f] in the word f inik , but more energetic |
| [z] | z oo, ha s | a voiced sound corresponding to Russian [z] in the word z ima , but more energetic; when pronouncing, the tip of the tongue is raised to the alveoli |
| [s] | s un, s ee | a dull sound corresponding to the Russian [s] in the word from or , but more energetic; when pronouncing, the tip of the tongue is raised to the alveoli |
| [g] | g ive, g o | voiced sound corresponding to Russian [g] in the word g irya , but pronounced softer |
| [k] | c at, c an | a dull sound corresponding to the Russian [k] in the word to mouth , but pronounced more energetically and aspirated |
| [ʒ] | vi si on, plea sur e | voiced sound corresponding to Russian [zh] in the word zh ara , but pronounced more intensely and softer |
| [ʃ] | sh e, Ru ss ia | a dull sound corresponding to the Russian [sh] in the word sh ina , but is pronounced softer, for which you need to raise the middle part of the back of the tongue to the hard palate |
| [j] | y ellow, y ou | a sound similar to the Russian sound [th] in the word th od , but pronounced more energetically and intensely |
| [l] | l itt l e, l ike | sound similar to Russian [l] in the word l isa , but you need the tip of the tongue to touch the alveoli |
| [m] | m an, m erry | a sound similar to Russian [m] in the word m ir , but more energetic; when pronouncing it, you need to close your lips more tightly |
| [n] | n o, n ame | a sound similar to Russian [n] in the word n os , but when it is pronounced, the tip of the tongue touches the alveoli, and the soft palate is lowered, and air passes through the nose |
| [ŋ] | si ng , fi ng er | a sound in which the soft palate is lowered and touches the back of the back of the tongue, and air passes through the nose. To pronounce it like Russian [ng] is wrong; should be a nasal overtone To pronounce it like Russian [ng] is wrong; should be a nasal overtone |
| [r] | r ed, r abbit | a sound, when pronouncing which the raised tip of the tongue should touch the middle part of the palate, above the alveoli; tongue does not vibrate |
| [h] | h elp, h ow | a sound reminiscent of Russian [x] as in the word x aos , but almost silent (slightly audible exhalation), for which it is important not to press the tongue against the palate |
| [w] | w et, w inter | a sound similar to a very quickly pronounced Russian [ue] in the word Ue ls ; at the same time, the lips need to be rounded and pushed forward, and then vigorously pushed apart |
| [dʒ] | j ust, j ump | a sound similar to [j] in a Russian loan word j insy , but more energetic and softer.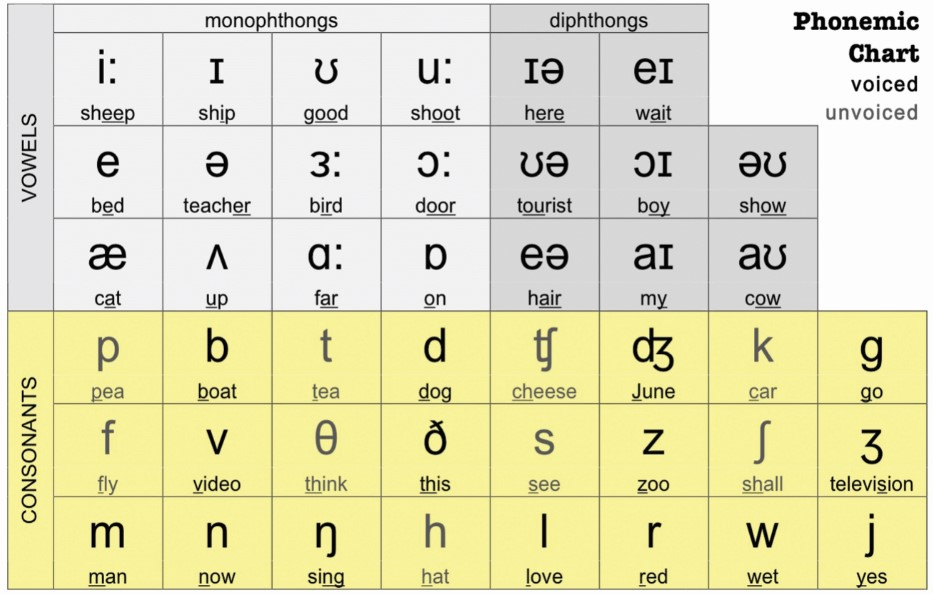 Cannot be pronounced separately [d] and [ʒ] Cannot be pronounced separately [d] and [ʒ] |
| [tʃ] | ch eck, mu ch | a sound similar to Russian [h] in the word h as , but harder and more intense. Cannot be pronounced separately [t] and [ʃ] |
| [ð] | th is, th ey | a ringing sound, when pronouncing which the tip of the tongue must be placed between the upper and lower teeth and then quickly removed. Do not clamp the flat tongue with your teeth, but slightly push it into the gap between them. This sound (since it is voiced) is pronounced with the participation of the vocal cords. Similar to Russian [z] interdental |
| [θ] | th ink, seven th | A voiceless sound that is pronounced the same as [ð], but without a voice. Similar to Russian [s] interdental |
English vowel sounds
- The reading of each vowel depends on:
- from other letters standing next to it, in front of it or behind it;
- from being in a shock or unstressed position.
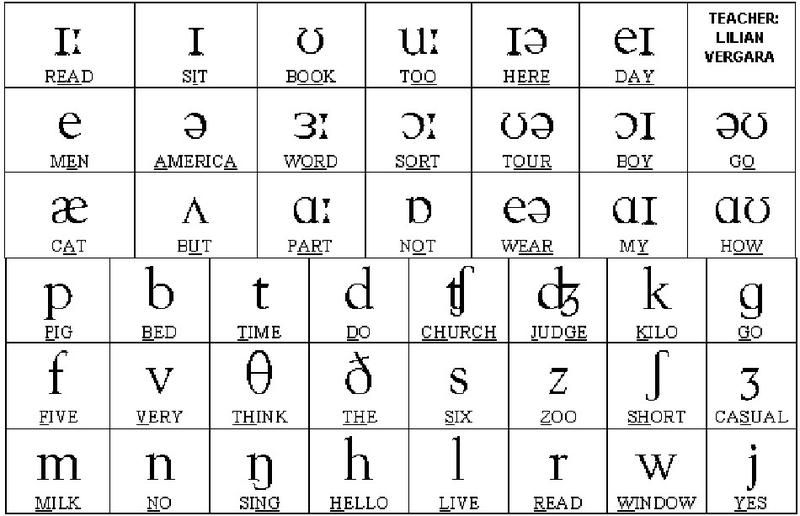
- Peculiarities of vowel sounds in English.
- English vowels (unlike Russian) are divided into long and short.
Under stress, long sounds last almost three times longer than short ones. It is necessary to observe the longitude and brevity of sounds, otherwise there will be a confusion of the meanings of words.
In transcription, the length of a vowel sound is indicated by two vertical dots (i.e., a colon) behind the icon denoting that sound [:] . - There are diphthongs in English.
Diphthongs are combinations of two vowel sounds that are pronounced together and both fit into one syllable: the organs of speech after pronouncing the first sound quickly but smoothly move into the position required for the next sound; the first sound is pronounced distinctly and for a long time, and the second sound is very short and merges with the first.
Rules for reading vowels in English: link 1, link 2, link 3, link 4
| Pronunciation table for simple English vowels | ||
|---|---|---|
| Phonetic transcription | Examples | Approximate matches in Russian |
| [æ] | c a t, bl a ck | short sound, middle between Russian sounds [a] and [e].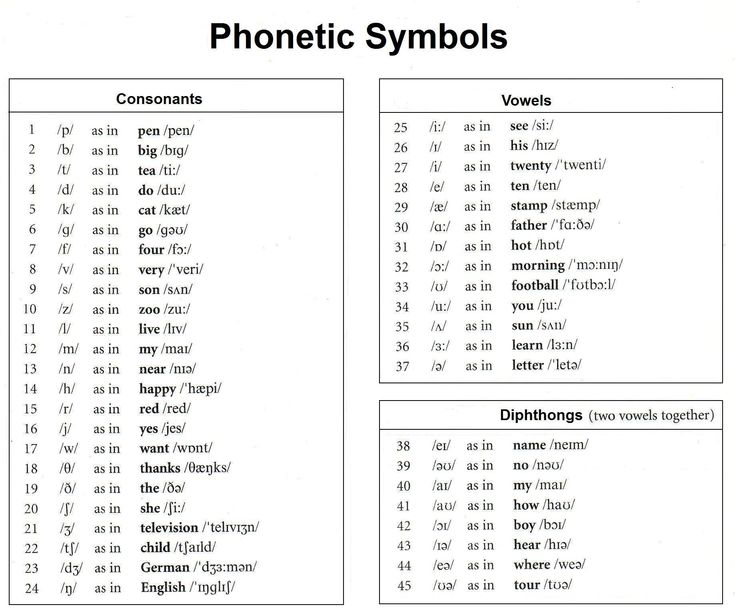 To get this sound, you need to pronounce Russian [a], open your mouth wide, and position your tongue low. Pronouncing just Russian [e] is wrong To get this sound, you need to pronounce Russian [a], open your mouth wide, and position your tongue low. Pronouncing just Russian [e] is wrong |
| [ɑ:] | ar m, f a ther | is a long sound similar to Russian [а], but it is much longer and deeper. When pronouncing it, you need to yawn, as it were, but do not open your mouth wide, while pulling your tongue back |
| [ʌ] | c u p, r u n | is a short sound similar to Russian unstressed [a] in the word from a dy . To get this sound, you need, while pronouncing Russian [a], almost do not open your mouth, while stretching your lips a little and pushing your tongue back a little. Pronouncing just Russian [a] is wrong |
| [ɒ] | n o t, h o t | a short sound similar to Russian [o] in the word d about m , but when pronouncing it, you need to completely relax your lips; for Russian [o] they are slightly tense |
| [ɔ:] | sp o rt, f ou r | is a long sound similar to Russian [o], but it is much longer and deeper. When pronouncing it, you need to yawn, as it were, with your mouth half open, and tighten and round your lips When pronouncing it, you need to yawn, as it were, with your mouth half open, and tighten and round your lips |
| [ə] | a bout, a lias | sound, which is often found in Russian, is always in an unstressed position. In English, this sound is also always unstressed. It does not have a clear sound and is referred to as a vague sound (it cannot be replaced by any clear sound) |
| [e] | m e t, b e d | short sound similar to Russian [e] under stress in words such as e ti , pl e d , etc. English consonants cannot be softened before this sound |
| [ɜː] | w or k, l ear n | this sound is not in Russian, and it is very difficult to pronounce. It resembles the Russian sound in the words m ё d , sv ё kla , but it needs to be pulled much longer and at the same time the lips are strongly stretched without opening the mouth (a skeptical smile is obtained) |
| [ɪ] | i t, p i t | is a short sound similar to the Russian vowel in the word sh and t .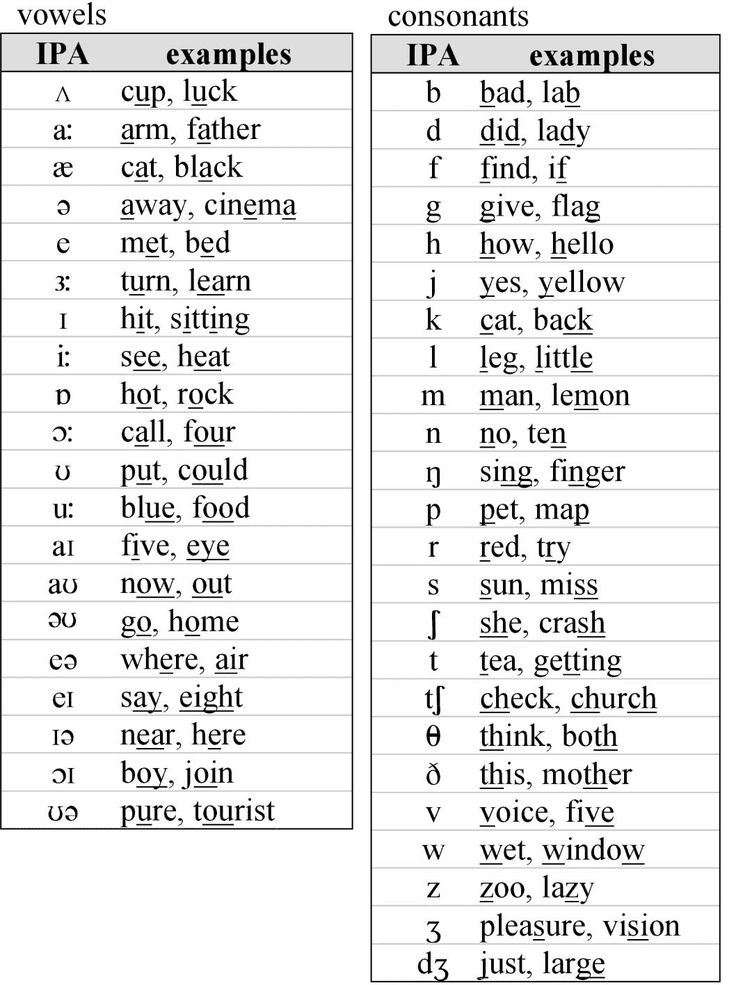 You have to pronounce it abruptly You have to pronounce it abruptly |
| [i:] | h e , s ee | a long sound, similar to Russian [and] under stress, but longer, and they pronounce it as if with a smile, stretching their lips. There is a Russian sound close to it in the word verse ii |
| [ʊ] | l oo k, p u t | a short sound that can be compared with the Russian unstressed [u], but it is pronounced energetically and with completely relaxed lips (lips cannot be pulled forward) |
| [u:] | bl u e, f oo d | is a long sound, quite similar to the Russian percussion [y], but still not the same. To make it work, you need, while pronouncing Russian [y], do not stretch your lips into a tube, do not push them forward, but round and smile slightly.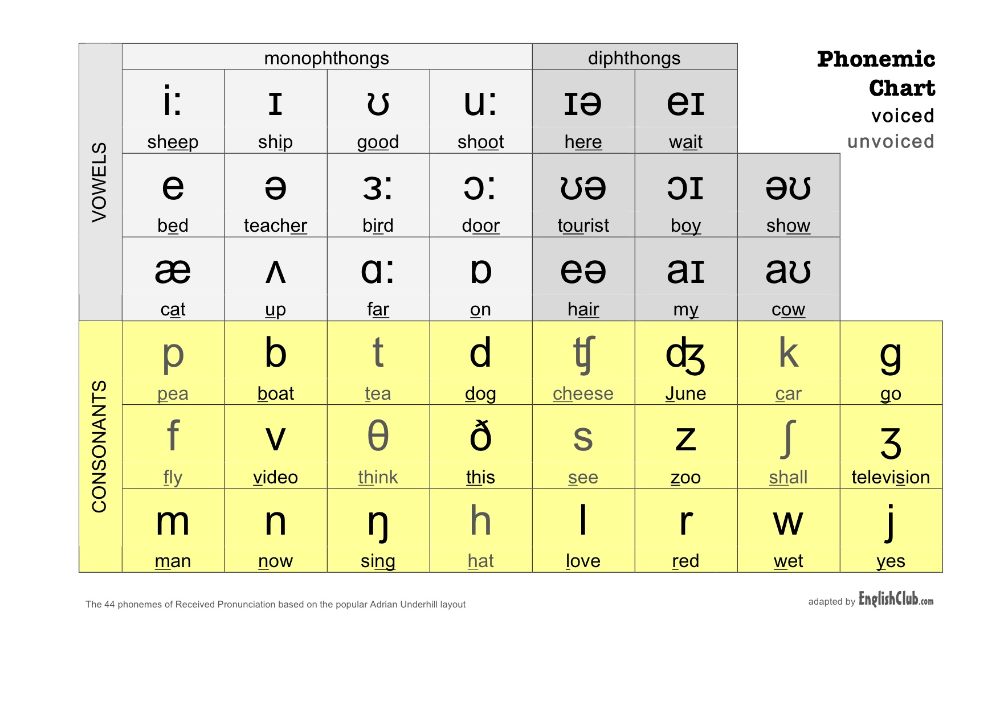 Like other long English vowels, it needs to be drawn much longer than Russian [y] Like other long English vowels, it needs to be drawn much longer than Russian [y] |

 Second element, sound [ɪ], very short
Second element, sound [ɪ], very short