Reading level for 4th graders
What Reading Level Should a Fourth Grader Be At?Making English Fun
The change in emphasis between third grade and fourth grade reading curriculum, and 4th grade reading level assessments can come as a surprise to both students and parents. While in Key Stage 1 the focus is firmly placed on learning the skills to read with decoding, vocabulary building, sentence constructions and phonics playing the keyrole. The move to fourth grade and Key Stage 2, while retaining elements of phonics and vocabulary, starts to move to higher order skills and reading comprehension skills.
Fourth grade average reading levels range between 18 to 28 on PM benchmark levels or up to level 40 on DRA levels. Grade 4 reading levels can vary greatly between individual students. Grade four reading tuition starts to move focus from phonics and reading skills to reading comprehension and critical thinking skills.
Our “What reading level should a fourth grader be at” article will address some of these changes to make them as smooth as possible as your children and students transition into upper elementary and grade 4.
- What are reading levels and how they can be used to help your 4th graders to improve their reading skills especially comprehension.
- What are the major differences between reading levels in 4th grade and 3rd grade
- What you can do to support your children and students in 4th grade
- Reading skills and concepts are covered in fourth grade classrooms.
- Links to free 4th grade reading resources (and other resources) to help you teach these reading skills.
If you are looking for quick access to reading and writing worksheets for grade 4 we have a large collection here in the article below. As a note, we have called some of these grade 3-4-5 etc. However they can be used as you see fit with your students.
What Is a Reading Level?
There are multiple different programs and tools to assess students of all grades reading levels. Including:
Including:
- DRA reading assessments
- PM Benchmark
- Reading Recovery
- Reading AtoZ
- Fountas and Pinnell
And many MANY more as mentioned below these can often be tied to a reading scheme or set of levelled readers. .
However, the majority of these reading level assessments all share common indicators. They assess the comprehension, pronunciation, decoding and fluency ability of a student of English while they are reading a short leveled text.
Fourth graders are highly unlikely to be reading advanced texts just yet, and although they will be developing skills to help with this they are still at a transition stage and care needs to be taken to ensure that their move from learning to read to reading to learn is as smooth as possible.
In fourth grade, if your 4th graders are around the average 4th grade reading level of 20 or so ( PM Benchmark), you should start to be able to introduce shorter chapter books in class. and to also allow them time to read alone if they are able. Choosing popular or funny books like Roald Dahl books is a great way to introduce longer stories to 4th graders.
and to also allow them time to read alone if they are able. Choosing popular or funny books like Roald Dahl books is a great way to introduce longer stories to 4th graders.
Reading comprehension is included in 4th grader lessons on a much more frequent basis as at this level, barring any barriers or additional needs, their hard reading skills will be developed enough to start to look at whole text meaning and looking at higher order reading comprehension skills.
We have a resource below for this if you need, as well as posts and articles on the Reading comprehension skills, however its a better deal to pick it up in the bundle offer we have on this page as well as that comes with reading material, worksheets, games and this higher order set!
Reading A2Z have detailed information on the different reading level assessments and programs which as mentioned all have commonalities
. They also have differences as well, with some like Lexile concentrating on word count or difficulty of words and others like the PM benchmark looking at simplicity of both words and sentence construction as well as including comprehension of text as a ranking and leveling factor.
Globally it is unfortunate but educational systems, nationally and internationally, all use different methods to level their grade 4 students. This means they will also use different reading assessment tools. However we explore some of the expectations of a grade 4 reader below to help you match your students to reading materials of your own choice
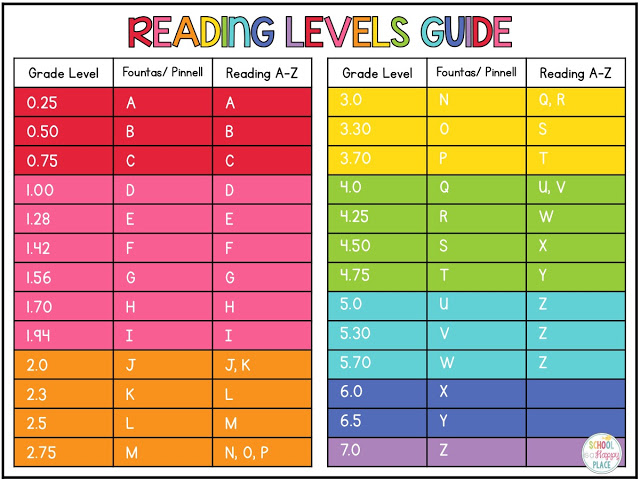
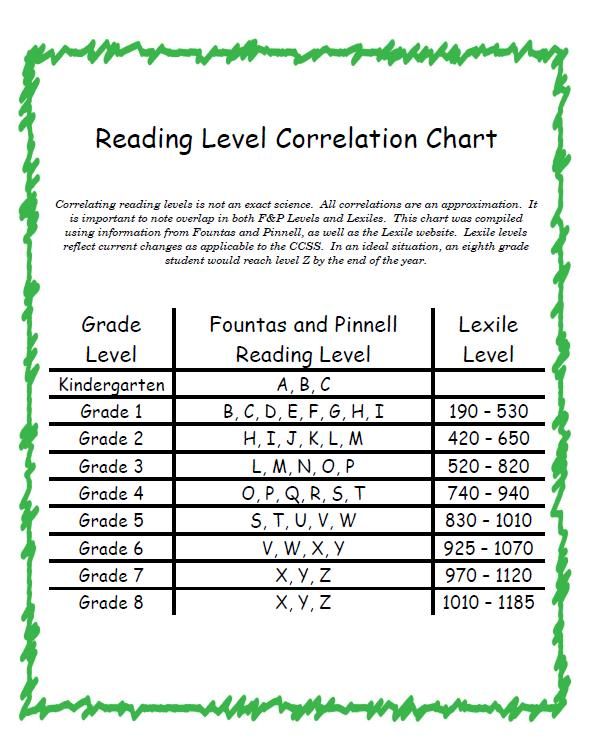
To bring some clarity to this the chart below offers a handy comparison (we use this in all our guide to levels and grades articles) to help both teachers and parents when it comes to choosing reading materials.
When choosing which readers are suitable for your grade 4 students it is definitely of use to take some time with both your reading resources and the chart to make sure they fit the reading level of your students.
However never underestimate motivation! If you can tap onto your students interests then it is possible to use higher levelled books with them. ( though don’t go overboard with this!) if a child is interested in the subject and the book then they will make extra efforts to be able to understand .
As an example i have done this for years and years with Space and Dinosaurs as topics. Children’s natural curiosity helps them make serious effort to understand the concepts, and to try to pronounce the VERY difficult names of dinosaurs and planets. (we have resources in the linsk if you want to try that for yourself. Grade 4 is perfect for these subjects.
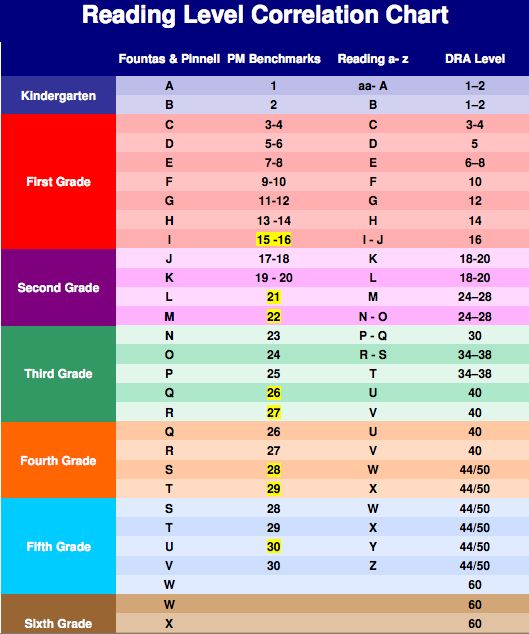
We use the chart below in all our reading level articles.
Many Guided reading publishers have developed their own systems as well.
- Scholastic Guided Level Reading Program
- CCSS Lexile Recommendations
- DRA Level
- PM Benchmark
- Reading AtoZ ( online resources – which have become or important in the recent past!)
For both ease and continuity, (as we have used this Pm benchmarks, readign recovery and DRA assessment tools in our other reading level articles) we will use the DRA reading level today as RR tends to stop and move to comprehension after level 20+) As you can see DRA goes up to level 80. With an expectation that grade 4 will be around 30-40 on this reading framework.
With an expectation that grade 4 will be around 30-40 on this reading framework.
The DRA ( Developmental Reading Assessment) is a reading skill assessment tool that aims to evaluate students reading levels to enable teachers and parents to assess students reading skills including fluency, comprehension and phonics. They aim to discover the independent and instructional reading level of students. it is suited for grade 4 levelling and beyond as their leveling system expands beyond reading ability and into reading comprehension.
What is Instructional Reading Level?
Instructional Reading level is the reading level below independent. Students should be able to comprehend and decode upwards of 80% of the text at an instructional level. At grade 4 texts will be introducing more complex topics as well as language.
What is Independent Reading Level?
An independent reading level is a level of reading ability that allows students to read texts without assistance from teachers or parents. Most grade 4 students will be moving towards becoming independent readers, depending on the level of text given to them. ( no encyclopedias etc!)
Most grade 4 students will be moving towards becoming independent readers, depending on the level of text given to them. ( no encyclopedias etc!)
When reading this level of text students will be able to decode over 90% of words and answer increasingly complex comprehension questions independently.
What is Frustration Reading Level?
Frustration level reading can be defined as texts that are too complex for a students current reading level. Students will not be able to decode or get the gist of the text, especially if no pictures. It may have the effect of decreasing their willingness to engage with reading and should be avoided.
In 4th grade reading lessons, as well as other grades, classrooms and homes teachers and parents should aim at using an instructional reading level book. This allows students to comprehend and therefore engage with texts with some assistance, and gives them the motivation to see they are doing well.
Other Grades Average Reading Levels.
We have a selection of articles on reading level expectations for different grades below.
The Seven Reading Comprehension Strategies
At the end of grade three students will be asked more open ended questions. this is to start to prepare them for the shift to key stage 2 and the shift in focus from phonics and reading skills and to reading comprehension skills.
We have a table with some advice below to help you if you are unaware of how to introduce these to your 4th grade students.
Check out the links to know more. We also have an article here on what age you can start teaching guided reading.
What 4th Graders Learn Throughout the Year.
As we mentioned above a fourth grader can be reading from about reading level 20 to level 30+ (on Pm benchmark) (in our expereicne) or up to level 40 with the DRA reading levels. However please don’t worry if your students or children are below this reading level, or be too confident if they are above this.
Also phonics skills will become rarer in grade 4 as this emphasis to comprehension starts. It is now important to look at and introduce reading comprehension, critical thinking and higher ordering thinking.
Children will develop their reading levels and skills at different paces to each other. If your Fourth grade students still need a little extra time to nail down those phonics skills we have countless resources to help with these skills if you need. Including the bundle below.
The next section covers what skills they will learn to help them improve their reading levels throughout the fourth grade.
What Reading Skills Will Students Learn in Fourth Grade
In fourth grade and the move to key stage 2 is , in our opinion, as big a move as the move from kindergarten to elementary, and the move from elementary to High School. However it is not given the same importance.
The early stages of Reading comprehension will appear in this grade. They will have to look at texts as more than stories or information and start to evaluate and form opinions on them, and the most difficult for a lot of 4th graders learn how to express those opinions both my presentation and written work. .
They will have to look at texts as more than stories or information and start to evaluate and form opinions on them, and the most difficult for a lot of 4th graders learn how to express those opinions both my presentation and written work. .
They will have to learn and practice skills like interference, summarizing and questioning. and apply them to their reading texts. fourth grade lessons, in good English classrooms at least, should be gradually introducing this skills.
Common Core Standards for English Language Arts in Grade 4.
We have highlighted some of the more important reading skills grade 4 should be practicing below with resources we have to help where we have them. You can read more about the Common Core Standards on this link.
| Common Core | Resource | How it can help |
| CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.4.2 Determine characters and themes of a story, drama, or poem and give text examples.  Also be able to summarize the story. Also be able to summarize the story. | Reading Materials at Grade 4 level. | -Comprehension Questions -Vocabulary Matching |
| CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from the text. | Grade 4 Readers | Mix of fiction and nonfiction short passages and comprehension questions. |
| .CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.4.5 Explain major differences between poems, drama, and prose, and refer to the structural elements of poems (e.g., verse, rhythm, meter) and drama (e.g., casts of characters, settings, descriptions, dialogue, stage directions) when writing or speaking about a text | The Complaint letter, The Lizard and the Sparrow and the Stupid crocodile | All of these texts offer the chance to do a character comparisons or discuss how they react to a situation. |
| CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.4.9 Compare and contrast the treatment of similar themes and topics (e.g., opposition of good and evil) and patterns of events (e.g., the quest) in stories, myths, and traditional literature from different cultures. | Adverbs, Reported speech, passive voice | Selection of grade 4 grammar and reading skills worksheets. Adverbs for example |
| CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RL.4.10 By the end of the year, read and comprehend literature, including stories, dramas, and poetry, in the grades 4-5 text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. | A complaint letter | Could be used to write a reply for each complaint from the person its aimed at to explore different views. |
As you can see in grade 4 there are significant changes from grade 3 reading level expectations.
- there will be a greater selection of text types, including poetry, dramas and prose. They will be taught how to recognise the differences between theses and how to evaluate them.
- They will look at retelling and summarizing skills
- They will learn how to compare and contrast with other texts or stories they may have heard or read and the concepts included including from other cultures.
- There Is also an introduction to inferencing skills. Which will include the use of metaphor and simile
- And as a last hurrah to phonics and reading skills (almost) there is the requirement to be able to read these texts fluently and confidently.
What Can Teachers Do to Improve Reading Levels at 4th Grade.
We believe Text choice is vital in Grade 4 classrooms. If you can choose, or at least adapt, reading materials to inspire your 4th graders you are going to have half the battle won. They are moving from just reading to reading to learn and they will need both your support and great motivation to really excel at this.
- Have a selection of levelled readers and text types suitable for 4th graders covering fiction and NON fiction texts. Thi would be ranging from about level 14 to level 30 on Pm benchmark scales.
- Introduce poetry ( child friendly) and some readers theatre to your lessons so they can do more than just read about these text types they can actually experience them.
- Read with your students. Set aside time where you all read. This can be the same book, or it can be quiet time with a book of their choice. However model how a good reader behaves for your children or students.
- Mix your teaching resources are presented, online games, worksheets, readers, multi media etc.
- Take time to read to your class, it doesn’t happen often and students can learn alot from teachers putting correct emphasis and time into literature especially if introducing poems or dramas.
 ( check this out as a Roald Dahl story telling!) .
( check this out as a Roald Dahl story telling!) . - Give handouts on reading skills, and reading comprehension skills and have them displayed in the classroom.
- Ask your grade 4s their opinion wherever you can, it helps them practice their critical thinking skills.
How Can Parents Help Their Fourth Grader Develop a Love for Reading?
Here’s a list of ways that you can help your fourth grader develop a love for reading:
- Read with your children, both story time and as a family.
- let them tell you about their books, what is happening and what they think will happen. if it is non fiction then ask if they want to go to the museum, or similar to explore in more detail.
- There was a lovely quote i pu in the fifth grade article from from a parent saying they offered their son or daughter a dollar for every book they read over the summer, and it was the best 120 dollars they have ever spent.
 Incentives shouldn’t be your first step but if needed they could be a great investment.
Incentives shouldn’t be your first step but if needed they could be a great investment. - Ask your 4th grader what they think often, allow them to start practicing their critical thinking skills.
- Look at competitions to join ( although the less pressure the better) if your children like to perform consider a youth theatre or readers theater group.
Grade 4 students, whatever their reading level, are always learning. Parents can help to steer that away from getting high scores on PUGB or an Xbox and into reading to learn.
Finally
As we have highlighted above the average reading level of a fourth grade can fall between a wide range of levels. From around 16 to 30 using a PM Leveling benchmark and 20 to 40 using a DRA reading level framework.
We cannot stress enough the importance of not getting caught up with these numbers though. All grade 4 students are different and their individual circumstances will impact their reading levels.
THe key change in grade four reading lessons is to give opportunity for students to form and express their own opinions, and to start to become aware of the higher reading comprehension skills they will need for their progress through key stage 2.
Here’s a quick recap of the post:
- Fourth graders typically fall between a 20 to 30 reading level depending on the leveling framework.
- Use different text types, allow them time to read independently
- Encourage them forming opinions on what they read
- Follow their interests, it helps motivate them to read
- Expand their vocabulary, including academic vocabulary.
- Start to develop awareness of empathy and looking at texts from other points of view.
Sources
- Scholastic – Learn About Leveled Reading
- Reading A to Z – Levelled Books
- Amazon Fourth Grade Reading.

- Common Core ELA Standards
Hi I’m Marc. A teacher of over 15 years, English, General Studies and Outdoor Education. Thought it was about time to sharing both what I have learnt during that time and the resources I have put together. On this site we aim to teach the theory and share our thoughts, but also go that one step further and give you access to the hard resources you need for your class or for you children
Like this:
Like Loading...
Making English Fun!
I have been a teacher of English for over 15 years, in that time i made hundreds and thousands of resources and learnt so much i think its worth sharing. Hopefully to help teachers and parents around the world.
📚 Making Sense of Reading Levels plus booklists for every Grade
Books to Read • Mom StuffAugust 30, 2021
by Beth Gorden
Anyone else completely confused by reading levels? There are guided reading levels, Lexile numbers, and Book Levels like the library uses. I found this especially confusing when my kindergarten and grade 1 students were beginning to read. I assumed you just get a beginner reader, but guess what – it’s NOT that easy! Many beginner readers are actually for 3rd graders! YIKES! Don’t worry, I can explain reading levels, give you book recommendations by grade, and take all the work out of finding your child the best books to read by reading level!
I found this especially confusing when my kindergarten and grade 1 students were beginning to read. I assumed you just get a beginner reader, but guess what – it’s NOT that easy! Many beginner readers are actually for 3rd graders! YIKES! Don’t worry, I can explain reading levels, give you book recommendations by grade, and take all the work out of finding your child the best books to read by reading level!
Making Sense of Reading Levels
What Level Books should my Child be reading by Grade!
I think one needs a masters degree in nonsense to make sense of reading levels! Seriously there are 3 different systems used: Lexile, Book Level (like most libraries) and Guided Reading (Scholastic) that parents must try to understand. And if you google it, there isn’t much useful information out there either.
I even talked with my local librarian who gave me a lot of misinformation, ugh! So I did deeper research so I could pick out readers for my kids.
Reading levels by grade
I don’t claim to be an expert on reading levels by any means, but for all you confused parents here is some help from a mom that was just as confused as you are!
Note: All kids read at their own pace and this is just an average generalization. Please work on reading books at your child’s reading level. For kids who are great readers, they may be reading at books above their reading level.
Kindergarten Reading Level
Kindergartners are just beginning to read using some basic sight words and decoding simple words. In the library look for books labeled 0.1 – 1.3. For those using the Scholastic Guided Reading level, look for A, B, or C. (That is 25-75 in Lexile). Remember they need 30 minutes of daily reading; practice makes perfect!
- 50 Books for Kindergartners to Read by Themselves
- 45 Must Read Books for Kindergartners (Read Aloud)
First Grade Reading Level
1st Grade students are decoding more words, learning rule breaker rules, and adding more and more sight words. Through the course of the year they can be anywhere from a 1.0 – 1.9 for readers at the library. For those using Scholastic Guided Reading that is B-I or Lexile 50-275. Remember they need 30 minutes of daily reading; practice makes perfect!
Through the course of the year they can be anywhere from a 1.0 – 1.9 for readers at the library. For those using Scholastic Guided Reading that is B-I or Lexile 50-275. Remember they need 30 minutes of daily reading; practice makes perfect!
- 100 Books for 1st Graders to Read Themselves
- Favorite 1st Grade Read Aloud Picture Books
- 17+ 1st Grade Read Aloud Chapter Books you won’t want to miss!
- Top 25 Chapter Book Series for 1st-3rd Grade
2nd Grade Reading Level
2nd Graders are reading well independently. Although they may start their year in advanced readers, most are ready for simple chapter books by the end of the year. Just like Kindergarten and 1st graders, they need lots of practice to continue advancing. Even though 2nd graders are reading well on their own, they still need time reading aloud to an adult who can help them correct pronunciation, flow, and check reading comprehension to ensure no issues creep up. At the library look for books labeled 1.6-2.9. Using a Guided Reading system look for H-M or 225-450 in Lexile.
At the library look for books labeled 1.6-2.9. Using a Guided Reading system look for H-M or 225-450 in Lexile.
- Best 2nd Grade Reading List
- 2nd Grade Read Aloud Chapter Books
- Top 25 Chapter Book Series for 1st-3rd Grade
3rd Grade Reading Level
3rd Graders are comfortable reading simple chapter books on their own. They continue to need lots of practice and time reading aloud as well. At the library look for books 2.2 – 3.9, Guided Reading level L-P, and Lexile 400-650.
- 3rd Grade Reading List
- Top 25 Chapter Book Series for 1st-3rd Grade
4th-8th Grade Reading Level
Although at this point most kids are reading chapter books that are no longer labeled with a reading level, I wanted to give you some tools in case you feel the need to further assess what your child is reading.
- 4th Grade Book List – 3.3-5.5 Book Level, O-T Guided Reading, 600-850 Lexile
- 5th Grade Reading List – 5.
 0-7.4 Book Level, S-W Guided Reading, 800-1000 Lexile
0-7.4 Book Level, S-W Guided Reading, 800-1000 Lexile - 6th Grade 6.7-8.6 Book Level, V-Y Guided Reading, 950-1050 Lexile
- 7th &8th Grade 8.0-9.0 Book Level, X-Z Guided Reading, 1035-1100 Lexile
Find out any Books Reading Level
You can find out any books reading level (Lexile, library Book Level, and Scholastic Guided Reading) by checking AR Book Finder.
Free Printable Reading Logs
- Monthly Reading Log – this free printable has ‘traditional’ monthly themes
- Bookshelf Free Printable Reading Logs – super cute and fun for kids of all ages!
- Pencil Free Printable Reading Logs -print reading worksheet and color a pencil for each book you read
- Frozen Free Printable Reading Logs – kids will have fun tracking their reading and the books they’ve read with this motivating free printable for kids of all ages
- Princess Free Printable Reading Logs – students will have fun tracking their reading with these free printable reading logs
- Super Hero Free Printable Reading Logs – using a favorite theme of kids will encourage kids to read
- Cars Free Printable Book Logs – children will have fun tracking the books they’ve read with these clever free reading log
- Summer Free Printable Reading Logs – students will be motivated to read this summer with these ideas
- Reading Comprehension Bookmarks – this is a great tool for making sure kids are understanding what they are reading
- Reading Levels by Grade – how to pick the right books for every reading level and tons of printable book lists too
Book Report Idea
Looking for other ways to help kids work on reading comprehension and summarizing a book they read? Try these free resources:
- Handy Reading Comprehension Bookmarks (any book: fiction or non fiction)
- Book Report Template
- Book Report for Kids
- Pizza Book Report Idea
- Sandwich Book Report Idea
- 26 more clever Book Report Ideas
- Library Scavenger Hunt – help kids learn to navigate a library, the Dewey decimal system, book genres, and so much more with this pack of free printable scavenger hunts for kids!
- Bookshelf Reading Log – to help encourage kids to read!
Plus, here are some great ideas for Creating a Reading Nook where kids will want to curl up and read a book!
You may also like
September 3, 2020
July 26, 2021
September 25, 2014
March 24, 2020
November 12, 2020
July 14, 2014
September 18, 2020
September 29, 2021
About the author
Beth Gorden
Beth Gorden is the creative multi-tasking creator of 123 Homeschool 4 Me. As a busy homeschooling mother of six, she strives to create hands-on learning activities and worksheets that kids will love to make learning FUN! She has created over 1 million pages of printables to help teach kids ABCs, science, English grammar, history, math, and so much more! Beth is also the creator of 2 additional sites with even more educational activities and FREE printables - www.kindergartenworksheetsandgames.com and www.preschoolplayandlearn.com
As a busy homeschooling mother of six, she strives to create hands-on learning activities and worksheets that kids will love to make learning FUN! She has created over 1 million pages of printables to help teach kids ABCs, science, English grammar, history, math, and so much more! Beth is also the creator of 2 additional sites with even more educational activities and FREE printables - www.kindergartenworksheetsandgames.com and www.preschoolplayandlearn.com
standards for grades and quarters
Reading is a key skill that opens the gate to the land of knowledge for a child. Thanks to this skill, children learn about the phenomena and events of the world around them, get acquainted with the characters and actions of people, meet new problems and ideas. This skill helps them to expand their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
To understand how well a child develops this skill, it helps to check the reading technique. Reading technique is a multifactorial test that characterizes the development of a skill from different angles. In the technique of reading are evaluated:
- reading speed,
- reading method,
- reading awareness,
- correct reading,
- expressiveness of reading.
A difficult reading skill consists of both a technical and a semantic component and is aimed at achieving the main goal - understanding and assimilation of the information read.
Reading technique parameters
Let's consider all the components of reading technique in more detail.
- Reading speed - the number of words read in a certain period of time. Often, parents focus on the formation of fluent reading, while the child makes many mistakes, does not understand and does not remember what he read. It is not necessary to force only speed, slower conscious reading and a gradual increase in tempo are better than fast mechanical reading with errors and inaccuracies.

- Way of reading — syllabic reading or reading the whole word, smoothly. With the development of the skill, the child has a gradual transition from syllabic reading to smooth reading in whole words.
- The correct reading of is characterized by the absence of errors and hesitation. Inattention, problems of diction lead to inaccurate reading, indistinct articulation and, as a result, to a distortion of meaning. Pay attention to the correct reading - this will be the key to competent writing.
- Reading awareness involves reading comprehension, awareness of the idea and meaning of the text, and in the future - this is the ability to catch the subtext, humor, irony, the attitude of the author. Interfering with reading comprehension can be low reading speed, distorted reproduction - guessing words, changing the shape of words, not reading endings.
- Reading expressiveness - the use of pauses, finding the right intonation, the correct placement of stresses.
 The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
Reading speed standards for elementary school
GEF standards determine the desired reading speed for a child by a certain point in learning, help to understand whether the development of a skill is successful or whether additional attention is required. Standards - indicative values; it is important to take into account the individual psychophysiological characteristics of each child and evaluate the growth of his personal indicators.
Grade 1 reading speed standards
Reading speed standards in grade 2
Reading speed standards in grade 3
Reading velocity
Reading speed, to which it is necessary schools, is reading at the speed of conversational speech, 110-120 words per minute. The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
Other parameters of reading technique
Grade 1
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading is smooth syllabic, conscious and correct, with a clear pronunciation of syllables and words.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading is conscious, correct, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable.
Grade 2
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Compound words can be read syllable by syllable.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading meaningful, correct, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable.
Grade 3
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, with the help of which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
4th grade
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With the help of observed pauses and intonations, the child not only expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read, but is able to express his attitude to what he has read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read.
How can I test my child's reading skills on my own?
Have your child see how well they read already. Children usually love to know how many centimeters they have grown, and they may also be interested in knowing their progress in reading. Warn about the upcoming test and ask the child to read quickly.
The control of reading technique in sensitive children who, due to their temperament, can hardly tolerate various tests, can be carried out imperceptibly or in the form of a game. Do not create unnecessary excitement around the upcoming test, do not arrange a test in the form of an exam. If the child is worried, stutters, transfer control to another time.
Verification process:
- Prepare a clock with a second hand or use the stopwatch on your phone, and choose the appropriate text.
- Ask the child to take a seat.
- Show him the text and ask him to read it aloud.
- Track the time from the moment your child starts reading.
 Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results.
Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results. - Usually, one minute is noted for checking, but some experts recommend taking 2 minutes for monitoring, since not all children are equally quickly included in the work. Divide the result obtained in 2 minutes in half.
- Do not correct or interrupt while reading. It is better to discuss the mistakes made after the child has finished reading.
- Assess the speed, correctness, awareness and expressiveness of reading.
- Retest and compare results. Reading technique may differ depending on the child's fatigue, health status and mood.
Which text is suitable for verification?
Both fiction and non-fiction texts appropriate for the child's age are suitable for this purpose. The text should be unfamiliar, but understandable to the child, have educational and educational value. The texts of V. Bianchi, L. Tolstoy, N. Nosov, B. Zhitkov, K. Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
You should find the text that is located on the spread of the book so that the child does not have to waste time turning pages. Choose text without an abundance of punctuation marks and distracting illustrations. It is not desirable that the passage contains common complex sentences and dialogues. The font must be large enough and legible. The text should not have a technical focus and contain terms incomprehensible to the child.
Test score
Speed score
Count how many words the child read in one minute. When counting words, pay attention:
- prepositions, conjunctions, particles of 1-2 letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, the word is counted as 2 words;
- if the word is written with a hyphen, look at how many letters are on both sides of the hyphen: if there are more than three, we count it as 2 words, for example, “long-long”, if less than three, for example, “somehow”, - as one .

Compare your score with the recommended range and your child's previous performance.
Comprehension score
Determine how well the child understood what they read. If the student reads slowly and has read only a couple of sentences, let him read the passage to the end. Ask your child a few questions about the text. Ask what or who he read about. Ask the child to identify the main idea of what they read and retell the text.
For a deeper check of the meaning of the reading and learning, use special teaching kits.
Correctness assessment
Pay attention to whether the child reads what is written correctly, whether he pronounces words clearly, whether there are hesitations and corrections, whether he alters words, whether he changes endings, whether he places stresses correctly. Discuss the mistakes with the student.
Evaluation of expressiveness
To assess the expressiveness of reading, the child is offered a familiar text. Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Improving reading technique
Poor results in reading technique are not a reason to be upset, but only a signal that additional efforts need to be made to improve the skill. You can work with the child on your own or contact a specialist who will analyze the weak points and select the appropriate exercises. Conduct additional activities with the child in the mode of "sparing reading" without pressure. It is more important to observe the regularity and frequency of classes: 10-20 minutes daily.
How can you motivate your child to read:
- Reward your efforts with stickers, stars.
- Mark progress visually - create a success board so your child can visually see their progress
- Conduct activities in the form of a game, such as "going to the library" or "reading to your favorite toys.
 "
" - Choose books and texts that are interesting for your child.
- Let the child read to the pets, they are grateful and accepting listeners. Reading to them, the child is not afraid to make a mistake, he relaxes and overcomes the fear of failure.
- Have a reading competition between peers and siblings.
To improve the speed of reading will help:
- Reading by syllabic tables.
- Multiple reading. Read the same text several times, increasing the pace. From the second time the child will be able to read faster.
- "Tug". An adult leads a finger along the line, setting the pace. The child tries to read at a given pace.
- Tops and roots. The child reads the words, covering the upper or lower half of the letters with a ruler.
- Reading in a book turned upside down.
- Lightning. Alternating reading at a comfortable pace with reading at the highest possible speed for 20 seconds on the command "Lightning!".
- "Sprint". Reading speed competition between classmates.
- Work on expanding the field of view according to Schulte tables.
- Reading with a window to eliminate "regression" - recurrent eye movements that lead to repeated reading.
For correct reading:
- Work on clear diction, do articulation exercises.
- Read tongue twisters and tongue twisters.
- Invite the child to correct the deformed sentences: "The weather is good on the street."
- "Imaginary word". When reading, the wrong word is pronounced, the child must correct it.
Reading comprehension
- Wave Reading. First, the child reads aloud, then retells what he read.
- Drawing up a plan for reading.
- The student reads to himself at a comfortable pace, tells what he understood and felt, what he thought about
- Discuss unfamiliar words and expressions.
- Invite the child to draw a picture of the passage they read.

- Ask them to tell you what they liked about the text, what they remember.
For expressive reading
- Role-playing, staging.
- Put on a "radio show".
- Expressive recitation of poems.
- Voice flexibility training. The ability to speak quieter-louder, higher-lower.
- Conducting reading indicating the tone or strength of the voice.
- Live Picture. One reads, the other reacts with facial expressions.
Improving reading skills in elementary school is very important. It is fluent and meaningful reading that activates the processes of thinking, attention, memory and is the basis for a child's successful learning in the future. This detailed instruction on reading technique control will help you track and improve your child's skill development.
Russian language for students in grades 1-4
We develop thinking skills, prepare for the Olympiads and improve the results of the Russian language in an interactive format
learn more
Reading technique.
 Norms 1-4 class.
Norms 1-4 class. Since many parents stubbornly refuse to understand what is the point of testing reading technique in elementary school (grades 1-4), I give up and publish reading norms. At the same time, I ask you to carefully read not only the quantitative norm of words per minute, but also my explanations both in the table and below it.
Reading Speed Standards Grades 1-4
→ Number of words may vary slightly depending on curriculum. Increased rates are given in parentheses.
→ Grade 1: no mark is given, the student "did" or "did not do it". In the first half of the year, the reading technique may not be carried out.
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 cl. | at least 10 - 15 (20 - 25) wpm | by 2 -> less than 15 (25) words per minute by 3 -> 15-19 (25-34) words by 4 -> 20-24 (35-40) words by 5 -> from 25 ( 41) words |
| 2 cl. | 2 -> less than 25 (40) wpm 3 -> 25-29 (40-48) wpm by 4 -> 30-34 (49-54) words by 5 -> from 35 (55) words | by 2 -> less than 40 (50) words per minute by 3 -> 40-44 (50-58) words by 4 -> 45-49 (59-64) words by 5 -> from 50 ( 65) words |
| 3 cells | by 2 -> less than 40 (55) words per minute by 3 -> 40-49 (55-64) words by 4 -> 50-59 (65-69) words by 5 -> from 60 (70) ) words | by 2 -> less than 65 (70) words per minute by 3 -> 65-69 (70-79) words by 4 -> 70-74 (80-84) words by 5 -> from 75 (85) ) words |
| 4 cells | by 2 -> less than 65 (85) words per minute by 3 -> 65-74 (85-99) words by 4 -> 75-84 (100-114) words by 5 -> from 85 (115) ) words | 2 -> less than 70 (100) wpm 3 -> 70-88 (100-115) wpm by 4 -> 89-94 (116-124) words by 5 -> from 95 (125) words |
Other reading parameters 1-4 class
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 cl. | Reading is conscious, correct, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | |
| 2 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Words of a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable. |
| 3 cells | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. |
| 4 cells | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what he read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what he read. |
Criteria when setting an estimate for reading technique:
- reading by syllables or word completely,
- Availability of errors when reading,
- number of words per minute,
- expressiveness,
- awareness.
can be clicked to enlarge
As you can see, the number of words read is not decisive.
That is, parents need to understand that such a concept as reading speed is only one of the criteria for determining the level of reading technology . way of reading is being checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
way of reading is being checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
The expressiveness of reading, the presence of errors and / or stammers are also taken into account. Sometimes there is a return to re-reading the previous word, this indicates a lack of awareness and is considered a mistake.
It should also be taken into account that the standards for the speed (rate) of reading may differ depending on the educational institution, the requirements for a student of a gymnasium will be higher, for a student of a correctional class - lower.
The frequency of checking reading technique in elementary school is usually 2 times a year: the end of the first half of the year and the end of the second half of the year.
Learn more