Teachers reading to children
How a flawed idea is teaching millions of kids to be poor readers | At a Loss for Words
Listen to this audio documentary on the Educate podcast. Subscribe now.
Molly Woodworth was a kid who seemed to do well at everything: good grades, in the gifted and talented program. But she couldn't read very well.
"There was no rhyme or reason to reading for me," she said. "When a teacher would dictate a word and say, 'Tell me how you think you can spell it,' I sat there with my mouth open while other kids gave spellings, and I thought, 'How do they even know where to begin?' I was totally lost."
Woodworth went to public school in Owosso, Michigan, in the 1990s. She says sounds and letters just didn't make sense to her, and she doesn't remember anyone teaching her how to read. So she came up with her own strategies to get through text.
Strategy 1: Memorize as many words as possible. "Words were like pictures to me," she said. "I had a really good memory. "
Strategy 2: Guess the words based on context. If she came across a word she didn't have in her visual memory bank, she'd look at the first letter and come up with a word that seemed to make sense. Reading was kind of like a game of 20 Questions: What word could this be?
Strategy 3: If all else failed, she'd skip the words she didn't know.
Most of the time, she could get the gist of what she was reading. But getting through text took forever. "I hated reading because it was taxing," she said. "I'd get through a chapter and my brain hurt by the end of it. I wasn't excited to learn."
No one knew how much she struggled, not even her parents. Her reading strategies were her "dirty little secrets."
Molly Woodworth (left) with her aunt, Nora Chahbazi, outside the Ounce of Prevention Reading Center in Flushing, Michigan. Emily Hanford | APM ReportsWoodworth, who now works in accounting,1 says she's still not a very good reader and tears up when she talks about it. Reading "influences every aspect of your life," she said. She's determined to make sure her own kids get off to a better start than she did.
Reading "influences every aspect of your life," she said. She's determined to make sure her own kids get off to a better start than she did.
That's why she was so alarmed to see how her oldest child, Claire, was being taught to read in school.
As long as this disproven theory remains part of American education, many kids will likely struggle to learn how to read.
A couple of years ago, Woodworth was volunteering in Claire's kindergarten classroom. The class was reading a book together and the teacher was telling the children to practice the strategies that good readers use.
The teacher said, "If you don't know the word, just look at this picture up here," Woodworth recalled. "There was a fox and a bear in the picture. And the word was bear, and she said, 'Look at the first letter. It's a "b." Is it fox or bear?'"
Woodworth was stunned. "I thought, 'Oh my God, those are my strategies.' Those are the things I taught myself to look like a good reader, not the things that good readers do," she said. "These kids were being taught my dirty little secrets."
"These kids were being taught my dirty little secrets."
She went to the teacher and expressed her concerns. The teacher told her she was teaching reading the way the curriculum told her to.
Woodworth had stumbled on to American education's own little secret about reading: Elementary schools across the country are teaching children to be poor readers — and educators may not even know it.
For decades, reading instruction in American schools has been rooted in a flawed theory about how reading works, a theory that was debunked decades ago by cognitive scientists, yet remains deeply embedded in teaching practices and curriculum materials. As a result, the strategies that struggling readers use to get by — memorizing words, using context to guess words, skipping words they don't know — are the strategies that many beginning readers are taught in school. This makes it harder for many kids to learn how to read, and children who don't get off to a good start in reading find it difficult to ever master the process. 2
2
A shocking number of kids in the United States can't read very well. A third of all fourth-graders can't read at a basic level, and most students are still not proficient readers by the time they finish high school.
Percentage of U.S. fourth-graders below basic level in reading
SOURCE: The National Assessment of Educational Progress. *In 1992 and 1994, testing accommodations were not permitted.
When kids struggle to learn how to read, it can lead to a downward spiral in which behavior, vocabulary, knowledge and other cognitive skills are eventually affected by slow reading development.3 A disproportionate number of poor readers become high school dropouts and end up in the criminal justice system.4
The fact that a disproven theory about how reading works is still driving the way many children are taught to read is part of the problem. School districts spend hundreds of millions of taxpayer dollars on curriculum materials that include this theory. Teachers are taught the theory in their teacher preparation programs and on the job. As long as this disproven theory remains part of American education, many kids will likely struggle to learn how to read.
Teachers are taught the theory in their teacher preparation programs and on the job. As long as this disproven theory remains part of American education, many kids will likely struggle to learn how to read.
Percentage of U.S. 12th-graders proficient in reading
SOURCE: The National Assessment of Educational Progress. *In 1992 and 1994, testing accommodations were not permitted.
The origins
The theory is known as "three cueing." The name comes from the notion that readers use three different kinds of information — or "cues" — to identify words as they are reading.
The theory was first proposed in 1967, when an education professor named Ken Goodman presented a paper at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association in New York City.
In the paper,5 Goodman rejected the idea that reading is a precise process that involves exact or detailed perception of letters or words. Instead, he argued that as people read, they make predictions about the words on the page using these three cues:
graphic cues (what do the letters tell you about what the word might be?)
syntactic cues (what kind of word could it be, for example, a noun or a verb?)
semantic cues (what word would make sense here, based on the context?)
Goodman concluded that:
Skill in reading involves not greater precision, but more accurate first guesses based on better sampling techniques, greater control over language structure, broadened experiences and increased conceptual development. As the child develops reading skill and speed, he uses increasingly fewer graphic cues.
As the child develops reading skill and speed, he uses increasingly fewer graphic cues.
Goodman's proposal became the theoretical basis for a new approach to teaching reading that would soon take hold in American schools.
Previously, the question of how to teach reading had focused on one of two basic ideas.
One idea is that reading is a visual memory process. The teaching method associated with this idea is known as "whole word." The whole word approach was perhaps best embodied in the "Dick and Jane" books that first appeared in the 1930s. The books rely on word repetition, and pictures to support the meaning of the text. The idea is that if you see words enough, you eventually store them in your memory as visual images.
The other idea is that reading requires knowledge of the relationships between sounds and letters. Children learn to read by sounding out words. This approach is known as phonics. It goes way back, popularized in the 1800s with the McGuffey readers.
These two ideas — whole word and phonics — had been taking turns as the favored way to teach reading until Goodman came along with what came to be known among educators as the "three-cueing system."
In the cueing theory of how reading works, when a child comes to a word she doesn't know, the teacher encourages her to think of a word that makes sense and asks: Does it look right? Does it sound right? If a word checks out on the basis of those questions, the child is getting it. She's on the path to skilled reading.
Teachers may not know the term "three cueing," but they're probably familiar with "MSV." M stands for using meaning to figure out what a word is, S for using sentence structure and V for using visual information (i.e., the letters in the words). MSV is a cueing idea that can be traced back to the late Marie Clay, a developmental psychologist from New Zealand who first laid out her theories about reading in a dissertation in the 1960s.6
Clay developed her cueing theory independently of Goodman, but they met several times and had similar ideas about the reading process. Their theories were based on observational research. They would listen to children read, note the kinds of errors they made, and use that information to identify a child's reading difficulties. For example, a child who says "horse" when the word was "house" is probably relying too much on visual, or graphic, cues. A teacher in this case would encourage the child to pay more attention to what word would make sense in the sentence.
Their theories were based on observational research. They would listen to children read, note the kinds of errors they made, and use that information to identify a child's reading difficulties. For example, a child who says "horse" when the word was "house" is probably relying too much on visual, or graphic, cues. A teacher in this case would encourage the child to pay more attention to what word would make sense in the sentence.
Goodman and Clay believed that letters were the least reliable of the three cues, and that as people became better readers, they no longer needed to pay attention to all the letters in words. "In efficient word perception the reader relies mostly on the sentence and its meaning and some selected features of the forms of words," Clay wrote.7 For Goodman, accurate word recognition was not necessarily the goal of reading. The goal was to comprehend text.8 If the sentences were making sense, the reader must be getting the words right, or right enough.
These ideas soon became the foundation for how reading was taught in many schools. Goodman's three-cueing idea formed the theoretical basis of an approach known as "whole language" that by the late 1980s had taken hold throughout America.9 Clay built her cueing ideas into a reading intervention program for struggling first-graders called Reading Recovery. It was implemented across New Zealand in the 1980s and went on to become one of the world's most widely used reading intervention programs.10
Goodman's three-cueing idea formed the theoretical basis of an approach known as "whole language" that by the late 1980s had taken hold throughout America.9 Clay built her cueing ideas into a reading intervention program for struggling first-graders called Reading Recovery. It was implemented across New Zealand in the 1980s and went on to become one of the world's most widely used reading intervention programs.10
But while cueing was taking hold in schools, scientists were busy studying the cognitive processes involved in reading words. And they came to different conclusions about how people read.11
First-graders in Oakland, California, practice reading. Hasain Rasheed for APM ReportsScientists take on three cueing
It was the early 1970s, and Keith Stanovich was working on his doctorate in psychology at the University of Michigan. He thought the reading field was ready for an infusion of knowledge from the "cognitive revolution" that was underway in psychology. Stanovich had a background in experimental science and an interest in learning and cognition due in part to the influence of his wife, Paula, who was a special education teacher.
Stanovich had a background in experimental science and an interest in learning and cognition due in part to the influence of his wife, Paula, who was a special education teacher.
Stanovich wanted to understand how people read words.12 He knew about Goodman's work and thought he was probably right that as people become better readers, they relied more on their knowledge of vocabulary and language structure to read words and didn't need to pay as much attention to the letters.
So, in 1975, Stanovich and a fellow graduate student set out to test the idea in their lab. They recruited readers of various ages and abilities and gave them a series of word-reading tasks. Their hypothesis was that skilled readers rely more on contextual cues to recognize words than poor readers, who probably weren't as good at using context.
They couldn't have been more wrong.
"To our surprise, all of our research results pointed in the opposite direction," Stanovich wrote. "It was the poorer readers, not the more skilled readers, who were more reliant on context to facilitate word recognition. "13
"13
The skilled readers could instantly recognize words without relying on context. Other researchers have confirmed these findings with similar experiments. It turns out that the ability to read words in isolation quickly and accurately is the hallmark of being a skilled reader. This is now one of the most consistent and well-replicated findings in all of reading research.14
Other studies revealed further problems with the cueing theory:15
Skilled readers don't scan words and sample from the graphic cues in an incidental way; instead, they very quickly recognize a word as a sequence of letters. That's how good readers instantly know the difference between "house" and "horse," for example.
Experiments that force people to use context to predict words show that even skilled readers can correctly guess only a fraction of the words; this is one reason people who rely on context to identify words are poor readers.
Weak word recognition skills are the most common and debilitating source of reading problems.
 16
16
The results of these studies are not controversial or contested among scientists who study reading. The findings have been incorporated into every major scientific model of how reading works.
But cueing is still alive and well in schools.
Picture Power!
It's not hard to find examples of the cueing system. A quick search on Google, Pinterest or Teachers Pay Teachers turns up plenty of lesson plans, teaching guides and classroom posters. One popular poster has cute cartoon characters to remind children they have lots of strategies to use when they're stuck on a word, including looking at the picture (Eagle Eye), getting their lips ready to try the first sound (Lips the Fish), or just skipping the word altogether (Skippy Frog).
There are videos online where you can see cueing in action. In one video posted on The Teaching Channel,17 a kindergarten teacher in Oakland, California, instructs her students to use "picture power" to identify the words on the page. The goal of the lesson, according to the teacher, is for the students to "use the picture and a first sound to determine an unknown word in their book."
The goal of the lesson, according to the teacher, is for the students to "use the picture and a first sound to determine an unknown word in their book."
The class reads a book together called "In the Garden." On each page, there's a picture of something you might find in a garden. It's what's known as a predictable book; the sentences are all the same except for the last word.
The children have been taught to memorize the words "look," "at," and "the." The challenge is getting the last word in the sentence. The lesson plan tells the teacher to cover up the word with a sticky note.
In the video, the wiggly kindergarteners sitting cross-legged on the floor come to a page with a picture of a butterfly. The teacher tells the kids that she's guessing the word is going to be butterfly. She uncovers the word to check on the accuracy of her guess.
"Look at that," she tells the children, pointing to the first letter of the word. "It starts with the /b/ /b/ /b/. " The class reads the sentence together as the teacher points to the words. "Look at the butterfly!" they yell out excitedly.
" The class reads the sentence together as the teacher points to the words. "Look at the butterfly!" they yell out excitedly.
This lesson comes from "Units of Study for Teaching Reading," more commonly known as "reader's workshop."18 According to the lesson plan, this lesson teaches children to "know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words."19
But the children were not taught to decode words in this lesson. They were taught to guess words using pictures and patterns — hallmarks of the three-cueing system.
The author of Units of Study for Teaching Reading, Lucy Calkins, often refers to cueing in her published work.20 She uses the term MSV — the meaning, structure and visual idea that originally came from Clay in New Zealand.
Then there is Fountas and Pinnell Literacy, started by Irene Fountas and Gay Su Pinnell, teachers who learned the MSV concept from Clay in the 1980s.21
Fountas and Pinnell have written several books about teaching reading, including a best-seller about a widely used instructional approach called "Guided Reading. " They also created a reading assessment system that uses what are called "leveled books."22 Children start with predictable books like "In the Garden" and move up levels as they're able to "read" the words. But many of the words in those books — butterfly, caterpillar — are words that beginning readers haven't been taught to decode yet. One purpose of the books is to teach children that when they get to a word they don't know, they can use context to figure it out.
" They also created a reading assessment system that uses what are called "leveled books."22 Children start with predictable books like "In the Garden" and move up levels as they're able to "read" the words. But many of the words in those books — butterfly, caterpillar — are words that beginning readers haven't been taught to decode yet. One purpose of the books is to teach children that when they get to a word they don't know, they can use context to figure it out.
When put into practice in the classroom, these approaches can cause problems for children when they are learning to read.
'That is not reading'
Margaret Goldberg, a teacher and literacy coach in the Oakland Unified School District, remembers a moment when she realized what a problem the three-cueing approach was. She was with a first-grader named Rodney when he came to a page with a picture of a girl licking an ice cream cone and a dog licking a bone.
The text said: "My little dog likes to eat with me. "
"
But Rodney said: "My dog likes to lick his bone."
Rodney breezed right through it, unaware that he hadn't read the sentence on the page.
Goldberg realized lots of her students couldn't actually read the words in their books; instead, they were memorizing sentence patterns and using the pictures to guess. One little boy exclaimed, "I can read this book with my eyes shut!"
"Oh no," Goldberg thought. "That is not reading."
Goldberg had been hired by the Oakland schools in 2015 to help struggling readers by teaching a Fountas and Pinnell program called "Leveled Literacy Intervention" that uses leveled books and the cueing approach.23
Around the same time, Goldberg was trained in a program that uses a different strategy for teaching children how to read words. The program is called "Systematic Instruction in Phonological Awareness, Phonics, and Sight Words," or SIPPS.24 It's a phonics program that teaches children how to sound out words and uses what are known as "decodable books. " Most words in the books have spelling patterns that kids have been taught in their phonics lessons.
" Most words in the books have spelling patterns that kids have been taught in their phonics lessons.
Goldberg decided to teach some of her students using the phonics program and some of her students using three cueing. And she began to notice differences between the two groups of kids. "Not just in their abilities to read," she said, "but in the way they approached their reading."
Goldberg and a colleague recorded first-graders talking about what makes them good readers.
One video shows Mia, on the left, who was in the phonics program. Mia says she's a good reader because she looks at the words and sounds them out. JaBrea, on the right, was taught the cueing system. JaBrea says: "I look at the pictures and I read it."
Courtesy of Margaret Goldberg, Oakland Unified School District
It was clear to Goldberg after just a few months of teaching both approaches that the students learning phonics were doing better. "One of the things that I still struggle with is a lot of guilt," she said.
"One of the things that I still struggle with is a lot of guilt," she said.
She thinks the students who learned three cueing were actually harmed by the approach. "I did lasting damage to these kids. It was so hard to ever get them to stop looking at a picture to guess what a word would be. It was so hard to ever get them to slow down and sound a word out because they had had this experience of knowing that you predict what you read before you read it."
Goldberg soon discovered the decades of scientific evidence against cueing.25 She was shocked. She had never come across any of this science in her teacher preparation or on the job.
And she started to wonder why not.
Balanced Literacy
People have been arguing for centuries about how children should be taught to read. The fight has mostly focused on whether to teach phonics.
The whole language movement of the late 20th century was perhaps the zenith of the anti-phonics argument.26 Phonics instruction was seen as tedious, time-consuming and ultimately unnecessary. Why? Because — according to the three-cueing theory — readers can use other, more reliable cues to figure out what the words say.27
Why? Because — according to the three-cueing theory — readers can use other, more reliable cues to figure out what the words say.27
Marilyn Adams came across this belief in the early 1990s. She's a cognitive and developmental psychologist who had just written a book summarizing the research on how children learn to read.28 One big takeaway from the book is that becoming a skilled reader of English requires knowledge of sound-spelling correspondences.29 Another big takeaway is that many kids were not being taught this in school.
Soon after the book was published, Adams was describing her findings to a group of teachers and state education officials in Sacramento, California. She was sensing discomfort and confusion in the room. "And I just stopped and said, 'What is it that I'm missing?'" she recalled. "'What is it that we need to talk about? Help me.'"
A woman raised her hand and asked: "What does this have to do with the three-cueing system?" Marilyn didn't know what the three-cueing system was. "I think I blew all of their fuses that I did not [know what it was] since this was so fundamental to being an elementary reading teacher," she said. "How could I present myself to them as an expert on reading and not know about this?"
"I think I blew all of their fuses that I did not [know what it was] since this was so fundamental to being an elementary reading teacher," she said. "How could I present myself to them as an expert on reading and not know about this?"
The teachers drew her a Venn diagram of the three-cueing system. It looked something like this:
Adams thought this diagram made perfect sense. The research clearly shows that readers use all of these cues to understand what they're reading.
But Adams soon figured out the disconnect. Teachers understood these cues not just as the way readers construct meaning from text, but as the way readers actually identify the words on the page. And they thought that teaching kids to decode or sound out words was not necessary.
"The most important thing was for the children to understand and enjoy the text," Adams said. "And from that understanding and joy of reading, the words on the page would just pop out at them."
She would explain to teachers at every opportunity that explicitly teaching children about the relationships between sounds and letters is essential to ensure all kids get off to a good start in reading. But she got tons of pushback from teachers. "They didn't want to teach phonics!" she recalled in frustration.
But she got tons of pushback from teachers. "They didn't want to teach phonics!" she recalled in frustration.
In 1998, Adams wrote a book chapter about how the three-cueing system conflicts with what researchers have figured out about reading. She hoped it would help put three cueing to rest.30
By this time, the scientific research on reading was gaining traction. In 2000, a national panel convened by Congress to review the evidence on how to teach reading came out with a report.31 It identified several essential components of reading instruction, including vocabulary, comprehension and phonics. The evidence that phonics instruction enhances children's success in learning how to read was clear and compelling. National reports on reading a few years later in the United Kingdom and Australia came to the same conclusion.32
"When I got into the classroom and someone told me to use this practice, I didn't question it."
-Stacey Cherny
Eventually, many whole language supporters accepted the weight of the scientific evidence about the importance of phonics instruction. They started adding phonics to their books and materials and renamed their approach "balanced literacy."
They started adding phonics to their books and materials and renamed their approach "balanced literacy."
But they didn't get rid of the three-cueing system.
Balanced literacy proponents will tell you their approach is a mix of phonics instruction with plenty of time for kids to read and enjoy books. But look carefully at the materials and you'll see that's not really what balanced literacy is mixing. Instead, it's mixing a bunch of different ideas about how kids learn to read. It's a little bit of whole word instruction with long lists of words for kids to memorize. It's a little bit of phonics. And fundamentally, it's the idea that children should be taught to read using the three-cueing system.
And it turns out cueing may actually prevent kids from focusing on words in the way they need to become skilled readers.
Mapping the words
PREVIOUSLY
To understand why cueing can get in the way of children's reading development, it's essential to understand how our brains process the words we see.
Reading scientists have known for decades that the hallmark of being a skilled reader is the ability to instantly and accurately recognize words.33 If you're a skilled reader, your brain has gotten so good at reading words that you process the word "chair" faster than you process a picture of a chair.34 You know tens of thousands of words instantly, on sight. How did you learn to do that?
It happens through a process called "orthographic mapping."35 This occurs when you pay attention to the details of a written word and link the word's pronunciation and meaning with its sequence of letters.36 A child knows the meaning and pronunciation of "pony." The word gets mapped to his memory when he links the sounds /p/ /o/ /n/ /y/ to the written word "pony."
That requires an awareness of the speech sounds in words and an understanding of how those sounds are represented by letters.37 In other words, you need phonics skills.
Here's what happens when a reader who has good phonics skills comes to a word she doesn't recognize in print. She stops at the word and sounds it out. If it's a word she knows the meaning of, she has now linked the spelling of the word with its pronunciation. If she doesn't know the meaning of the word, she can use context to try to figure it out.
She stops at the word and sounds it out. If it's a word she knows the meaning of, she has now linked the spelling of the word with its pronunciation. If she doesn't know the meaning of the word, she can use context to try to figure it out.
By about second grade, a typically developing reader needs just a few exposures to a word through understanding both the pronunciation and the spelling for that word to be stored in her memory.38 She doesn't know that word because she memorized it as a visual image. She knows that word because at some point she successfully sounded it out.
The more words she stores in her memory this way, the more she can focus on the meaning of what she's reading; she'll eventually be using less brain power to identify words and will be able to devote more brain power to comprehending what she's reading.39
But when children don't have good phonics skills, the process is different.
"They sample from the letters because they're not good at sounding them out," said David Kilpatrick, a psychology professor at SUNY Cortland and the author of a book about preventing reading difficulties. 40 "And they use context."
40 "And they use context."
In other words, when people don't have good phonics skills, they use the cueing system.
"The three-cueing system is the way poor readers read," said Kilpatrick.
And if teachers use the cueing system to teach reading, Kilpatrick says they're not just teaching children the habits of poor readers, they are actually impeding the orthographic mapping process.41
"The minute you ask them just to pay attention to the first letter or look at the picture, look at the context, you're drawing their attention away from the very thing that they need to interact with in order for them to read the word [and] remember the word," Kilpatrick said. In this way, he said, three cueing can actually prevent the critical learning that's necessary for a child to become a skilled reader.
In many balanced literacy classrooms, children are taught phonics and the cueing system. Some kids who are taught both approaches realize pretty quickly that sounding out a word is the most efficient and reliable way to know what it is. Those kids tend to have an easier time understanding the ways that sounds and letters relate. They'll drop the cueing strategies and begin building that big bank of instantly known words that is so necessary for skilled reading.
Those kids tend to have an easier time understanding the ways that sounds and letters relate. They'll drop the cueing strategies and begin building that big bank of instantly known words that is so necessary for skilled reading.
But some children will skip the sounding out if they're taught they have other options. Phonics is challenging for many kids. The cueing strategies seem quicker and easier at first. And by using context and memorizing a bunch of words, many children can look like good readers — until they get to about third grade, when their books begin to have more words, longer words, and fewer pictures. Then they're stuck. They haven't developed their sounding-out skills. Their bank of known words is limited. Reading is slow and laborious and they don't like it, so they don't do it if they don't have to. While their peers who mastered decoding early are reading and teaching themselves new words every day, the kids who clung to the cueing approach are falling further and further behind. 42
42
These poor reading habits, once ingrained at a young age, can follow kids into high school. Some kids who were taught the cueing approach never become good readers. Not because they're incapable of learning to read well but because they were taught the strategies of struggling readers.
Margaret Goldberg (second from left) and Lani Mednick (right) are literacy coaches for the Oakland Unified School District. Dana Cilono (left) was with the charter school network Education for Change, and Erin Cox is with Aspire Public Schools. They are working on projects to rid their schools of the three-cueing system. Hasain Rasheed for APM Reports'So what if they use the picture?'
Once Margaret Goldberg discovered the cognitive science evidence against cueing, she wanted her colleagues in the Oakland school district to know about it too.
Over the past two years, Goldberg and a fellow literacy coach named Lani Mednick have been leading a grant-funded pilot project to improve reading achievement in the Oakland schools. 43
43
They have their work cut out for them. Nearly half the district's third-graders are below grade level in reading. Goldberg and Mednick want to raise questions about how kids in Oakland are being taught to read.
They meet every couple weeks with literacy coaches from the 10 elementary schools in the pilot program. They read and discuss articles about the scientific research on reading. At a meeting in March, the coaches watched the video of the "picture power" lesson.
"This teacher meant well," Mednick said to the coaches after they watched the lesson. "It seemed like she believed this lesson would ensure her students would be on the road toward reading."
Mednick wanted the coaches to consider the beliefs about reading that would lead to the creation of a lesson like "picture power." The Oakland schools purchased the Units of Study for Teaching Reading series, which includes the "picture power" lesson, as part of a balanced literacy initiative the district began about 10 years ago. The district also bought the Fountas and Pinnell assessment system.
The district also bought the Fountas and Pinnell assessment system.
The coaches saw right away that "picture power" was designed to teach kids the cueing system. But they said many teachers don't see any problem with cueing. After all, one of the cues is to look at the letters in the word. What's wrong with teaching kids lots of different strategies to figure out unknown words?44
"I remember before we started looking at the science and everything, I thought to myself, 'Reading is so hard for kids, so what if they use the picture?'" said Soraya Sajous-Brooks, the early literacy coach at Prescott Elementary School in West Oakland. "Like, use everything you've got."
But she's come to understand that cueing sends the message to kids that they don't need to sound out words. Her students would get phonics instruction in one part of the day. Then they'd go reader's workshop and be taught that when they come to a word they don't know, they have lots of strategies. They can sound it out. They can also check the first letter, look at the picture, think of a word that makes sense.
They can also check the first letter, look at the picture, think of a word that makes sense.
Teaching cueing and phonics doesn't work, Sajous-Brooks said. "One negates the other."
Goldberg and Mednick want to show the district there's a better way to teach reading. Schools in the pilot project used grant money to buy new materials that steer clear of the three-cueing idea. Two charter school networks in Oakland are working on similar projects to move their schools away from cueing.
To see what it looks like, I visited a first-grade classroom at a charter school in Oakland called Achieve Academy.45
One part of the day was explicit phonics instruction.46 The students were divided into small groups based on their skill level. They met with their teacher, Andrea Ruiz, at a kidney-shaped table in a corner of the classroom. The lowest-level group worked on identifying the speech sounds in words like "skin" and "skip." The highest-level group learned how verbs like "spy" and "cry" are spelled as "spied' and 'cried" in the past tense.
There were also vocabulary lessons.47 The entire class gathered on a rug at the front of the classroom to talk about a book Ms. Ruiz read out loud to them. One of the words in the book was "prey."
"What animals are a chameleon's prey?" Ms. Ruiz asked the children. "Or we can also ask, what animals do chameleons hunt for food?"
The kids turned and talked to each other. "A chameleon's prey are bugs and insects and other chameleons and mice and birds," a little boy explained to his classmate. "That's it."
Other vocabulary words these first-graders had learned were posted on cards around the classroom. They included: wander, persevere, squint and scrumptious. The kids weren't expected to read those words yet. The idea is to build their oral vocabulary so that when they can read those words, they know what the words mean.
This comes straight from the scientific research, which shows that reading comprehension is the product of two things. 48 First, a child needs to be able to sound out a word. Second, the child needs to know the meaning of the word she just sounded out. So, in a first-grade classroom that's following the research, you will see explicit phonics instruction and also lessons that build oral vocabulary and background knowledge. And you will see kids practicing what they've been taught.
48 First, a child needs to be able to sound out a word. Second, the child needs to know the meaning of the word she just sounded out. So, in a first-grade classroom that's following the research, you will see explicit phonics instruction and also lessons that build oral vocabulary and background knowledge. And you will see kids practicing what they've been taught.
After their vocabulary lesson, the kids did "buddy reading." They retreated to various spots around the classroom to read books to each other. I found Belinda sitting on an adult chair at the back of the classroom, her little legs swinging. Across from her was her buddy Steven, decked out in a yellow and blue plaid shirt tucked neatly into his jeans. He held the book and pointed to the words while Belinda read.
"Ellen /m/," Belinda paused, sounding out the word "meets." She was reading a decodable book about some kids who visit a farm. Almost all of the words in the book contain spelling patterns she'd been taught in her phonics lessons.
"I am a farm here," Belinda read.
Steven did a double-take. "A farmer here," he said gently. Steven's job as Belinda's reading buddy was to help her if she missed a word or got stuck. But that didn't happen much because Belinda had been taught how to read the words. She didn't need any help from the pictures, either. She barely glanced at them as she read.
Steven and Belinda do "buddy reading." Hasain Rasheed for APM ReportsTo be clear, there's nothing wrong with pictures. They're great to look at and talk about, and they can help a child comprehend the meaning of a story. Context — including a picture if there is one — helps us understand what we're reading all the time. But if a child is being taught to use context to identify words, she's being taught to read like a poor reader.
Many educators don't know this because the cognitive science research has not made its way into many schools and schools of education.49
Ruiz didn't know about this research until the Oakland pilot project. "I didn't really know anything about how kids learn to read when I started teaching," she said. It was a relief when she came to Oakland and the curriculum spelled out that kids use meaning, structure and visual cues to figure out words. "Because I came from not having anything, I was like, 'Oh, there's a way we should teach this,'" she said.
"I didn't really know anything about how kids learn to read when I started teaching," she said. It was a relief when she came to Oakland and the curriculum spelled out that kids use meaning, structure and visual cues to figure out words. "Because I came from not having anything, I was like, 'Oh, there's a way we should teach this,'" she said.
I heard this from other educators. Cueing was appealing because they didn't know what else to do.
"When I got into the classroom and someone told me to use this practice, I didn't question it," said Stacey Cherny, a former teacher who's now principal of an elementary school in Pennsylvania. She says many teachers aren't taught what they need to know about the structure of the English language to be able to teach phonics well. She says phonics can be intimidating; three cueing isn't.
Another reason cueing holds on is that it seems to work for some children. But researchers estimate there's a percentage of kids — perhaps about 40 percent — who will learn to read no matter how they're taught. 50 According to Kilpatrick, children who learn to read with cueing are succeeding in spite of the instruction, not because of it.
50 According to Kilpatrick, children who learn to read with cueing are succeeding in spite of the instruction, not because of it.
Goldberg hopes the pilot project in Oakland will convince the district to drop all instructional materials that include cueing.
When asked about this, the Oakland superintendent's office responded with a written statement that there isn't enough evidence from the pilot project to make curriculum changes for the entire district and that the Oakland schools remain committed to balanced literacy.
Oakland's situation is no different from many other districts across the country that have invested millions of dollars in materials that include cueing.
"It feels like everyone's trusting somebody else to have done their due diligence," Goldberg said. "Classroom teachers are trusting that the materials they're being handed will work. The people who purchase the materials are trusting if they were on the market, that they will work. We're all trusting, and it's a system that is broken. "
"
'My science is different'
If cueing was debunked decades ago by cognitive scientists, why is the idea still in materials that are being sold to schools?
One answer to that question is that school districts still buy the materials. Heinemann, the company that publishes the Fountas and Pinnell and Lucy Calkins' products that the Oakland schools use, earned somewhere in the neighborhood of $500 million in 2018, according to earnings reports.51
I wanted to know what the authors of those materials make of the cognitive science research. And I wanted to give them a chance to explain the ideas behind their work. I wrote to Calkins, Fountas and Pinnell and asked for interviews. They all declined. Heinemann sent a statement that said every product the company sells is informed by extensive research.
I also asked Ken Goodman for an interview. It's been more than 50 years since he first laid out the three-cueing theory in that 1967 paper. I wanted to know what he thinks of the cognitive science research. Of the major proponents of three cueing I reached out to, he was the only one who agreed to an interview.
Of the major proponents of three cueing I reached out to, he was the only one who agreed to an interview.
I visited Goodman at his home in Tucson, Arizona. He's 91. He uses a scooter to get around, but he's still working. He just finished a new edition of one of his books.
Ken Goodman with his wife and frequent co-author, Yetta Goodman. Emily Hanford | APM ReportsWhen I asked him what he makes of the cognitive science research, he told me he thinks scientists focus too much on word recognition. He still doesn't believe accurate word recognition is necessary for reading comprehension.
"Word recognition is a preoccupation," he said. "I don't teach word recognition. I teach people to make sense of language. And learning the words is incidental to that."
He brought up the example of a child who comes to the word "horse" and says "pony" instead. His argument is that a child will still understand the meaning of the story because horse and pony are the same concept.
I pressed him on this. First of all, a pony isn't the same thing as a horse. Second, don't you want to make sure that when a child is learning to read, he understands that /p/ /o/ /n/ /y/ says "pony"? And different letters say "horse"?
He dismissed my question.
"The purpose is not to learn words," he said. "The purpose is to make sense."
Cognitive scientists don't dispute that the purpose of reading is to make sense of the text. But the question is: How can you understand what you are reading if you can't accurately read the words? And if quick and accurate word recognition is the hallmark of being a skilled reader, how does a little kid get there?
Goodman rejected the idea that you can make a distinction between skilled readers and unskilled readers; he doesn't like the value judgment that implies. He said dyslexia does not exist — despite lots of evidence that it does.52 And he said the three-cueing theory is based on years of observational research. In his view, three cueing is perfectly valid, drawn from a different kind of evidence than what scientists collect in their labs.
"My science is different," Goodman said.
This idea that there are different kinds of evidence that lead to different conclusions about how reading works is one reason people continue to disagree about how children should be taught to read. It's important for educators to understand that three cueing is based on theory and observational research and that there's decades of scientific evidence from labs all over the world that converges on a very different idea about skilled reading.
The cognitive science does not provide all the answers about how to teach children to read, but on the question of how skilled readers read words, scientists have amassed a huge body of evidence.
Goldberg thinks it's time for educators across the country to take a close look at all the materials they use to teach reading.
"We should look through the materials and search for evidence of cueing," she said. "And if it's there, don't touch it. Don't let it get near our kids, don't let it get near our classrooms, our teachers. "
"
READ NEXT Many kids struggle with reading – and children of color are far less likely to get the help they need
At a Loss for Words is one of three audio documentaries this season from the Educate podcast — stories about education, opportunity, and how people learn.
Share and discuss on Facebook
PRODUCER
Emily Hanford
EXECUTIVE EDITOR
Stephen Smith
EDITOR
Catherine Winter
ASSOCIATE PRODUCER
Alex Baumhardt
PRODUCTION HELP
John Hernandez
WEB EDITORS
Andy Kruse
Dave Mann
AUDIO MIX
Craig Thorson
Chris Julin
EDITOR-IN-CHIEF
Chris Worthington
PROJECT COORDINATOR
Shelly Langford
THEME MUSIC
Gary Meister
FACT CHECKER
Betsy Towner Levine
COPY EDITOR
Sherri Hildebrandt
SPECIAL THANKS
Sasha Aslanian
Heena Srivastava
Support for this program comes from the Spencer Foundation and Lumina Foundation.
Feedback
We're interested in hearing what impact APM Reports programs have on you. Has one of our documentaries or podcasts changed how you think about an issue? Has it led you to do something, like start a conversation or try to do something new in your community? Share your impact story.
Resources
Sign up for email notifications
Enter your address below and we'll let you know when we publish new stories.
Footnotes
1.
Molly Woodworth is finance director at a reading center in Flushing, Michigan, where she went for help in high school when she couldn't get through the ACT test. "I could not get through the reading fast enough," she said. "My tools were too slow."
↩
2.
In reading, the rich get richer and the poor get poorer. See this 1986 article by Keith Stanovich.
↩
3.
This blog has more on Matthew Effects in reading with many citations to research. You may also be interested in these articles:
You may also be interested in these articles:
Are reading and behavior problems risk factors for each other?
Do poor readers feel angry, sad, and unpopular?
Are reading difficulties associated with bullying involvement?
↩
4.
About 16 percent of children who are not reading proficiently by the end of third grade do not graduate from high school, a rate four times greater than that for proficient readers. The link between reading problems and incarceration has been known for decades. This 1993 report concluded that "reading failure is most likely a cause, not just a correlate, for the frustration that can and does result in delinquent behavior." Other studies on the prevalence of reading problems among inmates can be found here and here.
↩
5.
Reading: A Psycholinguistic Guessing Game
↩
6.
This article provides some background on Clay's theories about the reading process.
↩
7.
You can find this quote on page 8 of Clay's book, Becoming Literate. For discussion of how this idea is not supported by empirical evidence, see this article. (The full article is only available behind a paywall.)
↩
8.
See Goodman's book, On Reading. Reading "is not a matter of careful attention to detail or concern for accuracy" because readers "get to the meaning without attending to all the detail of the letters and the words." (p. 42) "What you think you see is more important than what your eyes pick up." (p. 37) Reading "isn't recognizing words, it's making sense of print." (p.7)
↩
9.
This 1991 book chapter discusses the growth of the whole language movement in the United States and explores its theoretical underpinnings.
↩
10.
According to this 2009 article, Reading Recovery was "by far the most widely researched and widely used tutoring program in the world. " For more background on Reading Recovery and problems researchers have identified with the approach, see this article.
" For more background on Reading Recovery and problems researchers have identified with the approach, see this article.
↩
11.
Some freely available articles that summarize what scientists have figured out about how reading works include: The Cognitive Foundations of Learning to Read; Ending the Reading Wars: Reading Acquisition from Novice to Expert; What Research Tells Us About Reading Instruction; Scientific Evidence for Effective Teaching of Reading; The Massive Impact of Literacy on the Brain and its Consequences for Education; How Psychological Science Informs the Teaching of Reading. This is a summary of some of the major research on reading over time.
↩
12.
Stanovich tells the story of how he became interested in the cognitive processes involved in reading in his book Progress in Understanding Reading.
↩
13.
See Progress in Understanding Reading, p. 6.
6.
↩
14.
See Romance and Reality and the references at the end of the essay.
↩
15.
Many of the scientific papers are technical and available only behind paywalls. If you are interested in reading more about these studies, here are some of the scientists whose work you may want to look up: Charles Perfetti, Tom Nicholson, Philip Gough, William Tunmer, Keith Rayner.
There are many blogs and essays that summarize the problems with the three-cueing theory, including several by Kerry Hempenstall (for example, The Three-Cueing System: Help or Hindrance? and The Three-Cueing Model: Down for the Count?) and this one by Sebastian Wren.
Books that discuss the research evidence against cueing include Language at the Speed of Sight and Essentials of Assessing, Preventing, and Overcoming Reading Difficulties.
The audio version of this story mentions research by Donald J.
 Bolger. You can find a paper he co-authored on the role of context in word recognition here and his dissertation that includes the experiment described in the audio story here.
Bolger. You can find a paper he co-authored on the role of context in word recognition here and his dissertation that includes the experiment described in the audio story here.
↩
16.
See the books Reading Ability, Beginning to Read and these articles: Early Reading Acquisition and Its Relation to Reading Experience and Ability 10 Years Later and Cognitive Processes in Early Reading Development. See also this synthesis of the research on reading: "In the NICHD intervention studies, teaching children to use context and prediction as strategies for word recognition resulted in greater numbers of reading disabilities than instruction that taught children to use their sound-spelling knowledge as the primary strategy for word recognition."
↩
17.
You can find the video here.
↩
18.
You can find the lesson plan on page 38 (Session 6: Super Readers Put Powers Together) of the book "Super Powers: Reading with Print Strategies and Sight Word Power," part of Units of Study for Teaching Reading, Grade K.
↩
19.
This is from the Common Core State Standards (RF.K.3 K): Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.
↩
20.
See, for example, A Guide to the Reading Workshop: Primary Grades, Word Detectives: Strategies for Using High-Frequency Words and for Decoding, and The Art of Teaching Reading. You can find references to cueing on the website of the Reading and Writing Project, founded by Calkins. For example, here and here.
↩
21.
See Guided Reading (1996 and 2017) and When Readers Struggle. You can also find references to cueing on the Fountas and Pinnell Literacy website, for example here and here.
↩
22.
See Fountas & Pinnell Benchmark Assessment System.
↩
23.
See Leveled Literacy Intervention, in particular Prompting Guide Part 1 that is included as part of LLI kits.![]()
↩
24.
Goldberg found unopened materials for the SIPPS program at the school where she worked. "It was just sitting on the shelves collecting dust," she said. She didn't know anything about SIPPS, but she recognized the nonprofit that publishes it, Center for the Collaborative Classroom. Goldberg had worked for Collaborative Classroom as a materials developer for two years before starting her job with the Oakland Unified School District.
↩
25.
The first article Goldberg came across that referred to the problems with cueing was Whole Language Lives On: The Illusion of 'Balanced' Reading Instruction. She also read The Three-Cueing System: Trojan Horse?, Ten Myths of Reading Instruction, and this book.
↩
26.
The quotes collected here provide background on whole language beliefs about phonics.
↩
27.
In the cueing theory of how reading works, just a bit of phonics knowledge is enough because readers have other ways to identify words. See this piece, for example: "Some knowledge of phonics can restrict the possibilities of what the unknown words are."
See this piece, for example: "Some knowledge of phonics can restrict the possibilities of what the unknown words are."
↩
28.
Beginning to Read: Thinking and Learning about Print.
↩
29.
Recent research using Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) provides further evidence of the critical role of phonology in learning to read. See this study and this one.
↩
30.
Adams' piece about the three-cueing system was originally published in the book Literacy for All. There are also versions of it published as an article online. (The online versions don't include the appendices.)
↩
31.
The National Reading Panel Report (NRP) can be found here. A 2011 report summarizing research on the efficacy of phonics instruction since the NRP can be found here.
↩
32.
National Inquiry into the Teaching of Literacy (Australia) 2005; Independent Review of the Teaching of Early Reading Final Report (United Kingdom) 2006.
↩
33.
See this 1980 article from Keith Stanovich and also this more recent overview of the research.
↩
34.
This was established in the late 19th century by a researcher named James Cattell who compared reaction times to words and images using a newly developed timing mechanism that could measure reactions to within 1/1,000th of a second. See this book, p. 30.
↩
35.
Linnea Ehri first described the process of orthographic mapping in the 1970s. Another prominent researcher in this area is David Share.
↩
36.
Here's a blog post that describes the basics of orthographic mapping.
↩
37.
See this article and this article by Ehri.
↩
38.
See How Does Orthographic Learning Happen?, Orthographic Learning During Reading: Examining the Role of Self-Teaching and this book, p. 34.
34.
↩
39.
See What Reading Does for the Mind.
↩
40.
David Kilpatrick is author of the Essentials book cited previously as well as Equipped for Reading Success. He was a school psychologist for 28 years.
↩
41.
Teachers might be especially interested in these articles. Decoding Before Context: "We have had many conversations with teachers about the fact that the system is not only void of research and evidence, but — equally important — it is also teaching children habits that are difficult to change. Worse yet, this approach sets children up for frustration and failure." The Three Cueing System: "Are you using the three cueing system? You will know if you are using a three cueing approach to reading if you have posters or prompts in your classroom that encourage the following ..."
↩
42.
See the Matthew Effect and the Self-Teaching Hypothesis. Also see this article, which notes that "decoding problems underlie the difficulties of most primary grade students who struggle with reading."
Also see this article, which notes that "decoding problems underlie the difficulties of most primary grade students who struggle with reading."
↩
43.
The project is funded by the Kenneth Rainin Foundation.
↩
44.
"If children are taught systematic phonics in one part of the reading program but are encouraged to use context to guess at words when reading passages, they may not apply their phonics skills consistently. Thus, the phonics component of the reading program may be undermined." — from The Use of Context Cues in Reading.
↩
45.
Achieve Academy is part of the Education for Change charter school network. The other charter school network is Aspire Public Schools.
↩
46.
Andrea Ruiz uses two different phonics programs. For her lowest-level readers, she uses SIPPS. For other students, she uses Being a Reader.
↩
47.
Vocabulary lessons come from a program called Making Meaning.
↩
48.
See "The Simple View of Reading." The 1986 article that first proposed this model is here. The model has been upheld by decades of research on reading. See this 2018 article by the original researchers. Some blog posts that explain the Simple View are here, here and here. Another helpful way to understand the relationship between word recognition and skilled reading is Scarborough's Rope.
↩
49.
There's a large body of research that shows teachers are not being taught what they need to know about how children learn to read. Teacher's Knowledge about Beginning Reading Development and Instruction provides an overview. R. Malatesha Joshi at Texas A&M has done a lot of research on this topic; see this and this. The U.S. Department of Education published a study back in 2010. A report on educator preparation to teach reading in Australia cites research from the United States. There are reports on teacher prep in North Carolina and Mississippi. The National Council on Teacher Quality has produced several reports (see here and this article here). There is also this article on what teachers aren't being taught about dyslexia.
A report on educator preparation to teach reading in Australia cites research from the United States. There are reports on teacher prep in North Carolina and Mississippi. The National Council on Teacher Quality has produced several reports (see here and this article here). There is also this article on what teachers aren't being taught about dyslexia.
↩
50.
This infographic compiles estimates from several studies and experts.
↩
51.
Heinemann is a division of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. In 2018, HMH extensions businesses (which consist primarily of the "Heinemann brand, intervention and supplemental products as well as professional services") earned $584 million. Extensions businesses earnings increases in 2018 were driven primarily by higher Heinemann net sales and "the primary driver" of those sales increases were Fountas & Pinnell products.
↩
52.
There is an overwhelming amount of evidence in the research literature about the existence of dyslexia. There are many articles and other resources available at The Yale Center for Dyslexia and Creativity and on the Haskins Labs website, including this overview of the neurobiology of dyslexia. APM Reports did this "What is dyslexia?" interview in 2017 with neuroscientist Guinevere Eden. A summary of dyslexia with many citations to research is here.
↩
Teaching children to read isn’t easy. How do kids actually learn to read?
A student in a Mississippi elementary school reads a book in class. Research shows young children need explicit, systematic phonics instruction to learn how to read fluently. Credit: Terrell Clark for The Hechinger ReportTeaching kids to read isn’t easy; educators often feel strongly about what they think is the “right” way to teach this essential skill. Though teachers’ approaches may differ, the research is pretty clear on how best to help kids learn to read. Here’s what parents should look for in their children’s classroom.
Here’s what parents should look for in their children’s classroom.
How do kids actually learn how to read?
Research shows kids learn to read when they are able to identify letters or combinations of letters and connect those letters to sounds. There’s more to it, of course, like attaching meaning to words and phrases, but phonemic awareness (understanding sounds in spoken words) and an understanding of phonics (knowing that letters in print correspond to sounds) are the most basic first steps to becoming a reader.
If children can’t master phonics, they are more likely to struggle to read. That’s why researchers say explicit, systematic instruction in phonics is important: Teachers must lead students step by step through a specific sequence of letters and sounds. Kids who learn how to decode words can then apply that skill to more challenging words and ultimately read with fluency. Some kids may not need much help with phonics, especially as they get older, but experts say phonics instruction can be essential for young children and struggling readers “We don’t know how much phonics each kid needs,” said Anders Rasmussen, principal of Wood Road Elementary School in Ballston Spa, New York, who recently led the transformation of his schools’ reading program to a research-based, structured approach. “But we know no kid is hurt by getting too much of it.”
“But we know no kid is hurt by getting too much of it.”
How should your child’s school teach reading?
Timothy Shanahan, a professor emeritus at the University of Illinois at Chicago and an expert on reading instruction, said phonics are important in kindergarten through second grade and phonemic awareness should be explicitly taught in kindergarten and first grade. This view has been underscored by experts in recent years as the debate over reading instruction has intensified. But teaching kids how to read should include more than phonics, said Shanahan. They should also be exposed to oral reading, reading comprehension and writing.
The wars over how to teach reading are back. Here’s the four things you need to know.
Wiley Blevins, an author and expert on phonics, said a good test parents can use to determine whether a child is receiving research-based reading instruction is to ask their child’s teacher how reading is taught. “They should be able to tell you something more than ‘by reading lots of books’ and ‘developing a love of reading.’ ” Blevins said. Along with time dedicated to teaching phonics, Blevins said children should participate in read-alouds with their teacher to build vocabulary and content knowledge. “These read-alouds must involve interactive conversations to engage students in thinking about the content and using the vocabulary,” he said. “Too often, when time is limited, the daily read-alouds are the first thing left out of the reading time. We undervalue its impact on reading growth and must change that.”
“They should be able to tell you something more than ‘by reading lots of books’ and ‘developing a love of reading.’ ” Blevins said. Along with time dedicated to teaching phonics, Blevins said children should participate in read-alouds with their teacher to build vocabulary and content knowledge. “These read-alouds must involve interactive conversations to engage students in thinking about the content and using the vocabulary,” he said. “Too often, when time is limited, the daily read-alouds are the first thing left out of the reading time. We undervalue its impact on reading growth and must change that.”
Rasmussen’s school uses a structured approach: Children receive lessons in phonemic awareness, phonics, pre-writing and writing, vocabulary and repeated readings. Research shows this type of “systematic and intensive” approach in several aspects of literacy can turn children who struggle to read into average or above-average readers.
What should schools avoid when teaching reading?
Educators and experts say kids should be encouraged to sound out words, instead of guessing. “We really want to make sure that no kid is guessing,” Rasmussen said. “You really want … your own kid sounding out words and blending words from the earliest level on.” That means children are not told to guess an unfamiliar word by looking at a picture in the book, for example. As children encounter more challenging texts in later grades, avoiding reliance on visual cues also supports fluent reading. “When they get to ninth grade and they have to read “Of Mice and Men,” there are no picture cues,” Rasmussen said.
“We really want to make sure that no kid is guessing,” Rasmussen said. “You really want … your own kid sounding out words and blending words from the earliest level on.” That means children are not told to guess an unfamiliar word by looking at a picture in the book, for example. As children encounter more challenging texts in later grades, avoiding reliance on visual cues also supports fluent reading. “When they get to ninth grade and they have to read “Of Mice and Men,” there are no picture cues,” Rasmussen said.
Related: Teacher Voice: We need phonics, along with other supports, for reading
Blevins and Shanahan caution against organizing books by different reading levels and keeping students at one level until they read with enough fluency to move up to the next level. Although many people may think keeping students at one level will help prevent them from getting frustrated and discouraged by difficult texts, research shows that students actually learn more when they are challenged by reading materials.
Blevins said reliance on “leveled books” can contribute to “a bad habit in readers.” Because students can’t sound out many of the words, they rely on memorizing repeated words and sentence patterns, or on using picture clues to guess words. Rasmussen said making kids stick with one reading level — and, especially, consistently giving some kids texts that are below grade level, rather than giving them supports to bring them to grade level — can also lead to larger gaps in reading ability.
How do I know if a reading curriculum is effective?
Some reading curricula cover more aspects of literacy than others. While almost all programs have some research-based components, the structure of a program can make a big difference, said Rasmussen. Watching children read is the best way to tell if they are receiving proper instruction — explicit, systematic instruction in phonics to establish a foundation for reading, coupled with the use of grade-level texts, offered to all kids.
Parents who are curious about what’s included in the curriculum in their child’s classroom can find sources online, like a chart included in an article by Readingrockets.org which summarizes the various aspects of literacy, including phonics, writing and comprehension strategies, in some of the most popular reading curricula.
Blevins also suggested some questions parents can ask their child’s teacher:
- What is your phonics scope and sequence?
“If research-based, the curriculum must have a clearly defined phonics scope and sequence that serves as the spine of the instruction.” Blevins said.
- Do you have decodable readers (short books with words composed of the letters and sounds students are learning) to practice phonics?
“If no decodable or phonics readers are used, students are unlikely to get the amount of practice and application to get to mastery so they can then transfer these skills to all reading and writing experiences,” Blevins said. “If teachers say they are using leveled books, ask how many words can students sound out based on the phonics skills (teachers) have taught … Can these words be fully sounded out based on the phonics skills you taught or are children only using pieces of the word? They should be fully sounding out the words — not using just the first or first and last letters and guessing at the rest.”
“If teachers say they are using leveled books, ask how many words can students sound out based on the phonics skills (teachers) have taught … Can these words be fully sounded out based on the phonics skills you taught or are children only using pieces of the word? They should be fully sounding out the words — not using just the first or first and last letters and guessing at the rest.”
- What are you doing to build students’ vocabulary and background knowledge? How frequent is this instruction? How much time is spent each day doing this?
“It should be a lot,” Blevins said, “and much of it happens during read-alouds, especially informational texts, and science and social studies lessons.”
- Is the research used to support your reading curriculum just about the actual materials, or does it draw from a larger body of research on how children learn to read? How does it connect to the science of reading?
Teachers should be able to answer these questions, said Blevins.
What should I do if my child isn’t progressing in reading?
When a child isn’t progressing, Blevins said, the key is to find out why. “Is it a learning challenge or is your child a curriculum casualty? This is a tough one.” Blevins suggested that parents of kindergarteners and first graders ask their child’s school to test the child’s phonemic awareness, phonics and fluency.
Parents of older children should ask for a test of vocabulary. “These tests will locate some underlying issues as to why your child is struggling reading and understanding what they read,” Blevins said. “Once underlying issues are found, they can be systematically addressed.”
“We don’t know how much phonics each kid needs. But we know no kid is hurt by getting too much of it.”
Anders Rasmussen, principal of Wood Road Elementary School in Ballston Spa, New York
Rasmussen recommended parents work with their school if they are concerned about their children’s progress. By sitting and reading with their children, parents can see the kind of literacy instruction the kids are receiving. If children are trying to guess based on pictures, parents can talk to teachers about increasing phonics instruction.
By sitting and reading with their children, parents can see the kind of literacy instruction the kids are receiving. If children are trying to guess based on pictures, parents can talk to teachers about increasing phonics instruction.
“Teachers aren’t there doing necessarily bad things or disadvantaging kids purposefully or willfully,” Rasmussen said. “You have many great reading teachers using some effective strategies and some ineffective strategies.”
What can parents do at home to help their children learn to read?
Parents want to help their kids learn how to read but don’t want to push them to the point where they hate reading. “Parents at home can fall into the trap of thinking this is about drilling their kid,” said Cindy Jiban, a former educator and current principal academic lead at NWEA, a research-based non-profit focused on assessments and professional learning opportunities. “This is unfortunate,” Jiban said. “It sets up a parent-child interaction that makes it, ‘Ugh, there’s this thing that’s not fun. ’” Instead, Jiban advises making decoding playful. Here are some ideas:
’” Instead, Jiban advises making decoding playful. Here are some ideas:
- Challenge kids to find everything in the house that starts with a specific sound.
- Stretch out one word in a sentence. Ask your child to “pass the salt” but say the individual sounds in the word “salt” instead of the word itself.
- Ask your child to figure out what every family member’s name would be if it started with a “b” sound.
- Sing that annoying “Banana fana fo fanna song.” Jiban said that kind of playful activity can actually help a kid think about the sounds that correspond with letters even if they’re not looking at a letter right in front of them.
- Read your child’s favorite book over and over again. For books that children know well, Jiban suggests that children use their finger to follow along as each word is read. Parents can do the same, or come up with another strategy to help kids follow which words they’re reading on a page.
Giving a child diverse experiences that seem to have nothing to do with reading can also help a child’s reading ability. By having a variety of experiences, Rasmussen said, children will be able to apply their own knowledge to better comprehend texts about various topics.
By having a variety of experiences, Rasmussen said, children will be able to apply their own knowledge to better comprehend texts about various topics.
This story about teaching children to read was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Hechinger’s newsletter.
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
5 tips for teachers: how to instill in children an interest in reading the classics | Chalk
“They grew up with gadgets and just don’t take long texts,” literature teachers complain about their students.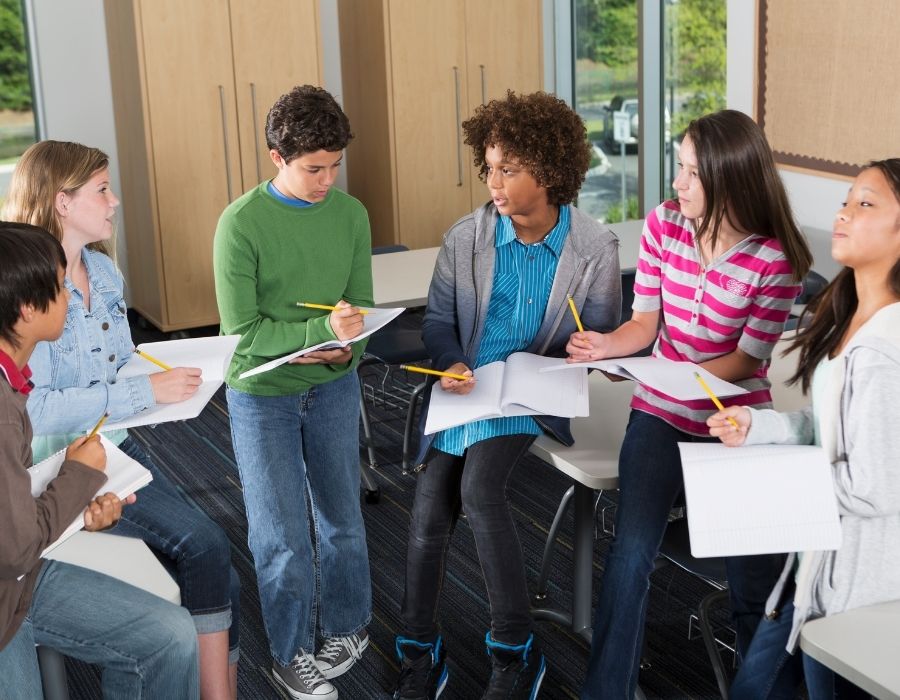 In some ways they are right, but this does not mean that nothing can be done here. Ileana Sherry, a literature teacher from the USA, did not give up and taught children to love books, who previously could not read even 10 pages. And she tells how she did it.
In some ways they are right, but this does not mean that nothing can be done here. Ileana Sherry, a literature teacher from the USA, did not give up and taught children to love books, who previously could not read even 10 pages. And she tells how she did it.
During my practice at school, I was the first to encounter a problem that is familiar to every teacher: many students simply did not want to pick up books. I read essays that looked more like carelessly copied condensed retellings for several months, got terribly angry, then began to punish children who did not read books to the end, and encourage those who did.
Unfortunately, at the end of the semester, some of my students turned out to be completely unprepared for the final work. After all, instead of helping them find the motivation to read, I completely undermined their desire to even look at books.
This experience prompted me to turn my attention to a key question in my profession: How do I encourage all students to read serious writing, including those who do not have book cravings?
Focus on those who find it difficult
Every student can read a novel. If you master this skill at school, then in the future it will be easier to develop a critical attitude not only to printed texts, but also to a wide variety of information that comes to us from the outside world. But some students avoid reading for subjective reasons.
If you master this skill at school, then in the future it will be easier to develop a critical attitude not only to printed texts, but also to a wide variety of information that comes to us from the outside world. But some students avoid reading for subjective reasons.
I had to shift my focus to help them. Previously, my program was designed for students who read whole works - that is, for those with whom it was more convenient and interesting for me to work. When I began to focus on children who experienced difficulties, for whom the full text of the work was difficult to be given, the whole class was involved in the work.
The methods that I will talk about will help organize the work in the class so that the material is accessible to students, regardless of which page they managed to read.
1. Read together
I usually review with the class the first chapter of the book, the central episode of the conflict, and quotes from different parts of the book that help to reveal its main ideas. The number of chapters and quotations that can be offered to the class will depend on the general level of knowledge.
The number of chapters and quotations that can be offered to the class will depend on the general level of knowledge.
Reading the first chapter aloud is extremely important, as it helps children overcome inertia and provides context for further independent work. And books such as The Art of Reading by Thomas Foster and The Structure of a Fiction Text by Yuri Lotman will help you learn to think more deeply about what you read.
2. Use audio books
Reading may not be available to children with dyslexia or those who have not yet fully mastered language skills. The barrier between students and the text can be overcome by providing them with an audio version of the book. To do this, teachers can use library resources, find an audio track on the Internet, or even record their own voice acting.
3. Draw parallels with real life
After graduation, students will forget most of the details, but we can help them gain knowledge that will be useful outside of school classrooms, including help to make a choice, make one or another decision . For example, while talking about Gogol's "Inspector General", you can talk about the consequences that can happen if you do the work in bad faith. And while reading "Eugene Onegin", think about what a provocation is and what it can lead to (quarrel and duel between Onegin and Lensky).
For example, while talking about Gogol's "Inspector General", you can talk about the consequences that can happen if you do the work in bad faith. And while reading "Eugene Onegin", think about what a provocation is and what it can lead to (quarrel and duel between Onegin and Lensky).
4. Prepare materials that complement the main text
Additional materials can be of different formats: poems, excerpts from newspaper articles, videos, songs. Thus, children will have several reference points that will help them learn the main themes and ideas of the work, and make their understanding more voluminous.
5. Let students choose books to read
Instead of focusing on one book, have three or more texts to choose from. In this way, you will be able to involve children in the work and provide an opportunity to tailor the curriculum to your taste and reading level.
Photo: file404 / shutterstockDon't give up
I consider myself fortunate to have been able to work at a small school. There I was able to closely monitor specific children and saw that my students were progressing from year to year. Looking at the graduates who studied with me in the 9th and 10th grades, I see that these methods gave good results.
There I was able to closely monitor specific children and saw that my students were progressing from year to year. Looking at the graduates who studied with me in the 9th and 10th grades, I see that these methods gave good results.
One of my former students in the first year after being transferred to our class opened a book to a random page and just pretended to read. In 10th grade, she could already read 100 pages. Now this girl is planning to choose English as her main subject for further study and sometimes comes to me to share her impressions of recently read books.
Don't give up if you encounter a child who doesn't seem to want to read. Read books in the classroom: together we can make education accessible to everyone.
Text adapted from Edutopia.
Cover image: Arthur Bargan / shutterstock
What teachers read during the holidays and what they advise students to read
Teachers also take a break during the winter holidays. They also walk, play with their children and read. What? We talked with three Moscow teachers about their favorite books, and also about what they discuss with their students and why it is important to read meaningfully even in math classes.
What? We talked with three Moscow teachers about their favorite books, and also about what they discuss with their students and why it is important to read meaningfully even in math classes.
Books not for “easy” reading
Vremya publishing house, 2021Svetlana Malysheva, teacher of Russian language and literature at school No. 1363:
This year my colleagues and I read some very deep stories by contemporary Russian writers. For example, Olga Gromova's novel "Sugar Child" is a story about a girl who turned out to be the daughter of an "enemy of the people". Elya and her mother, despite all the trials that they have to go through, do not lose heart: they read poetry, sing songs, really care about each other. This is a story about love and human dignity. Or another work - "The Book Thief" by Markus Zusak, a novel about the Second World War, the main character of which is a little nine-year-old girl Liesel, who fell into a foster family and loved to read. A story about honor, deprivation, true friendship, about the ability to rejoice in the midst of grief and devastation. The narration is led by Death, who observes the actions of the heroes and evaluates them. You can’t recommend all these books for “easy” reading, but they are very heartfelt, which is probably why they remained in our memory.
The narration is led by Death, who observes the actions of the heroes and evaluates them. You can’t recommend all these books for “easy” reading, but they are very heartfelt, which is probably why they remained in our memory.
I discuss such stories with my students, I try to explain what has remained misunderstood or unnoticed. But the most important thing in our communication is the ability to understand each other. Sometimes teenagers look at works that we adults are familiar with in a completely different way, they see something new in images that seemed to be exhausted. This is how real communication should be: the exchange of thoughts, opinions, ideas drawn from literature. It is much more interesting when the children themselves bring something new into the teacher's life. Therefore, we also discuss those works that the guys recommend. For example, about Olga Gromova, who was mentioned above, for the first time, a ninth-grader who read the novel "Walchen" spoke to teachers for the first time.
In our lessons with children, we use the techniques of "Meaningful Reading". We think over what we read, learn to focus on the text, analyze, work with additional sources of information. And we also develop reading speed, this is a very important skill today.
What to read: the choice of Svetlana Malysheva
- A. Zhvalevsky and E. Pasternak "Time is always good"
- R. Buie "All because of Mr. Terrapt"
- M. Ushenina "Uzlovaya Station"
- D. Accinelli "Domino effect"
- V. Kaverin "Two Captains"
- D. London "White Fang"
- E. Seton-Thompson, animal stories
Instill a love for reading and science
Book-Service AgencyMaria Galkina, mathematics teacher at school No. 1518:
Among my favorite fiction books are Fahrenheit 451 by Ray Bradbury, The Twelve Chairs by Evgeny Petrov and Ilya Ilf, "Heart of a Dog" by Mikhail Bulgakov, "The Little Prince" by Antoine de Saint-Exupery and others. After such books, I want to stop, think and talk about them not only with friends, but also with my students. At class hours, I can share with the guys my thoughts that we had and the tasks that we set after.
After such books, I want to stop, think and talk about them not only with friends, but also with my students. At class hours, I can share with the guys my thoughts that we had and the tasks that we set after.
Non-fiction literature is a great help for me as a teacher. This is a methodological storehouse for lessons and this is a wide field for working with projects and research papers of extracurricular activities on the subject. That's why I always pay a lot of attention to her in class. Well, the Mindful Reading program helps me show teenagers that math is not just a set of abstract concepts and actions with them. It is possible to isolate the mathematical essence not only when solving problems and studying new material, but also in an unusual situation for many people working with popular science texts. It is this type of literature, in my opinion, that now instills in teenagers to a greater extent not only a love of science, but also a love of reading.
Popular science magazines: the choice of Maria Galkina
- Kvantik magazine and Kvant magazine, section Kvant for younger students
- Think Magazine
- Magazine "Young Technician" and "Young Erudite"
Metasubjectivity and Literature
Phantom Press Publishing House, 2018Tatyana Nefyodova, teacher of the Russian language and literature at school No.
 1636:
1636: I try to keep abreast of all literary events. A special place on my bookshelf is occupied by stories related to moral values, cultural traditions of different peoples. It is these works that I advise children to read in accordance with their age.
Both adults and children learn life lessons from books they read. And this is possible only with careful reading and penetration into the meaning of the text. Analyzing what has been read, the child begins to pay attention to details that were not noticed during introductory reading, and, comprehending new information, to understand the content of the text more deeply. All this makes meaningful reading, for the development of which children and parents can be advised the following: put a few questions in front of the child at the beginning of reading; formulate conclusions after reading each chapter; invite students to transform the information into a mind map.
Teachers used to limit extra-curricular reading only to their subject area, but now more and more often we go into meta-subjects. The lessons include texts of different styles and content. It becomes clear that not only fiction captivates children, but also scientific and educational texts are of particular interest. I try to appeal to novelties by recommending works to my students for discussion in the class and for extracurricular reading.
The lessons include texts of different styles and content. It becomes clear that not only fiction captivates children, but also scientific and educational texts are of particular interest. I try to appeal to novelties by recommending works to my students for discussion in the class and for extracurricular reading.
What to read: the choice of Tatyana Nefedova
- Troepolsky, "White Bim Black Ear"
- L. Budogoskaya, "The Tale of a Red-haired Girl"
- I. Pirogova, "Spring rain"
- K. Bulychev, "Girl from Earth"
- T. Kryukova, "Trap for the Hero"
- A. Tolstoy, "Russian character"
- M. Boteva, T.S. Garden
- M. Shchigelsky, Ark of Time
- A. Ishimova, "History of Russia in stories for children"
- S. Soloveichik, "Teaching with passion"
- H. Hosseini, The Wind Runner
Educational program "Meaningful Reading" started in pilot mode in 102 schools in Moscow.