Teaching about syllables
Tips for Teaching Syllables - Lucky Little Learners
Written by: Jess Dalrymple
- Share
- Tweet
There’s no doubt about it – teaching syllables is an important part of reading instruction. After all, this skill shows up in primary grade level standards – regardless of where you teach. But how do you get your students to understand what syllables are, and what are the best ways to practice syllabication once it is introduced?
First, let’s dive into why it’s a benefit to young readers to understand syllables. From there, we will offer some suggestions for strategies and resources teachers can use to make teaching syllables a breeze!
Why do kids need to understand syllables?
When younger kids can hear the different sounds and syllables in words, they will have the foundation to be able to chunk apart and blend together sounds and word parts as beginning readers.
As children progress through grade levels, having a strong understanding of how words are broken into syllables can help them decode, pronounce, and spell longer words. In fact, did you know that over 80% of English words have two or more syllables! So, having a strategy for how to chunk multisyllabic words into single syllables is much more efficient than trying to sound out a long string of letters.
How to Teach Syllables
Download Under Construction HERE
Explain what syllables are
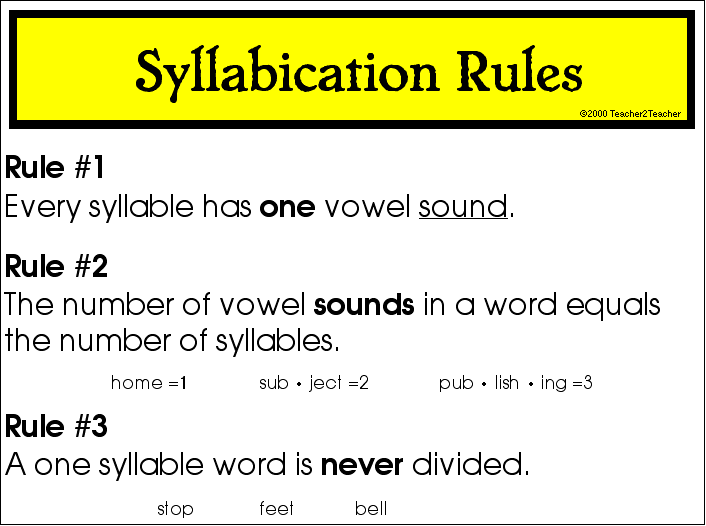
Basically, a syllable is a single vowel sound in a word. This can be confusing for kids because they will want to count the number of vowels they see in a written word. This will take some practice, but it is important to help kids understand that syllables are not single vowels; they are single vowel sounds. Try demonstrating this with a word like “beautiful”. There are five vowels, but when you listen closely, there are three vowel sounds.
- beau
- ti
- ful
Another way to explain is by calling syllables “beats” in words. Try clapping the syllables in students’ names and in names of objects around the classroom.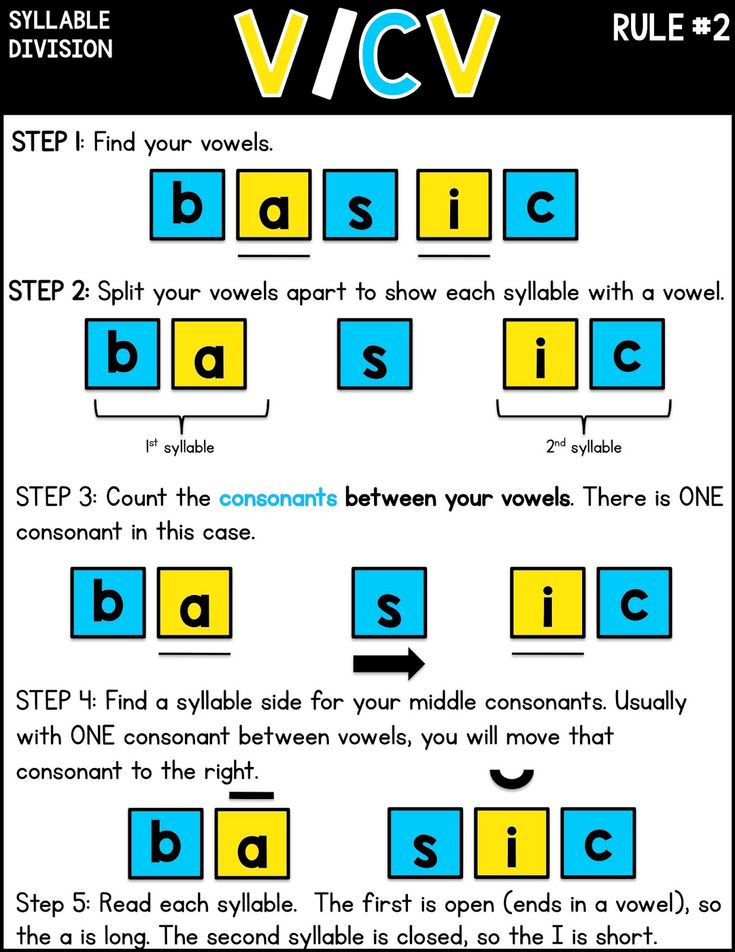 Have students join in as they get more comfortable! Take this one step further and sort the people and objects into groups by the number of syllables.
Have students join in as they get more comfortable! Take this one step further and sort the people and objects into groups by the number of syllables.
One more tip: Try putting your hand under your chin to count the number of syllables in words. The number of times your chin drops when you’re saying a word is the number of syllables the word has.
Try it! How many times does your chin touch your hand when you say the word ‘banana’? Your chin should have dropped three times – ‘ba-na-na’. This works because your mouth has to change positions to form a new vowel sound (aka syllable), causing your chin to drop.
Finally, kids will love this video explaining syllables:
Examples of Syllables
- ‘dog’ – one syllable
- ‘pen-cil’ – two syllables
- ‘bi-cy-cle’ – three syllables
- ‘cal-cu-la-tor’ – four syllables
- ‘hip-popot-a-mus – five syllables
Here’s a free site called “How Many Syllables” where you can type a word and it will tell you how many syllables, how to divide the word into syllables, and what the primary and secondary syllables are (to help with pronunciation).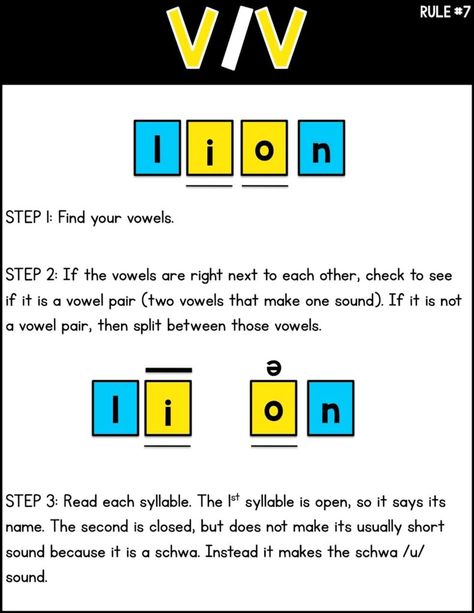
4 Strategies for Teaching Syllables
1- Count Syllables
Practicing syllable counting can be simple! Call out the number of syllables in names when dismissing kids to line up for lunch, “If your first name has three syllables, line up.” Or, send kids to their literacy center by telling them to hop for each syllable in their name. “Jess-i-ca, syllable hop on over to the writing center”.
2- Teach Younger Students to Segment by Syllables
When you notice a student struggling to read a longer word, cover up all but the first syllable. Once they sound out the first syllable, reveal the next syllable to sound out, then have them put the two syllables together. Learn more about reading strategies to use with young readers.
3-
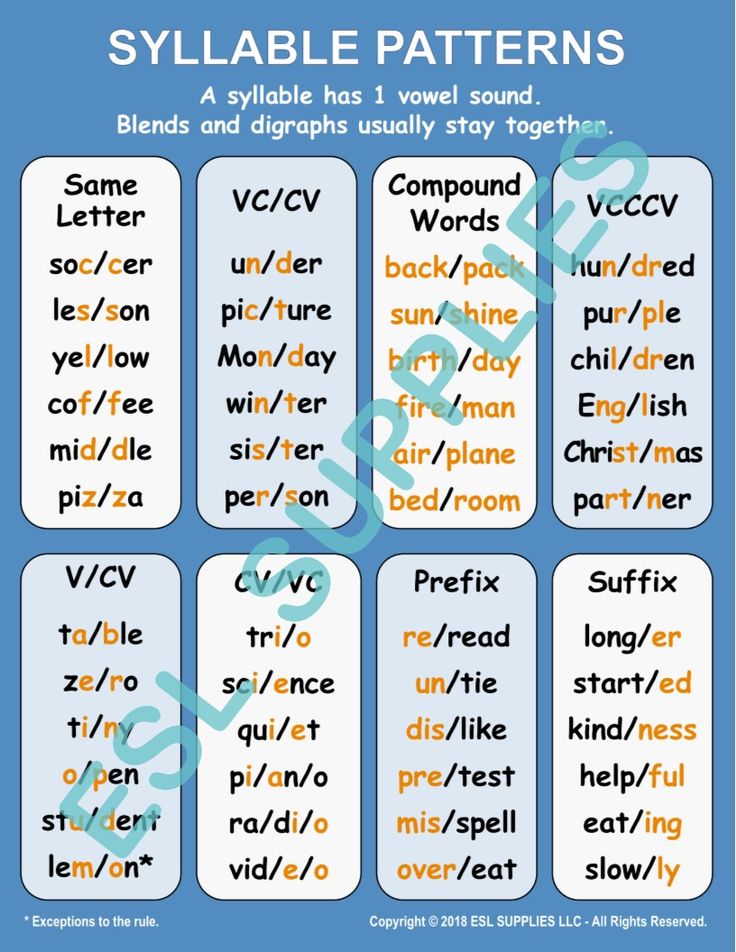
Teach Older Students Syllable Division- Look at the word. Mark the vowels.
- Determine which syllable division rule (VC/CV, V/CV, VC/V, or V/V) applies.
- Cut or mark the word accordingly.
- Read the word.
4- Practice Syllables With Poetry
Haikus
Haikus are fun to write! Kids can get creative and write about any topic, but the poem must be three lines long:
- 1st line – 5 syllables
- 2nd line – 7 syllables
- 3rd line – 5 syllables
Limericks
Limericks are also a form of poetry that requires syllable counting!
- They are five lines long.
- Lines 1, 2, and 5 rhyme with one another.
- Lines 3 and 4 rhyme with each other.

- They have a distinctive rhythm (based on number of syllables)
- They are usually funny.
This site has excellent directions for how to write a limerick.
Resources for Teaching Syllables
Lucky Little Learners has something for everyone when it comes to supporting the teaching of syllables in K-2 classrooms! Our syllables resources are organized by grade level below.
Kindergarten & 1st Grade Syllable Resources
Kindergarten ELA Toothy
- syllable counting: 1-4 syllable words
Download Syllable Counting Toothy HERE
1st & 2nd Grade Phonics Toothy
- Practice with spelling patterns to master decoding by syllables
Download 1st & 2nd Grade Syllables Toothy HERE
P
honological Awareness ToothyIt’s the Toothy® you know and love, with a twist! This phonological awareness resource includes 45 sets of phonological and phonemic awareness skills. It includes early, basic, and advanced phonological awareness activity sets. Toothy® task kits are highly engaging task card games that allow students to practice skills by answering questions in a fun, motivating way.
Toothy® task kits are highly engaging task card games that allow students to practice skills by answering questions in a fun, motivating way.
Download Phonological Awareness Toothy HERE
2nd Grade Syllable Resources
Phonics Day By DayDaily review all year with all essential 2nd grade phonics skills, including syllables!
- CVC Syllables
- CV Syllables
- CVCe Syllables
- CVVC Syllables
- R-Controlled Syllables
- C + le Syllables
- CV Two Syllables
- CVCe Two Syllables
- CVVC Two Syllables
- Multisyllabic Words
Download Phonics Day by Day HERE
Multisyllabic Words Toothy Pack
Kids get to play the Toothy game while focusing on syllable types and decoding multisyllabic words:
- Counting Syllables
- Closed Syllables / CVC
- Multisyllabic CVCe Words
- Open Syllables
- Two-Syllable Long Vowel Words
- Final Stable Syllables
Download MultiSyllabic Words Toothy HERE
Phonics Centers for 2nd Grade & 1st & 2nd Grade Phonics Toothy
Students get tons of practice with spelling patterns to master decoding by syllables with these resources.
Download Phonics Centers HERE
Download Phonics Toothy HERE
- Share
- Tweet
Syllable Games | Classroom Strategies
As students progress in their literacy understanding, they move from reading and writing single syllable words (often with consonant-vowel-consonant constructions) to reading and writing multisyllabic words. Instruction focused on teaching students about syllables often focuses on teaching different types of syllables (open and closed) and what occurs when syllables join together within a word.
| How to use: | Individually | With small groups | Whole class setting |
More phonological awareness strategies
Why teach about syllables?
- Dividing words into parts, or "chunks" helps speed the process of decoding.
- Knowing the rules for syllable division can students read words more accurately and fluently.
- Understanding syllables can also help students learn to spell words correctly.
Drumming out syllables
Students use a drum or tambourine to take turns drumming out the syllables in their names or other words. See the lesson plan.
This video is published with permission from the Balanced Literacy Diet. See many more related how-to videos with lesson plans in the Phonemic Awareness section.
Syllables: kindergarten
This video depicts a kindergarten small group engaging in a syllables activity. There are 5 students in this demonstration and they are using manipulatives. (From the What Works Clearinghouse practice guide: Foundational skills to support reading for understanding in kindergarten through 3rd grade.)
Collect resources
Marker activity
This activity, from our article How Now Brown Cow: Phoneme Awareness Activities, is an example of how to teach students to use a marker (i. e., token) to count syllables.
e., token) to count syllables.
The marker activity often used for word counting can be adapted for use in counting syllables. Teachers can provide each child with tokens and two or three horizontally connected boxes drawn on a sheet of paper. The children place a token in each box from left to right as they hear each syllable in a word.
Multisyllabic manipulation
This example includes several activities and a chart of multisyllabic words. One specific activity from this page is the Multisyllabic Words Manipulation Game. Teachers can divide words from reading selections into syllables, write each syllable on a note card and display the syllables in jumbled order. Have students arrange the syllables to form the words.
Multisyllabic words manipulation >
Clapping games
Associating syllables with a beat can help students to better learn the concept of syllables within words. Here's a clapping game to help young learners understand about dividing words into syllables.
Basic words clapping game >
Using mirrors
The following link includes information on introductory activities such as using mirrors for teaching students about syllables. Information is also provided about the different syllable spelling patterns.
Using a mirror to understand syllables >
Jumping syllables
This activity teaches student to separate words into syllables. Students move syllables around to create new "silly" words which gives them practice manipulating different sounds.
Jumping syllables >
Find many more syllable activities developed by the Florida Center for Reading Research.
Differentiated instruction
for second language learners, students of varying reading skill, and for younger learners
- Use pictures instead of words in activities for younger and lower level readers
- Include auditory and hands-on activities (i.e., clapping hands, tapping the desk, or marching in place to the syllables in children's names)
- Include a writing activity for more advanced learners.
See the research that supports this strategy
Adams, M., Foorman, B., Lundberg, I., & Beeler, T. (2004). Phonemic Activities for the Preschool or Elementary Classroom.
Ellis, E. (1997). How Now Brown Cow: Phoneme Awareness Activities.
Moats, L. & Tolman, C. (2008). Six Syllable Types.
Children's books to use with this strategy
Island: A Story of the Galápagos
By: Jason Chin
Genre: Nonfiction
Age Level: 6-9
Reading Level: Independent Reader
Young readers will explore the evolving terrain and animals of the Galápagos in this nonfiction picture book. Charles Darwin first visited the Galápagos Islands almost 200 years ago, only to discover a land filled with plants and animals that could not be found anywhere else on earth. How did they come to inhabit the island? How long will they remain? Thoroughly researched and filled with intricate and beautiful paintings by award-winning author and artist Jason Chin.
Where Else in the Wild? More Camouflaged Creatures Concealed & Revealed
By: David Schwartz
Age Level: 3-6
Reading Level: Beginning Reader
Close-up, full color photographs of camouflaged creatures and a variety of poems ask readers to examine the image while learning about characteristics. A gatefold opens to provide additional information. (This may appeal to children who like "real" things.)
Dogku
By: Andrew Clements
Age Level: 6-9
Reading Level: Independent Reader
The picture book story of a dog who finds a home is told in completely (and surprisingly successfully) using haiku.
Tap Dancing on the Roof: Sijo (Poems)
By: Linda Sue Park
Genre: Poetry
Age Level: 6-9
Reading Level: Independent Reader
Like haiku, sijo – a little known, brief poetic form from Korea – looks at everyday activities from breakfast to the weather. Sophisticated illustrations complement the seemingly simple language to delight readers and listeners.
Comments
The words "teaching" morphological and phonetic analysis
Explanation of the rules for dividing (breaking down) the word "teaching" into syllables for transfer.
Soosle.ru Online Dictionary will help: phonetically and morphologically parse the word " teaching " by composition, correctly divide into syllables according to the rules of the Russian language, highlight parts of the word, put stress, indicate the meaning, synonyms, antonyms and compatibility for the word " teaching ".
Contents:
- 1 Syllables in the word "teaching" division into syllables
- 2 How to transfer the word "teaching"
- 3 Morphological analysis of the word "teaching"
- 4 Parsing the word "teaching" by composition
- Similar morphemic structure of the word "teaching"
- 6 Synonyms of the word "teaching"
- 7 Stress in the word "teaching"
- 8 Phonetic transcription of the word "teaching"
- 9 Phonetic analysis of the word "teaching" into letters and sounds (Sound-letter)
- 10 Sentences with the word "teaching"
- 11 Matches of the word "teaching"
- 12 Meaning of the word "teaching"
- 13 Declension of the word "teaching" according to the conditions
- 14 How the word "teaching" is spelled correctly 50 k16 Associations the word "teaching"
Syllables in the word "teaching" division into syllables
Number of syllables: 4
By syllables: y-che-no-e
How to transfer the word “teaching”
Baby
Morphological analysis of the word “Teaching”
Part of speech:
Noun
Grammar
part of speech: noun;
animation: inanimate;
genus: middle;
number: singular;
case: nominative, accusative;
answers the question: (is) What?, (see/blame) What?
Initial form:
teaching
Analysis of the word "teaching" by composition
| uch | root |
| eni | suffix |
| e | ending |
teaching
Words similar in morphemic structure "teaching"
Words similar in morphemic structure
Synonyms for the word "teaching"
1. Dharmma
Dharmma
2. Kabbalah
3. Babuvism
4. Vedanta
5. Hedonism
6. Deim
7. Dualism
8. Asceticism
9. Study
10. Teaching
.11. Instruction
12. Training
13. Science
14. Doctrine
15. Theory
16. System
17. Training
18. Teaching
19. Learning
20. Phenomenalism 9. Phenomenalism 9.0008
21. Fictionalism
22. Building
23. Dogmat
24. Arkan
25. Lockyat
26. MAZHAB
27. Concept
28. Preparation
29. Pulling up
30. Lucing
31. Gilosoism
32. Creationism
33. God-enforcement
34. Demonology
Estimation in the word “Teaching”
Stress falls on the 2nd syllable
phonetic transcription of the word “teaching”
[uch’`en’i’e]
Phonetic analysis of the word “teaching” into letters and sounds (Sound-letter)
| Letter | Sound | Sound characteristics | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| at | [y] | vowel, unstressed | at |
| h | [h'] | consonant, voiceless unpaired, soft, hissing | h |
| e | [`e] | vowel, stressed | e |
| n | [n'] | consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), soft | n |
| and | [and] | vowel, unstressed | and |
| e | [y'] | consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), soft | e |
| [e] | vowel, unstressed |
Number of letters and sounds:
Based on the analysis made, we conclude that the word has 6 letters and 7 sounds.
Letters: 4 vowels, 2 consonants.
Sounds: 4 vowels, 3 consonants.
Sentences with the word “teaching”
Starting from this sacrifice, according to the Christian teaching , a direct path to salvation from death and from the torments of hell was opened to people.
Source: VG Rokhmistrov, Orthodoxy. Basic concepts.
The complexity of assessing a particular religion, in his opinion, lies in the fact that religious teaching is learned not rationally, but vitally.
Source: B. N. Tarasov, A. S. Khomyakov - thinker, poet, publicist. T. 2, 2007.
This philosophical teaching was a great step towards understanding the nature of the psychic.
Source: AS Luchinin, History of psychology: lecture notes.
Matching of the word “teaching”
1. Christian teaching
Christian teaching
2. new teaching
3. Religious exercises
4. The teachings of Christ
5. The teachings of Buddha
6. The teachings of the church
7. Fundamentals of teaching
8. The essence of the exercise
9. Years of teaching
10. The doctrine says
11. doctrine affirms
12. doctrine states
13. create doctrine
14. preach one's doctrine
15. conduct teachings
16. (complete combination chart)
0048
TEACHER, -i, cf. 1. Action by value. vb. teach and learn; learning something. (some kind of knowledge, skills). (Small Academic Dictionary, MAC)
Declension of the word "teaching" according to the terms
| Case | Question | Singular unit | Plural Mn. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative Name. | what? | teaching, learning | exercises, exercises |
GenitiveGen. | what? | exercises, exercises | exercises |
| DativeDat. | what? | learning, learning | teachings, teachings |
| accusatory | what? | teaching, learning | exercises, exercises |
| Creative TV. | what? | learning, learning | exercises, exercises |
| prepositional | about what? | learning, learning, learning | exercise, exercise |
How the word “teaching” is written correctly
Spelling of the word “teaching”
Spelling of the word “teaching”
Correctly the word is written: learning
Number of letters teaching" in forward and reverse order:
- 6
y
1 - 5
h
2 - 4
e
3 - 3
n
4 - 2
and
5 - 1
e
6
Associations to the word «teaching»
-
Buddhism
-
Buddha
-
Follower
-
Doctrine
-
Aristotle
-
Judaism
-
Apostles
-
Heresy
-
Christianity
-
Sect
-
Theology
-
view
-
Christ
-
Marks
-
Statement
-
Gospels
-
Yogi
-
Follower
-
Theologian
-
Darwin
-
Sacrament
-
Scripture
-
Philosophy
-
Belief
-
Ethics
-
Adept
-
Talmud
-
Sunday
-
Philosopher
-
Morality
-
Religion
-
Interpretation of
-
Sermon
-
NATO
-
Enlightenment
-
Plato
-
Kant
-
Thinker
-
Jesus
-
Testament
-
Mystic
-
Review
-
Islam
-
Landfill
-
Worldview
-
Koran
-
Saying
-
Heretic
-
Preacher
-
Gospel
-
Apostle
-
Tract
-
Reverence
-
Negation
-
Orthodoxy
-
Grace
-
Socrates
-
Cognition
-
Advent
-
Controversy
-
Piety
-
Commandment
-
Resettlement
-
Socialism
-
Tibet
-
Messiah
-
Buddhist
-
Christian
-
Evolutionary
-
Philosophical
-
Ethical
-
Theological
-
Christov
-
Mystical
-
Protestant
-
Religious
-
Tibetan
-
Apostolic
-
Alexandria
-
Moral
-
Jewish
-
Fathers
-
Tactical
-
Oral
-
Scheduled
-
Military
-
Afterlife
-
Divine
-
Ecumenical
-
Systematic
-
Pagan
-
Drill
-
Preach
-
Confess
-
Distribute
-
State
-
Reject
-
Justify
-
Borrow
-
State
Words "teachings" morphological and phonetic analysis
Explanation of the rules for dividing (breaking down) the word "teachings" into syllables for transfer.
Soosle.ru Online Dictionary will help: phonetically and morphologically parse the word " teachings " by composition, correctly divide into syllables according to the rules of the Russian language, highlight parts of the word, put stress, indicate the meaning, synonyms, antonyms and compatibility for the word " exercise .”
Content:
- 1 syllables in the word "Teaching"
- 2 How to transfer the word "teachings"
- 3 morphemic analysis of the word
- 4 Similar to the morphemic structure "Teaching"
- 5 Synonyms of the word “teachings”
- 6 Emphasis in the word “teachings”
- 7 Phonetic transcription of the word “teachings”
- 8 Phonetic analysis of the word “teachings” into letters and sounds (Sound-letter)
- 9 Sentences with the word "teachings"
- 10 Matches of the word "teachings"
- 11 Meaning of the word "teachings"
- 12 How to spell the word "teachings"
Syllables in the word "teachings"
0:04 Number of syllables By syllables: y-che-no-ya
How to transfer the word “teachings”
teachings
Morphemic analysis of the word “teachings” by composition
| uch | root |
| eni | suffix |
| e | ending |
teaching
Words similar in morphemic structure “teachings”
Words similar in morphemic structure
Synonyms for “teachings”
1. tactical exercises
tactical exercises
2. maneuvers
Stress in the word "exercises"
exercises - stress falls on the 2nd syllable
Phonetic transcription of the word "exercises"
[uch'`en'iy'a]
Phonetic analysis of the word "teachings" into letters and sounds (Sound-letter)
| Letter | Sound | Sound characteristics | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| at | [y] | vowel, unstressed | at |
| h | [h'] | consonant, voiceless unpaired, soft, hissing | h |
| e | [`e] | vowel, stressed | e |
| n | [n'] | consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), soft | n |
| and | [and] | vowel, unstressed | and |
| i | [y'] | consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), soft | i |
| [a] | vowel, unstressed |
Number of letters and sounds:
Based on the analysis made, we conclude that the word has 6 letters and 7 sounds.
Letters: 4 vowels, 2 consonants.
Sounds: 4 vowels, 3 consonants.
Sentences with the word "teachings"
Starting with this sacrifice, according to Christian teaching , people opened a direct path to salvation from death and from the torments of hell.
Source: VG Rokhmistrov, Orthodoxy. Basic concepts.
The complexity of assessing a particular religion, in his opinion, lies in the fact that religious teaching is learned not rationally, but vitally.
Source: B. N. Tarasov, A. S. Khomyakov - thinker, poet, publicist. Vol. 2, 2007.
This is philosophical Teaching was a great step towards understanding the nature of the psychic.
Source: AS Luchinin, History of psychology: lecture notes.
Compatibility of the word “teachings”
1.