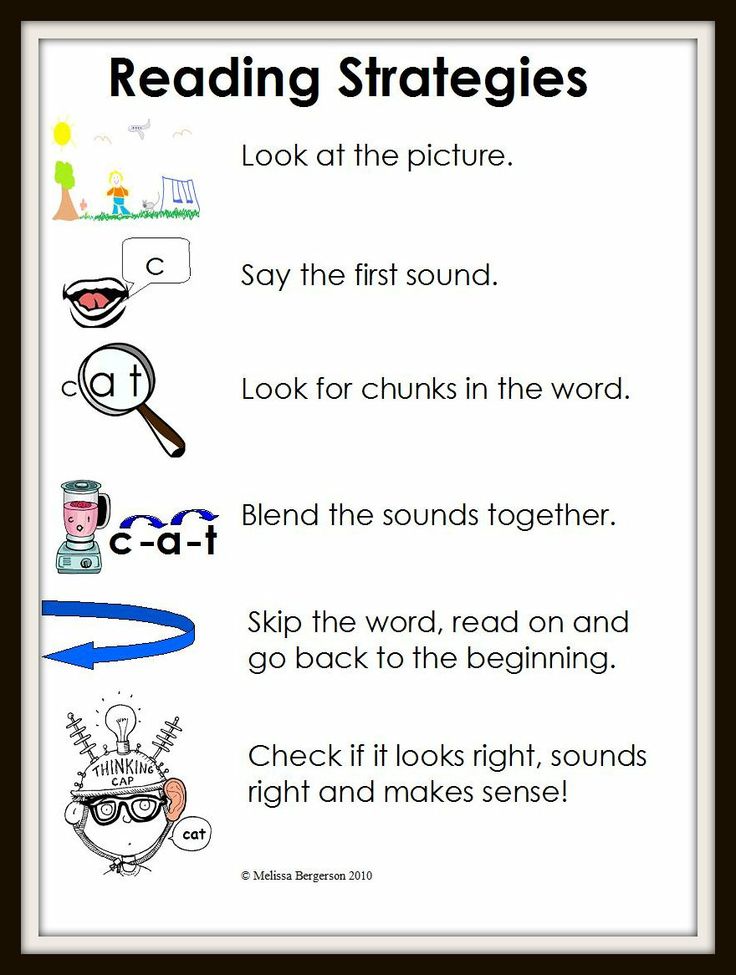
Teaching kindergarten reading strategies
Classroom Strategies | Reading Rockets
Strategy focus
AnyComprehensionFluencyPhonicsPhonological awarenessPrint awarenessVocabularyWriting
B/D/A
AnyBefore readingDuring readingAfter reading
Especially helpful for
AnyAcademic languageDecoding / encodingGrammarEnglish learnersOrganizing ideasSelf-monitoring
| Strategy | Focus | B/D/A | Template |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alphabet Matching | Phonics | ||
| Anticipation Guide | Comprehension |
| |
| Audio-Assisted Reading | Fluency |
| |
| Blending and Segmenting Games | Phonological awareness | ||
| Choral Reading | Fluency |
| |
| Concept Maps | Comprehension |
| |
| Concept of Word Games | Phonological awareness |
| |
| Concept Sort | Comprehension |
| |
| Descriptive Writing | Writing | ||
| Dictation | Writing | ||
| Directed Reading Thinking Activity (DRTA) | Comprehension |
| |
| Elkonin Boxes | Phonological awareness | ||
| Exit Slips | Comprehension |
| |
| First Lines | Comprehension |
| |
| Framed Paragraphs | Writing | ||
| Inference | Comprehension |
| |
| Inquiry Chart | Comprehension |
| |
| Jigsaw | Comprehension |
| |
| List-Group-Label | Vocabulary |
| |
| Listen-Read-Discuss (LRD) | Comprehension |
| |
| Matching Books to Phonics Features | Phonics |
| |
| Onset-Rime Games | Phonological awareness | ||
| Paired (or Partner) Reading | Fluency |
| |
| Paragraph Hamburger | Writing | ||
| Paragraph Shrinking | Comprehension |
| |
| Partner Reading | Comprehension |
| |
| Persuasive Writing | Writing | ||
| Possible Sentences | Vocabulary |
| |
| Question the Author | Comprehension |
| |
| Question-Answer Relationship (QAR) | Comprehension |
| |
| RAFT | Writing | ||
| Reader’s Theater | Fluency |
| |
| Reading Guide | Comprehension |
| |
| Reciprocal Teaching | Comprehension |
| |
| Revision | Writing | ||
| Rhyming Games | Phonological awareness | ||
| Semantic Feature Analysis | Vocabulary | ||
| Semantic Gradients | Vocabulary | ||
| Sentence Combining | Writing | ||
| Shared Reading | Fluency |
| |
| Story Maps | Comprehension |
| |
| Story Sequence | Comprehension |
| |
| Summarizing | Comprehension |
| |
| Syllable Games | Phonological awareness | ||
| Think-alouds | Comprehension |
| |
| Think-Pair-Share | Comprehension |
| |
| Timed Repeated Readings | Fluency |
| |
| Transition Words | Writing | ||
| Visual Imagery | Comprehension |
| |
| Word Hunts | Vocabulary |
| |
| Word Maps | Vocabulary | ||
| Word Walls | Vocabulary |
| |
| Writing Conferences | Writing |
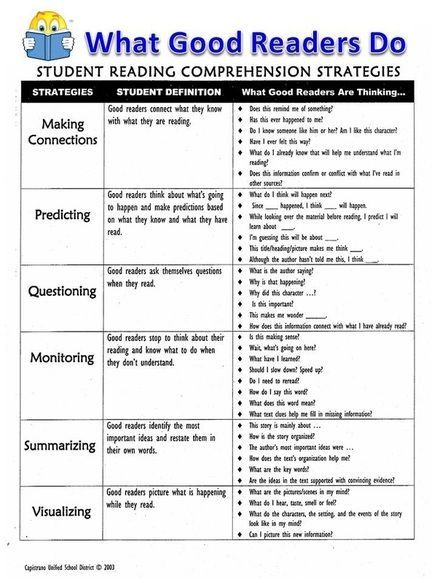
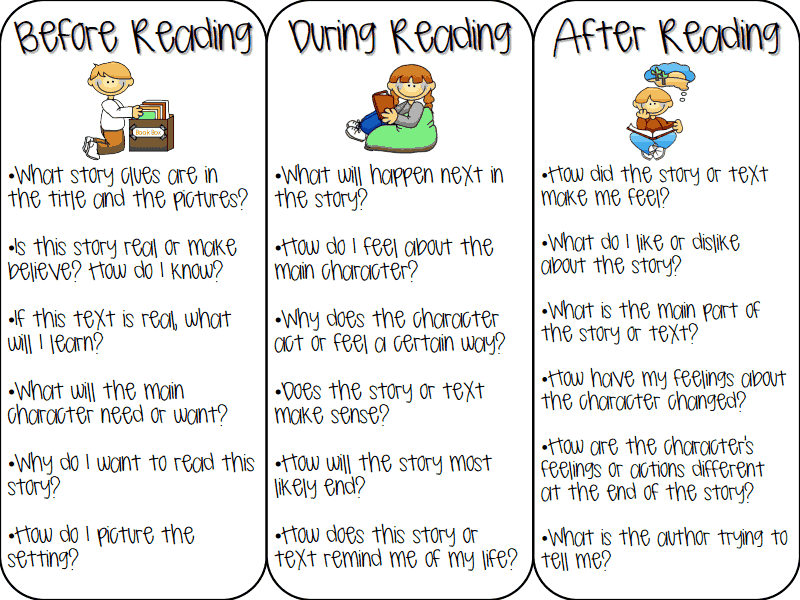
Comprehension: Activities for Your Kindergartener
Just 15 minutes each day makes a big difference! Reading aloud is a great way to help your kindergartener absorb new words and see how stories are structured. It's also one of the best ways to help children learn about the world and make connections between their own lives and what's in the book — that helps children see the world with empathy. And last but not least, it's a wonderful time to snuggle up with your child and share the experience of reading and discovery together.
Remember that reading together should spark curiosity, joy, and a desire to explore and learn. Conversations about books should be enjoyable, and not a set of quizzes and questions. As you try some of the activities listed below, remember to keep it light and lively for your child.
There are so many great nonfiction and informational books for very young kids (such as the popular DK Eyewitness series and National Geographic series). Try to include some of these during your next trip to the public library. Children love learning about the real world and are proud to share what they know!
Even a walk around the neighborhood or a trip to the grocery store can be a rich learning experience for young children. A child may see an urban bunny for the first time on a walk, and then be able to connect it to stories about rabbits. These personal connections help children connect what they read with what they know — a powerful way to build comprehension skills!
A child may see an urban bunny for the first time on a walk, and then be able to connect it to stories about rabbits. These personal connections help children connect what they read with what they know — a powerful way to build comprehension skills!
Signs of good reading comprehension in kindergartners
Try these comprehension activities at home
"I predict ..."
When you sit down for a read aloud, look at the book's cover together. Ask, "What do you think this book might be about? Why? Can you make some predictions?" Guide your child through the pages, discuss the pictures, and brainstorm what might happen in the story. Talk about any personal experiences your child may have that relate to the story.
Five-finger retell
After reading a story together, have your child tell you five things about the story, using her fingers to talk about each one:
- Characters: who was in the story?
- Setting: where did the story take place?
- Events: what happened in the story?
- End: how did the story end?
- Favorite character or part of the story
Active reading
Model active reading when you read with your child. Talk about what's happening as you're reading. Stop and discuss any interesting or tricky vocabulary words. Help your child make pictures of the story in his mind. Ask your child, "What just happened here? How do you think that character feels? Have you ever felt like that? What do you think will happen next?" Not only will this develop your child’s comprehension, but critical thinking skills as well.
Talk about what's happening as you're reading. Stop and discuss any interesting or tricky vocabulary words. Help your child make pictures of the story in his mind. Ask your child, "What just happened here? How do you think that character feels? Have you ever felt like that? What do you think will happen next?" Not only will this develop your child’s comprehension, but critical thinking skills as well.
Mind movies
When you come to a descriptive passage in a book, have your child close her eyes and create a mental movie of the scene. Encourage her to use all five senses. Read the passage over together, looking for details that bring the scene to life. Ask questions like, “How do you know it was a hot day? Which words help you understand that the child was lonely?”
Tell me about it
After a read aloud, one of the best and easiest ways to check for understanding is to ask your child to summarize what the book was about in their own words. You can ask a question or two to help your child clarify her thinking or to add more detail.
Can your child tell you what happened in the story?
This video is from Home Reading Helper, a resource for parents to elevate children’s reading at home provided by Read Charlotte. Find more video, parent activities, printables, and other resources at Home Reading Helper.
Think alouds
Connect the book to your child's own life experience. For example, A River Dream: "This book reminds me of the time my father took me fishing. Do you remember the time we went fishing?"
Connect the book to other books they have read. For example, Mufaro's Beautiful Daughters: "This story reminds me of Cinderella. Both stories are about sisters. Do you know any other stories about nice and mean sisters? Let's keep reading to find out other ways the stories are similar. "
"
Connect the book to big ideas/lessons. For example, Stellaluna: "This story helps me understand that we are all the same in many ways, but it's our differences that make us special."
Wordless
Wordless picture books provide your child with practice using clues to create meaning. There are no wrong stories with wordless picture books, only variations based on what the "reader" sees and puts together. Rosie's Walk, Good Dog, Carl, and Beaver Is Lost are all interesting and fun wordless picture books to explore. Find more wordless books on BookFinder.
Family stories
This is a wonderful activity for a family picnic or for a rainy day when you're snuggled together on the couch. Share a favorite story about your childhood or a family story that's been passed down from generation to generation. Use vivid language and details about people, places, and things. Funny or scary will really get your child's attention! Your child will probably have lots of questions, which keeps the storytelling alive. You could also ask your child if she has a favorite family story of her own.
You could also ask your child if she has a favorite family story of her own.
How sharing your stories helps kids with reading
Beginning readers love to hear stories about a parent's childhood! A parent's stories help children learn new vocabulary, story structure, and comprehension. (From GreatSchools)
Map this book!
Draw a map of the book's setting, and be sure to include the places where the main action happens!
Beginning-middle-end
This is a great way to see if your child understands the main parts of a story. After reading a book together, give your child three sheets of paper, with "beginning" on one sheet, "middle" on the second sheet, and "end" on the third sheet. Ask your child to think about the three parts of the story, and then draw what happened on each on the sheets. Arrange the sheets in order, left to right. What happens if you re-arrange the sheets? Does the story still make sense?
Arrange the sheets in order, left to right. What happens if you re-arrange the sheets? Does the story still make sense?
Words, words, words
Be sure to include books with rich vocabulary in your read alouds and call attention to interesting words and phrases from the story. This may include repeated phrases or idioms (such as "get cold feet" or "I'm all ears"). Offer a kid-friendly definition and connect the new word or phrase to something your child already knows.Talk about how the author used language or words to make the text interesting, informative, funny, or sad.
Picture walk
Talk about the book before you read it. Show the cover illustration and ask your child to predict what the book is about. Flip through the book, look closely at the pictures together, and talk about what's on the jacket flaps.
Take a picture walk
This video is from Home Reading Helper, a resource for parents to elevate children’s reading at home provided by Read Charlotte. Find more video, parent activities, printables, and other resources at Home Reading Helper.
Find more video, parent activities, printables, and other resources at Home Reading Helper.
Remember when ...?
Connect what your child reads with what happens in life. If reading a book about birds, relate it to birds you've seen on walks in your neighborhood.
Story detectives
As you read with your child, stop and ask questions such as: What’s happening in the picture? Why do you think the puppy is sad? Have you felt that way yourself? Why do you think the spider wanted to help the pig? What do you think is going to happen next? How do you think the story will end? Take turns and let your child to “be the detective” and ask you questions about the book. Not only will this develop your child’s comprehension, but critical thinking skills as well.
Picture the character (Part 1)
Try this activity from the Florida Center for Reading Research (FCRR).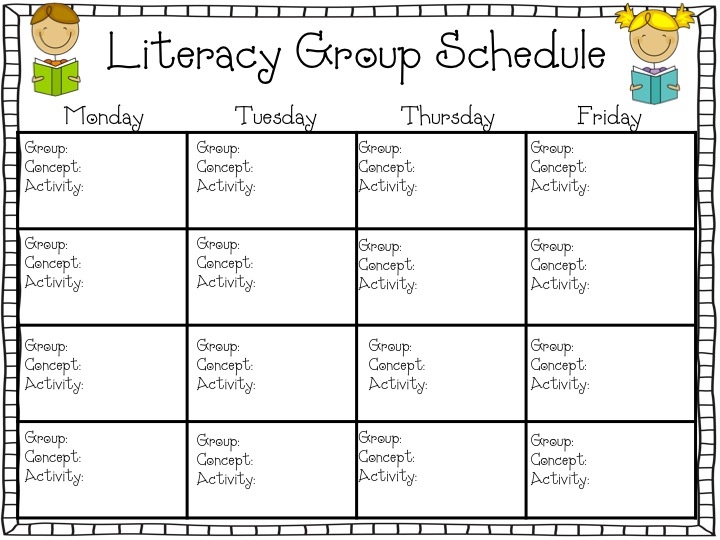 The FCRR "At Home" series was developed especially for families! Watch the video and then download the activity: Picture the Character. See all FCRR comprehension activities here.
The FCRR "At Home" series was developed especially for families! Watch the video and then download the activity: Picture the Character. See all FCRR comprehension activities here.
Picture the character (Part 2)
Try this activity from the Florida Center for Reading Research (FCRR). The FCRR "At Home" series was developed especially for families! Watch the video and then download the activity: Picture the Character. See all FCRR comprehension activities here.
More comprehension resources
Learning to read | Kindergarten No. 74 of a general developmental type
Home » Our consultations » From the experience of our teachers » Learning to read
For you, parents!
(from the work experience of the educator MADOU No. 74 Rubtsova Marina Vasilievna )
74 Rubtsova Marina Vasilievna )
Parents of preschool children attending kindergarten often rely on the fact that their children will be prepared for school by the efforts of educators. Indeed, specially organized classes help children prepare for school, but without the help of parents, such preparation will not be of high quality.
Experience shows that no best children's institution - neither kindergarten nor elementary school - can completely replace the family, family education. In a preschool institution, children are taught many useful skills, they are taught to draw, count, write and read. But if the family does not take an interest in the child’s activities, do not attach due importance to them, do not encourage diligence and diligence, the child also begins to treat them with disdain, does not strive to work better, correct his mistakes, and overcome difficulties in work. Some children are deeply offended by such inattention of their parents, they cease to be sincere and frank. On the contrary, the interest of parents in the affairs of the child attaches particular importance to all the achievements of the child. Help in overcoming the difficulties that arise in the performance of any kind of activity is always accepted with gratitude and contributes to the closeness of parents and children. At home, the ability to read can come as naturally to a child as the ability to walk or talk. Dear parents, grandparents! If you want to teach your child to read before he goes to school, pay attention and understanding to all our advice. To avoid the sad consequences of illiterate learning.
On the contrary, the interest of parents in the affairs of the child attaches particular importance to all the achievements of the child. Help in overcoming the difficulties that arise in the performance of any kind of activity is always accepted with gratitude and contributes to the closeness of parents and children. At home, the ability to read can come as naturally to a child as the ability to walk or talk. Dear parents, grandparents! If you want to teach your child to read before he goes to school, pay attention and understanding to all our advice. To avoid the sad consequences of illiterate learning.
Learning to read
It is believed that learning to read early gives a child great intellectual potential. A pre-reader or a first-grader who is already reading develops faster, learns easier and better, and remembers more.
Where to start?
- The main rule of learning to read: "Do not chase the result!". First, show your child the alphabet. If he is interested, consider it, name the letters, syllables. Learning to read is best started on their own initiative. Your task is to support, not to ruin the initiative with excessive zeal.
If he is interested, consider it, name the letters, syllables. Learning to read is best started on their own initiative. Your task is to support, not to ruin the initiative with excessive zeal.
- Learning to read can begin with the study of letters or syllables. Colorful tables, posters, cubes are well suited for these purposes. The material may change from time to time. And it is not at all necessary to memorize the alphabetic name of the letters with the kids.
- Pay special attention to the game form of the lessons, as well as their duration (15-20 minutes). Do not forget how joyful and interesting they will be, his further education largely depends. The main thing is not to forget that all this is just a game, and not preparation for the exam.
-If a child is ill or not in the mood to study, it is better to postpone the “lesson”, do not study by force.
-Lessons should be varied, change tasks often, because small children get tired quickly and their attention is scattered. So you will have to constantly maintain the interest of the child in what you propose to do.
So you will have to constantly maintain the interest of the child in what you propose to do.
-Read in front of the child. Mom is the best role model.
- In parallel with reading, you can learn to write. The child will be quite capable of performing graphic tasks: circle simple figures point by point with your hand. You can "type" on the old keyboard. Maze toys prepare a hand well for writing, in which small details need to be raised, for example, from bottom to top, or swiped from left to right.
Important about letters
You can often see such a picture on the street. Mom asks the child, pointing to any letter of the sign on the house: "What is this letter?" The child happily answers: "PE!", Or "EM!", Or "ES!" One feels like saying:
“Dear adults! If this is how you call letters to children,
, then how will your little student read the syllable "MA"? Imagine, he will most likely get "EMA"! And he will be right: EM + A = EMA. And the word "MA-MA" in this case will be read as "EMA-EMA"!
Most teachers and speech therapists agree that when teaching preschool children, the alphabetic army should be called in a simplified way: not “pe”, but “p”, not “me”, but “m”.
Learning to read at home
How to teach to read and not injure the psyche, not to force, but on the contrary, arouse interest and desire? If you actively played with the child, while attracting a book, then this will greatly facilitate the task.
The first unsuccessful experiences can completely discourage you from starting to learn to read. The child understands that learning to read is not so easy and hardly repeats attempts. Learn more letters back and forth. But to combine them into words and read, and then understand what you read - it's pretty hard. But gradually the child overcomes this difficulty.
Learn to read in the game. But, most importantly, what we should remember is not to torment the child and ourselves. Don't make it an unpleasant duty, don't compare one child to another.
Here we need patience, love, consistency, fantasy. You can beat the learning process, turn it into a holiday, into an exciting game. Keep it short but effective.
Keep it short but effective.
So, let's move on to the study of letters and sounds.
1. Learning is best to start with vowels.
Some parents have already introduced their children to different letters, but where do you start? You need to start with vowels, which you need to determine whether the child remembers them well.
To teach children to read, you can use cut out letters, paint, plasticine, whatever you want.
Now I'll show you some exercises that will help you reinforce the learned vowels.
- I will call you a letter, and you take it out of the magic box and we are building a house with you:
E e
A A A A
Ob of
and
U in
E E
This is needed for that. so that the child learns to read and write lines. ( Can be read)
It will take some time to memorize one letter, three, four, five or even six days. If the child remembers longer, it's okay. It is important that the child not only read a new letter, but also knows how to find it. You can ask the child to find the letter O , then the letter A , and so quietly the child makes a train.
If the child remembers longer, it's okay. It is important that the child not only read a new letter, but also knows how to find it. You can ask the child to find the letter O , then the letter A , and so quietly the child makes a train.
A U O E I S E Y Y Y Y E
Later, when the train is completed, the child can read it. If a child has a hard time remembering vowels, you can remember them associatively. But A , as always, does not cause difficulties, U are ears, And - we smile, O - this is a circle, what we see, then we say, the letter Yu - can be remembered as a skirt, E - the car is driving, E - hedgehog, If the child has forgotten the letter, then ask him: "Prickly with eyes."
The most difficult letter of the vowels is the letter E . This letter is difficult because some children pronounce it like E , this is wrong. It is necessary to monitor the correct pronunciation of the sound and correct the child.
It is necessary to monitor the correct pronunciation of the sound and correct the child.
A U O E I S E Y Y Y E
The letter E came out to the yard for a walk, which letter came out to her, choose.
EO , change places you get OE .
So, we have already learned the vowels, let's move on to the consonants.
Consonants
To study consonants, choose the first voiced letter, M, N, L, R .
Consonants are best studied immediately with a familiar vowel. It is easier for a child to remember a new letter. In addition, we thus imperceptibly approach the syllables.
To do this, the child needs to build a house out of vowels:
A E
O YU
and I
Next, we introduce the child with a new consonant letter. We tell the child to raise the letter on the elevator while reading the syllable.
We tell the child to raise the letter on the elevator while reading the syllable.
If a child cannot remember a letter or pronounces it incorrectly, an exercise called "Pens, Pens" will come in handy.
The child sits in front of you so that he is not distracted, take his hands. This exercise is difficult and requires a lot of attention.
You hold the child by the hands, and he, looking into your mouth, repeats after you.
The peculiarity of this exercise is that the child does not see the letter, he perceives it by ear.
First, show the child the letter with your hand, and let him name them, later you remove your hand and the child should show and name the letters. For example: with the letter , will have NU , etc. It is necessary to ensure that the child reads not only when you show him with your finger, but so that he himself can take and read.
Syllables
Children usually stumble at this stage. It is difficult for them to read syllables together. It is important that the child not only read the syllables first consonants and then vowels, but also to be able to distinguish when, on the contrary, there are first a vowel and then a consonant.
It is difficult for them to read syllables together. It is important that the child not only read the syllables first consonants and then vowels, but also to be able to distinguish when, on the contrary, there are first a vowel and then a consonant.
We offer you a manual that makes it easy for children to learn syllabic reading.
Didactic manual for teaching reading "Magic Windows"
At the stage of learning to read syllables, it is useful to use such a device. Making this educational game is not an easy task. But all preschoolers like to play with "windows", and you will not regret taking the time to make this manual.
You will need:
2 sheets of white or colored card stock;
sketchbook;
ruler;
simple pencil;
colored pencils or markers;
scissors, glue.
Make a markup on one sheet of cardboard: lay the sheet horizontally, divide it into 2 equal parts with a vertical line, mark windows at the same level in each half, observing the same indentation from the edges and from the middle line. Cut out the windows with scissors. On the reverse side, glue a cap from the second sheet of cardboard. Apply glue only along the middle line, along the right and left edges.
Cut out the windows with scissors. On the reverse side, glue a cap from the second sheet of cardboard. Apply glue only along the middle line, along the right and left edges.
Open the album in the middle, unfasten the staples and pull out the double sheet of paper. Cut it in half lengthwise so that you get two identical strips. Mark each strip along its entire length: draw rectangles with a width corresponding to the height of the window in the part made of cardboard earlier. On one strip, write the vowels A, O, U, Y, I, E, E, I, Yu, E (one letter in each rectangle). On the second strip, write the consonants M, P, N, K, C, C, T, B, D, G, 3, F (also one letter in each rectangle).
Insert the strips into the cardboard frame: the vowel strip on the right, the consonant strip on the left.
Now set any consonant letter in the left window, and move the right bar so that vowels appear in turn in the right window. Let the child read the resulting syllables. For example: MA - MO - MU - WE - MI - ME - MY - MY - MU - ME. Move the bar on the left to make a new consonant appear, move the right bar again, inviting the child to read new syllables.
Move the bar on the left to make a new consonant appear, move the right bar again, inviting the child to read new syllables.
Next time, leave the vowel you chose unchanged, and change the consonant by moving the left bar in the boxes. Ask the child to read the resulting syllables. For example: MA - PA - NA - VA - TA - BA - KA - SA - GA, etc.
You can swap the stripes, in this version the child will read chains of so-called reverse syllables, where the first letter is a vowel and the second is a consonant . For example: AP - AM - AN - AB - AT - AS - AF - HELL, AK - OK - UK - KY - IR - EK - YOK - YUK - YAK - EK.
Invite the child to move the strips independently. Ask to compose any syllable according to your task or the desire of the baby. Organize a "School for Toys" where the teacher - your child - will show his toys different syllables with the help of this manual. Good luck!
How easy it is to teach a child 4-6 years old to read - the best methods and exercises there is no ready answer, but we want to immediately warn against two misconceptions:
-
"You don't have to teach your child to read at home, they will teach you at school anyway.
 " Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child.
" Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child. -
"There is no time to waste - the sooner the baby begins to read, the better." All children are different and develop at their own pace. Therefore, you should not impose teaching reading to a preschooler as soon as he is 4-5 years old, if the student himself does not yet show interest in this activity. Instead, you can begin to develop an interest in reading through bright and engaging books. A good option would also be games that involve letters.
The indicator to be guided by is not the age of a preschooler, but his speech skills.
It's time to learn to read if...
If the speech development of a preschooler proceeds without gross violations. Let's figure out what criteria will help you find out if a child is ready to learn to read:
-
Understanding addressed speech. The kid must understand sentences, phrases, individual words that others refer to him.
-
Vocabulary. The more words a child knows, the better he will understand what he read. It will also help him communicate with adults and other children.
-
Grammar. The ability to correctly build sentences, select and change words is important for children who are learning to read.
-
Pronunciation.
 For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
Remember: at preschool age, a child may have minor flaws in grammar and pronunciation - this is normal. Over time, these violations will be corrected, and they should not be considered an obstacle to reading. But if the baby is not yet very confident in speaking, do not rush him to read - this will not help develop speech, but only demotivate.
Practicing child psychologist Ekaterina Murashova
Free course for modern moms and dads from Ekaterina Murashova. Sign up and participate in the draw 8 lessons
How to make learning to read easier for preschoolers
-
Praise more and never scold
It's hard for us adults to imagine how difficult it really is for a baby to learn from scratch such a complex skill as reading.
 After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text.
After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text. If parents take the child's progress for granted and express dissatisfaction when the child does not understand something, this will not push the future student to development, but will only complicate the process. Therefore, it is important to praise for small victories: I learned the letter that was passed last time - great, I coped without my father's help with the word as much as two syllables - clever.
Do not take failures as a consequence of the negligence of the little student. When a child does not understand the first time, this is an occasion to look for another explanation or give more time to practice. If you feel tired and irritated, you should stop the activity and return to it in a good mood.
-
Exercise little but regularly
Do not expect perseverance and a desire to spend hours figuring out unfamiliar letters from your baby.
 It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games.
It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games. But regular practice is important - much more important than the duration of the session. And it doesn’t have to be just lessons: you can look for familiar letters on signs during a walk, on a door plate in a children’s clinic, on a package of your favorite corn flakes.
-
Read books aloud
In a series of studies conducted by Dr. Victoria Purcell-Gates among five-year-olds who could not yet read, children to whom their parents regularly read aloud for two years were found to express thoughts in more literary language, build longer phrases and use more complex syntax.

In addition, reading aloud with adults contributed to the expansion of children's vocabulary, as parents explained the meanings of new words that children did not encounter in everyday life.
Expert Opinion
According to neuroscientist Marianne Wolfe, book evenings with parents help develop a love of reading because the child establishes a connection between reading aloud and feelings of love and warmth.
-
Discuss read
The role of communication in teaching literacy cannot be overestimated. At first, it is important to ask if the future student is interested, if he is tired, what was remembered from the lesson. When a preschooler learns to read coherent texts, be sure to ask questions about their content.
It's great if the child reads on his own and without the prompting of the parents, but even in this case, do not deprive him of the opportunity to discuss what he has read with you.
 For example, you might ask:
For example, you might ask: -
Which of the characters do you like?
-
Do you think this character is like you? Would you like to be like her?
-
What would you do if you were a hero?
-
Why did the described event happen? How are these two events related?
-
How did what you read make you feel?
-
What do you remember most from what you read?
-
What do you think the author wanted to teach? Why did he write this? Do you agree with the author?
-
-
Go from simple to complex
From the correspondence between sounds and letters to syllables, from short words to longer and more complex words. It would seem that this is obvious, but no: sometimes parents are so happy with the success of the child at first that they push him to study more complex topics than he is ready to accept. Of course, the program should adapt to the future student, but you should not skip steps, even if the child is making progress.
There are methods that offer to teach a child to read by memorizing whole words. Alas, experiments show that such techniques generally work worse. For example, a group of scientists from the United States came up with an artificial alphabet and offered subjects to learn it, and then read the words written using this alphabet.
 At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second.
At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second. Therefore, we advise you to choose those teaching methods that involve clear instructions about the relationship between sound and letter - and this is especially important for those children who have difficulty reading. Below we have compiled a few of these techniques that you can use to teach your preschooler at home.
It is important to select questions individually, based on the age of the child. With younger children, discuss everything together, ask simple questions, direct their attention to some facts. The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences.
The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences.
Methods of teaching preschoolers to read
Warehouse reading
The way to teach a child to read through warehouses was actually used in Rus', but for modern parents this technique is associated with the name of the philologist Nikolai Alexandrovich Zaitsev.
Zaitsev suggests not focusing on the study of individual letters, as it can be difficult for students to understand how letters can merge into syllables and words. Teaching a child to read by syllables is also not always easy: one syllable can be quite long ( shine, ruble ), and the boundaries of syllables are not obvious ( Lun-tik or Lu-ntik ?). Therefore, in Zaitsev's methodology, a warehouse is used as the main unit.
Warehouse can be a combination of a consonant and a vowel (pa-pa, ma-ma), a single consonant or vowel (de- d , i-s -li, A -le-sha), as well as a combination of a consonant with a hard or soft sign (ma- l -chi-k, use d -yem).
In order for a preschooler to understand the differences between the recording of voiced and soft, vowel and consonant sounds, different types of warehouses have their own cube size, color and content, thanks to which the cubes sound when they are shaken. Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective.
Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective.
One of the advantages of the technique is that children willingly play with blocks themselves, and the process of learning to read becomes active, mobile.
Syllabic reading
This technique, according to some sources, was developed by the Romans. Later, Nadezhda Sergeevna Zhukova, a Soviet and Russian speech therapist, created a primer based on it. In it, she built her own system in which sounds and letters are sequentially introduced into speech.
Due to the fact that the concept of a syllable is introduced at an early stage, it is faster and easier to teach a child to read syllables together. By the way, as in Zaitsev's technique, it is proposed to sing syllables, and not just pronounce them.
Based on the syllabic method, Zhukova developed a set of teaching aids - copybooks, copybooks and a book for reading. Benefits will help teach children to read correctly 6 and 7 years old at home.
Both techniques for teaching preschoolers to read are used in the Skysmart Ready for School course. The course consists of two stages: first, children get acquainted with letters and warehouses, which allows them to quickly start reading simple words, and then they learn what a syllable is. Gradually, we introduce more complex syllabic constructions, move on to reading phrases and sentences.
Sound analytical-synthetic teaching method
This method originated in the USSR and is still considered the main one in Russian schools and kindergartens. It was developed by the Soviet teacher and Russian language methodologist Voskresenskaya Alexandra Ilyinichna.
Like N.S. Zhukova, Voskresenskaya proposed her own order in which children should learn letters and sounds. The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
-
Two-letter syllables (including one consonant): am, ma, ra, etc. and simple words from them: ra-ma, ma-sha, Pa-sha, etc.
-
Three-letter syllables with a central vowel: poppy, lat, etc.
-
The combination of the first two stages into words: sa-lat, earth-la, etc.
-
Words of three syllables and six letters: az-bu-ka, ve-se-lo, etc.
-
Words of two syllables and six letters: question-ros, tea-nick, etc.
-
Words with a combination of vowels at the beginning and at the end of the word: chair, March, etc.

In this way, children simultaneously prepare for more complex syllables at each stage and reinforce what they have learned earlier.
Free English lessons with a native speaker
Practice 15 minutes a day. Learn English grammar and vocabulary. Make language a part of life.
Exercises for learning to read
Learning to read, as a rule, takes place in several stages. First, the child listens to the sound, visually remembers the letters. Different games will help with this, where you need to look for letters, invent words, etc. When this stage is over, you can move on to syllables and games to work them out. And only after that it will be possible to proceed to words, and then to sentences and texts.
Letter memory exercises
The first step is to teach your child to recognize letters. To do this, you can use pictures with hidden letters. We use such exercises in the preparation for school lessons in Skysmart.
Ask your child to identify what letter a word begins with, or name as many words as possible that begin with a certain letter.
Next, we train to distinguish correctly written letters from incorrect ones. This is also important for learning to write: preschoolers often mirror letters or distort individual elements.
Exercises for vowels and consonants
To learn to distinguish between vowels and consonants, tasks will help you determine the sound with which a word begins.
It will also help to remember the difference between vowels and consonants and search for an extra letter.
Word building exercises
When your child can read short words, ask him to make a word out of letters on his own.
Composing words from syllables is convenient if you have cubes at hand, but you can also try on paper.