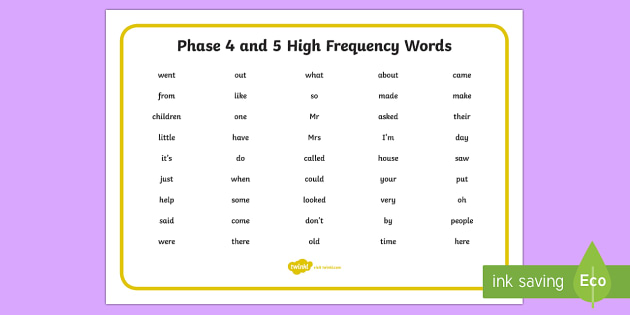
Things that start with c preschool
Words That Start With C For Kids
Children can challenge themselves with easy words that start with C! While there are many ways to approach spelling lessons, one option is to break up the alphabet and study new words by individual letters. Below, you'll find several C words for kids as well as activities to keep learning fun and engaging for little learners.
words that start with C for kids
Advertisement
Preschool C-Word List
A lifelong love of learning can begin as early as preschool or kindergarten with the right compassion and care. Use these three-letter words that begin with C for kids to jump-start their reading journey.
- can - a container normally made of metal with a lid
- cat - a small, soft-furred animal
- cob - a stick of corn
- cod - a fish with a mild flavor
- cot - a narrow bed that can be folded up
- cow - the female of domestic cattle
- cut - to divide with a sharp instrument
- cup - a dish for drinking
Include More Dolch Sight Words
Preschoolers who can read CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) words may be able to move on to Dolch sight words. Incorporate these words into your everyday classroom lessons, including preschool transitions between activities.
Write the Letter C Printable Worksheet
Once preschoolers can identify the letter C, it's time to write it! Download and print a tracing worksheet to master fine motor skills as well as letter recognition.
View & Download PDF
Advertisement
Kindergarten C-Word List
Kindergartners have a fundamental knowledge of the alphabet and are now ready to apply it to longer words. Check out these C words for kids, which include several CCVC words.
- cage - a structure with bars used to hold animals
- cake - a baked dessert made for special occasions
- call - to shout for someone's attention, or to reach someone via phone
- camp - to live outdoors in a tent for a short period of time
- cane - a curved walking stick designed to help someone walk
- cape - a piece of fabric worn at the shoulders
- card - a small piece of thick paper or plastic
- care - to have feelings about someone or something
- cash - money or currency
- cave - a hollowed-out section of a hill or mountain
- clam - a type of mollusk that lives in a tight shell
- clap - to make noise by slapping hands together
- club - a group of friends who gather for a purpose
- crab - a crustacean with two large pincers
Practice Silent E Words
Kindergartners who understand four-letter C words are ready to learn the phonics rules of silent E. Consider adding a lesson about words that end with a silent E as you teach kindergartners about the letter C.
Consider adding a lesson about words that end with a silent E as you teach kindergartners about the letter C.
Match the C-Word to the Picture Worksheet
Can your beginning readers match these words that begin with C to the correct pictures? Print up a fun matching worksheet that allows kindergartners to make connections between text and images.
View & Download PDF
Advertisement
Early Elementary C-Word List
Readers in grades 1-3 could use some C words in their vocabulary lists as well. Build foundational reading and spelling skills with these helpful words that start with C.
- cabin - a small house in the woods
- cable - a rope-like bunch of wires used to connect two things
- cactus - a desert plant
- candle - a mass of wax with a wick for burning
- capture - to take hold of or control of
- chair - a piece of furniture to sit on
- change - the act of becoming different
- cherry - a small, fleshy fruit with a hard pit
- chew - to use teeth to grind food into smaller pieces
- chill - a sudden feeling of coldness
- chin - the part of the face below the lower lip
- chirp - to make the short, shrill sound of birds
- classroom - a room in a school where classes are taught
- clerk - a person who works in an office, performing duties like filing and organizing
- climate - the weather of a location over a long period of time
- clock - a device for measuring and showing the time of day
- closet - a small space where clothes or other items are stored
- coast - land along the ocean
- coffee - a drink made from roasted beans
- contain - to serve as a holder for something
- could - a word used in place of "can" to demonstrate doubt
- coward - a person who lacks courage
- cracker - a thin, crisp wafer or biscuit
- craft - a special skill or art
- crash - to smash and make a loud noise
- crawl - dragging of the body along the ground
Make Spelling Fun (and Competitive)
If your elementary readers are tired of spelling quizzes, it's time to make spelling more engaging. Try out some fun DIY spelling games that are perfect for any classroom setting, and be sure to add these C words for kids in your weekly spelling activities.
Try out some fun DIY spelling games that are perfect for any classroom setting, and be sure to add these C words for kids in your weekly spelling activities.
Advertisement
Create a Visual For Young Learners
For words to stick in childrens' minds, it's useful to associate the words with the real world. As you practice each of the vocabulary words above, you might bring some props into the classroom. For example, hold up a candle, ask students to identify it, and then someone can walk up to the board and write out the word.
Upper Elementary C-Word List
You'll notice some lengthier additions here, including congratulate and calculate. Take a look at this sampling of words for upper elementary students.
- calculate - to use reason or common sense to determine something
- capable - having the skills to do something well
- capital - the seat of government
- century - a 100-year-long period of time
- challenge - an act of rebellion against someone or something
- character - a unique symbol, letter, or mark used in writing
- collaborate - to work together
- column - a vertical arrangement of something
- combine - to join together or unite
- commend - to recommend or praise someone
- companion - a partner or friend who accompanies
- compassion - to have sympathy and want to help someone
- compose - to put something in order to write a piece of music
- concise - brief and to the point
- confuse - to make someone unable to understand
- congratulate - to praise or compliment someone
- consequence - a natural result that flows from something else
- contaminate - to infect, corrupt, or make impure
- contribute - to give something
- convenient - something easy to do
- courteous - polite or considerate
- cumulative - increasing in size or quantity
Advertisement
Make Vocabulary Into Artwork
A fun way to encourage students to remember important vocabulary words is to ask them to draw one of the words. Give them some "free draw" time to select one of their vocabulary words on a sheet of paper. You can then staple their artwork to a piece of construction paper.
Give them some "free draw" time to select one of their vocabulary words on a sheet of paper. You can then staple their artwork to a piece of construction paper.
Play C-Word Charades
A great classroom activity here is one that will keep the students active and engaged. Write all of your vocabulary words on individual flashcards. Then, ask students to act out each of the words pulled. For this activity, they could easily act out companion or compose. Feel free to give them access to any props that may be required and, perhaps, you'll even create a word bank on the board so students have words to choose from.
Catapult Children's Vocabulary
The sooner the little learners of the world taste the triumph that comes with an ability to spell cat, the better positioned they will be to succeed in their academic endeavors. As you continue to shape lives, check out these free spelling printables.
You can also take a look at WordFinder's list of words that begin with the letter C for more spelling and vocabulary options. It allows you to easily create your own word list by filling up the advanced search fields by word length or letters included. Then, continue the alphabet journey with these words that start with D for kids.
It allows you to easily create your own word list by filling up the advanced search fields by word length or letters included. Then, continue the alphabet journey with these words that start with D for kids.
Staff Writer
List of Words That Start With Letter 'C' For Children
- List of C Words For Kids
- Words That Start With C For Kindergarten And Preschool Kids
- C Words For Lower Elementary Kids
- Cool Words That Start With The Letter C For Kids
- Positive Words That Start With Letter C For Children
- More Words That Start With The Letter C
- Activities That Will Help Your Child Learn Words With C
Every child is different, and so is the learning ability of each child. It’s vital to teach kids based on their learning abilities and learning speed. Introducing words that start with C to kindergarten, preschool, and nursery kids will teach them the new words and sounds. English words with C can have varied sounds and pronunciations based on its place in the word it the adjacent letter. It creates the /s/ sound in the word ‘city’, and the /k/ sound is in the cat word. Placed along with an H, it commonly creates a CH sound as in Choice or Change. In some cases, especially words adopted from french, it can also create a SH sound as in Chandelier and Chateau.
It’s vital to teach kids based on their learning abilities and learning speed. Introducing words that start with C to kindergarten, preschool, and nursery kids will teach them the new words and sounds. English words with C can have varied sounds and pronunciations based on its place in the word it the adjacent letter. It creates the /s/ sound in the word ‘city’, and the /k/ sound is in the cat word. Placed along with an H, it commonly creates a CH sound as in Choice or Change. In some cases, especially words adopted from french, it can also create a SH sound as in Chandelier and Chateau.
Parents and teachers must introduce kids to new words every time they get a chance, to expand their vocabulary. Teaching children words beginning with each letter individually also gives them a strong understanding of phonics. Listed below are various kinds of c words for your reference.
List of C Words For Kids
There are two types of sounds in words beginning with C. When the letter C appears in a word before or followed by the letters i, e, and y, then they are known as soft c words. If c is in front or followed by any other letter than these, they are known as hard c words. Let’s look into some of the words that start with C that are easy to grasp for kindergarten kids. Before going into long and complex words with C, start by introducing your kids to some commonly used words. These easy and simple words will help your child to quickly understand and recognise the letter C and the words beginning with C. Below are a few common words with C for fundamental learning.
If c is in front or followed by any other letter than these, they are known as hard c words. Let’s look into some of the words that start with C that are easy to grasp for kindergarten kids. Before going into long and complex words with C, start by introducing your kids to some commonly used words. These easy and simple words will help your child to quickly understand and recognise the letter C and the words beginning with C. Below are a few common words with C for fundamental learning.
| Cookie | Can | Cat |
| Call | Car | Cloud |
| Clock | clap | Cinema |
| Corn | Cow | Cake |
| Clean | Come | Cold |
| City | Close | Candy |
| Cap | Cycle | Cash |
| Collar | Coconut | Cream |
| Cheese | Circle | Castle |
| Circus | Calendar | Currency |
Words That Start With C For Kindergarten And Preschool Kids
If kindergarten, preschool or nursery kids can differentiate between the pronunciation of soft C and hard C, it’ll make them well-versed in understanding words that start with C. To make it easy for them to differentiate the words on their own, we must guide them to recognise and pronounce these words. Splitting the words letter by letter can help children in quickly grasping a particular word, its sound, and pronunciation. Let us introduce your child to two and three-letter words with C that are small, simple, and easy to teach kids.
To make it easy for them to differentiate the words on their own, we must guide them to recognise and pronounce these words. Splitting the words letter by letter can help children in quickly grasping a particular word, its sound, and pronunciation. Let us introduce your child to two and three-letter words with C that are small, simple, and easy to teach kids.
2 Letter Words That Start With C
3 Letter Words That Start With C
| Cub | Cab |
| Cow | Can |
C Words For Lower Elementary Kids
For lower elementary kids, teach these four-letter, five-letter, six-letter, and seven-letter c alphabet words to give a strong boost to their basic c words. For the kids up to class 3, these words will give a wider exposure related to c words. These big and slightly complex c words will add more information and details to your little tot knowledge. Honestly, kids are most of the time distracted when unsupervised and lack proper learning skills. To make sure they are engaged and participative; introduce them to new vocabulary activities at regular time intervals which also incorporate discipline to your little one. Given below are some of the four-letter, five-letter, six-letter, and seven-letter c alphabet words for strong vocabulary skills.
To make sure they are engaged and participative; introduce them to new vocabulary activities at regular time intervals which also incorporate discipline to your little one. Given below are some of the four-letter, five-letter, six-letter, and seven-letter c alphabet words for strong vocabulary skills.
4 Letter Words That Start With C
| Coat | Coin |
| Cure | Comb |
5 Letter Words That Start With C
| Curry | Click |
| Climb | Cloth |
6 Letter Words That Start With C
| Choice | Camera |
| Comedy | Clever |
7 Letter Words That Start With C
| Costume | Ceiling |
| Citizen | Curious |
Cool Words That Start With The Letter C For Kids
These cool words starting with c are the words that are used to express amazing and fun things that kids often find interesting. Teach these to your children and make their personalities even more cool and attractive. These words will be relatively in-depth, but your kids are going to love these cool words once they understand their meaning. So, here are some of the twenty cool c alphabet words:
Teach these to your children and make their personalities even more cool and attractive. These words will be relatively in-depth, but your kids are going to love these cool words once they understand their meaning. So, here are some of the twenty cool c alphabet words:
| Cosmic | Cacophony |
| Contextual | Consortium |
| Cahoots | Cosmetic |
| Crux | Catalyst |
| Crackerjack | Confectionary |
| Chronology | Courtesy |
| Chromosome | Calligraphy |
| Chivalry | Capacious |
| Chandelier | Cowabunga |
| Crucial | Colossal |
Positive Words That Start With Letter C For Children
Positive words should definitely be in your kid’s word bank to spread positivity and good vibes everywhere. To teach your little ones some good words starting with c, check out these positive words that start with C that add good personality and behaviour traits to your children’s learning journey. These words, along with creating positive thinking, also create empathy in your kids.
These words, along with creating positive thinking, also create empathy in your kids.
| Calm | Charity |
| Courageous | Caring |
| Comforting | Considerate |
| Communicative | Creative |
| Capable | Charming |
| Composed | Comdraderie |
| Classy | Confident |
| Champion | Cheerful |
| Charismatic | Congenial |
| Conscientious | Cool |
More Words That Start With The Letter C
If you are looking to teach your child the names of common things that start with C, then here are some names of animals, and places that start with C. Check out these words for making your kid’s vocabulary strong and diverse. Try creative ways that your kids find interesting to learn and retain the knowledge. Make them say out loud the words, write them down, pronounce them, and repeat them after you. This method guarantees their learning to be effective.
This method guarantees their learning to be effective.
Names Of Things That Start With C
| Cell | Computer |
| Cotton | Cake |
| Corset | Chimney |
| Camper | Cachet |
| Cape | Cage |
| Crust | Coral |
| Carpet | Centrepiece |
Names Of Animal That Start With C
| Cheetah | Cobra |
| Chicken | Chipmunk |
Names Of Places That Start With C
| California | Cambodia |
| Calcutta | China |
Activities That Will Help Your Child Learn Words With C
1. Let’s Make Cookies
Get your kids involved in engaging and participative activities to learn the letter C like making different types of cookies. Ask kids to bring a big cookie jar and then label it. Later, make cookies using cardboard cut-outs and write words with the letter C on every cookie. Pass on the jar to the kids and ask them to pick one cardboard cookie out of the jar and read aloud the word.
Later, make cookies using cardboard cut-outs and write words with the letter C on every cookie. Pass on the jar to the kids and ask them to pick one cardboard cookie out of the jar and read aloud the word.
2. Colouring And Connecting
Make them recognise and colour the objects that start with C. You can get your child some engaging worksheets and activity books for this exercise.
3. Flashcards And Charts
An easy and quick way to make your kids revise their lessons is through flashcards and charts. Hang a few visually appealing charts with both images and words with the letter C for effective learning.
4. Making A Cat-On-A-Cup
Ask your kid to paste stickers of googly eyes and pipe cleaners on a disposable cup along with small cut-outs of triangles as ears, and voila! The cat is ready.
Kids will not enjoy learning in a monotonous and boring environment. Fun and interactive learning sessions are the best way to introduce them to quality education. These engaging and participative sessions ensure that your kid learns genuinely and effectively. Take this step in your kid’s learning journey with words that start with C. Likewise, gradually introduce all the alphabet letters to make their vocabulary good and strong. Having a strong vocabulary will help your child in all areas related to communication, such as reading, writing, listening, and speaking.
These engaging and participative sessions ensure that your kid learns genuinely and effectively. Take this step in your kid’s learning journey with words that start with C. Likewise, gradually introduce all the alphabet letters to make their vocabulary good and strong. Having a strong vocabulary will help your child in all areas related to communication, such as reading, writing, listening, and speaking.
Also Read:
Learn Words that Start with D for Children
Words that Begin with ‘E’ for Kids to Improve Vocabulary
Words Starting with F for Children to Build Vocabulary
Letter A for preschool children
Tasks:
- to introduce the preschooler to the letter A, the correct pronunciation of the sound;
- to teach to write the capital letter A in the cells;
- to form an interest in learning with poems and riddles.
What does the doctor ask you to say when examining the throat? (Ahhh…)
Name what is drawn in the pictures below:
- Astra
- Stork
- Watermelon
- Bus
Ask what sound the words begin with - the names of the pictures?
To say A, you need to open your mouth wide and turn on your voice. Repeat: AAA.
Repeat: AAA.
Do your tongue, teeth or lips interfere with the free flow of air from your mouth? Notice how wide the mouth opens when we say A.
Write the letter A once on a blank piece of paper.
Remember and name the words that begin with A - animals, objects or names.
If the child is having difficulty, offer a simpler task:
AAALIK, AAAN - what do you hear at the beginning of the word?
Task: Letter A for preschoolers
Dot the corners of the cells with a simple pencil or ballpoint pen; draw - sticks neatly in the cells.
In cases where a child is asked to write a whole line of a letter, syllable, or word, an adult gives a spelling pattern at the beginning of the line.
If a preschooler has difficulties, then an adult can draw two reference lines, or put anchor points that the child will connect with lines, or write the letters in their entirety, and the child will simply circle them in a different color. Calligraphy at this stage of training should not be required.
Calligraphy at this stage of training should not be required.
Poems about the letter A
Do you know this letter? BUT?
The letter A is in front of you.
(S. Marshak)
Here is a letter like a hut.
Isn't it true, the letter is good!
And although it is simple in appearance,
A begins the ALPHABET.
(E. Tarlapan)
Let the alphabet
Begins with STORK -
It, like the alphabet,
Begins with A!
(V. Zakhoder)
Everyone knows,
The letter A is a very nice letter.
And besides, the letter A
is the main one in the alphabet.
They love this sound
Both Andrey and Allochka,
Stick like that and stick like that,
And in the middle there is a stick.
(E. Uspensky)
Tale about the letter A
Why A first?
There was a terrible noise in the room. All the letters crawled out of the alphabet and argued loudly: why is this A the very first letter of the alphabet?
“Down with impostor A,” the vowels shouted.
- Long live the Abracadabra! (i.e. confusion).
— What is it doing, huh? the hissers hissed.
- The letter with which a sore throat and a shark begins, put at the head of the alphabet! Wow w-jokes ...
- That's right, - the consonants silently thought, - it's not for nothing that the most delicious things - watermelon, orange, apricot, pineapple - begin with A.
But the letter Y screamed loudest of all.
— Therefore, — said A, who had been silent until now, — that the very first word of every baby begins with A.
— What kind of word is that? I persisted.
— Agu, — said A.
— And besides, I look like an admiral standing on the captain's bridge. And everyone knows that the admiral must always be ahead!
- Yes! said the firm sign.
(G. Yudin)
Proverbs and sayings starting with the letter A
The ABC is a step to wisdom.
Treasure is not needed if the family is in harmony.
Friendship is not strong, which is contained in words.
Water does not flow under a lying stone.
Mathematics is not learned without letters and grammar.
Without labor there is no fruit.
Small and daring.
Die yourself, but rescue a comrade.
Riddles for children starting with the letter A
Maple leaves turned yellow,
Swift-winged swifts flew to the countries of the south.
What a month, Tell me!
(August)
Does not fly, does not buzz,
A beetle runs along the street.
And burning in the eyes of the beetle
Two brilliant lights.
(car, bus)
Day and night standing on the roof
This miraculous sentry:
He will see everything, hear everything,
He will share everything with me!
(Antenna)
They came to us with melons
Striped balls.
(Watermelons)
On the page of the primer
Thirty-three heroes.
Wise men-bogatyrs
Every literate person knows.
(Alphabet)
Look, the house is standing,
Filled to the brim with water,
No windows, but not gloomy,
Transparent on four sides.
The inhabitants of this house are
All skillful swimmers.
(Aquarium)
My friend has been to such a port,
Where there is no water around at all.
But
were always going to this port with people and cargo ships.
(Airport)
Standing on the roof -
All pipes are higher.
(Antenna)
Lesson summary:
- Pronunciation of new words from pictures increases the preschooler's vocabulary, develops speech and memory.
- Cellular exercises develop fine motor skills of the hands.
- Poems affect not only the development of memory. It has been proven that if you learn several lines every day, new neural connections appear in the brain, and the overall learning ability increases.
- Riddles develop intelligence in children, the ability to analyze and prove. Educators use riddles when teaching children to increase interest during complex tasks.
All information is taken from open sources.
If you believe your copyright has been infringed, please contact write in the chat on this site, attaching a scan of a document confirming your right.
We will verify this and immediately remove the publication.
Features of the development of figurative memory in preschool children
Memory as a cognitive process ensures the integrity and development of the child's personality. Preschool childhood is the most favorable age for the development of memory, especially figurative. Figurative memory is the memorization, preservation and reproduction of images of previously perceived objects and phenomena of reality. There are subspecies of figurative memory - visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, gustatory.
As L. S. Vygotsky believed, memory becomes the dominant function and a long way goes in the process of its formation precisely at preschool age. Neither before nor after this period does the child memorize the most diverse material with such ease.
A. A. Lyublinskaya believes that figurative memory - representations, or preserved images of previously perceived objects, constitute the main content of the memory of a child - a preschooler. First of all, these are ideas about the surrounding people, their actions, about animals and birds, about space and time.
Purpose of work : to study the development of figurative memory in preschool children.
Object of study: memory of children at senior preschool age.
Subject of research : figurative memory of older preschoolers, features of its development.
Tasks:
1. Analyze various approaches to the development of figurative memory as a mental process.
2. Select the existing diagnostic techniques according to figurative memory.
3. Qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the data obtained
Memory can be defined as a psychophysiological process that performs the functions of storing, storing and reproducing material. These three subprocesses are the main ones for memory. They are distinguished not only on the basis of the fact that these are different processes in their structure, initial data and results, but also for the reason that each of these processes may be developed differently in different people. There are people who, for example, have difficulty remembering, but they reproduce well and retain the material they memorize for a long time. These are people with developed long-term memory. There are also individuals who, for example, quickly remember, but also quickly forget what they remember. They had strong short-term and working memory.
These three subprocesses are the main ones for memory. They are distinguished not only on the basis of the fact that these are different processes in their structure, initial data and results, but also for the reason that each of these processes may be developed differently in different people. There are people who, for example, have difficulty remembering, but they reproduce well and retain the material they memorize for a long time. These are people with developed long-term memory. There are also individuals who, for example, quickly remember, but also quickly forget what they remember. They had strong short-term and working memory.
“Short-term memory is a memory in which the storage of material is limited to a certain, usually short period of time. The short-term memory of a person is connected with his actual consciousness” [6, p. 125].
Long-term memory is designed for a long period of storage of information, as a rule, not predetermined. It is not connected with the actual consciousness of a person and assumes his ability at the right time to recall what he once remembered. In contrast to short-term memory, where recall is not required (since what has just been perceived is still in actual consciousness), with long-term memory it is always necessary, since information related to perception is no longer in the sphere of actual consciousness.
In contrast to short-term memory, where recall is not required (since what has just been perceived is still in actual consciousness), with long-term memory it is always necessary, since information related to perception is no longer in the sphere of actual consciousness.
Auditory memory is a good memorization and accurate reproduction of various sounds (speech, music). It is necessary for musicians, philologists, linguists.
Verbal-logical memory is characterized by the fact that a person who possesses it quickly and accurately remembers the meaning of events, the meaning of a read text, etc. This type of memory is often possessed by scientists and teachers of educational institutions.
In addition to those mentioned, there are other types of memory, in particular tactile, olfactory, gustatory, i.e., figurative memory.
In connection with the development of genetics and molecular physiology, as well as cybernetics, studies of the biological foundations and physiological mechanisms of memory have attracted attention. Some of these studies were carried out at the neuronal level, i.e., at the level of studying the work of individual nerve cells and their ensembles in the process of memorization. However, completely unambiguous, convincing answers to questions about the role of various brain cells in the processes of memorizing and reproducing information, as well as about the significance for memory of changes occurring at the molecular level, have not yet been received.
Some of these studies were carried out at the neuronal level, i.e., at the level of studying the work of individual nerve cells and their ensembles in the process of memorization. However, completely unambiguous, convincing answers to questions about the role of various brain cells in the processes of memorizing and reproducing information, as well as about the significance for memory of changes occurring at the molecular level, have not yet been received.
Thus, there are a huge number of types of memory and approaches to its study; currently, many different systems and methods have been developed to influence human memory in order to improve it. Memory allows a person to ensure the continuity of mental life. We know that we are alive if we remember ourselves. Depending on what a person remembers, they distinguish between motor memory (remembering one's own movements, developing skills), emotional (memory of feelings), figurative (images of perception, thinking and imagination) and verbal-logical (preservation of thoughts, the general meaning of the memorized information). Types of memory are related to each other and do not exist in isolation. However, depending on the intensity of use in activity, any situations, there is a dominance of certain types of memory, due to the activity of thinking, perception, imagination.
Types of memory are related to each other and do not exist in isolation. However, depending on the intensity of use in activity, any situations, there is a dominance of certain types of memory, due to the activity of thinking, perception, imagination.
Development of figurative memory in senior preschool age.
Preschool age is characterized by intensive development of the ability to memorize and reproduce. The period for which people are remembered, events in preschool age are postponed for an indefinitely long period. Indeed, if it is difficult or almost impossible for us to remember anything from the events of early childhood, then preschool childhood leaves many vivid memories. The memory of a preschooler is mostly involuntary. This means that the child most often does not set himself the conscious goal of remembering anything. Memorization and recollection occurs independently of his will and consciousness. They are carried out in the activity and depend on its nature. The child remembers what was paid attention to in the activity, what impressed him, what was interesting.
They are carried out in the activity and depend on its nature. The child remembers what was paid attention to in the activity, what impressed him, what was interesting.
The quality of involuntary memorization of objects, pictures, words depends on how actively the child acts in relation to them, to what extent their detailed perception, reflection, grouping occurs in the process of action. So, when simply looking at pictures, the child remembers much worse than when he is offered to put these pictures in their places, for example, put aside separately things that are suitable for the garden, kitchen, children's room. Involuntary memorization is an indirect, additional result of the actions of perception and thinking performed by the child.
Arbitrary forms of memorization and reproduction begin to take shape in the middle preschool age and are significantly improved in older preschoolers . The most favorable conditions for mastering voluntary memorization and reproduction are created in play, when memorization is a condition for the child's successful fulfillment of the role he has assumed. The number of words that a child memorizes, acting, for example, in the role of a buyer who fulfills an order to buy certain items in a store, turns out to be higher than the number of words memorized at the direct request of an adult.
The number of words that a child memorizes, acting, for example, in the role of a buyer who fulfills an order to buy certain items in a store, turns out to be higher than the number of words memorized at the direct request of an adult.
Mastering arbitrary forms of memory includes several stages. At the first of these, the child begins to single out only the very task of remembering and recalling, without yet mastering the necessary techniques. At the same time, the task of remembering is singled out earlier, since the child first of all encounters situations in which he is expected to remember exactly, to reproduce what he perceived or did before. The task of remembering arises as a result of the experience of remembering, when the child begins to realize that if he does not try to remember, then he will not be able to reproduce what is expected of him.
The child does not invent the methods of memorization and recall by himself. They are suggested to him in one form or another by adults. So, when an adult, for example, gives a child an instruction, he immediately offers to repeat it. Asking the child about something, the adult guides the memory with questions: “What happened next?” The child gradually learns to repeat, comprehend, connect material for the purpose of memorization, use connections when remembering. In the end, children realize the need for special memorization actions, master the ability to use auxiliary means in them.
So, when an adult, for example, gives a child an instruction, he immediately offers to repeat it. Asking the child about something, the adult guides the memory with questions: “What happened next?” The child gradually learns to repeat, comprehend, connect material for the purpose of memorization, use connections when remembering. In the end, children realize the need for special memorization actions, master the ability to use auxiliary means in them.
At younger preschool age, the main type of memory is figurative . Its development and restructuring are associated with changes taking place in various spheres of the child's mental life and, above all, in cognitive processes - perception and thinking. Perception, although it becomes more conscious, purposeful, still retains globality. Thus, the child predominantly singles out the most striking features of an object, not noticing other often more important ones. Therefore, the ideas that make up the main content of the memory of a preschooler are not infrequently fragmentary. Memorization and reproduction occur quickly, but unsystematically. The kid "jumps" from one sign or component of the situation to another. In memory, he often retains the secondary, and forgets the essential. The development of thinking leads to the fact that children begin to resort to the simplest forms of communication, and this ensures the systematization of ideas.
Memorization and reproduction occur quickly, but unsystematically. The kid "jumps" from one sign or component of the situation to another. In memory, he often retains the secondary, and forgets the essential. The development of thinking leads to the fact that children begin to resort to the simplest forms of communication, and this ensures the systematization of ideas.
Thus, figurative memory is a memory for representations, for pictures of nature and life, as well as for sounds, smells, tastes. It can be visual, auditory, gustatory, tactile, olfactory.
The development of figurative memory begins from preschool age and continues to develop and improve throughout a person's life.
In the development of a child's figurative memory during preschool age, noticeable shifts occur, which are expressed in the following:
1. The volume of saved representations increases.
2. Thanks to the culture of perception - ideas about objects and phenomena are schematic, fused and diffuse in children, they become more and more meaningful, clear and differentiated. At the same time, they are becoming more and more general.
At the same time, they are becoming more and more general.
3. Representations become connected and systematic. They can be combined into groups, categories or pictures.
4. The mobility of the stored images is growing, the child can freely use them in different activities and in different situations.
Individual differences in memory can also be due to innate characteristics of higher nervous activity and education. Individual features cause different types of memory. Individual differences in memory can be of two kinds. On the one hand, the memory of different people is distinguished by the predominance of one or another modality - visual, auditory, motor; on the other hand, the memory of different people may differ in the level of its organization.
Thus, it is necessary to take into account the following important points when forming figurative memory :
- ask the baby more often about what he remembers - this is how we give the child the opportunity to understand that we are interested in his person;
- ask the child about past events - this will allow the child to evaluate events and, to a certain extent, assume, foresee the future;
- fixing the baby's attention on the events of the past - this will help him capture in his mind memories of a certain order of things: for example, getting up, having breakfast, walking, etc. - and gives the child a sense of security, a sense of stability in life, he learns to control events in his life;
- and gives the child a sense of security, a sense of stability in life, he learns to control events in his life;
- to collect interesting events - this develops memory, the memory of the atmosphere of joy that reigned then remains.
Experimental study of the development of figurative memory
older preschoolers.
Study of the dependence of the amount of arbitrary figurative memory on the content of the memorized material.
Purpose: to study the level of development of figurative memory in children of senior preschool age, to analyze the result.
In accordance with the goal, I used the technique of Uruntaeva G.A.
Diagnostic method.
G. А.
Preparation of the study : pick up 6 objects well known to the child (matryoshka, pipe, boat, cube, orange, telephone), 6 pictures (duck, cactus, plane, candy, chick, fur coat), 6 cards depicting geometric shapes: a circle, square, triangle, rectangle, trapezoid, oval, sheets of paper, 6 colored pencils.
Conducting research . The experiment is carried out individually with children aged 5–7 years and includes 3 series that differ in the content of the material to be memorized: objects; Pictures; geometric figures. The material for the experiment is always placed randomly, at some distance from each other. Time is 20 seconds. The child is asked: "Look carefully at the objects lying on the table, remember them, and then name them." The playback time is no more than 5 minutes. When playing geometric shapes, the child is asked to draw them, offering paper and colored pencils. If the child draws the figures in the wrong color, he can be asked: “Why did you take a pencil of a different color?”
Data processing . The number of reproducible material is counted for all series of the experiment, the results are drawn up in a table. Find out what material is best remembered by children. It is especially necessary to analyze the results of memorizing geometric shapes, finding out whether the color chosen by the child for their image corresponds to the sample. It should be noted whether the child depicted new figures.
It should be noted whether the child depicted new figures.
In the study, I examined a group of children of senior preschool age of 10 children.
| 1 group |
| 1. Christina S. - 6 years, 1 month |
| 2. Nikita A. - 6 years old |
| 3. Tanya - 6 years, 2 months |
| 4. Sasha Z. - 6 years, 1 month |
| 5. Ksyusha Z. - 6 years, 6 months |
| 6. Misha M. - 6 years, 3 months |
| 7. Alyosha K. - 6 years, 3 months |
| 8. Oleg B. - 6 years old. |
| 9. Olesya K. - 6 years, 1 month |
| 10. Zhenya Zh. - 6 years, 3 months |
The children's answers were recorded in a table, which was then used to calculate the percentage of what preschool children remember better from the proposed material.
From the resulting table, we can conclude that the subject, visual and abstract material was memorized by children differently.
Table 1
Study of the formation of memorization of subject material
| Number of children | Amount of playback material | Percentage |
| one | 6 | ten % |
| 2 | 5 | twenty % |
| 7 | four | 70% |
table 2
The study of the formation of visual material memorization
| Number of children | Amount of playback material | Percentage |
| 3 | 6 | thirty % |
| 5 | 5 | fifty % |
| 2 | 3 | twenty % |
Table 3
The study of the formation of memorization of abstract material
| Number of children | Amount of playback material | Percentage |
| 2 | 6 | twenty % |
| 3 | 5 | thirty % |
| 2 | four | twenty % |
| 3 | 3 | thirty % |
Based on the results obtained, it can be concluded that the best children memorized pictures, in second place - objects, then geometric shapes.
These data testify to the peculiarities of age, since preschool children have developed visual-figurative thinking, and what they saw, perceived visually in the form of pictures, was remembered better. As for the memorization and reproduction of geometric shapes, here you should pay attention to the number of figures drawn by the child and whether the chosen color matches the sample.
The number of figures in most children does not correspond to the full set (6), only Sasha Z., Kristina S., depicted all the figures. The color is basically not the same as the sample. The quality of the image is explained by the lack of formation of graphic skills, not all children draw straight lines in geometric shapes, it is easier for them to draw rounded shapes.
After the results for each material have been calculated, it is necessary to derive the average according to the method used in the group. To do this, it is necessary to highlight the high level, above average, medium and low.
High level corresponds to - 6 reproduced items.
Above average corresponds to - 5 reproduced items.
Average corresponds to - 4 reproduced items.
Low level corresponds to - 3 reproduced items.
High level: 10% + 30% + 20% = 60%: 3 series = 20%
Above average: 20% + 50% + 30% = 100%: 3 = 33%
Average: 70% + 0% + 20% = 90%: 3 = 30%
Low level: 0% + 20% + 30% = 50%: 3 = 17%
After analyzing various approaches in studying the development of figurative memory as a mental process, we can conclude that such psychologists as L. S. Vygotsky, Luria A. R., Leontiev A. N. were engaged in the study of memory, its formation, contribution to the generalization of the concept of memory as a mental process.
R., Leontiev A. N. were engaged in the study of memory, its formation, contribution to the generalization of the concept of memory as a mental process.
Quantitative and qualitative analysis of the obtained data:
- visual material is remembered by children of preschool age better than subject material, which indicates the age norm. Abstract material from 10 children - 9 remembered - a circle, 8 - a square and an oval, a trapezoid was named - 5 children out of 10, which corresponds to the age norm. Children of senior preschool age named those figures that are constantly used in the classroom and they meet them in everyday life. The quality of involuntary memorization of objects, pictures, words depends on how actively the child acts in relation to them, to what extent their detailed perception, reflection, grouping occurs in the process of action.
In the process of studying the volume of figurative memory in older preschoolers, the following results were obtained:
High level of development of figurative memory - 20%,
Above average - 33%;
The average level is 30%;
Low level - 17%.
A qualitative analysis of the memorization of arbitrary figurative memory from the content of the memorized material shows:
High level - 10%
Average level - 20%
Mixed - 70%.
The material was memorized differently by boys and girls: boys out of 8 children had 2 children with an average level, 6 with a mixed level, 1 out of 2 girls with a mixed level, and 1 with a high level of memorization of the proposed material.
I have developed recommendations for the development of memory in preschool children for children with an average and low level:
- contribute to the continuous development of the child as a person, develop the figurative memory of children;
- apply in their work classes, games, training exercises that contribute to the development of figurative memory of children;
- use tasks for the development of memory that correspond to the individual capabilities of each child;
- ask the baby more often about what he remembers - this is how we give the child the opportunity to understand that we are interested in his person;
- ask the child about past events - this will allow the child to evaluate events and, to a certain extent, assume, foresee the future;
- fix the baby's attention on the events of the past - this will help him capture in his mind the memories of a certain order of things: for example, getting up, having breakfast, walking, etc. - and gives the child a sense of security, a sense of stability in life, he learns to control events in his life;
- and gives the child a sense of security, a sense of stability in life, he learns to control events in his life;
- to collect interesting events - this develops memory, the memory of the atmosphere of joy that reigned then remains.
Literature:
- Vygotsky L. S. Lectures on psychology. SPb Soyuz 1999 - 142 p.
- Vygotsky L. S. Memory and its development in childhood. M., 1979. 305 p.
- Gamezo M. V. Atlas of Psychology. M., "Enlightenment" 1986.– 206 p.
- Istomina Z.M. The development of arbitrary memory in preschool children / collection of articles, ed. Leontieva A. N., Zaporozhtsa A. V. "Issues of the psychology of a child of preschool age" M., 1995. 142 p.
- Krutetsky V. A. Psychology. M., "Enlightenment", 1980. - 295 p.
- Luria A. R. A little book about big psychology / reader in general psychology: Psychology of memory M., ed. Moscow State University, 1979. 195 p.
- Luria A.

Learn more