Verbs for i
Verbs That Start With I
DESCRIPTION
Verbs That Start With I
SOURCE
Aleksandra Nekrasova / iStock / Getty Images Plus
PERMISSION
Used under Getty Images license
When you think of the letter "i," what springs to mind? Maybe igloos and icicles? When the letter "i" takes on the verb form, we’re met with all kinds of interesting creations, from illuminate, to illustrate, to immortalize. An "i" verb may be just the ticket if you’re trying to improve your writing. Let’s take a look at 50 of the most popular verbs that start with "i."
What Is a Verb?
Verbs express action or a state of being. In the English language, every word sits in a specific place and plays a specific role in a sentence. Most of the time (but not always), verbs come after a sentence's subject and before its object. For example, "Ivy
imitates her friends. " In this sentence, "Ivy" is the subject, "imitates" is the verb showing action, and "friends" is the object receiving the action of the verb.
Advertisement
50 Verbs Starting With I
Advertisement
We love to idealize our favorite writers. Or is it idolize? Perhaps it’s both. Take the time to investigate the meaning of some illuminating verbs that start with "i."
| Verb | Definition |
idealize | to perceive as representative of perfection; to see as ideal |
identify | to determine who or what something is |
idle | to do nothing |
idolize | to look up to someone as a hero |
ignite | to start something on fire |
ignore | to deliberately avoid noticing |
illuminate | to light something up |
illustrate | to tell a story using drawings or pictures; to explain so something is clear |
imagine | to form a mental image; to consider what something would be like |
imbibe | to consume alcohol |
imbue | to fill with a particular quality |
imitate | to copy or model after; to mimic |
immerse | to dunk something in liquid; to become completely involved with something |
immigrate | to move permanently to a new country |
immobilize | to prevent the movement of something |
immortalize | to preserve in memoriam forever; to make immortal |
immunize | to render immune by inoculation |
impair | to hinder or weaken something |
impart | to share information; to make known |
impeach | to charge someone in an official position with misconduct |
impede | to block movement or progress |
impersonate | to mimic the appearance or manner of a person |
implant | to insert firmly or deeply |
implement | to put something into effect |
implicate | to show that someone is connected to a crime |
implode | to collapse and burst inward |
implore | to beg or plead |
imply | to suggest something indirectly |
import | to bring goods into one country from another |
impose | to force something to be accepted; to take advantage of someone's hospitality |
impress | to do something that causes others to view you with admiration |
improve | to make better |
incarcerate |
to put in jail |
incinerate | to burn something until only ashes remain |
incite | to rile people up |
include | to contain or consider something as part of a whole |
incorporate | to work into something that already exists |
increase | to grow in size or magnitude |
indicate | to point towards or be a sign of something |
indulge | to permit oneself to do or have something pleasurable |
infect | to contaminate someone or something with a disease |
influence | to have an impact on; to persuade indirectly |
inform | to provide knowledge or information |
insert | to put one thing into another |
inspire | to act in a way that gives someone an urge to do something |
interpret | to translate or explain what something means |
interrupt | to cause something to stop for a period of time |
intrude | to become involved in something where you don’t belong |
invest | to put resources into something in the hopes of earning a personal or financial gain |
itch | to cause an uncomfortable feeling that makes one want to scratch |
Advertisement
Identifying Verb Types
Advertisement
The primary category of verbs is action verbs, which are sometimes called dynamic verbs.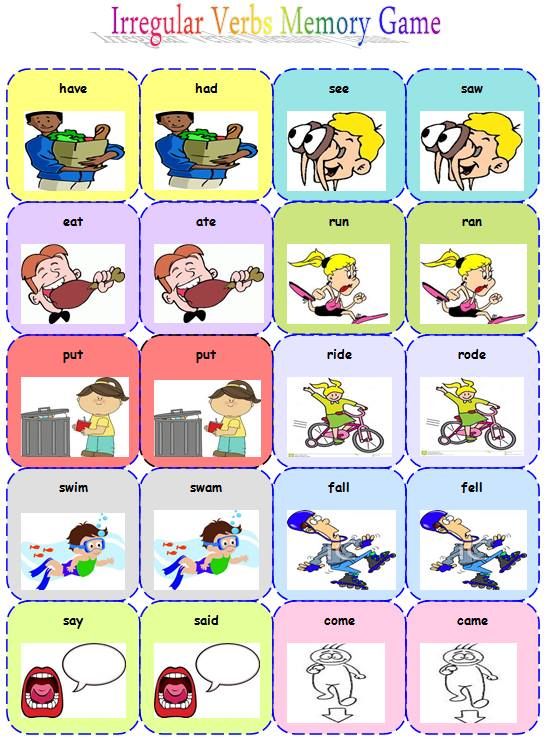 This type of verb expresses physical or mental action occurring in the sentence. For example, "Irene indulges in a weekly spa session." There are a lot of action verb examples in the English language, some of which are regular verbs, while others are irregular verbs.
This type of verb expresses physical or mental action occurring in the sentence. For example, "Irene indulges in a weekly spa session." There are a lot of action verb examples in the English language, some of which are regular verbs, while others are irregular verbs.
- Regular verbs transform from present to past tense with the simple addition of the suffix -ed at the end. For example, "They couldn’t influence his thinking, so they influenced his child’s thinking."
- Irregular verbs don't follow conventional conjugation patterns. For example, "keep" becomes kept in the past tense, not keeped (which is not a word). There aren't any common irregular verbs that start with "i."
Linking verbs are another type of verb. The word "is" is a form of the verb "to be" that begins with an "i." In the statement "Scott is nasty," the word "is" links the subject (Scott) to an adjective that describes him (nasty). There are also a number of helping verbs in English. These extend the meaning of main verbs. The word "is" can function as a helping verb. For example, in the statement "It is raining," the use of the word "is" as a helping verb lets readers know that the main verb (raining) is happening right now.
There are also a number of helping verbs in English. These extend the meaning of main verbs. The word "is" can function as a helping verb. For example, in the statement "It is raining," the use of the word "is" as a helping verb lets readers know that the main verb (raining) is happening right now.
10 Example Sentences Using I-Verbs
Are you ready to start inserting "i" verbs into your writing? As a final step of preparation, explore some sample sentences that feature some "i" verbs hard at work. Let them inspire you to craft some interesting sentences of your own!
- Readers tend to idealize life in a fairy tale.
- Let’s watch the stars illuminate the sky.
- She likes to imbue her characters with bravery and strength.
- He loves it when seasoned writers impart their knowledge on him.
- They’re going to implement a “no sugar” rule in their house.

- They always impose their viewpoints on us.
- Don’t follow any crowds that are trying to incite violence.
- Every year, they increase their budget for groceries.
- Let’s inspire everyone to higher levels of greatness.
- We should only invest our time in people who make us feel happy.
Instant Intensity
With an extensive selection of "i" verbs in your vocabulary, your writing may experience instant intensity. Who knows what heights you can inspire your readers to explore once you illuminate their minds? Don’t stop there! You can also dabble in the world of "i" adjectives with this list of 20 adjectives that start with the letter "i." Take your "i" word insights to the next level by exploring this full list of words that begin with "i" on WordFinder by YourDictionary. Then, get refocused on verbs by moving on to verbs that start with "j. " You'll jostle your way through the entire alphabet in no time at all.
" You'll jostle your way through the entire alphabet in no time at all.
Verbs that start with i
Here is a list of verbs that start with I. Verbs may appear in the below word list in a variety of tense such as past and present, and many types of I verbs are included in this online resource such as action verbs. Being able to find the right verb starting with I can be very useful for writers, college students, and anyone who likes English verbs.
iced.
idealized, identified, identifies, identify, identifying, idle, idled, idling, idolize, idolized.
ignite, ignited, ignore, ignored, ignores, ignoring.
illuminate, illuminated, illuminating, illumine, illumined, illumines, illustrate, illustrated, illustrates, illustrating.
imagine, imagined, imagines, imagining, imbedded, imbibe, imbibed, imbruing, imbued, imitate, imitated, imitates, imitating, immersed, immortalized, impacted, impair, impaired, impaled, impaling, impart, imparted, imparts, impeded, impelled, impelling, impending, imperil, imperiled, imperilled, impersonalized, impersonated, impersonates, impinge, impinging, implanted, implement, implemented, implementing, implicated, implied, implies, implore, implored, imploring, imply, implying, import, imported, imports, impose, imposed, imposes, imposing, imprecates, impress, impressed, impresses, impressing, imprint, imprinted, imprisoned, imprisons, improve, improved, improves, improving, improvise, improvised, improvises, impute, imputed.
inactivate, inaugurated, inaugurating, inbreeding, incanted, incapacitated, incarcerated, incarnate, incensed, incepted, incepting, inched, incise, incite, incited, inciting, inclined, inclosed, include, included, includes, including, incorporate, incorporated, incorporates, incorporating, increase, increased, increases, increasing, incriminating, incubated, incubating, inculcated, incur, incurred, incurring, incurs, index, indexing, indicate, indicated, indicates, indicating, indicted, indisposed, individualized, individualizing, indoctrinated, indorsed, induce, induced, induces, inducing, inducted, indulge, indulged, indulging, industrialized, indwelling, infect, infected, infer, inferred, infest, infested, infiltrated, infiltrating, inflame, inflamed, inflate, inflated, inflected, inflecting, inflict, inflicted, inflicting, influence, influenced, influences, influencing, inform, informed, informing, informs, infuriate, infuriated, ingested, inhabit, inhabited, inhabiting, inhaling, inheres, inherit, inherited, inheriting, inherits, inhibit, inhibited, inhibiting, inhibits, initialed, initiate, initiated, initiates, initiating, inject, injected, injecting, injured, injuring, inlaid, innovate, inquire, inquired, inquiring, inscribed, insert, inserted, insinuated, insinuates, insinuating, insist, insisted, insisting, insists, inspect, inspected, inspecting, inspire, inspired, inspires, inspiring, install, installed, installing, instigate, instigating, institute, instituted, instituting, institutionalized, instruct, instructed, instructing, instructs, insulate, insulated, insulating, insult, insulted, insulting, insure, insured, insures, insuring, integrate, integrated, integrates, integrating, intend, intended, intending, intends, intensified, intensify, intensifying, interact, interacting, interacts, intercede, intercept, intercepted, interconnected, interest, interested, interests, interfere, interfered, interferes, interfering, interjected, interlaced, interlacing, interlocking, intermeshed, internalized, internationalized, interned, interpenetrate, interpenetrates, interpolated, interposed, interposing, interpret, interpreted, interpreting, interprets, interred, interrelated, interrupt, interrupted, intersect, intersecting, interspersed, intertwined, intervene, intervened, intervening, interview, interviewed, interviewing, interweaving, interwoven, intimated, intimating, intimidate, intimidated, intoned, intoxicated, intoxicating, intrigued, introduce, introduced, introduces, introducing, introjected, introverted, intrude, intruded, intrudes, intruding, inundated, inundating, inure, inured, invade, invaded, invades, invading, invalidate, invalidated, inveigh, invent, invented, inventing, inventory, invert, inverted, invest, invested, investigate, investigated, investigates, investigating, investing, invests, invigorating, invite, invited, invites, inviting, invoke, invoked, invoking, involve, involved, involves, involving.
iodinate, iodinated, iodinating, ionized, ionizing.
iron, ironed, ironing, irradiated, irrigate, irrigating, irritated, irritates.
isolate, isolated, isolating, issue, issued, issues, issuing.
italicized, itch, itches, itching, itemized, itemizing.
Verbs1.com has many examples of verbs which begin with various letters. Hope you enjoy this page of verbs that start with i and the rest of this verb list site as well.
Verb tenses - conjugation, forms and examples
We will teach you how to write without errors and tell stories in an interesting way
Start learning
“Yesterday I passed the test, today I am writing a report, and tomorrow I will have a rest” - this is how we travel through time with the help of verbs when we tell our stories. Let's find out how the 3 tenses of verbs differ and how to determine them.
Definition of a verb
First, let's remember what a verb is.
The verb is an independent part of speech that denotes the action of an object.
Verbs answer the questions: “what to do?”, “what to do?”, “what did you do?”, “what did you do?”, “what are you doing?”, “what will you do?”.
Examples of verbs:
The verb has a set of grammatical features that is characteristic only for this part of speech:
-
Permanent features of the verb:
a. view,
b. transitivity,
c. repayment,
nine0012 d. conjugation. -
Variable signs of the verb:
a. inclination,
b. time,
c. face,
d. number,
e. genus.
In this article we will talk about one of the non-permanent grammatical features of the verb - tense. And if you want to repeat the material about other features of verbs, then take a look at our other articles.
And if you want to repeat the material about other features of verbs, then take a look at our other articles.
Demo lesson in Russian
Take the test at the introductory lesson and find out what topics separate you from the "five" in Russian. nine0003
What are tenses of verbs
In fact, the verb not only denotes the action of an object, but also carries information about what tense this action belongs to.
In Russian, verbs have three tenses:
-
A verb in the present tense indicates that the action is taking place at the moment of speech.
-
A verb in the future tense is a sign that the action will take place after the moment of speech.
-
The past tense of the verb indicates that the action has already happened before, before the moment of speech. nine0003
The type of the verb directly affects the tense in which the verb can be used:
-
imperfective verbs have forms of all three tenses ( dances - danced - will dance, cooks - cooked - will cook ),
-
perfective verbs have only past and future tenses ( danced - will dance, cooked - will cook ).

Remember!
In the present and future tenses, verbs change according to numbers and persons, and in the past - according to numbers and genders. nine0003
To figure out how to distinguish verb tenses from each other, let's look at each of them with examples.
Russian language at Skysmart online school is a fascinating lesson on an interactive platform with examples from contemporary texts.
Present tense
If the verb denotes an action that is happening at this moment and answers the question “what is he doing?” is a verb in the present tense.
Examples of verbs in the present tense:
-
girl (what is she doing?) dancing ;
-
dad (what is he doing?) cooking ;
-
fish (what is he doing?) swimming ;
-
sun (what is he doing?) setting ;
-
birch (what does it do?) costs .

Not like everyone else
Perfective verbs (that is, those that answer the question “what to do?”) Are not used in the present tense. For example, the verb dance is only past ( danced ) and future ( dance ) tense.
Present tense verbs change in person and number and have a different set of endings depending on the conjugation.
Verb endings of I conjugation in present tense
| 1 person | 2nd person | 3rd person | |
| singular | i buy ayu I write y | you kupa eat you write eat | coupa et she writes em |
| plural | we buy eat we write eat | buy buy you write you go | they buy ute they write ut |
Verb endings of II conjugation in present tense
| 1 person | 2nd person | 3rd person | |
| singular | i sit y i lepl yu | nine0168 he sid it she lep it | |
| plural | we sid im we lep im | you sit ite you lep ite | they sid yat oni lep yat |
Future tense
The future tense verb denotes an action that will take place and answers the questions “what will he do?”, “what will he do?”. These actions will be implemented after the moment when we talk about them, that is, in the future.
These actions will be implemented after the moment when we talk about them, that is, in the future.
Examples of verbs in the future tense:
-
girl (what will she do?) will dance ;
-
girl (what will he do?) will dance ;
-
Petya (what will he do?) will make a postcard ;
-
dog (what will he do?) barks ;
-
we (what are we going to do?) we will cook dinner .
Verbs in the future tense change in person and number.
The future tense of a verb in Russian can be simple and complex. And here we again need to recall the concept of the form of verbs. nine0003
Simple future tense form perfective verbs - those that answer the question "what to do?". Examples of simple future tense:
Examples of simple future tense:
-
cook - I will cook;
-
carry - you carry;
-
attach - she will attach;
-
fly away - we will fly away;
-
move away - you will move away;
nine0036 -
answer - they will answer.
The complex future tense is actually not that complicated, but it is called so because it is composed of two words: the verb to be in the personal form and the infinitive of the semantic verb. Examples of a complex future tense:
-
cook - I will cook;
-
wear - you will wear;
-
do - she will do; nine0084
-
fly - we will fly;
-
walk - you will walk;
-
answer - they will answer.

Past tense
A past tense verb denotes an action that happened in the past and answers the questions “what did you do?”, “what did you do?”. These actions have already taken place up to the moment when we are talking about them.
Examples of verbs in the past tense:
-
girl (what did you do?) danced ;
-
girl (what were you doing?) dancing ;
-
dad (what did he do?) cooked dinner ;
-
dad (what was he doing?) cooking dinner ;
-
apple tree (what did you do?) grew in the garden ;
-
Polina (what did you do?) made cocoa ;
-
chick (what did you do?) jumped on the branches .

In the past tense, verbs change according to gender and number.
The grammatical indicator of the past tense of the verb in Russian is the suffix -l- . It occurs in most verbs, although there are exceptions. For example, verbs with stems ending in -eret- form the masculine past tense without this suffix: die - died, lock - locked. But in the feminine and neuter forms the suffix is in place: died l a, locked l a .
Suppletivism of stems
Some verbs do not form the past tense from the stem from which the infinitive is formed. For example, the past tense of the verb to go is walked, walked, walked. Linguists call this phenomenon suppletivism.
Table "Tenses of verbs in Russian"
To memorize new material faster, use special tablets. You can print them out and peek when you do your homework in Russian.
You can print them out and peek when you do your homework in Russian.
| Times | Answer questions | Indicate actions | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real | what does it do? what are they doing? what am I doing? what are you doing? nine0003 | that take place in the present, at the moment of speech | draws draw draw drawing |
| Past | what did you do? What diddo? what did they do? what did they do? | which have already happened or happened in the past tense before the moment of speaking | painted nine0012 drewpainted painted |
| Future | what will he do? what will they do? what will do? what will they do? | which will take place in the future tense, after the moment of speech | will draw draw will draw draw |
How to determine the tense of a verb
The easiest way to determine tense is to ask a question about the verb. In what tense we ask the question, the verb is in the same tense. For example:
In what tense we ask the question, the verb is in the same tense. For example:
-
Marina (what was she doing?) was reading;
-
you (what are you doing?) going;
-
we (what are we going to do?) write down the examples.
Also, pay attention to the grammatical features of the verb. We have already listed them above, now let's put them all together in a handy table. nine0003
Table "Grammatical signs of tenses of verbs"
| Present | Past tense | Future tense |
|---|---|---|
| Personal forms of conjugated imperfective verbs have different endings depending on the conjugation: - duma yu , duma eat , duma no , duma em —I conjugation; - School U , View See , View , View YAT - IIII GURNING. | Suffix -l- with stem of both types: read , read . Suppletivism basics: go - went . Base on -heret without suffix -l- : lock up - locked up, die - died . | A simple future - from a perfect look: caress - caress Difficult future - verb to be in personal form + infinitive of the main meaning: you will answer, you will love . |
An example of changing a verb by tenses
And finally, for consolidation - the paradigm of changing verbs in all three tenses. nine0003
Please note that the perfective verb draw does not have a present tense, and the future tense is formed differently for different types of verbs.
For clarity, we have highlighted the grammatical indicators of tenses: personal endings, the suffix -l- and the verb be in the future tense.
| Past tense | Present | Future tense | |||||
| Unit number | Mn. number | Unit number | Mn. number | Unit number | Mn. number | ||
| Male genus | see l , draw l | 1st person | see y , mo yu | see im , mo em | will be see is , draw | will be see is , draw eat | |
| Female genus | see l a, draw l a | 2nd person | see ish , mo eat | see or , mo no | will see , draw eat | will see , draw ee | |
| Wed. | see l o, draw l o | 3rd person | see et , mo no | see yat , mo yut | will be see is , draw et | will be see is , draw yut | |
Cheat sheets for parents
All Rules for the Russian language at hand
Lidia Kazantseva
Author Skysmart
to the previous article
12 Full and brief form of adjectivesto the next article
9000 154. 2K 9000
2K 9000 transitional and non -transitions.
Get a free speaking and writing plan with a free introductory lesson
In an introductory lesson with a methodologist
-
We will identify knowledge gaps and give tips on learning
-
We will tell you how classes
-
We will select
times of English verb
times in English in English in English. however, as in any other, it is an indicator that expresses the relationship between the time to which the statement refers and the moment of the statement itself. The tenses of English verbs allow you to understand when a certain event happened. nine0003
There is no language that has more than three tenses: past, present and future. Basic tenses in English are formed as follows:
- Past
Example: I learned English.
 — I studied English.
— I studied English. - Present
Example: I learn English. - I learn English.
- Future
Example: I will learn English. — I will study English .
Linguists call other subtypes of tenses of the English verb aspects. They characterize the duration of the described action, its frequency and completeness.
There are three key aspects to the English language:
- Simple (or Indefinite - simple or indefinite)
Example: I learn English. - I learn English.
- Progressive (or Continuous) nine0002 Example: I am learning English. - I learn English.
- Perfect (perfect, perfect or complete)
Example: I have learned English. — I learned English.
Combining the last two aspects gives rise to another aspect:
Three tenses and four aspects create 12 different verb forms.
Category Simple
This is the group of simple tenses. It includes actions that are performed / were performed / will be performed frequently and / or regularly, as well as one-time acts and events. nine0003
It includes actions that are performed / were performed / will be performed frequently and / or regularly, as well as one-time acts and events. nine0003
Present Simple
The present tense in this category is formed from the infinitive of the verb without to. Moreover, if the subject is in the 3rd person (he / she / it), then the ending -s is added to the predicate. The interrogative and negative forms are built using the auxiliary verb do (in the 3rd person - does).
Formula : I/We/You/They + verb
Examples: I think. - I think. We smile. We are smiling. you know. - You (you) know (-eat). Boy jump. The boys are jumping. nine0084
Formula : He/She/It + verb + -s (-es)
Examples: He goes. - He walks. She speaks. - She is talking. A boy jumps. - The boy is jumping.
Past Simple
In the past, the second form of the verb is used with the ending -ed (if the verb is correct), did is added for questions and denials, and the verb is left in the first form.
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + 2nd form of the verb nine0003
Examples: I played. - I played. He told. - He said. She stopped. She stopped. It worked. - It worked. We discussed. - We discussed. You did. - You did it. They forgot. - They forgot.
Future Simple
The future tense is also characterized by a verb in the infinitive, only an auxiliary word will is added before it. With its help form questions and denials.
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + will + verb nine0003
Examples: I will come. - I will come. He will win. - He will win. She will understand. She will understand. It will break. - It will break. We will find. - We'll find. You will see. - You will see. They will agree. - They will agree.
Continuous category
English verb tenses representing the Continuous group are continuous. The times of this group mark the duration of the ongoing process, the performance of actions at a particular point in time. The emphasis is not on the fact of doing something, but on the time at which these actions are performed / performed / will be performed. nine0003
The emphasis is not on the fact of doing something, but on the time at which these actions are performed / performed / will be performed. nine0003
Present Continuous
The continuous present tense in English is characterized by the use of the construction to be + verb ending -ing. The creation of interrogative and negative sentences does not require an auxiliary do, since the predicate to be is used for this.
Formula : I am + verb-ing
Example: I am singing. - I sing.
Formula : He/She/It is + verb-ing nine0003
Examples: He is smiling. - He smiles. She is lying. - She's lying. It is shining. - It shines.
Formula : We/You/They are + verb-ing
Examples: We are listening. - We are listening. You are dancing. - You are dancing. They are swimming. - They are swimming.
Past Continuous Tense
The past tense is built in the same way, but to be is used in the past form - was / were. nine0003
nine0003
Formula : I/He/She/It + was + verb-ing
Examples: I was singing. - I sang. He was walking. - He was walking. She was writing. - She wrote. It was falling. - It was falling.
Formula : We/You/They + were + verb-ing
Examples: We were reading. - We read. You were talking. - You were talking. They were running. - They were running.
Future Continuous
The future tense requires the verb will with the particle be. nine0003
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + will be + verb-ing
Examples: I will be speaking. - I will speak. He will be building. He will build. She will be eating. - She will eat. It will be operating. - It will work. We will be drawing. We will draw. You will be thinking. - You will think. They will be walking. - They will walk.
Category Perfect
English verb tenses belonging to the Perfect group express completed actions, the result of which is directly related to a given moment in time. In such expressions, the simple past tense cannot be used, because the context suggests that the time interval be underlined. This action was either completed just now, or by a certain moment. nine0003
In such expressions, the simple past tense cannot be used, because the context suggests that the time interval be underlined. This action was either completed just now, or by a certain moment. nine0003
Present Perfect
The present tense construction contains the verb have/has and the 3rd form of the verb.
Formula : I/We/You/They + have + 3rd form of the verb
Examples: I have started. - I started. We have gone. — We left. You have finished. - You're done. They have come. - They came.
Formula : He/She/It + has + 3rd form of the verb
Examples: He has decided. - He decided. She's done. - She did. It has turned off. - It turned off. nine0084
Past Perfect
The same scheme is typical for the past tense, but have is used in the past form - had.
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + had + 3rd form of the verb
Examples: I had done. - I did. He had seen. - He saw. She had found. - She found. It had fallen. - It fell. We had learned. - We have learned. You had decided. - You decided. They had gone. - They left.
- I did. He had seen. - He saw. She had found. - She found. It had fallen. - It fell. We had learned. - We have learned. You had decided. - You decided. They had gone. - They left.
Future Perfect
The construction of the future tense is completed with the verb will.
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + will have + 3rd form of the verb
Examples: I will have finished. - I will finish. He will have decided. He will decide. She will have painted. She will draw. It will have produced. - It will produce. We will have arrived. - We will arrive. You will have confirmed. - You will confirm. They will have received. - They'll get it. nine0084
Category Perfect Continuous
All tenses of English verbs included in the Perfect Continuous group are perfect continuous. Their main purpose is to emphasize that the action / event will still continue when the specified point in time comes, or another action will already begin / take place. In other words, the action has been in progress for some time and will still continue.
In other words, the action has been in progress for some time and will still continue.
Present Perfect Continuous
The present tense construction includes the verb have been and the verb ending -ing.
Formula : I/We/You/They + have been + verb-ing
Examples: I have been reading. - I read. We have been waiting. - We expect. You have been playing. - You're playing. They have been working. - They work.
Formula : He/She/It + has been + verb-ing
Examples: He has been running. - He is running. She has been laughing. - She is laughing. It has been working. - It is working. nine0084
Past Perfect Continuous
When forming a sentence in the past tense, have been becomes had been.
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + had been + verb-ing
Examples: I had been waiting. - I was waiting. He had been singing. - He sang. She had been walking. - She was walking. It had been ringing. - It rang. We've been learning. - We studied. You had been building. - You built. They had been swimming. - They were swimming. nine0084
She had been walking. - She was walking. It had been ringing. - It rang. We've been learning. - We studied. You had been building. - You built. They had been swimming. - They were swimming. nine0084
Future Perfect Continuous
Will is used for the future tense formula.
Formula : I/He/She/It/We/You/They + will have been + verb-ing
Examples: I will have been playing. - I will play. He will have been reading. - He will read. She will have been solving. She will decide. It will have been showing. - It will show. We will have been waiting. - We'll be waiting. You will have been translating. - You will translate. They will have been calculating. They will count. nine0084
All tenses of verbs in English with the most characteristic tenses for each category can be presented in the form of a table:
Future in the Past
There is another category of tenses in the English verb - future in the past. Sentences with these constructions refer to the future from the point of view of a certain moment in the past.
Sentences with these constructions refer to the future from the point of view of a certain moment in the past.
Example: We wondered if the train would arrive on time. We thought about whether the train would arrive on time. nine0084
The tenses Future in the Past are used in subordinate clauses after the words said (that), told (that), thought (that), etc.
Future in the Past can also refer to present, continuous, perfect, or continuous perfect.
- Simple Future in the Past denotes actions in the future perceived from the past.
Example: He said he would go to the dentist. He said he's going to the dentist. nine0084
- Continuous Future in the Past denotes a process that will last at a certain moment in the future, perceived from the past.
Example: He was imagining how he would be sipping a cocktail on his vacation. He imagined how he would be sipping a cocktail on vacation.
- Perfect Future in the Past expresses an action that will be completed by a certain moment in the future, perceived from the past nine0002 Example: We hoped we would have finished our homework by midday.



 genus
genus 









