What are the dra levels
Understanding Your Child's DRA Reading Level
The Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) is an individually administered assessment of a child’s reading capabilities. It is a tool to be used by instructors to identify a students reading level, accuracy, fluency, and comprehension. Once levels are identified, an instructor can use this information for instructional planning purposes.
Want even more book and reading ideas? Sign up for our Scholastic Parents newsletter.
DRA Testing
The DRA test is traditionally administered on an annual or semi-annual basis. The test measures nine categories of reading behavior and six types of errors. It was developed in 1986 (and revised in both 2000 and 2003) by a committee of educators and is intended to evaluate certain aspects of your child’s reading level.
How DRA Levels and Testing Work Together
Tasks measured by the DRA test are divided into several skill sets. Rhyming, alliteration, segmentation, and phonemic awareness are tested in the phonemic awareness section. Letter naming, word-list reading, spelling, decoding, analogies, structural analysis, and syllabication are tested in the alphabetic principle/phonics portions. Oral reading fluency or words per minute for contextual reading are tested under fluency. Vocabulary, comprehension, and reading engagement skills are also measured in the test.
After the test is evaluated and scored, your child is assigned a numeric (or alphanumeric for very early readers) DRA level A1 through 80. Children with stronger reading abilities yield higher numbers. Teachers are easily able to give children books they can read by choosing a text with the corresponding DRA level.
How to Find Books on Your Child’s Level
Once your teacher gives you your child’s level, you can search for books at a particular DRA level on Scholastic’s Book Wizard. By providing your child with books on his level at home, you are ensuring reading advancement and success with materials that will not cause your child stress or discouragement.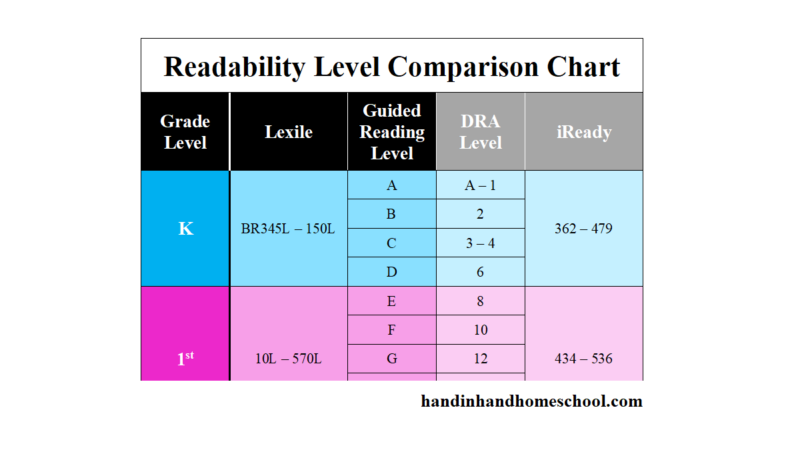
Raise a reader by getting the best book recommendations, reading tips, and discounts delivered straight to your inbox.
PLEASE ENTER A VALID EMAIL ADDRESS.
PLEASE SELECT A NEWSLETTER OPTION.
Preschool View Sample
Elementary School View Sample
Privacy Policy
<div><h3>Thanks for signing up! Look out for a confirmation email from us.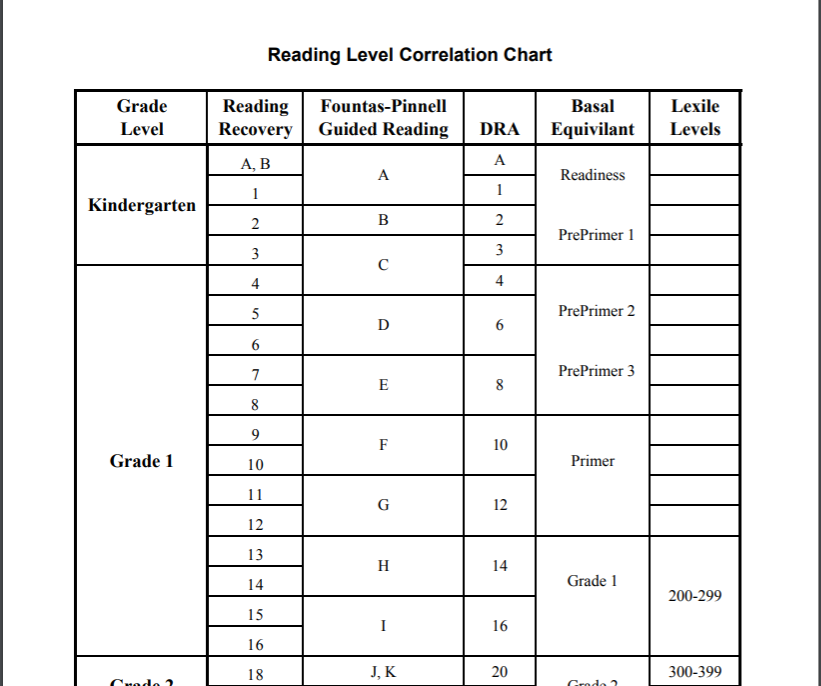 </h3><h4>Want to connect now? Find us on social media!</h4><h3><a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.facebook.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/facebook.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
</h3><h4>Want to connect now? Find us on social media!</h4><h3><a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.facebook.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/facebook.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
How to 'Read' Your Child's Reading Scores
Is your child a G or an L? A 13 or a 24? As a second grader, is a DRA 32 a good reading score?
In most schools, and especially around report card time, kids come home with reports that detail a child's reading level.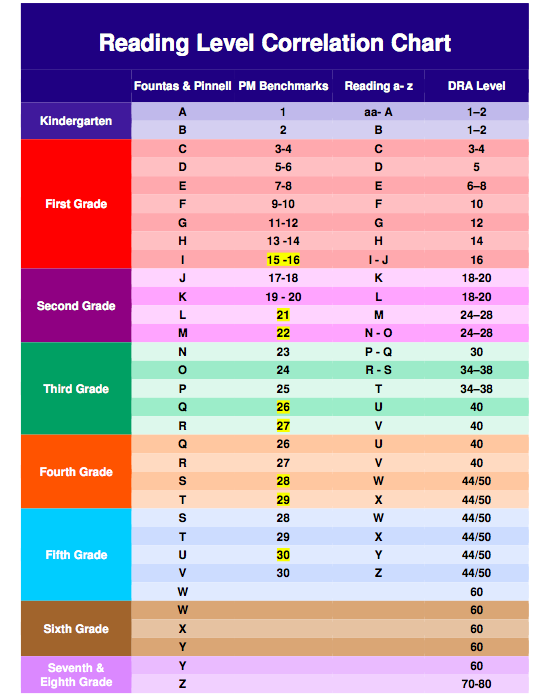 Oftentimes, these reports make little sense to parents. While most kids make terrific progress during the school year, parents sometimes struggle to make the same progress in interpreting reading scores and different leveling systems.
Oftentimes, these reports make little sense to parents. While most kids make terrific progress during the school year, parents sometimes struggle to make the same progress in interpreting reading scores and different leveling systems.
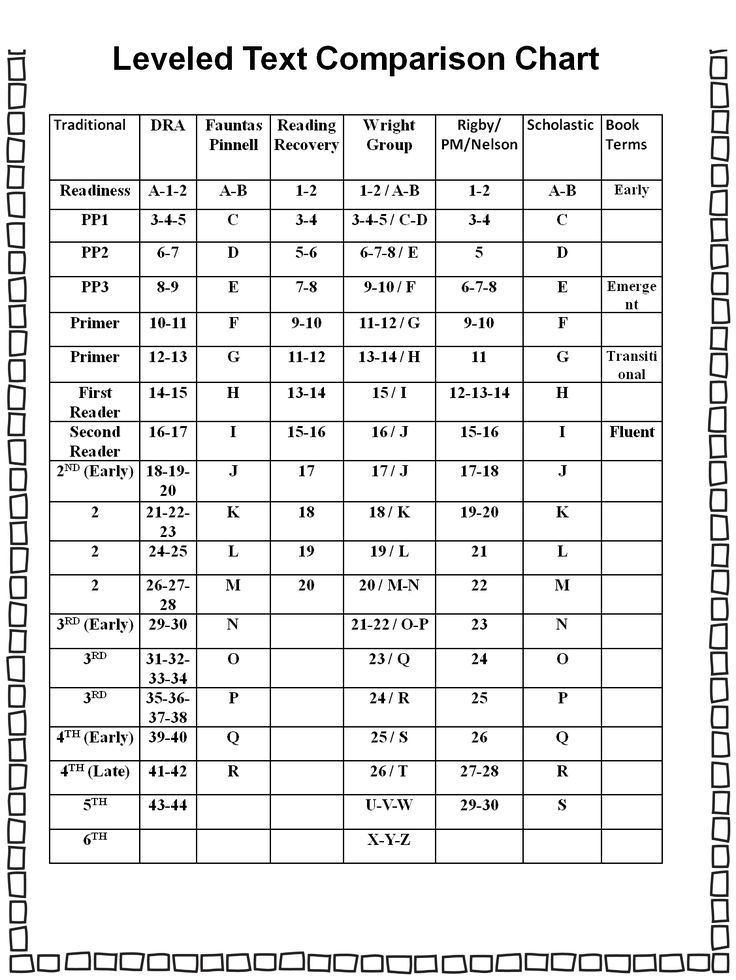
Most schools use one of three major leveling systems to define a child's reading level: Guided Reading, Reading Recovery, and Developmental Reading Assessment. Although some variations exist, the procedure for determining a child's reading score follows a sequence. First, a teacher (or school) chooses a benchmark book for a grading period. Then, each child sits one-on-one with a teacher and reads that book. The teacher reads along with a child and keeps track of the child's reading accuracy. After the story is read, teachers typically ask for a retelling of the book, or may ask some comprehension questions. With each assessment, a teacher is trying to find the level at which a child can read with 90 to 95% accuracy with good comprehension. That is considered your child's instructional reading level.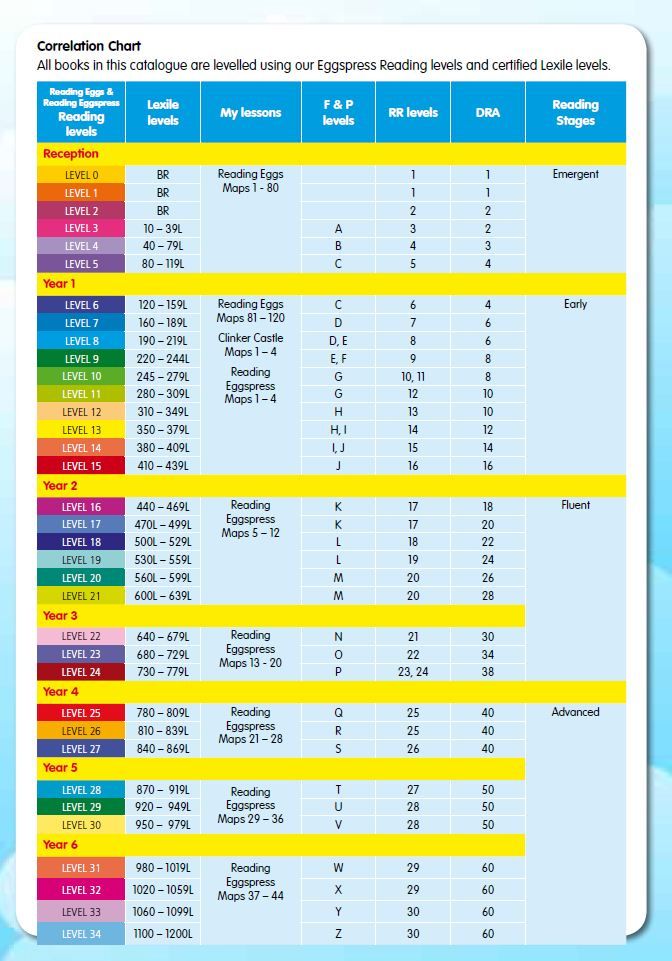
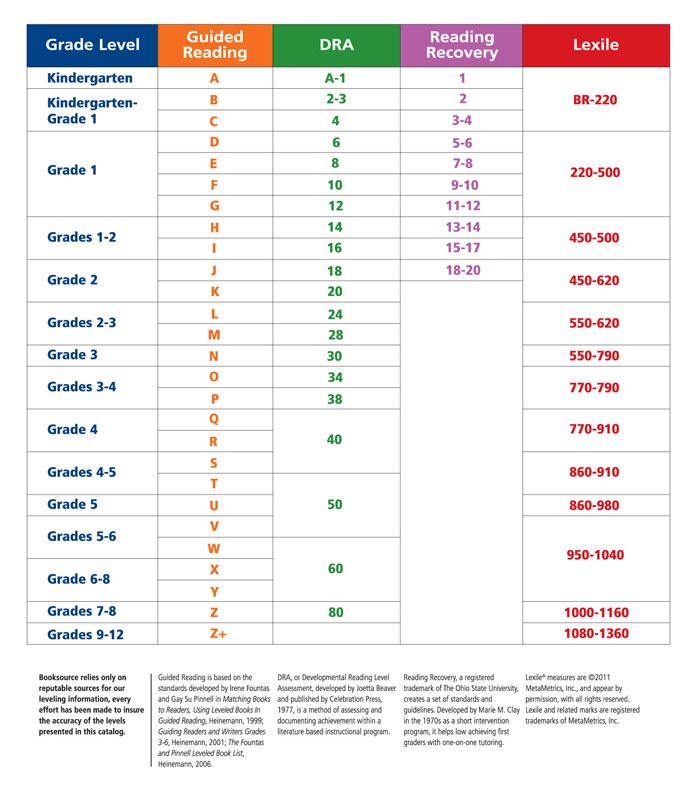
Here's a little about each leveling system, and a chart that shows you how they relate to each other and to a grade level assignment.
Guided Reading levels
This leveling system is based on the understanding that good teachers carefully match a reader with a book. Based on several characteristics of a book, such as text length, and vocabulary, books are assigned a Guided Reading letter. There are 26 levels, identified by letters A-Z (A being the easiest), and each book level has its own characteristics. If your child is "reading on a Level G," for example, he or she is able to read books with several events and a variety of characters. Sentences are longer than in previous levels, and the book may contain more difficult high-frequency words.
Reading Recovery
This leveling system is based on Reading Recovery, a one-on-one intervention program designed for low achieving first graders. Books used within this intervention program are grouped by characteristics and range from 1-50 (1 being the easiest).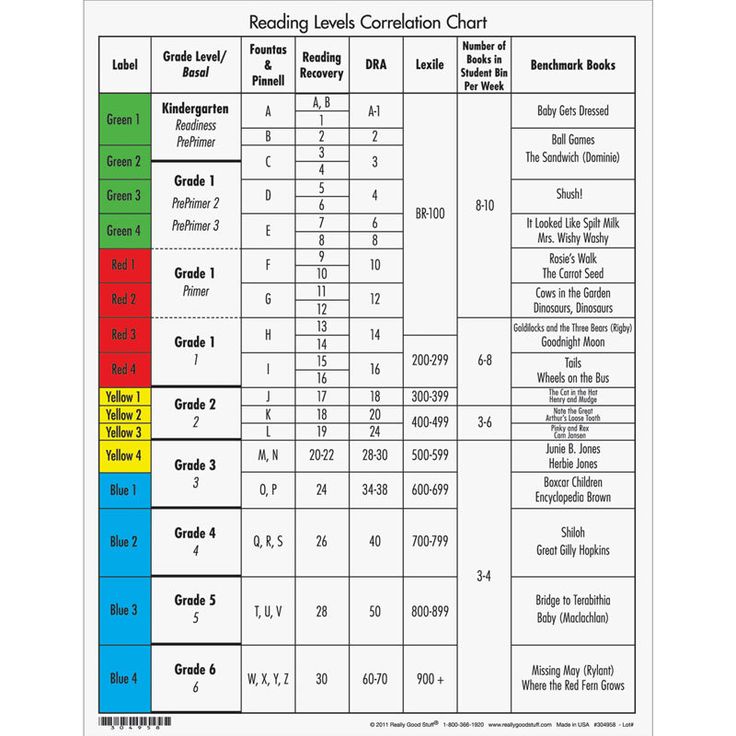 As with Guided Reading, books within a certain level share similar features. If your child is, "reading on a Level 2," he or she is able to follow a pattern within a book after it has been introduced by the teacher.
As with Guided Reading, books within a certain level share similar features. If your child is, "reading on a Level 2," he or she is able to follow a pattern within a book after it has been introduced by the teacher.
Developmental Reading Assessment
The Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) is a series of leveled books and recording sheets designed to allow teachers to determine students' reading accuracy, fluency, and comprehension levels. Texts range from A-80 (A being the easiest). In most schools, teachers collect DRA information at the end of each grading period to determine student progress. Students are determined to be near, at, or above grade level, below grade level, or significantly below grade level based on their performance.
As a parent, it's important to understand the leveling system used at your school and how your child is doing toward meeting grade level expectations. Keep track of those letters and numbers being sent home, and if you don't see progress in your child's reading level, make an appointment to sit down with the teacher.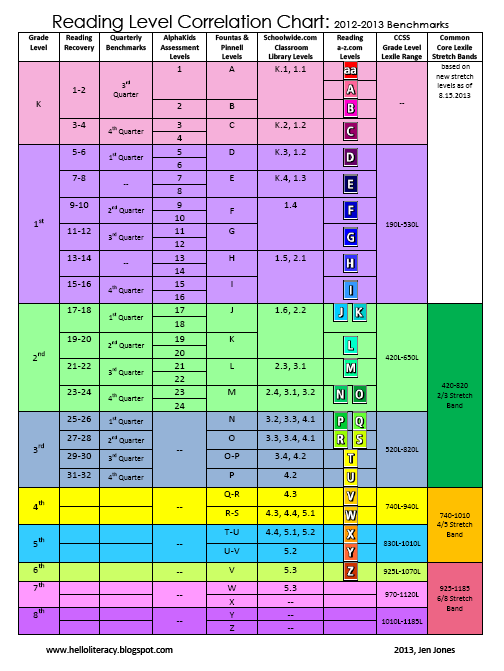
Clash of Clans | Clash of clans | Dragon
Dragon is one of the normal warriors in Clash of Clans.
Dragons are known throughout the world for their strength. This scaly, flying terror knows no mercy, and nothing escapes its fiery breath.
Description
Dragon is a formidable flying unit capable of attacking both ground and air troops . When attacking, dragons deal area damage.
In contrast to balloon , dragons attack all buildings one after another, not just defensive buildings .
The dragon's area damage has a very short range. This can be seen when he attacks troops or walls .
Description of the general tactics of using the dragon on the battlefield is here .
Base stats
| Barracks level: | 9 | Priority target: | any, ground and air |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hiring time: | 30 min. | Attack type: | area damage |
| Seat: | 20 | Attack speed: | 1.5 sec. |
| Movement speed: | 16 | Attack Range: | 3 cells |
Upgrade Changes
The dragon gets significant graphical changes on all 5 levels.
At level 1, dragon has green skin with white eyes.
At level 2, dragons change their skin color from green to purple. The eye color of dragons is the same as the color of elixir .
At level 3, dragon changes its skin color to brown.
At level 4, dragon becomes a deep red, eyes engulfed in flames. Supercell called this unit level " Ancient Dragon ".
Supercell called this unit level " Ancient Dragon ".
At level 5, the dragon turns brown, its eyes are engulfed in flames, the spikes on its back turn gold . Supercell called this unit level " Golden Dragon ".
Visual changes (swipe images right and left)
Dragon Enhancements (swipe table right and left)
| Level | Damage per attack | Damage per second | Damage per second/place | Health | Cost of recruitment | Laboratory Level | Research cost | Study time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210 | 140 | 7 | 1.900 | 25,000 | - n/a - | - n/a - | - n/a - |
| 2 | 240 | 160 | 8 | 2.100 | 29,000 | 5 | 2,000,000 | 7 days |
| 3 | 270 | 180 | 9 | 2. 300 300 | 33,000 | 6 | 3,000,000 | 10 days |
| 4 | 300 | 200 | 10 | 2,500 | 37,000 | 7 | 7,000,000 | 14 days |
| 5 | 330 | 220 | 11 | 2.700 | 42,000 | 8 | 8,000,000 | 14 days |
| Total: | 20,000,000 | 45 days | ||||||
Interesting details
You can have a maximum of 12 dragons in your army camps . This number can be increased to 13 if one more dragon out of 9 is included.0003 clan fortress .
The first person to reach 4000 trophies (Jorge Yao) used an army consisting entirely of dragons . He used 4 lightning spells , one for the clan fortress troops and the rest to destroy air defenses. This method provided 50% damage to the bases almost every time he attacked, thanks to which he received this achievement.
This method provided 50% damage to the bases almost every time he attacked, thanks to which he received this achievement.
Dragon was given an area attack of update on March 12, 2013 to , which made them much more powerful against groups of troops .
Upon death, the skeleton of the dragon takes on a human form.
The shadow of the dragon has an oval shape, it does not follow the contours of the owner .
Dragon is one of five air units (along with healer , minion , hellhound and hellpup ) that never stop flapping 's wings because they can't land.
The first version of the dragon
When the dragon spews fire, it does not come out of its mouth, but from its chin.
In the update on May 23, 2013 dragon added an extra pair of legs and fire from its mouth. The appearance has also been seriously changed, so that dragon looks more like a living creature, and not like robot .
Dragon is one of two types of troops (along with P.E.K.K.A ) that changes its appearance at each level.
A very thin, transparent line runs along the base of the wing of the dragon level 3 and above, but it is barely noticeable.
Dragon is one of two troops whose picture in barracks is not a first-level warrior, the other is wall-breaker .
January update 2013 , when black elixir was added, it was stated that this resource is formed for the fossils of black dragon (at that time, the maximum level of dragon was 3). However, there was no relation between black elixir and dragon .
However, there was no relation between black elixir and dragon .
Dragons do not attack walls , however, they can damage them when attacking a target in the area of the wall.
Level 5 Dragon - Art
. . .
Types of WDM drivers - Windows drivers
Twitter LinkedIn Facebook E-mail address
- Article
- Reading takes 2 minutes
There are three types of WDM drivers: bus drivers, function drivers, and filter drivers.
- The bus driver controls a single I/O bus device and provides per-slot device-independent functionality. Bus drivers also detect and report on child devices connected to the bus.

- The function driver controls a single device.
- A filter driver filters I/O requests for a device, device class, or bus.
In this context, a bus is any device to which other physical, logical, or virtual devices are connected; the bus includes traditional buses such as SCSI and PCI, as well as parallel, serial, and i8042 ports.
It is important for driver developers to understand the different kinds of WDM drivers and to know which driver they are writing. For example, whether a driver handles each Plug and Play IRP and how such IRPs are handled depends on what type of driver is being written (bus driver, function driver, or filter driver).
The following figure shows the relationship between bus driver, function driver, and device filter drivers.
Each device typically has a bus driver for the parent I/O bus, a function driver for the device, and zero or more filter drivers for the device. Driver designs that require a large number of filter drivers do not provide optimal performance.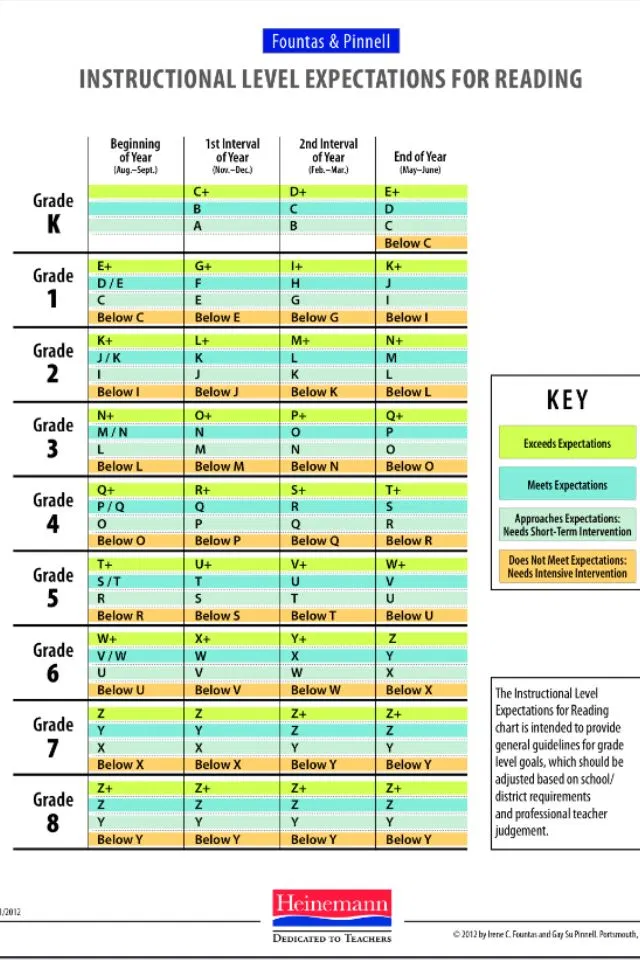
The drivers in the previous figure are shown below.
-
The bus driver serves the bus controller, adapter or bridge. Bus drivers are mandatory drivers; There is one bus driver for each type of bus on the computer. Microsoft provides bus drivers for most common buses. IHV and OEMs may provide other bus drivers.
-
The bus filter driver typically adds a value to the bus and is provided by Microsoft or the system's OEM. There can be any number of bus filter drivers for a bus.
-
low-level filter drivers typically change the behavior of a device's hardware. They are optional and are usually provided by IHV. There can be any number of low-level filter drivers for a device.
-
Function driver is the main driver for the device. The feature driver is usually written by the device vendor and is required (unless the device is used in raw mode ).
-
top-level filter drivers typically provide additional functionality to the device.
Learn more