What is fluent reading
Fluency | Reading Rockets
Fluency is defined as the ability to read with speed, accuracy, and proper expression. In order to understand what they read, children must be able to read fluently whether they are reading aloud or silently. When reading aloud, fluent readers read in phrases and add intonation appropriately. Their reading is smooth and has expression.
Children who do not read with fluency sound choppy and awkward. Those students may have difficulty with decoding skills or they may just need more practice with speed and smoothness in reading. Fluency is also important for motivation; children who find reading laborious tend not to want read! As readers head into upper elementary grades, fluency becomes increasingly important. The volume of reading required in the upper elementary years escalates dramatically. Students whose reading is slow or labored will have trouble meeting the reading demands of their grade level.
What the problem looks like
A kid's perspective: What this feels like to me
Children will usually express their frustration and difficulties in a general way, with statements like "I hate reading!" or "This is stupid!". But if they could, this is how kids might describe how fluency difficulties in particular affect their reading:
- I just seem to get stuck when I try to read a lot of the words in this chapter.
- It takes me so long to read something.
- Reading through this book takes so much of my energy, I can't even think about what it means.
A parent's perspective: What I see at home
Here are some clues for parents that a child may have problems with fluency:
- He knows how to read words but seems to take a long time to read a short book or passage silently.
- She reads a book with no expression.
- He stumbles a lot and loses his place when reading something aloud.
- She reads aloud very slowly.

- She moves her mouth when reading silently (subvocalizing).
A teacher's perspective: What I see in the classroom
Here are some clues for teachers that a student may have problems with fluency:
- Her results on words-correct-per-minute assessments are below grade level or targeted benchmark.
- She has difficulty and grows frustrated when reading aloud, either because of speed or accuracy.
- He does not read aloud with expression; that is, he does not change his tone where appropriate.
- She does not "chunk" words into meaningful units.
- When reading, he doesn't pause at meaningful breaks within sentences or paragraphs.
How to help
With the help of parents and teachers, kids can learn strategies to cope with fluency issues that affect his or her reading. Below are some tips and specific things to do.
What kids can do to help themselves
- Track the words with your finger as a parent or teacher reads a passage aloud.
 Then you read it.
Then you read it. - Have a parent or teacher read aloud to you. Then, match your voice to theirs.
- Read your favorite books and poems over and over again. Practice getting smoother and reading with expression.
What parents can do to help at home
- Support and encourage your child. Realize that he or she is likely frustrated by reading.
- Check with your child's teachers to find out their assessment of your child's word decoding skills.
- If your child can decode words well, help him or her build speed and accuracy by:
- Reading aloud and having your child match his voice to yours
- Having your child practice reading the same list of words, phrase, or short passages several times
- Reminding your child to pause between sentences and phrases
- Read aloud to your child to provide an example of how fluent reading sounds.
- Give your child books with predictable vocabulary and clear rhythmic patterns so the child can "hear" the sound of fluent reading as he or she reads the book aloud.

- Use books on tapes; have the child follow along in the print copy.
What teachers can do to help at school
- Assess the student to make sure that word decoding or word recognition is not the source of the difficulty (if decoding is the source of the problem, decoding will need to be addressed in addition to reading speed and phrasing).
- Give the student independent level texts that he or she can practice again and again. Time the student and calculate words-correct-per-minute regularly. The student can chart his or her own improvement.
- Ask the student to match his or her voice to yours when reading aloud or to a tape recorded reading.
- Read a short passage and then have the student immediately read it back to you.
- Have the student practice reading a passage with a certain emotion, such as sadness or excitement, to emphasize expression and intonation.
- Incorporate timed repeated readings into your instructional repertoire.
- Plan lessons that explicitly teach students how to pay attention to clues in the text (for example, punctuation marks) that provide information about how that text should be read.
More information
Find out more about fluency issues with these resources:
< previous | next >
Top Articles
Especially for Parents
Research Briefs
Fluent Reading | Reading Rockets
Fluency means being able to decode individual words accurately and quickly… and understand the words as you read them. This is a crucial skill. A child who reads haltingly will work so hard at the mechanics of the task that there's little mental energy left to understand the meaning.
Developing fluency
An after-school program called RAVE-O helps to teach reading fluency in Malden, Massachusetts.
Word families
At Sudduth Elementary School in Starkville, Mississippi, Tina Scholtes teaches first graders a handy spelling pattern that helps them recognize word clusters.
Eye Movements in Skilled Readers
A research lab at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, investigates what good readers do with their eyes.
Community Volunteers
The Charlottesville, Virginia, school district has started an innovative community volunteer program called Book Buddies. Six-year-old Trey now has a book buddy who will work with him twice a week during his first-grade year.
William Joyce: A Writer's Secret
Writer William Joyce (George Shrinks) talks about the people and places that have inspired his work.
Assessing Reading Skills
At the Stern Center in Williston, Vermont, struggling students get a leg up on reading and other skills.
The Sounds of Speech
At Fort Pitt Elementary School in Pittsburgh, a second grader named Azeeza gets reading help from a dedicated mentor — a software program called The Reading Tutor.
Recommended resources
Additional Resources
Transcript
Transcript by segment:
Introduction: Fluent Reading
Announcer: Funding for the Reading Rockets Launching Young Readers series was provided by the United States Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs.
Deborah Norville: Hi, I'm Deborah Norville. Today I'm interviewing a well-known reading expert and librarian here from the PBS kids show "Between the Lions" is Theo Lion.
Theo Lion: Hi, Deborah. Boy, I'm a big fan of yours. I've always lionized you.
Deborah: Thank you. So Theo, tell me what is reading fluency?
Theo: Oh, Deborah, if I may, I've actually prepared some remarks on the subject. Hamburger, steak, lamb chops. Oh, I'm sorry. That's my shopping list. Oh, yeah. Here we go. Yes. Fluency is the ability to read quickly and easily. It means you can decode individual words accurately and automatically and understand those words as you read them. Much as I did just now.
Hamburger, steak, lamb chops. Oh, I'm sorry. That's my shopping list. Oh, yeah. Here we go. Yes. Fluency is the ability to read quickly and easily. It means you can decode individual words accurately and automatically and understand those words as you read them. Much as I did just now.
Deborah: Yes, you really read that with feeling.
Theo: Well, thank you.
Developing Fluency (Malden, Massachusetts)
Cathy MacDonald: Good afternoon, Word Wizards! Welcome back to RAVE-O.
Deborah: Teacher Cathy MacDonald leads a daily after-school class for second- and third-grade struggling readers at Salemwood Elementary.
Cathy: We're going to start off today by doing the Word Web.
Deborah: This reading program, called RAVE-O, directly targets fluency-the ability to read aloud without hesitations or false starts and with good inflection that can only come from understanding the text.
Dr. Maryanne Wolf: The RAVE-O program was the direct outgrowth of our understanding that at least two-thirds of the children were actually not receiving any emphasis at all on fluency. So the RAVE-O program was really specifically designed to have the children not only be able to decode but decode rapidly and with comprehension.
Cathy: If I were to go out, and I were to see someone with a bat, where might I see someone using one? Danny?
Danny: Fenway.
Cathy: Fenway Park. Yes.
Deborah: Today Ms. MacDonald is exploring the different meanings of a single word.
Cathy: Does anyone know a very popular baseball team around here? Rudy!
Rudy: Red Sox!
Cathy: Red Sox. Red Sox. What kind of championship do they usually end up in if the baseball team does a real good job? The World…
Student: Series.
Cathy: Very good!
Cathy: The children come here after a full day of school and you would assume that they would be tired of reading and learning but when they enter the classroom it's a whole new experience and they come in ready to learn and very excited. And the fact that the skills are things that they can accomplish and they look at themselves in a whole new way. They look at themselves as readers.
Deborah: Organized around one core word a week, a tool called a "word web" makes multiple meanings easy to grasp. Kids expand the web by adding words or phrases with related meanings.
Cathy: Let's move on now to this kind of a bat. Casey?
Casey: A fruit bat?
Cathy: And where does a fruit bat go, Casey? Where would you find it?
Casey: Um, at a fruit tree.
Cathy: At a fruit tree, uh huh. Do you know what they call animals that are asleep during the day and are up at night? Give it a try, go ahead, Chevere.
Chevere: Nocturnal animals.
Cathy: You are correct!! Nocturnal animals. Excellent!
Deborah: A rich knowledge of words helps build fluency.
Dr. Wolf: Fluency is one piece of the entire process. The more rapid you are, the more time you can actually allocate to understanding what you've read.
Dr. Reid Lyon: It's like riding a bike. You watch little ones beginning to ride a bike, they're wobbling all over the place. They fall down. They don't have the process well consolidated. But as we go along as kids and we begin to practice and practice and practice riding a bike, we don't even think about peddling anymore until it gets hard. We don't think about keeping the bike straight and we can ride with no hands.
Deborah: RAVE-O combines vocabulary-building exercises like the word web with lessons specifically designed to speed up decoding. These two ingredients are the key to any good fluency program, and sure enough, this after-school program has produced big gains in fluency.
Cathy: Boys and girls, look at all of the words we came up with from one little word "bat."
Word Families (Starkville, Mississippi)
Deborah: All kids must learn the correspondence between individual letters and sounds. But the next step is critical: understanding that certain groups of letters are pronounced alike in families of words.
Deborah: Fast decoders rely on common spelling patterns. And it's only when you decode quickly that you can become a fluent reader.
Tina Scholtes: The first word that I'm going to write is…
Class: Fight!
Tina>: Very good!
Deborah: At Sudduth Elementary School, Tina Scholtes is teaching her first-graders about a handy spelling pattern.
Tina: And we can change "fight" to…everybody look.
Class: Might.
Tina: Very good. And we can change "might" to…don't say it 'til I write it.
Class: Bright.
Tina: Bright. Very good.
Dr. Barbara Foorman: In the beginning of reading, teachers will teach individual letter-sound connections and then they'll start to focus on groups of letters, vowel teams or consonant clusters, and eventually they'll even move to larger chunks of words that may be at the syllable level or there may be prefixes or suffixes and the teachers trying to get the child to move to larger and larger units which eventually include the whole word. So that the child can quickly and automatically recognize the word at a glance so that they're able to pay attention to the meaning of the story.
Tina: Ok boys and girls, you know, Ms. Scholtes has told you, that sometimes you can learn many many words by just knowing one word, and that's what we're doing when we know the word "fight. " We can change the beginning sound and you will know a new word.
" We can change the beginning sound and you will know a new word.
Tina: For example, a word that is not even right here that I guarantee you you can read is this word. What is that?
Class: Sight!
Tina: That is a word that is not even…:
Tina: For my children to be able to look at words that end in "ight" and figure out new words is a big step, because "ight" is an ending cluster for a whole group of words. They run into words that end in "ight" all the time.
Tina: We've got fight, might, right, bright, daylight, delighted, tight…
Deborah: Thanks to this lesson, these first-graders are moving beyond letter-by-letter decoding. By learning to read common letter groups at a glance, they're taking a big step toward fluency.
Eye Movements in Skilled Readers (Amherst, Massachusetts)
Lindsey Buckley: We are reading a new book. And I have one little girl who's just really struggling with the book. And she's trying to sound out some of the words. But she's just having some problems. And so about halfway through the book, she just closed the book. And she slid the book across the table to me and said, you know what, Ms. Buckley? I don't need to know how to read this book. Because I'm going to be a supermodel. And whenever I'm a supermodel, I don't have to read these books.
And I have one little girl who's just really struggling with the book. And she's trying to sound out some of the words. But she's just having some problems. And so about halfway through the book, she just closed the book. And she slid the book across the table to me and said, you know what, Ms. Buckley? I don't need to know how to read this book. Because I'm going to be a supermodel. And whenever I'm a supermodel, I don't have to read these books.
Deborah: Reading is one of the most dazzling mental skills that people learn. We seldom think about just how much is involved. Our eyes move from left to right in a series of quick leaps, resting or fixating on a word for a sliver of a second before moving ahead.
Researcher: Okay. If you could look straight ahead, please.
Deborah: At the University of Massachusetts, a research lab is investigating what good readers do with their eyes. Dr. Keith Raynor is director of the lab.
Keith Raynor: I've spent my life using eye movements as a way to understanding reading and seeing perception and visual search and other things. Because it seems to me that eye movements are a very good indicator of the mental processes that people engage in.
Researcher: Okay. Could you look at the upper right hand corner of the screen, please?
Deborah: Dr. Raynor has found that skilled readers take in information from a surprising small area around the fixation point. Three or four letters to the left of fixation and about fifteen letters to the right.
Dr. Steve Pinker: Simply because of the physical wiring of the eye, you don't get much detail outside the point that you're looking at. You can try this experiment for yourself. Hold out your hand just a little bit off the line of sight and you won't even be able to count your own fingers. That's how fuzzy it gets. So if you need fine detail, whether you're looking at, you know, a P or a Q or an H or a J, your eye has got to land right on the word. And indeed, studies of eye movements and reading have shown that good, even skilled rapid readers pretty much land on every content word.
And indeed, studies of eye movements and reading have shown that good, even skilled rapid readers pretty much land on every content word.
Deborah: Good readers seldom backtrack. They fixate on each word for a quarter second before leaping ahead eight or nine letters.
Researcher: Look straight ahead, please.
Deborah: Good readers are highly systemic. Younger, less skilled readers, spend more time on each word. They leap ahead shorter distances. And they backup more often.
Dr. Raynor: They're going much slower. Because they're having much more difficulty in coding what the words are that they look at.
Deborah: Though they are slower, young readers follow going same pattern as adults. They don't hunt around the page for context clues, but instead decode one word at a time as their eyes move methodically across the text.
Community Volunteers (Charlottesville, Virginia)
Deborah: The Johnson School has many kindergarteners at-risk for reading failure. So the school district has started an innovative community volunteer program called book buddies.
So the school district has started an innovative community volunteer program called book buddies.
Trey: Where are you going?
Deborah: Six-year-old Tray is one of twenty kids who've been assigned a reading tutor, a book buddy, who will work with him twice a week during his first grade year.
Gail Rubin: One of my rewards is going to the playground to pick him up twice a week and seeing him run towards me with a big grin on my face. It makes my heart sing.
Gail: There's my book buddy Trey. How are you?
Deborah: Trey's book buddy is Gail Rubin, now in her sixth year of volunteering.
Gail: Want to play a rhyming game on the way?
Deborah: New volunteers get a three hour course in the program and also watch and expert model the tutoring. Like Melville Krebs, the book buddy's coordinator at the Johnson School. She tailors two-45 minute lessons a week for each of the kids in the program.
She tailors two-45 minute lessons a week for each of the kids in the program.
Melville Krebs: Trey began the year as a total non-reader. And he's learned just about everything that has been taught him along the way.
Gail: Hi, Trey. Let's get started with the familiar books. Which one would you like to read first?
Deborah: A book buddy session begins with the child reading a familiar text. Rereading is a great way to build fluency and comprehension.
Trey: Stan packed his trumpet, drum and a…
Gail: That's a tough word.
Trey: …bandage.
Gail: Good for you.
Trey: For his thumb.
Deborah: After a systematic phonics lesson, Trey practices reading words with the sounds he has learned.
Trey: Chop, quilt.
Gail: There's no L in there. So it's?
So it's?
Trey: Quit.
Gail: Quit. That's wonderful. All right. I don't supposed you'd like to play a game.
Trey: Mmm.
Gail: All right. I think we can find one in here.
Deborah: What looks like a game to Trey is a continuation of the phonics lesson. Trey must identify the pictured objects and then spell their names.
Gail: What's that?
Trey: Truck.
Gail: Okay. Truck. Time to choose a book to take home to read to your mom. Which one is it going to be?
Trey's mom: What's the name of it?
Trey: Quick as a Cricket.
Deborah: Book buddies has put together everything researchers know will help struggling readers. Parental support, systematic phonics, good children's literature and lots of individual attention.
Trey: I'm as slow as a snail. I'm as slow as a basset. I'm…p; I'm as…tame.
I'm as slow as a basset. I'm…p; I'm as…tame.
Deborah: First graders are selected for book buddies because they are far behind their peers. But thanks to community help, by the end of the year, a remarkable 85 percent of them will be reading at grade level.
Trey: Put them all together and you've got me.
William Joyce: A Writer's Secret
Theo: Just as in the sky at night, there are many stars that shine. A kid can stand out in many ways and feel happy all the time. Wow. Boy, Deborah. You're a really good writer.
Deborah: Oh, thank you, Theo. That means a lot to me coming from a critic like you.
Theo: Yeah. Well, you know, writers are really important. Without them, readers would have nothing to read. And we wouldn't have had anything to say today. Because a writer wrote what I just said. And what I just said now.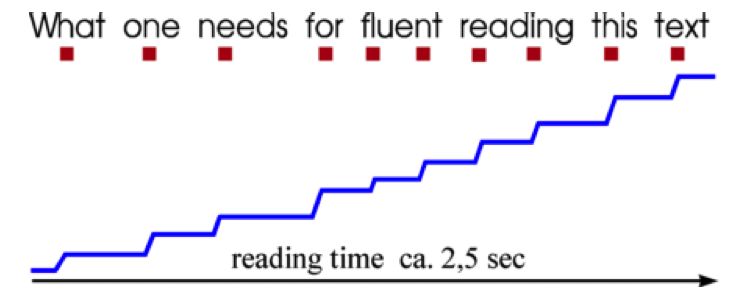 And what you're going to say next.
And what you're going to say next.
Deborah: Deep, Theo. Very deep.
Theo: Deborah Norville thinks I'm deep.
Deborah: William Joyce, the author of "George Shrinks" and "Rolly Polly Olly" says the best children's books have a frisky, subversive intelligence. In Joyce's words, anything can come alive, stuffed animals, toys, even forks and spoons.
William Joyce: I grew up in Louisiana. And it wasn't exactly a hub for artistic endeavors. Luckily enough, I had some really great teachers that guided me and really just like said this kid loves what he's doing. He loves to draw. He loves to make up stories. And that's unusual. So let's encourage it. Let's not bury it. And if I hadn't had those teachers doing that, I wouldn't be doing this. My two like heroes of childhood, the two things that got me on the road of doing children's books or stories, were "King Kong" and "Where the Wild Things Are. "
"
William: There's so much of "George Shrinks" that evokes King Kong and even wild things. And I just took the idea that King Kong was too big for everything and reversed it. And put George in the land of giants. Which is basically what every kid goes through anyway. Towards the end, there's an illustration where you can see a little stuffed King Kong doll in the background sitting next to a little Empire State Building. Rolly Polly Olly for me is like Leave it to Beaver with robots. I guess Rolly Polly Olly is a show entirely made up of wouldn't it be cool if? Wouldn't it be cool if your dad had a machine that could make things shrink and grow. And that you one day when you're not supposed to make yourself really, really small.
William: Almost everything in the day with Will Robinson has some basis in truth. Yes, my sister did pay me to feed her grapes while she talked to her boyfriend on the phone. In the book, it is a frog with a turbine that's feeding the sister grapes while she talks to her boyfriend on the phone.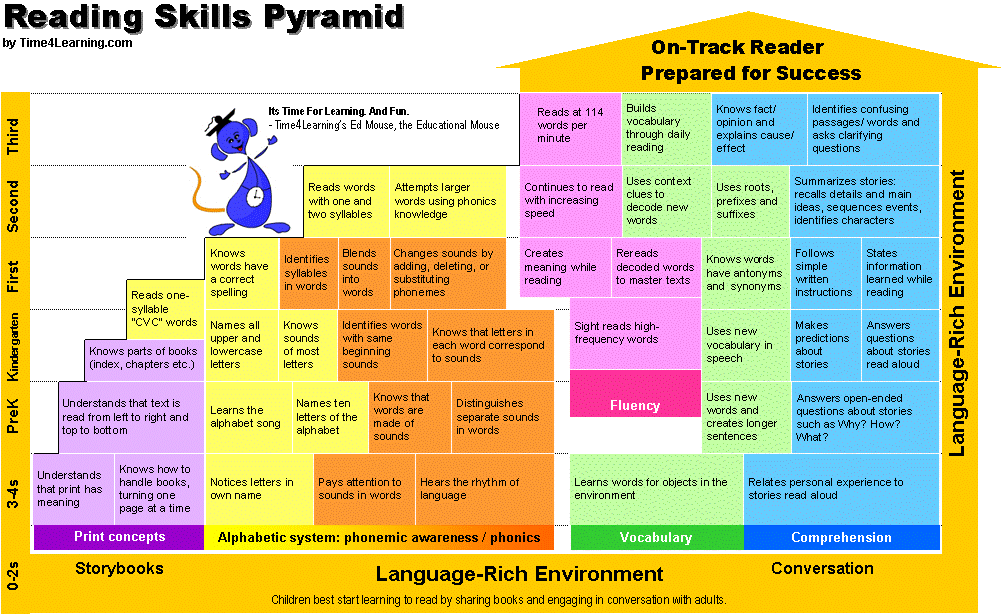 My grandfather had false teeth and a glass eye. I had an uncle who swore he was from outer space. And he was so convincing. Why would a grownup lie about that? My kids have been a constant source if not inspiration, co-conspirators in my work. They usually find out after the fact. Books not printed in the store. Oh, look. There's me. They don't seem to mind. I even put myself in there occasionally. Though, taller and, you know, with more hair.
My grandfather had false teeth and a glass eye. I had an uncle who swore he was from outer space. And he was so convincing. Why would a grownup lie about that? My kids have been a constant source if not inspiration, co-conspirators in my work. They usually find out after the fact. Books not printed in the store. Oh, look. There's me. They don't seem to mind. I even put myself in there occasionally. Though, taller and, you know, with more hair.
Assessing Reading Skills (Williston, Vermont)
Deborah: At the non-profit Stern Center, struggling students can get a leg up on reading and other skills.
Dr. Andrea Brown: Okay, good. Now I'm going to have you read a list of words as fast as you can.
Deborah: Stern Center's Director of Diagnostic Services, Dr. Andrea Brown, has been doing an in-depth assessment of 10-year-old Becca ever since her public school teacher noticed she was falling behind. Because Becca is a slow decoder she has difficulty in comprehending what she reads.
Because Becca is a slow decoder she has difficulty in comprehending what she reads.
Dr. Brown: Okay, ready? Start.
Becca: (reading)
Blanche Podhajski: This is a youngster with intelligence in the 90th percentile. Who's doing math at the 94th percentile but reading at the 12th percentile.
Becca: (reading)
Deborah: Reading researchers now know that a high IQ does not guarantee reading success.
Becca: (reading)
Deborah: By assesing Becca frequently, the Stern Center can tailor the instruction to meet her needs. Ongoing assessment is a tool teachers should use for all children.
Dr. Reid Lyon: The teacher needs to understand how to diagnose difficulties, that requires assessment. How does that youngster link the sounds to the letters? How are the phonics skills coming along? How many words per minute can the kid read, fluency? All of those require a form of assessment or testing and teachers have to do that continuously. You cannot let people move along in a complex activity doing things wrong. You've got to catch it while it occurs and fix it.
You cannot let people move along in a complex activity doing things wrong. You've got to catch it while it occurs and fix it.
Deborah: The last test will assess Becca's reading comprehension. Extracting meaning from text is, after all, the ultimate goal of reading.
Dr. Brown: Ready? Begin.
Becca: (reading) One bright summer day, a young boy and his grandmother walked to a nearby pond…
Deborah: Any trouble Becca has understanding this passage can likely be blamed on her slow reading. Poor readers exhaust their mental resources decoding words and holding them in memory. Little is left for understanding what the words mean.
Deborah: Better fluency leads to better comprehension.
Becca: …they both had a good laugh.
Dr. Lyon: Not being able to read just isn't an academic issue. It's a, an emotional issue.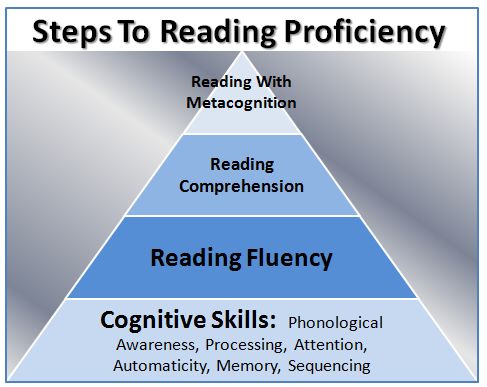 It's an a-a motivational issue, it's very dear to the kid. Consider: kids who come into the first grade in particular and second grade and third grade. Their job is to read and they read out loud a great deal, they read in groups. Well if you don't do that well and that's the job of schooling, the major job, and people think you're stupid if you sound like you don't know how to do it, it doesn't take very long to begin to withdraw from that practice. Kids aren't as resilient as we thought.
It's an a-a motivational issue, it's very dear to the kid. Consider: kids who come into the first grade in particular and second grade and third grade. Their job is to read and they read out loud a great deal, they read in groups. Well if you don't do that well and that's the job of schooling, the major job, and people think you're stupid if you sound like you don't know how to do it, it doesn't take very long to begin to withdraw from that practice. Kids aren't as resilient as we thought.
Dr. Brown: A, did not like to fish…
Deborah: With the help of excellent tutoring and lessons informed by assessment, one struggling reader is on the road to fluency.
Dr. Brown: …or D, did not know how to cook fish.
Becca: B, liked to have fun with, with the boy.
Dr. Brown: Good job.
The Sounds of Speech (Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania)
Computer: First click on your name.
Deborah: At Fort Pitt Elementary School, a second grader named Azeeza gets reading help from a dedicated mentor.
Computer: Choose a story to read.
Computer: Old Mother Hubbard.
Deborah: Software called the reading tutor listens to Azeeza and offers help.
Computer: Please read aloud.
Azeeza: Old Mother Hubbard.
Deborah: The reading tutor is part of a new wave of computer software now being used to supplement classroom instruction. The system's designer is Dr. Jack Mostow.
Dr. Jack Mostow: It is very easy to explain in four words. Children read, computer listens. What the reading tutor provides is lots of infinitely patient assisted practice in oral reading. And that's a missing ingredient for all too many children whose parents or teachers don't have time or in some cases ability to listen to them read aloud.
Azeeza: Went to the…
Deborah: When Azeeza gets stuck, the reading tutor can sound out a tricky word.
Computer: Cupboard.
Azeeza: Cupboard.
Computer: You're a great reader.
Deborah: To keep young readers interested, the computer can offer a variety of clues.
Computer: Rhymes with bone.
Azeeza: Phone.
Deborah: Getting a computer to understand spoken words is a big challenge. The reading tutor software must cope, just like our ears and brains, with the fact that the same word can be pronounced in different ways.
Various: Old Mother Hubbard. Went to the cupboard. Cupboard. Cupboard to get her. To get her poor dog. Poor dog a bone. Bone. Bone. But once she got there. The cupboard was bare. Bare. Bare. And so the poor dog had none. Had none. Had none.
Had none.
Deborah: Isolating the sounds of speech is difficult even for high powered computers. No wonder children sometimes struggle as they try to develop phonemic awareness.
Computer: Let's read this sentence together.
Deborah: But with help from the reading tutor, Azeeza is making good progress.
Computer: To.
Azeeza: To get.
Computer: A.
Azeeza: A poor dog.
Barbara Prevost: Azeeza came to me at the beginning of the year pretty much a non-reader. She had a very limited sight vocabulary. She was very insecure about her reading. A very reluctant reader. She's ready to take a challenge now. She'll try anything. She loves to read.
Azeeza: Dog a bone.
Computer: Very good.
Deborah: One of the first to test Mostow's technology, Ms. Privo wasn't thrilled about the idea at first. But she's become a supporter.
Privo wasn't thrilled about the idea at first. But she's become a supporter.
Barbara: It's a part of the classroom environment. The kids move back and forth from it without it interrupting any of our routines. It's become a friend more than a threat. Which it was at the very beginning when I first started to use it.
Deborah: The system is now running in twenty classrooms around Pittsburgh. And Mostow's studies indicate it's working.
Dr. Mostow: When I explain these results to the principal in my long-winded academic way, she boiled it down beautifully. The children who use the reading tutor were closing the gap.
Azeeza: And so the poor dog had none.
Computer: You're a fantastic reader.
Close & Credits
Deborah: So tell me, Theo, as fluently as possible, what's your final word on the subject?
Theo: Well, I'll tell you, Deborah, this show has given us a lot to chew on. You know, I think a lot of people don't realize what a challenge teaching reading can be.
You know, I think a lot of people don't realize what a challenge teaching reading can be.
Deborah: A famous reading expert once said teaching reading is rocket science.
Theo: That's right. It takes precise proven strategies to launch a kid. Into reading.
Deborah: To learn more about how you can help a child learn to read, visit our website. And thanks for watching. And thank you, Theo, for joining me.
Theo: Oh, thanks for having me, Deborah. Hey, you should come visit us on Between the Lion sometime.
Deborah: I would love to. And I promise I'll read my lines fluently.
Theo: There you go.
Announcer: To learn more about Reading Rockets Launching Young Readers and how you can help a child learn to read, visit PBS online. You'll find tips for parents, classroom strategies for teachers, and profiles of children's book authors, all at PBS. org.
org.
Teacher: The word is daylight. What about it? A compound word. We know that a compound word has two little parts to it. The first word in daylight is an "ight" word that comes from that family. Let's look at the board. You all are great. You have gotten these so fast. The first word that I am going to write&$133;
Announcer: Funding for the Reading Rockets Launching Young Readers series was provided by the United States Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs. You may order the five part Reading Rockets Launching Young Readers series on VHS or DVD. Individual episodes are also available on VHS. To order, call 1-800-228-4630.
5 Simple and Effective Ways to Improve Reading Fluency
Reading fluently means reading at a natural pace, with expression, and at the same time understanding what you read. How can you help your students and children learn to read fluently? Isn't it enough just to read more?
In fact, non-verbal reading (note: reading to oneself, not out loud) does not help people who have difficulty reading fluently. The National Reading Panel states: "Empirical studies show that independent non-verbal reading has little effect on the development of reading speed." In this case, it is necessary to consider whether the student should continue to read in the wrong way in the hope of gradually improving his skills if he has difficulty reading?
The National Reading Panel states: "Empirical studies show that independent non-verbal reading has little effect on the development of reading speed." In this case, it is necessary to consider whether the student should continue to read in the wrong way in the hope of gradually improving his skills if he has difficulty reading?
This is very similar to learning to paint. Having received some useful advice from the teacher, the student begins to understand the basic techniques of painting. The teacher breaks down each step and then checks how each one works to make sure the students have understood everything correctly.
Should we do the same for our students - make sure they read diligently, progressing step by step, the way an art teacher approaches each student to make sure that our technique will lead us to the desired result? Would a student have a better understanding of the technique of the art of painting if he silently and clumsily tried to draw something on his own? This is exactly what happens to the student who does not talk about his reading problems.
Despite this, non-verbal reading plays an important role in a student's life. Once he reaches the level of fluent reading, he should continue to read everything that comes to hand at his usual speed.
Here are the best ways to improve reading fluency:
-
Show an example of fluent reading: demonstrate how to read aloud correctly. Other adults can help with this too: tutors, parents, siblings, etc. In this way, the student will hear how the text should sound in order to get a clearer understanding of how speech is built, including correctly spaced pauses at the end of sentences, rising intonation when using questions, etc.
-
Reading aloud: have your students read aloud loudly and clearly, not necessarily fast. As you gain experience in reading and improve his skills, the speed will most likely increase as well.
-
Choral reading (or reading in unison): this is a group practice in which you read a passage of text to your students and they repeat it in unison.
 This provides group reading practice and can also help a child who is too shy to read aloud in front of others.
This provides group reading practice and can also help a child who is too shy to read aloud in front of others. -
Reader's Theatre: This is a fun transformation of ordinary reading into a kind of performance. Each student should work as a team with their classmates, reading with expression and conveying the meaning of what is written. This will help improve not only reading efficiency, but also teamwork skills.
-
Praise for fluent reading: a little praise sometimes works wonders. Remember to also gently point out problem areas so that students know what to work on. Reading is extremely difficult for some, so do not forget to encourage them to continue their work!
Now that you know that independent non-verbal reading does not help students with reading difficulties, what approach would you take for literature lessons to make them more effective? Pay attention to the Fast ForWord software package, which now includes the Reading Assistant, which is:
-
demonstrates a sample of correct reading (reads aloud to a student)
-
listens and analyzes how the child reads aloud
-
helps you practice the correct pronunciation of
-
helps build vocabulary
-
helps to understand the meanings of unfamiliar words
This is a kind of personal reading tutor built into your computer, and this program is very effective, especially for children who are not helped by silent reading.
Practice, backed by the right methods and the right support, is the key to the success of beginning readers.
Source
Conscious and fluent reading is the key to a child’s success in understanding the world around him
their right to free creative labor and peaceful happy life. Introduction of new generations to mental and moral values - a matter of paramount importance. In this case, not do without a book, without the art of the word. Real literature, first of all, teaches to love of people. Books, according to M.A. Gorky, elevate the soul, teach good things, and in difficult times give strength not to lose heart, to endure, win. Everyone draws wisdom and strength from books to the extent that he has mastered the ability to read, so as an educational effect - reading books is always directly proportional the results of reading learning, desire and the reader's ability to take everything from the book that it can to give. [ 1
From the ability to read fluently, expressively, understand reading content, analyze actions heroes, to draw appropriate conclusions depends on them academic achievement throughout school years. Therefore, it becomes clear what a huge importance should be given to the elementary school teacher teaching reading and what responsibility he has in front of the student, his parents, teachers middle level. Often it is the middle link reproaches the primary for the fact that students passed into the 5th grade, reads slowly, do not know how retell, reason and evaluate read.
Therefore, it becomes clear what a huge importance should be given to the elementary school teacher teaching reading and what responsibility he has in front of the student, his parents, teachers middle level. Often it is the middle link reproaches the primary for the fact that students passed into the 5th grade, reads slowly, do not know how retell, reason and evaluate read.
Reading is the main skill of a person in life, without which he cannot comprehend the world around him. And this much-needed skill of the child is taught elementary school teacher. How to make a lesson reading became a favorite? How to teach reading to children fell in love with a book, because a book read in childhood, remains in memory for life and affects for their future development? [9]
Therefore, in front of an elementary school teacher, in First, the goal is to teach students fluent and conscious reading of the text. To To achieve this goal, students need to form interest in books, evoke positive attitude towards independent reading;
Reading, as a type of speech activity, has two varieties: reading aloud and reading to yourself. The quality of reading is characterized from different angles. Reading aloud should be conscious, fluent, correct and expressive, and reading to oneself - conscious and fugitive.
The quality of reading is characterized from different angles. Reading aloud should be conscious, fluent, correct and expressive, and reading to oneself - conscious and fugitive.
Consciousness - clear and precise understanding readable. Consciousness is the most important thing leading reading quality. [1]
Fluency - correct, fluent reading, without division into syllables, with an understanding of the content readable. [8]
Correctness is one of the necessary qualities loud reading. She suggests:
- reading without distortion, gaps and permutations sounds and syllables, without repetition of words, without swallowing endings;
- correct placement of stress;
- compliance with the basic rules of literary pronunciation. [1]
If in the first, second grades, based on the tasks teaching the technique of reading, the main place is occupied loud reading, then in the third, fourth grades, in connection with the growing role of independent reading, more attention is paid to reading about myself.
According to the measurement of reading technique, with the transition to reading to oneself there is a decrease pace and awareness.
Consciousness of reading is closely connected with reading fluency. Slow reading makes it difficult understanding the meaning of what is being read. When too fast while reading, the student does not have time to link the meaning spoken words with the previous one. Consequently, reading fluency should be combined with conscientiousness, understanding the content readable. [ 1
The reasons for the decline in fluent and conscious student readings can be:
- insufficient attention from the teacher to work on reading technique;
- expanding the range of interests of students;
- Low level, side reading control parent;
- social factors.
Of all the problems mentioned above, the teacher can primary grade first. Therefore, in our practice, various types of work were used on the development of reading skills and abilities.
We have selected the most efficient types of work:
- dynamic reading method;
- chain reading;
- reading in pairs, group reading;
- fast reading;
- weekly five-minute reading sessions;
- reading speed self-meter.
Success in learning to read depends largely on from student motivation. And vice versa, it is success that gives rise to the motive: "I succeed, so I want!". With the development of interest in it is important for the reading process to create for everyone child situation of success.
For independent reading (especially at low speed) suggested children to reread their favorite poems and fairy tales. it stimulates their development of anticipation (semantic guess), promotes reading whole In other words, it brings joy from communication with the book. Significant importance in the development of interest in reading and increased reading speed have everyday listening exercises.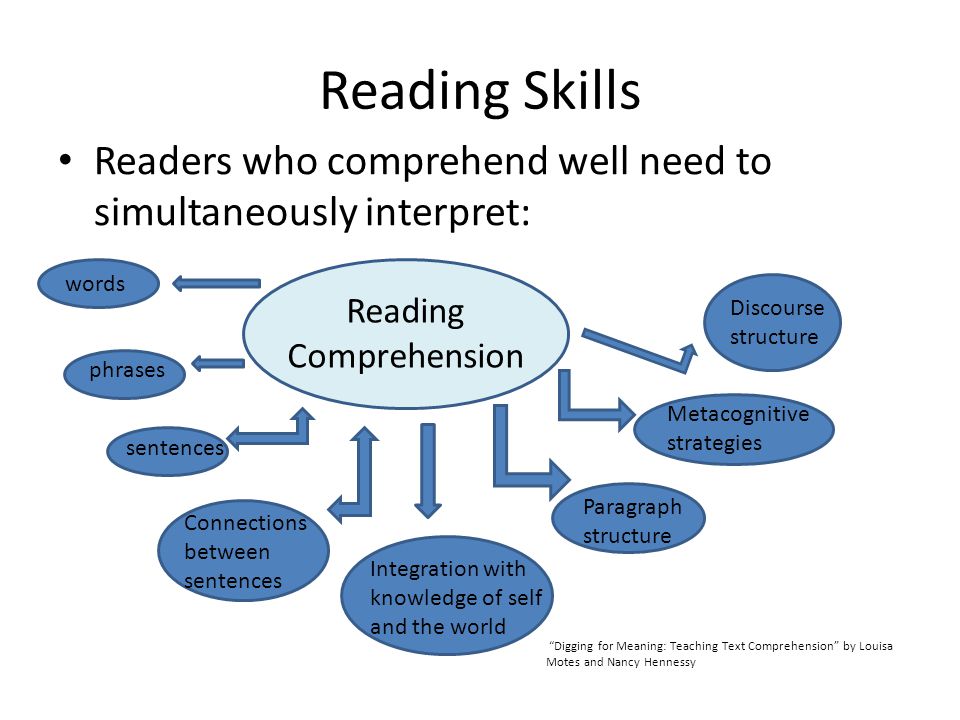
Reading material should be close to subjective experience of the child, personally significant for him, emotionally charged or have bright educational orientation. Should give the student the right to choose the material for reading depending on his interests, mood, even well-being. Can be offered to children choice of reading works of different subjects, volume, style, genre, difficulty of content and other. The possibility of such a choice is faster develops in a younger student an individual reading taste.
A library has been organized in the classroom for this purpose. To expand the reading material, students brings books to the library. The books that are read are replaced by others, started from the first class notebook for observation of reading technique.
Correct perception and reproduction sound phenomena of the Russian language by students with native language of instruction purposefully and skillfully teach, for which they can the following methodological tricks:
- demonstration (show) of exemplary pronunciation (sound, syllable, word, sentence, text) teacher or speaker;
- imitation (imitation) of exemplary pronunciation.
 The technique is that students listen to how a sound (a syllable of a word) is pronounced and repeats it first in chorus, and then each separately;
The technique is that students listen to how a sound (a syllable of a word) is pronounced and repeats it first in chorus, and then each separately; - explanation of articulation. Bodies explained speech when pronouncing a particular sound Russian language. Explaining the way of education sound, the teacher shows the children what position while occupies one or another organ of speech (lips, mouth, tongue, teeth): demonstrates it himself and applies special drawings, diagrams, tables according to articulation of sounds. Explanation and demonstration sound is accompanied by an imitation of an exemplary teacher's pronunciation. [1
In addition, the early elimination of speech therapy violations, increased work on reading technique, where individual characteristics are taken into account students, and the promotion of family reading play important role in solving the problem of fluent and conscious reading.