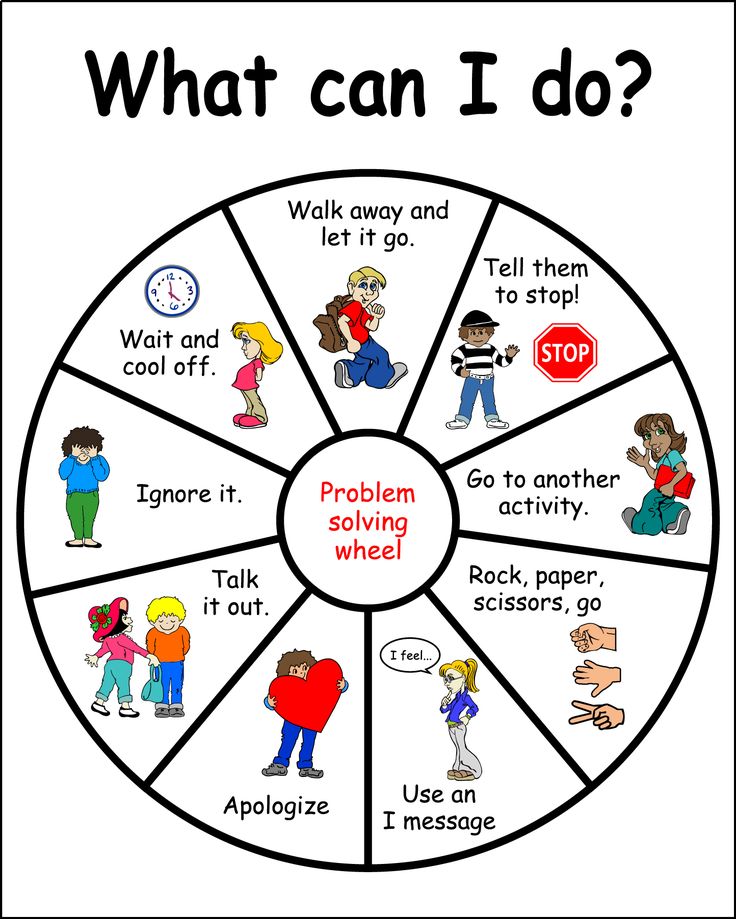
What is kindergarten math
Kindergarten Online Math Lesson Plans
View Our Lesson Demos!
The Time4Learning kindergarten math lessons put a fun spin on learning important foundational skills for the youngest of students. In addition to engaging, interactive activities that teach the lessons, each of the chapters features an overarching theme such as safari, playtime, and cooking.
This page provides information on what kindergarten math a student should know, math objectives for the year, and why Time4Learning is the best choice to help your child reach all of the kindergarten math goals and objectives.
What Math Should a Kindergarten Student Know?
Kindergarten math is all about becoming familiar with the basics and setting a solid foundation. Students will learn to count and recognize numbers, identify shapes and their attributes, add and subtract numbers, and complete patterns.
Below are some of the other skills that a student should know in kindergarten math.
- Create, describe and compare 2-D and 3-D shapes
- Compare groups using the terms greater, less, fewer, more
- Use tally charts and picture graphs to represent numbers
- Recognize that larger numbers are made up of smaller numbers
- Order events in a sequence
Kindergarten Math Objectives
For most students, kindergarten is their first official year of schooling. Gaining a solid understanding of basic concepts now, will help them feel confident and prepared as they learn new math skills in the years to come. That’s why it’s so important that students use a comprehensive curriculum, like Time4Learning, to help them master these concepts and reach all their kindergarten math goals and objectives.
Below are some of the math objectives a kindergarten math curriculum should help your child achieve.
- Count objects up to 20
- Use an analog and digital clock to identify time to the nearest hour
- Identify pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters and know their value
- Compare the length and weight of objects
- Explore properties of addition and subtraction
Time4Learning’s Kindergarten Math Lesson Plans
Chapter 1: “Tutorial”
Lesson 1: Tutorial –
1 ActivityFunctionality of buttons and interactions, and practice questions from lessons based on objectives.
Chapter 2: “Under the Sea”
Lesson 1: Adventures Under the Sea –
4 ActivitiesRecognize likenesses and differences between pairs of items.
Lesson 2: Searchers of the Sunken Ship –
4 ActivitiesSort objects by appearance (e.g., color, size, and shape). Recognize items that are the same and different. Extend and identify a repeating pattern.
Lesson 3: Sea Sorting –
4 ActivitiesSort representations of living things by appearance. Create items with given attributes. Recognize one-to-one correspondence.
Lesson 4: Fantastic Fish –
4 ActivitiesAlign sorted objects to determine whether a one-to-one match exists. Determine which set has more or fewer members when a one-to-one match does not exist. Create and interpret picture-graph displays.
Lesson 5: Sea Symphony –
4 ActivitiesCopy, continue, and complete patterns involving two attributes.
Chapter Test: Under the Sea
Chapter 3: “Playtime in the Park”
Lesson 1: Moose Park Footrace –
4 ActivitiesUse positional words to describe vertical and horizontal relationships. Recognize that more than one term may be appropriately used to describe a positional relationship. Create a positional relationship by following directions.
Lesson 2: Digby Hide-and-Seek –
4 ActivitiesUse positional words to direct investigations that occur in different locations. Use positional words to describe locations.
Lesson 3: A New View –
4 ActivitiesRecognize that vertical and horizontal relationships are often determined by point of view. Recognize that individual items may each appear different from different perspectives.
Lesson 4: Shape Hunt –
4 ActivitiesInvestigate the features of a circle, triangle, square, and rectangle, and identify their presence in contextual settings. Identify likenesses and differences between pairs of shapes. Construct shapes.
Identify likenesses and differences between pairs of shapes. Construct shapes.
Lesson 5: Shapes, Shapes, Everywhere –
17 ActivitiesAnalyze, compare, create, and compose two- and three-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their similarities, differences, parts, and other attributes.
Lesson 6: Photo Finish –
8 ActivitiesConstruct and/or complete simple scenes formed with plane figures. Construct, complete, and describe patterns formed with plane figures.
Chapter Test: Playtime in the Park
Chapter 4: “Let’s Go On a Safari”
Lesson 1: Jungle Safari –
6 ActivitiesRecognize that objects can be counted and represented by numerals. Recognize that cardinal numbers represent a quantity (numbers 1-5). Read and represent numbers 1-5. Recognize that different arrangements represent the same quantity (numbers 1-5).
Lesson 2: Safari Tales –
6 ActivitiesCompare groups to determine more/greater/less/fewer.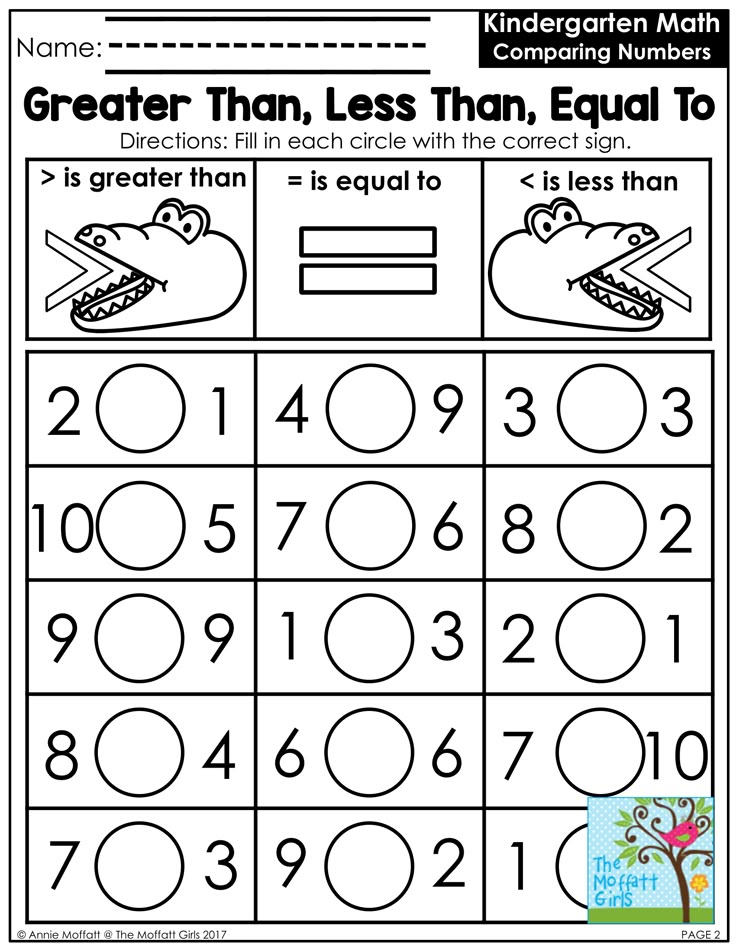 Use one-to-one correspondence when comparing sets. Recognize the concept of zero as representing an empty set. Construct and interpret picture graphs.
Use one-to-one correspondence when comparing sets. Recognize the concept of zero as representing an empty set. Construct and interpret picture graphs.
Lesson 3: Wild Animals –
10 ActivitiesRecognize that objects can be counted and represented by numerals (0-20). Recognize that cardinal numbers represent a quantity (numbers 0-20). Read, write, and represent numbers 0-20. Recognize that different arrangements represent the same quantity (numbers 0-20).
Lesson 4: Sounds Wild! –
8 ActivitiesUse one-to-one correspondence to represent and compare quantities of 0-10. Use tally charts and picture graphs to represent 0-10. Recognize sequence of numbers on a number line. Describe position in a sequence of whole numbers on a number line up to 10.
Lesson 5: Animal Keeper at Work –
10 ActivitiesRecognize that larger numbers are formed from combinations of smaller numbers. Explore addition models. Recognize that smaller numbers are formed by taking apart sets. Informally explore subtraction models.
Informally explore subtraction models.
Chapter Test: Let’s Go On a Safari
Chapter 5: “What’s Cooking?”
Lesson 1: Snack Time –
9 ActivitiesUse a calendar as a tool to identify months, days, and dates. Use a calendar as a tool to identify today, yesterday, and tomorrow. Identify parts of a day (morning, afternoon, evening). Use an analog clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Use a digital clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Order events in a sequence. Identify temperature using a thermometer.
Lesson 2: Harriets Piggy Bank –
5 ActivitiesIdentify penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Identify value of penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Combine coins to make values up to 10 cents.
Lesson 3: Tasty Treats –
6 ActivitiesCompare the length of objects. Identify and correct common errors in linear measurement. Estimate and measure length using nonstandard units. Measure length using standard units.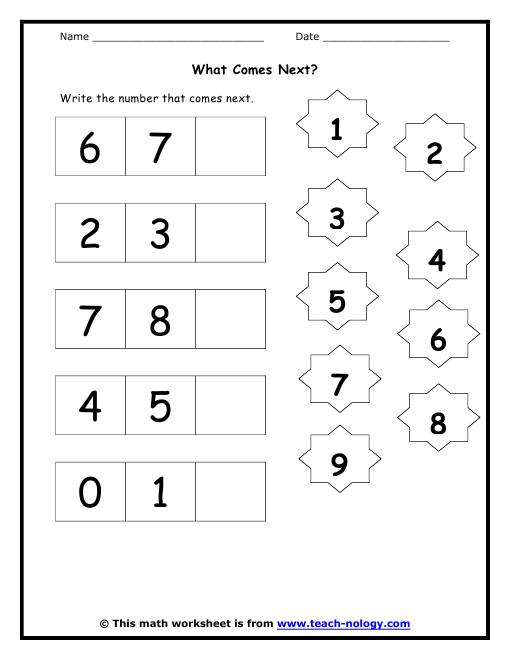
Lesson 4: Sharing Snacks –
4 ActivitiesSeparate items into equal parts through an active comparison of their length. Informally explore commonly used fractional parts of a whole (fourths, thirds, halves).
Lesson 5: Measurement Matters –
6 ActivitiesCompare the weight of objects. Compare the capacity of objects. Recognize tools of measurement. Informally explore the concept of area.
Lesson 6: Writers Corner –
1 ActivityUse a calendar as a tool to identify months, days, and dates. Use a calendar as a tool to identify today, yesterday, and tomorrow. Identify parts of a day (morning, afternoon, evening). Use an analog clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Use a digital clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Order events in a sequence. Identify temperature using a thermometer. Identify penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Identify value of penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Combine coins to make values up to ten cents. Compare the length of objects. Identify and correct common errors in linear measurement. Estimate and measure length using nonstandard units. Measure length using standard units. Separate items into equal parts through an active comparison of their length. Informally explore commonly used fractional parts of a whole (quarters, thirds, halves). Compare the weight of objects. Compare the capacity of objects. Recognize tools of measurement. Informally explore the concept of area.
Compare the length of objects. Identify and correct common errors in linear measurement. Estimate and measure length using nonstandard units. Measure length using standard units. Separate items into equal parts through an active comparison of their length. Informally explore commonly used fractional parts of a whole (quarters, thirds, halves). Compare the weight of objects. Compare the capacity of objects. Recognize tools of measurement. Informally explore the concept of area.
Chapter Test: What’s Cooking?
Chapter 6: “Numbers in the Neighborhood”
Lesson 1: Number Sense Center –
7 ActivitiesRead and represent numbers 11-20. Recognize that larger numbers are formed from combinations of smaller numbers (11-20). Demonstrate understanding of conservation of number (recognizing that size does not affect number). Explore numbers 0-100. Explore number patterns, counting by 1s, 2s, 5s, and 10s.
Lesson 2: Graphing Data Drive –
5 ActivitiesUse data to create picture graphs.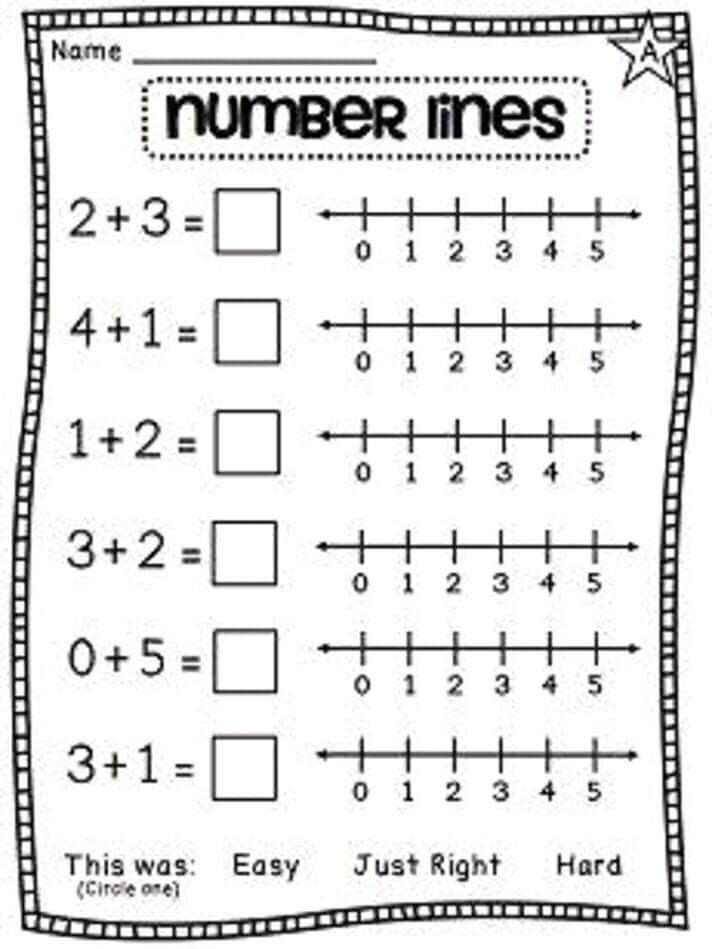 Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems.
Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems.
Lesson 3: Probability Place –
4 ActivitiesUnderstand basic concepts of chance and probability. Describe events as likely or unlikely.
Lesson 4: Addition Avenue –
10 ActivitiesRecognize that larger numbers are formed from combinations of smaller numbers. Explore addition models. Explore properties of addition. Use addition number sentences to record the combining of sets. Solve addition number sentences.
Lesson 5: Subtraction Street –
6 ActivitiesExplore subtraction models. Explore properties of subtraction. Use number sentences to record subtraction. Solve subtraction number sentences.
Lesson 6: Writers Corner –
1 ActivityUse data to create picture graphs. Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems. Use data to create picture graphs. Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems. Understand basic concepts of chance and probability. Describe events as likely or unlikely. Explore addition models. Explore properties of addition. Use addition number sentences to record the combing of sets. Solve addition number sentences. Explore subtraction models. Explore properties of subtraction. Use number sentences to record subtraction. Solve subtraction number sentences.
Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems. Understand basic concepts of chance and probability. Describe events as likely or unlikely. Explore addition models. Explore properties of addition. Use addition number sentences to record the combing of sets. Solve addition number sentences. Explore subtraction models. Explore properties of subtraction. Use number sentences to record subtraction. Solve subtraction number sentences.
Chapter Test: Numbers in the Neighborhood
Scope & Sequence Copyright © 2022 Edgenuity, Inc. All rights reserved.
Why Choose Time4Learning Kindergarten Math Homeschool Curriculum
Setting up students for success in math or any other subject starts as early as kindergarten. Helping them master counting, shapes, basic addition and subtraction will have a big impact on their performance in later years.
Time4Learning’s kindergarten math curriculum uses bright, colorful and engaging activities to make math fun and enjoyable for the little ones. Students are able to log in on their time and progress at their own pace. The curriculum is simple to follow and material is presented in a suggested sequence that builds on itself.
Students are able to log in on their time and progress at their own pace. The curriculum is simple to follow and material is presented in a suggested sequence that builds on itself.
Parents have access to lesson plans, student planners, and plenty of resources to make homeschooling simple. In addition, our automated grading and recordkeeping system keeps track of all of your child’s work and makes it simple to print reports and create homeschool portfolios. And if you plan on using the kindergarten math curriculum as a supplement, you will have full access to these features as well.
Interested in other kindergarten subjects? Learn more about our online kindergarten curriculum, designed to teach your student their fundamental concepts.
Math Skills for Kindergarten, What Your Child Will Learn, Komodo Math
- Math Tips
- Education
- K
As your child heads into kindergarten, you’ll be feeling all sorts of emotions. You may be wondering: How can my baby be that old? Is she ready? What exactly is he going to learn in kindergarten?
You may be wondering: How can my baby be that old? Is she ready? What exactly is he going to learn in kindergarten?
While kindergarten may have changed since you were a child, it still forms the foundation of your child’s schooling and we wrote earlier about how to prepare for a successful start to the school adventure.
In math, students will learn the basics of how numbers work while exploring place value and the concepts of addition and subtraction.
But there’s no need to figure everything out as your child does - this article will help you get a head start by knowing what to expect.
In kindergarten your child will learn how to:
1. Count to 100
Going into the school year, your child may be able to orally count to 10 or beyond. By the end of kindergarten, expect that counting to advance to 100. But don’t worry, we’re only talking about counting orally. Your kindergartner will not be expected to write all the numbers to 100.
In most kindergarten classrooms, teachers count the days of school with the children. By counting each day, children gradually become more fluent with bigger and bigger numbers. At the end of 100 days, kindergarten classrooms often have a big celebration with many more opportunities for counting.
At home: To support your child’s counting skills, encourage your kindergartner to count as high as possible. This is a great task to give your child in the car - or even at bedtime!
2. Answer “how many?” questions about groups of objects
As well as counting to 100, kindergartners will be asked to count how many objects are in a group. Students need to be able to physically count objects one at a time, assigning one number to each object as they count. This is a skill called one-to-one correspondence.
At home: Ask children to tell you how many toys they are playing with and watch how they keep track of each object that is counted. If your kindergartner counts the same object twice or skips an object, encourage another try.
If your kindergartner counts the same object twice or skips an object, encourage another try.
3. Solve basic addition and subtraction problems
In kindergarten, children start to develop an understanding of addition and subtraction within 10. Kindergartners start by solving problems involving physical objects, and as the year goes on, students learn to draw pictures to represent addition and subtraction problems. They will even begin to solve simple word problems.
At home: Present two groups of blocks (less than 10 in all) and have your child add the blocks together. As your child develops understanding, you can ask simple addition or subtraction problems without using the physical objects as a support.
4. Understand the numbers 11-19 as a ten plus some ones
Though it may seem quite advanced, your kindergartner will begin to understand the concept of place value and that position makes some numbers bigger than others - ie get to grips with the idea that 21 is bigger than 12. Students may use place value blocks to be able to “see” how ten ones become a ten.
Students may use place value blocks to be able to “see” how ten ones become a ten.
At home: When counting blocks or lego bricks at home, make a group of ten. Then add on extra “ones” to make the numbers 11-19. You can even talk about place value when looking at written two-digit numbers.
5. Name shapes
Kindergartners will learn about 2D and 3D shapes. They should be able to name different shapes while describing their features. Kindergartners love to recognize shapes in the real world!
At home: Help your child by having them spot squares, cubes, spheres, rectangles, etc. Challenge your kindergartener to draw pictures using basic 2D shapes, then talk to you about the drawings. Making and continuing shape patterns is another fun way to help engage your kindergartner as they learn about shapes.
Throughout the year, make sure to ask your child about what’s happening in kindergarten math. Give your child an opportunity to teach you by sharing what he or she has learned. Get ready for a fun year in kindergarten!
Found this useful? Check out our grade by grade math guides from Kindergarten to 5th grade
Written by Lily Jones, Lily loves all things learning. She has been a kindergarten & first grade teacher, instructional coach, curriculum developer, and teacher trainer. She loves to look at the world with curiosity and inspire people of all ages to love learning. She lives in California with her husband, two kids, and a little dog.
About Komodo – Komodo is a fun and effective way to boost K-5 math skills. Designed for 5 to 11-year-olds to use in the home, Komodo uses a little and often approach to learning math (15 minutes, three to five times per week) that fits into the busy family routine. Komodo helps users develop fluency and confidence in math – without keeping them at the screen for long.
Find out more about Komodo and how it helps thousands of children each year do better at maths – you can even try Komodo for free.
Back to School - 5 Tips to Help you Ease Back into the Routine
Here are some steps you can take to ease children back from full vacation mode so that the first week of school doesn't knock you sideways.
Mindset - The Path to Mastery
People who have a growth mindset believe that they always have the potential to learn and improve. They are more motivated to persevere with difficult tasks, to take risks and to learn from failure.
Math for Kids: Addition
on the App StoreDescription
A fun and free way for preschoolers to learn how to add and subtract!
It is never too early for a child to learn. Preschoolers, kindergarteners, preschoolers and older kids all want to learn the ABCs, counting, addition, subtraction and more! The best way to help them do this is to engage with them every day with thoughtful, conscientiously made educational apps and games. nine0005
nine0005
Math for Kids is a free educational game to teach kids numbers and math. It contains several mini-games that toddlers and preschoolers will love, and the more they enjoy them, the better they will be at counting! "Math for Kids" will help preschoolers, kindergarteners and first graders learn and identify numbers, as well as start learning addition and subtraction puzzles. They will enjoy spending time winning and earning stickers, and you will enjoy watching your kids grow and learn. nine0005
"Math for kids" contains several puzzles that will teach your children in a playful way.
1. Counting Learn to count objects with a simple addition game.
2. Comparison Children can gradually learn how to count and compare using groups of large and small objects.
3. Addition Puzzles A fun mini-game in which kids create math problems by dragging numbers onto the screen.
4. Addition fun Count items and select by pressing the missing number.
5. Addition Quiz Test your child's math skills in addition. nine0011 6. Subtraction puzzle Filling in the missing characters in a math problem.
nine0011 6. Subtraction puzzle Filling in the missing characters in a math problem.
7. Fun subtraction Counting items to add the puzzle!
8. Subtraction Quiz Check your child's ability to subtract.
If children learn while playing, they learn much faster. In addition, they have a desire to study more often, which will give them a great advantage when they go to kindergarten.
Math for Kids also has several features that allow parents to track and guide their child's progress. You can customize game modes to increase or decrease the difficulty level, as well as check your previous scores. nine0005
Math for Kids is a great start to learning the basics of counting, addition and subtraction. It will teach your preschooler, kindergartener or first grader how to classify objects into groups and reason logically, help you master elementary mathematics, thereby preparing the necessary basis for further learning.
Support us in helping 1 billion children!
Version 1.3.8
Math for Kids is a free fun learning app that gets kids all over the world to start learning! We have translated the text and audio into 8 languages so that more kids can take care of their education!
New in this update:
- Graphics and interface improvements
- Supported languages: English, Russian, Deutsch, español, français, Português, हिंदी, मराठी
Ratings and reviews
nine0006 Ratings: 19Russian language problem
Russian language is not loaded
Math kids
Not loaded in Russian
Thank you!
Thank you!
Developer RV AppStudios LLC has indicated that, in accordance with the application's privacy policy, data may be processed as described below. Detailed information is available in the developer's privacy policy. nine0005
Detailed information is available in the developer's privacy policy. nine0005
No data collection
The developer does not collect data in this application.
Sensitive data may be used differently depending on your age, features involved, or other factors. Read more
Information
- Provider
- RV AppStudios LLC
- Size
- 169.5 MB
- Category
- Education
- Age
- 4+, for children 0-5 years old
- Copyright
- © 2022 RV AppStudios
- Price
- Free
- Developer site nine0114 Application Support
- Privacy Policy
Other apps from this developer
You may like
Mathematics online - courses for students in grades 1-4 of the school
Mathematics is one of the most important school subjects that every student has to master. Even at kindergarten age, kids memorize numbers and numbers, learn to understand the meanings of “more-less” - that is, they get acquainted with the basics of mathematics. nine0005
Even at kindergarten age, kids memorize numbers and numbers, learn to understand the meanings of “more-less” - that is, they get acquainted with the basics of mathematics. nine0005
In elementary school, arithmetic is taught in stages. First, students deal with the concepts of the whole and the part, learn about quantities, learn to add, subtract, multiply and divide, master values within a thousand. Also, gradually, the guys delve into the basics of algebra and geometry. It all starts with general concepts, gradually delving into more extensive knowledge. Children repeat the past and learn new things at the same time.
Teaching mathematics from simple to complex is considered the most effective and accessible for all students. The principle of succession works best when studying mathematics. What is the importance of this subject, why is it so difficult for some children to learn it and how to solve this problem are questions that bother many parents so much. nine0005
Why teach math to children
Some adults think that children are overburdened in grades 1-4. After all, the kids just came to school, just started their learning path - it’s quite difficult for them to delve into such a serious subject. However, learning mathematics from elementary school has a positive effect on the overall development of each student. And here's why:
After all, the kids just came to school, just started their learning path - it’s quite difficult for them to delve into such a serious subject. However, learning mathematics from elementary school has a positive effect on the overall development of each student. And here's why:
- Intellectual abilities develop - logical thinking, mathematical speech, imagination. nine0115
- Kids use examples of tasks to train to reason, defend their point of view, prove their case, accept someone else's opinion, distinguish validity from an empty statement, look for information, bring what they started to the end.
- There is a mathematical foundation for further knowledge. For example, a child learns to understand quantities and how to measure them, apply mathematics in practice, solve everyday situations with the help of mathematical actions, and follow algorithms of actions. nine0115
- Mathematics develops the human brain - new neural connections are created, there is a desire for learning.
The main task of studying this subject from early childhood is to instill in children a love for the exact sciences and show their importance in everyday life.
Why kids don't understand math
Math problems in high school don't just happen. If in grades 8-9 a student experiences difficulties even when performing elementary tasks, it means that everything started much earlier. Parents should be attentive to the abilities of their children, in particular, pay attention to his predisposition to mathematics. In order to avoid problems at school, it is important to understand at the age of six or seven whether a preschooler has difficulties with perception. For example:
- the child cannot count to one hundred;
- does not understand which number precedes or follows another;
- it cannot recognize numbers up to 20;
- cannot count in tens;
- does not understand that one number can include a group of items;
- has hesitations when arranging objects according to shape or color.
School age also has its own “bells” that require parental attention. This is:
- difficulty adding and subtracting elementary numbers or counting with a given step;
- does not recognize math characters;
- does not distinguish tens from ones;
- difficulty remembering simple facts, eg 2x2=4;
- does not answer when you need to name the right or left side of an example or equation;
- cannot play strategy games like checkers;
- does not apply mathematics in real life, for example, is not able to count change in a store; nine0115
- is unable to understand the diagram.
There are quite a few cases when parents think that they will teach everything at school, so they completely ignore the fact that the student is lagging behind. However, this is a big mistake, because you can see gaps in a son or daughter much earlier than they start having problems with mathematics. If adults have noticed even a minimal lag of a preschooler or primary school student, it is worth paying attention to this and solving the problem. Developed computing skills will help children succeed in school. nine0005
Developed computing skills will help children succeed in school. nine0005
How to improve your child's math skills
You can help your child improve their understanding of mathematics even at home. There are some tips from experienced teachers and psychologists that will help in solving this problem.
Integrate math into your daily life. For example, ask your child to bring you 5 potatoes, 2 onions while preparing dinner. Or you can ask him to count how many guests will come to visit, how many eggs still need to be bought so that there are ten of them. Every day there are many situations where you need an account - use this. nine0005
It is much clearer to learn something if you use the visualization method. For example, you can draw a task, enliven the numbers, depicting funny characters from them. It is also easy to come up with games where instead of an unknown in the equation lies, for example, a fruit or a coin.
Talk to the child's teacher - let him tell you in more detail what exactly the student has difficulties with.