What is sight words for kindergarten
Sight Words for Kindergarten & Kids
No matter whether kindergarten children will be learning in person, online, or a hybrid of the two, parents and teachers are still focused on ensuring their emerging readers develop a love for reading while learning to read effectively and efficiently. One critical skill that children need in order to build solid foundational reading skills is sight word recognition.
What Are Sight Words?
When we teach children to read, we are basically helping them to crack a code. Children learn to hear and say the sounds of the alphabet and then how to blend those sounds to make words. These sounds usually follow basic spelling rules or phonetic principles, but there are some words that did not follow rules. These words are called sight words.
Most sight words cannot be decoded or sounded out, and they are also difficult to represent with a picture. As a result, children must learn to recognize these words automatically, or at first sight. Children who are able to quickly and instantly recognize sight words are more likely to become more fluent readers who read at a good speed because they are not stopping to try to decode every word. When children recognize sight words within three seconds, they are also more likely to comprehend what they are reading. Children who are able to instantly recognize sight words are more likely to be confident readers because over 50-70 percent of the general English text is made up of sight words.
There are several sight word lists for emerging readers. One list is called the Dolch Word List, created by E.W. Dolch in 1936. The list contains 220 of the most commonly used words that should be recognized by first sight. The list is divided by grade level from Pre-K through third grade, but many educators believe that these words should be mastered by first grade. In addition to the 220 sight words, the Dolch Word List also includes 95 high-frequency nouns. In the 1950’s, Dr. Edward Fry expanded the Dolch Word List to include 1,000 commonly used words in the English language. Fry updated the Fry Sight Word List in 1980, which is comprised of the most commonly used words in books, newspapers, and other publications. Like the Dolch Word list, the Fry Sight Word List is made up of both sight words and high-frequency words and is divided by grade level. Teachers will generally pull from one or both of these lists to create the sight words that children should learn. It is important for parents to keep in mind that children are expected to be able to instantly recognize sight words they have learned previously.
Fry updated the Fry Sight Word List in 1980, which is comprised of the most commonly used words in books, newspapers, and other publications. Like the Dolch Word list, the Fry Sight Word List is made up of both sight words and high-frequency words and is divided by grade level. Teachers will generally pull from one or both of these lists to create the sight words that children should learn. It is important for parents to keep in mind that children are expected to be able to instantly recognize sight words they have learned previously.
Examples of Sight Words for Kids
Here is a list of sight words and high-frequency words for Pre-K, kindergarten, and first grade that have been taken from both the Dolch Word and Fry Sight Word Lists.
| Grade | Sight Words |
| Pre-K (40 words) | a, and, away, big, blue, can, come, down, find, for, funny, go, help, here, I, in, is, it, jump, little, look, make, me, my, not, one, play, red, run, said, see, the, three, to, two, up, we, where, yellow, you |
| Kindergarten (100 words) | about, all, am, an, are, as, at, ate, be, been, black, brown, but, by, call, came, could, day, did, do, each, eat, first, four, from, get, good, had, has, have, he, her, him, his, how, if, into, like, long, made, many, may, more, must, new, no, now, number, of, oil, on, or, other, our, out, part, people, please, pretty, ran, ride, saw, say, she, sit, so, some, soon, than, that, their, them, then, there, these, they, this, time, to, under, use, want, was, water, way, well, went, were, what, when, which, white, who, will, with, word, would, write, yes, your |
| 1st Grade (100 words) | add, after, again, air, also, America, animal, another, answer, any, around, ask, back, because, before, boy, change, different, does, end, even, every, fly, follow, food, form, found, give, going, great, hand, high, home, house, just, kind, know, land, large, learn, let, letter, line, live, man, mean, men, most, mother, move, much, must, name, need, near, off, old, only, once, open, over, page, picture, place, point, put, read, right, round, same, say, sentence, set, should, show, small, sound, spell, still, stop, study, such, take, tell, thank, things, think, through, too, try, turn, us, very, walk, want, well, why, work, world, year |
Site Words FAQs
Q: What is the difference between sight words and high-frequency words?
A: While both sight words and high-frequency words are important, they are not the same. Sight words are words that cannot be decoded, so knowing spelling rules or phonics will not help a child sound out the word. High-frequency words are commonly used words that students need to know. Some high-frequency words are decodable using spelling and phonics rules, and some are not. As a result, it is important to help students recognize both sight word and high-frequency words by sight, so that they can recognize them automatically. As you begin to introduce spelling rules, phonics and syllabication to Kindergarten children, be sure to highlight high-frequency words they have memorized that fit a given rule. Regardless of whether the word is a sight word or high-frequency words, they both must be taught explicitly and systemically so that children will know them automatically.
Sight words are words that cannot be decoded, so knowing spelling rules or phonics will not help a child sound out the word. High-frequency words are commonly used words that students need to know. Some high-frequency words are decodable using spelling and phonics rules, and some are not. As a result, it is important to help students recognize both sight word and high-frequency words by sight, so that they can recognize them automatically. As you begin to introduce spelling rules, phonics and syllabication to Kindergarten children, be sure to highlight high-frequency words they have memorized that fit a given rule. Regardless of whether the word is a sight word or high-frequency words, they both must be taught explicitly and systemically so that children will know them automatically.
Q: When should sight words be taught?
A: While most Pre-K children are able to master some sight words, it is important to remember that children learn language skills at different rates. They also have different interest levels when it comes to learning words. Some children are eager and ready to learn while others may not be. As a result, there is no specific age to begin teaching sight words. So try some fun sight word activities with your two- or three-year old children, but do not push if they are not interested. Let your child’s developmental readiness and interest level guide you.
Some children are eager and ready to learn while others may not be. As a result, there is no specific age to begin teaching sight words. So try some fun sight word activities with your two- or three-year old children, but do not push if they are not interested. Let your child’s developmental readiness and interest level guide you.
Q: How many sight words should kindergarteners learn?
A: There are varying opinions as to how many words children should learn. Some literacy experts like Tim Shanahan believe that kindergarteners should master 20 sight words by the end of kindergarten. The Dolch word list has 40 words listed for Pre-K students and some school districts require that kindergarteners learn 100 sight words by the end of the school year. Consider your children’s progress and interest levels as well as your school district’s expectation to help decide on the appropriate number of sight words for your children.
Q: What order should I teach sight words?
A: There is no one set prescribed order to teach sight words. Some teachers and parents teach the sight words from the Dolch or Fry lists in alphabetical order. Others use the lists and create their own order. Consider using the Frequency Fry List that has words ranked by the frequency of use for reading and writing. To help children learn sight words and get them to stick, create your own lists to teach students the words not only in isolation, but also in context. For example, if you decide to read a specific book, teach the sight words from the book you are reading. This gives children practice reading the word in isolation and also helps them to see how the word is used in language.
Some teachers and parents teach the sight words from the Dolch or Fry lists in alphabetical order. Others use the lists and create their own order. Consider using the Frequency Fry List that has words ranked by the frequency of use for reading and writing. To help children learn sight words and get them to stick, create your own lists to teach students the words not only in isolation, but also in context. For example, if you decide to read a specific book, teach the sight words from the book you are reading. This gives children practice reading the word in isolation and also helps them to see how the word is used in language.
Q: How many sight words can be taught in a day?
A: Before determining a set number of sight words to teach, it is important to focus on the number of words that children are actually learning. It is important to consider the quality of their learning, not the quantity. Make certain that children can recognize sight words instantly and accurately before rushing to complete a certain number of words. Before starting, be sure to consider the child’s age, motivation and memory skills. Keep in mind that a child who can instantly and accurately name 50 sight words is building a more solid reading foundation versus a child who “kind of knows” 100 words.
Before starting, be sure to consider the child’s age, motivation and memory skills. Keep in mind that a child who can instantly and accurately name 50 sight words is building a more solid reading foundation versus a child who “kind of knows” 100 words.
Start by introducing children to three to five new words during a given lesson. During the next day’s lesson, review the previously introduced words. If children remember all of the words, consider introducing three to five new words. If children do not remember the previous words, review the previously introduced words and wait to introduce new words. Also, consider reducing the number of words you introduce in each lesson to one or two words if children are struggling or feel overwhelmed.
Learning Without Tears Knows Sight Words!
There are lots of fun, engaging strategies to teach children sight words. Before you begin teaching sight words, make certain you have broken down the word lists into manageable and differentiated lists for your students.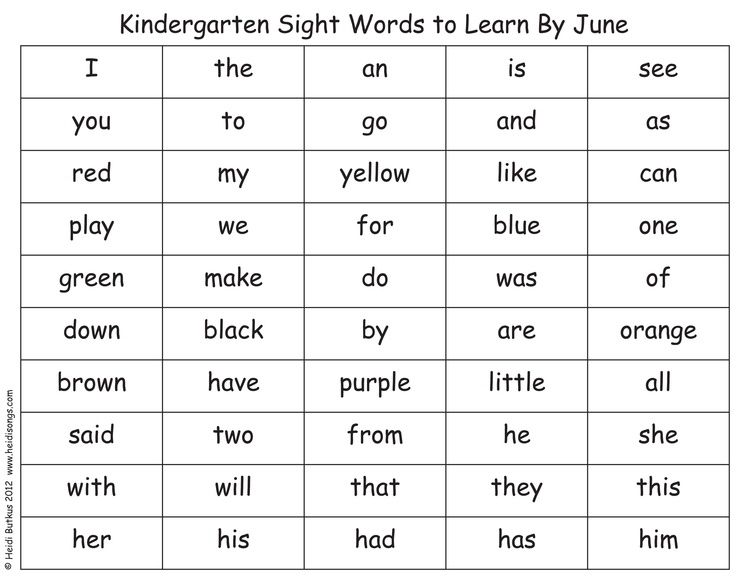 Secondly, no matter whether you are teaching your children in person or virtually, it is important to devote at least 15-20 minutes a day to teaching sight words. Lastly, make learning sight words is a fun and interactive activity. Below are 10 engaging sight words activities to do with your children.
Secondly, no matter whether you are teaching your children in person or virtually, it is important to devote at least 15-20 minutes a day to teaching sight words. Lastly, make learning sight words is a fun and interactive activity. Below are 10 engaging sight words activities to do with your children.
Sight Word Concentration – On index cards, write the same sight words on two separate cards. Make two piles – one with the word and the other with the matching word. Mix the two piles and place them face down. Have children take turns to find the matching cards. Consider having children write down the words that they found. Use Learning Without Tears’ A+ Worksheet Maker to create worksheets where they can copy the words.
Build-A-Sight Word – Children love building words with manipulatives like magnetic alphabet letters. Learning Without Tears’ Magnetic Lowercase & Blackboard Set contains magnetic lowercase letters and a magnetic blackboard with double lines so that children can build and write sight words. Children can also build sight words using Learning Without Tears’ free Make Your Own Letter Cards.
Children can also build sight words using Learning Without Tears’ free Make Your Own Letter Cards.
Sight Word Bingo – Create individual bingo cards using sight words that you have introduced. You can also give students a blank board and have them write the words in the boxes from a list you provide. Be sure to have the words written on index cards and pull them out of a container to call the sight words. Students should place a marker on the word when it is called. Students must yell "Sight Word Bingo!" when they have covered a vertical, horizontal, or diagonal row.
Stamp Out Sight Words – Using alphabet cookie cutters, have students stamp out letters using dough, then have children build sight words. Model for students first, then have them do it with you. After guiding them, have them try to build it independently. This fun activity is also great for building fine motor skills.
Sentences with Sight Words – Learning Without Tears’ Sentence School is a great way to help students learn sight words and write sentences. Students will love the engaging, hands-on lessons, and the guide is a great resource for teachers and parents alike.
Students will love the engaging, hands-on lessons, and the guide is a great resource for teachers and parents alike.
Sight Word Detective – Show children a sight word with a missing letter. Have children act as detectives to find the missing letter. You can play as a whole class, in teams, or individually. To make it more challenging, remove more than one letter. Also consider using the word with the missing letter in a sentence to help children practice context clues. You can write letters on a white board or use magnetic letters.
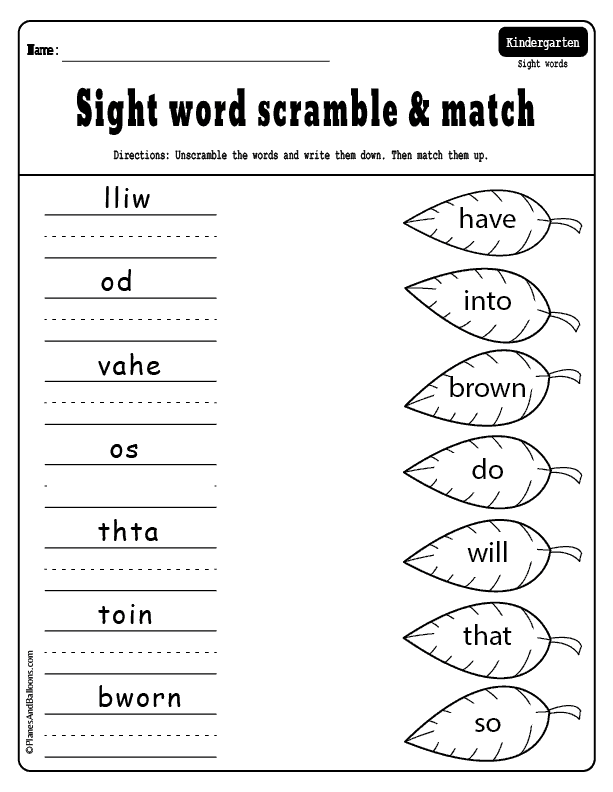
Sight Word Scramble – Using magnetic letters or letter cards, mix up the letters of the sight word and have children unscramble the words to reveal the correct spelling of the sight word. You can involve more children by giving each child a letter and have them spell out a sight word.
Sight Word Sing-a-Long – Music is a great teaching tool for children and adults. Learning Without Tears has lots of fun, engaging, and catchy songs to help students learn sight words. Consider displaying the lyrics from Learning Without Tears’ Rock, Rap, and Learn CD on a white board and have children circle all of the sight words. Lyrics to all songs are located on Learning Without Tears’ Handwriting Interactive Teaching Tool.
Consider displaying the lyrics from Learning Without Tears’ Rock, Rap, and Learn CD on a white board and have children circle all of the sight words. Lyrics to all songs are located on Learning Without Tears’ Handwriting Interactive Teaching Tool.
Read and Write Engaging Stories – Children feel more confident and excited when they begin to recognize words in a book. When reading to children, help them to identify sight words. Learning Without Tears’ MatMan Book series contains lots of sight words. Give sight word readers to children to begin reading on their own. After reading a story, write the sight words that they see and have children copy them. Also, encourage your students to create a funny story by writing down a sentence from each child. Circle all of the sight words they use.
Hand Activity Sight Words – To help children recognize sight words automatically and make them stick, teach them the attributes of the words using Learning Without Tears’ Hand Activity Method. Some lowercase letters are tall (b,f,h), some are small (a, e, n), and some are descending (j, p, y). Have them use their hands to spell out the words or use the hands and letters from LWT’s Magnetic Lowercase & Blackboard Set to help them visualize the words. Also, consider highlighting other attributes of words—like the number of letters, consonants, and vowels—in order to help students connect with sight words.
Some lowercase letters are tall (b,f,h), some are small (a, e, n), and some are descending (j, p, y). Have them use their hands to spell out the words or use the hands and letters from LWT’s Magnetic Lowercase & Blackboard Set to help them visualize the words. Also, consider highlighting other attributes of words—like the number of letters, consonants, and vowels—in order to help students connect with sight words.
Explicitly teaching children sight words in a fun, engaging manner will help to build their reading rate, fluency, and confidence. Sight words will build a solid foundation for students to become proficient readers. Have fun!
FREE Printable List of Kindergarten Sight Words & How to Teach Them
If you’ve got a child in kindergarten, you’ll want to get familiar with kindergarten sight words and learn how to teach your child to read & learn sight words.
As a child play therapist and teacher, I understand how important it is to understand what sight words are, as well as understanding which activities, games, and apps are best to use to teach them.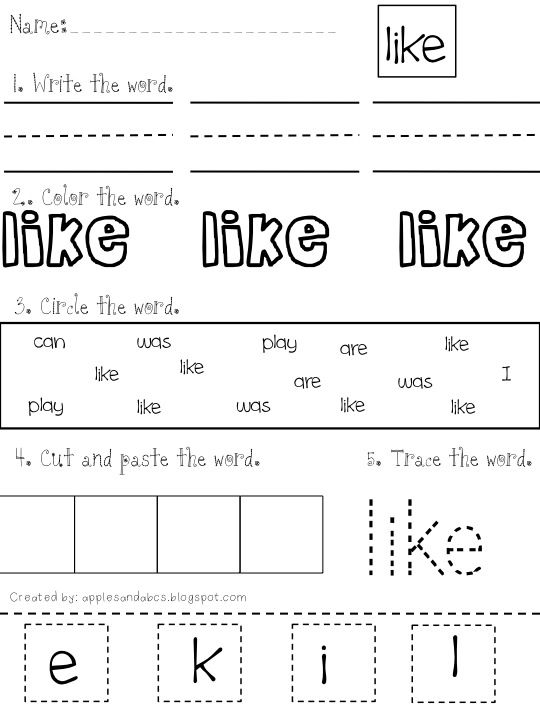
This post has been updated to include more Kindergarten Sight Word Resources for parents and teachers (like this Kindergarten Sight Word Bundle Packet).
Sight words are words that kindergarteners will see the most. Sight words are a commonly used term that usually refers to a set of words that reappears on almost any page of text.
Kindergarten Sight Words and How to Teach ThemThese high-frequency words are seen often. In fact, between 50-75% of your child’s text will include sight words from pre-primer & primer Dolch word lists.
What are sight words?
To become a great reader, children must master their sight words. It is essential to learn their sight words and to continue to practice them. Once your child has mastered them, it is time to move onto the next list.
Kindergarten sight word listWhen your child is looking at these words on a daily basis, they will learn them quickly. Repetition is the key to fluency (reading smoothly, without a lot of pauses), so practicing these words over and over will help to achieve that goal.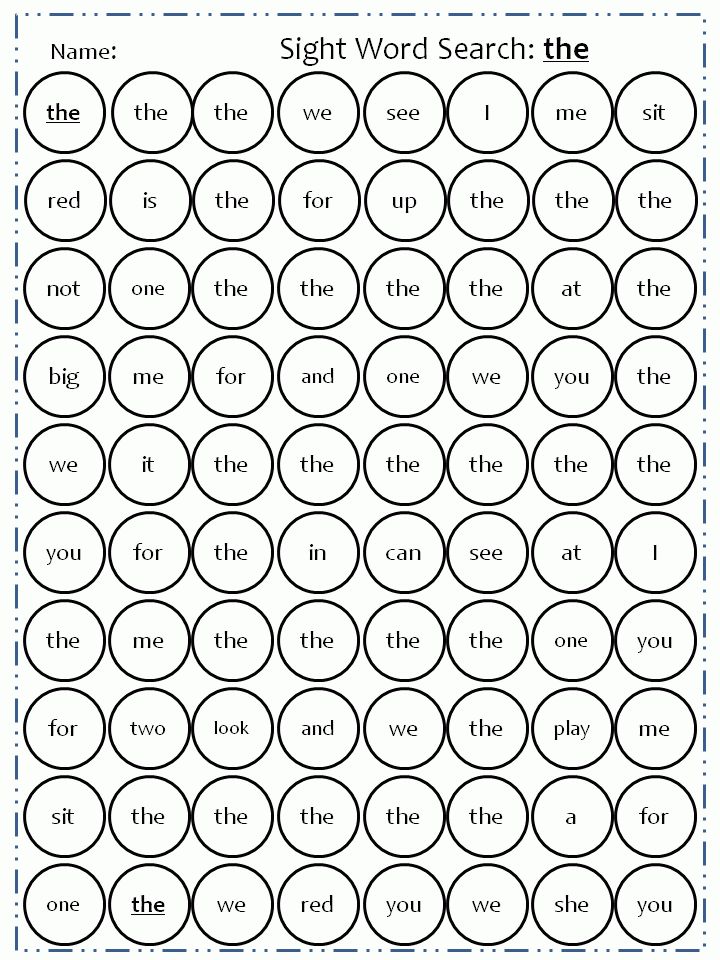 Here is a FREE printable list of Kindergarten Sight Words (click here, and I will send you the list)
Here is a FREE printable list of Kindergarten Sight Words (click here, and I will send you the list)
Or if you really want the complete package, get this Kindergarten Sight Word Bundle Packet. As a child play therapist, I put this packet together so you can help your child learn sight words. You can print it over and over again to help your child learn his or her sight words.
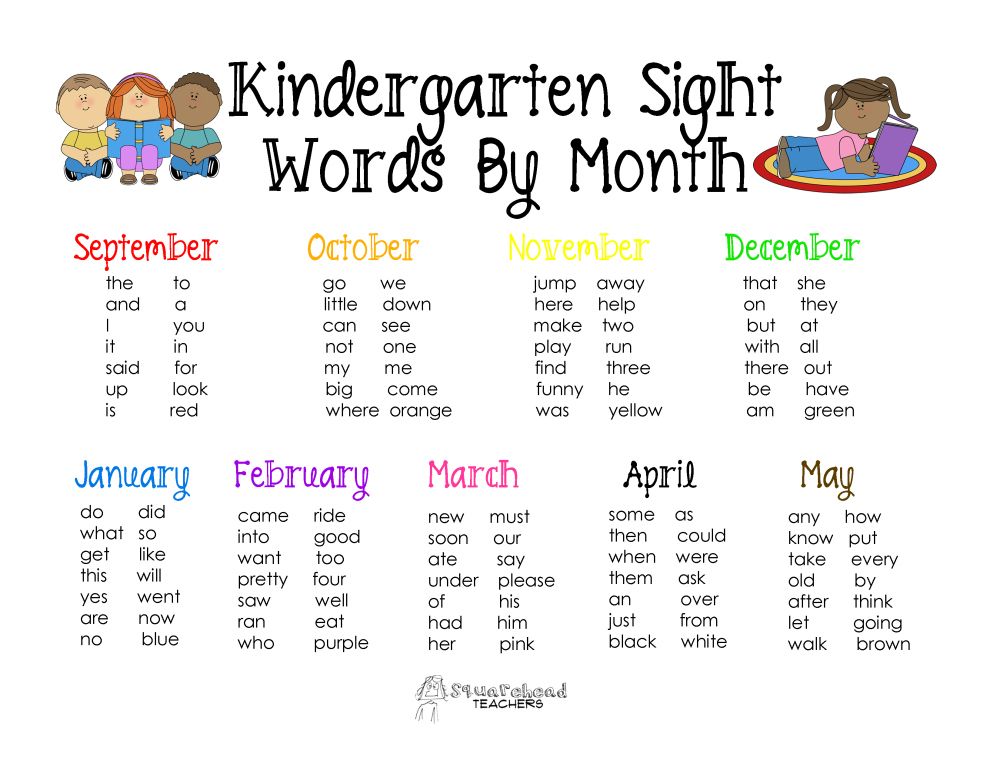
How many sight words are there?There are 52 sight words that are typically taught in kindergarten.
The Kindergarten Sight Words are:
all, am, are, at, ate, be, black, brown, but, came, did, do, eat, four, get, good, have, he, into, like, must, new, no, now, on, our, out, please, pretty, ran, ride, saw, say, she, so, soon, that, there, they, this, too, under, want, was, well, went, what, white, who, will, with, yes.
These are the 52 most commonly seen words in kindergarten level books. When a child is able to master those words, it not only makes it easier for them to read the words, it also improves their fluency or how quickly and smoothly they can read a passage.
To begin, simply introduce your child to the list (show your child, hang it up, read them).
Read all of the words to your child (every day) and explain that he will be learning a new word every day (or every other day). Be excited about it.
On day one, see if your child knows any of the words. If they do, put a sticker, a checkmark, or a smiley face to the left of the word (there is space for that). If not, that’s OK! He will.
Every single day, go over the new word, as well as the OLD words that they know. I start by going over the old words with the sticker and then picking a new word. I say it, spell it, say it again, and ask my child to repeat it.
During the day, we will talk about that word and go back to the wall where it is hanging to look at it. I do this at least three times. I keep my chart in the pantry, so anytime our kids eat a snack or want to grab something, they see the words.
Continue to add a sticker, checkmark, or a smiley face to their new words, until the whole list has been completed. From then on, you can just review them every day or every few days.
As the days go on, find these words in other areas (words in books, service words on signs, flash cards before bed…)
Related: YOU ARE WELCOME TO DOWNLOAD THIS SIGHT WORD CHECKLIST ↓ (free) by clicking here.
SIGHT WORDS TO TRACE
Tracing kindergarten sight words gives children a chance to engage with the words in a new and different way. By combining multiple learning styles in one lesson, kids are more likely to learn and recall their sight words. Here are a couple of methods for creating kindergarten sight words to trace.
- Rainbow Writing: At the beginning of the school year, have students trace the sight words in three different colors. This repetition helps them develop motor memory while also solidifying the spelling of the word. As the school year progresses, have students write the words independently in three colors. They can overlap the colors or write them three separate times.
- Dry Erase Words: Kids love writing with different writing tools, so dry erase markers always make things more fun!
– Print out the kindergarten sight words you’d like students to practice on a sheet of heavy cardstock.
– Slip the cardstock into a transparent page protector and clip it to a clipboard.
– Then, with a dry erase marker, students can trace the sight words on the page protector.
If they make a mistake, it can be erased with a tissue or an old sock!
Technology has made even the youngest students digitally savvy. If you have access to a computer or tablet and a printer, have your students type their kindergarten sight words and print them out.
If you have access to a computer or tablet and a printer, have your students type their kindergarten sight words and print them out.
Kids love working in word processing programs and learning how to type. They can print the words in different colors, fonts, and sizes. Use the sight words they printed to decorate the room or as part of their reading folder.
If you minimize the page size, you could even use their printed words as Kindergarten sight word flashcards!
SIGHT WORDS IN SENTENCES
Learning sight words are important, but kids need to learn how to identify those words in sentences.
For early readers, being able to pick out kindergarten sight words in sentences means they have a complete understanding of the word.
Not only can they trace and write the word, but they can pick it out amidst other words. This is an important skill as they continue to develop their reading abilities.
How do you find them?One way to help kids identify their sight words in sentences is to play a modified version of I Spy. Instead of looking for objects, they are tasked with finding sight words. Give them a highlighter or highlighter tape to cover the word once they have found it.
Instead of looking for objects, they are tasked with finding sight words. Give them a highlighter or highlighter tape to cover the word once they have found it.
Since kindergarteners have a limited reading vocabulary, make the sentences as uncomplicated as possible. Even three-word sentences allow students to practice finding and identifying sight words. If you want to make it more challenging, add a couple of sight words in each sentence!
KINDERGARTEN SIGHT WORDS WITH PICTURESKindergarten sight words are basic words that are seen the most frequently in grade-level books. Many of the words are hard to illustrate because of their simplicity. One way to create flashcards of kindergarten sight words with pictures is to have students decorate them or create an illustration that helps them remember the word.
For example, they may draw someone crawling under a table, or they might draw a picture of a toy that has fallen under a bed to illustrate the word “UNDER. ”
”
Whatever image helps them remember the word is fine to use. The goal is to help them learn the words so there is no right or wrong.
KINDERGARTEN SIGHT WORD FLASHCARDSKindergarten sight word flashcards are especially helpful for quick practice. They can be useful for reviewing words at home or on the go.
Some people even uploaded them as virtual flashcards to a tablet or smartphone to be practiced while in the car, visiting relatives, or on vacation.
It doesn’t matter if you print them out to review alone, study them from a device, or turn them into a game; sight word flashcards are a great way to reinforce kindergarten vocabulary.
When using Kindergarten Sight Word Flashcards, start with three sight words. When your child knows these three words, add one additional word at a time to the existing words the child already knows.
If you add more, your child will likely become frustrated – and we want this to be fun! Continue adding one word at a time until your child can recognize all Kindergarten sight words.
Learning is always more effective when it’s turned into a game! Here are some of our favorite sight word games and apps.
Sight Word Games- Go on a Word Hunt: Look for sight words in your Kindergartener’s favorite book! Count how many you can find. You could also print out a list of kindergarten sight words and put a checkmark next to each one you find.
- Sight Word Hopscotch: Draw a hopscotch board on the sidewalk with chalk and write different sight words in each square. As your child hops from square to square, have him call out the sight word he’s jumping to.
- Sight Word Water Balloon Smash: Fill water balloons and write sight words on each balloon in a permanent marker. On the sidewalk, write the sight words in chalk. Have your child choose a balloon, match it to the word on the sidewalk, and smash it on the chalked word. Not only is it a lot of fun, but it’s also a great way to stay cool.
- There are more Games in this Kindergarten Sight Word Bundle Packet, like these puzzles, etc.
- Sight Words by Photo Touch – Free. This no-frills sight word app lets kids match the sight words and progress through the different levels.
- Sight Words List by Innovative Mobile Apps – $1.39. Bright and simple, this app lets you use pre-built lists of sight words or create your own. There are also challenges where kids can pick the sight word out of a group of words. The clear font makes the words easy to read.
- Sight Words: Kids Learn by Teacher Created Materials – Free. This sight words app features more frills than the two above. The pictures are colorful, the font is clear, and there are multiple games to help students practice their sight words.
- Print this FREE Kindergarten sight word list – Hang it by your door or on your refrigerator. Review the list daily until your child can read them fluently and confidently.
You’ll also want to think about helping them even more by using this Kindergarten Sight Word Bundle Packet.
This printable packet is easy to use; you can download it and print it over & over to help your child. The kids love it & they learn so much from the repetition of seeing the same words again & again. It’s a great way to help your child learn their sight words, which helps them to learn to read well.
See these other posts to get your child ready for school
- Teach kids their name and number with ONE tip
- How to read to your preschooler
- 5 practical, time-saving tips for school mornings
© YourModernFamily.com. Content and photographs are copyright protected. Sharing of this article is encouraged and appreciated, copying and/or pasting articles to any social media is strictly prohibited.
Doshkolnik. ru ru TeachersHolidaysNeedleworkDoshkolnik.ru Doshkolnik.ru - site of an educator, speech therapist, defectologist, music director, methodologist, physical education instructor, parent. We offer teachers assistance in certification. ServicesPosting articles
| Visual impairment in children
| Magazine"Preschooler.RF" | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Impairment and prevention of vision in humans
The article studied the factors that affect visual impairment in people Revealed the dependence of visual impairment on age and labor activity of a person on the example of one family. And also identified the causes that affect visual impairment in primary school students using the example of 4 "A" and "B" classes of the MBOU School No.
And also identified the causes that affect visual impairment in primary school students using the example of 4 "A" and "B" classes of the MBOU School No.
Key words: organ of vision, factors affecting visual impairment, recommendations.
The organ of vision is the most important of all the sense organs for a person. Vision is necessary for a person for any activity: study, work, leisure, everyday life. Reduced vision is constant discomfort, self-doubt.
Vision is a complex and not fully understood process. The main functions of the organ of vision are: the ability to distinguish the size and shape of environmental objects; navigate in space; to perceive the distances between environmental objects, the volume of these objects, the ability to observe objects in motion; perception of surrounding objects with two eyes; the ability to perceive more than two thousand shades of color, depending on the wavelength of light radiation; the ability to perceive light in the range of solar radiation and adapt to the perception of visual images at different levels of illumination [1].
The diameter of the eyeball is approximately 25 mm, it is located in the orbit, well protected by the bones of the skull.
The process of vision is as follows - light from an object passes through the pupil, a hole in the center of the iris, then through the lens, which is a lens that collects the sun's rays and sends them to the retina. On the retina, the sun's rays excite the endings of the optic nerves, and further along the optic nerve the information enters the brain, where the image is formed. Such an arrangement of the eye allows us to see [2].
The main visual impairments include diseases such as farsightedness, myopia, astigmatism. With farsightedness , parallel rays enter the eye and gather in focus behind the retina. In this case, the image on the retina will be blurry. The far-sighted eye sees far better than near. Farsightedness is often congenital.
With myopia rays enter the eye and focus in front of the retina. Nearsighted people can't see well at a distance, but they can see clearly up close. Myopia is mainly an acquired visual impairment that develops in older groups of kindergarten and, more often, in the process of studying at school.
Nearsighted people can't see well at a distance, but they can see clearly up close. Myopia is mainly an acquired visual impairment that develops in older groups of kindergarten and, more often, in the process of studying at school.
Astigmatism is an unequal curvature of the cornea, while in one eye there may be myopia along one meridian, and farsightedness in the other. A clear image on the retina of such an eye cannot be obtained. With astigmatism, visual acuity can be reduced both far and near.
Normal visual acuity (equal to 1.0) is not given from birth even to absolutely healthy children, but is formed as they grow and develop [2].
Nowadays, the formation of a child's vision is influenced by many unfavorable external factors that lead to early and rapidly progressive visual impairment. Therefore, the organ of vision needs not only protection from damage, but also the creation of favorable conditions for normal development.
There are the following factors that contribute to the formation of myopia in children.
Heredity. If the parents of a child have good eyesight, then the probability of developing myopia in school is 5-7%. If one of the parents suffers from myopia, the risk for the child increases to 27%, both parents - up to 45% [3].
visual overload. It has been proven that the frequency and progression of myopia are directly related to the number of hours spent reading.
Insufficient illumination of the workplace. All visual functions are sharply reduced in poor lighting conditions.
Unsuitable or ill-adapted study furniture. It is very important that both in the home and in the school environment, the size of the furniture corresponds to the height of the children.
Poor posture at the desk. Violation of posture, the habit of reading lying down, writing with the head strongly bowed, hunched over, tilted to the side, in an uncomfortable position contributes to the weakening of vision.
Computer and vision. In as a result of a long, continuous gaze at the monitor screen, the eye muscles are in constant tension, which leads to visual fatigue, which is accompanied by blurred vision, difficulty in perceiving words, vagueness, blurred vision.
TV and vision. Long-term viewing of television programs causes visual fatigue, which is accompanied by a violation of the blood supply to the tissues of the eye, tension of the eye muscles, which ultimately leads to a decrease in vision.
Low physical activity. During physical exercises, the eyes are in constant motion, looking either close or far, while on the one hand, the muscles of the eye are relaxed, and on the other, they are trained.
Daily regime. The efficiency of visual work is ensured by a clear organization of work and active rest. It is the organization of the child’s day regimen that should provide for the alternation of visual loads at close range with breaks for any physical activity - sports, household help, walks, etc.
Features of the diet. It is an unbalanced diet, deficiency of protein and vitamins, especially A, E, C, group B, that can provoke or aggravate the development of visual impairment in childhood and adolescence.
General diseases. Myopia often develops and progresses in weaker children with concomitant background pathology - diseases of the respiratory, musculoskeletal, and endocrine systems [3].
In order to identify factors influencing visual impairment, a family survey was conducted. I interviewed great-grandfathers and great-grandmothers, grandfathers and grandmothers, aunts and uncles, cousins, parents. The survey involved 21 people of different ages and genders. The youngest participant is 5 years old, the oldest is 83 years old.
In order to determine the causes that affect a person's vision, it is necessary to determine the social portrait of this person (Table 1).
Table 1
Composition and structure of respondents
| Composition and structure of respondents | Groups | Qty human | % | visually impaired | No visual impairment | ||
| 1. | Husband. | eleven | 52% | 7 | 64% | four | 36% |
| Female | ten | 48% | 5 | fifty % | 5 | fifty % | |
| 2. Age | Less than 30 | 9 | 43% | 3 | 33% | 6 | 67% |
| 30–50 | 5 | 24% | 2 | 40% | 3 | 60% | |
| 50–70 | four | 19 % | four | 100 % | 0 | 0% | |
| Over 70 | 3 | fourteen % | 3 | 100 % | 0 | 0% | |
| 3. | A) students | eight | 38% | 2 | 25% | 6 | 75% |
| B) professions related to the work of a PC | 5 | 24% | 2 | 40% | 3 | 60% | |
| C) professions not related to the work of a PC | 5 | 24% | four | 80% | one | twenty % | |
| D) pensioners | 3 | fourteen % | 3 | 100 % | 0 | 0% | |
Based on the results of the questionnaires, the composition and structure of respondents was determined: 48% of them were women, 52% were men; students at school and university - 38%; employed — 48%; pensioners - 14%. It was found that, depending on age, a person's vision deteriorates. In this way:
It was found that, depending on age, a person's vision deteriorates. In this way:
- under the age of 30 years, vision is impaired in 33% of people,
- aged 30 to 50 - 40% of people with visual impairment,
- over 50 years of age, vision is impaired in each person.
25% of students under the age of 22 are currently visually impaired (this is every fourth student). It was also found that visual impairment is more common in men than in women.
To determine the impact of modern technical means on different age categories, the average age at which visual impairment began was calculated (Table 2).
table 2
Determining the age from which visual impairment began
| Age category | Qty human | Average age at which visual impairment began | Myopia | farsightedness | ||
| Up to 35 years old | four | eleven | four | 33% |
| 0% |
| 36 to 50 | one | eleven |
| 0% | one | eight % |
| 51 to 70 | four | 34 | 3 | 25% | one | eight % |
| From 71 and older | 3 | 58 |
| 0% | 3 | 25% |
| Total: | 12 | 30 |
| 58 % |
| 42 % |
The table shows that in older people, visual impairment occurred at a later age than in the age category up to 30 years. On average, in the respondents, visual impairment began at the age of 30, and in the age category under 35 years old, on average, from 11 years old, in the age category over 35 years old, on average, from 40 years old. Technical means played a big role in the deterioration of vision in the younger age category.
On average, in the respondents, visual impairment began at the age of 30, and in the age category under 35 years old, on average, from 11 years old, in the age category over 35 years old, on average, from 40 years old. Technical means played a big role in the deterioration of vision in the younger age category.
The survey showed that people younger than 35 years of age are more likely to have myopia, and the older age category of people have farsightedness. In general, people are more likely to suffer from myopia.
The next stage of our work was to identify the causes of visual impairment in elementary school students. The survey involved students of grades 4 "A" and 4 "B" of MBOU School No. 176 in the amount of 54 people, of which 33 were girls and 21 were boys.
A questionnaire was used to conduct a study to identify an indicative assessment of the risk of visual impairment (Table 3).
Table 3
Questionnaire
| one | I have impaired vision | Yes |
| No |
|
| 2 | What grade is visual impairment | one | 2 | 3 | four |
| 3 | I read a lot | Yes |
| No |
|
| four | I often read in low light or lying down | Yes |
| No |
|
| 5 | I spend more than an hour a day at the computer | Yes |
| No |
|
| 6 | I spend more than two hours a day watching TV | Yes |
| No |
|
| 7 | I read, I write "with my nose buried" in the text | Yes |
| No |
|
| eight | Doing my homework in low light | Yes |
| No |
|
| 9 | I go in for sports (I go to sports sections) | Yes |
| No |
|
| ten | I follow the daily routine | Yes |
| No |
|
| eleven | I have a proper, balanced diet (3 meals a day, enriched with vitamins) | Yes |
| No |
|
| 12 | I do not pay attention to eye fatigue (if my eyes are tired, I continue to play computer games, watch TV, read) | Yes |
| No |
|
| 13 | When my eyes are tired, I do exercises for vision | Yes |
| No |
|
| fourteen | Parents have poor eyesight (wear glasses) | Yes |
| No |
|
| fifteen | I often get colds | Yes |
| No |
|
| 16 | I regularly (once a year) visit an ophthalmologist | Yes |
| No |
|
The survey results are presented in Table 4.
Table 4
Identification of visual impairment in 4th grade students
| Groups | Number of people (%) | visually impaired | No visual impairment | |||
| Girls | 33 | 61% | fourteen | 42% | 19 | 58% |
| boys | 21 | 39% | four | 19 % | 17 | 81% |
| Total students | 54 | 100 % | eighteen | 33% | 36 | 67% |
It follows from the table that vision is impaired in one three of all students (33%). Of the girls, 42% were identified with visual impairment, and boys accounted for 19%. Note that in the study of the family, there were more men with visual impairment than women.
Of the girls, 42% were identified with visual impairment, and boys accounted for 19%. Note that in the study of the family, there were more men with visual impairment than women.
The identification of factors influencing visual impairment in students showed that out of 18 students with visual impairment, 5 people (28%) have a hereditary visual impairment, and 13 students (72%) have an acquired one.
Rice. 1. Visual impairment in 4th grade students by age category
Visual impairment by age category is presented in Diagram 1, we see that the number of students with visual impairment has increased annually by an average of 8%.
Visual impairment is significantly affected by such factors as reading books at close range, non-compliance with the diet, non-compliance with the daily routine, insufficient illumination of the workplace, low physical activity, colds, and prolonged stay at the computer. We identified factors that affect visual impairment in all respondents. The results of the study are presented in Table 5.
The results of the study are presented in Table 5.
Table 5
Factors affecting visual impairment in 4th grade students
| No. p/n | Factors | Qty (%) |
| one. | Reading books at close range | 31% |
| 2. | Not following the diet | twenty % |
| 3. | Non-compliance with the daily routine | 54% |
| four. | More than an hour a day spent at the computer | 28% |
| 5. | More than two hours a day are spent watching TV | 24% |
| 6. | Do their homework in low light | 7% |
| 7. | Do not play sports (do not attend sports sections) | 39% |
| eight. | Often suffer from colds | 9 % |
It follows from the table that a very large number of students do not observe the daily routine (54%), this is more than half of the respondents! 31% of students do not observe reading hygiene. Also, 28% of students do not comply with the rules of working at a computer and 24% sit in front of the TV. Quite a lot of guys do not go in for sports (39%). We have noticed that many factors affecting visual impairment are observed in all students with visual impairment.
It should be noted that the ophthalmologist is regularly visited by those schoolchildren who have visual impairment, and only 41% of students visit without visual impairment. The study also showed that children whose parents have poor eyesight are more likely to visit an ophthalmologist, which is 43% of the respondents.
The study also showed that children whose parents have poor eyesight are more likely to visit an ophthalmologist, which is 43% of the respondents.
The survey showed that eye exercises are more often performed by students with visual impairments - 33% of students, and only 9 people out of the total number of respondents with good vision also perform exercises for prevention - this is 17% of students.
For the prevention of visual impairment in the literature, there are a lot of recommendations from specialists. First of all, it is the observance of the rules of visual hygiene regarding reading, watching TV, working on a computer, as well as eating and walking in the fresh air.
Experts recommend performing the exercise for training the accommodative eye muscle “mark on the glass” (Prof. E. S. Avetisov) [3].
The child stands at the window at a distance of 30–35 cm from the window pane. A round mark with a diameter of 3–5 mm is attached to this glass at eye level. In the distance, at the level of the gaze passing through this mark, he outlines some object for fixation, then alternately transfers his gaze first to the mark on the glass, then to this object in the distance. Exercises daily 2 times a day for 15-20 days. The first two days the duration of the exercise is 3 minutes, the next two days - 5 minutes, then - 7 minutes.
In the distance, at the level of the gaze passing through this mark, he outlines some object for fixation, then alternately transfers his gaze first to the mark on the glass, then to this object in the distance. Exercises daily 2 times a day for 15-20 days. The first two days the duration of the exercise is 3 minutes, the next two days - 5 minutes, then - 7 minutes.
This exercise trains the accommodation muscle and is recommended both for the prevention of visual impairment (during the breaks between visual load when reading, working at a computer), and for spasm of accommodation (false myopia), initial manifestations of myopia.
Unfortunately, healthy eyes and good vision are not always found. In Russia, according to the Ministry of Health, more than a million children suffer from various eye diseases and visual impairments: myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism and strabismus. The number of such children is growing every year. Therefore, specialists attach great importance to the prevention and early diagnosis of visual impairment [2].

 He has a media license and is registered with Roskomnadzor (EL No. FS77-55754). To publish in a journal and receive a Publication Certificate, you need to: send your material to:
He has a media license and is registered with Roskomnadzor (EL No. FS77-55754). To publish in a journal and receive a Publication Certificate, you need to: send your material to:  24 "Bee" of the combined type Berdsk, Novosibirsk region
24 "Bee" of the combined type Berdsk, Novosibirsk region 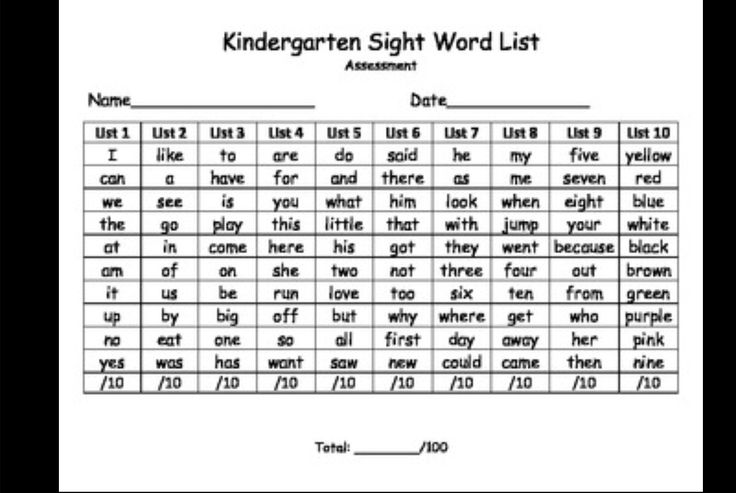 But how do our eyes work all day long without rest? Often children sit close to the TV or do not leave the computer all day. Read in low light or lying on the couch.
But how do our eyes work all day long without rest? Often children sit close to the TV or do not leave the computer all day. Read in low light or lying on the couch.  How to protect the eyes and help them, tells the French professor of ophthalmology Marcel Menou.
How to protect the eyes and help them, tells the French professor of ophthalmology Marcel Menou.  24 "Bee" of the combined type Berdsk, Novosibirsk region
24 "Bee" of the combined type Berdsk, Novosibirsk region  At this time of the year, children with visual impairments, with the help of adults, can expand and clarify their ideas about the world around them, develop attention, memory, observation, and also show their creative abilities. All this is very important for their emotional and moral well-being and the development of visual perception and visual functions.
At this time of the year, children with visual impairments, with the help of adults, can expand and clarify their ideas about the world around them, develop attention, memory, observation, and also show their creative abilities. All this is very important for their emotional and moral well-being and the development of visual perception and visual functions.  S. Poptsova
S. Poptsova 



 en»
en»  These disorders are especially noticeable in children with organic damage to the nervous system, which are many among the pupils of compensatory groups.
These disorders are especially noticeable in children with organic damage to the nervous system, which are many among the pupils of compensatory groups. 
 Gender
Gender  Occupation
Occupation