Words sentences making
Sentence Examples | Examples of Words Used in a Sentence
Advertisement
A Word Can Be Used in a Sentence Many Ways
Sometimes to understand a word's meaning you need more than a definition; you need to see the word used in a sentence. At YourDictionary, we give you the tools to learn what a word means and how to use it correctly. With this sentence maker, simply type a word in the search bar and see a variety of sentences with that word used in its different ways. Our sentence generator can provide more context and relevance, ensuring you use a word the right way.
How Do Our Sentence Examples Help You?
Whether it’s simple sentences for those just learning the English language or phrasing for an academic paper, this easy-to-use sentence generator will help you choose your words with confidence.
With our sentence examples, seeing a word within the context of a sentence helps you better understand it and know how to use it correctly. From long to short, simple to complex, this tool can assist you with how to use words that may have more than one meaning.
How to See a Word Used in a Sentence
If you want to hear how the word is said, we can assist with that too. Just click on the speaker icon at the top of the page to listen to a clear pronunciation of the word.
What is a Sentence?
There are many types of sentences, all with different structures and complexities. In its most basic form, a sentence is made up of a subject and predicate, which is the verb and the words that follow. But no matter how simple or complex, a sentence consists of words. Words in a sentence are what make it come alive and make sense.
Understand how words are used within the sentence, no matter the structure, and get inspiration for writing your own sentence correctly with the help of these example sentences.
We’re Here to Make Learning Easy
We get it. Learning the meaning of the many words that make up the English language can seem overwhelming. Take away the nerves and make it simple and easy to understand with the use of our sentence maker.
Learning the meaning of the many words that make up the English language can seem overwhelming. Take away the nerves and make it simple and easy to understand with the use of our sentence maker.
YourDictionary strives to make learning as stress-free as possible, no matter what your age or understanding is. And our sentence examples are no different.
We understand that sometimes the best way to truly understand a new concept is to see it used in an example. With the help of our useful tool, you can be one step ahead with grasping the complexity and workings of English vocabulary.
With an increased understanding of how words can be used, you can make your writing come to life with an arsenal of words of varying difficulties and meanings.
Simply type the word into the sentence generator and we’ll do the rest.
Use word in a sentence
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
-
Advertisement
The word usage examples above have been gathered from various sources to reflect current and historical usage. They do not represent the opinions of YourDictionary.com.
They do not represent the opinions of YourDictionary.com.
Related Articles
Are Base Words and Root Words the Same?
The English language is made up of many closely related words. In fact, it's possible to build new words from existing words by adding affixes to the beginning and/or end of a base word or root. Base words and roots are slightly different. Exploring the meaning of base word vs. root word will help you understand what these are and how to use them, which will help you improve your vocabulary skills.
How to Teach Sight Words in Fun (but Simple) Ways
From the earliest days of school, we begin to develop the techniques required to read. Sight words are the 220 words that a reader can readily recognize as soon as he or she sees them, without using phonics techniques. Learn how to teach sight words to young readers with these effective (and fun!) teaching strategies that work in the classroom and at home.

Also Mentioned In
- bubukle
- Three-Way Handshake
- noise word
- sten·o·type
- epanalepsis
- Schwartz, Randal Case
- u·til·ize
- grump·y
- lemon-platt
- interfix
- anthropophaginian
- adprep
Words near word in the Dictionary
- worcester china
- worcester joseph emerson
- worcester-sauce
- worcestershire
- worcestershire-sauce
- worcs
- word
- word art
- word-association
- word-association test
- wordable
- wordage
"Working on a phrase: Compiling sentences from three words.
 Four-word sentences with the addition of a definition." | Outline of the lesson on the development of speech (senior group):
Four-word sentences with the addition of a definition." | Outline of the lesson on the development of speech (senior group): Topic: “Working on the phrase: Compiling sentences from three words. Four-word sentences with the addition of a definition.
Purpose: to form the skill of making sentences from three words, the skill of grammatical formulation of sentences and their dissemination by adding definitions.
Tasks:
1. Learn how to make three-word sentences correctly, make sentences according to the model and make up your own sentences.
2. Develop attention, memory, logical thinking, speech.
3. Raise interest in studies.
Equipment: Subject and plot pictures.
GCD move:
1. Organizational moment: the one who affectionately calls his name will sit down.
2. Subject message:
Today we will work with a proposal. A sentence is a sequence of words related to each other in meaning. A sentence can have three, four, five or more words. But we will learn to make sentences of three or four words.
But we will learn to make sentences of three or four words.
3. Studying the topic:
1. “Compilation of three-word sentences based on plot pictures”.
Look carefully at the picture. (A picture is displayed on the board, which depicts a girl reading a book). The girl is reading. Who is it? (Girl). What she does? (is reading). What is the girl reading? (Book). The girl is reading a book.
Which word was added to the sentence? (Book). How many words are in the sentence? (Three).
Next, the following pictures are displayed. The work is carried out in a similar way.
2. “Making three-word sentences based on two object pictures”.
Look carefully at the pictures. (Two subject pictures are put on the board, for example: a boy and a fish). Let's try to make a sentence by choosing a word denoting an action for the picture:
The boy is fishing.
Next, the following pictures are displayed. The work is carried out in a similar way.
3. "Compilation of three-word sentences by each child."
Each child is given one plot picture and is asked to independently compose a three-word sentence based on it.
4. Physical education minute:
We raise our hands to the top,
And then we lower them,
And then we separate them,
And we will quickly press them to ourselves.
And then faster, faster
Clap, clap more cheerfully.
5. “Complication of sentences. Compilation of sentences from four words with the addition of a definition.
Now let's complicate these sentences. For example: A girl is watering flowers. Which flowers? (Beautiful) or What kind of girl? (Small).
Next, the following pictures are exposed. The work is carried out in a similar way.
6. Exercise "Collect a sentence from words."
And now I will call you the words, and you listen carefully to them and collect sentences from them.
Example: Ball, Tanya, catches, big. – Tanya catches a big ball.
– Tanya catches a big ball.
- Sweater, mother, knitted, beautiful. (Mom knitted a beautiful sweater)
- Fishermen caught a big one. (The fishermen caught a big fish)
-Katya is reading an interesting book. (Katya is reading an interesting book)
- Rita saw a big dragonfly. (Rita saw a big dragonfly)
- Vova bought a bun, delicious. (Vova bought a delicious bun)
- With pencils, children, draw, color. (Children draw with colored pencils)
- Tree, storm, broke, old. (The storm broke the old tree).
4. Result:
- You are great today! Worked very well. Now the children from the last row will get up and go to the group, then from the second row, then from the first row.

 Motivation for learning activities (2 min.)
Motivation for learning activities (2 min.) 


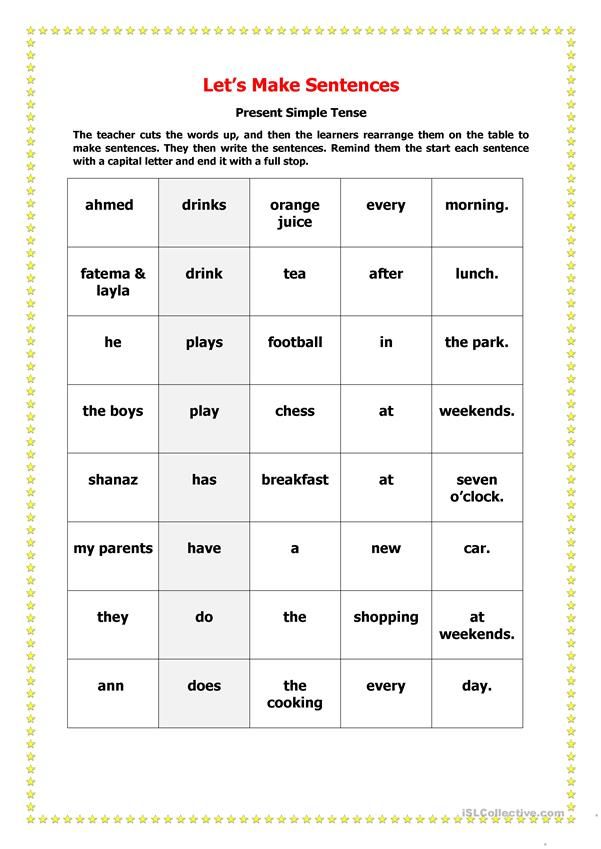
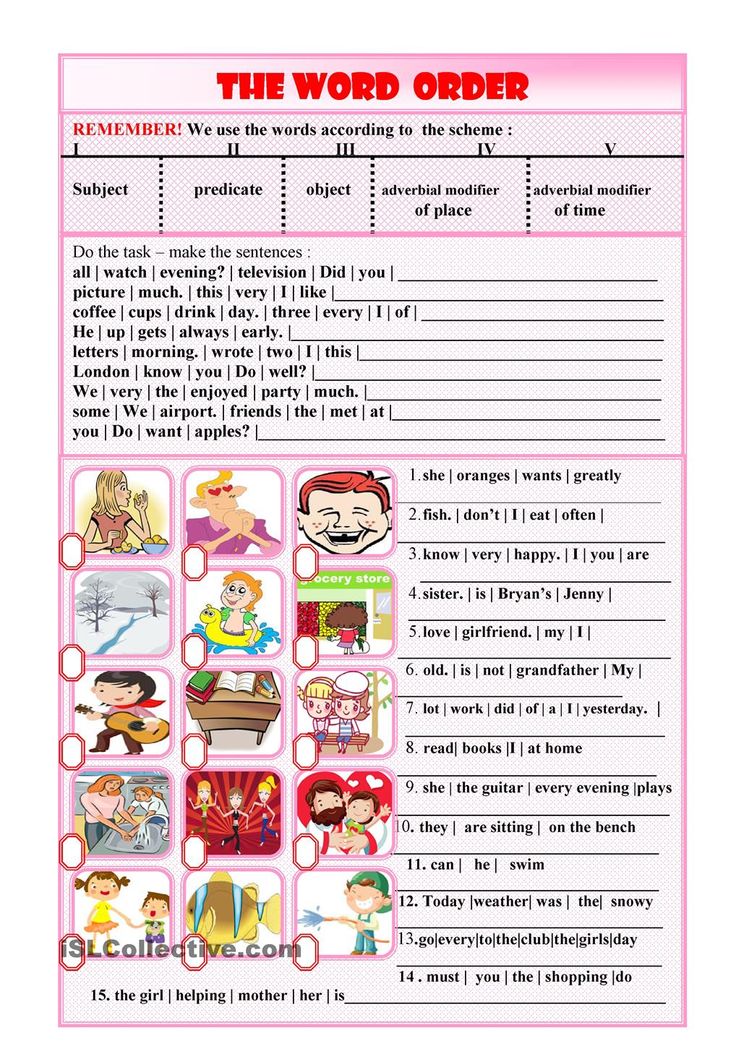 And try to choose the right parts of speech.
And try to choose the right parts of speech.  )
)