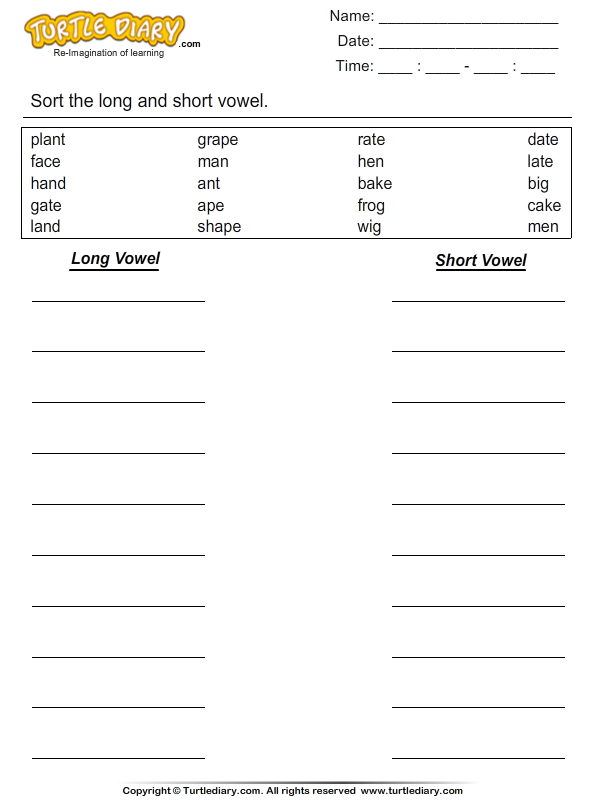
Worksheets on long and short vowel sounds
Phonics Worksheets - Vowel Sounds
Short A Vowel Sound
Here is a collection of worksheets and games for reviewing the long a vowel sound. There's a classroom scavenger hunt, word sort activity, cut-and-glue projects, worksheets, and word wheels.
Long A Vowel Sound
These printable phonics worksheets focus on writing and reading words with the long a vowel sound. This collection includes color-and-read minibooks, reading sliders, printable card games, worksheets, and phonics learning centers.
Short A & Long A (Mixed)
These files focus on differentiating between the short a and long a sounds.
Short E Vowel Sound
Here you have a variety of printable worksheets and games for teaching students about the short e sound. There are reading and writing worksheets, as well as learning centers that involve cutting and gluing.
Long E Vowel Sound
This page contains a collection of long e printables. Includes flashcards, reading strips, games, as well as several cut-n-paste projects.
Short E & Long E (Mixed)
The worksheets in this section have students determining the differences between words with a long-E sound and a short-E sound.
Short I Vowel Sound
Phonics worksheets that focus on words that have a short-I vowel sound.
Long I Vowel Sound
This pages has a variety of printable worksheets, games, and activities to help students recognize words with the long-I vowel sound.
Short I & Long I (Mixed)
This page has printable worksheets to help students discern and understand the differences between words with a long-I vowel sound and words with a short-I vowel sound.
Short O Vowel Sound
Phonics worksheets that focus on words with the short O sound.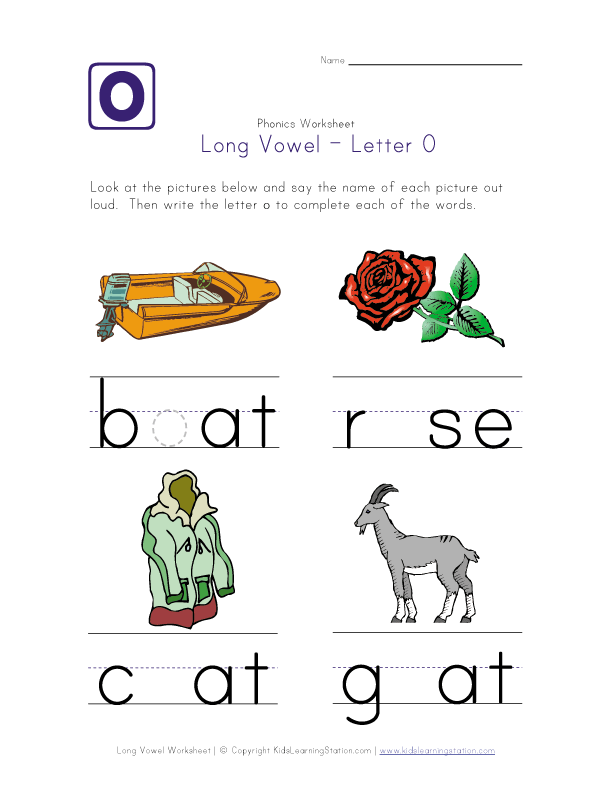 Print out cut and glue activities, word wheels, games, and more.
Print out cut and glue activities, word wheels, games, and more.
Long O Vowel Sound
Students will learn about words that have a long-O vowel sound with these worksheets. Some of the words in this section include: row, home, snow, code, goat, boat, and store.
Short O & Long O (Mixed)
Check out the worksheets in this section that feature words with both short-O and long-O sounds.
Short U Vowel Sound
Printable phonics worksheets that focus on words with the Short U vowel sounds.
Long U Vowel Sound
Try out the printable word wheels, cut-and-glue activities, and other worksheets to practice reading words that have the long-U sound. Some of the words include: unicorn, music, use, and unicycle.
Short U & Long U (Mixed)
The printable phonics worksheets on this page feature words with long-U sounds and words with short-U sounds. Students will learn the differences between the two.
Students will learn the differences between the two.
Digraphs and Diphthongs
Vowel Digraphs: EE and EA
These resources cover words with the long-e sound, spelled with the letters ee and ea. Words in this set include feet, meat, leaf, clear, and green.
Vowel Digraph: OO
These printables cover words with oo in them. The letters oo can make two vowel sounds. Short-oo is the vowel sound you hear in words like book and floor. The long-oo sounds is heard in words like school and moon.
Vowel Diphthongs: OI and OY
Learn about OI and OY words with these wheels, flashcards, sliders, and activity sheets.
Vowel Diphthongs: OW and OU
Learn about the /ow/ sound, spelled with the diphthongs ow and ou. This page includes a mini-book and several worksheets.
R-Controlled Vowel: -AR
These files can help you teach students about the vowel sound in words like car, mark, arm, and far.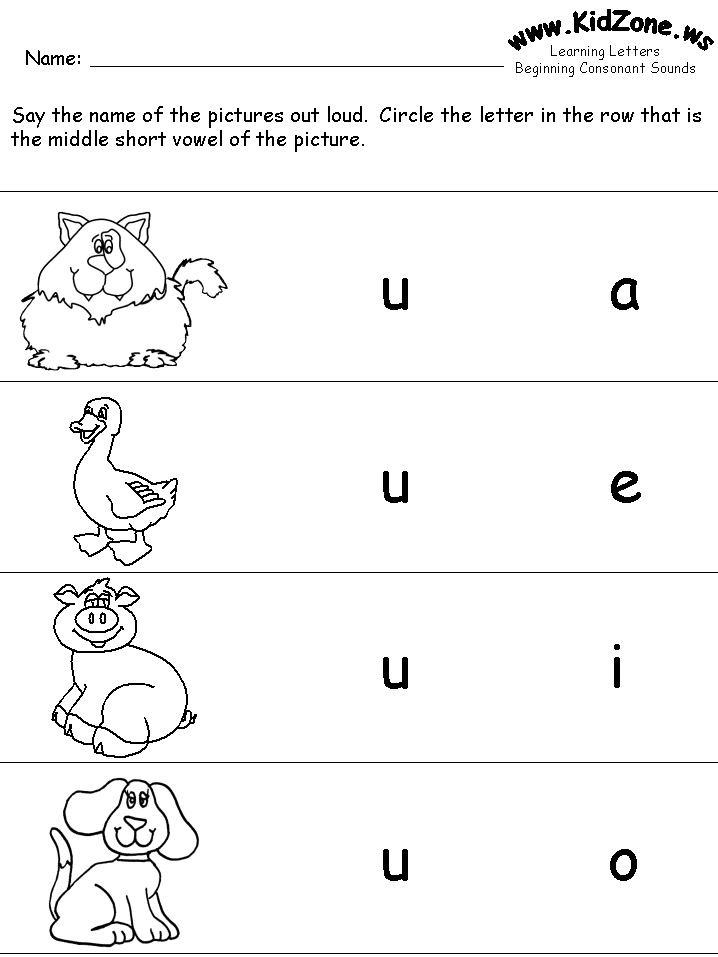 There's a mini-book, a sorting game, and a word search.
There's a mini-book, a sorting game, and a word search.
Also on Super Teacher Worksheets...
Phonics: Consonant Sounds
Phonics worksheets for consonant letters sounds, including beginning consonants and ending consonants.
R-Controlled Vowel Sounds
Find worksheets, flash cards, and word wheels for teaching r-controlled vowel sounds. These sounds include /är/ as in star, /ôr/ as in short, /ûr/ as in bird, /âr/ as in hair, and /îr/ as in deer.
Word Family Units
We have dozens of word family units. Word families are collections of words with the same ending. For example: -ar words (car, far, star)
Dolch Sight Words
Printable activities, flash cards, and word wheels for the Dolch sight words.
Phonics: Word Wheels
Spin the wheel to make new words. Manipulative read-and-spell phonics activities.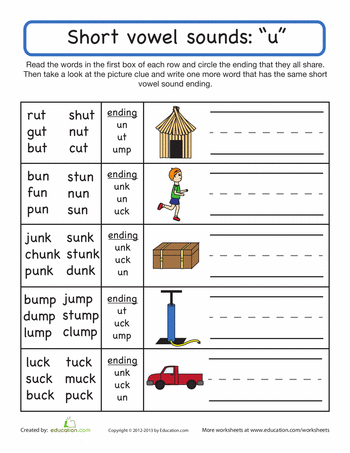
Long and Short A Vowel Sounds Worksheets
Vowels are speech sounds that are made by our vocal bands. They also happen to be five / twenty-sixth of our alphabet. Depending on how a vowel sound is stressed within a word determines the classification of a vowel. There are two standard classifications. Long vowels are vowels that sound the same as the letter that they represent. For example, in the word "bake", the vowel a is said the same exact way as you say it when reciting the alphabet for your teacher. Short vowels do not have the same sound within a word as they do within the alphabet. For example, the vowel a in the word "apple". If you look at the entire language short vowels are much more common. The best way to identify the use of a long and short a vowel is to say the word aloud to yourself and ask yourself if the vowel sound is the same as the name of the vowel. If the vowel (in this case "a") says it's name, it is consider a long vowel. Such as in the word "take". If the vowel does not do that and make another sound, it's considered a short vowel. Many people don't understand the importance of understanding long and short vowels. It becomes a very valuable skill once you start to encountering higher level vocabulary words. The most common long a words are: baby, lady, paper, bake, rake and lane. The most common short a words are: dad, hat, man, sat, fan and lane.
If the vowel does not do that and make another sound, it's considered a short vowel. Many people don't understand the importance of understanding long and short vowels. It becomes a very valuable skill once you start to encountering higher level vocabulary words. The most common long a words are: baby, lady, paper, bake, rake and lane. The most common short a words are: dad, hat, man, sat, fan and lane.
Get Free Worksheets In Your Inbox!
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.
Circle the objects that have a long A (ā) sound. Then write the word under the picture.
Circle the indicated words. It's best to sound all of them out aloud.
Color the words RED if they have words that give off the same tone and pitch as the letter itself. Color the Short a words BLUE. Color all other words GREEN.
Complete each sentence with a Long A word from the word box. This is a two part activity.
Circle the word in each pair that has the long a sound. Write that word on the line. Say the name of each picture. If it has a Long A sound, draw a line to connect the picture to the Long A.
Say the name of the picture. Circle the word in the stream of letters.
Underline the Long A words in the story and write them on the lines. Only write each word once. The story: Jane was going on vacation. She was very excited, because she was going to travel on a plane.
Cut out the pictures. Glue them next to the correct long a words.
Say the name of each picture. If it has a short a sound, draw a line to connect the picture to the it. Can you think of two things whose name contains the short a sound? Draw a picture of each thing. Then write its name on the line.
Read each word. Does it have a long (ā) sound, or a short (ă) sound? Color in the circle next to the correct sound.
Read each word. Then add an e. Read the new word and write it on the line.
Then add an e. Read the new word and write it on the line.
Read each word. Then draw a picture of it.
Draw a line to match each picture to the correct word.
Name each picture. Spell its name on the line.
Circle the word in each set that starts with a short a (ă) sound and the word that just contains it as well.
What is the Difference Between Long and Short Vowels?
The English language is full of complexities. The more you seem to know it, the less you do. Several components combine to make a sentence. One of the critical parts of the English alphabet is vowels. Out of the total twenty-six alphabet letters, only five are vowels. However, all of these are commonly used in our daily conversations. Today, we will examine the key differences between long vowels and short vowels. Before we get started, let's look at the definition first.
What Are Vowels?
The five letters of the English alphabet, A, E, I, O, and U, are known as vowels. These are the letters that we can pronounce with open mouths. All these letters have everyday use in many words of the English language. While this may be correct, we can classify them into two types based on their pronunciation and usage.
These are the letters that we can pronounce with open mouths. All these letters have everyday use in many words of the English language. While this may be correct, we can classify them into two types based on their pronunciation and usage.
Long Vowels
Long vowels are those with long pronunciations. The sound of these vowels depends on their positioning in different words. Typically, the sound of these vowels is similar to their alphabetical title. For example, the sound of 'A' in the word "Name" and 'E' in the word "Sheet" is similar to the sound of their titles.
Such vowels are used in open syllables, usually ending with a vowel. If two vowels consecutively arrive between the first and the last letter of any word, the first of the two will have a dominant sound. For example, the sound of 'O' in "Toad" dominates the sound of 'A,' making it a long vowel. Similarly, the sound of 'E' in the word "Beat" dominates the sound of 'A.'
If we talk about the spellings, these vowels may have complicated patterns compared to short vowels. For the words in which a vowel arrives after the first letter and in the last position, the sound of the last one remains silent. However, the dominant sound of the first vowel makes it a long vowel. For example, the sound of 'E' in the word "Take" is silent.
For the words in which a vowel arrives after the first letter and in the last position, the sound of the last one remains silent. However, the dominant sound of the first vowel makes it a long vowel. For example, the sound of 'E' in the word "Take" is silent.
Short Vowels
Short vowels refer to those vowels with shorter pronunciations. Like long vowels, the sound of these vowels also depends on their position in any word. The sounds of these may not be similar to their alphabetical names. For example, the sound of 'A' in the word "Hat" and 'E' in the word "Beg" are not similar to their alphabetical names.
Since short vowels have a shorter pronunciation, you can easily pronounce them without stressing your jaws. However, this may not entirely be true. There are a few exceptions when you may need to stress your tongue to pronounce them. For example, the first 'O' in the word "Potato" demands more stress in pronunciation compared to the last 'O.
Unlike long vowels, short vowels are primarily present in closed syllables. This is one of the reasons that these vowels do not demand stress in pronunciation in most cases. In some instances, you may also find these at the initial position of a word. For example, "Egg," "At," etc.
This is one of the reasons that these vowels do not demand stress in pronunciation in most cases. In some instances, you may also find these at the initial position of a word. For example, "Egg," "At," etc.
Summing Up
The key differences between the two types of vowels highlighted above can help you identify the use of each in different syllables. Minor differences can change the sounds of different words used in our daily conversations.
It is worth remembering that most of the differences lie based on the positioning of vowels. Keeping these factors in view allows you to differentiate between differently sounding words using the same vowels. If you want to look into more examples, you can conduct online research to find complex syllable structures.
Essay on the topic "Sounds of Russian and English as an object of study"
OOO Training center
"PROFESSIONAL"
Abstract by discipline:
"Linguistics and intercultural communications”
Practical phonetics of the English language
subject:
Sounds Russian and English languages as an object of research”
Contractor:
Daniletskaya Oksana Sergeevna
Moscow 2017
Contents
Introduction.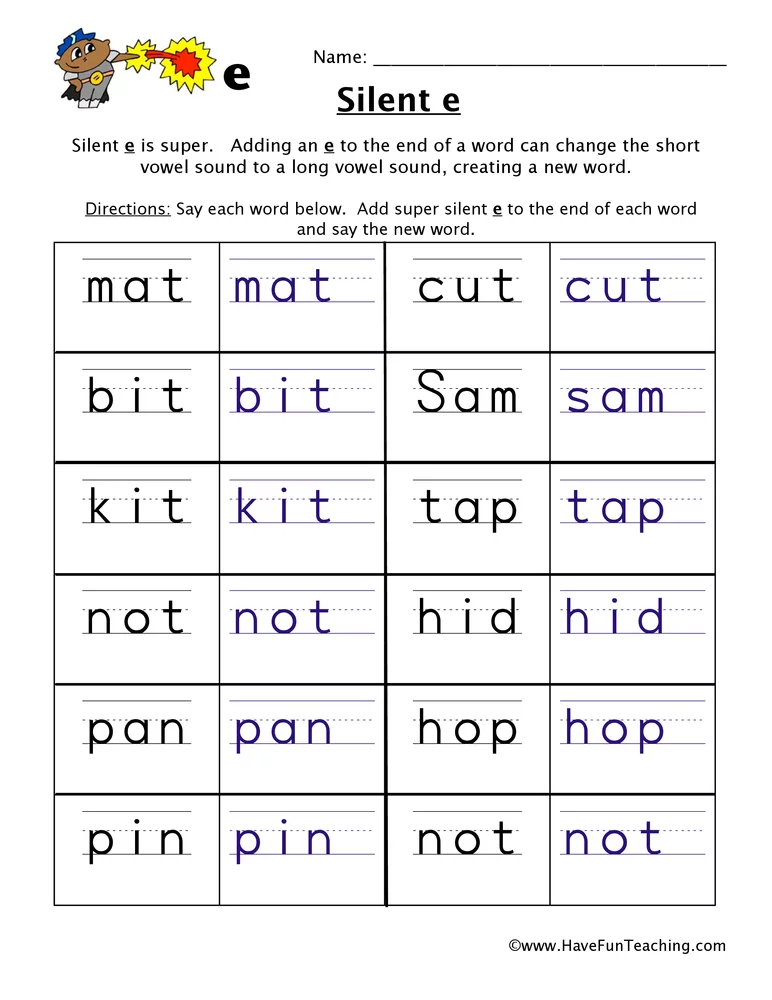 3
3
Phonetics of English language. 4
Differences between phonetics of English and Russian. 5
Sounds of English language. 7
Comparative characterization of the sounds of Russian and English. 8
The sound composition of the language constantly undergoing change as the spelling of words changes So slow. That is why there is a discrepancy in English sound and letter composition of words. It is believed that this discrepancy is one of the main difficulties in learning English, however, all difficulties can be overcome if you have the desire and not be afraid of difficulties.
phonetics - this is category - this linguistics, which studies the sound structure of the English language. All sounds can be divided into two categories:
1. Vowels - in the time of pronunciation for the air does not create any barrier. At the same time, the pressure minimum.
At the same time, the pressure minimum.
2. Consonants - the throat tract narrows, completely or partially blocking the flow of air. He overcomes obstacles by changing its direction in one way or another.
All sounds in writing displayed using phonetic transcription - a special way of transferring sounds, in which each of them has its own written symbol. Transcription absolutely accurately conveys all the features of the sound, I demonstrate longitude and stress.
It should also be noted that in English words can be either strong or weak. When on the word falls under stress, it is considered that it is in a strong form. If the word is not shock, then it, accordingly, stands in a weak form. Often weak conjunctions, pronouns and prepositions. For example, in the preposition of the sound [ɒv] - the strong form, and the [əv] sound is the weak form. In almost all cases, the appearance weak form is explained by the replacement of the stressed vowel in the strong form by unstressed [ə], in all other cases, the sound is reduced. In transcriptions all textbooks in English, the sounds are displayed in a strong form, because, knowing a strong form of sound, one can quite easily turn it into a strong form.
In transcriptions all textbooks in English, the sounds are displayed in a strong form, because, knowing a strong form of sound, one can quite easily turn it into a strong form.
Important to know:
1. In English sounds never soften, but are always pronounced firmly.
2. Sounds do not double, for example, the word running is pronounced as [ˈrʌnɪŋ].
English, in unlike Russian, has an extensive system of vowel sounds, so the speakers of the Russian language have difficulty pronouncing and recognizing in speech English vowels, which sometimes leads to a confusion of the meanings of words. For example man (man) [mæn] - men (men) [men].
In English there is a division into long and short vowels, the replacement of a long sound short and vice versa can lead to confusion of the meanings of words. For example, sick [sık] (sick) - seek [sı: k] (search).
Sounds in Russian are divided into vowels and consonants, in English, in addition to vowels, which are the same throughout, there are diphthongs (vowels consisting of two elements). For example, rain (rain) [reın].
For example, rain (rain) [reın].
In English consonants are never softened, always pronounced firmly. For example, in the word “Silence” sound [t ’] is soft, in the word “time” the sound [t] is hard.
English at the end of a word voiced consonants are never stunned. For example, send (send) [send].
In English, in unlike Russian, one-syllable and two-syllable words predominate. For example, bad, take, cat, left, seven, mother.
sound and its phonetic classification in Russian and English.
Sound is the result vibrations of a sounding physical body in a medium that transmits these vibrations to organs hearing. At the same time, the sound has such physical characteristics as height, strength, timbre, duration. In this quality, sound is capable of producing various objects and people. To become the sound of speech, sound as an acoustic the phenomenon must be produced by the organs of speech (articulation) of a person and be part of the phonological system of a particular language.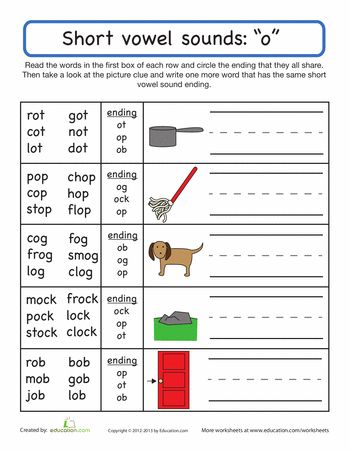 Phoneme as a sound term units was introduced into science in the 70s of the XIX century to distinguish the general concept and actual sound. A phoneme is the smallest meaningful unit of a language. which stands out only in the composition of morphemes, i.e. higher level units.
Phoneme as a sound term units was introduced into science in the 70s of the XIX century to distinguish the general concept and actual sound. A phoneme is the smallest meaningful unit of a language. which stands out only in the composition of morphemes, i.e. higher level units.
Classification of sounds speech. The primary division of sounds is carried out on the basis of articulation into vowels and consonants.
Russian alphabet modern language has 33 letters:
Aa Bb Vv Gg Dd Her Yoyo Fzh Zz Ii Yy Kk Ll Mm Nn Oo Pp Rr Ss Tt Uu Ff Xx Ts Chh Shsh Shch b Yy b Ee Yuyu Yaya.
(In fact, the alphabet from 33 letters used since 1918, and officially since 1942)
Also Russian has 42 sounds:
6 vowels: [a] [and] [o] [y] [s] [e]
36 consonants: [b] [b] [c] [v] [g] [g] [d] [d] [g] [d] [h] [s] [k] [k] [l] [l] [m] [m] [n] [n] [n] [p] [r] [r] [s] [s] [t] [t] [f ] [f] [x] [x] [c] [ch] [w] [u].
To represent sounds often use characters that represent letters of the alphabet, called transcription.
For all Russian vowels tongue is characterized by the presence of a voice, and their articulation is due to vibration vocal cords and the free passage of inhaled air through the oral cavity.
Dot vowels articulations differ in the degree of elevation of the tongue (lower, middle and upper), the place of rise, called the row (front, middle and back), and the participation of lips in sound production (labialized and non-labialized).
Vowels can be distinguished according to the following features:
according to the row (the position of the language in the horizontal plane): front, middle (mixed, central) and back row:
ü front vowels: [and] [e];
middle vowels: [s] [a];
back vowels: [y] [o];
according to the degree of elevation of the tongue to palate (its position in the vertical plane): upper, middle and lower lift:
u high vowels: [and], [s], [y];
middle vowels: [e], [about];
low vowels: [a];
by the presence or absence labializations, i.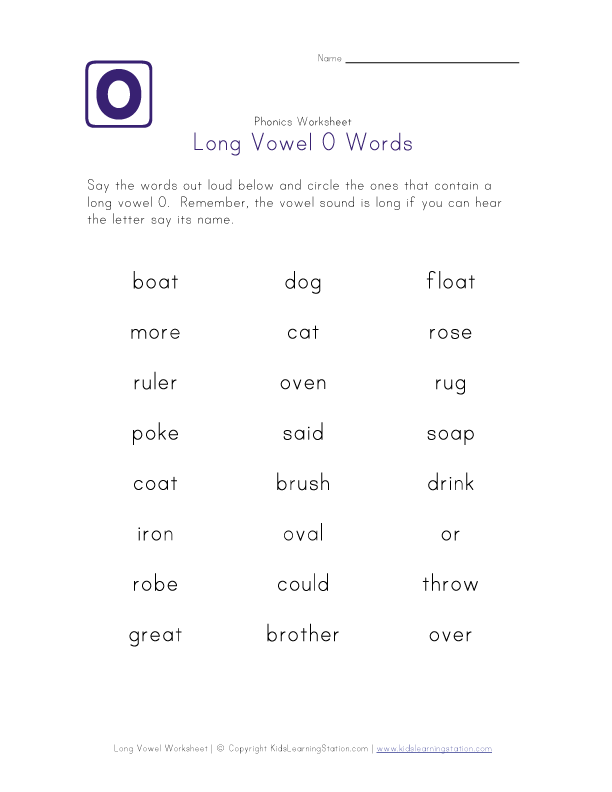 e. degrees of lip involvement: rounded (labialized) and unrounded (non-labile) vowels:
e. degrees of lip involvement: rounded (labialized) and unrounded (non-labile) vowels:
ü labialized vowels: [y], [about];
non-labialized vowels: [and], [s], [e], [a].
Consonant sounds are divided according to the sound composition (presence of voice and noise) into noisy and sonorous (without noise or with faint noise), also noisy are divided into voiced (with a voice) and deaf (without a voice), sonorous voiced, but there are deaf allophones (see Appendix 3)
English has been around since the 5th century. Currently English The alphabet has 26 letters and 44 sounds.
Depending on your positions in a word, the same letter can be read as several different sounds. In order to accurately convey the pronunciation of words, transcription is used, the so-called phonetic transcription, i.e. each sound corresponds one specific icon.
English 20 consonants:
Bb Cc Dd Ff Gg Hh Jj Kk Ll Mm Nn Pp Qq Rr Ss Tt Vv Ww Xx Zz
These letters stand for 24 consonants:
There are 5 vowels in English: Aa Ee Ii Oo Uu
The letter ‘Yy’ is considered a semi-vowel.
Vowels convey 20 vowels:
12 monophthongs (vowels, sounding the same throughout their length):
8 diphthongs (vowels, consisting of two elements):
2 triphthongs (vowels, consisting of three elements):
Vowel length (monophthong) is indicated in transcription by two vertically arranged dots: [:]. Diphthongs and triphthongs are long vowels by definition.
When speaking English vowels, it is very important to keep their longitude or shortness, because short replacement a long vowel can distort the meaning of the word:
full [ful] full - fool [fu: l] fool
ship [ʃip] ship - sheep [ʃi: p] sheep.
English and Russian languages belong to different branches of the Indo-European family of languages, and therefore there are quite a few differences in their phonetic structure.
Consider the most characteristic differences between the sound systems of English and Russian.
1. Russian has twenty-one consonants, ten vowels letters and two characters - ь, ъ.
In English, twenty consonants, six vowels (letter Y can convey both vowel and consonant sounds).
2. There are six in Russian vowel sounds, and in English - twenty-two.
3. In Russian there is no division of vowels on the basis of longitude, at the same time in English longitude and diphthongization of monophthongs is distinctive trait.
4. Diphthong, i.e. double vowel - combination of two vowels elements, pronounced together through sliding articulation, without a pause, in within one stressed syllable. The first sound, called the main element or the core of a diphthong - always stressed, second, always weak and relaxed, - called slip. There are no diphthongs in Russian. There are vowel combinations sounds belonging to different syllables, such as clown, pause, sauce. Triphthong (three-vowel sound) - a combination of three vowel elements pronounced together in one stressed syllable. They also don't exist. Combinations of vowels with sound (Y) are characteristic: give, lay, bark, white. In the same way, reverse sound combinations (Y) are formed with four vowels: (YA) - (I), (YO) - (Yo), (YU) - (Yu), (YE) - (E), which are the alphabetic reading of the corresponding letters.
In the same way, reverse sound combinations (Y) are formed with four vowels: (YA) - (I), (YO) - (Yo), (YU) - (Yu), (YE) - (E), which are the alphabetic reading of the corresponding letters.
English has eight diphthongs and two triphthongs.
5. In Russian thirty-six consonants. Sounds have both hard and soft forms; there are only hard ones - w, c, w, and only soft ones - u, d, h. In English language twenty-four consonants. In the pronunciation of English consonants sounds have features in comparison with the Russian language.
6. In Russian voiced consonants at the end of a word and before voiceless consonants, as a rule, stunned: horn [k], cart [c], ford [t]. In English, consonant stuns not happening. Replacing a voiced consonant with a paired deaf consonant can lead to confusion of words, because in English there are words similar in sound, the difference between which is only the pronunciation of the final consonant.
7. In English, in unlike Russian, vowels are
long and short.
8. But I also want to note that, as in Russian, the stress in English can fall on any syllable of the word. In these two languages, stress is not fixed by rules. However, there is still such a prescription that the stress is preserved in borrowed words from the original source.
characteristic differences between the sound systems of Russian and English, we concluded that they have both similarities and differences. Differences in the phonetic structure of the two languages is also related to the fact that Russian and English belong to different branches of the Indo-European family of languages.
Describe the specifics the phonetic system of the English language in comparison with the phonetic system Russian language, and showed differences in the phonetic base of English and Russian languages.
2. Bonk N. A., Kotiy G. A., Lukyanova N. A. Textbook of the English language. In 2 books. M.: Firma ART, 1992. Book. 1. 684 p.; Book. 2. 604 p.
In 2 books. M.: Firma ART, 1992. Book. 1. 684 p.; Book. 2. 604 p.
3. Sokolova M. A., Gintovt K. P., Tikhonova I. S., Tikhonova R. M. Theoretical phonetics of English language. M.: Higher school, 2001. - 240 p.
4. Wells J/C/ Pronunciation Dictionary. Bristol: LONGMAN, 2010.–802 pp.
5. Jones D. English Pronouncing Dictionary. Cambridge: University Press, 2013. - 567 p.
Long and short vowels in English
Longitude is one of the characteristics of a vowel sound, which shows the relative duration of its sound compared to other sounds.
Longitude is positional and phonemic. In the first case, the duration of the vowel depends on the position in the word and stress, while this characteristic does not affect the meaning. The phonemic length of a vowel has a semantic function, that is, depending on the length of the sound, the meaning of the word changes.
Length of vowel sounds in English
In Russian, the length of vowel sounds does not affect the meaning of words and changes only depending on stress.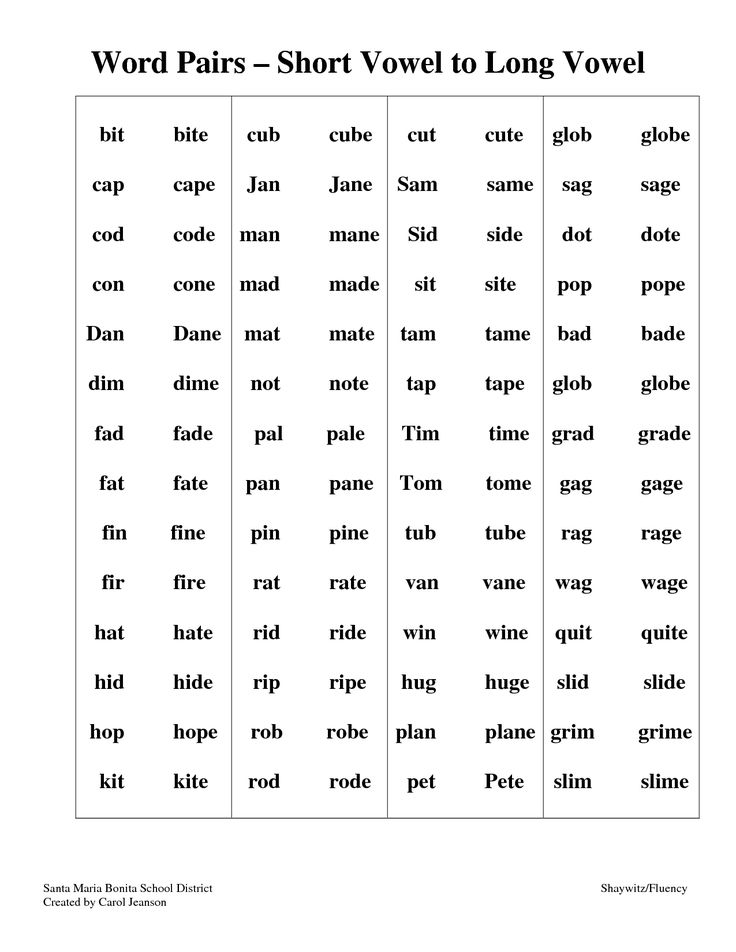 In English, vowels differ not only in positional but also in phonemic length. This means that long and short sounds, similar in other characteristics, represent different phonemes. Words that differ only in these phonemes have different meanings: ship – sheep , fit - feet , pull - pool . Therefore, it is so important to pronounce long and short sounds correctly.
In English, vowels differ not only in positional but also in phonemic length. This means that long and short sounds, similar in other characteristics, represent different phonemes. Words that differ only in these phonemes have different meanings: ship – sheep , fit - feet , pull - pool . Therefore, it is so important to pronounce long and short sounds correctly.
In transcription, long vowels are denoted with a colon: [i:], [α:], [ɔ:], [u:], [ә:]. In some cases, long vowels in an unstressed position are reduced and become semi-long, which in transcription is indicated by one dot from above: [α ].
The long vowels listed above are opposed to short vowels, forming the following pairs in English:
- [i:] - [ı]
- [uː] - [u]
- [ɔ:] - [ɒ]
- [α:] - [ʌ]
- [ә:] - [ə]
The pronunciation of long and short English vowels often causes difficulties for Russian learners of English, since in Russian vowels do not have phonemic longitude, and we are not used to hearing the length of a vowel sound. We often do not hear the difference between long and short vowels when listening to English speech. It is still not clear how long you need to draw a sound when speaking, so very unnatural, or almost inaudible, or too long vowels are obtained. It is impossible to correctly pronounce short and long sounds so that a native speaker hears the difference, even if you diligently shorten short vowels and stretch out long ones.
We often do not hear the difference between long and short vowels when listening to English speech. It is still not clear how long you need to draw a sound when speaking, so very unnatural, or almost inaudible, or too long vowels are obtained. It is impossible to correctly pronounce short and long sounds so that a native speaker hears the difference, even if you diligently shorten short vowels and stretch out long ones.
Sometimes it seems that native speakers themselves do not know the difference between short and long sounds, they seem to pronounce them the same way - but they themselves understand each other. But it's not. Let's see what are the differences between long and short English vowels, how to learn to hear them and how to train their pronunciation.
Differences between long and short English sounds
It is logical to assume that if vowels are called long or short, they differ in sound length. This is the main difference between them, but not the only one. It is important to understand that long and short sounds have other differences, which consist in articulatory features. This means that the sounds are not just of different lengths, they are also different in sound. And most often it is these articulatory features that determine the length of the vowel sound: the duration of the sound depends on the position of the tongue and the tension of the vocal apparatus.
It is important to understand that long and short sounds have other differences, which consist in articulatory features. This means that the sounds are not just of different lengths, they are also different in sound. And most often it is these articulatory features that determine the length of the vowel sound: the duration of the sound depends on the position of the tongue and the tension of the vocal apparatus.
Long and short English vowels differ in such a characteristic as tension. Long vowels are tense, in English they are also called tense . When they are pronounced, the root of the tongue seems to be tense, under tension. The sound is pronounced, bright, rich, clear.
Short vowels are called lax – relaxed. The tongue in the region of the root is relaxed, the vowel sound is articulated quickly, easily, without additional effort, as if bursting. It turns out short, inconspicuous, faded and fuzzy.
Qualitative differences in sounds in different pairs of English vowels range from pronounced to almost imperceptible. It is easy to notice the difference between long and short sounds a: pay attention to how the words cart and cut are pronounced, they differ not only in duration, but also in sound. But the differences between long and short u are almost imperceptible: pool and pull sound very similar, only slightly different in length. The Scots generally pronounce them the same way, differing only in context.
It is easy to notice the difference between long and short sounds a: pay attention to how the words cart and cut are pronounced, they differ not only in duration, but also in sound. But the differences between long and short u are almost imperceptible: pool and pull sound very similar, only slightly different in length. The Scots generally pronounce them the same way, differing only in context.
In addition, the duration of the pronunciation of vowels is also affected by positional longitude - for example, stressed or unstressed position in a word. As a result, a short vowel sound in one word may sound longer than a long sound in another word.
Thus, it is not enough to rely only on the subjective duration of a vowel sound. All the features of short and long vowels described above must be taken into account when learning English. It remains to understand how to master the pronunciation of long and short sounds in practice.
How to learn to pronounce long and short English vowels
The main mistake foreigners make when pronouncing long and short English sounds is focusing only on duration. But with this approach, it is intuitively incomprehensible where the boundary between a long and a short sound passes: you can’t measure the length of a sound with a stopwatch. When trying to artificially lengthen or shorten a vowel, the sounds are unnaturally short or drawn out.
But with this approach, it is intuitively incomprehensible where the boundary between a long and a short sound passes: you can’t measure the length of a sound with a stopwatch. When trying to artificially lengthen or shorten a vowel, the sounds are unnaturally short or drawn out.
To learn how to pronounce long and short English sounds, you need to forget about the usual terminology "long" and "short". Try not to think about the duration of the sound at all. To correctly pronounce long and short vowels, you need to focus on their articulation, and not on duration. If we correctly reproduce the pronunciation of the vowel, then the duration will turn out to be correct automatically. Remember that long vowels require more tension at the root of the tongue, while short ones are pronounced without additional effort, easily and without tension.
Pay attention to how native speakers pronounce vowels - don't watch how long they draw them out, but watch the pronunciation, the articulation, the quality of the sound. Repeat, imitate, practice. For practice, it is best to use video lessons or a conversation with a native speaker, since audio materials do not make it possible to see articulation.
Repeat, imitate, practice. For practice, it is best to use video lessons or a conversation with a native speaker, since audio materials do not make it possible to see articulation.
It is best to train long and short sounds not separately, but as part of words. First, this way you will note the influence of positional longitude on the duration of the sound in specific examples. Secondly, just as words are best learned in context, sounds are also best learned in the environment.
Practice pronunciation of long and short vowels in pairs of words to notice the difference between sounds, for example:
- Sport – hot
- Arm-cut
- See-hit
- Food-put
- Fur – ago
When you learn to pronounce long and short vowels correctly in English, it will become easy to distinguish between them in speech. When listening to speech, forget about the differences in duration, pay attention to the qualitative differences in sounds - how intensely the vowel is pronounced, how bright or faded it sounds, how pairs of sounds differ from each other, except for duration.