Activities in reading for kids
10 Fun Reading Activities for Kids
Home Seasonal Back to School 10 Fun Reading Activities
By: Britni Vigil
This post may contain affiliate links. Privacy policy.
These fun reading activities will make reading at home more fun for all ages! Perfect for anyone looking for how to make reading more fun at home!
This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase via these links, I may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you.
I may not be a teacher, but I am an avid reader. I love reading, love it so much that when I was young my parents would ground me from books instead of toys.
Now that I’m a mom myself, I am so excited to share that love of reading with my boys. And over the next few weeks as we’re stuck at home, I’m planning to use some of these fun reading activities to make reading at home as much fun as it is at school!
Fun Reading Activities
I’ve put together not only ideas for fun reading activities but also specific examples based on some of my family’s favorite books! Have different favorite books? Use the general activity ideas and make them specific for you!
1 – Have a book themed day.If you’re doing your own school at home, why not do a themed book day once a week. Pick out your favorite book and plan your day around it.
Here are just a few fun examples you could try!
- Pajama Time – wear pajamas all day, play Pajama party games, eat breakfast for dinner (everyone loves this breakfast casserole), have a pillow fight. You could even do an entire Pajama Time party like this one?
- Harry Potter – Make butter beer treats, play Harry Potter games, practice making your own homemade potions, and maybe even make some chocolate frogs!
- Dr. Seuss Books – Talk only in rhyme for an hour, eat Green Eggs and Ham, play one of these Dr. Seuss activities, and make a bucket list of all the places you want to go!
Set the stage with fun props, put on costumes, and start acting. Don’t forget to use different voices for each of the characters. Let your littles be creative and put on their favorite princess or superhero costume for the afternoon without cringing.
Let your littles be creative and put on their favorite princess or superhero costume for the afternoon without cringing.
Or if you have kids in school that want to do the reading, have one person read while the other people act it out. You could even mix it up by adding silly things to how you act it out – use an accent, do it backwards, act like a dinosaur, etc.
3 – Create and play a game based on your favorite book.You could create a matching game with all of the opposites in Sandra Boynton’s Opposites. To get a match, you have to turn over cards with the two things that are opposite each other.
Or how about making yarn words like the words Charlotte spun in Charlotte’s web and see who can guess the yarn word you spun?
Or you could hide a golden ticket somewhere in the house and have kids go on a scavenger hunt to find the golden ticket like in Charlie and the Chocolate Factory.
4 – Write and illustrate your own book.
This one is great for practicing reading, writing, and art skills – all things kids would normally do in school. Give them blank pieces of paper or a journal and have kids create their own story or recreate one of their classic favorites.
5 – Read books to other people.If you haven’t seen it already, Josh Gad (the voice of Olaf) is doing a nightly book reading over on Twitter here. Just because you can’t go to the libraries or meet up with friends to read books doesn’t mean you can’t do it anyway.
Call grandparents, friends, neighbors and read books aloud to each other in silly voices. This would be especially awesome if you have a grandparent or someone who’s on lockdown in an assisted living facility and just needs a pick me up.
6 – Make treats based on a book.Make your favorite chocolate chip cookies after reading If You Give a Mouse a Cookie or blueberry muffins for Blueberries for Sal. Here are some more great ideas to get you started – you could really do this one every single day if you wanted! Almost every book, especially children’s books, has some sort of food you could make!
- Where the Wild Things Are – make these monster cookies
- The Very Hungry Caterpillar – make pizza loaf or chocolate sheet cake
- The Rainbow Fish – make these rainbow donuts or these rainbow cupcakes

Try making a Very Hungry Caterpillar out of pom poms or Where the Wild Things Are masks. The possibilities are endless but here are some book crafts to get you started!
- Bedtime shadow puppets to go with Sleepy, the Goodnight Buddy
- Lady Bug Craft for The Grouchy Ladybug
- Horton Hears a Who Elephant for Horton Hears a Who
Pick out your favorite book and come up with 10 things that you have to find from the book. If your favorite book is Green Eggs and Ham, your scavenger hunt might include looking for a mouse (or picture of), a house, a fox, and a box.
Or do one of these fun scavenger hunt ideas that matches your book theme. For example, this animal scavenger hunt would be great to go with If I Ran a Zoo, and this dinosaur hunt would be good for any dinosaur books!
9 – Draw a scene from your favorite book.Put a big sheet of white mural paper up on the wall and get creative. Channel your inner Harold and the Purple Crayon. Pull out a sketch pad and draw your best version of what you see around the room, kind of like in Brown Bear, Brown Bear.
Channel your inner Harold and the Purple Crayon. Pull out a sketch pad and draw your best version of what you see around the room, kind of like in Brown Bear, Brown Bear.
Read books with different voices for the characters. Read out loud to your kids while doing dance moves. Have your kids read in loud, quiet, and dinosaur voices. Just change up the way you read to make it more of an experience than a chore.
And if all else fails, there are plenty of great reading apps, games, and websites out there that you can listen to books read out loud, do fun reading activities, and turn reading into a true game.
More Fun Ideas for Kids
- Minute to win it games
- Learning games
- Best board games for kids
- Spelling games
- 50+ boredom busters
Reader Interactions
25 Activities for Reading and Writing Fun
These activities have been developed by national reading experts for you to use with children, ages birth to Grade 6. The activities are meant to be used in addition to reading with children every day.
The activities are meant to be used in addition to reading with children every day.
In using these activities, your main goal will be to develop great enthusiasm in the reader for reading and writing. You are the child's cheerleader. It is less important for the reader to get every word exactly right. It is more important for the child to learn to love reading itself. If the reader finishes one book and asks for another, you know you are succeeding! If your reader writes even once a week and comes back for more, you know you have accomplished your beginning goals.
Activities for birth to preschool: the early years
Activity 1: Books and babies
Babies love to listen to the human voice. What better way than through reading!
What you'll need:
Some books written especially for babies (books made of cardboard or cloth with flaps to lift and holes to peek through).
What to do:
- Start out by singing lullabies and folk songs to your baby.
 When your baby is about six months old, choose books with brightly colored, simple pictures and lots of rhythm in the text. (Mother Goose rhymes are perfect.) Hold your baby in your lap so he/she can see the colorful pages of the book. Include books that show pictures and names of familiar objects.
When your baby is about six months old, choose books with brightly colored, simple pictures and lots of rhythm in the text. (Mother Goose rhymes are perfect.) Hold your baby in your lap so he/she can see the colorful pages of the book. Include books that show pictures and names of familiar objects. - As you read with your baby, point out objects in the pictures and make sure your baby sees all the things that are fun to do with books. (Pat the Bunny by Dorothy Kunhardt is a classic touch-and-feel book for babies.)
- Vary the tone of your voice with different characters in the stories, sing nursery rhymes, make funny faces, do whatever special effects you can to stimulate your baby's interest.
- Allow your child to touch and hold cloth and sturdy cardboard books.
- When reading to a baby, keep the sessions brief but read daily and often.
As you read to your baby, your child is forming an association between books and what is most loved – your voice and closeness. Allowing babies to handle books deepens their attachment even more.
Allowing babies to handle books deepens their attachment even more.
Activity 2: Tot talk
What's "old hat" to you can be new and exciting to toddlers and preschoolers. When you talk about everyday experiences, you help children connect their world to language and enable them to go beyond that world to new ideas.
What you'll need:
Yourself and your child
What to do:
- As you get dinner ready, talk to your child about things that are happening. When your 2- or 3-year-old "helps" by taking out all the pots and pans, talk about them. "Which one is the biggest?" "Can you find a lid for that one?" "What color is this one?"
- When walking down the street and your toddler or preschooler stops to collect leaves, stop and ask questions that require more than a "yes" or "no" answer. "Which leaves are the same?" "Which leaves are different?" "What else grows on trees?"
- Ask "what if" questions. "What would happen if we didn't shovel the snow?" "What if that butterfly lands on your nose?"
- Answer your child's endless "why" questions patiently.
 When you say, "I don't know, let's look it up," you show how important books are as resources for answering questions.
When you say, "I don't know, let's look it up," you show how important books are as resources for answering questions. - After your child tells you a story, ask questions so you can understand better. That way children learn how to tell complete stories and know you are interested in what they have to say.
- Expose your child to varied experiences – trips to the library, museum, or zoo; walks in the park; or visits with friends and relatives. Surround these events with lots of comments, questions, and answers.
Talking enables children to expand their vocabulary and understanding of the world. The ability to carry on a conversation is important for reading development. Remember, it is better to talk too much rather than too little with a small child.
Activity 3: R and R – repetition and rhyme
Repetition makes books predictable, and young readers love knowing what comes next.
What you'll need:
- Books with repeated phrases (Favorites are: Alexander and the Terrible, Horrible, No Good, Very Bad Day by Judith Viorst; Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See? by Bill Martin, Jr.
 ; Horton Hatches the Egg by Dr. Seuss; and The Little Engine That Could by Watty Piper.
; Horton Hatches the Egg by Dr. Seuss; and The Little Engine That Could by Watty Piper. - Short rhyming poems.
What to do:
- Pick a story with repeated phrases or a poem you and your child like. For example, read:
(Wolf voice:) "Little pig, little pig, let me come in."
(Little pig:) "Not by the hair on my chinny-chin-chin."
(Wolf voice:) "Then I'll huff and I'll puff and I'll blow your house in!" - After the wolf has blown down the first pig's house, your child will soon join in with the refrain.
- Read slowly, and with a smile or a nod, let your child know you appreciate his or her participation.
- As the child grows more familiar with the story, pause and give him or her a chance to fill in the blanks and phrases.
- Encourage your child to pretend to read, especially books that contain repetition and rhyme. Most children who enjoy reading will eventually memorize all or parts of a book and imitate your reading.
 This is a normal part of reading development.
This is a normal part of reading development.
When children anticipate what's coming next in a story or poem, they have a sense of mastery over books. When children feel power, they have the courage to try. Pretending to read is an important step in the process of learning to read.
Activity 4: Poetry in motion
When children "act out" a good poem, they learn to love its rhyme, rhythm, and the pictures it paints with a few well-chosen words. They grow as readers by connecting feelings with the written word.
What you'll need:
Poems that rhyme, tell a story, and/or are written from a child's point of view.
What to do:
- Read a poem slowly to your child, and bring all your dramatic talents to the reading. (In other words, "ham it up.")
- If there is a poem your child is particularly fond of, suggest acting out a favorite line. Be sure to award such efforts with delighted enthusiasm.
- Suggest acting out a verse, a stanza, or the entire poem.
 Ask your child to make a face the way the character in the poem is feeling. Remember that facial expressions bring emotion into the performer's voice.
Ask your child to make a face the way the character in the poem is feeling. Remember that facial expressions bring emotion into the performer's voice. - Be an enthusiastic audience for your child. Applause is always nice.
- If your child is comfortable with the idea, look for a larger setting with an attentive, appreciative audience. Perhaps an after-dinner "recital" for family members would appeal to your child.
- Mistakes are a fact of life, so ignore them.
Poems are often short with lots of white space on the page. This makes them manageable for new readers and helps to build their confidence.
Activity 5: Story talk
Talking about what you read is another way to help children develop language and thinking skills. You won't need to plan the talk, discuss every story, or expect an answer.
What you'll need:
Storybooks
What to do:
- Read slowly and pause occasionally to think aloud about a story. You can say: "I wonder what's going to happen next!" Or ask a question: "Do you know what a palace is?" Or point out: "Look where the little mouse is now.
 "
" - Answer your children's questions, and if you think they don't understand something, stop and ask them. Don't worry if you break into the flow of a story to make something clear. But keep the story flowing as smooth as possible.
- Talking about stories they read helps children develop their vocabularies, link stories to everyday life, and use what they know about the world to make sense out of stories.
Activity 6: Now hear this
Children are great mimics. When you tell stories, your child will begin to tell stories, too.
What you'll need:
Your imagination
What to do:
- Have your child tell stories like those you have told. Ask: "And then what happened?" to urge the story along.
- Listen closely when your child speaks. Be enthusiastic and responsive. Give your child full attention.
- If you don't understand some part of the story, take the time to get your child to explain. This will help your child understand the relationship between a speaker and a listener and an author and a reader.

- Encourage your child to express himself or herself. This will help your child develop a richer vocabulary. It can also help with pronouncing words clearly.
Having a good audience is very helpful for a child to improve language skills, as well as confidence in speaking. Parents can be the best audience a child will ever have.
Activity 7: TV
Television can be a great tool for education. The keys to successful TV viewing are setting limits, making good choices, taking time to watch together, discussing what you view, and encouraging follow-up reading.
What you'll need:
A weekly TV schedule
What to do:
- Limit your child's TV viewing and make your rules and reasons clear. Involve your child in choosing which programs to watch. Read the TV schedule together to choose.
- Monitor what your child is watching, and whenever possible, watch the programs with your child.
- When you watch programs with your child, discuss what you have seen so your child can better understand the programs.

- Look for programs that will stimulate your child's interests and encourage reading (such as dramatizations of children's literature and programs on wildlife and science.)
Many experts recommend that children watch no more than 10 hours of TV each week. Limiting TV viewing frees up time for reading and writing activities.
It is worth noting that captioned TV shows can be especially helpful for children who are deaf or hard-of-hearing, studying English as a second language, or having difficulty learning to read.
Activities for preschool to grade two: moving into reading
Check out Reading Rockets' new summer website, Start with a Book. You'll find a treasure trove of themed children's books, parent–child activities, and other great resources for summer learning.
Activity 8: World of words
Here are a few ways to create a home rich in words.
What you'll need:
- Paper
- Pencils, crayons, markers
- Glue
- Newspapers, magazines
- Safety scissors
What to do:
- Hang posters of the alphabet on the bedroom walls or make an alphabet poster with your child.
 Print the letters in large type. Capital letters are usually easier for young children to learn first.
Print the letters in large type. Capital letters are usually easier for young children to learn first. - Label the things in your child's pictures. If your child draws a picture of a house, label it with "This is a house." and put it on the refrigerator.
- Have your child watch you write when you make a shopping list or a "what to do" list. Say the words aloud and carefully print each letter.
- Let your child make lists, too. Help your child form the letters and spell the words.
- Look at newspapers and magazines with your child. Find an interesting picture and show it to your child as you read the caption aloud.
- Create a scrapbook. Cut out pictures of people and places and label them.
- By exposing your child to words and letters often, your child will begin to recognize the shapes of letters. The world of words will become friendly.
Activity 9: Write on
Writing helps a child become a better reader, and reading helps a child become a better writer.
What you'll need:
- Pencils, crayons, or markers
- Paper or notebook
- Chalkboard and chalk
What to do:
- Ask your child to dictate a story to you. It could include descriptions of your outings and activities, along with mementos such as fall leaves and flowers, birthday cards, and photographs. Older children can do these activities on their own.
- Use a chalkboard or a family message board as an exciting way to involve children in writing with a purpose.
- Keep supplies of paper, pencils, markers, and the like within easy reach.
- Encourage beginning and developing writers to keep journals and write stories. Ask questions that will help children organize the stories, and respond to their questions about letters and spelling. Suggest they share the activity with a smaller brother, sister, or friend.
- Respond to the content of children's writing, and don't be overly concerned with misspellings. Over time you can help your child concentrate on learning to spell correctly.

- When children begin to write, they run the risk of criticism, and it takes courage to continue. Our job as parents is to help children find the courage. We can do it by expressing our appreciation of their efforts.
Activity 10: Look for books
The main thing is to find books you both love. They will shape your child's first impression of the world of reading.
What you'll need:
Good books
What to do:
- Ask friends, neighbors, and teachers to share the titles of their favorite books.
- Visit your local public library, and as early as possible, get your child a library card. Ask the librarian for help in selecting books. Have your child join you in browsing for books and making selections.
- Look for award-winning books. Each year the American Library Association selects children's books for the Caldecott Medal for illustrations and the Newbery Medal for writing.
- Check the book review section of the newspapers and magazines for the recommended new children's books.

- If you and your child don't enjoy reading a particular book, put it aside and pick up another one.
- Keep in mind that your child's reading level and listening level are different. When you read easy books, beginning readers will soon be reading along with you. When you read more advanced books, you instill a love of stories, and you build the motivation that transforms children into lifelong readers.
Activity 11: Read to me
It's important to read to your child, but equally important to listen to them read to you. Children thrive on having someone appreciate their developing skills.
What you'll need:
Books at your child's reading level
What to do:
- Listen carefully as your child reads.
- Take turns. You read a paragraph and have your child read the next one or you read half the page and your child reads the other half. As your child becomes more at ease with reading aloud, take turns reading a full page. Keep in mind that your child may be focusing more on how to read the words than what they mean, and your reading helps to keep the story alive.
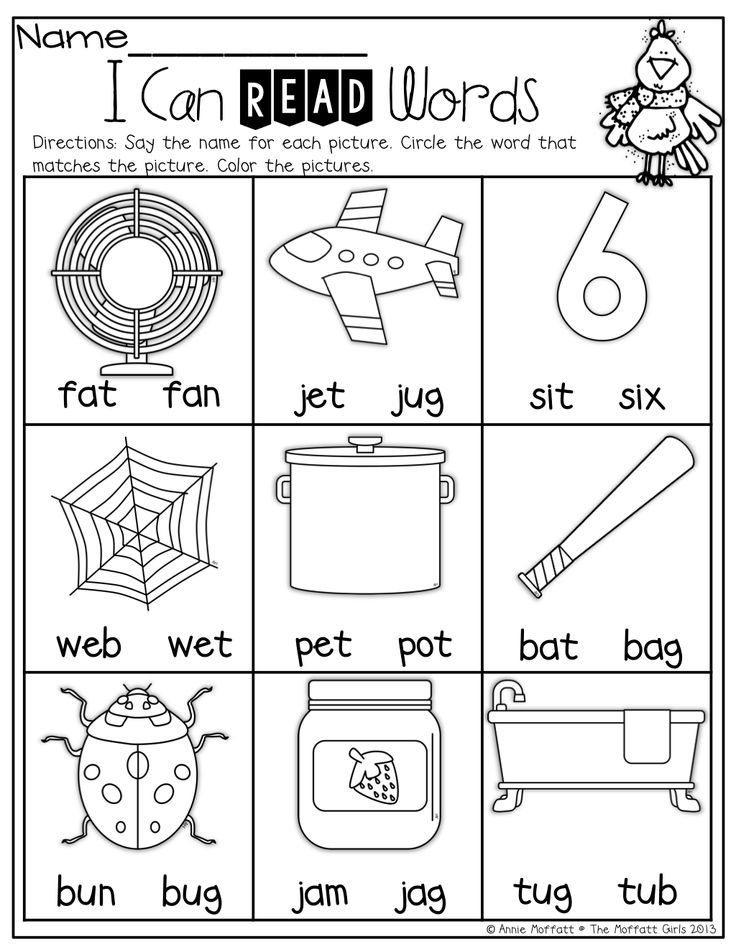
- If your child has trouble reading words, you can help him or her in several ways:
- Ask the child to skip over the word, read the rest of the sentence, and then say what would make sense in the story for the missing word.
- Guide the child to use what he or she knows about letter sounds.
- Supply the correct word.
- Tell your child how proud you are of his or her efforts and skills.
Listening to your child read aloud provides opportunities for you to express appreciation of his or her new skills and for them to practice their reading. Most importantly, this is another way to enjoy reading together.
Activity 12: Family stories
Family stories enrich the relationship between parent and child.
What you'll need:
Time set aside for talking with your child.
What to do:
- Tell your child stories about your parents and grandparents. You might even put these stories in a book and add old family photographs.

- Have your child tell you stories about what happened on special days, such as holidays, birthdays, and family vacations.
- Reminisce about when you were little. Describe things that happened at school involving teachers and subjects you were studying. Talk about your brothers, sisters, or friends.
- Write a trip journal with your child to create a new family story. Recording the day's events and pasting the photographs into the journal ties the family story to a written record. You can include everyday trips like going to the market or the park.
- It helps for children to know that stories come from real people and are about real events. When children listen to stories, they hear the voice of the storyteller. This helps them hear the words when they learn to read aloud or read silently.
Activity 13: P.S. I love you
Something important happens when children receive and write letters. They realize that the printed word has a purpose.
What you'll need:
- Paper
- Pencil, crayon, or marker
What to do:
Language is speaking listening, reading, and writing. Each element supports and enriches the others. Sending letters will help children become better writers, and writing will make them better readers.
Activities for grades 3–6: encouraging the young reader
Activity 14: Good books make reading fun
Stories for young children should be of all kinds – folktales, funny tales, exciting tales, tales of the wondrous and stories that tell of everyday things.
What you'll need:
A variety of interesting books
What to do:
- An essential step in learning to read is good books read aloud. Parents who read aloud to their children are teaching literacy concepts simply by sharing books. Encourage your children to listen, ponder, make comments, and ask questions.
- Be flexible enough to quickly abandon a book that does not appeal after a reasonable try at reading it.
 No one is meant to enjoy every book. And no one, especially a child, should be forced to read or listen to books that bore.
No one is meant to enjoy every book. And no one, especially a child, should be forced to read or listen to books that bore. - Even after children have outgrown picture books they still enjoy hearing a story read aloud. Hearing a good story read well, especially if it is just a little beyond a child's own capabilities, is an excellent way to encourage independent reading. Not all books are best read aloud; some are better enjoyed silently.
- There are plenty of children's books that are twice as satisfying when they are shared a chapter at a time before bed or during long car rides. There are some books that children should not miss, books that they will want to hear many times and ultimately read for themselves.
- Young children want to read what makes them laugh or cry, shiver and gasp. They must have stories and poems that reflect what they themselves have felt. They need the thrill of imagining, of being for a time in some character's shoes for a spine-tingling adventure.
 They want to experience the delight and amazement that comes with hearing playful language. For children, reading must be equated with enjoying, imagining, wondering, and reacting with feeling. If not, we should not be surprised if they refuse to read. So let your child sometime choose the story or book that they want you to read to them.
They want to experience the delight and amazement that comes with hearing playful language. For children, reading must be equated with enjoying, imagining, wondering, and reacting with feeling. If not, we should not be surprised if they refuse to read. So let your child sometime choose the story or book that they want you to read to them.
Give your child many opportunities to read and write stories, lists, messages, letters, notes, and postcards to relatives and friends. Since the skills for reading and writing reinforce one another, your child's skills and proficiency in reading and writing will be strengthened if you help your child connect reading to writing and writing to reading.
Activity 15: Artful artists
Children love to be creative when it comes to drawing, and illustrations add visual imagery to stories.
What you'll need:
- Drawing paper
- Pens and pencils
- Magic markers or crayons
What to do:
Find a fable, fairy tale, or other short story for your child to read.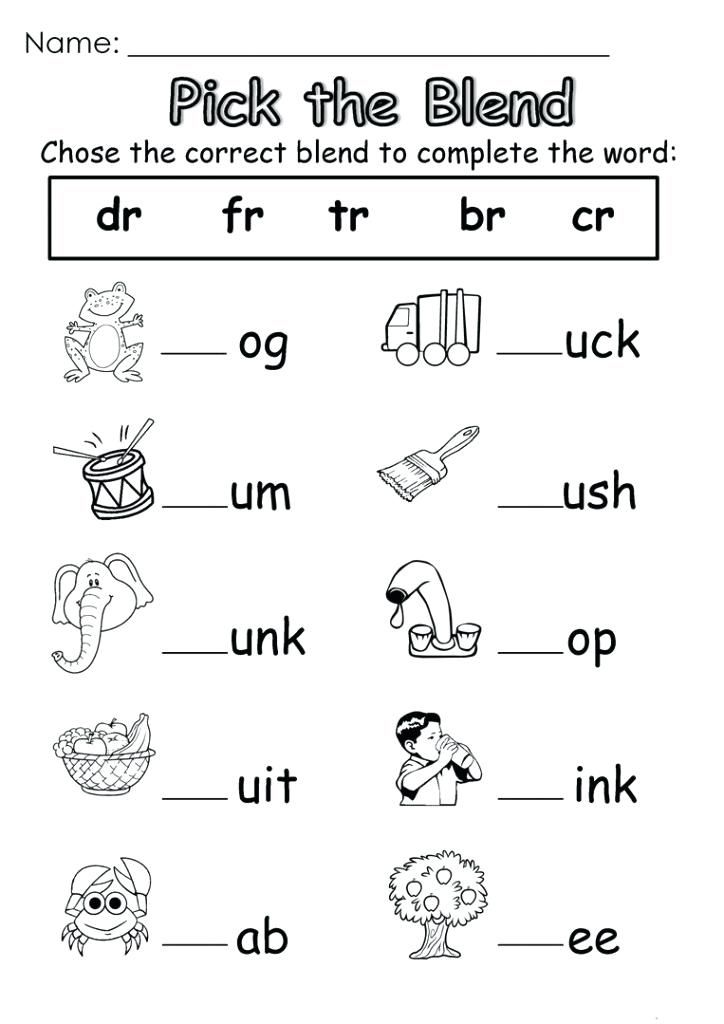 Then ask your child to illustrate a part of the story he or she likes best or describe a favorite character. Have the child dictate or write a few sentences that tell about this picture.
Then ask your child to illustrate a part of the story he or she likes best or describe a favorite character. Have the child dictate or write a few sentences that tell about this picture.
Activity 16: Shopping your way with words
Use your weekly shopping trip as an opportunity to help your child develop reading and writing skills.
What you'll need:
- Paper and pencils
- Newspaper ads
- Supermarket coupons
What to do:
As you make out your grocery shopping list, give your child a sheet of paper and read the items to him or her. If the child asks for spelling help, write the words correctly for him or her to copy or spell the words aloud as your child writes them.
Ask your child to look through the newspaper ads to find the prices of as many items as possible. Your child can write these prices on the list and then look through your coupons to select the ones you can use. Take your child to the supermarket and ask him or her to read each item to you as you shop.
Activity 17: Cookbooking
Cooking is always a delight for children, especially when they can eat the results!
What you'll need:
- Easy-to-read recipes
- Cooking utensils
- Paper and pencils
What to do:
Show your child a recipe and go over it together. Ask your child to read the recipe to you as you work, and tell the child that each step must be done in a special order. Let your child help mix the ingredients. Allow your child to write down other recipes from the cookbook that he or she would like to help make.
Activity 18: Dictionary words
A dictionary is a valuable learning tool, especially if your child makes up his or her own booklet of words that are challenging.
What you'll need:
- Paper and pencils
- A stapler
- Old magazines
- Newspaper and supplements
What to do:
Encourage your child to make a dictionary by putting together several sheets of paper for a booklet.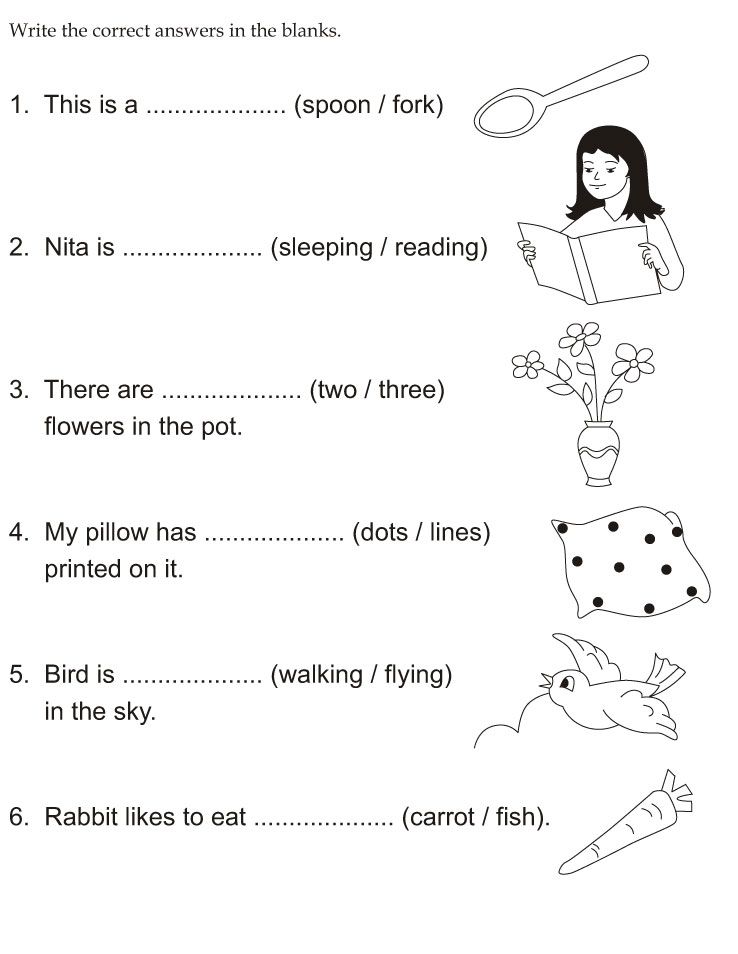 Ask your child to write at the top of each page a new word he or she has recently learned. If the word can be shown in a picture, have him or her look through magazines and newspapers to find pictures that illustrate the words and paste them on the correct pages.
Ask your child to write at the top of each page a new word he or she has recently learned. If the word can be shown in a picture, have him or her look through magazines and newspapers to find pictures that illustrate the words and paste them on the correct pages.
Have your child write the meaning of each word and a sentence using each new word. Your child can then use some or all of these sentences as the basis for a creative story. Have your child read this story to you and other family members.
Activity 19: Journals
Keeping a journal is a way for your child to write down daily events and record his or her thoughts.
What you'll need:
Two notebooks - one for your child and one for you!
What to do:
Help your child start a journal. Say what it is and discuss topics that can be written about, such as making a new friend, an interesting school or home activity just completed, or how your child felt on the first day of school. Encourage your child to come up with other ideas. Keep a journal yourself and compare notes at the end of the week. You and your child each can read aloud parts of your journals that you want to share.
Keep a journal yourself and compare notes at the end of the week. You and your child each can read aloud parts of your journals that you want to share.
Activity 20: Greetings and salutations
Everyone loves to get mail, especially when the card has been personally designed.
What you'll need:
- Paper and pencils
- Crayons and magic markers
- Stamps and envelopes
What to do:
Ask your child to list the birthdays of family members, relatives, and friends. Show your child some store-bought birthday cards with funny, serious, or thought-provoking messages. Your child can then create his or her own birthday card by using a folded piece of paper, making an attractive cover, and writing a short verse inside. Then your child can mail the cards to friends and relatives for their birthdays.
Activity 21: Giving the gift of reading
Reading a book is more fun when you have a homemade bookmark to mark your spot.
What you'll need:
- Pieces of lightweight cardboard
- Pens and pencils
- Paper
- Crayons and magic markers
What to do:
Provide your child with a piece of cardboard about 6" long and 2" wide.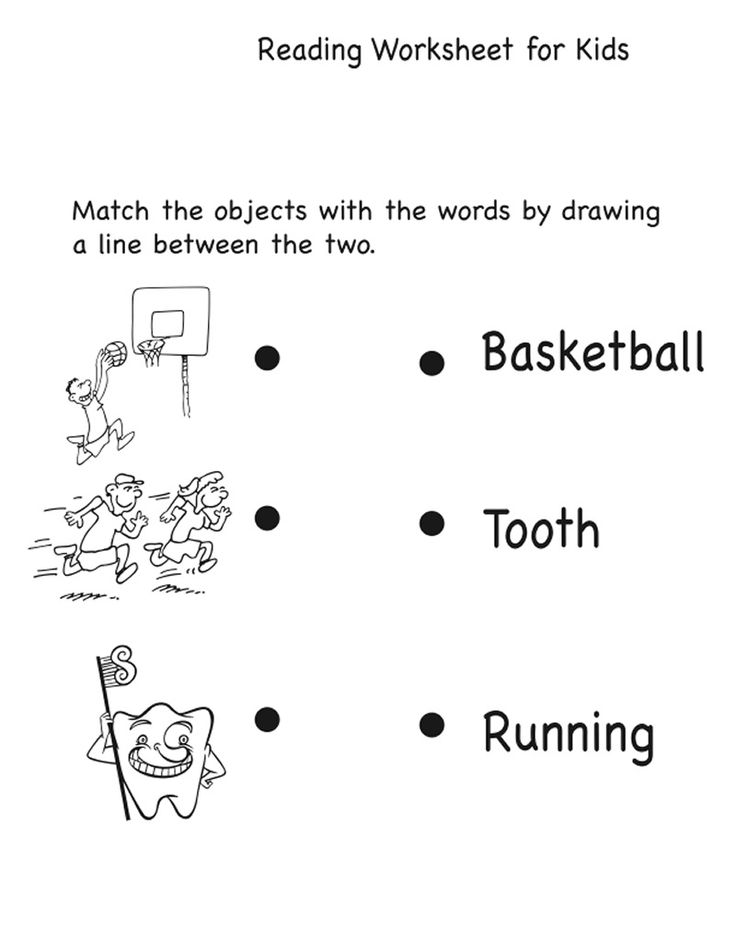 On one side of the bookmark, have your child draw a picture of a scene from a book he or she has read. On the other side, ask your child to write the name of the book, its author, publisher, publication date, and a few sentences about the book. After making several of these bookmarks, you might ask the child to send them to friends and relatives as gifts accompanied by a short note.
On one side of the bookmark, have your child draw a picture of a scene from a book he or she has read. On the other side, ask your child to write the name of the book, its author, publisher, publication date, and a few sentences about the book. After making several of these bookmarks, you might ask the child to send them to friends and relatives as gifts accompanied by a short note.
Activity 22: Let your fingers do the walking
The telephone book contains a wealth of information and is a good tool for reading and writing.
What you'll need:
- A telephone book, including the yellow pages
- Paper and pencils
What to do:
Have your child look through the yellow pages of the telephone directory, select a particular service, and write a clever or funny ad for it. Have your child read this ad to you. Help your child to find your own or a friend's listing in the white pages of the telephone book. Explain the different entries (for example, last name and address), along with the abbreviations commonly used.
Activity 23: Map your way to success
Children love to read road maps and this activity actually helps them with geography.
What you'll need:
- A road map or atlas
- Paper and pencil
- Stamps and envelopes
What to do:
When planning a vacation, let your child see the road map and help you plan where you will drive. Talk about where you will start and where you will end up. Let your child follow the route between these two points. Encourage your child to write to the Chamber of Commerce for brochures about places you will see on your trip.
Activity 24: What's in the news?
Newspapers are a form of daily communication with the outside world, and provide lots of learning activities for children.
What you'll need:
- Newspapers
- Scissors
- Colored pencils
What to do:
- Clip out an interesting news story and cut the paragraphs apart. Ask your child to read the paragraphs and put them in order.
- Ask your child to read a short editorial printed in your local newspaper and to underline all the facts with a green pencil and all the opinions with an orange pencil.
- Pictures fascinate children of all ages. Clip pictures in the newspaper. Ask your child to tell you about the picture or list adjectives to describe the picture.
- Do you take your child to the movies? Have your child first look up the movie page by using the index in the newspaper. After a movie has been chosen, have your child study the picture or text in the ad and tell you what he or she thinks the movie is about.
- Have your child pick a headline and turn it into a question. Then the child can read the article to see if the question is answered.
- Ask your child to clip food coupons from the newspaper for your grocery shopping trips. First, talk about which products you use and which you do not. Then the child can cut out the right coupons and putt hem into categories such as drinks and breakfast items.
 You can then cash in the coupons at the store.
You can then cash in the coupons at the store. - Pick out an interesting article from the newspaper. As you are preparing lunch or dinner, tell your child that you are busy and ask him or her to read the article to you.
- Many newspapers publish materials especially written for children, such as the syndicated "Mini Page," "Pennywhistle Press," and "Dynamite Kids." In addition, some newspapers publish weekly columns for children, as well as tabloids and summer supplements written by educators.
Activity 25: Using television to stimulate reading
What child doesn't enjoy watching TV? Capitalize on this form of entertainment and use TV to help rather than hinder your child's learning.
Some important ideas to consider before turning on the TV: Limit in some way the amount of TV your child watches so as to leave time for reading and other activities. Decide how much time should be set aside for watching TV each day.
Serve as an example by limiting the amount of TV you yourself watch. Have time when the TV set is off and the entire family reads something. You may want to watch TV only for special shows. Before the TV set is turned on, encourage your child to select the programs he or she wishes to watch. Ask your child to give you the reason for the choices made.
Have time when the TV set is off and the entire family reads something. You may want to watch TV only for special shows. Before the TV set is turned on, encourage your child to select the programs he or she wishes to watch. Ask your child to give you the reason for the choices made.
In addition, watch some of the same TV programs your child watches. This helps you as a parent share in some of your child's daily activities.
What you'll need:
- A TV
- A TV selection guide
- Colored highlighters
- A calendar page for each month
- Paper and pencils
What to do:
- Ask your child to tell you about favorite TV characters using different kinds of words.
- As your child watches commercials on television, ask him or her to invent a product and write slogans or an ad for it.
- Encourage your child to watch such programs as Reading Rainbow. Urge older children to watch such programs as 60 Minutes and selected documentaries.
 These programs are informative. Discuss interesting ideas covered in the programs and direct your child to maps, encyclopedias, fiction, or popular children's magazines for more information.
These programs are informative. Discuss interesting ideas covered in the programs and direct your child to maps, encyclopedias, fiction, or popular children's magazines for more information. - Have your child name 10 of his or her favorite shows. Ask your child to put them into categories according to the type of show they are, such as family shows, cartoons, situation comedies, sports, science fiction, or news and information. If you find the selection is not varied enough, you might suggest a few others that would broaden experiences.
- Prepare a monthly calendar with symbols such as a picture of the sun to represent an outdoor activity or a picture of a book to represent reading. Each time your child engages in a daily free time activity, encourage him or her to paste a symbol on the correct calendar date. This will give you an idea of how your child spends his or her free time. It also encourages a varied schedule.
- Ask each child in your family to pick a different color.
 Using the TV listing, have each child use this color to circle one TV program that he or she wants to watch each day. Alternate who gets first choice. This serves two purposes. It limits the amount of time watching TV and it encourages discriminating viewing.
Using the TV listing, have each child use this color to circle one TV program that he or she wants to watch each day. Alternate who gets first choice. This serves two purposes. It limits the amount of time watching TV and it encourages discriminating viewing. - Devise a rating scale from 1 to 5. Ask your child to give a number to a certain TV program and to explain why such a rating was given.
- Have your child keep a weekly TV log and write down five unfamiliar words heard or seen each week. Encourage your child to look up the meanings of these words in the dictionary or talk about them with you.
How easy it is to teach a child 4-6 years old to read - the best methods and exercises
How to understand that it's time
To the question "When is it time for a child to be able to read?" there is no ready-made answer, but we want to immediately warn against two misconceptions:
-
“It is not necessary to teach a child to read at home, they will teach you at school anyway.
 ” Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child.
” Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child. -
"There is no time to waste - the sooner the baby begins to read, the better." All children are different and develop at their own pace. Therefore, you should not impose teaching reading to a preschooler as soon as he is 4-5 years old, if the student himself does not yet show interest in this activity. Instead, you can begin to develop an interest in reading through bright and engaging books. A good option would also be games that involve letters.
The indicator to be guided by is not the age of the preschooler, but his speech skills.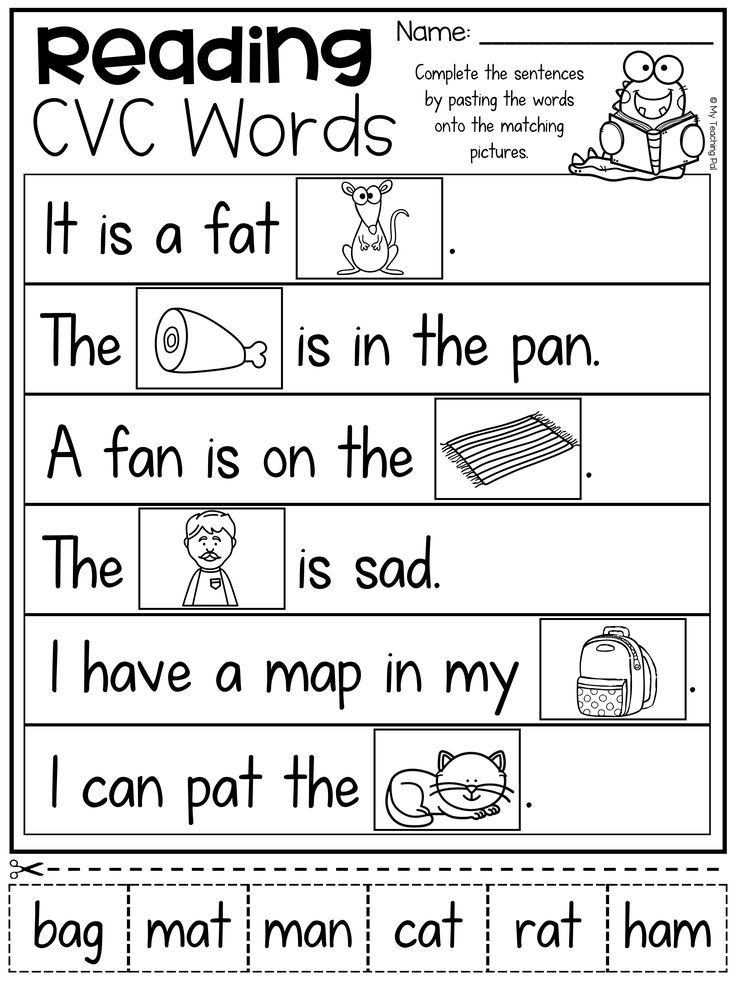
It's time to learn to read if...
If the speech development of a preschooler proceeds without gross violations. Let's figure out what criteria will help you find out if a child is ready to learn to read:
-
Understanding addressed speech. The kid must understand sentences, phrases, individual words that others around him turn to.
-
Vocabulary. The more words a child knows, the better he will understand what he read. It will also help him communicate with adults and other children.
-
Grammar. The ability to correctly build sentences, select and change words is important for children who are learning to read.
-
Pronunciation.
 For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
Remember: at preschool age, a child may have minor mistakes in grammar and pronunciation - this is normal. Over time, these violations will be corrected, and they should not be considered an obstacle to reading. But if the baby is not yet very confident in speaking, do not rush him to read - this will not help develop speech, but only demotivate.
Practicing child psychologist Ekaterina Murashova
Free course for modern moms and dads from Ekaterina Murashova. Sign up and participate in the drawing of 8 lessons
How to make learning to read easier for preschoolers
-
Praise more and never scold
It's hard for us adults to imagine how difficult it really is for a baby to learn from scratch such a complex skill as reading.
 After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text.
After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text. If parents take the child's progress for granted and express dissatisfaction when the child does not understand something, this will not push the future student to development, but will only complicate the process. Therefore, it is important to praise for small victories: I learned the letter that was passed last time - great, I coped without my father's help with the word as much as two syllables - clever.
Do not take failures as a consequence of the negligence of the little student. When a child does not understand the first time, this is an occasion to look for another explanation or give more time to practice. If you feel tired and irritated, you should stop the activity and return to it in a good mood.
-
Exercise little but regularly
Do not expect perseverance and a desire to spend hours figuring out unfamiliar letters from your baby.
 It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games.
It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games. But regular practice is important - much more important than the duration of the session. And it doesn’t have to be just lessons: you can look for familiar letters on signs during a walk, on a door plate in a children’s clinic, on a package of your favorite corn flakes.
-
Read books aloud
In a series of studies conducted by Dr. Victoria Purcell-Gates among five-year-olds who could not yet read, those children to whom their parents read aloud regularly for two years, expressed their thoughts in more literary language, built longer phrases and used more complex syntax.

In addition, reading aloud with adults contributed to the expansion of children's vocabulary, as parents explained the meanings of new words that children did not encounter in everyday life.
Expert Opinion
According to neuroscientist Marianne Wolfe, book evenings with parents help develop a love of reading because the child establishes a connection between reading aloud and feelings of love and warmth.
-
Discuss read
The role of communication in teaching literacy cannot be overestimated. At first, it is important to ask if the future student is interested, if he is tired, what was remembered from the lesson. When a preschooler learns to read coherent texts, be sure to ask questions about their content.
It's great if the child reads on his own and without the prompting of the parents, but even in this case, do not deprive him of the opportunity to discuss what he has read with you.
 For example, you can ask:
For example, you can ask: -
Which of the characters do you like?
-
Do you think this character is like you? Would you like to be like her?
-
What would you do if you were a hero?
-
Why did the described event happen? How are these two events related?
-
How did what you read make you feel?
-
What do you remember most from what you read?
-
What do you think the author wanted to teach? Why did he write this? Do you agree with the author?
-
-
Go from simple to complex
From the correspondence between sounds and letters to syllables, from short words to longer and more complex words. It would seem that this is obvious, but no: sometimes parents are so happy with the success of the child at first that they push him to study more complex topics than he is ready to accept. Of course, the program should adapt to the future student, but you should not skip steps, even if the child is making progress.
There are methods that offer to teach a child to read by memorizing whole words. Alas, experiments show that such techniques generally work worse. For example, a group of scientists from the United States came up with an artificial alphabet and offered subjects to learn it, and then read the words written using this alphabet.
 At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second.
At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second. Therefore, we advise you to choose those teaching methods that involve clear instructions about the relationship between sound and letter - and this is especially important for those children who have difficulty reading. Below we have compiled a few of these techniques that you can use to teach your preschooler at home.
It is important to select questions individually, based on the age of the child. With younger children, discuss everything together, ask simple questions, direct their attention to some facts. The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences.
The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences.
Methods of teaching preschoolers to read
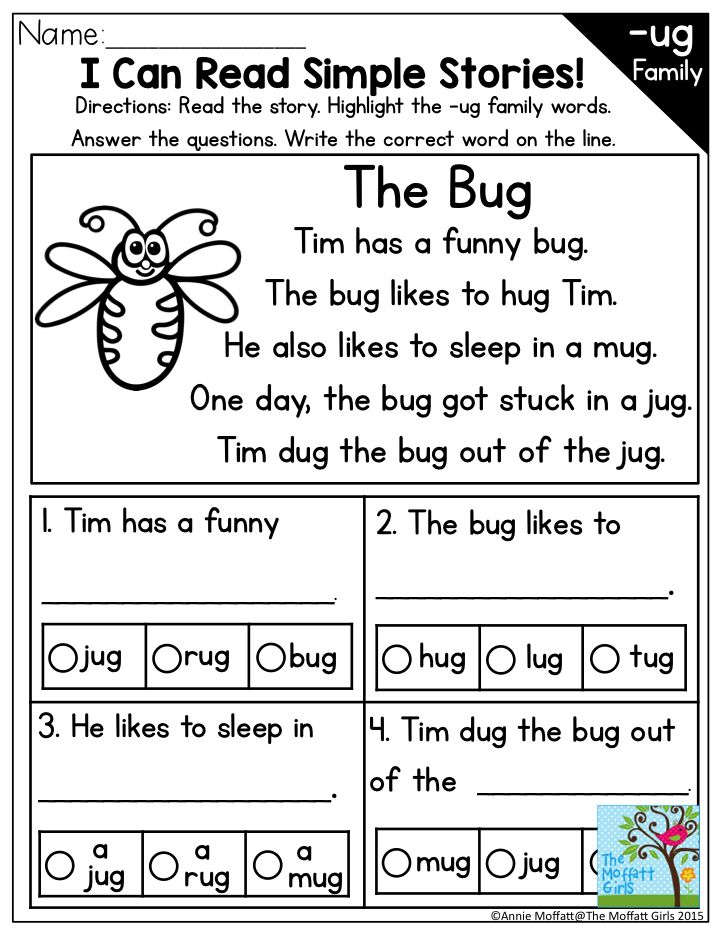
Warehouse reading
The way to teach a child to read through warehouses was actually used in Rus', but for modern parents this technique is associated with the name of the philologist Nikolai Alexandrovich Zaitsev.
Zaitsev suggests not focusing on the study of individual letters, as it can be difficult for students to understand how letters can merge into syllables and words. Teaching a child to read by syllables is also not always easy: one syllable can be quite long ( shine, ruble ), and the boundaries of syllables are not obvious ( Lun-tik or Lu-ntik ?). Therefore, in Zaitsev's methodology, a warehouse is used as the main unit.
Warehouse can be a combination of a consonant and a vowel (pa-pa, ma-ma), a single consonant or vowel (de- d , i-s -li, A -le-sha), as well as a combination of a consonant with a hard or soft sign (ma- l -chi-k, po- d -yem).
In order for a preschooler to understand the differences between the recording of voiced and soft, vowels and consonants, different types of warehouses have their own cube size, color and content, thanks to which the cubes sound when they are shaken. Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective.
Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective.
One of the advantages of the technique is that children willingly play with blocks themselves, and the process of learning to read becomes active and mobile.
Syllabic reading
This technique, according to some sources, was developed by the Romans. Later, Nadezhda Sergeevna Zhukova, a Soviet and Russian speech therapist, created a primer based on it. In it, she built her own system in which sounds and letters are sequentially introduced into speech.
Due to the fact that the concept of a syllable is introduced at an early stage, it is faster and easier to teach a child to read syllables together. By the way, as in Zaitsev's technique, it is proposed to sing syllables, and not just pronounce them.
Based on the syllabic method, Zhukova developed a set of teaching aids - copybooks, copybooks and a book for reading. Benefits will help teach children to read correctly 6 and 7 years old at home.
Both techniques for teaching preschoolers to read are used in the Skysmart Ready for School course. The course consists of two stages: first, children get acquainted with letters and warehouses, which allows them to quickly start reading simple words, and then they learn what a syllable is. Gradually, we introduce more complex syllabic constructions, move on to reading phrases and sentences.
Sound analytical-synthetic teaching method
This method originated in the USSR and is still considered the main one in Russian schools and kindergartens. It was developed by the Soviet teacher and Russian language methodologist Voskresenskaya Alexandra Ilyinichna.
Same as N.S. Zhukova, Voskresenskaya proposed her own order in which children should learn letters and sounds. The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
-
Two-letter syllables (including one consonant): am, ma, ra, etc. and simple words from them: ra-ma, ma-sha, Pa-sha, etc.
-
Three-letter syllables with a central vowel: poppy, lat, etc.
-
Combination of the first two stages into words: sa-lat, earth-la, etc.
-
Words of three syllables and six letters: az-bu-ka, ve-se-lo, etc.
-
Words of two syllables and six letters: question-ros, tea-nick, etc.
-
Words with a combination of vowels at the beginning and at the end of the word: chair, March, etc.
In this way, children simultaneously prepare for more complex syllables at each stage and reinforce what they have learned earlier.
Free English lessons with a native speaker
Practice 15 minutes a day. Learn English grammar and vocabulary. Make language a part of life.
Exercises for learning to read
Learning to read, as a rule, takes place in several stages. First, the child listens to the sound, visually remembers the letters. Different games will help with this, where you need to look for letters, invent words, etc. When this stage is over, you can move on to syllables and games to work them out. And only after that it will be possible to proceed to words, and then to sentences and texts.
Letter memory exercises
The first step is to teach your child to recognize letters. To do this, you can use pictures with hidden letters. We use such exercises in the preparation for school lessons in Skysmart.
Ask your child to identify what letter a word begins with, or name as many words as possible that begin with a certain letter.
Next, we train to distinguish correctly written letters from incorrect ones. This is also important for learning to write: preschoolers often mirror letters or distort individual elements.
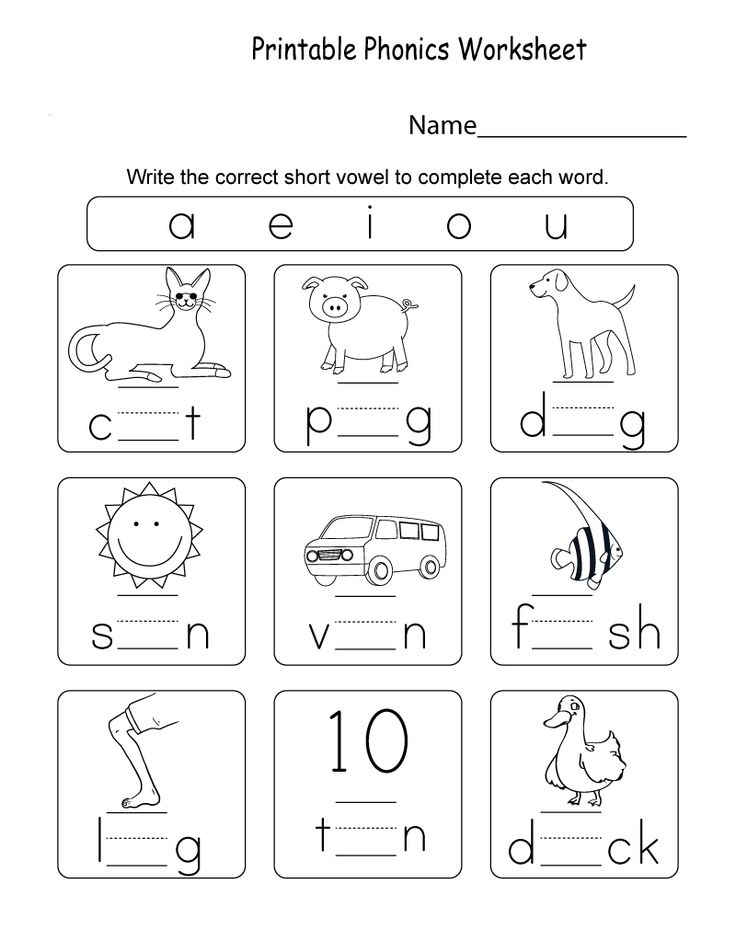
Exercises for vowels and consonants
To learn how to distinguish between vowels and consonants, tasks will help you determine the sound with which a word begins.
It will also help to remember the difference between vowels and consonants and search for an extra letter.
Word building exercises
When the child can read short words, ask him to form a word from the letters on his own.
Composing words from syllables is convenient if you have cubes at hand, but you can also try on paper.
Another good exercise is to fill in the missing letter in a word. Children perform such tasks in the lessons in the Skysmart online school.
For more colorful and fun reading activities, check out the Skysmart Ready for School course. Attentive teachers will help the child learn to read, count and express themselves through creativity. Classes are held online at a convenient time for the child and parents. Try it for free with an introductory lesson!
Teaching Reading - A set of games and tasks to develop reading skills
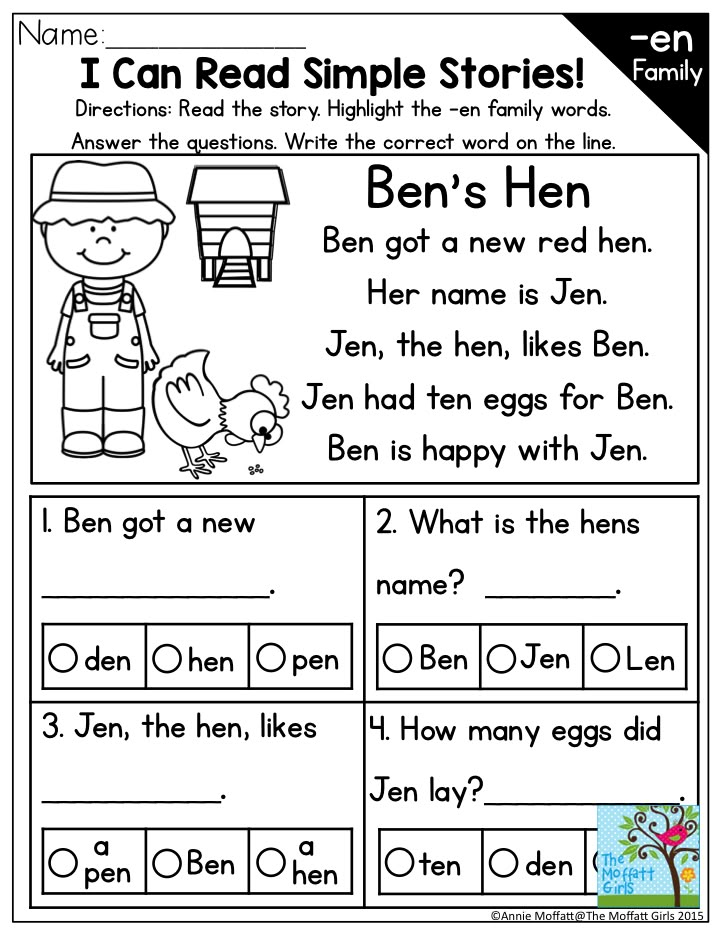
In the "Teaching Reading" section you will find a lot of interesting educational materials for children of preschool and primary school age. Here are a variety of printable educational materials designed to teach preschoolers to read, as well as to test the child's level of knowledge in the humanities. These tasks are suitable for regular homework with the child, developing his speech and intellectual abilities, as well as fully preparing him for the school curriculum.
Also in this section you will find classes on the development of reading skills and verbal-logical thinking. This category contains printable tasks that educators can use as didactic material for working with a group of children. Teaching reading to preschoolers is always faster and more effective when it sparks a child's interest. So do not neglect the variety of materials presented to make classes with your child more fun and interesting.
Making a word from letters - Reading task
In this section you will find many tasks, in each of which you need to make a word from letters. In some tasks, you need to compose words from given letters, and in some you need to learn the letters yourself (by the first letter of each word-picture). There are also tasks in which you need to make words from mixed letters or find hidden words.
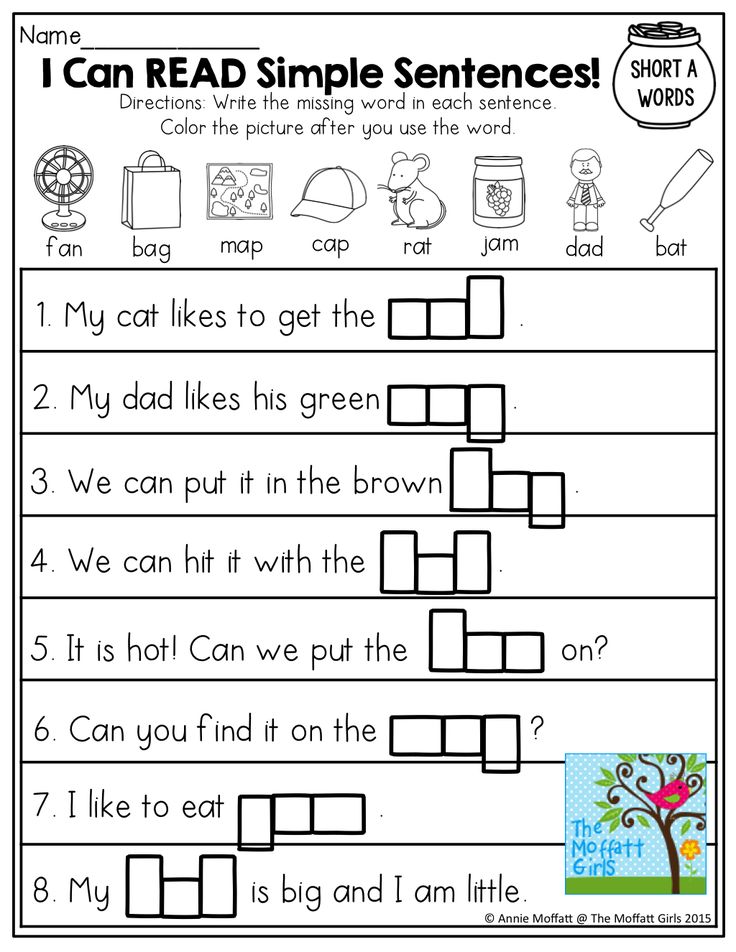
Stories with pictures instead of words for children
Here you can download short stories for children with pictures instead of words for children of preschool and primary school age. When reading the presented stories, you need to insert the right words instead of pictures. This kind of learning to read is very interesting for children who are learning to read.
When reading the presented stories, you need to insert the right words instead of pictures. This kind of learning to read is very interesting for children who are learning to read.
Russian alphabet in order for preschoolers
Here we will study the Russian alphabet in order, from the letter A to the letter Z. Two letters are given on each worksheet. Each letter corresponds to several pictures. You need to circle only those picture words that begin with a given letter.
Learning the Russian alphabet
In this section you can download materials that will help you learn the Russian alphabet easily and simply. Here are special tasks for teaching the Russian alphabet, and cards with letters for printing, and much more ...
Find a word by spelling in a square
In these colorful tasks for learning to read, the child needs, guided by pictures, to find a word by spelling in a special square, where the letters are arranged in a chaotic order. Each search word corresponds to one picture outside the square. The order of letters in words can be horizontal, vertical and diagonal. Here you need not only to be able to read words, but also to be very careful to find them...0020
Each search word corresponds to one picture outside the square. The order of letters in words can be horizontal, vertical and diagonal. Here you need not only to be able to read words, but also to be very careful to find them...0020
Read by syllables are tasks and printouts in which children will learn how to form words from syllables. Here you can download various tasks, print on a printer and work with your child following the instructions for each task.
Semantic reading - Working with text for children
Here you have to complete tasks for semantic reading. Working with text is a very important stage in teaching children to read. In these tasks, the child will practice finding synonyms and antonyms for words, understand and interpret the meaning and meaning of words and sentences, summarize and name the signs of objects, analyze the read text and answer questions asked about it, learn to compose sentences and stories, write dictations and much more other.