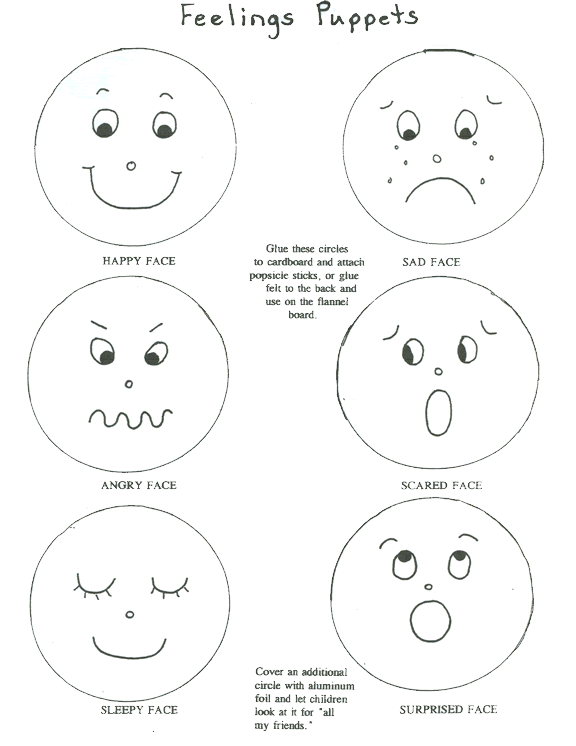
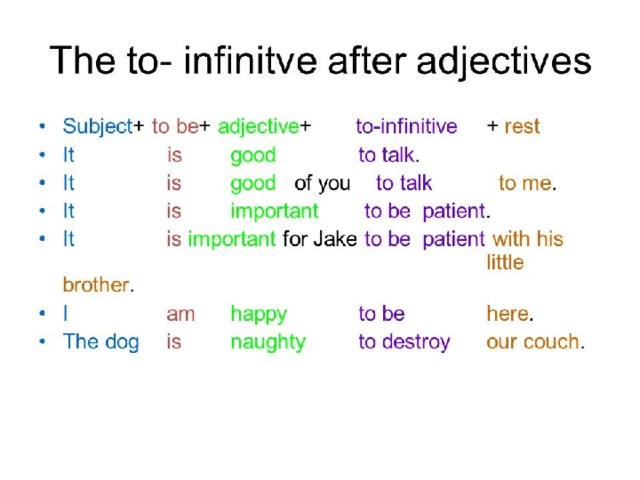
Why are adjectives important
What is an adjective? Learn about adjectives with EasyBib's guide.
Share to Google Classroom
3.9
(20)
With its multiple types, forms and rules of use, the adjective can be a slippery element of language to master. Get a firm grip on it, however, and you’ll be rewarded with the power to elevate your work to a more engaging, interesting and expressive level.
Adjectives are words that modify (describe) nouns. Adjectives give the reader more specific information about an object’s color, size, shape, material, and more. This guide will help you understand their function so you can use them effectively in your essays and papers.
Additionally, EasyBib Plus’s easy grammar check solution can help improve your essays. With a subscription, you can upload your paper to check for structural or grammatical errors and receive suggestions that may help improve your writing style. It can also check for unintentional plagiarism, help you to cite sources, and generate MLA or APA format citations.
If you need to create citations in a different format, our library of resources contains free guides for many more styles.
For information on the structural role these modifiers play in a sentence, you may find this further reading helpful.
Guide Overview
- What is an adjective?
- Types of adjectives
- Which comes first?
- Why they’ll never be lonely
- The unspoken order
- If in doubt, take it out!
- What can an adjective add?
- The wonder word
- Flip reverse with adjectival opposites
- Cool, cooler or the coolest?
- A master of disguise
- Unusual adjective examples
- Still struggling?
What is an Adjective?
As a child, you might have learned that it is a describing word. This adjective definition is correct and, as mentioned above, it can be used to describe, modify or qualify a noun, essentially giving more information about the object, person, place, thing or idea in question.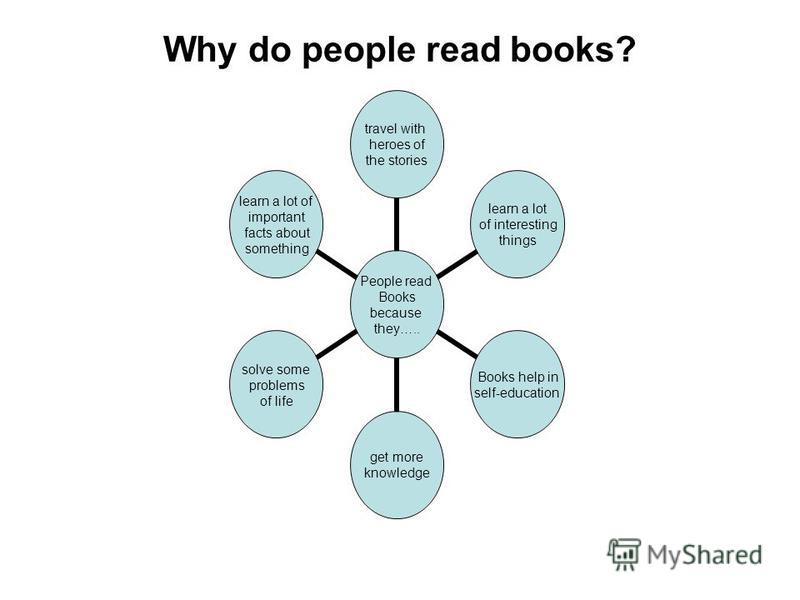
In its most basic form, it is a single word. However, as the English language is anything but basic, you’ll also want to understand the adjectival clause and phrase—more on those later!
When used well, this essential part of the English language can become your most potent writing ally. They’ll make your writing more specific and lucid, enabling you to convey your ideas in a clear and appealing manner. They add the meat to the bare bones of a sentence!
Struggling with writing in general? Our grammar checker, that comes with EasyBib Plus, can help. You’ll also find lots of additional free resources at EasyBib.com too, including guides for Chicago/Turabian, APA and MLA format. It’s an easy, one-stop online toolkit that can help you understand tricky topics, such as creating an MLA citation for a website or citing an image found online, to make sure that the work you’re handing in for marking doesn’t contain avoidable mistakes that could let you down.
Types of Adjectives
When it comes to learning the different types, some are more interesting than others—however, there’s no picking and choosing with grammar! Let’s take a look at both the fun and the functional, and the part they each play in the English language.
The Exciting
Descriptive adjectives are the grammatical icing on the cake or bubbles in the bathwater. They follow the classic adjective definition of a descriptive word that comes before or after a noun to modify it. Often, you can take them away and the sentence will still technically make sense, although it’s likely to be less informative, thought-provoking, and engaging for the reader.
For example:
The woman was wearing a dress.
vs
The beautiful woman was wearing a long, white dress.
When it comes before a noun it is known as an attributive adjective.
When it comes after a noun it is known as a predicate adjective. Note that these usually follow a linking verb.
For example:
- Attributive — the beautiful woman
- Predicate (also known as predicative) — the woman looked beautiful
To learn more click here or check your paper with EasyBib Plus’s paper checker to ensure that you’re using different aspects of language, including spelling, punctuation, style and word choice, correctly. Otherwise, let’s continue on our exploration of describing words.
Otherwise, let’s continue on our exploration of describing words.
Did you know that describing words can also be subjective or objective?
Objective: A descriptor, based in fact, that will often be quantifiable and measurable. Descriptors of age, color, pattern, size, shape, condition, type, purpose, origin and material are objective. For example: old, red, checked, large, square, clean, four-sided, running (to indicate purpose, e.g., running shoes), French and paper.
Subjective: These words provide opinion-based descriptions which may be open to interpretation. It could be an ‘in the eye of the beholder’ descriptor such as beautiful or ugly. Or it could describe a relative measure such as cheap, best, favorite or cold. Words used to describe an emotion or feeling such as happy or hungry are also subjective.
There are multiple objective and subjective sub-types, so you should be spoiled for choice when choosing that perfect describing word. Find a list of adjectives and the order they should follow further down.
Find a list of adjectives and the order they should follow further down.
The Essential
Words in this category are more likely to modify (or give information about) a noun than describe it. Take them away, and you’ll often find that you no longer have a fully formed sentence. These are the ‘toothbrush in the bathroom words’—nothing about them is exciting, but they perform an essential function, we use them daily, and we’d be lost without them.
Take articles. They always come before the noun they’re indicating. There are three articles in the English language: a, an, and the. A and an are used to denote non-specific things, while the indicates something specific. The is known as the definite article, while a and an are indefinite articles.
For example:
Pass me the book
The word the tells us that the request is for a specific book.
Pass me a book.
A, however, shows that any book will do.
Demonstrative: Similar to the definite article in that they indicate specific things. For example: these, those, this and that.
Indefinite: Similar to the indefinite article in that they indicate non-specific things. For example: any, many, several and few.
Interrogative: Used to ask questions. There are three in the English language: which, whatand whose.
Possessive: Indicate that a thing belongs to someone. My, your, his, and our are examples of a possessive adjective.
Numerical: Answer the question “how many?” in a sentence. For example:
She ate six cupcakes.
Which Comes First?
We’ve answered the question, ‘what is an adjective?’.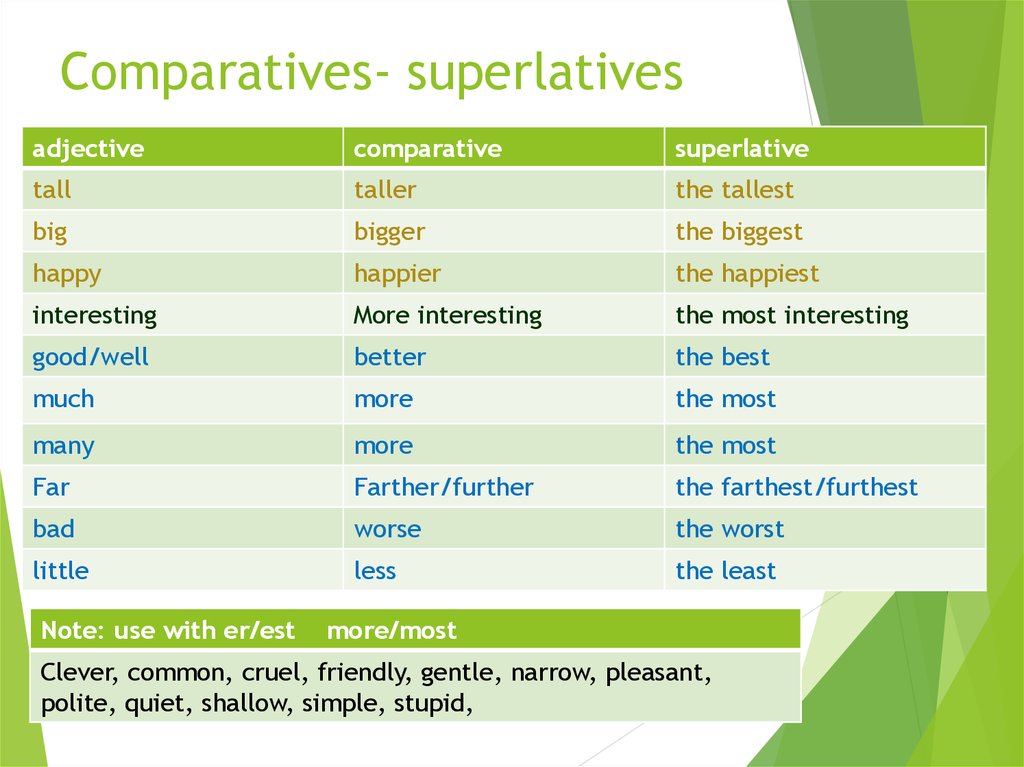 Now let’s look at where they sit in a sentence. Typically, a describing word is a pre-modifier, this means that it comes before the noun, pronoun or the noun phrase that it’s looking to modify. Also known as a prepositive (NOT a preposition, that’s different!) or, as previously mentioned, attributive.
Now let’s look at where they sit in a sentence. Typically, a describing word is a pre-modifier, this means that it comes before the noun, pronoun or the noun phrase that it’s looking to modify. Also known as a prepositive (NOT a preposition, that’s different!) or, as previously mentioned, attributive.
For example:
A lovely day
In the case of an indefinite pronoun (someone, something, anybody), however, the descriptor comes after.
For example:
Something blue
We’ve also mentioned predicatives that come after the noun they modify and follow a linking verb.
For example:
The sky looked blue.
Why They’ll Never Be Lonely
Although a describing word will always be singular (even if the noun is plural), it will never be lonely—it will always team up with a noun or pronoun in a sentence.
The adjective phrase is a phrase that performs the describing or modifying function in a sentence. It can be a string of describing words or it can be an intensifier plus descriptor.
String example:
It was a cold but sunny day.
Intensifier example:
She was very happy.
Coordinates
When one just isn’t enough you can use coordinate adjectives separated by a comma or commas. These are a perfect pairing—or trio or full-on gang—of words used to describe or modify a single noun.
For example:
A long, white, lacy dress
Long, white and lacy are coordinates: they are adjectives with a parallel function in describing the dress, and none carries more weight than the others. You can test this by replacing a comma with a conjunction, such as and or but, and checking if the sentence still makes sense.
For example:
A long and white and lacy dress
A beautiful but expensive dress
Non-Coordinates
In some sentences, however, replacing the commas with conjunctions yields a sentence that no longer makes sense. When this occurs, the describing words are non-coordinate.
If one word holds more weight than the other, they are non-coordinate—also known as cumulative. Another easy way to test this is to switch the words around to see if the sentence still makes sense.
For example:
My two red skirts were in the laundry.
My two and red skirts were in the laundry.
My red two skirts were in the laundry.
Non-coordinates don’t need to be separated by a comma.
The Unspoken Order (mess with this at your peril!)
Native English speakers intuitively follow a particular order when using describing words in a sentence. Intriguingly, many of us aren’t even aware that there is an order, let alone that we’re complying with it.
For those learning English as a foreign language, however, it’s a bit of an uphill battle. To help make sense of it, the following list of adjectives follows the order used when forming sentences:
- Determiner — a, an, the, that, some, six
- Opinion — beautiful, easy, expensive, happy, angry, boring, strange
- Size — large, small, tiny, deep, medium
- Condition/Physical Quality — broken, cold, smooth, rich, poor, sharp, slow, heavy, light
- Age — new, old, seven-year-old, modern, antique
- Shape — round, square, oval, flat
- Color — red, blue, monochrome, bright, dull
- Pattern — striped, spotty, flowery, chevron, plaid
- Origin — American, French, English, public, private
- Material — gold, silver, cotton, silk, wooden
- Type — general, four-sided, wireless
- Purpose/Qualifier — sleeping, frying, hunting, swimming
- Noun — bag, pan, hat, pool, woman, house
For example:
- That is a beautiful American house.
 (opinion + origin + noun)
(opinion + origin + noun) - It’s a tiny silver ring. (size + material + noun)
- I love smooth, round pebbles. (condition + shape + noun)
Note, however, that the order isn’t entirely set in stone. For example, you might find a list of adjectives that places shape before age.
More resources on this can be found online, including handy downloadable charts. You can also check your word choice, grammar and punctuation with EasyBib Plus.
If in Doubt, Take it Out!
Just because you can use several words to modify one noun doesn’t mean that you should. No one wants their work to be described as ‘wordy’ or ‘flowery’!
Exercise restraint with subjective descriptors like lovely, interesting and beautiful. The ‘show don’t tell’ rule is an oldie but a goodie—rather than telling your reader that something is beautiful, show them what makes it so and trust that they’ll reach the same conclusion.
What Can an Adjective Add?
When you’ve finished trying to say that tongue twister ten times fast, let’s look at what the right word can add to a sentence.
- Opinion — a beautiful dress
- Relative information — a huge house
- Factual information — a red car
- Detail — a shiny floor
- Context — old toys
- Purpose — the dining table
- Character traits — a patient teacher
The Wonder Word
To define adjective solely as a describing word may, arguably, do it a disservice. Used correctly, it’s one of the most capable tools of the English language.
In addition to providing us with the super functional determiners (a, her, those, that, some,etc. ), they can also: clarify and articulate information; alter the meaning or context of a sentence; and turn tedious, flat tales into riveting, page-turning prose.
), they can also: clarify and articulate information; alter the meaning or context of a sentence; and turn tedious, flat tales into riveting, page-turning prose.
Here are some examples:
Alter the Meaning of a Sentence
Original:
The woman was wearing a dress.
Revised:
The woman was wearing a long, white wedding dress.
The words long, white and wedding add meaning and clarity in the revised sentence. You could even take away the word wedding and the connotations of a ‘long white dress’ would still remain.
Alter the Context of a Sentence
Original:
The girl was playing with old, broken toys.
Revised:
The girl was playing with shiny, new toys.
These two sentences paint very different pictures, by merely changing the modifiers. If they were the first line of a story, they’d instantly conjure very different assumptions and set different moods.
If they were the first line of a story, they’d instantly conjure very different assumptions and set different moods.
Convey Information
Original:
John opened the door to his apartment.
Revised:
John opened the door to his expensive, new apartment.
Transform Dull Prose
Original:
John opened the door to the house.
Revised:
A nervous John opened the heavy, creaking door to the spooky, old house.
These wonder words have the power to change the impact of a sentence entirely!
Need more information on a determiner? Check out our determiner page from EasyBib Plus.
Flip Reverse With Adjectival Opposites
These words are masters of transformation, and you’ll see one of their most impressive tricks when you employ them to achieve the opposite meaning or, to add a degree of negativity.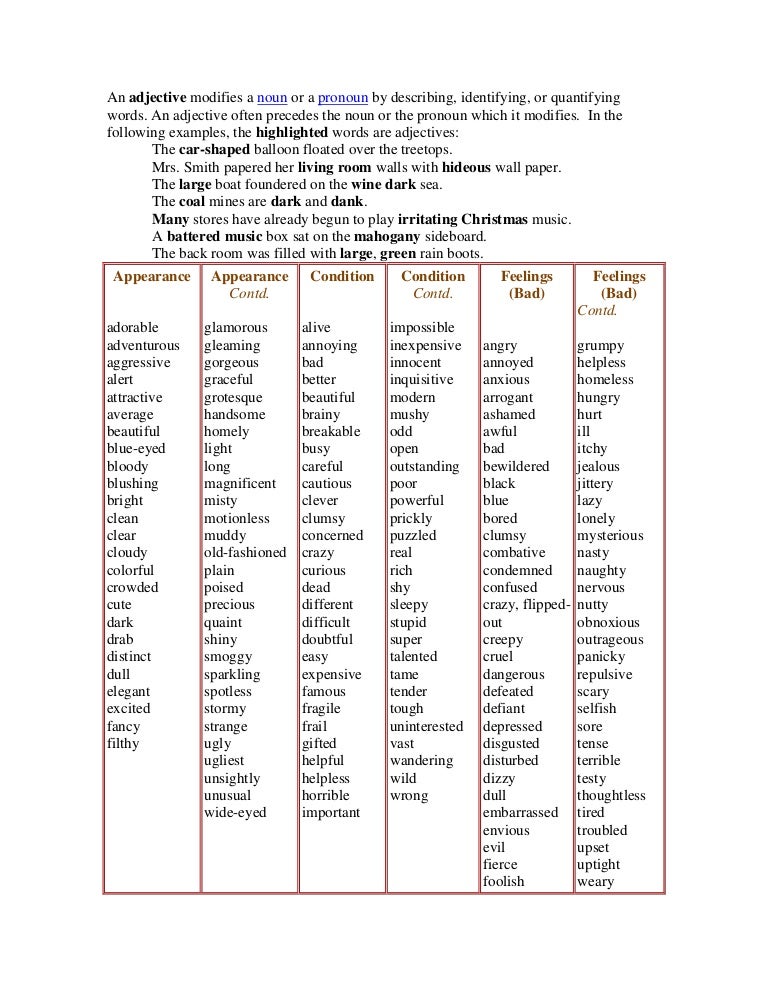
For example:
- Positive — my favorite show
- Negative — my least favorite show
- Positive — my teacher is patient
- Negative — my teacher is not patient
Interestingly, you can convey a scale of meaning with this method.
My art teacher is less patient than my music teacher.
Prefixes can also be used to achieve the same result.
For example:
- Patient — impatient
- Alcoholic — non-alcoholic
- Kind — unkind
Cool, Cooler or the Coolest?
Not content to present themselves in only one form, the not-so-humble adjectives can also be used to compare two or more nouns. Adjectives have three degrees of comparison: positive, comparative, and superlative.
Positive/Absolute: This is the standard base form of the word. Positive adjectives don’t compare anything. These include words such as sunny, messy, and great, which describe an object in its own right. Other examples are: red, hot, angry.
Comparative: Comparative adjectives compare two or more objects by degree. Adjectives such as sunnier, messier, and greater are comparative.
Most adjectives can be made comparative by adding –er or –ier to the end. You may also need to double the final consonants. For example: Big, bigger, biggest.
In some cases, adjectives must be preceded by comparative terms like more or less. For example: more interesting, less intelligent.
Superlative: Superlative adjectives indicate that a noun has the highest degree of the quality being described. Examples include sunniest, messiest, and greatest.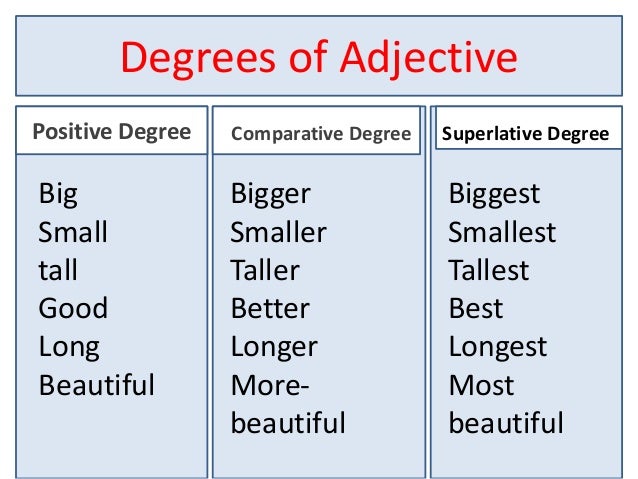
You can typically make adjectives superlative by adding –est or –iest. Some adjectives, however, must be preceded by most to become superlative.
Irregulars: As seen in the examples above, most degrees of comparison can be formed by adding:
- er and est — bright, brighter, brightest
- r and st — brave, braver, bravest
- Removing the y and adding ier and iest — dry, drier, driest
- By adding words such as more and most
Some, however, don’t like to follow the rules. These words, known as irregulars, express degrees of comparison with sometimes drastic changes in form.
For example:
- Little, less, least
- Bad, worse, worst
Forming comparatives or superlatives of words that already express an extreme of comparison is also a sticky subject.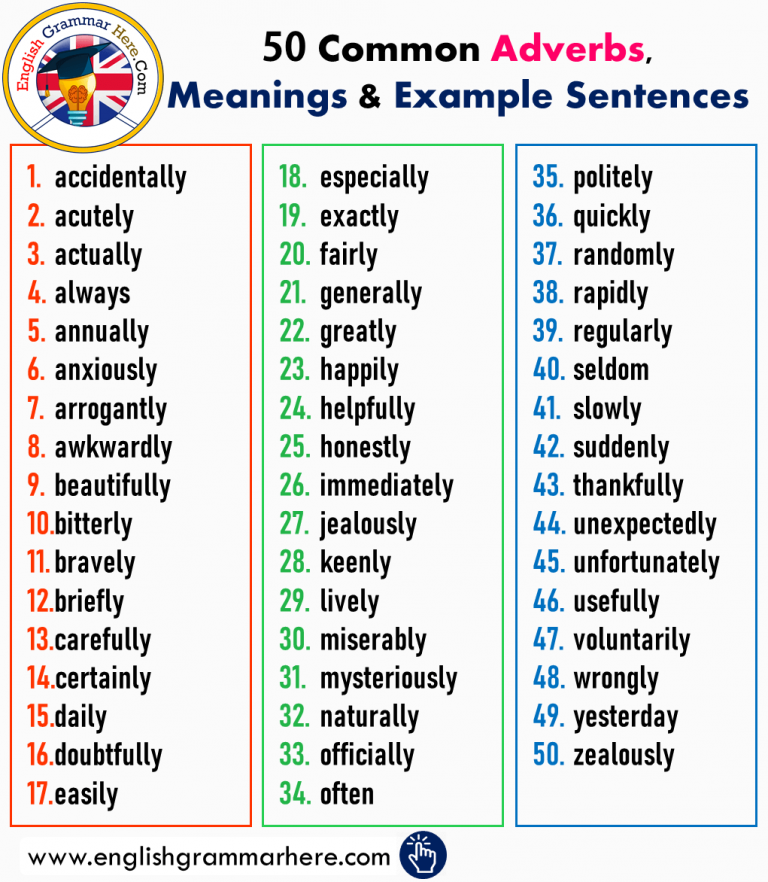
If something is already perfect, can it be more perfect or the most perfect? There’s a puzzle for the language philosophers among you!
To learn more about and other parts of speech, review our grammar quick guide.
A Master of Disguise
Now here’s where things can get really tricky! Grammar is full of sneaky double agents—a verb or a noun can become a describing word, and a describing word can become a noun or an adverb. Confused? Let’s break it down.
Noun as a Descriptor
Sometimes a noun is used to describe another noun. The first noun then functions as the descriptor.
For example:
- Thing — a bar of gold
- Descriptor — a gold necklace
- Thing — basketball
- Descriptor — a basketball player
Compound Nouns
In some cases these then become compound nouns, which are recognized as single words because they need both words to convey their meaning accurately.
For example:
- Thing — wedding
- Descriptor — wedding dress — the word wedding modifies the noun dress.
- Compound Noun — wedding dress
Compound nouns can also be formed from a descriptor plus noun or a descriptor plus verb.
For example:
- red-head
- soft-ball
- dry-cleaning
- public-speaking
Participles
A participle is a word that has been formed from a verb but functions as a describing word.
For example:
- Verb — to run
- Participle — running water — the word running modifies the noun water.
Nominals
Nominals precede a describing word with the and function as nouns.
For example:
- Descriptor — the best singer
- Nominal — the best is yet to come
You’ll notice that the word best is not modifying a noun in this sentence. Instead it is acting as the noun.
Instead it is acting as the noun.
Collectives
Collectives are a sub-type of nominals that refer to a group sharing a certain characteristic.
For example:
- Descriptor — the old man
- Collective — the old may suffer health problems
Again, the old is acting as a noun to identify a group of people.
Flat Adverbs
A flat adverb doesn’t have the distinctive ‘ly’ on the end of it, which allows it a double function as both adjectives and adverbs.
For example:
- the fast car
- he drove fast
The Adjective Clause
This clause functions as a descriptor in a sentence, and includes a verb and a subject. It always begins with a relative pronoun (who, whom, which, whichever, that, etc) or a relative adverb (where, when, why).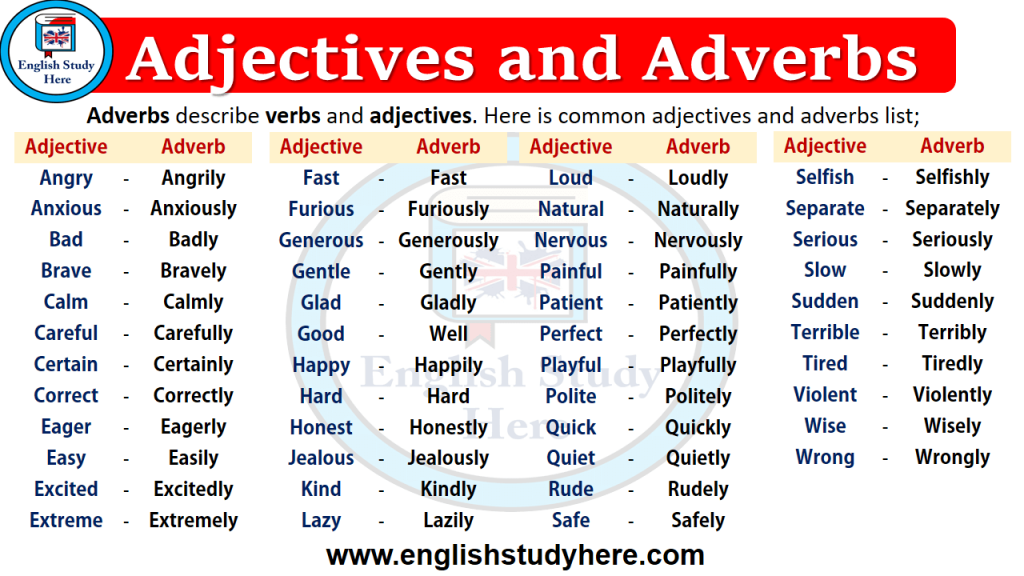 It’s a dependent clause, which means that it cannot stand alone as a sentence.
It’s a dependent clause, which means that it cannot stand alone as a sentence.
For example:
The jacket that Todd bought yesterday looked smart.
Notice that a descriptive clause doesn’t even have to contain a describing word—go figure!
Unusual Adjective Examples
If you’re still struggling with the question ‘what is an adjective?”, seeing examples may help! Or are you searching for a wonder-word that’s sure to impress your lecturer? Our unusual adjectives list might have the inspiration you need.
Adjectives That Start With A
- Abhorrent — offensive
- Abject — unfortunate
- Adamant — unyielding
- Adroit — skilful, clever
- Auspicious — lucky
Adjectives Starting With D
- Decrepit — worn out, ruined
- Dapper — smart dress and mannerisms
- Decorous — good manners and conduct
- Didactic — instructive
- Draconian — harsh
Adjectives That Start With E
- Effulgent — radiant
- Efficacious — having a striking effect
- Equanimous — balanced, calm
- Erratic — prone to sudden change
- Execrable — detestable, very bad
Adjectives That Start With N
- Nebulous — vague, lacking definition
- Necessitous — poor and needy
- Nescient — ignorant
- Nefarious — wicked
- Noxious — harmful, corrosive
Adjectives Starting With P
- Parsimonious — frugal
- Pernicious — harmful, deadly
- Piquant — stimulates taste or mind
- Plucky — brave
- Precipitate — steep, sudden, hasty
Adjectives That Start With U
- Ubiquitous — everywhere at once
- Unvanquishable — invincible, unbeatable
- Uppity — self-important
- Urbane — courteous
- Utilitarian — useful, practical
A thesaurus is your friend! Use one to find an adjective list and stop using the same tired words over and over. You can also check your word choice using EasyBib.
You can also check your word choice using EasyBib.
Still Struggling?
If you don’t have adjectives 100% nailed down just yet, or are still finding it difficult to answer the question ‘what are adjectives?’, don’t worry. Grammar is one of the most challenging aspects of the English language to learn, and it’s a long road to mastery. This guide is here to help you along your way, along with others such as our research paper and interjection pages.
An EasyBib Plus subscription comes with a useful online tool for checking grammar. If you want to try it before subscribing, simply upload your paper or essay for a free review with up to 5 grammar suggestions. An EasyBib Plus subscription also allows you to check for information that may need a citation, and offers tools and resources to help you create an MLA annotated bibliography, MLA works cited, and MLA in-text citation.
Don’t let grammar or unintentional plagiarism let you down. EasyBib Plus can help you ensure that you’re handing in your best work every time.
Adjectives starting with A-Z
Improve your writing with better usage of the right adjectives.
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Importance of Adjective in English Language | by vaibhavseo
Importance of Adjective in English Language
An Adjective is a word that changes a describing so as to a noun or a pronoun to making it more descriptive. For instance, with the expansion of adjective, the thing “man” turns into “the tall, attractive man” or “the short, plain man.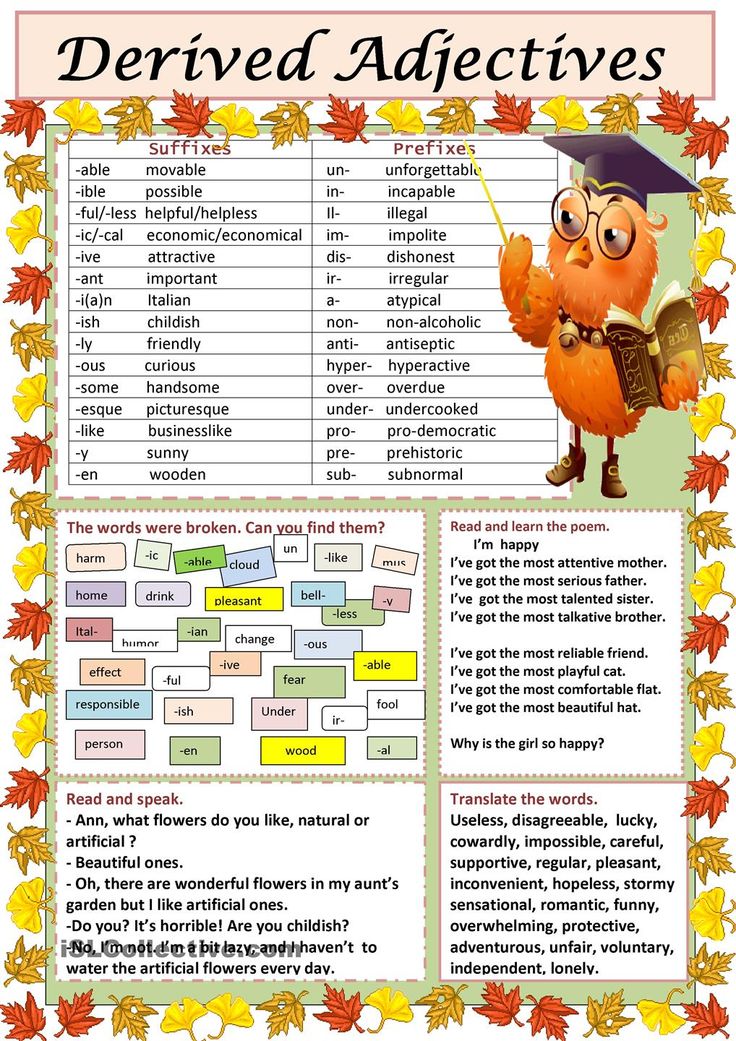 ”
”
Descriptive words additionally incorporate the articles “a, an,” and “the.” Though “a” and “an” are called uncertain articles since they don’t determine a specific individual or thing. “The” is known as a certain article since it specifies a specific individual or thing. For example, “a man” (any man) when contrasted with “the man” (a specific man). In each language, adjectives are vital components of sentences. Utilizing adjectives implies that we can express the nature of any individual or item. Without descriptive words we couldn’t say how any article resembles. Not just pronouns and nouns are the words which are utilized for portrayal of something or some individual.
Furthermore; when we read a paper which is a clear one, adjectives help us to picture the substance of what we read about.
If we consider about importance of adjectives in English language, the following things come to our knowledge.
1. It properly describes the noun. It marks what is the noun is all about? A place, a person or a thing?
2. It also tells some descriptive idea of the same noun so that we can find out the proper meaning and condition of particular article.
It also tells some descriptive idea of the same noun so that we can find out the proper meaning and condition of particular article.
3. Adjective totally affects the meaning of a sentence. Its presence makes the sentence more interesting.
At whatever point we utilize adjectives, they make our works more visual and distinctive. Readers will show signs of improvement thought of what we wish them to picture when they read our compositions. It speaks to our readers’ detects; in this way, they can listen, see, touch, taste, and even notice what you’re portraying. Likewise, utilization of adjectives makes our reading and writing substantially more fun. It sets the tone for our composition. You have to utilize them for engaging papers or in our day by day life. Besides; we utilize descriptive words since we need to communicate, things, characters in a decent or awful way. It will stand out enough to be noticed and can make the book a decent read or discourse a decent, a compelling discourse.
Adjectives can make other individuals need to get the book or you are needed to be listened again and again and perceive how well you composed and chatted with some person and descriptive words is a major succeed . They may even be searching for descriptive words that draw close. At whatever point we consider our discourses, compositions or readings without utilizing adjectives, we would prefer not to tune in, compose and read. Along these lines, with the exception of a scholarly written work, we normally be watchful about that issue in our speeches, or writings.
If you want to know more related info, you can visit englishleap.com
At whatever point we utilize adjectives, they make our works more visual and distinctive. Readers will show signs of improvement thought of what we wish them to picture when they read our compositions. It speaks to our readers’ detects; in this way, they can listen, see, touch, taste, and even notice what you’re portraying. Likewise, utilization of adjectives makes our reading and writing substantially more fun.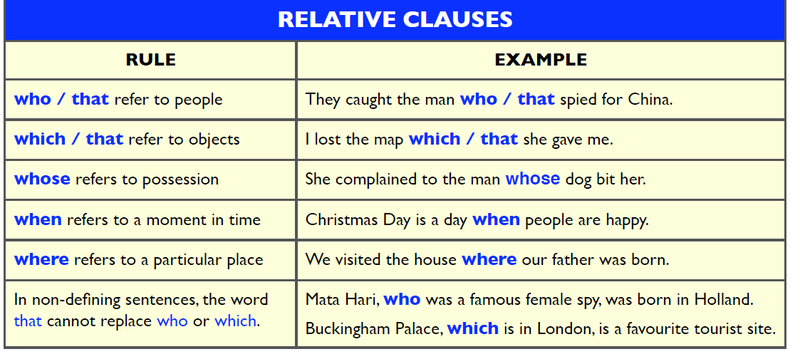 It sets the tone for our composition. You have to utilize them for engaging papers or in our day by day life. Besides; we utilize descriptive words since we need to communicate, things, characters in a decent or awful way. It will stand out enough to be noticed and can make the book a decent read or discourse a decent, a compelling discourse.
It sets the tone for our composition. You have to utilize them for engaging papers or in our day by day life. Besides; we utilize descriptive words since we need to communicate, things, characters in a decent or awful way. It will stand out enough to be noticed and can make the book a decent read or discourse a decent, a compelling discourse.
Adjectives can make other individuals need to get the book or you are needed to be listened again and again and perceive how well you composed and chatted with some person and descriptive words is a major succeed . They may even be searching for descriptive words that draw close. At whatever point we consider our discourses, compositions or readings without utilizing adjectives, we would prefer not to tune in, compose and read. Along these lines, with the exception of a scholarly written work, we normally be watchful about that issue in our speeches, or writings.
If you want to know more related info, you can visit englishleap.com
At whatever point we utilize adjectives, they make our works more visual and distinctive.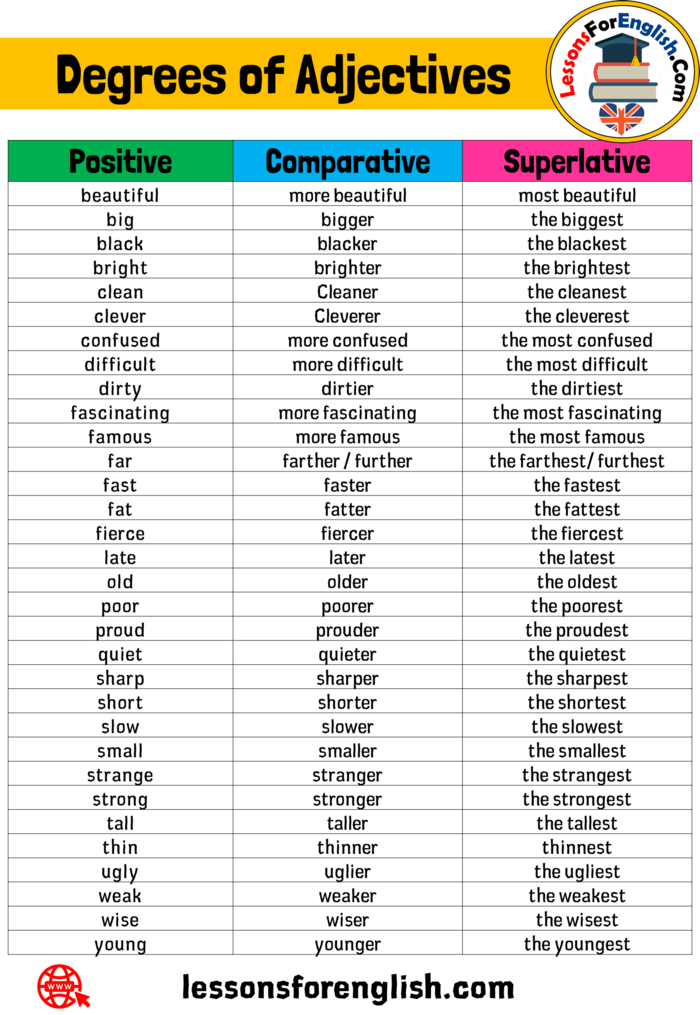 Readers will show signs of improvement thought of what we wish them to picture when they read our compositions. It speaks to our readers’ detects; in this way, they can listen, see, touch, taste, and even notice what you’re portraying. Likewise, utilization of adjectives makes our reading and writing substantially more fun. It sets the tone for our composition. You have to utilize them for engaging papers or in our day by day life. Besides; we utilize descriptive words since we need to communicate, things, characters in a decent or awful way. It will stand out enough to be noticed and can make the book a decent read or discourse a decent, a compelling discourse.
Readers will show signs of improvement thought of what we wish them to picture when they read our compositions. It speaks to our readers’ detects; in this way, they can listen, see, touch, taste, and even notice what you’re portraying. Likewise, utilization of adjectives makes our reading and writing substantially more fun. It sets the tone for our composition. You have to utilize them for engaging papers or in our day by day life. Besides; we utilize descriptive words since we need to communicate, things, characters in a decent or awful way. It will stand out enough to be noticed and can make the book a decent read or discourse a decent, a compelling discourse.
Adjectives can make other individuals need to get the book or you are needed to be listened again and again and perceive how well you composed and chatted with some person and descriptive words is a major succeed . They may even be searching for descriptive words that draw close. At whatever point we consider our discourses, compositions or readings without utilizing adjectives, we would prefer not to tune in, compose and read. Along these lines, with the exception of a scholarly written work, we normally be watchful about that issue in our speeches, or writings.
Along these lines, with the exception of a scholarly written work, we normally be watchful about that issue in our speeches, or writings.
If you want to know more related info, you can visit englishleap.com
Parts of speech in English: nouns, adjectives, pronouns -
Download: This post is available as a handy PDF document that you can take anywhere. Receive a copy of this post by email.
Basically, the classification of parts of speech in English, Russian and many other European languages is the same. Here, independent (notional) and service (functional) parts of speech are distinguished according to the grammatical meaning, syntactic functions, and form. Today we will consider three independent parts of speech: nouns, which denote objects and phenomena, as well as adjectives and pronouns, which define and replace them, respectively.
The noun (Noun) denotes abstract concepts (for example, poverty, freedom ), phenomena ( thunderstorm, light ), concrete objects ( building, plate ), living beings ( brother, waitress ). Nouns can be singular (singular) and plural (plural). Usually the plural is formed by adding –s at the end of a word ( songs ), but there are exceptions that do not obey this rule ( mouse - mice, tooth - teeth) . The following categories of nouns are also distinguished:
Nouns can be singular (singular) and plural (plural). Usually the plural is formed by adding –s at the end of a word ( songs ), but there are exceptions that do not obey this rule ( mouse - mice, tooth - teeth) . The following categories of nouns are also distinguished:
Adjectives describe nouns or pronouns (answer the question what kind of? - which one?), indicate their number (how much of? - how many?) and identify them (which one? - which one? ). In other words, adjectives define people, objects, phenomena, concepts and separate them from other objects, concepts, people, phenomena. Examples:
In other words, adjectives define people, objects, phenomena, concepts and separate them from other objects, concepts, people, phenomena. Examples:
He has blue eyes. – He has blue eyes . Here blue is an adjective that answers the question what kind of?
There are five books on the table. – There are five books on the table . In this case, five is also an adjective, since it answers the question how many books?
There are several main types of adjectives:
- possessive (possessive) - my, your, their, his, her, its ,
- quality (descriptive) - beautiful, tall, big , etc.,
- numerals (numeral): defined (definite) - first, fifth two ; indefinite (indefinite) - some, much, little ; distribution (distributive) - another, every , etc. Please note that in Russian numerals are a separate part of speech.
- demonstrative - this, that, these, those .
 In Russian, these are demonstrative pronouns.
In Russian, these are demonstrative pronouns. - interrogative (interrogative) - which, what, where , etc. In Russian - interrogative pronouns.
Pronoun replaces a noun or a nominal phrase. Thanks to pronouns, you can avoid a lot of repetition of nouns in speech. There are several types of pronouns:
- personal (personal) - I, you, he, she, it, we, they ,
- index (demonstrative) - this, that, these, those ,
- possessive (possessive) - mine, yours, his, theirs etc.,
- interrogative (interrogative) - who, what, which etc.,
- reflexive - myself, yourself, herself etc.,
- mutual (reciprocal) - one another, each other etc.,
- indefinite - another, nobody, much, few etc.,
- relative (relative) - whom, which , etc.
Many types of pronouns and adjectives have the same name and words related to them. It is important to remember that when a word defines a noun, for example, in combination this book , it is an adjective, but when it replaces a noun, for example, What book? – This turns into a pronoun.
It is important to remember that when a word defines a noun, for example, in combination this book , it is an adjective, but when it replaces a noun, for example, What book? – This turns into a pronoun.
Download: This post is available as a handy PDF document that you can take anywhere. Receive a copy of this post by email.
Tell a friend
Tweet
See also
-
Communication
Sign Language: Non-Verbal English
Many researchers wonder why students are not taught sign language, which is typical for native English speakers, along with teaching English. In fact, non-verbal communication is an integral part of various presentations, speeches, and ordinary interpersonal communication. Continue reading →
-
Education
Russian mistakes in English: words that are sources of confusion 1
There are a number of mistakes in English that Russians usually make because they confuse words with close meanings.
 Sometimes in Russian there is one word for what in English is called two different or vice versa, sometimes the meaning changes depending on the context. Continue reading →
Sometimes in Russian there is one word for what in English is called two different or vice versa, sometimes the meaning changes depending on the context. Continue reading →
The order of adjectives before the noun.
Do you ever feel like when you're describing something, one adjective isn't enough for you? And it happens that even two or three are not enough?
Has it ever happened that when you hear or read a sentence in English, you feel that “something is wrong” in it? This feeling can arise because the sentence has a broken word order, because in English, where everything has its own order, word order is very important.
It is a mistake to think that only word order is important subject + verb . Adjectives also have a certain sequence in which they must be placed before the noun.
And before speaking or writing, it is useful to think a little about the order in which it is better to arrange adjectives if there are more than one.
The place of an adjective in a sentence is before the noun it describes. But if there are several adjectives, then its order is determined by its meaning, so we will divide the adjectives into three categories. This classification is simplified, we present it in order to make it easier for you to understand the order of using adjectives before nouns. If you are interested in a scientific theoretical approach, then you better turn to a textbook on theoretical grammar :)
So, we will consider three categories into which adjectives can be divided by meaning.
-
Descriptive adjectives ( descriptive or qualitative adjectives ) convey an attribute of an object that can be manifested to a greater or lesser extent. These include:
adjectives denoting size (Size): small, large, big, tiny;
adjectives denoting color (Colour): red, white, blue, green;
adjectives denoting age (Age): young, old, recent, ancient;
adjectives denoting shape (Shape): round, square, long, heart-shaped;
adjectives denoting emotions (Emotions): sad, glad, happy, upset.
In addition, descriptive adjectives also include those that describe the material (Material): wooden, silk, leather, metal and origin (Origin): American, Russian, Latin. Although the last two types are sometimes referred to the next category of adjectives.
-
Allocate classifying adjectives , which assign a noun to a specific class . For example, this category includes adjectives that refer a noun to any area: political, linguistic, economics, musical.
Are these adjectives usually non-gradable and have no degrees of comparison? since an object can belong to only one class. The phrases sound rather strange: more musical instrument, less pedagogical report and the like. Although there are exceptions when authors may specifically use classifying adjectives in a comparative or superlative degree to achieve a certain stylistic effect.
-
And another important category is adjectives that characterize the personal opinion, judgment or assessment of the speaker ( opinion adjectives ): good, bad, excellent, terrible.
 Compared to descriptive and classifying adjectives, opinion adjectives can change depending on the speaker's opinion: for some, the dish is tasty, for some not, the picture seems beautiful to one, terrible to another.
Compared to descriptive and classifying adjectives, opinion adjectives can change depending on the speaker's opinion: for some, the dish is tasty, for some not, the picture seems beautiful to one, terrible to another. This category can include: adjectives that express a qualitative assessment ( Personal opinion and Quality ): beautiful, nice, pleasant, cheap, good, bad, excellent, terrible and so on; adjectives denoting sensations (Senses): tasty, cold, hot, smooth.
So we come directly to our topic: the order of using adjectives before nouns. You need to remember just a few simple rules in order to always use adjectives accurately in a sentence.
Rule #1. Description first, then class.
Descriptive adjectives come before classifying adjectives:
|
| Description | Class/Classification | Noun |
| a | thick | grammar | book |
| a | new | economic | reform |
| a | useful | computer | program |
Rule number 2.
 Rating before description.
Rating before description. If one of the adjectives expresses judgment, evaluation or opinion, then this place of this adjective is before the one that gives the description:
|
| Opinion/Opinion | Description | Noun |
| a | nice | comfortable | hotel |
| a | delicious | sweet | pie |
| wonderful | friendly | atmosphere |
Rule number 3. Descriptive adjective order.
What if all adjectives are descriptive? The order of their use before a noun is quite flexible, but there is a certain sequence and patterns. For example, adjectives denoting material and origin always come last. Of course, it is unnatural to immediately put five or six adjectives before a noun, but two or three is a very real phenomenon. In English, this order must be observed, even if there are no adjectives with any of these meanings, then it is not violated:
Of course, it is unnatural to immediately put five or six adjectives before a noun, but two or three is a very real phenomenon. In English, this order must be observed, even if there are no adjectives with any of these meanings, then it is not violated:
|
| Size | Age | Shape | Color | Origin | Material | Noun |
| a | tiny | old | - | - | - | golden | ring |
| a | large | - | round | - | - | - | room |
|
| - | new | - | red | - | silk | curtains |
| a | long | ancient | - | - | Greek | - | legend |
| a | short | - | - | black | French | - | skirt |
| a | - | modern | square | - | - | wooden | table |
Accordingly, if, along with descriptive adjectives, there are classifying or evaluative adjectives, then rules 1 and 2 apply.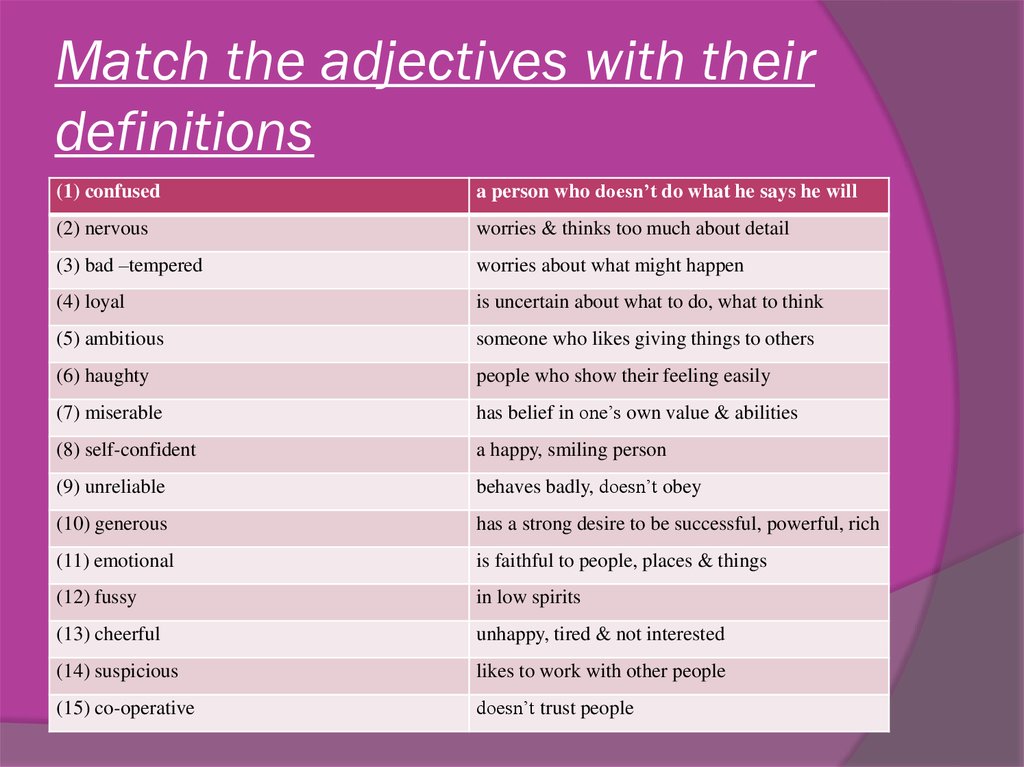
|
| Opinion | Description | Class | Noun |
| a | nice | young | English | teacher |
|
| beautiful | green | tropical | forests |
| a | lovely | old | folk | song |
In place of the article, adjectives can be preceded by a numeral if you indicate the amount:
two thick grammar books
the first useful computer program
And when you need to use both ordinal and cardinal numbers before adjectives, then 9 is put first0213 ordinal , and after quantitative :
the first two important grammar rules
the first ten international students
The same rule applies to the words last, next and the like:
the next three sunny hot days
his last two popular online projects
And the last point: commas.