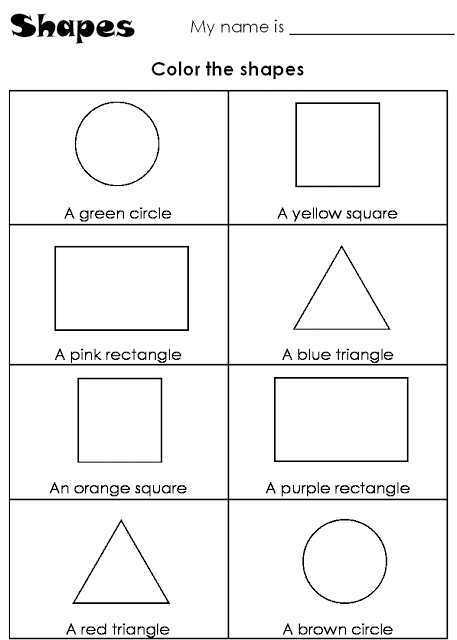
Different kinds of shapes for kids
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
| 5. | Conclusion |
| 6. | About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
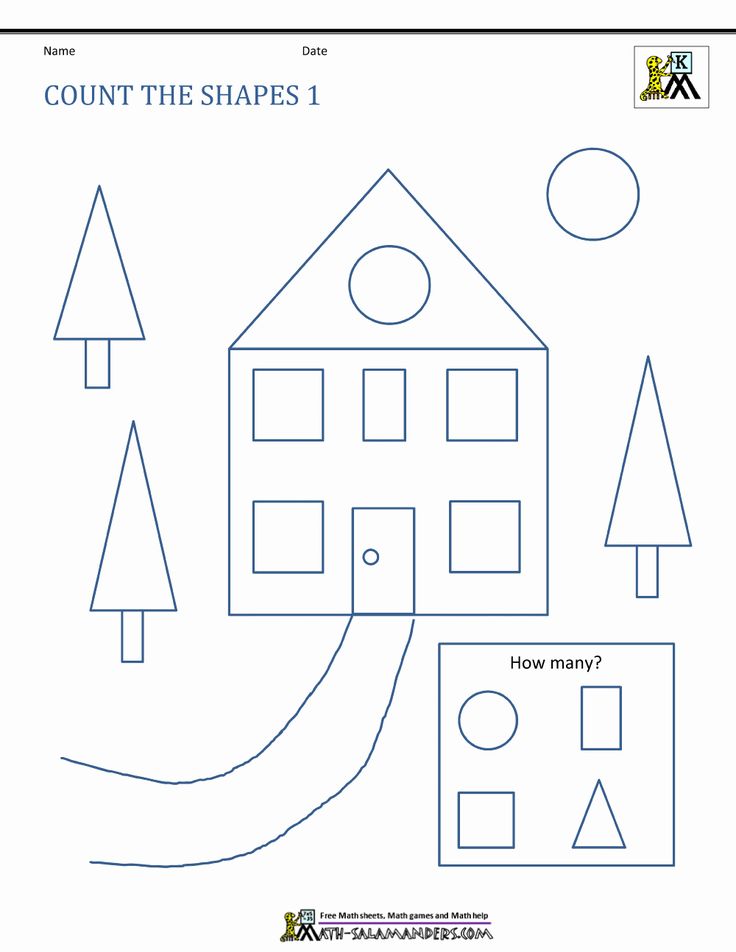
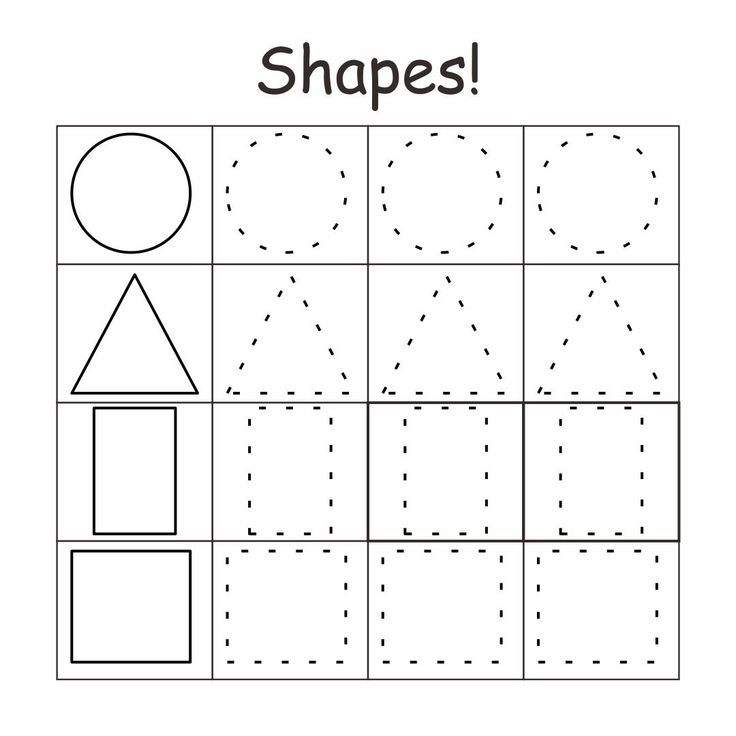
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
-
Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day.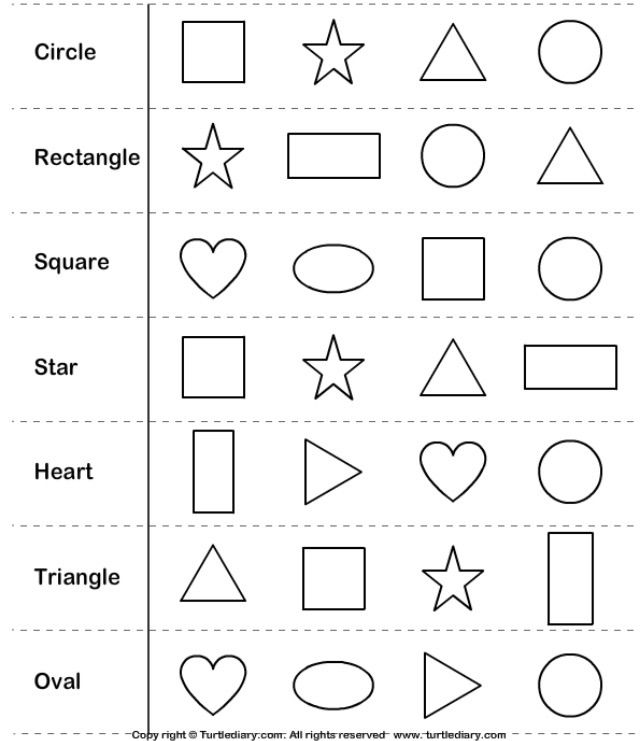 Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction.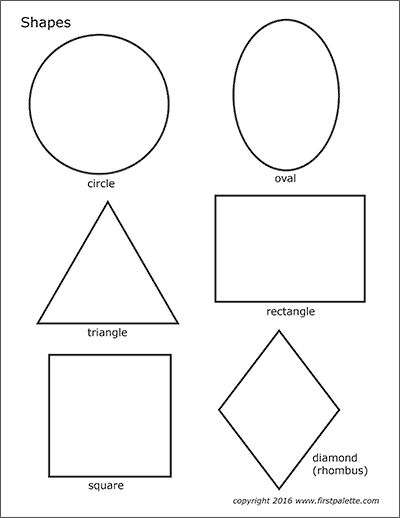 Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten.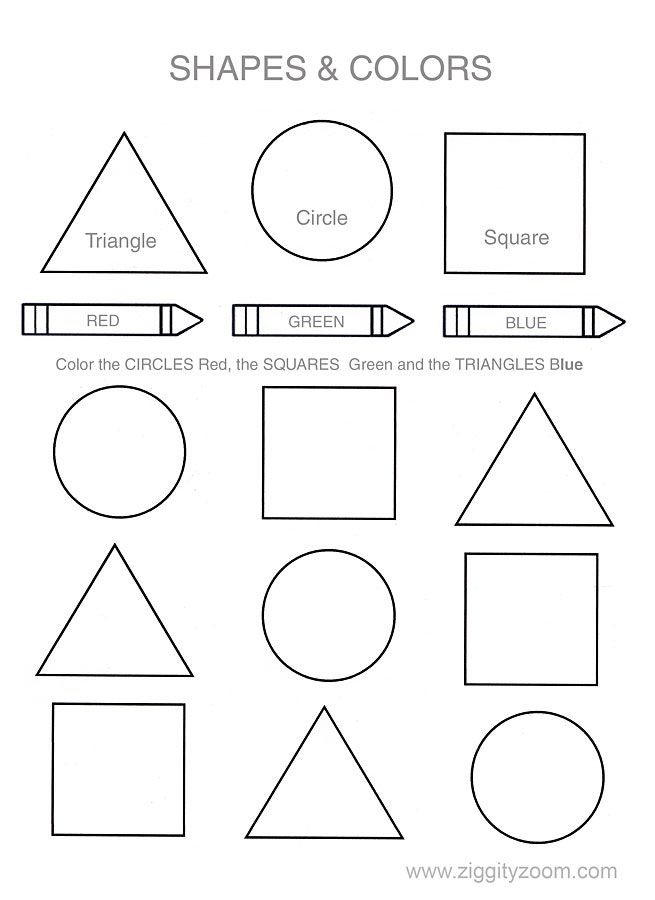 Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids.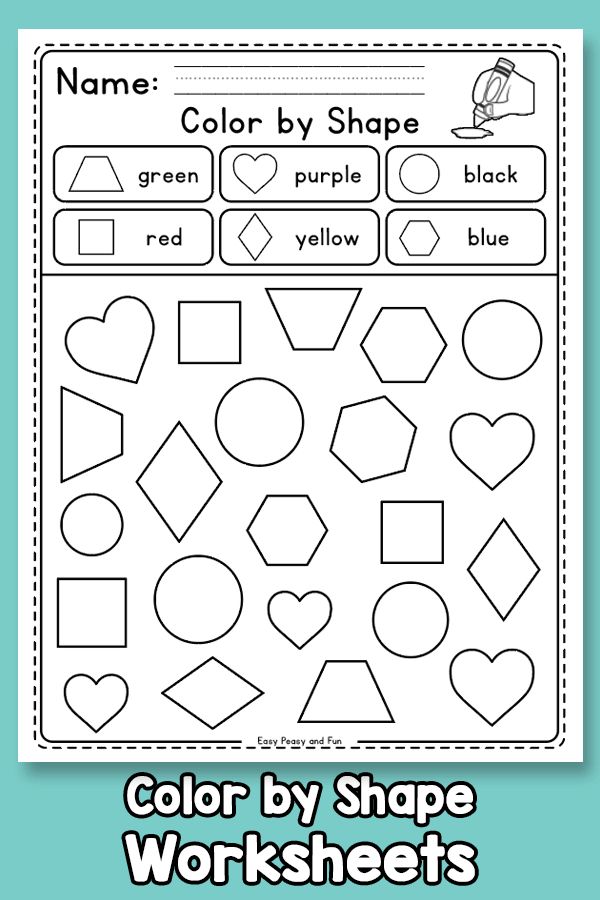 This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
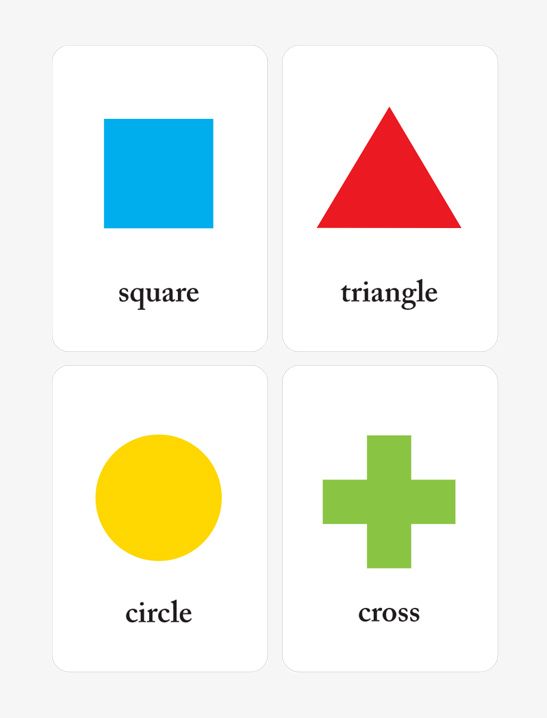
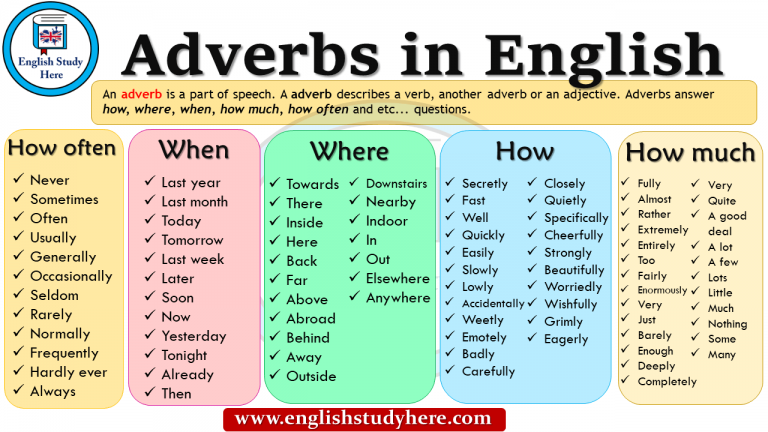
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc. Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them. Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card.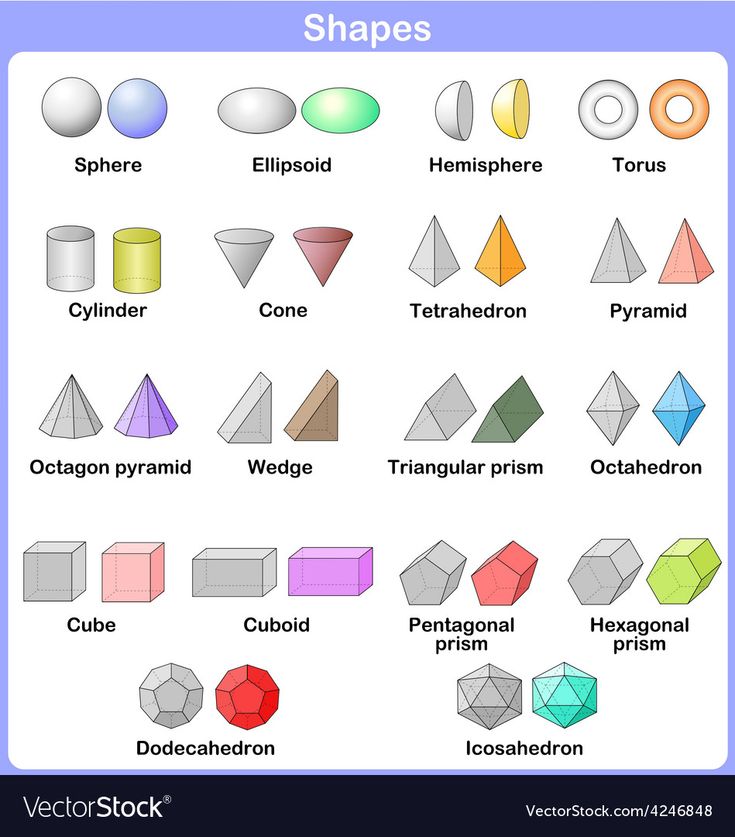 Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus.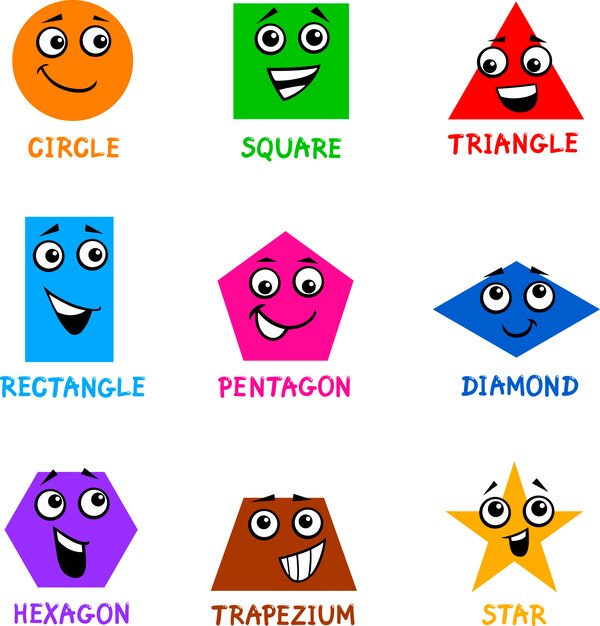 Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
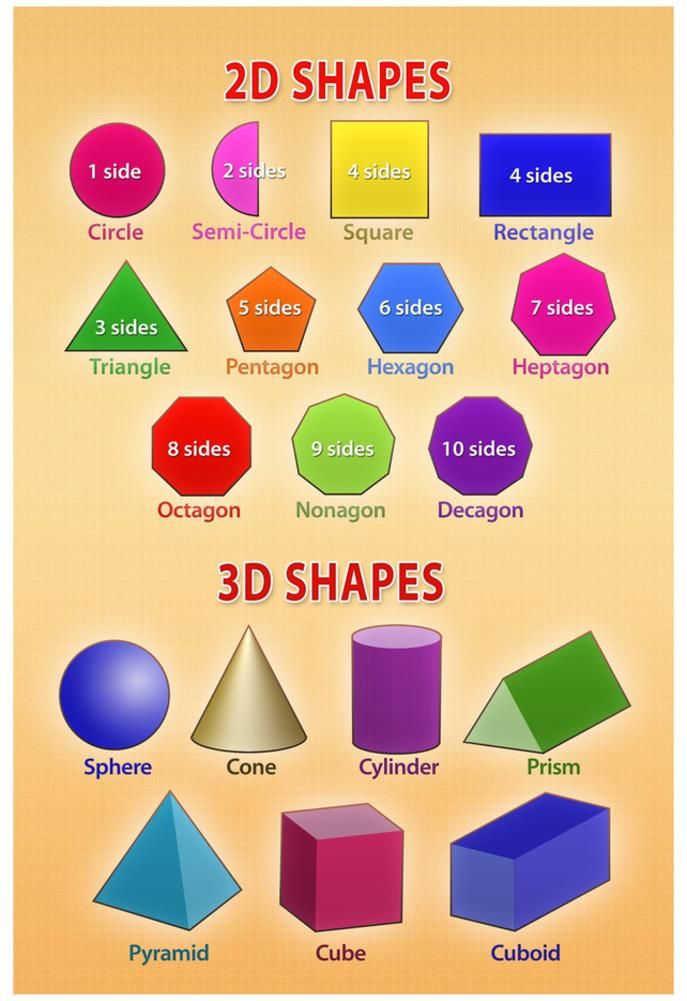 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
| 5. | Conclusion |
6. |
About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
- Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction. Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten. Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc. Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them. Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card. Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.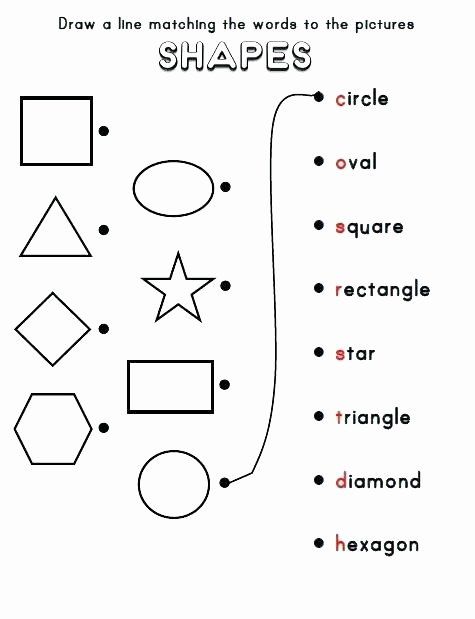
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus. Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
Moon for children - interesting facts about the Moon for children
The moon is the closest celestial body to the Earth, it is clearly visible, it shines in the night sky and constantly changes shape. It is not surprising that the moon is always of interest to children.
How to tell a child about it in a simple and correct way?
Satellite of the Earth
When asked what the Moon is, people usually answer: “Satellite of the Earth”. This is an absolutely correct answer. Just like in ordinary life, where a satellite is someone who accompanies you on your journey, the Moon follows the Earth in outer space.
It must be understood that the Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth, that is, it was formed without human intervention. The Earth has many satellites (they are launched for various scientific research, for establishing communications and television), but these are artificial satellites, they are created by people.
Where did the moon come from?
It is impossible to answer this question exactly. Scientists make several assumptions:
- it broke away from the Earth when a large cosmic body hit the Earth;
- it was an asteroid, but, flying past the Earth, it fell into its zone of attraction and became a satellite;
- The moon was formed from cosmic dust or there were several "moons" that merged into one;
- some believe that the Earth "pulled" the Moon from another planet.
One way or another, the Moon has been with us for a very long time: it was formed a little later than the planet Earth, more than 4. 5 billion years ago.
5 billion years ago.
Why doesn't the Moon move away from the Earth?
All bodies are attracted to each other; the force of attraction depends on the weight (mass) of objects and their distance relative to each other. The greater the mass, the stronger the attraction, it weakens as one body moves away from another.
The Moon has such a mass and is at such a distance from the Earth that it can neither fly away from it nor connect with it: the force of attraction is just enough to keep it in the Earth's orbit and not let go.
How far is the Moon from us?
The Moon is the closest celestial body to the Earth. The average distance from the Earth to the Moon is 380 thousand kilometers.
Of course, it is very far away. But by cosmic standards - very close.
So much so that a satellite can fly to the moon in less than 4 hours. The spacecraft flies much longer - from 3 to 5 days, but even this is not enough in comparison with the duration of flights to other space objects.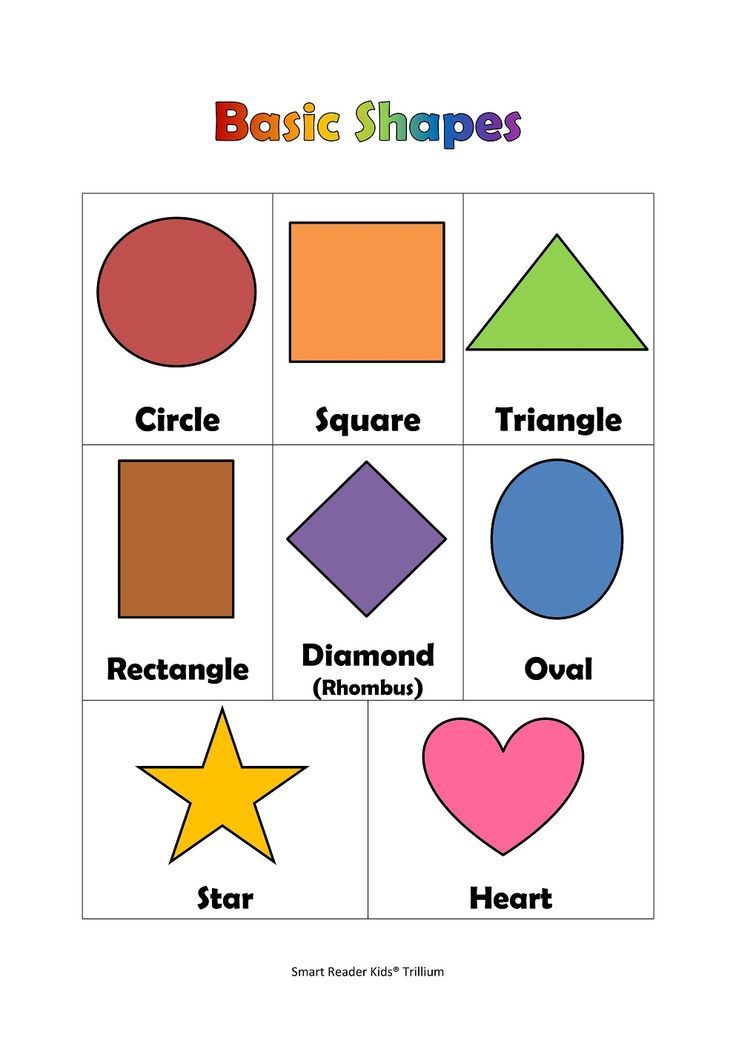
Interestingly, the Moon is gradually moving away from the Earth. Very slowly, by 3.8 centimeters a year, and it is impossible to notice it at such distances.
Size, weight and shape of the Moon
The Moon is 81 times lighter than the Earth. And 4 times smaller. That is, it is a relatively large celestial body. Therefore, researchers sometimes call the Earth and the Moon not a planet with a satellite, but a double planet.
From Earth it seems to us that the Moon is absolutely round. Indeed, its shape is close to a sphere (with a radius of 1737 km). But this is not quite the right ball, it is slightly flattened.
Climate on the Moon
The Moon has practically no atmosphere - it is, but very rarefied; it is not able to protect from sunlight and radiation or retain heat. Therefore, significant temperature fluctuations are observed here. When the Moon gets heat from the Sun, the surface temperature can reach 127 degrees Celsius. When the Sun sets, cool down to -173 degrees.
There is no "winter" or "summer" on the Moon - for this the axis of this celestial body is not inclined enough with respect to the Sun, by less than 2 degrees (the earth's axis is tilted by 23.44).
Surface of the Moon
Even without a telescope, one can see that the surface of the Moon is not uniform: there are dark and light areas on it. They were observed by ancient astronomers and, by analogy with the Earth, they gave them names: the dark areas became “seas”, and the light, more elevated ones became “continents”.
But the lunar "seas" are not at all like the earthly ones. They don't have water. Seas are depressions filled with hardened volcanic lava. They occupy about 16 percent of the entire surface of the moon. The largest "moon sea" is called the Ocean of Storms.
The entire surface of the Moon (both the seas and the continents) seems to be pitted - covered with large and small depressions, which are called craters. In shape, they are a bit like a plate: the bottom is flat, and the edges are raised. There are a huge number of them - more than 100 thousand. And new craters are constantly formed.
There are a huge number of them - more than 100 thousand. And new craters are constantly formed.
Scientists attribute their occurrence to impacts on the lunar surface of various celestial bodies: comets, asteroids, meteorite fragments.
Geography courses for children aged 6-13
The online course "Amazing Planet" introduces children to the most important places in Russia and the world in an exciting format through games, stories and riddles
learn more
The internal structure of the Moon
The Moon, like many celestial bodies, has a walnut-like structure: in the middle is the core, around it is the mantle and outside the crust.
The main element of the nucleus is iron. Inside it is solid (about 240 km), outside it is liquid (300 km).
Above the core, under the crust - a mantle about 1000 km thick. It also mainly consists of metals: magnesium, iron, silicon oxides.
The crust is the upper, thinnest layer, only about 50 km. It is covered with lunar soil: a gray porous material called regolith.
It is covered with lunar soil: a gray porous material called regolith.
Phases of the Moon
The most interesting feature of the Moon is its ability to change shape: we see it in the sky either as a ball, or as a crescent, or even as a very narrow sickle. Sometimes we don't see it at all.
The fact is that the Moon shines in the night sky not because it is able to glow like the Sun, but because sunlight is reflected from its surface.
Since during its movement in space the Moon changes its position in relation to the Sun and the Earth, it is illuminated in different ways. The shape of the part of the Moon visible from Earth is called the Phase of the Moon.
During the new moon the Moon is not visible: it is between the Earth and the Sun and the reflected light from the Earth is not visible.
During the full moon the Earth is located between the Moon and the Sun. Sunlight is reflected from the surface of the moon completely, and we can observe the correct circle.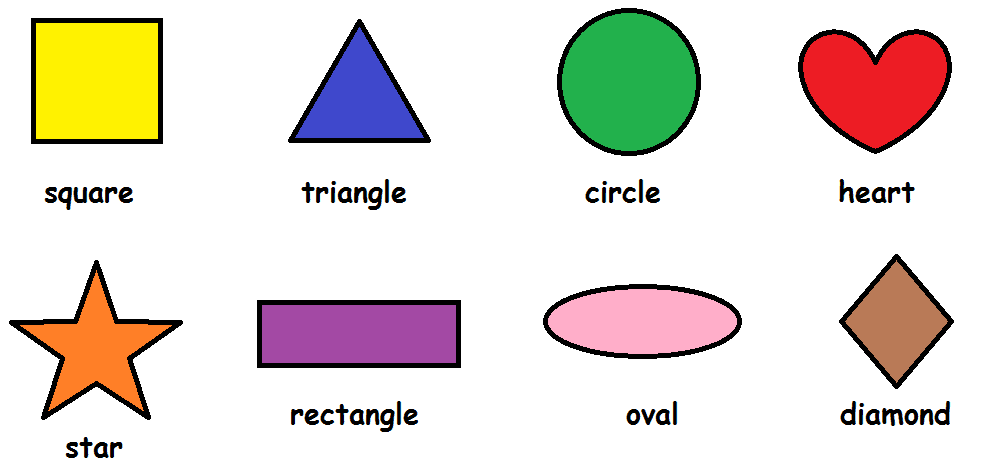
Thus, the Moon goes through several phases:
new moon - waxing moon - first quarter (when exactly half of the circle is visible, its right side) - full moon - waning moon - last quarter (half of the moon is illuminated again, but another one) , old moon. Behind her is another new moon.
There is an interesting way to determine the phase of the moon: when only a sickle is visible in the sky, you need to look in which direction it is directed: if you can put a stick on the left so that the letter “P” is obtained, then the moon is growing, and if it looks like a letter "S" is decreasing.
What is "Month"?
There is no celestial body called "moon". A month is one of the phases of the moon - its such a state when we see only a small part in the form of a crescent illuminated.
This name comes from antiquity: our ancestors called the bright part of the Moon, and the dark part of the Moon as the Moon.
But even now it is customary to call the "Moon" precisely the "round" Moon, and the luminous crescent - the "horned Moon".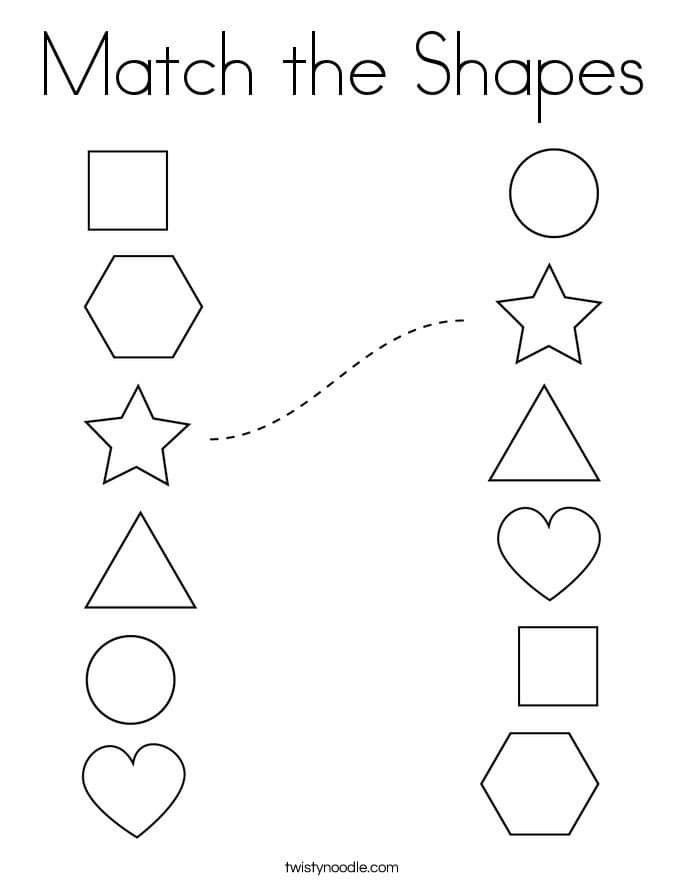
Lunar eclipses
The phenomenon when the Earth covers the sun's rays falling on the Moon is called a lunar eclipse.
It can be partial or complete.
In a partial eclipse, sunlight is not completely blocked.
But even during a total eclipse, the Moon can be observed - it changes its color to dark red. This is due to the angle at which the sun's rays hit the moon: they slide over the Earth's surface and are partially scattered in its atmosphere. We observe the same phenomenon at sunset.
Far side of the Moon
The Moon moves around the Sun together with the Earth. But at the same time, it also rotates around its axis. Why, then, do we not see it from different angles, why is there some mysterious “reverse side” that we never see?
It turns out that the time of the Moon's revolution around its axis is equal to the time of its revolution around the Earth. - 27.3 days. Therefore, the Moon is always turned to the Earth with one of its sides.
But there are no riddles in its "reverse" side for a long time. She was photographed by research vehicles back in 1959 year. A map of the surface, an atlas of the moon, and even a globe of the moon were prepared.
The reverse side is somewhat different in relief from the one we see: it has fewer "seas" and more mountains.
Exploration of the Moon
The Moon, as the closest space object to the Earth, of course, was the first to hit the lens of space explorers.
At first, people simply watched her appearance, movement, phases.
With the invention of the telescope (in 1609), a more detailed study of the lunar surface, the study of mountains and craters on it became possible. They were recorded, they were given names.
Since the middle of the 19th century, the Moon has been actively photographed and photographs have been closely studied - but even then it was just an external study.
Only after a spacecraft was launched to the Moon (this happened in 1959), it became possible to acquire really important data about it.
Samples of lunar soil were obtained, the atmosphere of the Moon was investigated, even water was found - however, only in the state of ice.
To date, the Moon is the only celestial body other than the Earth that has been visited by man. American astronaut Neil Armstrong was the first to land on the moon on July 20, 1969 years old. In total, 12 earthlings stepped on the surface of the moon.
Is there life on the moon?
Now that the Moon can be considered a fairly well-studied object, scientists are sure that life - in the form in which it exists on Earth - cannot exist on the Moon. The atmosphere is too rarefied there, the temperature fluctuations are too great - in such conditions, living organisms cannot exist.
How does the Moon affect the Earth?
For millennia, the Moon has been seen as a mysterious, formidable and incomprehensible object, and a variety of phenomena on Earth have been associated with its influence.
Most of these theories have now been debunked.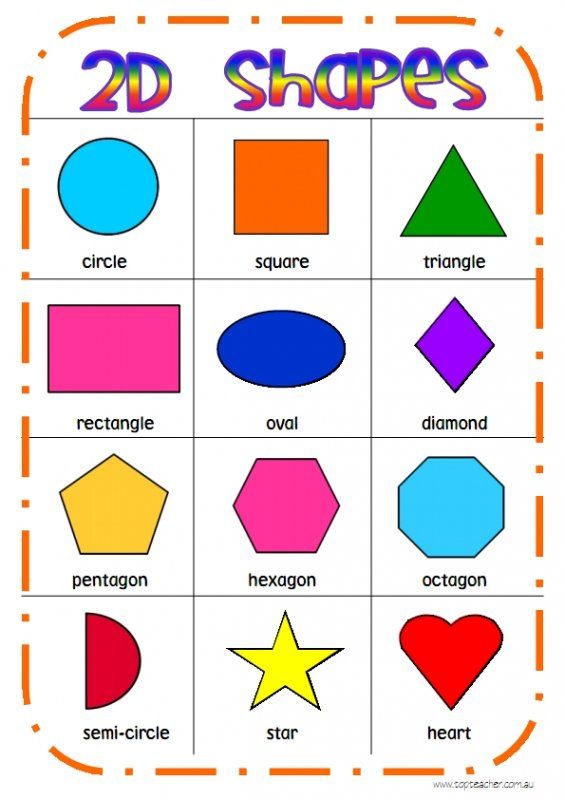 But some have been confirmed.
But some have been confirmed.
In particular, the tides in the water bodies of the Earth are explained precisely by the influence of the gravitational forces of the Moon. Moreover, the rise and fall of water is stronger in the part to which the Moon is currently closer.
The slowdown of the Earth's rotation is also associated with the influence of the Moon: every hundred years the length of the day on our planet increases (not by much, by 2.3 milliseconds, but still).
Interesting facts about the Moon
- We see the Moon as white, but in fact its surface is dark gray, almost black. It appears bright due to the reflected light of the Sun
- Man is not the first living creature to approach the Moon: steppe turtles, flies, beetles and various plants were present on board the Soviet spacecraft Zond-5, which circled the Moon on September 15, 1968.
- On the maps of the Moon, you can see the faces of people - these are schematically drawn portraits of those whose name is given to the seas, mountains and other objects on the surface.
- The force of gravity on the Moon is 6 times less than on Earth: on the lunar surface it would be very fun to jump, and lifting weights is much easier.
- Due to the lack of an atmosphere on the Moon, there are no dusks and dawns: day and night are replaced instantly.
- There are "moonquakes" on the Moon. But not as strong as on Earth.
You may be interested in:
Is your child seriously interested in space topics? You will find more fascinating facts for children about space and the planets of the solar system in our other articles.
Physics courses for children aged 7-14
We teach physics and natural sciences in an exciting game format.
Short courses adapted for the perception and enjoyment of children
learn more
Why the moon is different how to explain to a child. Why does the moon come in different shapes? What shape does the moon have in the sky
Moon phases
On a clear, cold autumn night, you go outside. The moon has just risen, a huge round orange moon. A few days later, you notice that the moon is no longer so round. A few more days pass - the moon has turned into a horned month. After two weeks, the moon disappears altogether.
The moon has just risen, a huge round orange moon. A few days later, you notice that the moon is no longer so round. A few more days pass - the moon has turned into a horned month. After two weeks, the moon disappears altogether.
Why does the moon change shape?
What happened? Why is the Sun always facing us with its round, sparkling face, while the Moon has phases? The moon passes them regularly every month, either increasing or decreasing, like a balloon that is either inflated or released from it.
In reality, of course, the Moon always remains a ball, invariably hard and rocky. What actually changes is the amount of part of the illuminated surface of the Moon that we can see.
The Moon makes one revolution around its axis in almost the same time that it makes one revolution around the Earth (in 27/3 days), so the Moon almost always faces the Sun with only one side. But it is wrong to think that eternal night reigns on one side of the moon. Although slowly, but the change of day and night is still happening.
Related materials:
Why do the Moon and the Sun change color? Description, photo and video
Why does the moon glow?
What we call moonlight is actually sunlight reflected from the gray rocky surface of the moon. The Moon moves with the Earth around the Sun and is illuminated by the Sun. As the Moon moves, we see either a larger or a smaller part of the illuminated surface of the Moon, that is, the position of the Moon in relation to the Earth changes all the time.
What we call the "phases" of the moon are the angles from which we see the illuminated part of the moon. When we see it in full, this position is called the full moon. When, after a few days, the Moon becomes "flawed", we already see part of its illuminated half (the first quarter after the full moon).
Theme of the lesson: Why is the Moon different?
Purpose: To develop the cognitive interests of students; to form an idea of the Moon as a satellite of the Earth; explain to children why people do not live on the moon using a multimedia presentation; educate children's interest in the world around them; to form friendly relations between students, the ability to understand themselves and others .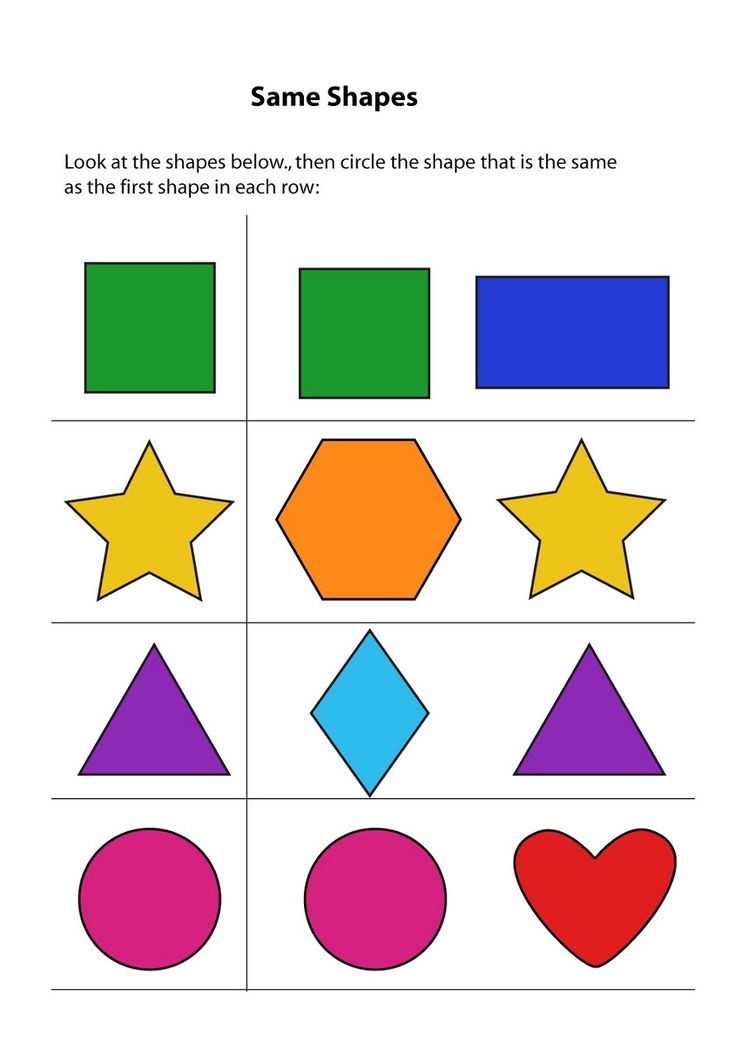
Tasks : Educational: To expand and deepen students' knowledge of the Moon - a natural satellite of the Earth.
Educational : Develop ideas about the shape, size, color of objects; speech, attention, memory, logical thinking, fine motor skills.
Educational: To cultivate love for nature and respect for the environment.
UUD : Cognitive : general educational - a conscious and arbitrary verbal statement in oral form about changes in the appearance of the moon; logical - the search for the necessary information (from the story of the teacher, parents, from their own life experience, stories, fairy tales, etc.).
Personal : understand the meaning of knowledge for a person and accept it.
Regulatory : predict the results of the level of assimilation of the studied material.
Communication : they are able to exchange opinions, listen to another student - a communication partner and a teacher.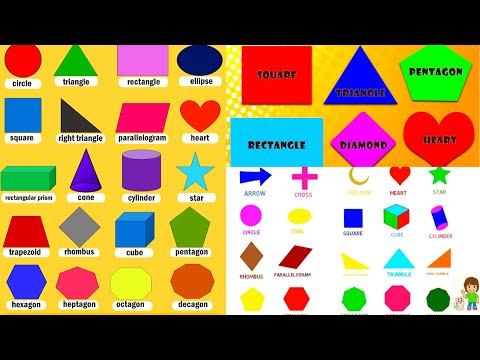
Equipment: netbooks for students; teacher's laptop, multimedia projector, interactive whiteboard, textbook, workbook.
1. Organizational moment.
2. Self-determination for learning activities.
Hello!
Today you will not be ordinary students of the 1st grade, but astronomers.
Who are astronomers? (Scientists who study the location and movement of celestial bodies)
What do astronomers use to observe the planets? (telescope, space telescope)
You and I can observe the stars with an ordinary telescope.
Raise your hand if you've ever looked through a telescope.
And scientists-astronomers have a special space telescope, which transmits data to the Earth with the help of a satellite.
For astronomers, an assistant in the study of planets is a space telescope.
What kind of assistant do we have at the lesson? (textbook)
Check if everyone has textbooks on their desks.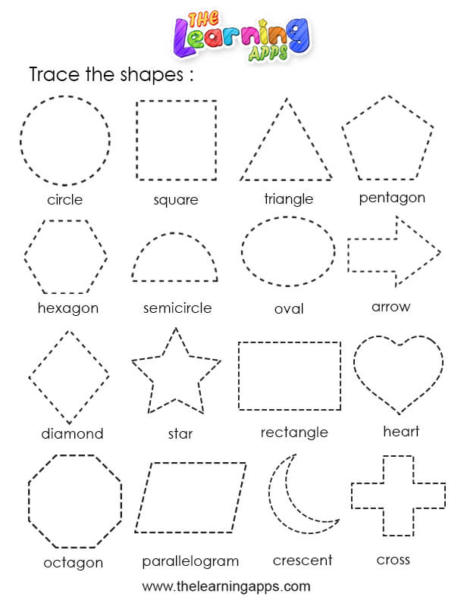
3.Updating knowledge.
Before learning something new, what do we need to do? (Repeat what we already know)
The crossword puzzle will help us with this, guessing it, we will find out the topic of the lesson.
- Well done! And today we will talk about the moon. Namely, why is the moon different?
Reading a poem to students.
If you really try,
If you really want,
You can rise to the sky
And fly to the sun.
And seriously, not pretending,
Get to know the Moon.
Take a walk along it a little
And come back home again!
At the end of the lesson, we will understand whether it is actually possible to walk on the moon.
4. Explanation of new material
Growing up, growing up,
Was horned-round became.
Circle only, miracle circle
Suddenly became horned again. (month)
Guys, are the moon and the month the same thing?
Today in the lesson we will learn why we see something in the sky the moon, then the month
Let's read the objectives of the lesson.
- Today at the lesson, guys, We
find out what the moon is.
find out what shape the moon has.
find out why the moon looks different.
find out how people study the moon.
– So, let's start. The first thing we need to know is what is the moon? Let's go into space for a moment
- Galaxy (teacher reads a poem)
The planets around the Sun dance like children:
Mercury starts their round dance,
A little further Venus floats in space.
We meet the Earth next to the Moon
And the fiery Mars that circles behind the Earth.
Behind them is Jupiter, of all the giants,
And then we see Saturn in rings.
The last three are barely distinguishable,
Gloomy and cold, but we can distinguish them:
Uranus and Neptune, and little Pluto ...
- All the planets, guys, revolve around the Sun and their imaginary axis. And some planets have moons.
- What is a satellite?
A satellite is. ..
..
- So, guys, the satellites that nature itself created and that revolve around the planets are called natural, or natural. Such a satellite for our Earth is the Moon.
- Moon around the Earth - natural satellite
- And satellites created by man are called artificial.
- Man launches them into space for certain purposes, for example: to observe the weather, for scientific research and other purposes.
- But back to the moon. The moon is a satellite. It revolves around the Earth, but does not rotate on its own axis.
Does our planet Earth move?
Planet Earth moves around its axis, i.e. rotates around itself
A) Watch the tutorial video.
Let's see how the Moon rotates around the Earth, and the Earth around its axis.
B) Practical work
2 students come to the blackboard: one is the Moon, the other is the Earth and show the rotation.
The moon revolves around the earth slowly and a lunar day is equal to two of our weeks. The moonlit night also lasts 2 of our weeks.
The moonlit night also lasts 2 of our weeks.
Work in a notebook (p. 22)
In ancient times, people did not know how the Moon works and thought that some monster swallowed it, and then a new one appeared. And so they came up with various myths, legends and fairy tales. Let's listen to one of these tales, after which you will answer the question
Did the moon have a dress?
Why the month has no dress
Decided to make a dress for a month.
The tailor took his measurements and sat down to work. At the appointed time came a month for work. At the appointed time, a month came for the dress.
And the dress is narrow and short.
- Apparently, I made a mistake, - says the tailor. And got back to work.
At the appointed time, a month came for the dress.
Again, the dress is small.
- Apparently, and now I'm wrong, - said the tailor.
And again he began to cut and sew.
For the third time the month came to the tailor.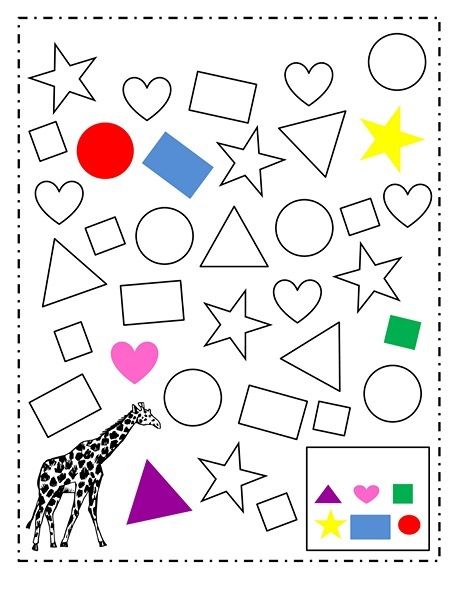
The tailor saw: a whole month is walking across the sky - not a month, but a whole moon, but twice as wide as the dress that he just sewed. What was a tailor to do? He took off running. I searched for it for a month, I searched, but I did not find it.
So a month remained without a dress.
- After being in space, the astronauts photographed the moon. Look at the screen, this is what the moon looks like in outer space.
- And what color do we see the Moon from Earth when we have the opportunity to observe it?
- Yellow Moon
– Why is that?
C) Conversation, work on the textbook.
To find out this secret, open the textbook on page 34, find the 2nd picture.
What is shown in blue? (Earth)
- What is the Earth doing? (she sleeps)
- So what part of the day is it now? (night)
- What is shown in yellow? (Moon)
- What about red? (Sun)
- What does the Sun do? (Shines on the Moon)
- What is the Moon doing? (she reflects rays and sends them to earth)
- Can the moon emit light? (no, only reflects)
- The moon itself does not emit light.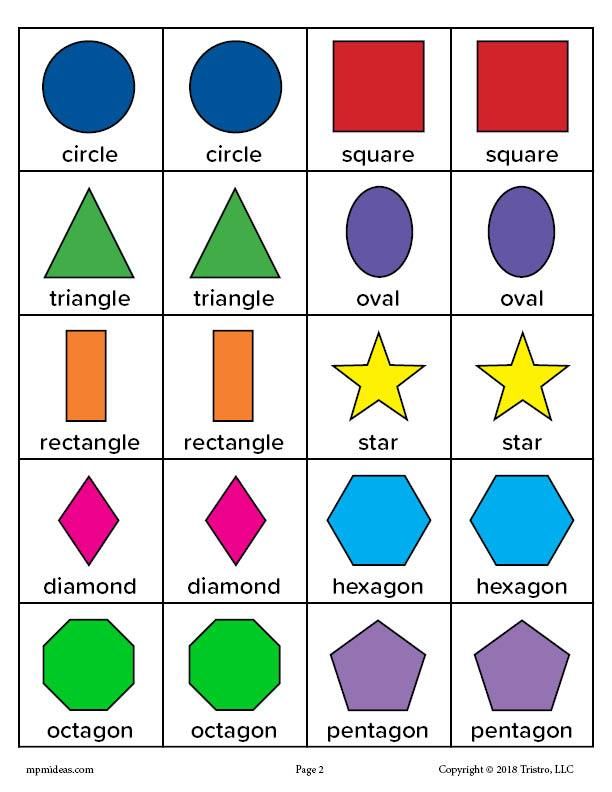 It is like a mirror reflecting the light of the sun. Since the moon itself does not shine, we can only see that part of it that is illuminated by the Sun. At different times, the Sun illuminates the Moon in different ways. Therefore, it seems to us that its form is changing.
It is like a mirror reflecting the light of the sun. Since the moon itself does not shine, we can only see that part of it that is illuminated by the Sun. At different times, the Sun illuminates the Moon in different ways. Therefore, it seems to us that its form is changing.
Moon phases
- Scientists call these shapes the phases of the moon. When the moon is between the earth and the sun, the unlit half of the moon is facing the earth, and the moon is not visible in the sky. This phase is called new moon.
After 2-3 days the moon appears in the sky in the form of a narrow sickle. This is a new month. It increases every day.
And over time, the Moon takes the form of a whole disk - this full moon. The Earth is already between the Sun and the Moon. Then the moon begins to decrease and again becomes a sickle.
Exercise for the eyes (video)
The moon looks small from Earth. But actually it is not. If you draw the Earth with a watermelon, then the Moon will be an apple (the size of an apple).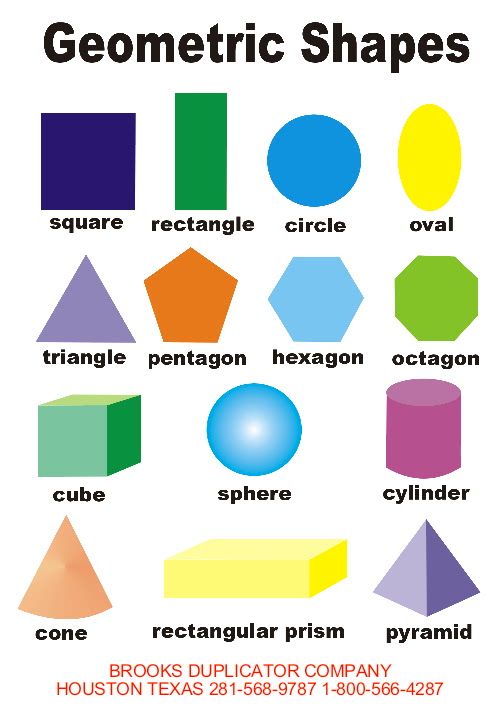 The Moon is six times smaller than the Earth. Models from plasticine.
The Moon is six times smaller than the Earth. Models from plasticine.
Craters of the Moon
- Guys, let's look through a telescope, a device that magnifies the image several times.
And through this instrument we will examine the surface of the Moon.
What do we see on this surface? Circles, dark spots, mountains.
Dark and light spots can be seen on the Moon, light ones are lunar seas.
Do they contain water? In fact, there is not a drop of water in them. Previously, people did not know this, which is why they called them seas.
Dark spots are flat areas, plains. Lunar craters are visible everywhere on the Moon, which were formed from impacts of meteorites - stones that fell from space. The entire surface of the moon is covered with a thick layer of dust, as if it had not been wiped off for many, many years. During the day it is very hot on the Moon, the temperature reaches up to + 130 g, and at night it is very cold, up to - 170 g.
American astronauts on the Moon
- The moon, guys, has always attracted people's attention. And they really wanted to study this cosmic body.
- And American astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin were the first to walk on the Moon 48 years ago.
How can one say "landed on the moon" in one word? (landed)
Their spaceship was called Apollo n -eleven. American astronauts explored the surface of the moon, planted the national flag, collected a collection of stones, took photos and filmed.
– Science was advancing, astronautics was developing, the Moon was fraught with many secrets and people came up with a lunar rover to study it. This is a robot for collecting material from space objects, on remote control. The study of the moon showed that there is neither air nor water on the moon.
Fizminutka
One-two, there is a rocket (children put their hands up)
Three-four, take off soon (arms apart)
To reach the sun (hand circle)
Astronauts need a year (takes hands on cheeks, shakes head)
But dear, we are not afraid (arms to the sides, body tilts left and right)
Each of us is an athlete (bend arms at the elbows)
Flying over the earth (arms apart)
Say hello to her (raise hands and wave)
Reading the textbook output.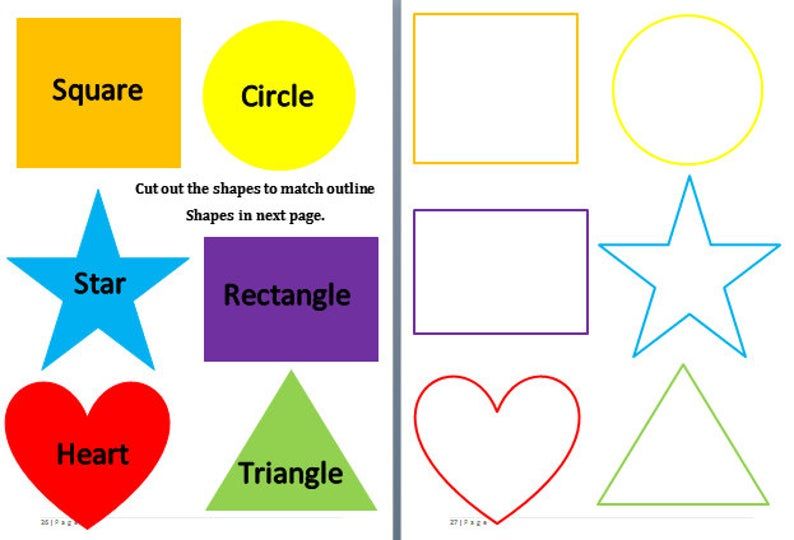
6. Primary fastening. Job on macbook
We must distribute who lives on the planet Earth and who can live on the Moon.
7. Reflection.
1.-What is the Moon?
2.-What shape does the moon have?
3-how do people study the moon?
8 . Testing knowledge with self-test in pairs.
Now we will check who is ready to become a real astronaut.
Place the test papers in front of you.
I am reading a sentence, if it is correct, then you put +, if not, then the sign -.
The Moon is larger than the Earth. (+)
The moon does not emit light, but reflects the light of the sun.
(+)
There is air and water on the moon. (-)
The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth. (+)
People live on the moon. (-)
The moon revolves around the sun.(-)
The moon is very hot during the day and very cold at night.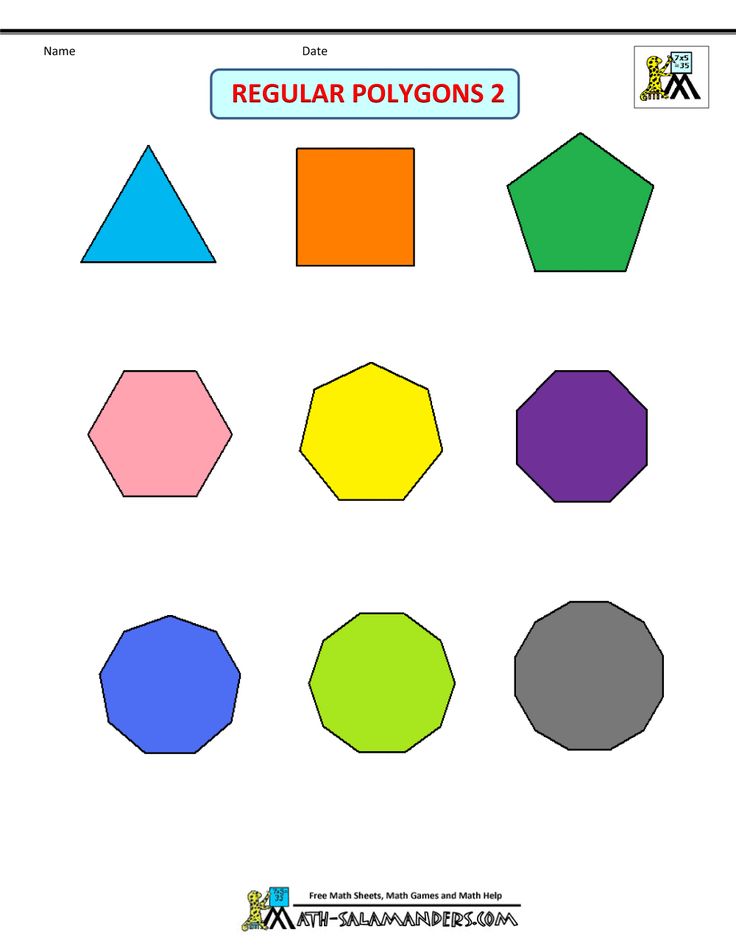
(-)
There is a lot of water in the lunar seas.(-)
1 lunar day is equal to one of our days. (-)
From Earth, people always see the round shape of the Moon.
(+)
Now swap jobs with a neighbor and take a red pencil, start checking.
What interesting things did you learn at the lesson?
What can you talk about at home?
Evaluation using emoticons.
To use the preview of the presentations, create a Google account (account) and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Why is the moon different? Textbook: The world around. 1 class. Pleshakov A.A. Teacher: Antipova I.I. Moscow, 2016
Why is the Moon different?
The cycle of lunar phases begins with the young moon. This happens when the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun. The young moon is not visible. Then the side of the Moon facing the Earth begins to be illuminated by the Sun. The illuminated part looks like a thin, narrow slice of a circle. It is called the waxing moon.
It is called the waxing moon.
The solar part of the Moon grows rapidly and reaches a semicircle. This is called the first quarter. Then the surface of the moon is less and less illuminated and reaches the last quarter. So the cycle ends and is replaced by a new, young, growing moon. A full cycle from one young moon to another takes 29.5 days.
The moon itself does not emit light, it reflects the light of the Sun like a mirror. Secret of the Moon. How it shines..
What is a satellite? A satellite is a celestial body that moves around a larger body. The natural satellites of the planets are their natural satellites, that is, those that are not created by man.
The Earth is 6 times larger than the Moon. The moon is a satellite of the earth. Compare the sizes of the Earth and the Moon.
Rotation of the Moon around the Earth. The moon moves around the earth and circles it once a month.
Earth is separated from the Moon by a distance of 384,000 kilometers.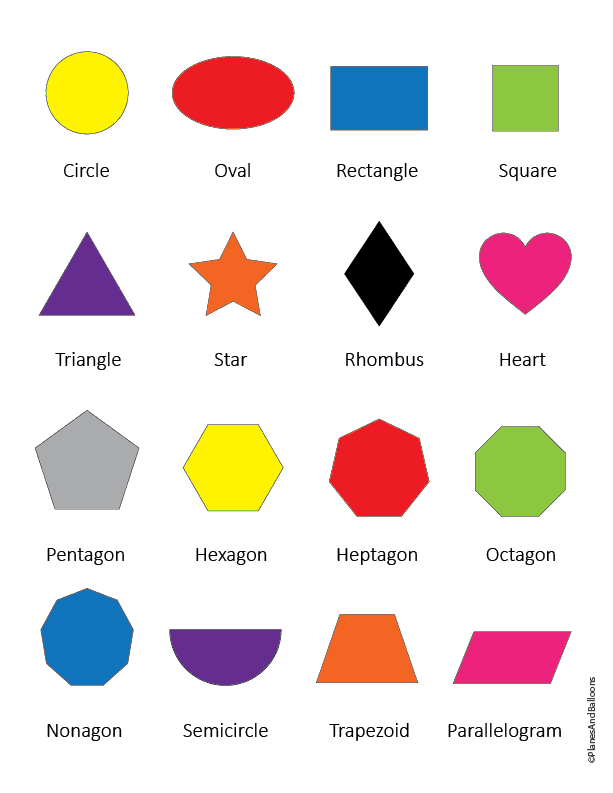 On a space rocket, this distance can be overcome in 2-3 days.
On a space rocket, this distance can be overcome in 2-3 days.
How do scientists study the moon?
There are dark and light spots on the Moon. The bright spots are lunar seas, but there is no water in them. Dark spots are flat areas. Lunar craters are visible on the Moon. They were formed from impacts of meteorites - stones that fell from space. What do we see on the surface of the moon when we look through a telescope?
Lunar seas. Grayish spots on the moon in the old days, people considered the seas. In these "seas" there is not a drop of water. The lunar "seas" are deep depressions covered with hardened volcanic mass. The color of this mass is darker than the surrounding stones, so it is clearly visible from the Earth. Although scientists now know that there are no seas on the Moon, they have decided not to change the names on the map of this planet.
Therefore, one can find there the Ocean of Storms, the Sea of Clouds, the Sea of Rains and many other seas.
Mountain regions of the Moon. The bright parts of the Moon are its mountainous regions. There are high mountain ranges on the Moon and many ring mountains - craters. Craters are large pits surrounded by hills. Some of these craters were formed when meteorites fell on the Moon. The largest craters were formed during volcanic eruptions.
Lunokhod. An automatic apparatus, controlled from the Earth by radio, which was sent to the Moon.
Why don't people live on the Moon? There is no air on the moon. There is no grass or trees here either. Around one dust and stone desert.
The day lasts for two weeks, then the night lasts for two weeks. During such a long day, the surface of the moon has time to heat up to a temperature of + 130 degrees. When night falls, the stones quickly cool down and the frost reaches a temperature of 170 degrees.
1. If you want to jump, keep in mind that you will jump 6 times higher than on Earth, and you will fall much more slowly.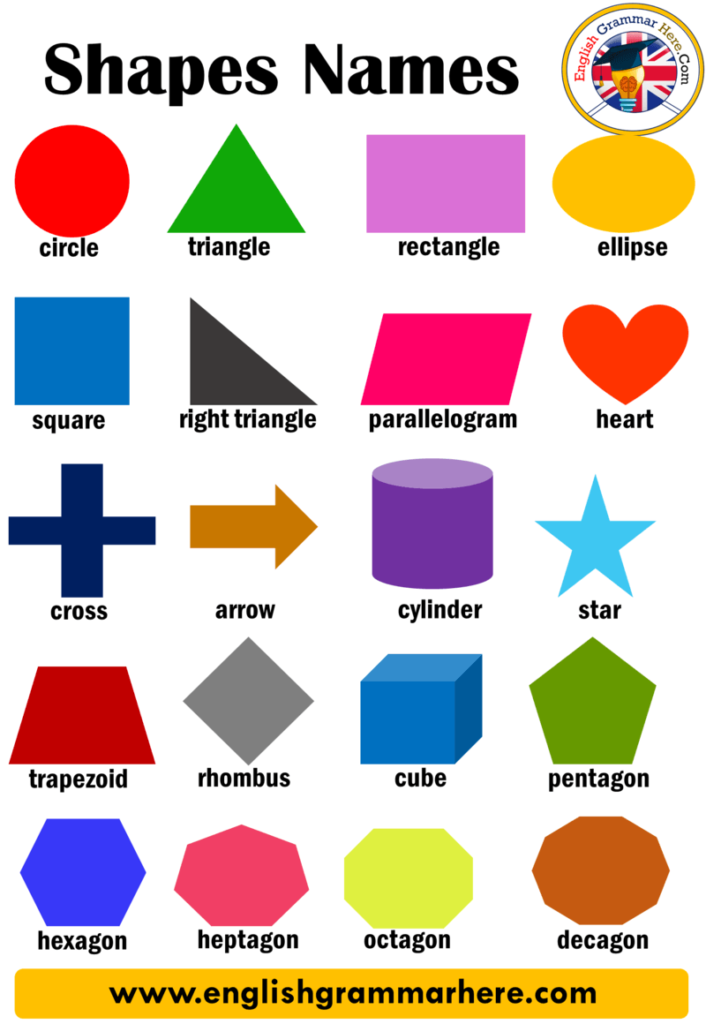 The force of gravity on the moon is 6 times less. 2. If you go for a walk, look under your feet. The entire surface is littered with rocks that fall from space. 3. Don't forget to take a watch with a calendar. On the Moon, one of our days lasts 2 of our weeks. 4. You won't need an umbrella: it doesn't rain on the moon. There is no water at all, no clouds, fogs and rainbows. Rains only meteoritic and stone. 5. Do not forget that you can only talk with the help of Radio Transmitters. There are no sounds on the moon. This is because there is no atmosphere. 6. Think about how you will breathe? After all, there is no air on the moon. 7. Think about how you dress, because during the day the surface of the moon heats up to +130 degrees, and at night it cools down to -170 degrees. A few tips for flying to the moon
The force of gravity on the moon is 6 times less. 2. If you go for a walk, look under your feet. The entire surface is littered with rocks that fall from space. 3. Don't forget to take a watch with a calendar. On the Moon, one of our days lasts 2 of our weeks. 4. You won't need an umbrella: it doesn't rain on the moon. There is no water at all, no clouds, fogs and rainbows. Rains only meteoritic and stone. 5. Do not forget that you can only talk with the help of Radio Transmitters. There are no sounds on the moon. This is because there is no atmosphere. 6. Think about how you will breathe? After all, there is no air on the moon. 7. Think about how you dress, because during the day the surface of the moon heats up to +130 degrees, and at night it cools down to -170 degrees. A few tips for flying to the moon
Thank you for your attention!!
The moon has several main phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon, last quarter. Why is the moon different every day (or rather night)? Why, when she is very "thin", is she visible only a few hours before dawn or after sunset? Does it shine all night on a full moon? The answers to these questions lie in the relative position of the Earth, Moon and Sun.
The Earth revolves around the fixed Sun, and the Moon revolves around the Earth. Let's start with the time when the Moon is not visible to us (phase new moon -1). At this time, the moon is facing us with its unlit side. It is during this phase that we can observe (though very rarely) solar eclipses .
In 2-3 days after sunset we can see a thin crescent in the still bright part of the sky with its "belly" facing the Sun. If you substitute a wand to the sickle, you get the letter "P" - born or early. This is a new month. Astronomers most of all like to "catch" this particular phase of the moon. After another 4-5 days, we can already observe half of the moon. This is the first quarter(2). At this time, the Moon is facing us both with its illuminated and unlit sides.
Approximately 7 days after the first quarter, the Moon enters the full moon phase (3). How many mysterious properties were attributed to the full moon by astrologers, magicians and wizards in ancient times! And how many poets sang it in their poems! At this time, the Moon and the Sun are on opposite sides of the Earth.
 And it is at this time that we can observe a lunar eclipse from the Earth . In this phase, the Moon is visible all night.
And it is at this time that we can observe a lunar eclipse from the Earth . In this phase, the Moon is visible all night. After another 7 days, the Moon enters a phase called the last quarter (4). We again see the half of the Moon, but already facing the other way, but facing the Sun anyway. After 4-5 days at dawn, you can see a thin crescent moon in the form of the letter "c" - the old one. And in 2-3 days the moon will not be visible again.
Some terms and concepts on this topic:
Distance from the Earth to the Moon is 384,400 km. Full turn The Moon makes around its axis and around the Earth in 29.5 Earth days, so we always see only one side of the Moon.
Synodic month (lunar) - the period of complete change of lunar phases (between two successive new moons). Approximately equal to 29.5 Earth days.
Sidereal month (star) is the time it takes for the moon to complete one revolution around the earth relative to the stars.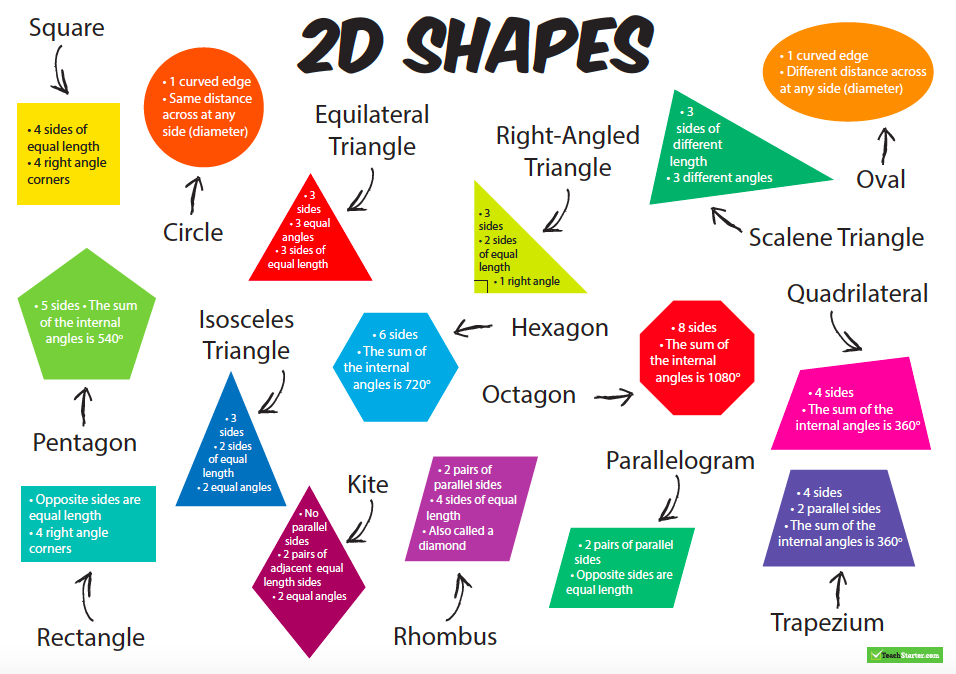 Approximately equal to 27.3 Earth days
Approximately equal to 27.3 Earth days
Terminator - the line separating the dark part of the visible disk of the planet from the light one.
Ash Light - the light of the "dark" side of the moon. The Earth, reflecting the light of the Sun, illuminates the Moon, and she, in turn, sends this light to us, as if returning it. It is very well visible at a young month - a thin crescent shines very brightly, and behind it the faint outlines of the disk of the Moon are visible
Theme of the lesson: Why is the Moon different?
Purpose: To develop the cognitive interests of students; to form an idea of the Moon as a satellite of the Earth; explain to children why people do not live on the moon using a multimedia presentation; educate children's interest in the world around them; to form friendly relations between students, the ability to understand themselves and others
Tasks : Educational: To expand and deepen students' knowledge of the Moon, a natural satellite of the Earth.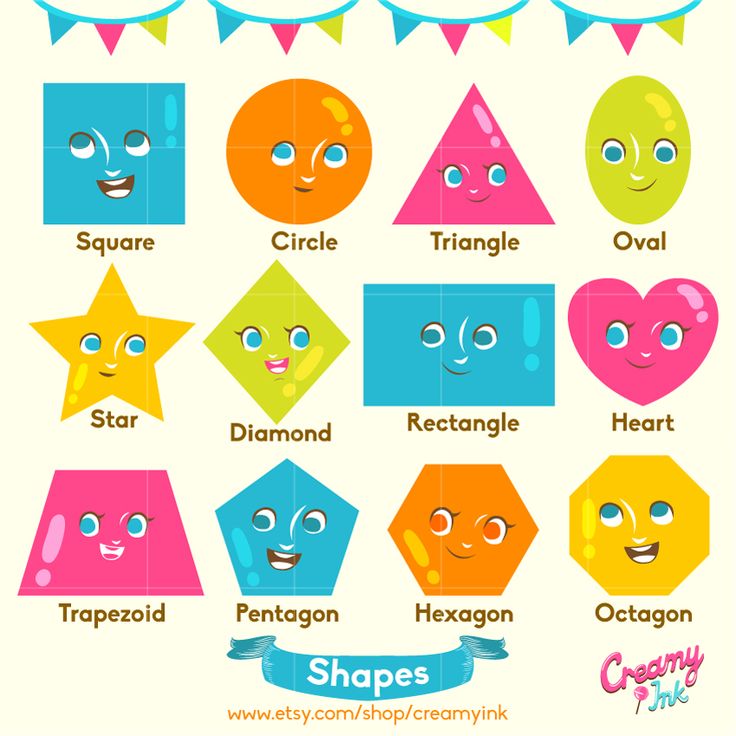
Educational : Develop ideas about the shape, size, color of objects; speech, attention, memory, logical thinking, fine motor skills.
Educational: To cultivate love for nature and respect for the environment.
UUD : Cognitive : general educational - conscious and arbitrary speech statement in oral form about changes in the appearance of the moon; logical - the search for the necessary information (from the story of the teacher, parents, from their own life experience, stories, fairy tales, etc.).
Personal : understand the meaning of knowledge for a person and accept it.
Regulatory : predict the results of the level of assimilation of the studied material.
Communication : able to exchange opinions, listen to another student - communication partner and teacher.
Equipment: Proclass , ball, moon globe, mirror, flashlight, textbook, workbook, two motorcycle helmets
1. Organizational moment. Greetings.
Organizational moment. Greetings.
— Nana - in - in the yard is spring
Lo- lolo - we are warm from the sun
- Rub your palms. Did you feel warm? (Yes).
— Touch your palms to each other and pass it.
— May you feel warm and comfortable during the lesson.
— And now to work!
2. Updating knowledge
game "Tell me a word" (the teacher says a sentence, while throwing the ball, the one who caught and answers)
The Sun is a huge flaming ………………..(ball)
The Sun is the nearest to the Earth …………………..(star)
The Sun creates for us ………………… ………………(day)
The sun seems to us a small circle, because it is ………….(far from the Earth)
Stars are huge flaming ………………(balls)
Stars are different from each other by……………(color, size)
There are a lot of stars in the sky and people united them into ……………(constellations)
3. Self-determination for activity
P Ant looked at the sky and saw something else. Guess the riddle and find out what the Ant saw? (slide 1 ).
Guess the riddle and find out what the Ant saw? (slide 1 ).
Students: (Moon, Moon).
Which one of you has seen the moon?
Draw on netbooks with the Moon Paint program. (students use netbooks)
Why is it so different for everyone?
Can you guess what the lesson will be about? (children's answers)
Do you want to know this? (slide 2)
- And for this we will go on a space journey.
— What will we fly on? (children's answers) (slide 3)
— What can we be called? (children's answers)
-Before you go to journey, I need to find out if our team is ready to fly.
Fastened seat belts. Back straight.
- We start the countdown.
- And from what date will we start the countdown? (children's answers)
Chorus: 10-9-8-7-6-5-4-3-2-1-start!
4. Explanation of new material
If you really try,
If you really want to,
You can rise to the sky
And fly to the sun.
And seriously, not pretending,
Get to know the Moon.
Take a walk along it a little
And come back home again! (slide 4)
-B from us and approached the moon.
-Ever since man appeared on Earth, the Moon has been a mystery to him. In ancient times, people worshiped the moon, considering her the goddess of the night. Today we know much more about what it is.
- So what is the Moon? (children's answers), (slide 5)
— The moon is not a star or a planet. The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth. Because nature created. It rotates around the Earth and around its own axis. But it spins slower. (slide 6). The Moon is the closest celestial body to Earth. However, when a rocket is launched from the cosmodrome to the moon, scientists are waiting for 3 days and 3 nights. That's how long it takes a spacecraft to get to the moon. (3 days - 3 days and 3 nights) - Even in ancient times, people noticed that the moon changes its shape all the time.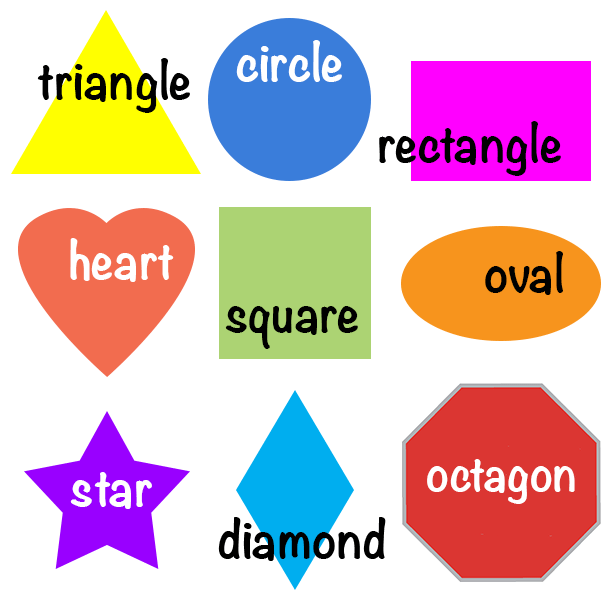 Either it looks like a round plate, or it looks like a sickle, which they called the Moon. People could not explain this phenomenon and invented fairy tales, legends, myths. (slide 7)
Either it looks like a round plate, or it looks like a sickle, which they called the Moon. People could not explain this phenomenon and invented fairy tales, legends, myths. (slide 7)
— Can you and I explain why the Moon changes its appearance?
Teacher concludes:
- To explain this, you need to know one secret of the moon. The secret is in how she shines. The sun is a flaming ball, it itself emits light, and the moon ... Let's find the drawing in the textbook on page 34 (below) and find out what is the secret of the moon, how it shines.
Questions: - What is depicted in blue? (Earth)
- What does the Earth do? (she sleeps)
— So what part of the day is it now? (night)
- What is shown in yellow? (Moon)
- What about red? (Sun)
- What does the Sun do? (Shines on the Moon)
- What is the Moon doing? (she reflects the rays and sends them to the earth)
- Can the moon emit light? (no, only reflects)
Experience projected onto the interactive whiteboard using a document camera:
— "Now I will show you how the moon works (directs the sun's beam onto the globe with the help of a mirror). "
"
- Does the mirror itself glow? (no)
- And now, when I catch a ray of the Sun with it? What is this light? (sunbeam reflection)
- So we learned the secret of the moon. Since it does not shine, we can only see the part of it that is illuminated by the Sun. (slide 8)
In ancient times, people did not know how the Moon works and thought that some monster swallowed it, and then a new one appeared. But we know that this is not so! (slide 9,10)
From the Earth, the Moon seems small. But actually it is not. If you draw the Earth with a watermelon, then the Moon will be an apple (the size of an apple). The Moon is six times smaller than the Earth. (slide 11)
Sometimes the moon seems to have a face. This impression is created by mountains that cast a shadow on its surface. And the bright spots are the lunar seas. But in fact, there is not a drop of water in these seas. But people didn't know this before. That is why they are called seas. (slide 12,13,14)
- The flight was long and we had to warm up.
5.
The astronaut suddenly stretched.
Bending down once, bending down twice,
Spread his arms to the side
I couldn't find my helmet.
To get a helmet for him
You need to stand on your toes,
(stretched, sat down.) (slide 15)
6. Continuation of work on the topic of the lesson
— Who are these mysterious guests? (Two boys in motorcycle helmets enter)
Astronauts: We are American astronauts. (slide 16)
A: We were the first to go to the moon.
A: I'm Armstrong.
A: I'm Aldrin.
A: We came to warn you that during the day on the moon the heat is up to 130 degrees,
A: And at night it's 170 degrees below zero.
Teacher: Why can't you see anything?
A: The entire surface of the moon is covered with a thick layer of dust. The moon looks like it hasn't been dusted for years.
A: Be very careful! Look under your feet, as there are many stones on the moon.
A: Yes, and only talk on the radiotelephone (because there is no air on the moon and you still can't hear each other). Even meteorites on the moon fall silently.
A: And don't take big steps or you'll bounce a lot.
A: There are no flowers, no trees, no rainbows on the Moon, only sand and stones.
A: And, most importantly, there is no water, no air, no atmosphere on the Moon. There is neither rain nor snow.
A: No clouds, no fogs, only black sky around. True, there are still rains - meteorite, stone.
A: Man cannot live on the Moon. Goodbye, guys!
7. Work in the workbook
Let's work in the logbooks
(p. 22) complete the 1st task (slide 17)
B from us and it's time to go back.
8. Fastening
— But what is it, nothing starts? (does not work)
- So this is our hero!
-Which literary hero went to the moon? (children's answers)
-Who wrote this book? (showing the book)
- He left a message for each of you. And until we do, we can't go back. (slide 18)
And until we do, we can't go back. (slide 18)
-Set up your visual apparatus;
9. Visual gymnastics "Stargazer" (slide 20-24 )
Ready for the last task!
-O answering questions with the help of a program for monitoring the quality of knowledge Proclass (students use the remote control to select the correct answer and press the appropriate button in the ask question mode)
— I say a sentence if you agree "answer A", if not "answer B". With every offer we are closer to home. (slide 25-28 )
1. There is no air on the Moon (+)
2. The moon glows (-)
3. There is a lot of water in the Lunar seas (-)
4 . Life is possible on the moon (-)
- Completed the task and l let's go home. (children pretend to fly)
— Here we are at home.
10. Reflection
— Belts are fastened. We sit quietly. I turn on the brakes.
— How did the flight go?
— The flight went well! (in chorus)
— What are you talking about at home?
— What was the most interesting thing you learned?
11.