Dra reading levels assessment
Understanding Your Child's DRA Reading Level
The Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) is an individually administered assessment of a child’s reading capabilities. It is a tool to be used by instructors to identify a students reading level, accuracy, fluency, and comprehension. Once levels are identified, an instructor can use this information for instructional planning purposes.
Want even more book and reading ideas? Sign up for our Scholastic Parents newsletter.
DRA Testing
The DRA test is traditionally administered on an annual or semi-annual basis. The test measures nine categories of reading behavior and six types of errors. It was developed in 1986 (and revised in both 2000 and 2003) by a committee of educators and is intended to evaluate certain aspects of your child’s reading level.
How DRA Levels and Testing Work Together
Tasks measured by the DRA test are divided into several skill sets. Rhyming, alliteration, segmentation, and phonemic awareness are tested in the phonemic awareness section. Letter naming, word-list reading, spelling, decoding, analogies, structural analysis, and syllabication are tested in the alphabetic principle/phonics portions. Oral reading fluency or words per minute for contextual reading are tested under fluency. Vocabulary, comprehension, and reading engagement skills are also measured in the test.
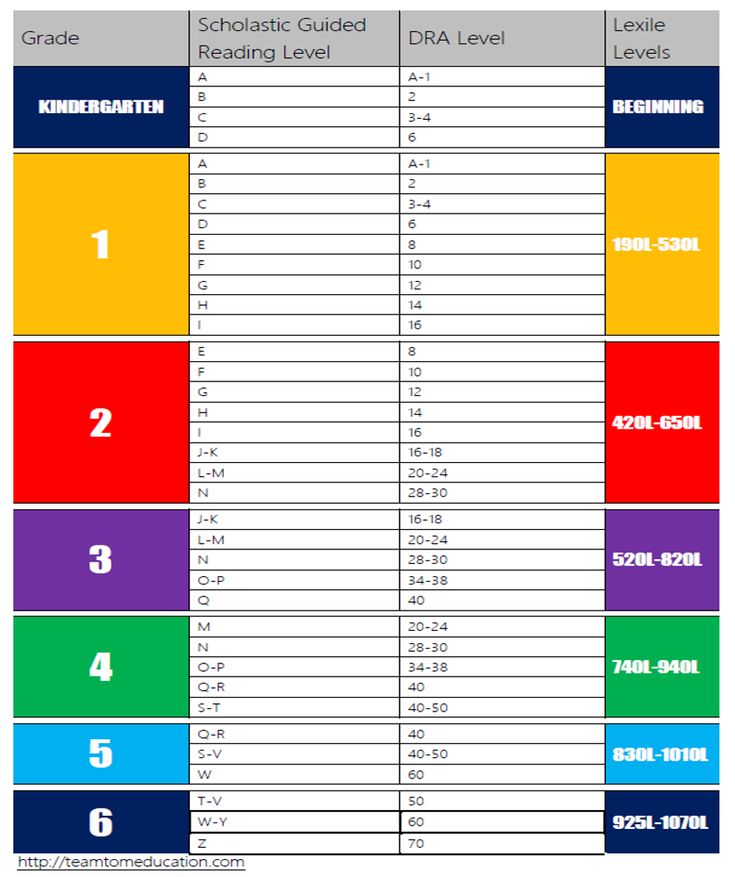
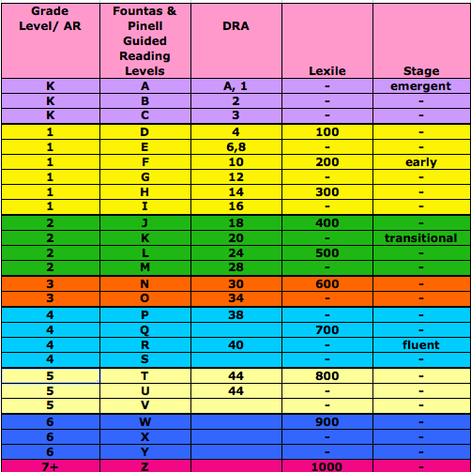
After the test is evaluated and scored, your child is assigned a numeric (or alphanumeric for very early readers) DRA level A1 through 80. Children with stronger reading abilities yield higher numbers. Teachers are easily able to give children books they can read by choosing a text with the corresponding DRA level.
How to Find Books on Your Child’s Level
Once your teacher gives you your child’s level, you can search for books at a particular DRA level on Scholastic’s Book Wizard. By providing your child with books on his level at home, you are ensuring reading advancement and success with materials that will not cause your child stress or discouragement.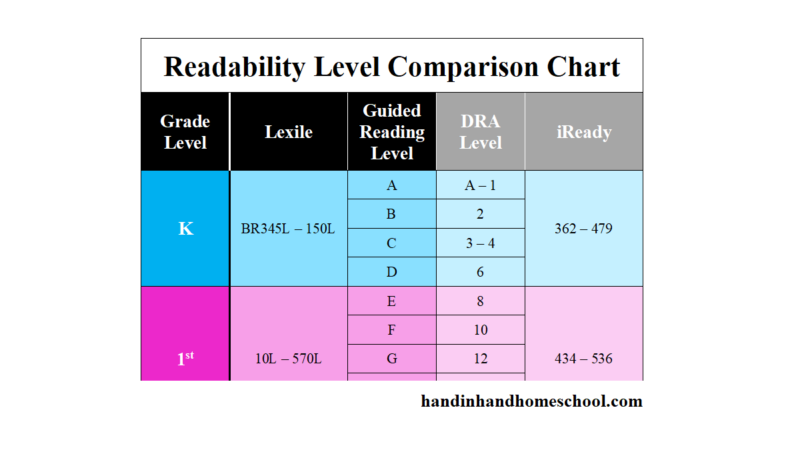
Raise a reader by getting the best book recommendations, reading tips, and discounts delivered straight to your inbox.
PLEASE ENTER A VALID EMAIL ADDRESS.
PLEASE SELECT A NEWSLETTER OPTION.
Preschool View Sample
Elementary School View Sample
Privacy Policy
<div><h3>Thanks for signing up! Look out for a confirmation email from us.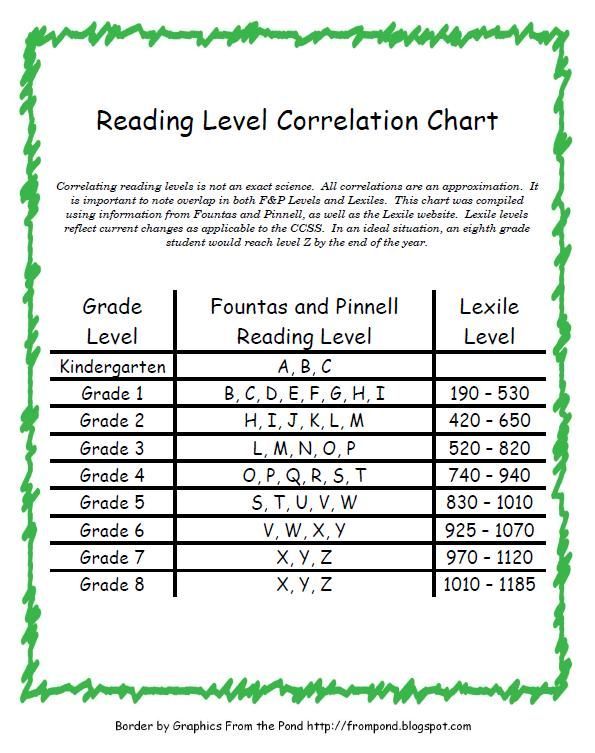 </h3><h4>Want to connect now? Find us on social media!</h4><h3><a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.facebook.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/facebook.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
</h3><h4>Want to connect now? Find us on social media!</h4><h3><a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.facebook.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/facebook.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
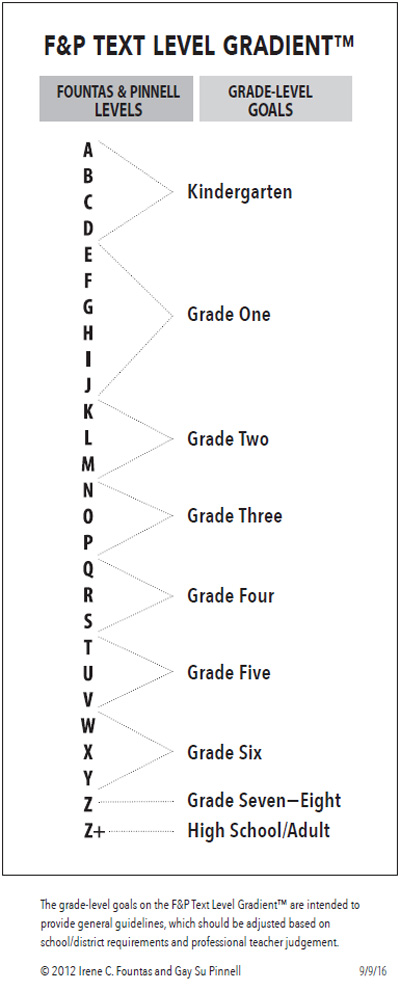
Developmental Reading Assessment, Third Edition
DRA™3
- Joetta Beaver
- Mark Carter
- DRA offers educators the tools they need to observe and document student reading level and helps inform instructional practice.
 Further information regarding remote administration of this assessment
Further information regarding remote administration of this assessment
Choose from our products
Sort by
Filter by
- Answer Sheets (10) Directions for Administering (10) Guides (10) Manuals (10) Other Materials (10) Record Forms (10) Stimulus Books (10) Test Booklets (10)
- Subscriptions (10)
- Digital (10) Hand/Manual Scoring (10)
- English (10)
- In-person (10) Live webinar (10)
Overview
- Qualification level:
-
A
Qualification Level
Level A
This approval level enables you to buy our assessments that require no professional degree, accreditation, organization membership, or license/certificate.

Level B
This approval level enables you to buy our assessments requiring A or B qualification levels.
Level C
This approval level enables you to buy all our assessments.
- Scoring options:
-
Manual or online
- System requirements:
-
DRA3 can be used on a laptop, desktop, or tablet. Mac recommendations: Safari or Chrome. PC recommendations: Firefox or Internet Explorer.
Product Details
| The DRA3 combines three decades of teacher input with the latest research to validate the premier reading assessment of individual student reading behaviors in the classroom. BenefitsDRA3 offers:
With DRA3, teachers can:
Features
DRA3's consolidated digital offering:
DRA3's instructional guidance helps reading teachers interpret DRA3 scores and use them to improve classroom instruction by providing:
|
|
Resources
| The following resources are available. | |
DRA3 Infographics | |
DRA3 Reading Lists | |
DRA3 Common Core Alignment | |
Webinars
| The following events are available for DRA-3. |
Reading Development Assessment (DRA) (key tips)
Reading Development Assessment (DRA) is an assessment conducted to assess a child's reading ability from kindergarten to 8th grade. This test is administered individually to students.
DRA is a tool that helps teachers assess children's reading abilities. It also helps teachers determine the next step to take to improve a child's reading ability.
It also helps teachers determine the next step to take to improve a child's reading ability.
This assessment is usually given to students at least twice a year and goes a long way in improving children's reading ability, making them better readers.
It also allows them to read with correct intonation and punctuation.
In September 2009, all priority school districts (PSDs) were required to use DRA 2 districts for grades 1-3.
"Each school year beginning on or after st Effective July 2011, each local and regional board of education of a priority school district must require schools under its jurisdiction to assess the reading level of students enrolled in kindergarten in end of the school year, while students in grades 1-3 inclusive, at the beginning, middle and end of the school year.
Connecticut General Bylaws (CGS) Section 10-265g (b)
Students in grades 1-3 are generally assessed in September, and all kindergarten students are assessed at the end of the school year.
If a student is found to be handicapped, this must be based solely on measures established by the Board of Education.
The reason the rules were put in place was to make sure that any student who could not read well could be easily identified and errors easily corrected. It is difficult to get a child to read after 3rd grade, so it is easier to teach a child to read early in life.
The Reading Development Assessment (DRA) was adopted as a standardized test to help identify students with reading problems on December 1, 1999.
Contents
Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
Benefits of Developmental Reading Assessment
- DRA helps teachers know students' reading levels.
- This can help the teacher to better observe the students.
- Teachers use DRA to record and evaluate student work.
- It helps teachers to learn about students' weaknesses and how the student can be helped.

- Students can be assessed individually as they are given the opportunity to read different texts and say what they could learn from the texts.
- It also helps the teacher figure out where the growth has taken place.
- It measures every aspect of students' reading skills; reading accuracy, fluency and comprehension.
- DRA performs a thorough diagnosis.
- This helps the teacher know the next line of action.
Read this: Academic probation - all you need to know
How can parents help?
- Parents can help improve their child(ren's) reading ability by reading to and with them on a regular basis.
- They should spend time listening to their child read on their own.
- When a child reads a book, parents should talk about the book with their child and ask for a summary of the story.
- Your child needs to learn how to use facial expressions when reading.
 This will make it easy to play any scene.
This will make it easy to play any scene. - Parents should also help their child(ren) identify and understand their reading strategies.
- Have your mentee write a story on paper or in a book.
Required DRA2 components include:
- Aligned Texts
- Teacher Observation Manual
- DRA 2 Continuum, which is part of the Teacher's Observation Guide.
- DRA2 Focus for Instruction, which is also part of the Teacher Observation Guide.
Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
At what time of the year are students assessed?
DRA 2 assessment is carried out 3 times a year for students from grades 1 to 3. Children in kindergarten usually take a test at the end of the year. The first introduction is usually completed in September.
The Board of Education is sometimes flexible because holidays, vacations and even the weather are taken into account.
In the middle of the year, children are assessed for a four-week period from January to February. At the end of the year, a four-week period in April and May is also taken.
Read this: Critical Literacy (All You Need to Know)
DRA Cons:
1. Time.
Evaluation takes time. You can spend 10 minutes assessing a student in first grade. In most cases, you spend more time if you need to get more access to it to find out their highest independent level.
As the student progresses through the level, more time is wasted. You can spend 30 minutes or even more on a student when you need to find out his highest independent level.
Sometimes it's so bad that the classroom period has to be used to complete the test because there wasn't enough time allotted for the test.
At a certain level, where students are now required to write down their responses, more time is spent reading their responses.
Teachers observe students, record and evaluate their performance. Then, based on their performance, he will now know how to help the student improve their skills.
2. Assessment content
The assessment consists of different stories of varying difficulty and requires students to read the story and then tell it in their own words.
The teacher then evaluates the student's reading level by noting how effectively he or she reads and the methods used to read or pronounce words he or she is unfamiliar with.
The teacher checks how fluently the student reads when reading, as well as the student's ability to write a complete summary of the story he has read.
Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
DRA2 results
Accuracy level: Level A - 40 independent or higher
- Comprehension: Level 4-38 on the continuum corresponds to 19 points or even higher. Level 40 is 17 points or even higher.
- Oral reading: level 14 and above is independent
or higher.
Now some people will be wondering what happens to children with disabilities. Well, it's very simple.
The Planning and Placement Team (PPT) determines whether a child with a disability will take the exam and, if not, what alternative can be provided. The decision as to which alternative is provided to the student is based on the PPT.
Great, I hope this Reading Development Assessment (DRA) article answered your question.
Share this information.
Read/write spinlocks - Windows drivers
Twitter LinkedIn Facebook E-mail address
- Article
- Reading takes 2 minutes
Beginning with Windows Vista SP1, a set of related routines uses spinlocks to support synchronized access to data structures shared by readers and writers. A thread that only needs read access to a data structure can use a spinlock to share that structure with other reader threads. A thread that needs to write to a shared data structure must use a spinlock to gain exclusive access to the data structure before it can write to that structure.
A thread that only needs read access to a data structure can use a spinlock to share that structure with other reader threads. A thread that needs to write to a shared data structure must use a spinlock to gain exclusive access to the data structure before it can write to that structure.
If a reader thread needs to acquire a spinlock for shared access, and the lock is already held for exclusive access by a writer thread, then the reader must first wait for the writer to release the lock. Similarly, if a writer thread needs to acquire a spinlock for exclusive access, and the lock is already held for shared access by one or more reader threads, the writer thread must wait for all reader threads to release the lock. While the writer is waiting, no new reader threads will be able to acquire the lock. Instead, a reader that needs to acquire a lock waiting for a writer must first wait until the writer acquires and releases the lock.
A thread can switch roles between reader and writer. A thread that already holds a shared spinlock MAY attempt to convert the spinlock's access mode from shared mode to exclusive mode. This attempt will be made if no readers already hold a shared spinlock, and if no writer is already waiting to acquire an exclusive spinlock.
A thread that already holds a shared spinlock MAY attempt to convert the spinlock's access mode from shared mode to exclusive mode. This attempt will be made if no readers already hold a shared spinlock, and if no writer is already waiting to acquire an exclusive spinlock.
Acquiring a spinlock recursively results in a lock and is not allowed.
The following is a list of routines available to manage read/write thread spinlocks starting with Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1).


 View the platform!
View the platform!