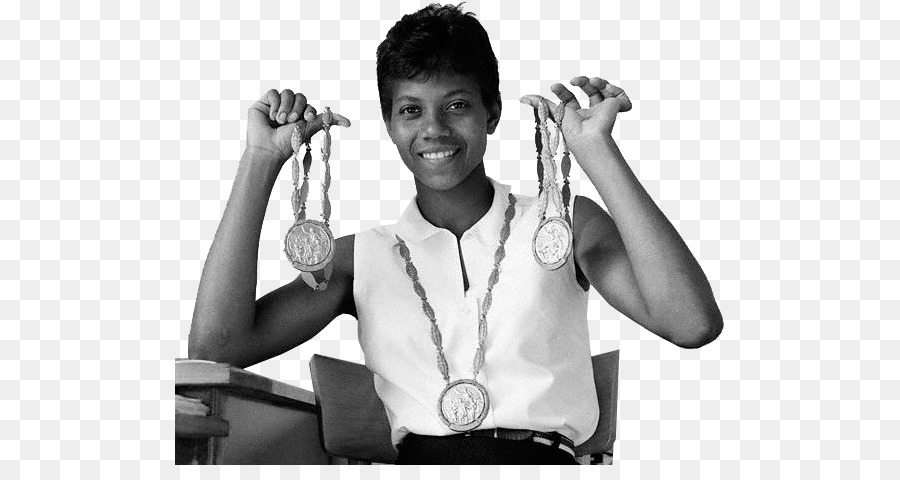
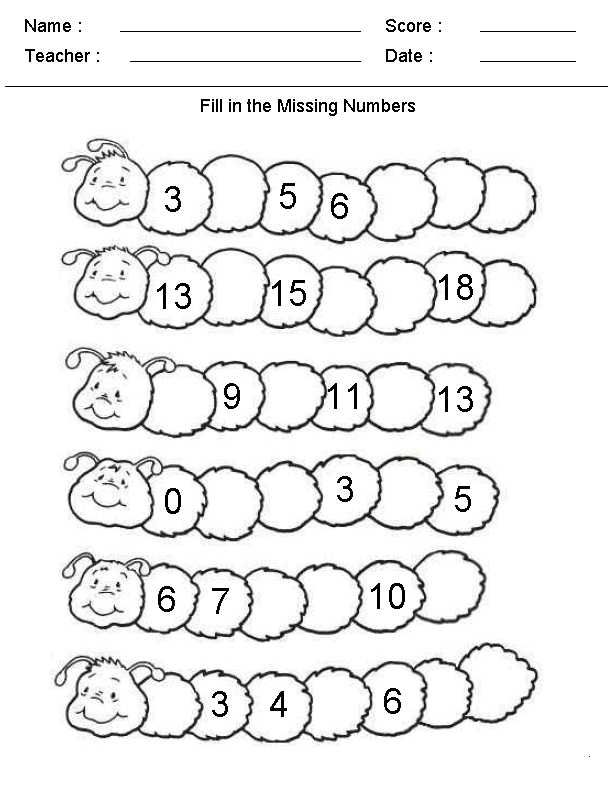
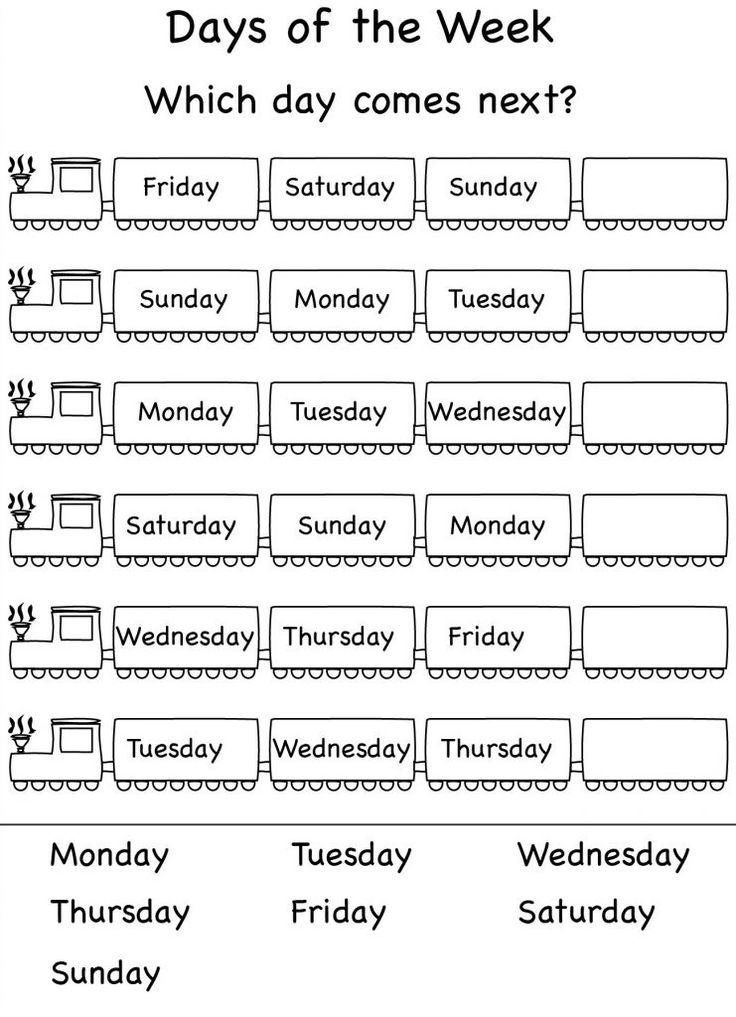
Following directions activities kindergarten
7 Core Following Directions Activities for Kids That'll Improve Listening
Inside: Quick and easy following directions activities for kids that will help them practice self-control, emotional regulation and improve listening skills.
There was a joke traveling around years ago from Carrie On Y’all that said, “Maybe if I start yelling ‘Get your shoes on!’ the night before, we could get to school on time the next day.”
Honestly, the struggle is real.
Kids need A LOT of practice to learn basic life skills.
Following directions activities can support better listening skills in your child.
Teaching kids to follow directions isn’t as simple as doing a listening activity for kids, watching fairy dust shower from above, and seeing your kids transform into magical listeners.
Several years ago I was getting ready to take my son to school. He insisted—like life or death insisted—that he needed to wear his green shoes.
So I helped him find his green shoes, laid them out on the floor, and then realized I made a horrible mistake.
He shook his head and said, “No green shoes, mom. Nooo!”
In exactly two minutes, the green shoes went from being my complaining child’s most prized possession to the most horrible and disgusting shoes one could don.
Related Posts:
- 2 year old not listening? Try this remarkable tip.
- 10 Totally Awesome Tricks for Independent Kids
Teaching kids to follow directions – let’s simplify.
1. Connection first. Attention follows.
A few brief moments using SAY WHAT YOU SEE®, where you describe what your child is thinking, doing, feeling or saying, makes a big difference. This is the building block of connection, and when kids feel connected to you, they are for more likely to cooperate.
It might sound something like, “You’re drawing a picture with big green squares and red lines.”
No brainer, right? And yet, I still find myself talking to my kids without taking a brief moment for connection.
Sharing a set of instructions before you briefly connect with your child is like speaking foreign language. It can fall flat.
It can fall flat.
I know I have my child’s full attention when I have two things:
- Eye contact
- Eyes level (get down to the child’s level).
2. Be short and specific.
Kids tend to hear a lot of conversational white noise when adults are speaking to them. Say exactly what needs to be said for your child to follow your directions. Trim everything else out.
Instead of… “Hurry up. We gotta get out the door for this appointment. Get your coat lets go.”
Try… “Coat please.” Or, “You’re missing a coat.”
3. Use “wait time.”
This is a great strategy that I learned from a teacher. After giving a set of instructions to your kids, pause for 3-7 seconds to allow their brain to process and apply the information. Research shows kids are more likely to follow directions if you give them “wait time” or a hearty pause.
As adults, we are used to processing information much quicker, but kids…they take time.
Think of it this way:
Keeping realistic expectations and waiting is the difference between you giving up and throwing your tea in the air vs. you calmly taking a sip of your tea while you employ “wait time.”
you calmly taking a sip of your tea while you employ “wait time.”
4. Unless you are offering a choice, don’t ask.
If your directions aren’t up for negotiation, keep that door firmly closed. Offering choices is a fabulous way to help end power struggles and enjoy a happier home.
But…everything in life is not always a choice. If you can’t offer a choice within a parental boundary you feel good about, give instructions as a statement, rather than a question.
Instead of… “Can you pick up your toys?”
Try… “I see toys on the floor and it’s time to leave.”
Or if you’d like to offer a choice, you can say something like, “I see blocks and dolls. Show me which one you want to put away first.”
5. Practice using following directions activities.
In order to build great listening skills, kids need a lot of practice…A LOT.
Which makes sense! I think we all can relate to needing a lot of practice before we can get good at anything. I could tell you a few stories about burnt dinner rolls for the past five years, but that’s a story for another day 🙂
Related:
- 50+ Best Simple Games for 2 Year Olds and Up
- The Ultimate List of Board Games for 2 Year Olds
7 core following directions activities for kids.

There are several good ‘ole fashioned standby games to play with kids to help them 1) Listen and hear what you are instructing and 2) Practice following the directions you shared.
1. Simon Says
One person is Simon or Elmo or Dora or Spiderman or Teacher or Whoever, and this person is the “leader.” Simon gives a set of instructions and everyone else follows. The person who doesn’t follow the instructions is “out.” And the person who follows the instructions throughout the game, wins Simon Says.
2. Red Light, Green Light.
One person is the leader who calls out “Red Light” or “Green Light.” When the leader calls out “Red Light,” everyone stops. When the leader calls out “Green Light,” everyone goes. Anyone who doesn’t stop or freeze during “Red Light” is out.
3. Follow the Leader.
Take a walk around your house or outside and whatever you (or the leader) does, everyone else must follow. This is a great game to allow your child to be the leader and have you follow your child. It’s a perfect opportunity to model following directions for your child!
It’s a perfect opportunity to model following directions for your child!
4. Map Game
Try this map game and help your kids work their way through the grid following the directions given. Practice counting and using the words left, right, forward, and backward.
5. Two-step direction games.
Do one of these 2-step direction games with your kids. This is perfect for preschoolers and above! Have your kids follow some of the 2-step directions throughout the day (e.g. Shake your head “yes” and then quack like a duck.) Brilliant!
6. Lego® Game
If you have kids who are old enough to play a board game, try this Lego Game to help your kids practice reading directions and following them.
7. Visual direction activities.
With kids, visual directions are so important! You can make life simpler and fun using visual directions for your kids, such as a printable daily schedule for kids.
- Bedtime routine cards
- Morning routine cards
- Mealtime routine cards
Using routines is a great way to support cooperation and help your kids learn to follow directions.
They are also energy saving, AND a great way to avoid yelling “Green shoes!” ten times every morning or “Eat your dinner!” six times every evening.
Grab your FREE Following Directions Checklist Here!
More popular parenting posts
- 2 Year Old Sleep Schedule to Help Kids Fall Asleep and Wake Happy
- Best Morning Routine Tips and Tricks Your Kids Will Actually Follow
- 3 Things Every Parent of a Strong Willed Toddler Should Know
- 50+ Outdoor Toys for Kids That’ll Bring Hours of Fun
- Best Summer Schedule for Kids That You Can Print and Use Daily
I've created a free email series just for you! If you are struggling with teaching your child to listen, this series will help transform your parenting. Yes, really. I've seen my proven strategies work time and time again for parents. I know it can work for you too.
After taking my free email series, you will:
- Learn simple, yet highly effective listening strategies
- Experience a stronger connection with your child
- Enjoy more peaceful parenting days
- Gain more cooperation from your child
Click here to sign up!
Are you new to this community? Start here, friend.
Following Directions Worksheet and Activities
Learning to follow directions is an important skill for all students to master, and by the time students start Kindergarten, they should be able to handle simple 2 to 3 step instructions. Still, the school environment is a busy and exciting one, and even older students can benefit from activities that support listening to, and complying with, instructions. To help, we assembled several following directions worksheets and activities.
Following Directions: Leveled Worksheets for StudentsThis fun pack is themed on characters from Zoo Academy and Zoo U and provides three levels of worksheets that challenge students to listen or read carefully and to closely follow directions in order to complete a task. In order of increasing difficulty:
Owlivia and the Balloons (worksheet): Students will help Owlivia with a coloring project as Miss Castillo asks her to color the biggest balloon blue, the smallest balloon yellow, and the medium balloon red.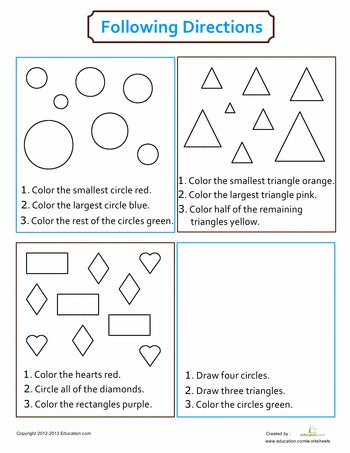
On the Playground (worksheet): Just after recess, Ms. Bergstein has asked Owlivia to help put away many toys and tools around the playground.
Joke’s on Zoo U (worksheet): In this logic puzzle for older students, players must use clues to crack a secret code that reveals the answer to a silly joke. Whether you choose to read the prompts and clues out loud to students, or have them work independently, they will enjoy the fun of interacting with the game characters while tuning in their attention.
Following Directions Activity
The second following directions activity is a twist on the classic game Simon Says. Students will follow “Principal Wild’s” instructions to make different movements with their body, such as hopping on one foot or hands on their head, only moving when the instruction is preceded by “Principal Wild says…” To challenge their Impulse Control Skills, a few students will act as distractors, trying to engage students in conversation while the instructions are happening. Students will need to focus intently on the instructions and ignore the distractions to know when and when not to move.
Students will need to focus intently on the instructions and ignore the distractions to know when and when not to move.
Note: For remote learning environments, this activity may work better if you do not have students acting as distruptors.
Recommended Grade Level: Upper Elementary and Middle School
SEL Skill(s): Impulse Control, Communication
Duration: 30 minutes
Materials: Educator lesson guide
Pre-activity discussion
Talk with your students about it is important for everyone to pay attention and follow directions and by not being a distractor to classmates.
Discussion questions will include:
- Have you ever missed something important in class, like directions, because a classmate was talking to you? If someone is talking to you or distracting you in some other way, and you miss something, is it your fault or theirs?
- Do you think you’ve ever been a “distractor” during class? How do you think the other students felt when you were talking while the teacher was talking?
Even if someone is purposely trying to distract you or make you break the rules, your behavior and how you respond is always your choice. A classmate can make it difficult, but they can’t force you to not pay attention or not follow directions.
A classmate can make it difficult, but they can’t force you to not pay attention or not follow directions.
Additional Resources
Books
- Me and My Feelings by Vanessa Green Allen
- Following Directions: The Fun and Easy Way by Dr. Erica Warren
- What Should Danny Do? by Adir Levy
- What Were You Thinking? by Bryan Smith
With a Centervention Account, you will receive free lessons and a free trial for our online SEL programs.
Please Create My Account
Priority direction of the kindergarten
VERSION FOR THE VISIONLY LIMITED
Priority activities of the educational institution for the implementation of the main educational program of preschool education.
The ongoing changes in the kindergarten, taking into account the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, are due to the objective need for changes that are adequate to the development of society and the educational system as a whole. Based on previous experience and positive results in health improvement, correctional and developmental, artistic and aesthetic work with preschoolers, kindergarten teachers are aware of the need for changes in the work of the institution. nine0007 The main direction: purposeful socialization of the child's personality, education of a physically healthy, diversified, proactive and liberated preschooler. Improvement of pedagogical systems for children, through the solution of program educational tasks not only within the framework of directly specially organized forms of education (classes), but also the implementation of educational areas in the joint activities of an adult and children and the independent activities of children, and during regime moments in accordance with the specifics of preschool education
The following areas of priority in the activities of the kindergarten are:
· Preservation and strengthening of children's health;
· physical and psychological health protection of children, formation of healthy lifestyle habits;
· ensuring the conditions for the safety of the life of children in kindergarten;
· formation of emotional and volitional qualities and universal values among pupils;
· interaction with families of children as a partnership;
humanization of the goals and principles of educational work with children; nine0007 · raising the educational level of pupils through additional education.
Goals and objectives of the activity of an educational institution for the implementation of the main general educational program of preschool education.
Purpose: creation of conditions for the implementation of the right guaranteed to citizens of the Russian Federation to receive public and free preschool education; the formation of a general culture, the development of physical, intellectual and personal qualities, the formation of the prerequisites for educational activities that ensure social success, the preservation and strengthening of the health of preschool children, the correction of shortcomings in the physical and (or) mental development of children. nine0003
Main tasks:
· To create optimal conditions for the preservation and promotion of children's health.
· To create conditions for leveling the starting opportunities for children of senior preschool age to study at school.
Provision of cognitive-speech, social-personal, artistic-aesthetic and physical development of children, taking into account their individual characteristics and abilities;
· To create conditions for the development of cognitive-speech and artistic-aesthetic abilities of children above the basic level. nine0007 · Education taking into account age categories in children of citizenship, universal values, respect for human rights and freedoms, love for the environment, Motherland, family;
nine0007 · Education taking into account age categories in children of citizenship, universal values, respect for human rights and freedoms, love for the environment, Motherland, family;
· Ensuring the social adaptation and integration of the child into society and the successful transition to the next educational level - primary school;
· Creation of conditions for maximum involvement of parents (legal representatives) in participation in educational and leisure activities;
· Meeting the additional educational needs of children and parents (legal representatives) and the choice of programs and technologies by kindergarten teachers. nine0003
LLC "Education and Consulting Center
Volgograd 2008-2023
Entrance
version of the site for visually impaired
90,000 Innovative activities of kindergarten Innovative activities of kindergarten
,000 9000, DOU educational program (main and variable) 66666666
In accordance with the federal state standard for preschool education, the main general educational program for preschool education of a preschool educational organization (hereinafter referred to as the Program) must contain two parts: main and part formed by participants in educational relations (often called variable part).
Variable part is not a separate document in the Program, but a part of each section (target, content and organizational). For the convenience of working and evaluating the Program, it is recommended to draw it up from a new page, highlighting the name of this part. To create a variable part of the Program, it is necessary to take into account the educational needs, interests and motives of pupils, their families and teachers and, in particular:
1. the specifics of national, socio-cultural, economic, climatic conditions in which the educational process is carried out;
2. selection of those partial programs and forms of organization of work with children that best meet the needs and interests of the pupils of the Organization, as well as the capabilities of its teaching staff;
3. supporting the interests of the teaching staff of the Organization, the implementation of which corresponds to the goals and objectives of the Program; nine0003
4. established traditions of the Organization.
established traditions of the Organization.
Therefore, at the initial stage of creating this part of the Program, it is necessary to monitor the educational needs, interests and motives of pupils, their families and teachers. Namely:
1. To study the results of a diagnostic examination of pupils for the past period, which will give an idea of the children's assimilation of the knowledge system, their needs, interests, development of motivation. (Conducted by teachers - educators, a teacher-psychologist of a preschool organization, a senior educator). nine0003
2. Conduct surveys and surveys among parents pupils and members of their families to identify their educational needs regarding their children, interests and motives of the pupils' parents as members of the educational process, or take into account the results of such a survey for the previous academic year.
3. Determining the possibilities of the surrounding macrosociety and using it in the process of upbringing and education of the child. How can interaction be organized between an educational institution and institutions of culture, education, etc.
How can interaction be organized between an educational institution and institutions of culture, education, etc.
At the next stage, it is necessary to select several educational programs of various directions from among partial or created independently by an educational organization and meeting the requirements of all participants according to their needs and motivation. An important addition: all copyrighted and modified programs implemented in the institution must comply with the Federal State Educational Standard of DO (for this they must pass an examination at the regional or municipal level). To discuss the selected programs, it is important to involve not only teachers, but also parents. nine0003
For the implementation of the selected programs, it is necessary to determine the forms of organization of work with pupils.
Next, the actual writing of a part of the program is carried out, taking into account the selected programs and forms of organizing work with pupils.
As is known, parts of the program are distributed as follows : 60 by 40. That is, the mandatory part of the Program should take 60% or more, and the variable part - 40% or less. The distribution is carried out according to the time of implementation and is considered as a whole for the academic year. But if a preschool organization creates several Programs for work (taking into account different types of groups, based on various exemplary educational programs, then this ratio may change. So for groups of a general developmental orientation, this ratio will be optimal, and for groups of a compensating orientation, the ratio may be 80 to 20 , and for the group of short stay - 90 to 10. Of course, this should already be decided by the teaching staff specifically for their organization, since such an opportunity is provided by the Federal State Educational Standard of Education, clause 2.10.
As part of the Program formed by the participants of educational relations , you can issue it in accordance with clause 2. 11. FOS DO in the form of links to the relevant methodological literature, which allows you to get acquainted with the content of the partial programs, methods, forms of organization of educational work selected by the participants in educational relations. nine0003
11. FOS DO in the form of links to the relevant methodological literature, which allows you to get acquainted with the content of the partial programs, methods, forms of organization of educational work selected by the participants in educational relations. nine0003
Thus, the work on compiling the variable part of the Program requires a lot of in-depth and long-term work of the entire teaching staff of the organization.
The staff of our preschool (under the control of the Governing Council) conducted a survey among parents. The results of this survey and conclusions will be presented on the DOE website on the structural page "Innovative activity".
Currently, the kindergarten is exploring the possibilities and material and technical base for the implementation of programs that received the most votes from the parent community. It is planned to conduct a survey among teachers, create a creative group to write a variable part of the educational program of the preschool educational institution and, based on the results of the work, begin its implementation. nine0006
nine0006
In the 2015-2016 academic year, the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution uses elements of the Shchetkin A.V. program. "Theatrical activity in kindergarten", which includes the following areas:
- Theatrical game
Theatrical game is a historically established social phenomenon, an independent type of activity, characteristic of a person.
- Rhythmoplasty
Rhythmoplasty includes complex rhythmic, musical, plastic games and exercises designed to ensure the development of natural psychomotor abilities of preschoolers, freedom and expressiveness of body movements, gaining a sense of harmony of one's body with the outside world. nine0003
- Culture and technology of speech
This section of the work combines games and exercises aimed at developing breathing and freedom of the speech apparatus.
- Fundamentals of theater culture
This section of the work is intended to acquaint children with elementary concepts, professional terminology of theatrical art (features of theatrical art; types of theatrical art, the basics of acting; the culture of the viewer).