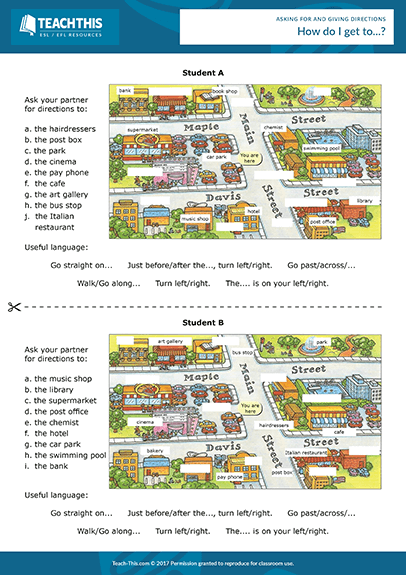
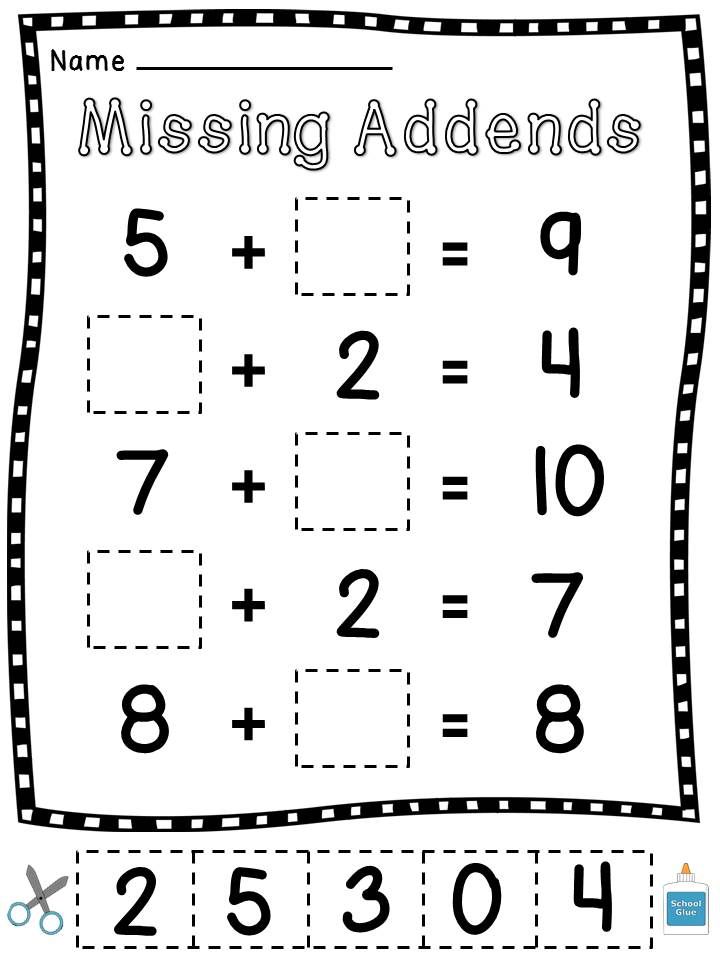
Fun maths games for kindergarten
Kindergarten Math Games That Make Learning Fun from the Start
Looking for ways to make math fun for young learners? Check out these kindergarten math games! They teach all the basic math skills kindergartners need to master and are sure to engage every kid in the learning process.
(Just a heads up, WeAreTeachers may collect a share of sales from the links on this page. We only recommend items our team loves!)
ADVERTISEMENT
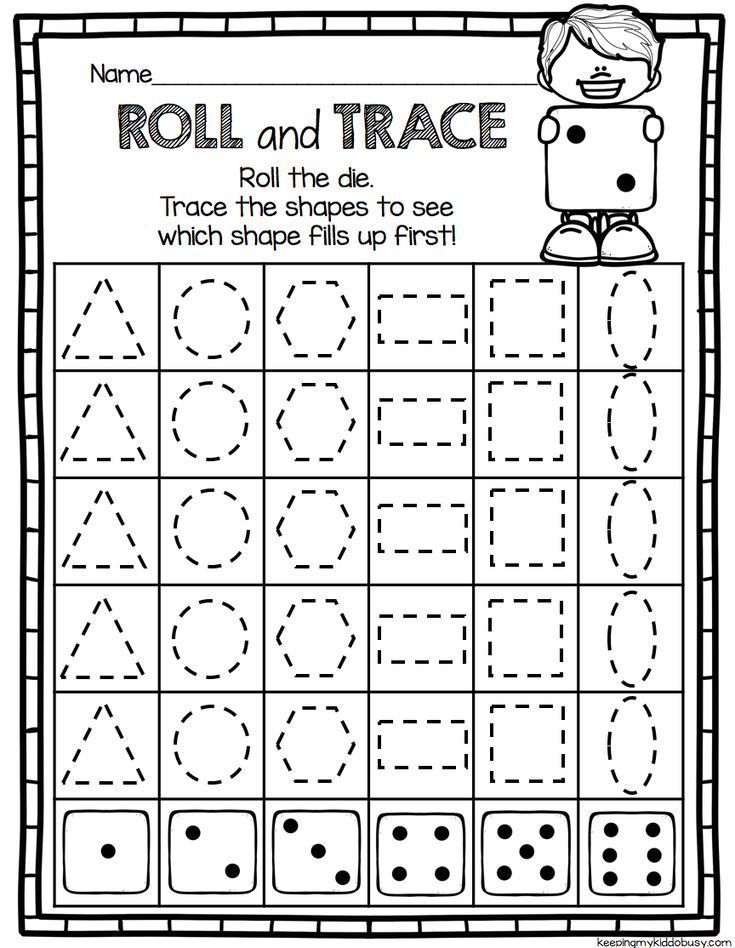
1. Conquer cardinality with penguin dominoes
Kindergarten math students work to master cardinality, understanding that written numerals correspond to the number of items pictured. These free printable penguin dominoes make the concept fun to practice.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
2. Put together puzzles to gain number sense
Kindergarten math students learn to understand that numbers can be represented in a variety of ways. These free printable puzzles help them practice those skills.
Learn more: Tickled Pink in Primary
3. Play teen-number bingo
This free printable game helps little ones master their numbers from 11 to 20, both as numerals and represented on ten-frames.
Learn more: The Measured Mom
4. Stack cups and count to 100
Kids love stacking things, so they’ll get a kick out of kindergarten math games that make use of stackable cups. This one has them doing it with 100 cups while they count! Turn it into a competition by putting them in teams and timing them to see who can finish the task the fastest.
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard/100 Cups
5. Visit the skip-counting store
How fun is this? Grab some toys and label them with price tags in increments of 10 cents. Give kids a handful of plastic dimes, and have them count out the amount needed for each “purchase.”
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Skip Counting Store
6. Have a rubber duck race
In this game, kids race to see who can be the first to get their rubber duckies to 10 (or any number you choose). They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
Learn more: Happy Toddler Playtime
7. Practice counting on with cards and dice
Remove the face cards from a deck of playing cards and grab a pair of dice. The first player turns over a card and then rolls the dice. The number on the dice indicates how far they “count on” from the card. (For example, a player turns over a three and rolls a four. They say, “Three: four, five, six, seven.”) If the player gets it right, they keep the card, and the other player(s) get a turn.
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Counting On
8. Skip-count with craft sticks
There are endless ways to use craft sticks in the classroom. For this game, number a series of colorful sticks by fives, as shown. Kids can practice by putting them in order first. Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Learn more: Simply Kinder
9. Match teen numbers
Once they’ve mastered the numbers 1 to 10, it’s time to understand how those numerals add up to make bigger numbers. These free printable cards show numerals and matching bundles of sticks that deconstruct each teen number into tens and ones.
Learn more: The Kindergarten Connection
10. Compare numbers with dominoes
Kindergartners learn to compare numbers to determine which is larger and which smaller. Stacking math cubes based on the numbers on dominoes is a fun, hands-on way to compare the two numbers side by side, making it easier to see the difference.
Learn more: My Fabulous Class
11. Face off and compare numbers
You’ll need some small toys for this game, as well as polyhedral dice. Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Learn more: Natalie Lynn Kindergarten
12. Make 10 with two-sided chips
You’ll need counting chips that are a different color on each side for this activity. Kids shake up 10 chips in a cup and pour them out on the table. Then they see how many they have of each color and write that number bond to make 10.
Learn more: First Grade Fairytales
13. Throw snowballs to make 10
Make “snowballs” from paper (or any way you like), then place them in a bucket at one end of the room. Start kids out by having them toss snowballs into another bucket until they reach 10 (or any target number). Then, up the challenge by placing some snowballs in each bucket and have kids figure out how many more they need to toss in to make 10.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Snowball Math Games
14. Use Uno cards to play addition war
In the card game War, players each flip an Uno card, and the one whose card is greatest takes them both. In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Addition Game
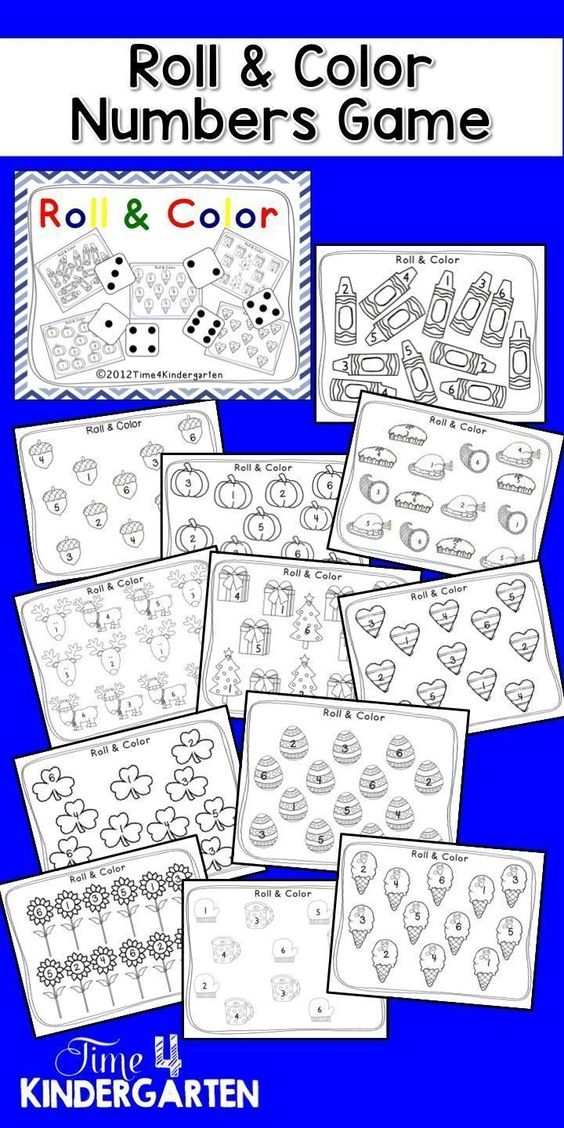
15. Roll and add for fluency within 5
Kindergarten math students work to become fluent in adding and subtracting within 5. This free printable board game makes it fun!
Learn more: Liz’s Early Learning Spot
16. Get four in a row and learn place value
This customizable game helps teach the early place-value concept of tens plus ones. Get it for free at the link.
Learn more: Two Boys and a Dad
17. Bowl and subtract within 10
Set up a toy bowling pin set (or make one from plastic bottles or toilet-paper tubes). Kids bowl and see how many pins they knock down, subtracting that number from 10. Then they repeat, this time subtracting from the previous answer. First to get to zero wins!
First to get to zero wins!
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Subtraction Worksheets
18. Get off my boat!
So simple, so engaging, so fun! Use tape to outline a boat shape on the floor (or try this outside with sidewalk chalk). Let some kids board the “boat,” then make some get off. Use those numbers to write a subtraction number sentence and solve the equation!
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard—Get Off My Boat!
19. Drive and compare numbers to music
Prep for this game by using dot markers on paper plates as shown (visit the link below for more examples). Each kid takes a plate then uses it to “drive” around the room as you play music. When the music stops, they find a nearby partner and compare what they see on each other’s plates (e.g., “8 dots is more than 4 dots. 1 green dot is less than 4 green dots.” Then start the music up and repeat!
20. Build a weigh station
Use a hanger and plastic cups to build a super-simple weigh station.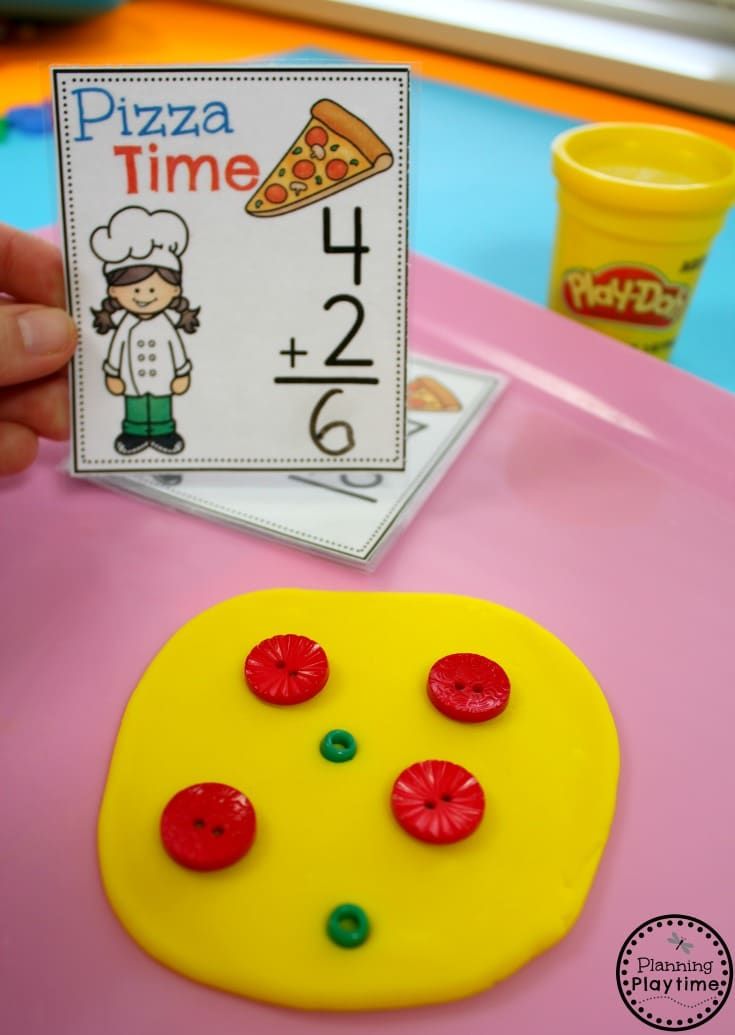 Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
21. Battle it out in ribbon war
Looking for kindergarten math games that teach non-standard measurement? This idea is fun and easy. Cut colorful ribbons into a variety of lengths and place them in a bag. Each student pulls a ribbon from the bag. Then, put students in pairs and have them compare their ribbons to identify the longer one. The student with the longer ribbon keeps both, and the game continues.
22. Hold a shape scavenger hunt
Kindergarten math students are learning to recognize shapes in their environment and also to categorize and sort. This scavenger hunt does it all! Send them out to find objects in the room that match the shapes. Then count and compare to see how many you have in each category.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Shape Scavenger Hunt
23.
 Hop along a shapes maze
Hop along a shapes mazeUse sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun—Shape Maze
24. Make a match to learn shapes
Grab these free printable memory cards at the link. Then play and learn the basic shapes.
Learn more: Life Over C’s
25. Guess the mystery shapes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing 3D shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like “The shape in this bag has 4 sides. What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
Love these kindergarten math games? You’ll also enjoy these 50 Kindergarten Math Word Problems of the Day!
Want more articles like this? Subscribe to our newsletters!
Math Games for Kindergarten Online
Kindergarten Math GamesMath games for kindergarten primarily focus on two critical areas: (1) number names and counting sequence (2) describing shapes and space. Children begin their math journey in kindergarten and this forms the basis of all known mathematics. It is important to make learning fun, engaging and interactive at this stage so that the child develops an early interest in math.
Children begin their math journey in kindergarten and this forms the basis of all known mathematics. It is important to make learning fun, engaging and interactive at this stage so that the child develops an early interest in math.
This can be easily done using fun-filled math games that are visually appealing and captivating. There is no better way to teach your little ones about numbers and shapes! Games like sorting games, matching games, counting games, etc. help increase the child’s understanding of numbers.
- Developing cognitive skills: Learning math through games in kindergarten helps to develop children’s cognitive skills. Their brains are like sponges at this stage, so it is important to stimulate their minds with the right assets. Games engage multiple areas of the brain and allow the learner to interact with concepts like number sense and sequence, addition, subtraction, etc.
 at their own pace. These games also promote math talk and enhance reasoning abilities.
at their own pace. These games also promote math talk and enhance reasoning abilities. - Making math learning fun and engaging: Online math games eliminate rote learning from a young age and incorporate a more practical approach to learning. Children can start their math journey by singing the number song or by counting objects along with a friendly character using colorful images. This holds their attention and interest in math right from the start!
- Building curiosity: Children are naturally curious and it is important to nurture this natural inquisitiveness. Math games are a brilliant way to foster their curiosity by engaging their imagination and creative skills. Sorting games, finding and matching shape games, aligning and comparing length games, etc. all boost curiosity and learning.
- Building motivation, memory and motor skills: Math games allow children to practice their concepts repeatedly that increase their proficiency and boost their motivation.
 Math games are also amazing at developing motor skills as they involve actions like tapping, clicking, dragging on the screen at the right time at the right place, etc. Memory and concept retention are also increased with repeated practice.
Math games are also amazing at developing motor skills as they involve actions like tapping, clicking, dragging on the screen at the right time at the right place, etc. Memory and concept retention are also increased with repeated practice.
- Play on multiple devices: Math games can be played online on multiple devices like; iPad, laptop, phones, etc.
- Engaging and rewarding games: Children can purchase assets for their characters and more through the coins they win through practice.
- Easy Connect for Parents: Parents are instantly notified about their child’s progress.
- Offline access: Games can also be played offline through apps for an interruption-free experience.
Counting, writing numbers in words, and identifying shapes are some concepts taught in kindergarten which are useful in everyday life.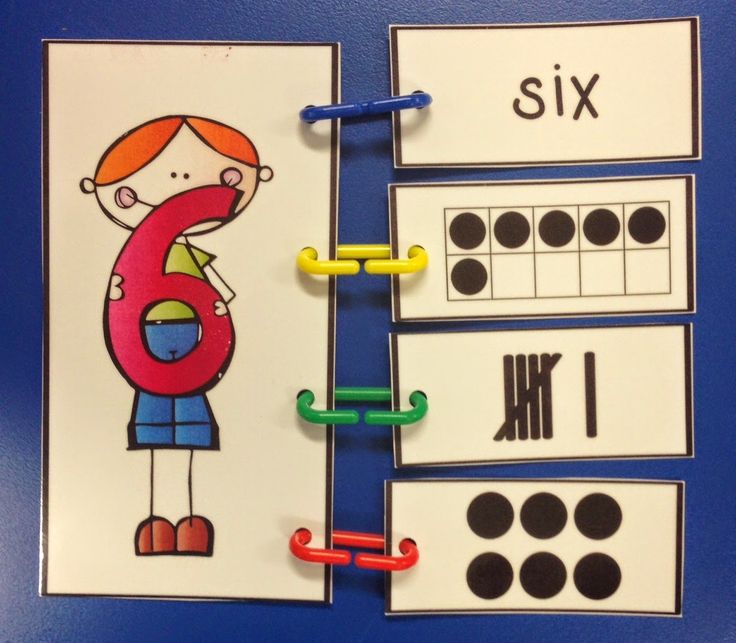 Math games make these concepts fun and easy to comprehend for the youngest learners out there!
Math games make these concepts fun and easy to comprehend for the youngest learners out there!
Yes! They can help build an interest right from the start. They not only teach concepts effectively but also relate them to the real world with a touch of wonder and fascination. As such, kindergarteners are able to develop as well as practice necessary math skills to take their learning forward.
3. Are math games for kindergarten easy to use and understand?Yes, they are extremely age and user-friendly and perfect for little learners. They come with interactive characters and colorful imagery that help retain the attention of your child. Patience with young children is extremely important and interactive games allow streamlined productive learning to be fun and simple simultaneously.
4. How can I make my kindergarten math learning fun through games?Incorporating games is a wonderful method to keep the spark of learning alive. Kindergarten math games online cover a wide range of topics that are aligned with Common Core Standards that will make learning hassle-free and enjoyable.
Kindergarten math games online cover a wide range of topics that are aligned with Common Core Standards that will make learning hassle-free and enjoyable.
The best way to teach math to children is to let them experience and play with math around them. Make them feel that math is everywhere. Whether you are explaining them counting sequences or telling them about days and months, math is always involved. Online games can be inculcated in their learning routine to make learning exciting and relatable.
Try SplashLearn for Free
Educational games in mathematics in kindergarten | Plan-summary of the lesson (senior group):
Afanasyeva S.G., teacher
Kindergarten No. 93 of the Krasnoselsky district
St. Petersburg
"Developing games in mathematics in kindergarten"
a window through which a life-giving stream of ideas, concepts about the surrounding world flows into the spiritual world of the child.
Play is a spark that ignites the flame of inquisitiveness and curiosity.
(V A. Sukhomlinsky)
Purpose: to increase the level of knowledge of teachers on the formation of children's mathematical abilities with the help of educational games.
Tasks:
1. To acquaint teachers with non-traditional technologies for using games in the work on FEMP.
2. To equip teachers with practical skills for conducting mathematical games.
3. Present a set of didactic games for the formation of elementary mathematical concepts in preschool children.
Relevance of the problem: Mathematics provides great opportunities for the development of children's thinking in the process of their learning from an early age.
Dear colleagues!
The development of the mental abilities of preschool children is one of the urgent problems of our time. A preschooler with a developed intellect remembers material faster, is more confident in his abilities, and is better prepared for school. The main form of organization is the game. The game contributes to the mental development of the preschooler.
The main form of organization is the game. The game contributes to the mental development of the preschooler.
The development of elementary mathematical concepts is an extremely important part of the intellectual and personal development of a preschooler. In accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard, a preschool educational institution is the first educational level and a kindergarten performs an important function.
Speaking about the mental development of a preschooler, I would like to show the role of the game as a means of forming a cognitive interest in mathematics in preschool children.
Games with mathematical content develop logical thinking, cognitive interests, creativity, speech, instill independence, initiative, perseverance in achieving goals, overcoming difficulties.
Playing is not only pleasure and joy for a child, which is very important in itself, it can help develop a child's attention, memory, thinking, and imagination. While playing, a child can acquire new knowledge, skills, abilities, develop abilities, sometimes without realizing it.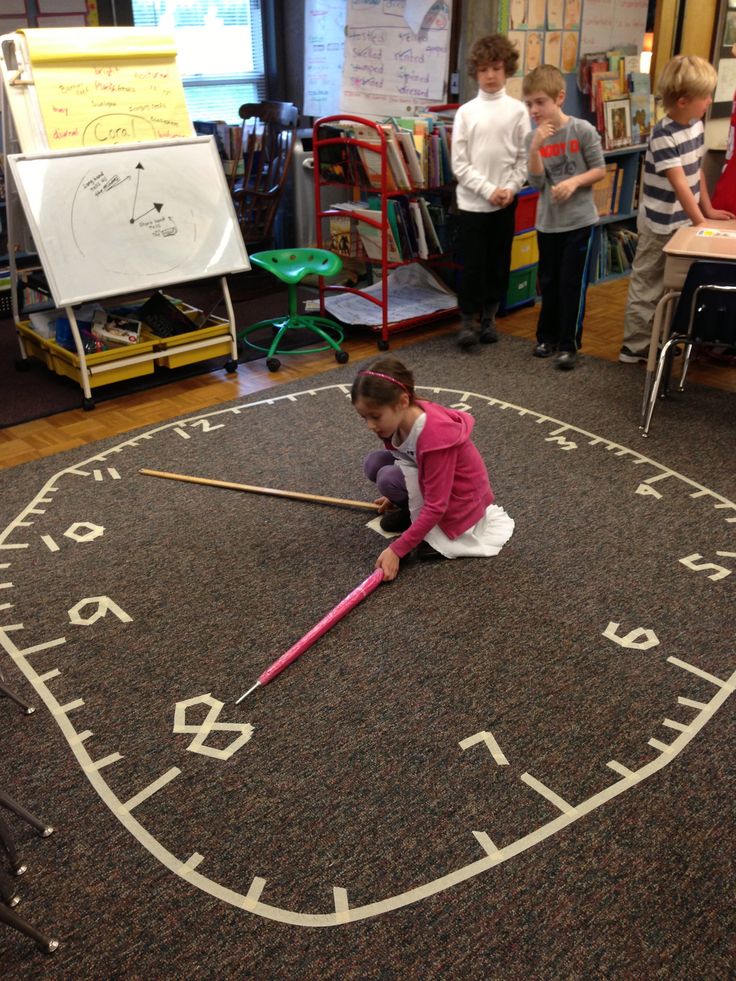 The most important properties of the game include the fact that in the game children act as they would act in the most extreme situations, at the limit of their ability to overcome difficulties. Moreover, such a high level of activity is achieved by them, almost always voluntarily, without coercion.
The most important properties of the game include the fact that in the game children act as they would act in the most extreme situations, at the limit of their ability to overcome difficulties. Moreover, such a high level of activity is achieved by them, almost always voluntarily, without coercion.
The following features of the game for preschoolers can be distinguished:
1. The game is the most accessible and leading activity for preschool children.
2. The game is also an effective means of shaping the personality of a preschooler, his moral and volitional qualities.
3. All psychological neoplasms originate in the game.
4. The game contributes to the formation of all aspects of the child's personality, leads to significant changes in his psyche.
5. Play is an important means of mental education of a child, where mental activity is connected with the work of all mental processes.
At all stages of preschool childhood, the play method plays an important role in educational activities.
Didactic games are included directly in the content of educational activities as one of the means of implementing program tasks. The game can be used as a training task, an exercise aimed at performing a specific task of forming ideas.
In the formation of mathematical representations in children, various didactic game exercises that are entertaining in form and content are widely used.
Didactic games are divided into:
- games with objects
- board games
- word games
Didactic games for the formation of mathematical representations are conditionally divided into the following groups:
1. Games with numbers and numbers 9002 9002 2. Time travel games
3. Orientation games in space
4. Games with geometric shapes
5. Games for logical thinking
Starting work, it would be nice to study the emotional well-being of the child, his attitude to mathematics. This can be helped by a projective conversation, which is conducted individually with each child in an atmosphere of goodwill and in the complete absence of an evaluative attitude on the part of an adult.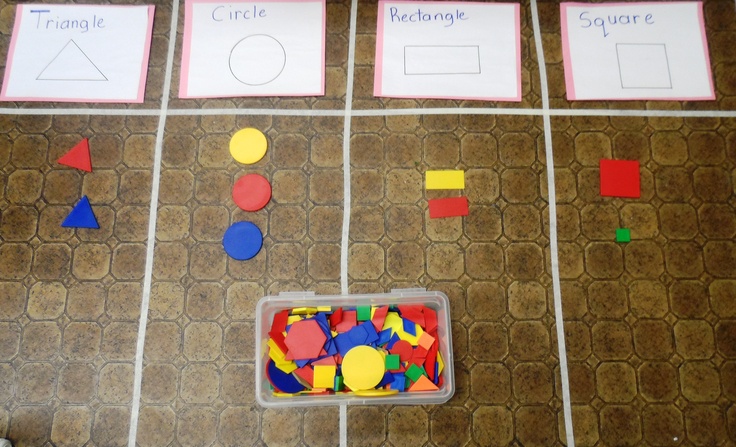
One of the tests helps to determine the child's preference in choosing an activity. The teacher shows the child a table with the image of five houses, each of them schematically depicts something that emphasizes belonging to a certain area:
1. "Math house" - decorated with numbers
2. Literacy house - with letters
3. Pencils on the house show that it is intended for fine arts.
4. Toy - you can play here
5. Fairy house - where fairy tales live
The teacher asks the child: - play. In the fifth, get acquainted with the letters and learn to read. Which house are you most interested in? Why? What other house would you like to visit? What house do you not want to go to? Why? 9
1) Someone turned an old chair at night
Turned it back down
And now in our apartment
It has become a number (4)
barely,
Where are her legs, head (8).
3) Guess this number!
She is a big nerd.
Add one to two,
And you get the number (3).
2. "Beads" simulator
Purpose: assistant in solving the simplest examples and tasks for addition and subtraction
Tasks:
to develop the ability to solve simple examples and problems for addition and subtraction;
cultivate attentiveness, perseverance;
develop fine motor skills of hands.
Material: rope, beads (no more than 10), colors of your choice.
Children can first count all the beads on the machine.
Then they solve the simplest problems:
1) "Five apples hung on the tree." (Count five apples). Two apples have fallen. (Take away two apples). How many apples are left on the tree? (count beads)
2) Three birds were sitting on a tree, three more birds flew to them. (How many birds are left to sit on the tree)
Children solve the simplest tasks both for addition and subtraction.
3. "Colored palms" simulator
Purpose: formation of elementary mathematical representations
Tasks: to develop color perception, orientation in space; teach counting; develop the ability to use diagrams.
Tasks:
1. How many hands (red, yellow, green, pink, orange) are there?
2. How many squares (yellow, green, blue, red, orange, purple) are there?
3. How many palms are facing up in the first row?
4. How many palms are facing down in the third row?
5. How many palms in the third row from the left are facing right?
6. How many palms in the second row from the left are facing left?
7. A green palm in a red square is looking at us, if we take three steps to the right and two steps down, where will we end up?
8. Set the route for a friend
The manual is made of multi-colored colored cardboard using children's pens
4. And now I offer you the game "Half a minute for a joke" - this game can serve as a dynamic pause.
Tasks:
a) How many green Christmas trees, so many slopes (2)
b) Stomp your foot as many times as we have hedgehogs (7)
c) How many circles I show, so many jumps (3)
d) We will sit down so many times.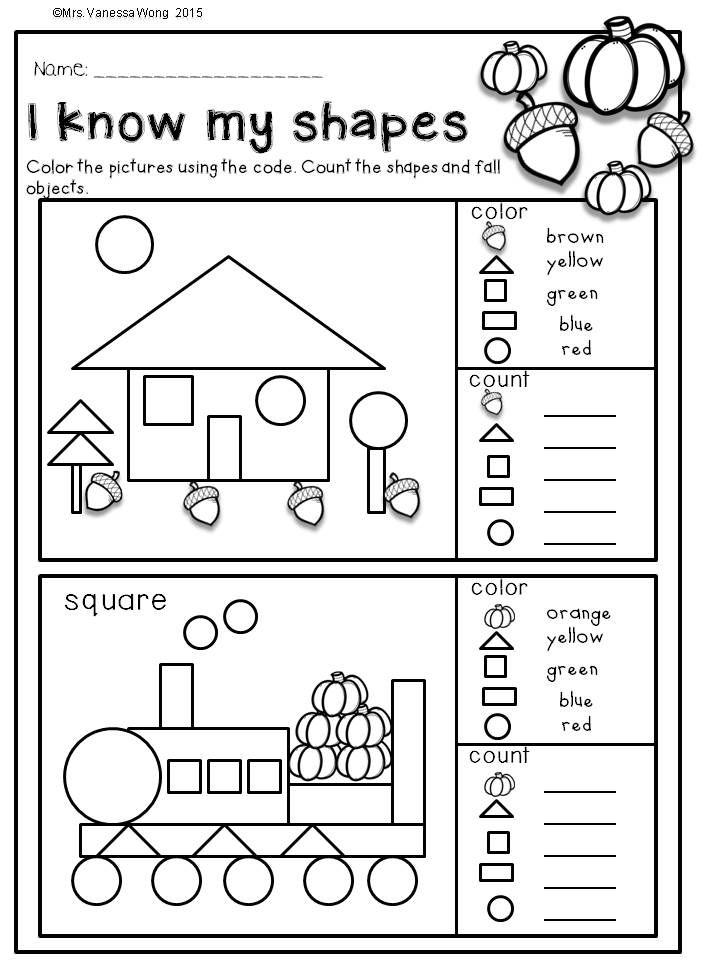 How many butterflies do we have (4)
How many butterflies do we have (4)
e) How many dots there will be in the circle, so many times we will raise our hands (5)
5. We play further: “Orientation in time”
“Who knows, he answers!
- What is Thursday?
- What day of the week is after Tuesday?
-Today is Friday - what day is tomorrow?
-What is the day of week 1? 2? 5? (by account)
Very good.
“Number and count”
- Game “Who knows he answers
- “Name the numbers up to 6” (5,4,0,3,2,1)
-"Name the numbers after 7" (8,9,10)
-How many angles does a triangle have? What about the square?
- How many days are there in a week?
- How many fingers are on one hand? And for two?
- How many traffic lights?
- How many hands does a person have?
- how many legs does a beetle have? What about the spider?
- How many legs does the table have?
- How many giraffes live in our apartment?
Entertaining mathematics for preschoolers - ABC of education
Table of contents- How to introduce logic to a child?
- How to remember the graphic representation of numbers?
- Preschool Math and Counting
- Preschool Math and Counting
- Playing Activities for Toddlers 5 to 5 (2 yr 6 mo)
- Household Counting (1 yr 6 mo)
- Cards ( 1 year 6 months)
- Learning zero (2 years)
- Counting using poetry (1 year 6 months)
- Toddler math game
- Bears go for a walk
- Find a house for each bear
- Looking for a toy
- Looking for a toy 2
- Count, don't make a mistake!
- Find a toy
- We get acquainted with numbers
- Guess
- Who is more than
- Logical tasks for preschoolers
- Learning to determine the time by the hour
- Mosaic from buttons - a developmental game for children
- ?
- In no case should you count, just name four.
How to teach a child to count and love mathematics? What can be done to facilitate the process of learning the world of mathematics? It's not as difficult as it might seem. It is only necessary to methodically deal with this and create all the conditions for the baby.
Before you begin to work with your baby, read a few tips:
- A small child cannot maintain the same position for a long time, perform the same action. Therefore, there is no need to get angry if your baby is distracted, slides from a chair to the floor, or suddenly asks a question completely “from a different opera”.
- If you use some kind of visual material in your classes - cards, pictures, toys, then introduce the child to all this in advance. This is done so that during the lesson the baby is not distracted from studying by looking at new things for him.
- Most likely you will work with your baby on some book. Do not try to “pass” it quickly and be sure to return to the past from time to time.
 The memory of babies is still very unstable.
The memory of babies is still very unstable. - Young children are much better at assimilating emotionally perceived material. Therefore, use more games, counting rhymes and rhymes.
- For classes you will need counting material. As such, you can use large buttons, toys from Kindersurprise, parts from Lego. You will also need picture cards. You can use stickers for this.
How to introduce a child to logic?
You have a child, and you are beside yourself with surging happiness only from the realization that you have now become a happy mother and, finally, there will be someone to pass on your maternal love and knowledge. Not without reason, from time immemorial, all the leading philosophers have emphasized in every possible way that when parents want to raise their child in the image and likeness, hard or soft, they voluntarily or involuntarily want their baby to look like themselves. This process is called education.
Leading psychologists unanimously assure us that the kindness and breadth of your child's soul, voluntarily or involuntarily, should help in achieving his goals. Indeed, it is easier to be kind than smart. It is not for nothing that people say that a kind person helps everyone, while a smart one helps only those in need. And if you want to see your child not only kind, but also smart, then you need to start the whole process of education from infancy. But where do you start?
Indeed, it is easier to be kind than smart. It is not for nothing that people say that a kind person helps everyone, while a smart one helps only those in need. And if you want to see your child not only kind, but also smart, then you need to start the whole process of education from infancy. But where do you start?
Start small. From logic. In order for your child to believe in the existence of cause and effect, you must always and must fulfill your parental promises (for example, “if you behave, then we will definitely go to the zoo.”)
If your child is already seriously interested in children's books, then it will be useful to add verbal logic puzzles and tasks with answers, such as: “If this is so, then this is because ...” or “What will happen if I do everything the other way around?” “How can all this be explained?” The development of logic is helped by simple children's riddles, puzzles, rebuses. Make it a rule to have a mystery night at least once a week. Teach your child to make puzzles.
Your child is entering a stage when everything becomes extremely interesting for him and his curiosity can and should be played on so that he can quickly learn and, most importantly, understand the world around him. And simple worldly logic will only be to his advantage.
To make it easier for your child to understand and understand all this, it will be useful to include in role-playing games some elements of ready-made conclusions, such as: “Your dolls go to bed in the evening because they get tired during the day. But my Volodya is also tired, and it’s time for him to go to bed too.”
You can also show such an example from the world of “Moidodyr” that if “the children do not wash and comb their hair, then the rest of the children in the kindergarten will not play with him.” Already in the process of growing up your child will be able to give much deeper concepts with logical overtones. Here you need to apply the main and basic principle - so that your child already begins to clearly understand that in this world there is always both a cause and an effect.
How to remember the graphic representation of numbers?
Very often it happens that the baby can count perfectly from 1 to 10, but he cannot find the number shown in the picture on his own. The graphic image of a figure for him is a complex abstract concept. The development of abstract thinking is not a simple process, as child psychologists believe. And without the help of adults, this is not enough.
Very often babies confuse numbers that are a little similar to each other, for example 6 and 9, 8 and 3, 4 and 7. And this problem should by no means be overlooked. The baby needs help to understand such complex, for his perception, graphic images. It will be much easier for a kid to remember a number if he can find its similarity with some object or animal: 2-swan, 8-points.
If mom can pick up interesting poems about numbers, then the memorization process will be even easier. How to help kids? The main thing is not to get angry with children if they do not grasp everything “on the fly”.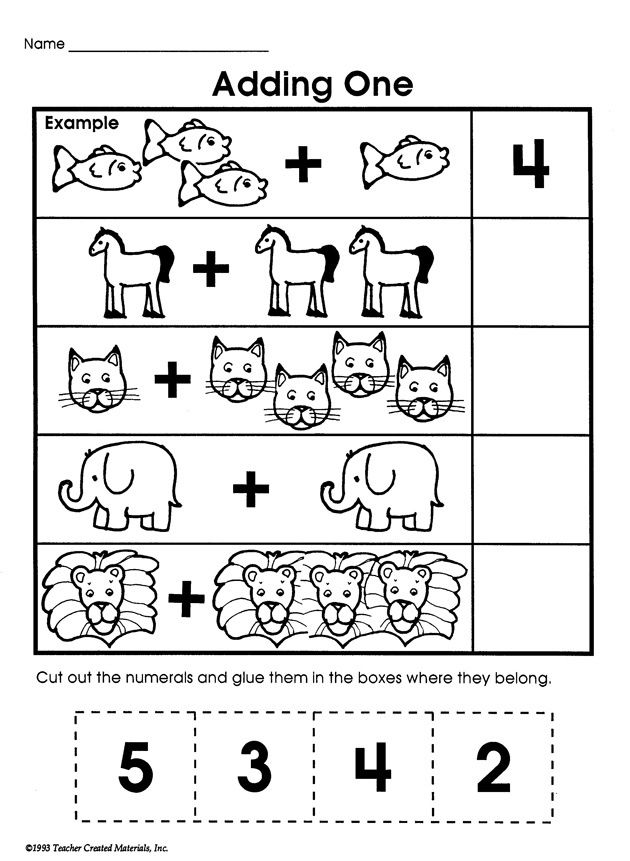 This is for you, adults, everything is easy and simple, but for children who have just begun to master numbers and counting, everything is very difficult. Any teacher or child psychologist in Moscow will confirm that the most effective way for children to memorize new material is to play math classes.
This is for you, adults, everything is easy and simple, but for children who have just begun to master numbers and counting, everything is very difficult. Any teacher or child psychologist in Moscow will confirm that the most effective way for children to memorize new material is to play math classes.
Find the number math game
For this game you will need:
drawn (printed) numbers on paper from 1 to 9
drawings similar to numbers, objects.
The kid looks at the drawing and then guesses what number is hidden in it. Then the mother shows the number 2 and asks the baby to find a picture similar to this number.
“What does the number look like”
Mom asks the child what number the glasses look like, and the baby should show the number 8.
Math game “Guess what number”?
Mom reads a poem, the child must name the number that was discussed in the poem, and then find it and show it.
Barely glides on the water,
Like a swan, number two.
Arched her neck,
Drives the waves behind her.
***
Four mice on the mountain
Mixed up all the skis,
And hedgehogs, four brothers,
Helped them figure it out!
***
What a cherry, my friend,
Is the stalk bent up?
You try to eat it,
This cherry is a number ...
Mathematical game “Cardboard Numbers”
For this game, you will need to cut out numbers from cardboard in advance. The kid closes his eyes, takes one cardboard number and guesses by touch what kind of number it is.
Lost Numbers Math Game
Numbers from 1 to 9 are printed on cardboard. Then each of them is cut into two parts. The kid must restore them. If this task is too easy for him, he can complicate it by cutting the numbers into 3, 4 or 6 parts.
“What's on the back”
The baby lies on his stomach, and his mother draws a number on his back with her finger.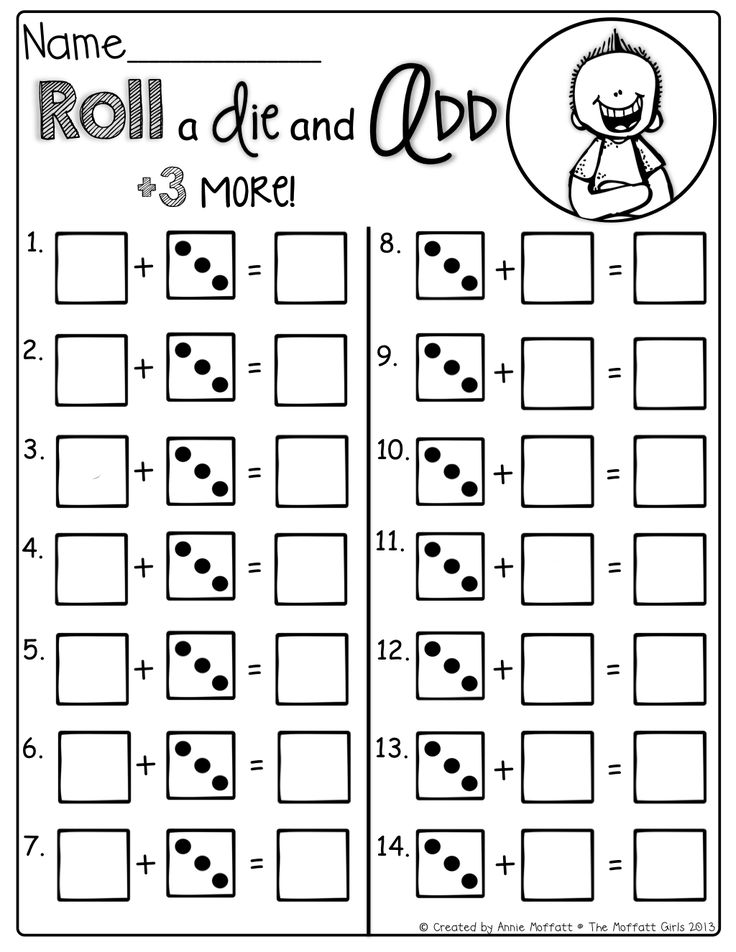 The baby must guess what this number is.
The baby must guess what this number is.
Preschool Math & Counting
Preschool & Toddler Math Fun
Math for young children is quite a difficult subject and can be difficult to learn at school. In addition, not all children have a mathematical mindset, and not everyone has a natural craving for the exact sciences.
Therefore, developing a preschooler's interest in mathematics at an early age will greatly facilitate his schooling. After all, the modern school curriculum is quite rich and far from simple even for first-graders.
Mastering counting skills and the basics of mathematics at home in a playful and entertaining way for a preschooler will help him in the future to quickly and easily learn the complex issues of the school course.
Entertaining problems
How many ears do three mice have?
How many paws do two cubs have?
Seven brothers have one sister. How many sisters are there?
Dasha's grandmother has a granddaughter Masha, a cat Fluff and a dog Druzhok.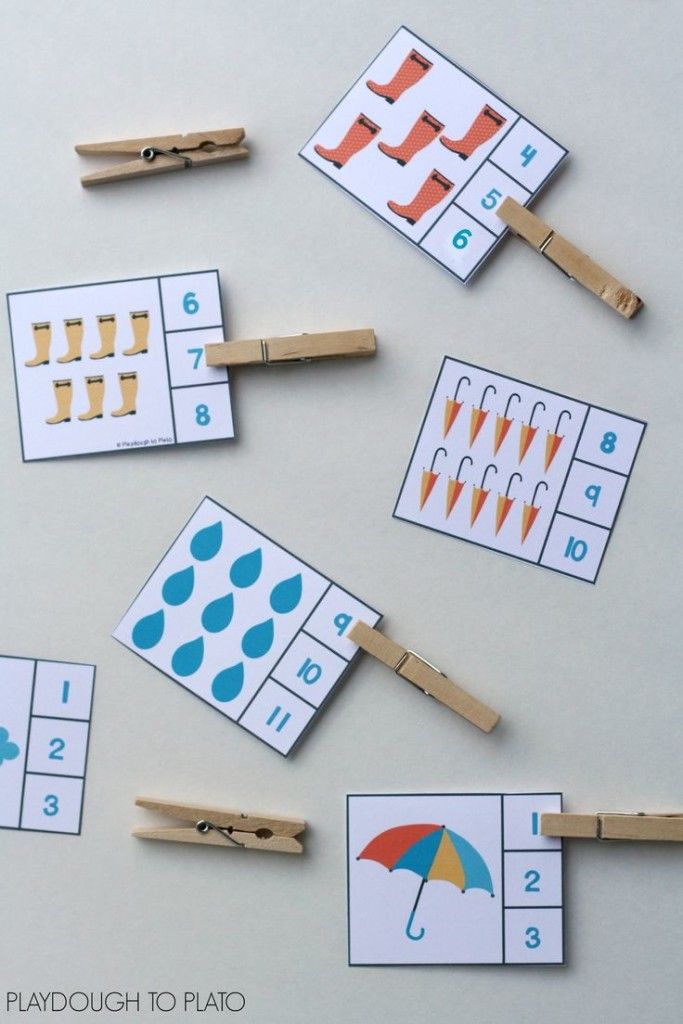 How many grandchildren does a grandmother have?
How many grandchildren does a grandmother have?
Birds flew over the river: dove, pike, 2 tits, 2 swifts and 5 eels. How many birds? Answer soon!
7 candles burned. 2 candles extinguished. How many candles are left? (2. the rest burned down)
There are three apples in the basket. How to divide them among three children so that one apple remains in the basket? (give one apple along with the basket).
There are three thick branches on a birch, each thick branch has three thin branches. On each thin branch, one apple. How many apples are there? (Not at all - apples do not grow on a birch.)
Tasks in verse
Apples fell from a branch to the ground.
Wept, wept, tears shed
Tanya collected them in a basket.
I brought as a gift to my friends
Two Earrings, three Antoshka,
Katerina and Marina,
Olya, Sveta and Oksana,
The biggest one - to my mother.
Speak quickly,
How many Tanya's friends?
An asterisk fell from the sky,
She ran to visit the children.
Two shout after her:
"Don't forget your friends!"
How many bright stars have disappeared,
Have fallen from the starry sky?
The holiday is coming soon. New Year,
Let's get up in a friendly round dance.
Let's sing a song loudly,
Congratulations to everyone on this day.
Let's prepare gifts for everyone,
This holiday is very bright.
Katya, Masha and Alenka
We will give a gift at Burenka,
Andryusha and Vityusha -
By car and pear.
Sasha will be happy with Petrushka
And a big colored cracker.
Well, Tanechka - Tanya -
Brown bear in a gray plush.
You, friends, count the guests
Call their names.
An old woman decided to bake cheesecakes.
I put down the dough and fired up the oven.
The old woman decided to bake cheesecakes,
And how many of them are needed - she completely forgot.
Two things for granddaughter,
Two things for grandfather,
Two things for Tanya,
Neighbor's daughters…
I counted, counted, but lost my way,
And the stove was completely heated!
Help the old lady count the cheesecakes.
In the fish kingdom to the sturgeon
They come in the morning
Three young pike,
To clean his cheeks,
And four chebak
Wash their belly and sides.
Count, kids,
How many servants does a sturgeon have?
V. Kudryavtseva
Once upon a time
at the waistcoat
Three loops
and two cuffs.
If you count them together
Three and two, of course, five!
Just know,
what is the secret?
The vest has no cuffs!
G.Novitskaya
Six nuts mother-pig
Carried for children in a basket.
Hedgehog met a pig
And gave four more.
How many nuts did the pig
bring to the children in the basket?
Three hares, five hedgehogs
They go to kindergarten together.
We will ask you to count,
How many kids are in the garden?
Five pies lay in a bowl.
Two pies were taken by Lariska,
Another one was stolen by a pussy.
How much is left in the bowl?
Our cat has five kittens,
They sit side by side in a basket.
And the neighbor's cat has three!
So cute, look!
Help me count,
How much is three and five?
Seven geese set off.
The two decide to take a break.
How many of them are under the clouds?
Count yourself, children.
The apples in the garden are ripe,
We managed to taste them
Five ruddy, bulk,
Two with sourness.
How many are there?
A rooster flew up on the fence,
I met two more people there.
How many roosters have become?
Three chickens are standing
They are looking at the shells.
Two testicles in the nest
Lying at the mother hen.
Count the turns,
Answer quickly:
How many chickens will my hen have
?
Six funny cubs
They rush to the forest for raspberries
But one of them is tired,
Now find the answer:
How many bears are ahead?
Arranged by Andryushka
Two rows of toys.
Next to the monkey -
Teddy bear.
Together with the fox -
Bunny oblique.
Following them -
Hedgehog and frog.
How many toys
did Andryushka arrange?
Granny fox gives
Mittens to three grandchildren:
“This is for you, grandchildren,
mittens, two each.
Take care, do not lose,
How many, count!”
A seagull warmed up the kettle,
Invited nine seagulls,
“Come all for tea!”
How many seagulls, answer!
Squirrel dried mushrooms on the Christmas tree,
She sang a song and said:
“I don’t know troubles in winter,
Because there is a fungus:
White, camelina, two oil cans,
Three cheerful honey mushrooms.
The boletus is large,
This is what he is famous for <
And there are exactly six chanterelles.
Try to count them all!”
My mother and I were at the zoo,
We fed the animals from our hands all day.
Camel, zebra, kangaroo
And long-tailed fox.
Big gray elephant
I could hardly see.
Tell me soon, friends,
What animals did I see?
And if you could count them,
You are simply a miracle! Well done!
Rain, pour more fun!
Do not be sorry for warm drops!
Five for Seryozhka, three for Antoshka,
Two for Valyusha and Katyusha.
And for mom and dad
Forty will not be enough.
Well, you friends count,
How many drops answer!
Along the path along the bushes
Eleven tails were walking.
I was also able to count,
That walked thirty feet.
It was going somewhere together
Roosters and pigs.
And now the question is this:
How many roosters were there?
And I would be glad to know
How many pigs were there?
Did you manage to find the answer?
Goodbye, hello everyone!
N.Razgovorov
Along the ravine
There was a cap,
Two kerchiefs,
Three baskets,
And behind them was stubbornly
Snow-white panama.
How many children were there in total?
Answer quickly!
One evening to the bear
Neighbors came to the cake:
Hedgehog, badger, raccoon, “oblique”,
A wolf with a cheating fox.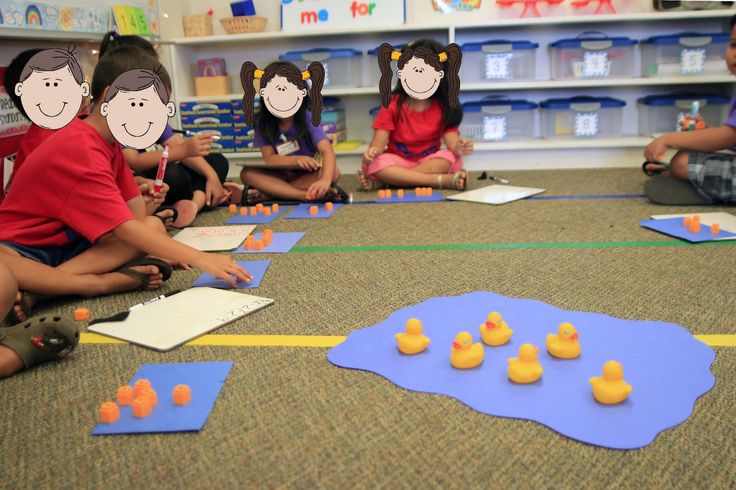
But the bear couldn't
Divide the pie.
The bear sweated from labor -
He didn't know how to count!
Help him quickly -
Count all the animals.
B. Zakhoder
Seven merry little pigs
Standing in a row at the trough.
Two went to bed to go to bed,
How many pigs have a trough?
Four goslings and two ducklings
Swimming in the lake, shouting loudly.
Well, count quickly -
How many babies are there in the water?
Good hedgehog at the market
Bought boots for the family.
Boots on the leg - for myself,
A little smaller - for my wife.
With buckles for my son,
With clasps for my daughter.
And he put everything in a bag.
How many legs does a hedgehog have in a family?
And how many boots did you buy?
Natasha has five flowers,
And Sasha gave her two more.
>Who can count here,
How much is two and five?
Mother goose brought
Six children to walk in the meadow.
All goslings, like balls,
Three sons, how many daughters?
Four ripe pears
Swinging on a branch
Pavlusha took two pears,
And how many pears are left?
Grandson Shura good grandfather
Yesterday gave seven pieces of candy.
Grandson ate one candy.
How many pieces are left?
Mom embroidered the carpet.
Look at the pattern.
Two large cells
Each with three branches
Masha sat down on the bed,
Wants to count the branches.
No way
Who will help her?
Once to the hare for lunch
A friend-neighbor galloped up.
Bunnies sat on a stump
And ate five carrots each.
Who counts, guys, dexterous?
How many carrots have you eaten?
Under the bushes by the river
May beetles lived:
Daughter, son, father and mother.
Who can count them?
Seryozhka fell into the snow,
Alyoshka followed him.
And behind him is Irinka,
And behind her is Marinka.
And then Ignat fell.
How many were all the guys?
Hedgehog gave the ducklings
Eight leather boots.
Who will answer from the guys,
How many ducklings were there?
How they stood in a circle under the Christmas tree
A hare, a squirrel and a badger,
A hedgehog and a raccoon stood up,
Elk, a wild boar, a fox and a cat.
And the bear was the last to stand,
How many animals are there? Answer!
Preschool Math and Counting Fun
Toddler Play Activities 5 to 5 (2yrs 6mths)
Make 5 shapes. For example: square, circle, rectangle, triangle, oval. Complete each shape in 5 colors. You will get 25 figures. Then you can expand the amount. Glue the shapes onto cardboard. It is advisable to stick with a sticky film. First lesson: ask the child to lay out all the red figures separately; separately - green, etc. Such an activity can be carried out for a very long time, constantly returning to it. Second lesson: offer to decompose into figures (separately - squares; separately - circles, etc.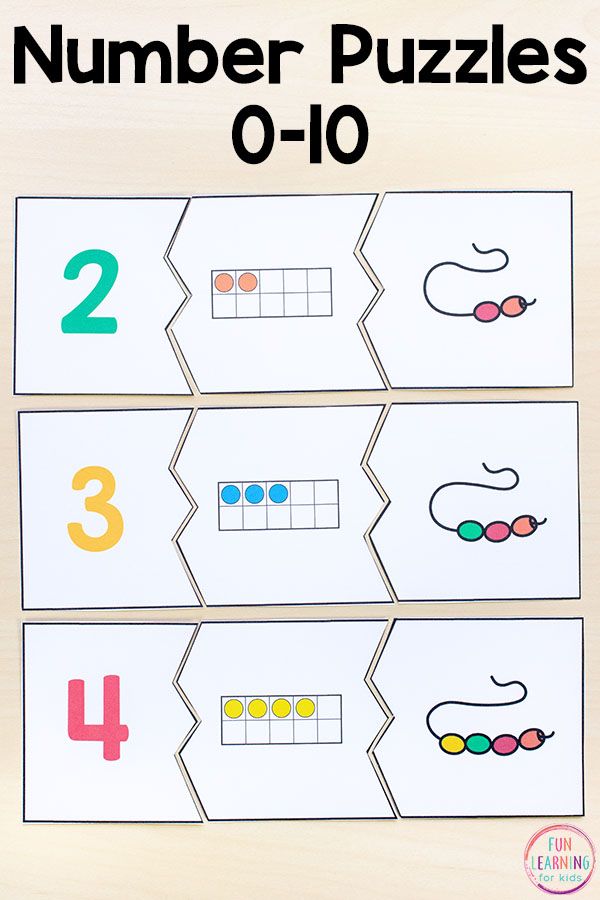 ) Third lesson: lay out the figures in this way: red figures are in front of the child, green ones are behind ...
) Third lesson: lay out the figures in this way: red figures are in front of the child, green ones are behind ...
Household account (1 year 6 months)
Count everything together with the child. We note that, as in most of these activities, you should not start with prodding like “Well, let's count the steps with you!”, But you yourself should count for your own pleasure. At the beginning, your goal is to demonstrate to the child the possibilities of oral counting, to arouse interest in him.
- How many steps.
- How many apples did you buy.
- How many forks are on the table. etc.
Cards (1 year 6 months)
Make cards with numbers (up to 10 at the beginning). Cover them with foil. Learn to put them in order.
Studying zero (2 years)
You can enter zero using the following questions:
- How many cows are in your pocket?
- How many crocodiles do we have at home? etc.
- Put 5 cubes on the table. Take one at a time and ask how much is left. First, 1 cube (4 will remain), then 1 more, etc. Until 0 remains.
First, 1 cube (4 will remain), then 1 more, etc. Until 0 remains.
Count using verses (1 year 6 months)
Leonid Yakhnin. "Bench". (Draw multi-colored benches or lay them out of geometric figures and count.)
| In our park on the alley Multi-colored benches: On a brown bench Two noisy families. On another bench, white, Only the girl was sitting. And near the red bench A big, dangerous bulldog lay down. Grandmother is sitting on blue, On her knees is a cat in a basket. | Two workers took a rail - Repairing a yellow bench. We will sit down with you On the blue bench. And on the most distant, On a green bench - Carved maple leaves. Everyone had enough for a bench In our park on an alley. |
Vladimir Orlov. “I’m counting” (After reading the poem, invite the child to lay out figures that look like animals or any geometric shapes, then count how many animals live in the zoo)
| Everything I see in the yard Everything I see on the way I can, I can Count to ten.  I'm going to the zoo with my mother And I'm counting everyone. A porcupine is running, This is it. An owl cleans its feathers, This is two. The third was a wolverine, And the fourth was a turtle. | The gray wolf went to bed, It's five. A parrot in dense foliage, He is the sixth. Here is the calf next to the elk, This will be seven and eight. Nine is a hippopotamus. Mouth like a grandmother's dresser. A shaggy lion walks in a cage, He is the last, he is the tenth. I can't count further - We must start again! |
From the book “Tell poems with your hands” (based on English folklore, translated by V. Egorov)
“Kittens”
(Ask the Child to prepare five geometric figures. While reading the poem, the Child should remove one figure at a time. How many kittens are left in the room?)
Here are five kittens.
One left - and he is gone.
Well, he doesn't exist - and he doesn't. There are four kittens left.
Here are four kittens. One at night sometimes
He climbed a tree - there were three kittens left.
But somewhere a little mouse squeaked thinly.
The kitten heard - there are two kittens left.
One of them with a ball disappeared in the doorway without a trace,
And the smartest one is the one left, the last one -
Milk from a bowl began to lap for five.
Curling or stroking fingers (2.5 years)
Who has more. This game can be played with two or three people. To play, you need a cube with dots. Buttons, cones, nuts, etc. can be used as counting material.
Place buttons (nuts) in a vase or box. Now take turns rolling the dice. What number falls out, so many are taken from the vase of objects. When the vase is empty, count who has more. Find a pair. Put 4-5 different toys in front of the child. (cube, ball, matryoshka, bunny…)
Put about the same number of toys aside. Invite your child to find 2 identical toys:
Invite your child to find 2 identical toys:
1) by color;
2) according to the form;
3) by size (size).
If the child chooses the wrong toy, place two toys next to each other. Ask: “Is it the same color?” “Is the cube also round?”
Option: The same task, but with pictures.
You should alternate classes with objects and pictures. What has changed? Option 1: develop visual memory.
Place 4-6 toys in front of the child. Count: the first is a Bear, the second is a bunny, etc. Then ask the baby to turn away and swap the two toys. The kid must guess what has changed. Option 2: Further, closer.
Put a house in front of the baby and 3 toys at different distances from it. Determine who is closer to the house, who is farther. Then ask the child to turn away and change the position of 2 toys. “Now who is closer to the house? Who is farther from the house? “Option 3: Above-below.
Place 3-4 cubes of different heights on the table with different toys on them. Find out which toy is higher than all, which is lower. Then ask the child to turn away and swap the two toys. “Which toy is the tallest now?”
Find out which toy is higher than all, which is lower. Then ask the child to turn away and swap the two toys. “Which toy is the tallest now?”
| Sing along, sing along: Ten birds flock. This bird is a nightingale, This bird is a sparrow. This bird is an owl, Sleepy little head. This bird is a waxwing, | This bird is a corncrake, This bird is a starling, A gray feather. This one is a finch. This one is a swift. This one is a cheerful siskin. Well, this one is an angry eagle. Birds, birds go home! |
Toddler math game
Cut out sets of animal figures or toys, such as dolls, nesting dolls, from construction paper. All figures in the set must be of different sizes and colors. On a sheet of paper, draw houses, also of different sizes.
The bears are going for a walk
Ask the child to find the biggest bear and put it down first. (underline this concept with intonation: “first”), then find the smallest one. And, finally, we will build according to the growth of all the others. If the child is at a loss, offer to attach one figure to another. When all the figures are lined up in height, come up with names for each character with the baby. Then ask: “who is our second?” Phil. Who is our last, sixth?” - "Motya".
(underline this concept with intonation: “first”), then find the smallest one. And, finally, we will build according to the growth of all the others. If the child is at a loss, offer to attach one figure to another. When all the figures are lined up in height, come up with names for each character with the baby. Then ask: “who is our second?” Phil. Who is our last, sixth?” - "Motya".
Find a house for each bear
The meaning of the game is the same - arrange objects according to their height and practice counting. First, we arrange the figures according to their height, and then we select the houses for them by size.
Looking for a toy
Take any toy, for example, a teddy bear, tell him that he is looking for a matryoshka doll that is in front of the blue one (after green, between yellow and red, to the right of blue, to the left of purple). Mastering the concepts of “before”, “after”, “between”, “right”, “left” will help your child navigate the world around him.
Looking for a toy 2
It is worth preparing for this game in advance - put the images of nesting dolls on a large sheet of paper and circle them. First, you can make drawings in one row, and when the baby can easily cope with this task, place the contours on the sheet “in loose”. Tell the baby that each nesting doll has its own place, show the contours of the nesting dolls. But one day, after a walk, the nesting dolls mixed up their places. Invite your child to help them. This game develops the eye well, develops the habit of bringing the work started to the end.
Make no mistake!
Helps to master the sequence of natural numbers, exercises in direct and backward counting. The game uses a ball. Children stand in a semicircle. Before starting, they agree in what order (forward or reverse) they will count. Then they throw the ball and call the number. The one who caught the ball continues to count further. The game is played at a fast pace.
Find a toy
The driver leaves the room. At this time, hide the toy. Then the child is explained where to find it: “You need to stand in front of the table, and go 3 steps forward, two steps to the left, etc. ". Children complete the task, find a toy. When the children begin to navigate well, the tasks can be complicated - to give not a description of the location of the toy, but a diagram. According to the scheme, children must determine where the object is hidden.
At this time, hide the toy. Then the child is explained where to find it: “You need to stand in front of the table, and go 3 steps forward, two steps to the left, etc. ". Children complete the task, find a toy. When the children begin to navigate well, the tasks can be complicated - to give not a description of the location of the toy, but a diagram. According to the scheme, children must determine where the object is hidden.
Getting to know the numbers
To play, you will need counting cards with pictures. (you can download zip. above), numbers (on cards or any other), chips.
It is best to play together. Lay out all the cards face up. Put the numbers in the box. Take turns taking the numbers out of the box. The task is to find cards with the corresponding number of items. A chip is placed on the found card. The number is put back in the box.
When the game is over, count who has the most chips. It’s better to do it like this - put the chip in two rows and compare whose row is longer.
Guessing game
Yogurt boxes or plastic cups can be used for this game. Write or stick a number on each cup. Pick up some toy that will fit in the cup.
This game is played by two people. Place cups upside down. One player turns away, and the second at this time hides the toy in one of the cups. The first player must guess under which cup the toy is hidden, and the second must give him hints. For example: the toy is hidden under the cup with the number 5. The player asks: “Under the second?”. - "No more".
Who has more
This game can be played with two or three people. To play, you need a cube with dots. Buttons, cones, nuts, etc. can be used as counting material.
Place buttons (nuts) in a vase or box. Now take turns rolling the dice. What number falls out, so many are taken from the vase of objects. When the vase is empty, count who has more.
Logic problems for preschoolers
Giraffe, crocodile and hippo
lived in different houses.
The giraffe did not live in a red house
or in a blue house.
The crocodile did not live in the red
and not in the orange house.
Guess what houses the animals lived in?Three fish swam
in different aquariums.
The red fish swam not in a round
and not in a rectangular aquarium.
Goldfish - not in a square
and not in a round.
In which aquarium did the green fish swim? Once upon a time there were three girls:
Tanya, Lena and Dasha.
Tanya is taller than Lena, Lena is taller than Dasha.
Which of the girls is the tallest,
and who is the shortest?
Which one of them is called?Misha has three carts of different colors:
Red, yellow and blue.
Misha also has three toys: a tumbler, a pyramid and a spinning top.
In the red cart he will carry neither a top nor a pyramid.
In yellow - not a top and not a roly-poly.
What will Mishka be lucky in each of the carts?The mouse is neither in the first nor in the last carriage.

The chicken is not in the middle and not in the last carriage.
In which carriages do the mouse and the chicken travel?The dragonfly does not sit on a flower or on a leaf.
The grasshopper sits neither on a fungus nor on a flower.
The ladybug does not sit on a leaf or on a fungus. Who is sitting on what? (better to draw everything)Alyosha, Sasha and Misha live on different floors.
Alyosha lives neither on the top floor nor on the bottom one.
Sasha doesn't live on the middle floor or on the bottom floor.
On which floor does each of the boys live?Anya, Yulia and Olya's mother bought fabrics for dresses.
Anya is neither green nor red.
Yulia - not green and not yellow.
Ole - not yellow and not red.
Which fabric for which girl?There are different fruits in three plates.
Bananas are not on a blue or orange plate.
Oranges not in a blue and pink plate.
Which plate contains plums?
What about bananas and oranges?The flower does not grow under the tree,
The fungus does not grow under the birch.
What grows under the tree,
What grows under the birch?Anton and Denis decided to play.
One with cubes and one with cars.
Anton did not take the typewriter.
What did Anton and Denis play with?Vika and Katya decided to paint.
One girl drew with paints,
and the other with pencils.
What did Katya start to draw with?Red and Black clowns performed with a ball and a ball.
The red clown did not perform with a ball,
A black clown did not perform with a ball.
What subjects did the Red and Black clowns perform with?Lisa and Petya went to the forest to pick mushrooms and berries.
Lisa did not pick mushrooms. What did Petya collect?Two cars were driving on a wide and a narrow road.
The truck was not driving on a narrow road.
Which road was the car driving on?
And the truck?Learning to tell the time by the clock
First, let's make a fake watch.

Perfectly made from a cake box, the cake can be eaten. The difficulty is different: many years and many children have led us to the idea that ordinary wall clocks are an unnecessary study load and these activities need to be simplified and done in stages.First, we make a regular dial, but we leave the minute dashes bare, without defining the number of minutes, and we also abolish the minute hand.
Time is divided into:
- hour,
- just over an hour,
- half past one (or one and a half),
- about two,
- two,
- is a little more than two, and so on.
When this part is over and the child is oriented clockwise with complete confidence, we proceed to work with the minute hand within one hour (60 minutes), but this can also be done in parallel. And do not rush to combine the arrows!
Work with the hour hand can be started in 3.5-4 years, and we see no particular reason to hurry.
Most of the first-graders are not able to tell the time by the clock with hands. This is a medical fact.
Very often it seems that a child of six or seven years old is about to learn to tell time accurately, but time passes and confusion continues.
It seems to us that this problem is easily explained by the fact that what to connect in the minds of two superimposed dials - hour and minute - for a child's mind is a colossal load , and a child should not be taught to determine the time by such a clock.
Throw away the minute hand and the dial division into minutes. There are 12 digits left and dividing the time by, for example, four, a little more than four, half past five, about five, five, a little more than five. There is plenty of such a rough division of time for a child, and this can be taught starting from four to four and a half years. Let it take a YEAR. Don't force things.
Only when the child perfectly feels the position of the hour hand, very slowly, minute by minute, enter the second parallel dial.
Take your time with quarters (Quarter and Quarter), take your time with five minutes, ten minutes, etc. This should be moved to the next, separate stage. Let your wall clock in the room or in the kitchen have only an hour hand for a long time, but the numbers can be changed, Roman numerals can be entered almost immediately.
And if we have long been giving all the concepts and it seems. that victory is near, is it right to go further or still return to the clock face?
We think that the introduction for some time of a dial with only an hour hand will create a correct sense of time in the child and improve his relationship with the clock.
Mosaic of buttons - educational game for children
At the age of 6, innervation occurs in children (supply of organs and tissues with nerves, which ensures their connection with the central nervous system). The upper phalanges of the fingers (pads) become sensitive.
Why buttons?
Different texture, many colors, shades, sizes and shapes.
There is no specified form for the composition. The child develops a sense of space and a sense of color. Button exercises help develop fine motor skills.
You can buy these buttons at any store, and for the first lessons, use the stocks in your home. Surely your closets store clothes that you don't wear. Argue with her buttons and you can start practicing.But the main idea of the “button mosaic” is that by school the child has formed images of the sets 2, 3, 4, 5. To do this, even before the age of six, the child needs to play enough to fix the images of the sets through objects. This should be done only through the real world, not informationally (cartoons and books), but through sensory perception: tactility, tangibility, smell, etc. Interaction with an object (a kitten, a chair, a toy car, etc.) is much more emotional, so the images are brighter and are fixed clearly.
How many eyes? Two. And the ear? Two. Show two fingers.
And the cat's paws? Four.
In no case should you count, just call - four.
When the images are fixed, i.e. the child easily shows 2,3,4 without counting, you can proceed to operate with sets on the fingers or on any other counting material. How else can you show four? Two and two. There are five fingers on the hand. And if you break it into two groups, into three? How else can you show three and three? It's five and one. And the more options are played, the more clearly the images of the sets are fixed in the child. How can you divide 10? Again looking for different options.
Large bones, nuts, stones, etc. can be used. An ideal occupation is to sort out cereals by 3 grains, by 2, by 4. Quite semantic and useful activity. You can also divide a large amount of something into sets. A dozen is enough for the school to easily give an oral count of four-digit numbers (without resorting to counting in a column), and the multiplication table - you don’t have to cram.