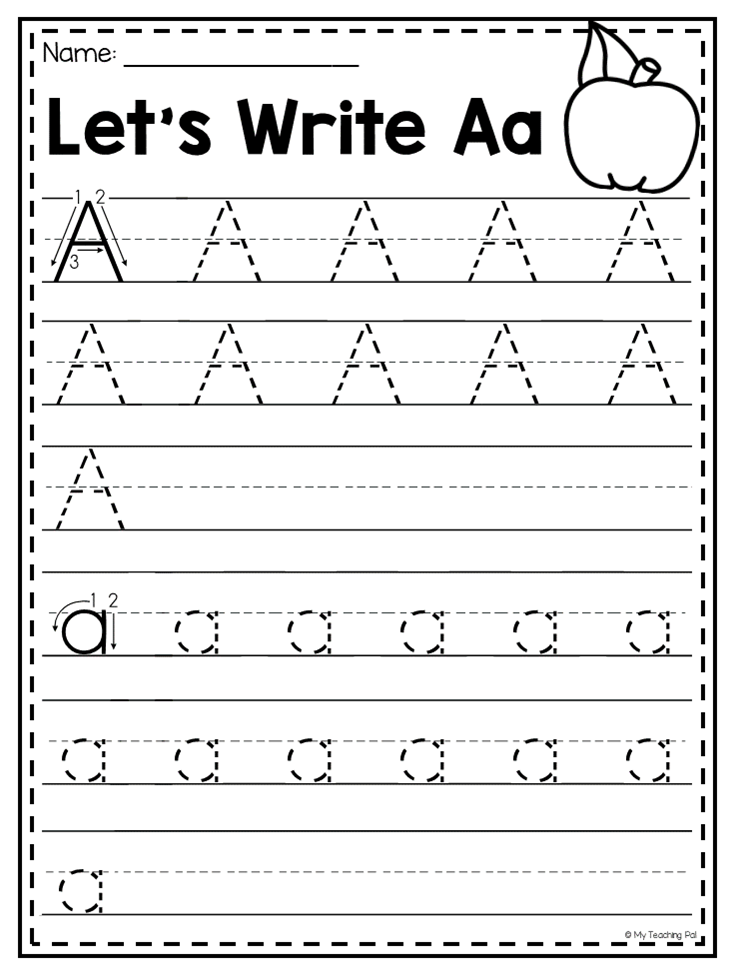
How many syllables in energy
سبورة - How many syllables?
1. Read, match and say.
a) Write the number of the missing sentence in the box.
| Disadvantage | Advantage | |
| 2 | you’ll save water. | If you don’t water the plants, |
| 5 | you’ll save energy. | If you turn off the lights, |
| you’ll sometimes get wet | 3 | If you walk to school, |
| you’ll be very cold. | 4 | If you switch off your fire, |
| 3 | you’ll produce clean energy. | If your dad gets a wind turbine |
| it won’t heat water at night. |
1 | If your dad gets a solar panel, |
b) Talk to a partner. Make dialogues.
If you turn off light, you will save energy.
Yes, but if I turn off light, I won't be able to see.
2. Write six sentences in your notebooks about the books.
- New Math's is the most difficult of the three books.
- New Math's is less exciting than Escape from lions.
- Escape from lions is the most exciting of the three books.
- Escape from lions is less interesting than Najd stories.
- ''Najd stories'' is the most interesting of the three books.
- ''Najd stories'' is less exciting than Escape from lions.
GRAMMAR STUDY
. Complete this information about adjectives with two or more syllables. Use words from the box
Use
When we 1compare two or more people, 2 places or things, we use more and most and less and 3 least with longer adjectives.
How many syllables?
We 4 use more and most and less and least with all 5 adjectives with three or more syllables.
We use more and most and less and least with lots of adjectives with two 6 syllables.
Pronunciation corner
a) Read and underline the word with a different sound.
1. a folk b float c cover d solar.
2. a message b teenage c advantage d fridge.
3. a check b measure c protects d leak.
4. a fashionable b wasteful c pastes d toothache.
5. a women b frequently c fix d businessman.
6. a waterproof b quarter c sauce d laugh.
Expert Tips And Activities For Helping Kids Understand Syllables
Do you remember when you first learned about syllables? Most people will answer “no” to this question, and that’s understandable — it was a very long time ago!
Regardless of how long ago it was, understanding syllables has played a significant role in helping you read and write more proficiently. And now that your child is on their journey of learning about syllables, you may want to know how you can help.
And now that your child is on their journey of learning about syllables, you may want to know how you can help.
This article will share what you need to know about helping your child understand syllables so that they can master this simple yet effective learning curve.
What Is A Syllable?
The dictionary describes a syllable as “an uninterrupted segment of speech consisting of a vowel sound, a diphthong, or a syllabic consonant, with or without preceding or following consonant sounds.”
In much simpler terms, we can describe a syllable as always having one (and only one) vowel sound. Quite often, this vowel sound is accompanied by consonants.
For example, the word bat is a one-syllable word, as you would expect because of its length. But it’s important to note here that the length of a word has nothing to do with how many syllables it has.
The word straight, for instance, has only one syllable since aigh makes the long A sound and that is the only vowel sound in the word.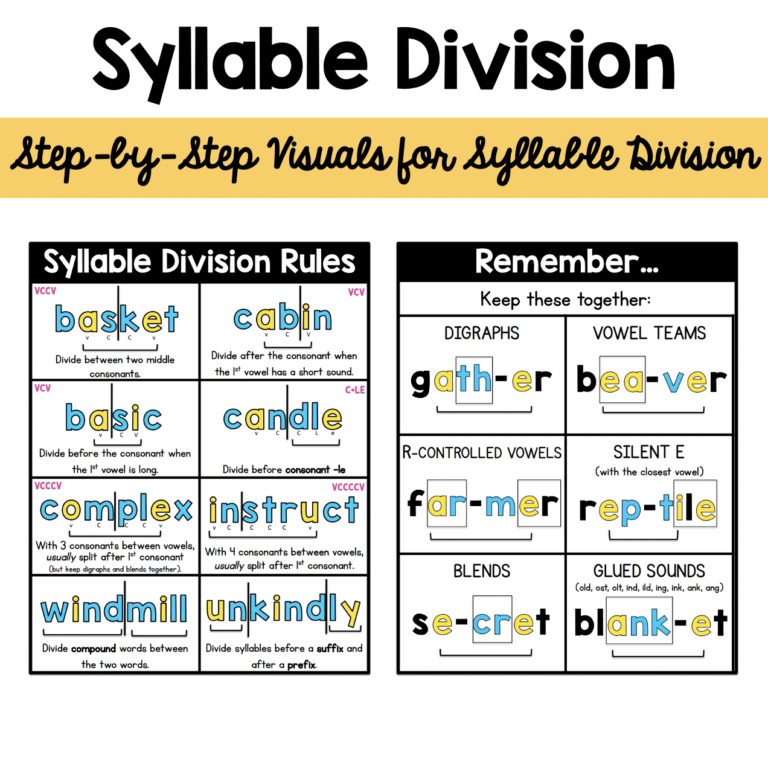 On the other hand, a shorter word — such as over — can have more than one syllable.
On the other hand, a shorter word — such as over — can have more than one syllable.
It’s also important to note that there are six types of syllables: open, closed, silent E, vowel pair, R-controlled, and final stable. Your child will start learning more about the different types of syllables in elementary school.
For now, understanding the basic elements of a syllable is what matters. This comprehension will help children as they get older and come across more complex words.
Why Is Understanding Syllables Important?
Now that we’re on the same page about what syllables are, let’s focus on why they are so important.
In a nutshell, learning syllables:
- Helps speed the process of decoding words
- Helps with accurate and fluent reading
- Helps with spelling
As children move from learning basic words to compound words with two syllables (e.g., railroad, pancake, etc.), understanding syllables can help them decode and blend them more quickly.
After all, it’s much easier to read an unfamiliar word in chunks than to read it as one continuous string.
Additionally, breaking a long word down into pieces makes it much easier to spell it correctly, rather than trying to remember each and every letter in the word and the correct sequence.
How To Help Kids Understand Syllables
Before we get into the activities that can help you teach your child about counting syllables, there are a few points we’d like to mention. Let’s take a look!
1) Think Of Syllables As “Chunks” Of A Word
With multi-syllable words, helping your child focus on the “chunks” rather than every letter of a long word will make grasping syllables much easier.
Breaking a longer word into pieces is an effective reading strategy that can help your child improve their reading speed and comprehension. It’s a strategy you likely use without even thinking about it anymore.
For example, if you see a long word, such as uncomplicated, your brain automatically applies what you know about syllables to make reading it a breeze.
You know that there’s a prefix (un) and a suffix (ed). Once you remove those chunks, you can easily break the remaining letters down into even smaller pieces: comp, li, cat. And you know that the A in that final syllable is long even though it looks like the word cat.
Then, your brain puts everything together again like this: un-comp-li-cat-ed. While it sounds like a hard process when you see it written out, all of this goes on behind the scenes in your mind. You no longer have to stop and decode every single word. It’s automatic.
And that’s the goal of this process: to help kids learn how to automatically break words down into pieces that are easier to read.
Of course, it won’t happen overnight. It’ll take years of learning and practicing. But each time you work on it together, you’re helping build a solid reading foundation.
2) Focus On The Vowel Sounds
A syllable only has one vowel sound. This means it doesn’t matter how many letters there are in the syllable. It also doesn’t matter how many vowels a syllable may have. The vowel sound produced is the real focus.
It also doesn’t matter how many vowels a syllable may have. The vowel sound produced is the real focus.
The first words your child reads will likely be short-vowel, one-syllable words, such as:
- Cat
- Fan
- Map
- Flag
- Clap
These words have only one vowel sound — often in the middle of the word — and are taught early on.
However, it won’t be long before your child will be reading words with multiple vowel sounds, such as:
- Paper
- Freedom
You have the letter A in the word paper, making the long A sound. Then, at the end, you find the vowel E being bossed around by the letter R to make the er sound. That means there are two different vowel sounds in this word.
If you count the vowels in the word freedom, you’ll find three vowels — two E’s and an O. However, since the two E’s work together to make a single vowel team, there are only two vowel sounds in this word.
Having a better understanding of how vowel sounds work will give your child the decoding skills they need to tackle multisyllabic words confidently in the future.
3) Continue Helping Them Develop Their Reading Skills
Reading is one of the core subjects in Homer’s early learning program. Why is that?
Early childhood reading provides lots of benefits, including improved vocabulary, better communication, and brain development.
In addition, the more a child reads, the more they’ll come across unfamiliar words and the more chances they’ll get to practice their syllable skills.
At this early-reading stage, it’s not important for your child to thoroughly understand the concept of syllables. They may not be able to correctly define the word or know the differences between the types of syllables.
And that’s OK! Your goal right now is to simply introduce the concept.
Then, when they’re learning even more about syllables later, they’ll have the background knowledge they need to anchor their learning.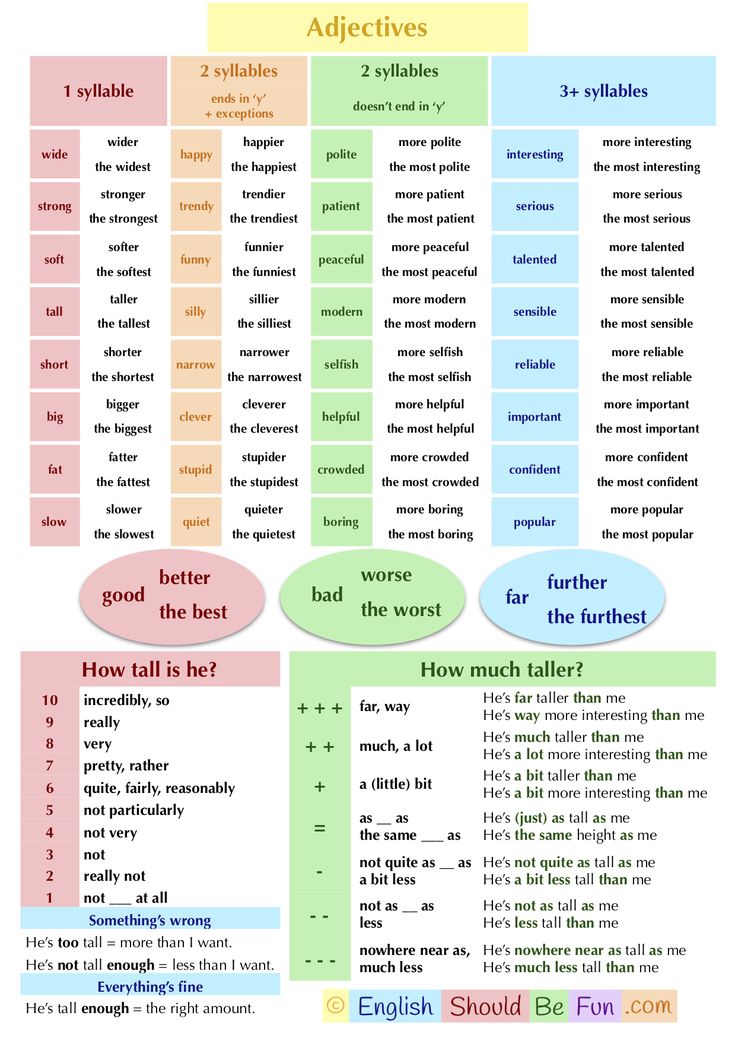 They’ll think back to these fun activities you used to do together and have an “ah-ha” moment when everything clicks.
They’ll think back to these fun activities you used to do together and have an “ah-ha” moment when everything clicks.
So, don’t worry if this concept seems challenging for your child right now. Just keep talking about syllables and doing these activities. Over time, you’ll help your child strengthen their reading skills.
And, since you’re doing it through play, they won’t even realize they’re learning.
8 Simple Syllable Activities
No matter what you’re working on with your child, it’s important to keep things light and fun! This helps your child stay engaged and eager to learn.
A great tactic you can use for teaching syllables in an engaging way is to start with words that already interest your child. These can be the names of the family pets, their friends, their favorite foods, and so on.
Here are some activities to help your young learner understand syllables while also having fun!
1) Clap Time
Associating the syllables of a word with “beats” is one of the most effective (and fun!) ways for children to grasp the concept of syllables. In this activity, your child will clap the beats of a word.
In this activity, your child will clap the beats of a word.
Start with simple words that your young learner will already be familiar with (mommy, daddy, apple, pizza, etc.).
When you begin, show your child how to clap the syllable: /pi/ (clap) /zza/ (clap). After demonstrating, ask them to join you as you clap the beats of other common words.
We recommend holding your hands wide apart and then making a big clap to help your child hear and see the number of syllables. Try to also have your child clap and say the syllable at the same time.
Don’t feel limited to two-syllable words for this activity. Instead, throw in some shorter, one-syllable words and longer, three or four-syllable ones. This way, your child understands that words come in all different lengths.
To help you mix things up, here are a few common words you can clap with your child, broken down by the number of syllables.
Single-Syllable Words:
- Tree
- Sign
- Book
- Shirt
- Shoe
Two-Syllable Words:
- Toybox
- Mountain
- Freeway
- Sweatshirt
- Toenails
Three-Syllable Words:
- Vacation
- Celebrate
- Afternoon
- Computer
Four-Syllable Words:
- Calculator
- Avocado
- Television
- Cauliflower
- California
Throughout the day, pick a couple of words to clap the beats of. This way, it becomes second nature for your child to think about the syllables in a variety of words.
This way, it becomes second nature for your child to think about the syllables in a variety of words.
2) Syllable Stomp
Sometimes we all make the mistake of thinking that learning should only take place with a child seated formally in front of a desk and listening attentively to your instructions. But that’s not always the case, especially with younger children.
Most kids love to get up and move. So why not use their endless energy to help them learn more about syllables?
This game works similarly to the previously mentioned one. However, instead of clapping each syllable, your young learner will be stomping the ground for each syllable they say in a word. The louder the stomp, the better!
3) Mark The Paper
For this activity, all you need is a marker (or pencil or crayon, whatever you prefer!) and a sheet of paper.
Hand your child the marker and place the sheet of paper on a table in front of them. Choose a word, and then encourage your young learner to press the marker on the paper every time they hear a syllable.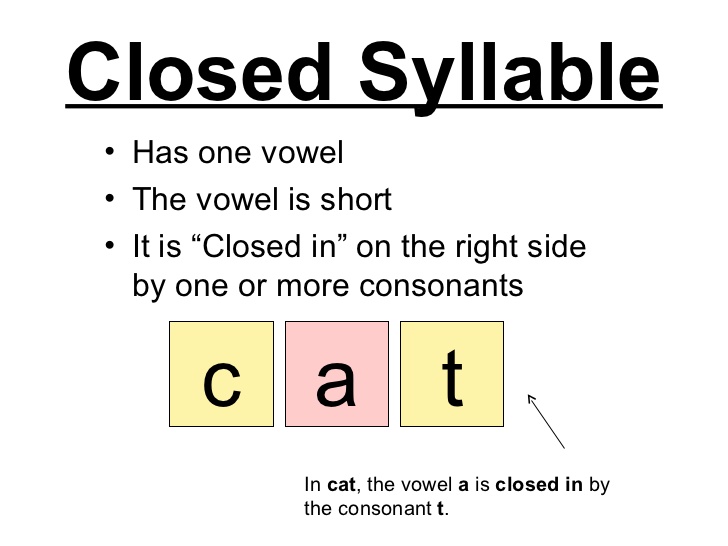
When they are done, they can count the number of marks on the paper to see how many syllables are in the word.
4) Hum The Word
Humming is a simple yet fun and effective way to teach your child about syllables. To get started, ask your child to close their mouth and hum a word. After that, have them count the distinct hums they made.
If your child has trouble with this, have them say the word aloud before they try humming it. You can also hum the word first and ask them to copy you. This modeling can give them the confidence they need to hum words on their own.
5) Robot Talk
“Speaking robot” is more than just fun and games. It can also help your young learner count the syllables of a word!
Have your child pretend to be a robot while talking. This will mean speaking in a very unnaturally stiff and stilted manner. As they say a word in “robot talk,” it is easy to count the syllables.
Really get into it by making a robot costume out of cardboard boxes for the occasion.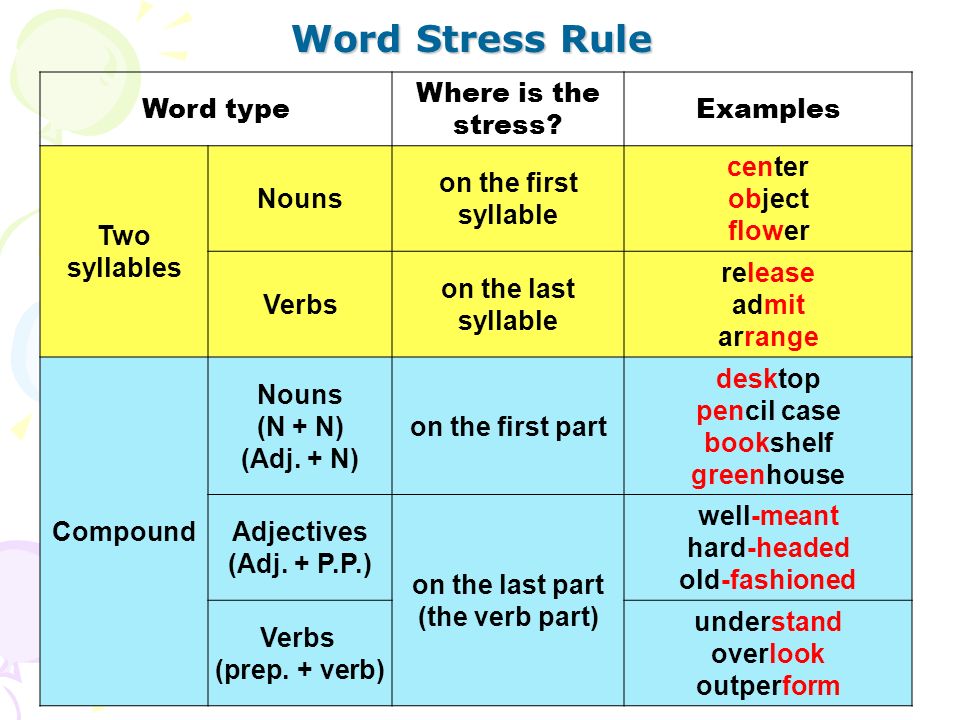 Pretend play and learning time combined? Yes, please!
Pretend play and learning time combined? Yes, please!
6) Hunt And Hop
Look around your home for a few simple items you can hide for your child to find. Try to pick objects with a different number of syllables.
Here are a few ideas:
- Key
- Jacket
- Potato
- Calculator
Once you hide them, ask your child to find one. For example, you can say, “Can you find the potato?” Let your child look around the room, hunting for the object you name.
Ask your child to say the word when the hidden item is found. Then, have them hop the number of syllables. For example, if your child found a potato, they’d jump three times.
Next, ask them to find another object. Continue until everything you’ve hidden has been found. Then, review the syllables once more. Have your child hop the right number of times for each object that you hid.
7) Jaw-Dropping Fun
By now, we’ve established that each syllable has one vowel sound. Our mouths need to open to help us make that vowel sound. This makes counting “jaw drops” the perfect opportunity to count syllables.
This makes counting “jaw drops” the perfect opportunity to count syllables.
Have your child place their hand under their chin and then count the number of times their jaw drops as they say a word. Those are the syllables!
If your child is having trouble with this, have them look in a mirror while they play. First, ask them to watch their mouth carefully while they say a word. Then, gently put your finger on their jaw. Finally, ask them to say a word.
As their mouth opens and closes, count each jaw drop aloud. Next, have your child put their hand where yours is. Once they understand what action they’re counting, they’ll be able to do this activity more independently.
8) Syllable Mix-Up
This fun game will help your child concentrate on unmixing syllables to make a word.
All you need to do is mix up the syllable order of a word and then encourage your child to unmix it. For instance, you can say /corn/pop. Then ask them what word you’re trying to make. They would answer “popcorn.”
They would answer “popcorn.”
As your child gets older and more comfortable with syllables, you can introduce harder words with three or more syllables. For example, /phant/e/el — elephant!
Once your child understands how to unmix the syllables, this is a fun, educational game to play in the car. Since it doesn’t require any materials, you can play it wherever you are.
You can give your child a mixed-up word, and then they can give you one to figure out. Take turns mixing and unmixing words until you arrive at your destination or you both get tired of the game.
Use the things around you in the car and on the road as ideas for words to mix up.
9) What’s My Word?
Say a word with three, four, or more syllables but leave gaps in between each syllable. For example, you can say /com/ /pu/ /ter. Your child would then put the syllables together to form the word.
You can also extend this game by beginning a word and having your child try to complete it. For instance, /re/ /frig/ /er/…and your child would add “/a/tor!”
For instance, /re/ /frig/ /er/…and your child would add “/a/tor!”
If you notice your child missing a syllable when they complete your word, don’t worry. Sometimes, they’re so busy focusing on syllables they don’t have enough mental energy left to think about the word.
Simply repeat the word and add the correct syllables to the end if this happens. Then, ask your child to say what you said. You can try it again later with a more familiar word to see if that helps.
10) Syllable I Spy
You can also incorporate syllables into familiar childhood games, such as “I Spy.”
To play this game, look around the room and pick an object you’d like your child to find. Then say, “I spy with my little eye something with two syllables.”
As your child guesses, you can reinforce their syllable knowledge. For instance, if they name something with only one syllable, you can say, “That is a good guess, but that word only has one syllable. I’m thinking of something with two syllables. ”
”
If they pick something with two syllables that isn’t the item you’ve selected, you can say, “That’s a great guess. You picked a word with two syllables. But it wasn’t the word I was thinking about. Can you find another item with two syllables?”
Because there can be a lot of things in a single room, it may be helpful to give your child a hint or two after they make an incorrect guess. Is the item brown, or is it made of wood, etc.?
Once they’ve correctly guessed your item, switch roles. Have them pick something and tell you how many syllables the item they’re thinking of has. Then, you try to guess.
11) Syllable Sort
Ask your child to go around the house and gather several small items. Have them place the items on a table or another flat, level surface.
While your child is off collecting things, gather two pieces of printer paper. On one of them, write “1 Syllable.” On the other piece, write “2 Syllables.”
Once your child returns, show them the papers you prepared. Point to the number on each so your child can see the difference between them. Ask your child to select one item they found and say what it is. Then, repeat the word. Ask, “How many syllables is in this word?”
Point to the number on each so your child can see the difference between them. Ask your child to select one item they found and say what it is. Then, repeat the word. Ask, “How many syllables is in this word?”
Next, have them place the item on the corresponding piece of paper. So, if it’s a one-syllable word, it would go on the “1 Syllable” paper.
Continue talking about each object and sorting them. When everything is sorted, ask your child to name the objects with one syllable and then those with two syllables. Keep going until everything has been named.
Once you’re done playing, you can ask your child to put the objects away by syllable count, too. For example, have them take all of the one-syllable items and put them where they belong. Repeat this process until everything is put away.
Make Learning Syllables Fun With HOMER
There are plenty of ways to help your child understand syllables. Whichever activity you choose, remember to make it fun and have patience as your child continues learning new concepts.
For more at-home activities to help your child learn to read, check out the HOMER Learn & Grow app, which is perfect for kids two to eight years old and makes learning fun, convenient, and effective. Just 15 minutes a day is proven to increase early reading scores by 74%!
Author
Words "energy" morphological and phonetic analysis
Explanation of the rules for dividing (breaking down) the word "energy" into syllables for transfer.
The Soosle.ru online dictionary will help: phonetically and morphologically parse the word " energy " by composition, correctly divide into syllables according to the rules of the Russian language, highlight parts of the word, put stress, indicate the meaning, synonyms, antonyms and compatibility for the word " energy ".
Contents:
- 1 Syllables in the word "energy" division into syllables according to the morpheme structure of the word "energy"
- 6 Synonyms of the word "energy"
- 7 Antonyms of the word "energy"
- 8 Stress in the word "energy"
- 9 Phonetic transcription of the word "energy"
- 10 Phonetic analysis of the word "energy" into letters and sounds (Sound-letter)
- 11 Sentences with the word "energy"
- 12 Matches for the word "energy"
- 13 Meaning of the word "energy"
- 14 Declension of the word "energy" by declensions
- 15 How to spell the word "energy" 16 k
- the word "energy"
Syllables in the word "energy" division into syllables
Number of syllables: 4
By syllables: e-ne-rgi-ya
r - unpaired voiced consonant (sonor), adjacent to the current syllable
How to transfer the word "Energy"
Ene - urgent
Energy
Morphological analysis of the word "Energy"
Part Speech:
Noun
Grammar:
part of speech: noun; nine0003 animate: inanimate;
gender: female;
number: singular;
case: nominative;
answers the question: (is) What?
Initial form:
energy
Analysis of the word "energy" by composition
| energy | root |
| i | ending |
energy
Words similar in morphemic structure “energy”
Words similar in morphemic structure
Synonyms of the word “Energy”
1. Heat energy
Heat energy
2. Electricity
3. Entertain value
4. Activity
5. Bioenergy
6. activity
7. hydropower
8. Shakti
2222 9. determination
10. perseverance
11. nutrition
12. temperament
Antonyms of the word “energy”
1. powerlessness
2. weakness in the word “
”0050
energy — stress falls on the 2nd syllable
Phonetic transcription of the word "energy"
[en'`erg'iy'a]
Phonetic analysis of the word "energy" into letters and sounds (Sound-letter)
| Letter | Sound | Sound characteristics | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| e | [e] | vowel, unstressed | e |
| n | [n'] | nine0103 consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), softn | |
| e | [`e] | vowel, stressed | e |
| p | [r] | consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), hard | p |
| g | [g’] | consonant, voiced double, soft | g |
| and | [and] | vowel, unstressed | and |
| i | [y'] | consonant, voiced unpaired (sonor), soft | i |
| [a] | vowel, unstressed |
Number of letters and sounds:
Based on the analysis made, we conclude that the word has 7 letters and 8 sounds.
Letters: 4 vowels, 3 consonants.
Sounds: 4 vowels, 4 consonants.
Sentences with the word "energy"
The task of removing nitrogen from the aquarium is performed by biofilters inhabited by bacteria, which use nitrogen-containing compounds as a source energy .
Source: Daria Kostina, Everything about the aquarium and fish, 2010.
It was then that he got acquainted with the role of the vital energy - qi (or ki).
Source: Yi-Shen, Reiki. The Art of Healing with Hands, 2006.
Full breathing allows you to accumulate a large amount of energy in the body, increases the useful volume of the lungs.
Source: Loy-So, Therapeutic self-massage. Basic techniques, 2009.
Matching of the word “energy”
1. life energy
life energy
2. magical energy
3. psychic energy
4. love energy
5. human energy 9008 60028 7. source of energy
8. flow of energy
9. amount of energy
10. energy runs out
11. energy runs out
12. energy ends
13. feel energy
14. use energy
15. possess energy
16. (complete compatibility table)
1. A general quantitative measure of the movement and interaction of all types of matter (it has various forms: mechanical, thermal, electromagnetic, nuclear, etc.). Law of energy conservation. (Small Academic Dictionary, MAC)
Declension of the word "energy" by declensions
| Case | Question | Singular unit | Plural Mn. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative Name. | what? | energy | energy |
| Genitive | what? | energy | energies |
DativeDat. | what? | energy | energy |
| AccusativeWin. | what? | energy | energy |
| Creative TV. | what? | energy, energy | energies |
| prepositional | about what? | energy | energies |
How to spell the word "energy"
Spelling of the word "energy"
Spelling of the word "energy"
The word is spelled correctly: energy
Numbering of letters in the word
Numbers of letters in the word "energy" in forward and reverse order:
- 7
e
1 - 6
n
2 - 5
e
3 - 4
p
4 - 3
g
5 - 2
and
6 - 1
i
7
Associations to the word «energy»
-
Electron
-
Clot
-
Throw
-
Cost
-
Accumulator
-
Absorption
-
Atom
-
Consumption
-
Radiation
-
Power plant
-
Particle
-
Generator
-
Reactor
-
Tide
-
Accumulation
-
Surplus
-
Conversion
-
Electricity
-
Molecule
-
Threads
-
Consumer
-
Matter
-
Supply
-
Impulse
-
Concentration
-
Source
-
Extraction
- nine0002 Emitter
-
Vacuum
-
Power engineer
-
Splash
-
Hydrogen
-
Charge
-
Pendulum
-
Production
-
Maintenance
-
Synthesis
-
Save
-
Cheerfulness
-
Plasma
- nine0002 Uranium
-
Substance
-
Electricity
-
Flow
-
Waste
-
Thermal
-
Double
-
Atomic
-
Redundant
-
Life
-
Solenoid
-
Indomitable
-
Mental
-
Energy
-
Quantum
-
Electric
-
Gravity
-
Nuclear
-
Colossal
-
Magical
-
Life-giving
-
Mental
-
Destructive
-
Negative
-
Power
-
Negative
-
Potential
-
Essential
-
X-ray
-
Positive
-
Magnetic
-
Consume
-
Consume
-
Radiate
-
Spend
-
Scoop
-
Work out
-
Suck
-
Concentrate
-
Consume
-
Accumulate
-
Load
-
Absorb
-
Accumulate
-
Save
-
Absorb
-
Deplete
-
Focus
-
Overflow
nine0017 -
suck
-
Dry out
-
Absorb
-
Supply
-
pour in
-
Release
-
Boil
-
Spend
-
Radiate
-
Charge
-
Emit
Kyrgyz language - Stress
Unlike Russian, two completely different stresses coexist in Kyrgyz: a power stress in a word and a musical stress in a phrase.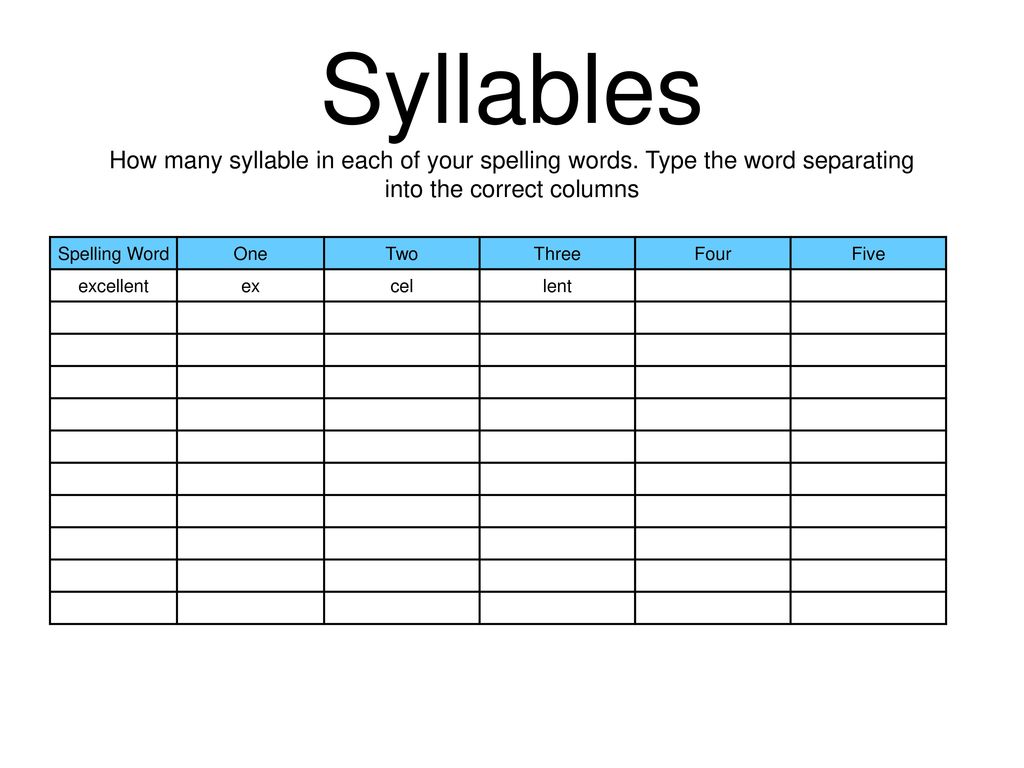 For a person with a native Russian who has not received special training in the field of phonetics, hearing these accents can be far from easy. Usually a surprise arises when you read in all textbooks of the Kyrgyz language that the stress must necessarily fall on the last syllable of a word, and then in speech you catch from time to time forms in which this is clearly not the case. What is the matter and how to be? nine0008
For a person with a native Russian who has not received special training in the field of phonetics, hearing these accents can be far from easy. Usually a surprise arises when you read in all textbooks of the Kyrgyz language that the stress must necessarily fall on the last syllable of a word, and then in speech you catch from time to time forms in which this is clearly not the case. What is the matter and how to be? nine0008
Let's first try to figure out the Russian accent, which, by the way, is one of the most difficult in the world. In Russian, the pre-stressed and stressed syllables form the so-called prosodic center. This is expressed in the fact that the energy that we spend on the pronunciation of the Russian word is distributed unevenly. If, say, a syllable consists of four syllables ( box , water cart ), then the energy "profile" will be something like this:
box barrel : co- (30% of energy) ro- (40%) barrel- (15%) ca- (15%)
water-wowo zka : w- (15% of energy) up- (30 %). - like in (a) dash (a) , where "a" in brackets is a strange sound that is approximately the same as "a", "o", "s" and "y".
- like in (a) dash (a) , where "a" in brackets is a strange sound that is approximately the same as "a", "o", "s" and "y".
In addition, the stressed syllable in the Russian syllable is pronounced 1.5-2 times longer than the pre-stressed syllable, and all other syllables are pronounced even shorter (about 0.6-0.8 of the length of the pre-stressed syllable). And one more nuance - on the pre-stressed syllable we usually raise the melody of the voice, on the percussion we raise it more, and then sharply "throw" down. If in word vodovo zka pronounce the first syllable (vo-) on the note MI, then the second syllable (do-) will be on FA, the third (voz-) will be somewhere in sol-sol sharp, and the last syllable (- ka) will return to MI again.
In other words, in Russian stress is at the same time power, longitudinal and musical, and it covers not one, but two syllables. In the ideal speech of speech, all this is approximately the same, but people are usually far from ideal. They swallow syllables, lisp, stutter, change intonation according to their own understanding, they are simply too lazy to open their mouths and pronounce words correctly. As a result, from childhood we get used to "catching" at least some signs of stress - strength or length or melody. And then with this skill honed over the years, we come across other languages. And it began...
They swallow syllables, lisp, stutter, change intonation according to their own understanding, they are simply too lazy to open their mouths and pronounce words correctly. As a result, from childhood we get used to "catching" at least some signs of stress - strength or length or melody. And then with this skill honed over the years, we come across other languages. And it began...
I used to learn Czech from a book and knew for sure that in Czech the stress is ALWAYS on the first syllable. When I first heard Czech speech, I was simply amazed that, for example, in the word Předkládám "offer" the stress is clearly on the second syllable. Then I listened again and decided that not on the second, but in general on the last! Then I asked a Czech who was very surprised at my doubts and said that, of course, the stress in this word is on the first syllable - as in any word of the Czech language. It didn't take long for me to figure out what was going on. The fact is that in Czech any syllable, both stressed and unstressed, can be short or long. And the stress is given out only by force. My "Russian" ear heard that the first syllable in the word Předkládám is pronounced stronger, but the second and third syllables are long. As a result, I got confused: all three syllables had some signs of the usual stress, but not a single syllable had the entire set, from the point of view of Russian phonetics. nine0008
Sorry for the long story, we're getting down to business.
So, in the Kyrgyz word the stress is always (more precisely, almost always with two exceptions) on the last syllable. And it is powerful. But here in the flow of speech , almost any syllable can be under intonational stress.
How to be? - Stay calm. You will be understood regardless of the accent. There is practically no chance that you will not understand someone because of the accent. If you still don't understand, ask to repeat. Gradually, everything will fall into place and you will begin to pronounce correctly. Or don't start. I, for example, have an accent in every language I use on a daily basis, but this does not prevent me from making long speeches in these languages.