How to boost reading comprehension
How to Improve Reading Comprehension: 8 Expert Tips
Reading is a skill many people take for granted, but the act of reading and properly comprehending a text is a complex and interactive process. It requires several different brain functions to work together and most often requires one to puzzle through multiple layers of context and meaning.
Because reading comprehension is so complicated, we can often find ourselves understanding the most basic interpretation of a text, but missing the emotional core or the "big picture." Or we might just find our brains spinning with no clue at all as to what a text is attempting to convey.
But luckily for everyone who struggles in English classes, on standardized tests, or in daily life, reading comprehension can be improved upon (and it's never too late to start!).
In this guide, I explain step-by-step how to improve reading comprehension over time and offer tips for boosting your understanding as you read.
What Is Reading Comprehension?
Reading comprehension is the understanding of what a particular text means and the ideas the author is attempting to convey, both textual and subtextual. In order to read any text, your brain must process not only the literal words of the piece, but also their relationship with one another, the context behind the words, how subtle language and vocabulary usage can impact emotion and meaning behind the text, and how the text comes together as a larger, coherent whole.
For instance, let's look at the first line from Jane Austen's novel, Pride and Prejudice:
"It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife."
Now, a completely literal interpretation of the text, just based on word-meaning, would have us believe that 'all rich men want wives.' But the context, word choice, and phrasing of the text actually belie that interpretation. By using the phrases "universally acknowledged" and "must be in want of" (emphasis ours), the text is conveying a subtle sarcasm to the words. Instead of it being an actual
truth that 'rich men want wives,' this one sentence instantly tells us that we're reading about a society preoccupied with marriage, while also implying that the opening statement is something people in that society may believe, but that isn't necessarily true.
By using the phrases "universally acknowledged" and "must be in want of" (emphasis ours), the text is conveying a subtle sarcasm to the words. Instead of it being an actual
truth that 'rich men want wives,' this one sentence instantly tells us that we're reading about a society preoccupied with marriage, while also implying that the opening statement is something people in that society may believe, but that isn't necessarily true.
In just a few short words, Austen conveys several ideas to the reader about one of the main themes of the story, the setting, and what the culture and people are like. And she does so all the while seeming to contradict the literal words of the piece.
Without practice in reading comprehension, nuances like these can become lost. And so it can happen that someone may find themselves reading, but not truly comprehending the full meaning of a text.
As you can see, reading comprehension involves many processes happening in your brain at once, and thus it can be easy for some aspects of a text to get lost in the muddle. But the good news for anyone who struggles is that reading comprehension is a skill just like any other. It must be learned through practice, focus, and diligence, but it absolutely CAN be learned.
But the good news for anyone who struggles is that reading comprehension is a skill just like any other. It must be learned through practice, focus, and diligence, but it absolutely CAN be learned.
Why Reading Comprehension Is Important
Proper reading comprehension can be difficult, so why bother? Even though learning how to properly read and comprehend texts is a complicated process, it is a necessary skill to master, both for work and for pleasure.
You will need to know how to read and interpret all kinds of different texts—both on the basic, literal level and on a more in-depth level—throughout your schooling, in college, and in the working world (as well as in your recreation time!). If we think about "reading" just as a literal or surface understanding of a piece and "reading comprehension" as the complete understanding, a person can only get by in the world on pure "reading" for so long.
Reading comprehension is essential for many significant aspects of daily life, such as:
- Reading, understanding, and analyzing literature in your English classes
- Reading and understanding texts from your other class subjects, such as history, math, or science
- Doing well on both the written and math sections of the SAT (or all five sections of the ACT)
- Understanding and engaging with current events presented in written form, such as news reports
- Properly understanding and responding to any and all other workplace correspondence, such as essays, reports, memos, and analyses
- Simply taking pleasure in written work on your own leisure time
Just like with any goal or skill, we can master reading comprehension one step at a time.
How to Improve Reading Comprehension: 3 Steps
Because reading comprehension is a skill that improves like any other, you can improve your understanding with practice and a game plan.
Dedicate yourself to engaging in a combination of both "guided" and "relaxed" reading practice for at least two to three hours a week. Guided practice will involve structure and focused attention, like learning new vocabulary words and testing yourself on them, while relaxed practice will involve merely letting yourself read and enjoy reading without pressure for at least one to two hours a week. (Note: if you already read for pleasure, add at least one more hour of pleasure-reading per week.)
By combining reading-for-studying and reading-for-pleasure, you'll be able to improve your reading skill without relegating reading time to the realm of "work" alone. Reading is a huge part of our daily lives, and improving your comprehension should never come at the cost of depriving yourself of the pleasure of the activity.
So what are some of the first steps for improving your reading comprehension level?
Step 1: Understand and Reevaluate How You're Currently Reading
Before you can improve your reading comprehension, you must first understand how you're currently reading and what your limitations are.
Start by selecting excerpts from different texts with which you are unfamiliar—text books, essays, novels, news reports, or any kind of text you feel you particularly struggle to understand—and read them as you would normally. As you read, see if you can notice when your attention, energy, or comprehension of the material begins to flag.
If your comprehension or concentration tends to lag after a period of time, start to slowly build up your stamina. For instance, if you continually lose focus at the 20 minute mark every time you read, acknowledge this and push yourself to slowly increase that time, rather than trying to sit and concentrate on reading for an hour or two at a stretch. Begin by reading for your maximum amount of focused time (in this case, twenty minutes), then give yourself a break. Next time, try for 22 minutes. Once you've mastered that, try for 25 and see if you can still maintain focus. If you can, then try for thirty.
Begin by reading for your maximum amount of focused time (in this case, twenty minutes), then give yourself a break. Next time, try for 22 minutes. Once you've mastered that, try for 25 and see if you can still maintain focus. If you can, then try for thirty.
If you find that your concentration or comprehension starts to lag again, take a step back on your timing before pushing yourself for more. Improvement comes with time, and it'll only cause frustration if you try to rush it all at once.
Alternatively, you may find that your issues with reading comprehension have less to do with the time spent reading than with the source material itself. Perhaps you struggle to comprehend the essential elements of a text, the context of a piece, character arcs or motivation, books or textbooks with densely packed information, or material that is heavily symbolic. If this is the case, then be sure to follow the tips below to improve these areas of reading comprehension weakness.
Improving your reading comprehension level takes time and practice, but understanding where your strengths and weaknesses stand now is the first step towards progress.
Step 2: Improve Your Vocabulary
Reading and comprehension rely on a combination of vocabulary, context, and the interaction of words. So you must be able to understand each moving piece before you can understand the text as a whole.
If you struggle to understand specific vocabulary, it's sometimes possible to pick up meaning through context clues (how the words are used in the sentence or in the passage), but it's always a good idea to look up the definitions of words with which you aren't familiar. As you read, make sure to keep a running list of words you don't readily recognize and make yourself a set of flashcards with the words and their definitions. Dedicate fifteen minutes two or three times a week to and quizzing yourself on your vocab flashcards.
To get started, you'll need some blank index cards and a system to keep them organized. These basic cards are an affordable option that are also available in fun colors. You can keep them organized with plastic baggies or rubber bands, or you can get an organizer.
These basic cards are an affordable option that are also available in fun colors. You can keep them organized with plastic baggies or rubber bands, or you can get an organizer.
Alternatively, try these easy-flip flashcards that include binder clips. Though we strongly recommend making your own flashcards, you can also buy pre-made ones —the best option is Barron's 1100 Words You Need to Know, a series of exercises to master key words and idioms.
In order to retain your vocabulary knowledge, you must employ a combination of practiced memorization (like studying your flashcards) and make a point of using these new words in your verbal and written communication. Guided vocabulary practice like this will give you access to new words and their meanings as well as allow you to properly retain them.
Step 3: Read for Pleasure
The best way to improve your reading comprehension level is through practice. And the best way to practice is to have fun with it!
Make reading a fun activity, at least on occasion, rather than a constant chore. This will motivate you to engage with the text and embrace the activity as part of your daily life (rather than just your study/work life). As you practice and truly engage with your reading material, improvement will come naturally.
This will motivate you to engage with the text and embrace the activity as part of your daily life (rather than just your study/work life). As you practice and truly engage with your reading material, improvement will come naturally.
Begin by reading texts that are slightly below your age and grade level (especially if reading is frustrating or difficult for you). This will take pressure off of you and allow you to relax and enjoy the story. Here are some fun, easy reads that we recommend to get you started:
- Aru Shah and the End of Time by Roksani Chokshi
- Brown Girl Dreaming by Jacqueline Woodson
- Ghost by Jason Reynolds
- The Westing Game by Ellen Rankin
- From the Mixed Up Files of Mrs. Basil E. Frankweiler by E.L. Konigsburg
- The Parker Inheritance by Varian Johnson
- I Am Malala by Malala Yousafzai
- Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone by J.
 K .Rowling
K .Rowling
Once you feel more comfortable reading and practicing your comprehension strategies (tips in the next section), go ahead and allow yourself to read at whatever reading or age level you feel like. Even if you feel that you don't understand some of the text right now—or even a large portion of it!—if you enjoy yourself and give it your best shot, you'll find that your reading comprehension levels will improve over time.
Ultimately, reading should be a fun and functional activity. So try to keep your reading exercises balanced between work and pleasure.
5 Reading Comprehension Tips
Improving your vocabulary and increasing the amount of time you spend reading overall will help you to improve your reading comprehension over time, but what do you do to help you to comprehend a particular piece of text?
Here, I'll walk you through the steps to take as you're reading so that you can understand the text and improve how you're reading, when you're reading.
Tip 1: Stop When You Get Confused and Try to Summarize What You Just Read
As you read, let yourself stop whenever you lose focus or feel confused. Just stop. Now, without re-reading, summarize aloud or in your head what you've comprehended so far (before the place where you became confused).
Skim back through the text and compare how you've summarized it with what's written on the page. Do you feel you've captured the salient points? Do you feel a little more focused on what's going on now that you've put the material into your own words?
Keep reading with your summation in mind and let yourself stop and repeat the process whenever the piece becomes confusing to you. The more you're able to re-contextualize the work in your own words, the better you'll be able to understand it and lock the information in your mind as you keep reading.
Tip 2: If You're Struggling, Try Reading Aloud
Sometimes, we can form a sort of "mental block" that can halt our reading progress for whatever reason (maybe the sentence looks complex or awkward, maybe you're tired, maybe you feel intimidated by the word choice, or are simply bored).
Reading these problematic passages aloud can often help circumvent that block and help you to form a visual of what the text is trying to convey.
Tip 3: Re-read (or Skim) Previous Sections of the Text
For the most part, reading is a personal activity that happens entirely in your head. So don't feel you have to read just like anyone else if "typical" methods don't work for you. Sometimes it can make the most sense to read (or re-read) a text out of order.
It is often helpful to glance backwards through a piece of text (or even re-read large sections) to remind yourself of any information you need and have forgotten—what happened previously, what a particular word means, who a person was...the list is endless.
Previous sentences, sections, or even whole chapters can provide helpful context clues. Re-reading these passages will help to refresh your memory so that you can better understand and interpret later sections of the text.
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.
You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.
Tip 4: Skim or Read Upcoming Sections of the Text
Just like with the previous step, don't feel that the only way to read and understand a text is to work through it completely linearly. Allow yourself the freedom to take apart the text and put it back together again in whichever way makes the most sense to you.
Sometimes a current confusion in a work will be explained later on in the text, and it can help you to know that explanations are upcoming or even just to read them ahead of time.
So skip forward or backwards, re-read or read ahead as you need to, take the piece in whatever order you need to in order to make sense of the text. Not everyone thinks linearly, and not everyone best understands texts linearly either.
Tip 5: Discuss the Text With a Friend (Even an Imaginary Friend)
Sometimes discussing what you know so far about a text can help clear up any confusion. If you have a friend who hasn't read the text in question, then explain it to them in your own words, and discuss where you feel your comprehension is lacking. You'll find that you've probably understood more than you think once you've been forced to explain it to someone who's completely unfamiliar with the piece.
If you have a friend who hasn't read the text in question, then explain it to them in your own words, and discuss where you feel your comprehension is lacking. You'll find that you've probably understood more than you think once you've been forced to explain it to someone who's completely unfamiliar with the piece.
Even if no one else is in the room, trying to teach or discuss what a passage says or means with "someone else" can be extremely beneficial. In fact, software engineers call this technique "rubber duck debugging," wherein they explain a coding problem to a rubber duck. This forces them to work through a problem aloud, which has proven time and time again to help people solve problems. So if a piece of text has your head spinning from trying to work through it by yourself, start chatting with your nearest friend/pet/rubber duck. You'll be surprised with how much easier it is to understand a text once you've talked it through with someone.
Even if that someone is a duck.
Quack.
The Take-Aways
Improving reading comprehension takes time and effort, but it can be done. Be patient with yourself, work through your reading comprehension steps, and try not to get frustrated with yourself if you feel your progress is slow or if you feel you're "falling behind." You will utilize your reading skills throughout your life, so go at a pace that works for you, and take care to maintain that balance between reading for pure pleasure and reading for dedicated improvement.
As you begin to incorporate more and more reading into your daily life, you'll find that comprehension will become easier, and reading will become more fun. In every piece of text, there are worlds of meaning to explore, and learning how to uncover them can be the ultimate rewarding journey.
What's Next?
Can't get enough reading? Whether as part of your reading practice or just for fun, check out our picks for the 31 best books to read in high school.
Problems with procrastination? Whether you're studying for the SAT's or studying your reading comprehension vocabulary check out how to beat procrastination and get your studies back on track.
Want to earn better grades? Our guide will help you get that 4.0 you're striving for.
Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points or your ACT score by 4 points? We've written a guide for each test about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Have friends who also need help with test prep? Share this article!
Courtney Montgomery
About the Author
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Reading Comprehension Tips – Learning Center
Do you ever feel overwhelmed with the amount of reading you have? Do you ever have trouble staying focused and motivated while reading? Do you sometimes have difficulty understanding and remembering what you read? If so, you’re not alone. Many students struggle with these things because reading in college can be challenging, time-consuming, and lot more rigorous than high school; however, with some effective strategies, you can make your reading time meaningful, focused, and productive.
Active reading
Research shows that you retain more when you actively engage and interact with texts, as opposed to simply reading and re-reading without a clear purpose.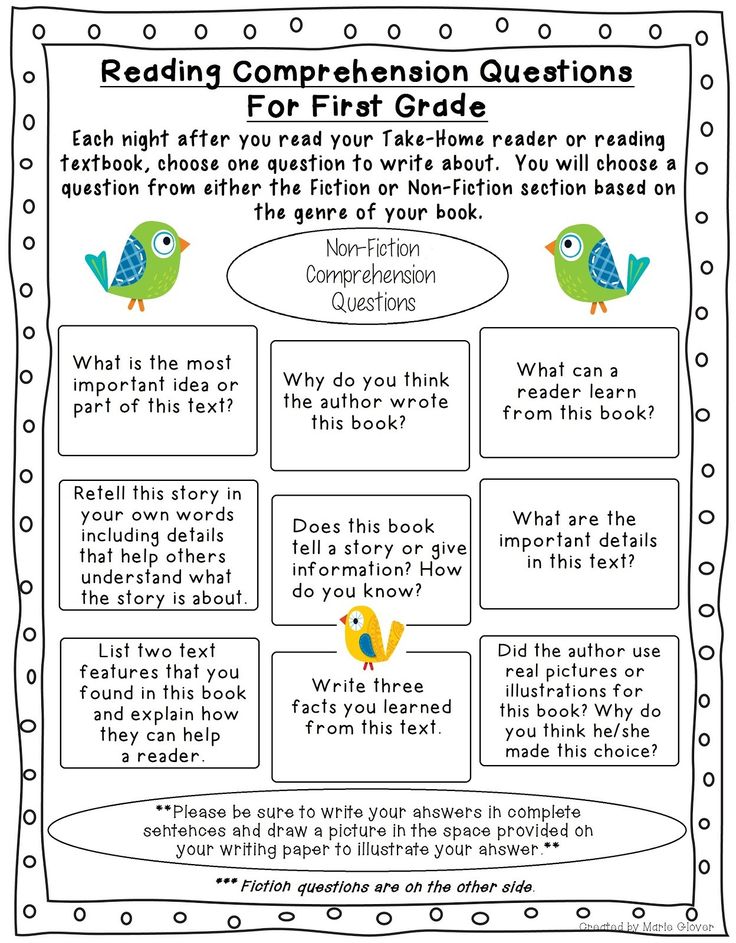 Many students can relate to the type of reading that involves copying down pages of notes word-for-word from the text or simply scanning over pages without really reading them or interacting at all. While these two approaches are on opposite ends of the spectrum, neither of them engages your brain in a way that elicits deep understanding and retention. Active reading engages your brain in effective strategies that force your brain to interact with the text before, during, and after reading and that help you better gauge what you are (and aren’t) learning.
Many students can relate to the type of reading that involves copying down pages of notes word-for-word from the text or simply scanning over pages without really reading them or interacting at all. While these two approaches are on opposite ends of the spectrum, neither of them engages your brain in a way that elicits deep understanding and retention. Active reading engages your brain in effective strategies that force your brain to interact with the text before, during, and after reading and that help you better gauge what you are (and aren’t) learning.
Before reading
Although many students don’t think about this step, engaging with a text before reading can crucially boost your understanding and retention. Below are some active reading strategies to use before you read.
Know your purpose
Yes, you’re reading because your professor told you to do so, but there is more to it than that. What will you be asked to do with the information you gather from your reading assignment? Reading in preparation for a multiple-choice exam requires a greater attention to detail (think keywords, definitions, dates and specific concepts and examples) than reading to prepare for discussion or to write an essay (think main points and relationships). Consider your purpose for reading and what you need to be able to understand, know, or do after reading. Keep this purpose in mind as you read.
Consider your purpose for reading and what you need to be able to understand, know, or do after reading. Keep this purpose in mind as you read.
Integrate prior knowledge
You already know so much; why not help yourself out? Before previewing the text, determine what you already know about the material you are to read. Think about how the reading relates to other course topics, and ask why your professor might have assigned the text. Identify personal experiences or second-hand knowledge that relates to the topic. Make a list of things you want to know about the text or questions that you want to try to answer while reading.
Preview the text
Don’t jump in all at once. Give the text an initial glance, noting headings, diagrams, tables, pictures, bolded words, summaries, and key questions. Consider reading introductions and conclusions to gather main ideas. After you preview, predict what the section or chapter will be about and what the main concepts are going to be.
Plan to break your reading into manageable chunks
Do you have five days to read twenty pages? Read four pages a night. Twenty pages in only one night? Read four pages and then take a fifteen-minute break to rest your mind and move your body. Taking breaks while reading improves focus, motivation, understanding, and retention. Plus, it’s healthier for our bodies! Try using a weekly calendar or the Pomodoro Technique to break up and schedule your time.
Decide whether and how to read from a screen
Especially if you are taking courses online or studying remotely, some of your course materials may be in a digital format, such as online journal articles or electronic textbooks. Before you read, decide if your reading is something you could and would want to print out. Sometimes it is easier to grasp content when it is on paper. If this is not your preference or is not an option, make reading breaks an even higher priority, consider adjusting your screen, and be strategic about the time of day when you are reading in order to avoid eye strain or headaches.
While reading
Keeping your brain active and engaged while you read decreases distractions, mind-wandering, and confusion. Try some of these strategies to keep yourself focused on the text and engaged in critical thinking about the text while you read.
Self-monitor
The only one who can make sure you’re engaged while reading is you! If you are able to think about what you will eat for dinner or what will happen next on that Netflix show you love, you are no longer paying attention! As soon as you notice your mind drifting, STOP and consider your needs. Do you need a break? Do you need a more active way to engage with the text? Do you need background noise or movement? Do you need to hear the text aloud? What about a change of environment? Before resuming, summarize the last chunk of text you remember to make sure that you know the appropriate starting point.
Annotate
Overusing the highlighter? Put it down and try annotation. Develop a key/system to note the following in the text: key ideas/major points, unfamiliar words/unclear information, key words and phrases, important information, and connections.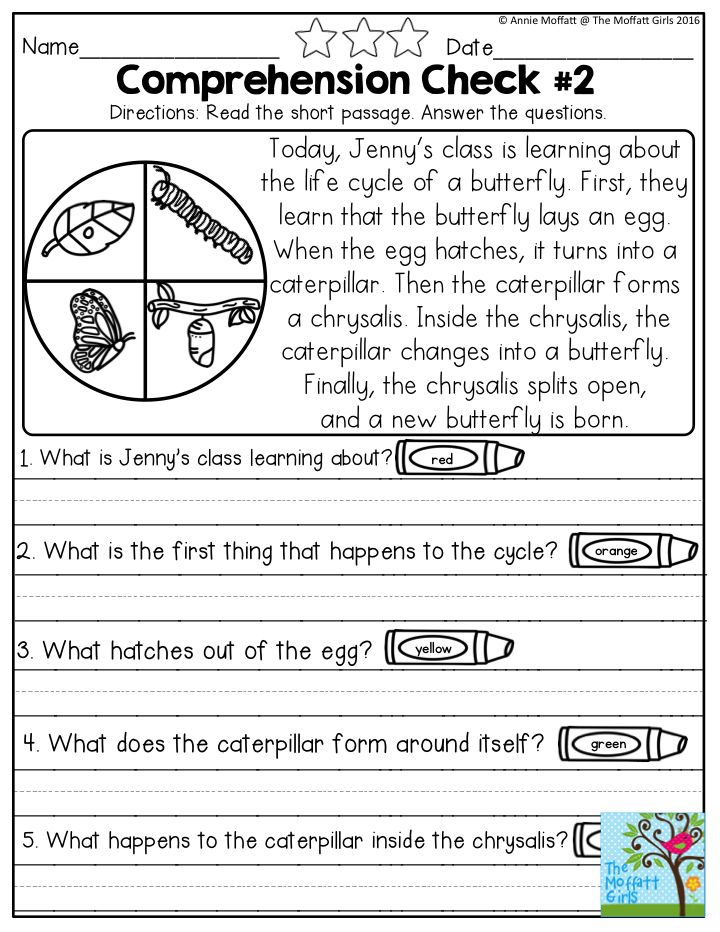
Summarize
After reading small sections of texts (a couple of paragraphs, a page, or a chunk of text separated by a heading or subheading), summarize the main points and two or three key details in your own words. These summaries can serve as the base for your notes while reading.
Ask hard questions
Think like a professor and ask yourself higher level, critical thinking questions, such as:
- What differences exist between ________________?
- How is ______________ an example of ______________?
- What evidence can you present for ________________?
- What are the features of ____________________?
- What would you predict from ________________?
- What solutions would you suggest for ______________?
- Do you agree that ________________? Explain.
- What is the most important feature of ______________?
- How is the text guiding the reader to come to certain conclusions?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What premises or prior knowledge does the text require to make its argument(s)?
After reading
Reading a text should not end at the end of the chapter. Using effective after reading strategies can help you better understand and remember the text long-term.
Using effective after reading strategies can help you better understand and remember the text long-term.
Check in with yourself
Whether you read a printed text or an online document, the most important thing to assess is how much you understood from your reading. This metacognitive skill is one of the hardest to practice because if you truly missed the mark on what you read, you might not know until you get to class—or worse, until test day.
Here are some ways to self-check your reading comprehension. Try “cross-referencing” the information you read with simpler writings on the same subject and discussing your takeaways with peers. If you and your peers vary widely in your takeaways, go back to the text to see if the presentation of evidence can account for these discrepancies. Some key questions:
- Are there multiple possible “answers” here?
- Is there a blind spot in your knowledge on the subject?
- Is the language of the text too difficult or unclear?
- Are different sources on the same topic using consistent language, or are they using different language to discuss the same or similar things?
Show what you know
- Create an outline of the text from memory, starting with the main points and working toward details, leaving gaps when necessary to go back to the text for facts or other things you can’t remember.

- Discuss the material with a friend or classmate.
- Call a family member and teach them what you now know.
- Brain dump: write down everything you remember from the reading in 5 minutes.
- Ask yourself critical questions about the reading and answer those questions in a timed format.
- Identify the important concepts from the reading and provide examples and non-examples of each concept.
- Create a concept map from memory to illustrate your learning from the assigned reading.
- Take screenshots from digital texts as a starting point for class notes or annotations.
Investigate further
If any information remains unclear, locate other resources related to the topic such as a trusted video source or web-based study guide. Still have questions you can’t answer on your own? Make note of them to ask a professor, TA, or classmate.
Self-test
- Create flashcards or an outline for the main concepts, terms, dates, etc.
 in the text.
in the text. - Use the flashcards or outline to test yourself on what you read and see how much you remember and can explain correctly.
- Cover the answers or explanations and don’t look at them until after you have already answered or explained in your own words.
- Pause videos periodically and use your own knowledge to supply an answer or predict where the video is going. Then hit play to see if you are on track.
Self-testing in this way will help you synthesize and think through the information and recall it better in the future.
Need help applying or practicing active reading strategies? Make an appointment with an Academic Coach or sign up for one of the reading workshops offered at the Learning Center. Our academic coaches can help you evaluate your current reading habits, discuss effective strategies, make a plan, and stick to it.
Works consulted
Falk-Ross, F. C. (2001). Toward the new literacy: Changes in college students’ reading comprehension strategies following Reading/Writing projects. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 45(4), 278-288.
Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 45(4), 278-288.
Griffiths, G. G., Sohlberg, M. M., Kirk, C., Fickas, S., and Biancarosa, G. (2016). Evaluation of use of reading comprehension strategies to improve reading comprehension of adult college students with acquired brain injury. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 26(2), 161-190. 10.1080/09602011.2015.1007878
Holschuh, J.P. (2019). College Reading and Studying: The Complexity of Academic Literacy Task Demands. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 62(6), 599–604. https://doi-org.libproxy.lib.unc.edu/10.1002/jaal.876
Lei, S. A., Rhinehart, P. J., Howard, H. A., and Cho, J. K. (2010). Strategies for improving reading comprehension among college students. Reading Improvement, 47(1), 30-42.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Learning Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
If you enjoy using our handouts, we appreciate contributions of acknowledgement.
Make a Gift
How to improve your ability to understand the text you read?
06.02.14
Strategies for autists, parents and teachers to overcome difficulties with reading
Source: Autism after 16
Many people can read, but after reading it is difficult for them to remember, about what they read. There may be several reasons for this. It is possible that a person puts so much effort into voicing words (out loud or to himself) that they lose their meaning. In other cases, the topic is so uninteresting that it is difficult to focus on the information in the text. Many children and adults with autism spectrum disorders have severe reading comprehension difficulties, even if they have no problems with reading as such. This can make schooling very difficult, even for children without intellectual disabilities, especially in secondary school, when the requirements for reading and understanding large amounts of text increase significantly, and texts become more complex. The following are strategies for improving text comprehension that adults with autism spectrum disorders and parents and educators of children with ASD can use.
The following are strategies for improving text comprehension that adults with autism spectrum disorders and parents and educators of children with ASD can use.
Metacognition - thinking about how we think - is the basis for improving understanding while reading. In other words, to improve text comprehension, we must consciously stop while reading and analyze our opinions, perceptions, and thoughts related to what we have read. For example:
Before reading
- Determine the purpose for the upcoming reading. Think in advance about what you should find in the text while reading.
Look at the title of the text and try to figure out what the text might be about.
- Skim through the entire text without reading carefully, paying attention to headings and subheadings, bold words and illustrations. Think about what this text might be about.
- Try to remember what you already know about the topic, the author, or this story.
While reading
- Reflect on what you have read after each paragraph or chapter.
Consider whether you agree with ideas, characters, or facts.
- If you do not understand the meaning of some sentences or paragraphs, write down what you do not understand.
- Write down unfamiliar words to find out their meaning after reading.
After reading
- Think about what you learned while reading.
— Write your own questions for the author.
Think about how what you read relates to your own life.
- Formulate a summary of what you have read.
- Review your notes and try to find answers to your questions through repeated reading, searching the Internet, or talking to another person.
Talk about what you read
Discussing what you read with another person provides another source of information instead of rereading the text. This is especially useful if you don't really enjoy reading. While talking about what you read, you will be able to ask questions that you have, this will allow you to learn more about the point of view of other people and provide you with the opportunity to put into words what you have read, which will help you remember and understand the text better.
Practice reading as often as possible
The best way to improve reading comprehension is to read as much as possible. It doesn't matter what the person is reading. The more you read, the better your comprehension skills will be. Here the “Matthew effect” takes place, when “he who has will be given and will be multiplied, and what he has will be taken away from the one who does not have.” Students who enjoy reading read a lot and often, and their reading skills improve. Those who do not enjoy reading devote little time to it, as a result, their skills lag more and more behind their peers. That is why our first priority is to motivate children to read. If they enjoy reading comics, sports articles, or online magazines, then encourage them to do so as often as possible.
Take the children to the library as often as possible and let them look at any books they want. Do not try to force on children what you think they should read. We want them to read—as much as possible. And that's it. If they liked a book by a certain author, then find all the books by that author so they can pick something. If the children are interested in a topic, then find them reading material according to their interest.
And that's it. If they liked a book by a certain author, then find all the books by that author so they can pick something. If the children are interested in a topic, then find them reading material according to their interest.
Reading Motivation
The first task for the unmotivated reader is to find reading material that is directly related to what interests him outside of reading. For example, if a child enjoys watching movies, they may enjoy reading movie reviews online or in movie magazines. You may think that this is not a "real" reading, but it is not at all the case. Many people believe that the only way to develop reading skills is with books. In fact, this is not necessary at all, especially in our age of the Internet.
Also, if children read often about things they are interested in, this will help them become better readers in general, especially if they practice reading comprehension skills in parallel. After the motivation to read begins to form, you can begin to practice reading less interesting materials. That said, if the strategies to improve comprehension have already been practiced on interesting texts, it will be easier to use them while reading on boring topics.
That said, if the strategies to improve comprehension have already been practiced on interesting texts, it will be easier to use them while reading on boring topics.
Strategies to improve reading comprehension
Start with the strategies that seem most attractive and try them one at a time. Don't try to master every single strategy, sometimes less is more. In other words, it's best to master a few strategies to perfection, rather than practicing all the strategies without exception, which can make it unclear what to use right now. Strategies to improve reading comprehension include:
- Conversational reading: Ask questions, argue, clarify, summarize, and predict as you read.
- Stickers: Use stickers to write words you don't understand, or write exclamation marks on them to mark sentences you like, and question marks to mark phrases or paragraphs you don't understand.
- Reading in pairs: Reading aloud with another person one paragraph at a time. Discuss what you have read with each other after each paragraph.
Discuss what you have read with each other after each paragraph.
- Thinking out loud: As you read aloud in pairs, voice out any thoughts, questions, or misunderstandings that come to mind. For example, if a character or event reminded you of something, stop and talk about that personal association. This technique helps to remember what has been read in the future.
- Re-reading: Read the text again, trying to find answers to the questions that have arisen.
- Text connections: As you read, determine how this text relates to you, to other texts, and to the world in general. In connection with yourself, you need to think about how the read relates to you personally. In World Links, you can link text to what you already know. Finally, in text links, you can link what you've read to what you've read about before.
- The Three Bears Principle: When choosing a book from a library or bookstore, think about whether it is too simple or too complex. Too simple means that the reader will easily understand all the words or have already read this book many times. Too complex means that there are more than five unfamiliar words on one page or the meaning of the first page is not clear. If the book is just right, then this is a new book, where the reader may not know some of the words on the page, but in general understands what is at stake.
Too simple means that the reader will easily understand all the words or have already read this book many times. Too complex means that there are more than five unfamiliar words on one page or the meaning of the first page is not clear. If the book is just right, then this is a new book, where the reader may not know some of the words on the page, but in general understands what is at stake.
- Dividing the text into parts: Read only a few paragraphs or sentences at a time. Think about what you read using reading strategies before continuing.
- Visualization: While reading, always try to visualize how the characters and the scenes described look like.
- Blogs: Check if there is any blog or forum on the Internet where this topic or book is discussed online, read what other people think about it and try to write your own opinion.
- Journaling: As you read, write down your thoughts in a special journal.
- Graphic organization: Make a chart showing your understanding before, during and after reading.
Progressive Implementation Model
If you are a parent or educator, you can use the Progressive Implementation Model to help a student with autism develop strategies for reading comprehension. First, demonstrate to the student how you yourself read using this strategy. Then use this strategy together, under your guidance. Then ask the student to apply this strategy again (in a different situation) on their own.
Make sure you discuss reading with the student and whether the strategy is helping or not. You may need to model this strategy for the student many times, or practice it many times together until it becomes a natural part of the reading process and the student can apply it completely on his own.
Availability of books to read
If reading skills are too low, use books on topics that are interesting to the student, but with very low reading requirements. As a rule, they have a lot of illustrations and little text. It can be children's encyclopedias and reference books. They keep the reader motivated, their topics are age-appropriate, and the reading isn't too difficult.
As a rule, they have a lot of illustrations and little text. It can be children's encyclopedias and reference books. They keep the reader motivated, their topics are age-appropriate, and the reading isn't too difficult.
You should also pay attention to the following books:
- Books with many photographs and illustrations, which will greatly facilitate understanding.
- Books with fairly large letters.
- Books with a small amount of text on one page so that the amount of text on the page does not cause stress.
- Books that have titles, subtitles, clear definitions of words in the glossary. These books are the easiest to understand.
Relationship between reading and writing
You may be wondering why it is so common to write things down while working on reading comprehension. The reason is that this is another way to better understand and assimilate the material read. For example, if someone finds it difficult to speak verbally about what they have read, then keeping a diary, blogging, or graphing can help analyze what they read and update the information in memory, but without verbal dialogue.
Closing Thoughts
The goal of all reading is to understand the text, so it is hoped that these strategies and ideas will enable you to improve your reading skills or help your child or student reach that goal. Remember that reading is a very complex individual process, and its development must be reflected in an individual educational program.
Autism in adults, Parenting children with autism, Education and training
6 key skills for reading comprehension
For some people, the process of reading is like a walk in the park on a warm summer day, an activity full of pleasure, which is no problem to master. labor. In fact, reading is a complex process that involves many different skills. Together, these skills lead to the ultimate goal of learning to read: comprehensive reading comprehension.
Text comprehension can be difficult for children for many reasons, but regardless of them, knowing what underdeveloped skills this is due to, you will be able to provide your child with the best help.
Let's take a look at the six reading comprehension skills and how you can help your child develop them.
1. Decoding
Decoding is an extremely important step in the reading process. Children use this skill to sound out words they have heard before but not seen written. The ability to decode is the foundation of all other reading skills.
Decoding relies on one of the first language skills to develop, phonemic awareness (this skill is part of a broader set of skills called phonological awareness). Phonemic awareness allows children to hear and distinguish individual sounds in words (also known as phonemes). It also allows them to "play" with sounds in syllables and words.
Decoding also relies on the ability to match individual sounds and letters. For example, to read the word "sun", the child must know that the letter "s" sounds like "s". Understanding the relationship between letters and sounds is an important step towards "voicing" words.
How to help: Many children learn phonological awareness naturally by reading books, listening to songs and poems. But for some children it is not so easy. In fact, one of the early signs of reading difficulties is trouble with rhyming, counting syllables, or identifying the first sound in a word.
The best way to help your child improve these skills is to guide them with precise instructions and lots of practice. Children need to be taught how to correctly identify sounds and work with them. You can also develop phonological perception by playing with words, reading poems aloud to your child, or using special computer techniques aimed at developing phonemic perception and decoding.
2. Reading fluently
To read fluently, children must recognize words immediately, including words that do not read as they are written. By developing reading fluency, the child increases not only reading speed, but also reading comprehension.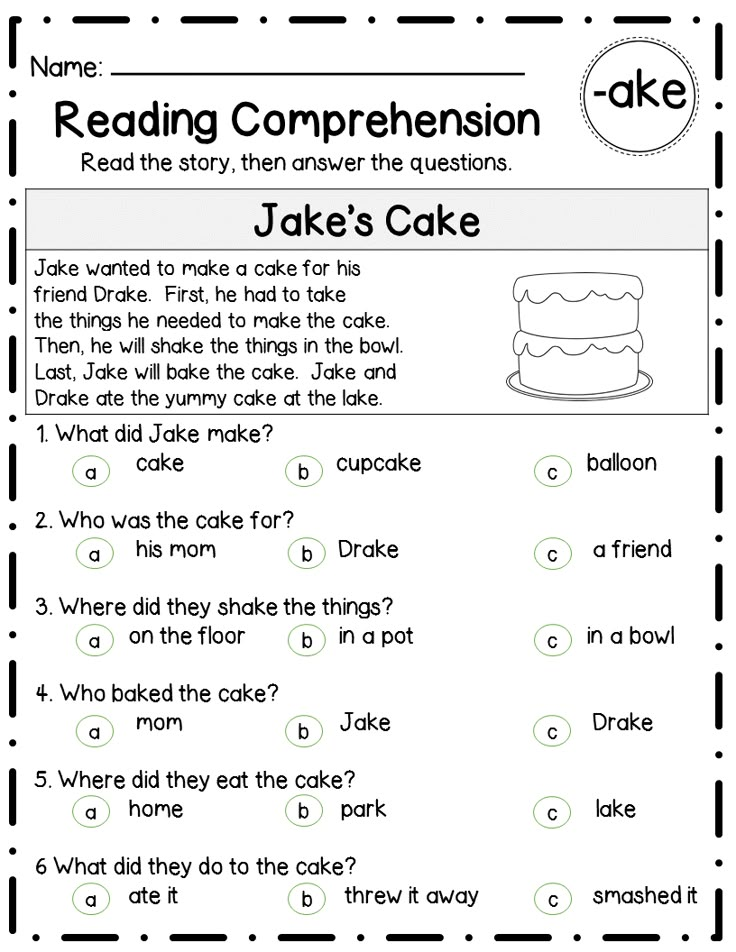
Decoding and reading each word can be a lot of work. Word recognition is the ability to recognize a word instantly just by looking at it, without having to read it out loud. When children can read quickly and with almost no errors, they are said to be able to read "fluently".
People who can read fluently read fluently and rhythmically. They use the context to understand the meaning and change the intonation in their voice depending on what they are reading about. The ability to read fluently is critical to a good understanding of the text.
How to help: Word recognition can be a big hurdle for beginning readers. Usually a person needs to see a word from 4 to 14 times in order to learn to automatically recognize it. But, for example, children diagnosed with dyslexia may need to see the word up to 40 times.
Many children have difficulty reading fluently. To improve word recognition and other reading skills, children need help and a lot of practice. The best way to strengthen these skills is to practice reading books. It is important to choose books that are appropriate for the child's reading level.
3. Vocabulary
To understand what you read, you need to understand at least most of the words in the text. A rich vocabulary is a key component of text comprehension. Students can learn new words during class, but they usually learn the meaning of words through everyday situations and while reading.
How to help: The more new words children learn, the more their vocabulary grows. You can help your child develop vocabulary by talking to him often about different topics, introducing him to new words and concepts. Word games and funny jokes are also fun ways for children to reinforce these skills.
Daily reading together also helps build vocabulary. When reading aloud to your child, stop when you encounter new words and explain their meaning. But it is also important that the child reads independently. Even if there is no one to explain the meaning of a new word, the child can guess its meaning from the context, and also learn with the help of a dictionary.
Teachers can also help by choosing interesting words to study and learning them all together in class. To practice vocabulary, the teacher can engage students in dialogue during the lesson, or play word games to make learning new words fun.
4. Sentence construction and cohesion
Understanding how sentences are built can seem like a skill necessary for writing. The same can be said about the connection of ideas within and between sentences, which is called cohesion. But these skills are also important for reading comprehension.
Knowing how ideas connect at the sentence level helps children make sense of passages and entire texts. This also leads to what is called coherence, or the ability to relate ideas to other ideas in a common work.
How to help: Explain the basics of sentence construction to your child. Work with him to connect two or more thoughts, both in writing and orally.
5. Expanding horizons and argumentation
Many children associate what they have read with previous experiences, so it is important to broaden your child's horizons so that they have some idea of the world around them before they start reading. It is also important to teach the child to “read between the lines” and find meaning where it is not literally written.
How to help: Your child can broaden their horizons through reading, socializing, watching movies and TV shows, and exploring art. Also many things come with years of personal experience.
Open up opportunities for your child to gain new useful knowledge in different areas and discuss with him what you have learned from experience, both together and separately. Help your child make connections between new and old knowledge and ask questions that require extended answers and thoughtful explanations.
You can also read these tips on how to use cartoons to help your child learn to judge for themselves.
6. Working memory and attention
These two skills are part of a group of skills also known as executive functions. They are different, but closely related.
When children read, attention allows them to absorb information from the text. Working memory helps them retain this information and use it to make sense and gain knowledge from what they read.
The ability to self-control while reading is also related to executive functions. The child must be able to recognize when he does not understand something, stop, go back and reread, so that there is no doubt about the understanding of what he read.
How to help: There are many ways to help your child improve working memory, and it doesn't have to look like a lesson. There are many games and daily activities that can help develop working memory in a way that your child won't even notice!
To improve your child's attention span, look for reading materials that interest and/or motivate your child. For example, some children love graphic novels. Teach your child to stop and reread the text when something is not clear to him. And show him how you “think out loud” when you read to make sure it makes sense.
More ways to help with reading comprehension
When children have difficulty learning the skills listed above, they may find it difficult to fully understand what they read.
Find out what might be causing your child's reading difficulties. Remember, if a child has difficulty reading, it does not mean that he is not smart. But some children need extra support to successfully develop reading skills. The sooner you contact a specialist or start applying a special corrective technique, the less stress and lag in learning and development your child will receive. Pay attention to the computer technique Fast ForWord, aimed at developing the skills of phonemic perception, decoding, memory, concentration and other executive functions.