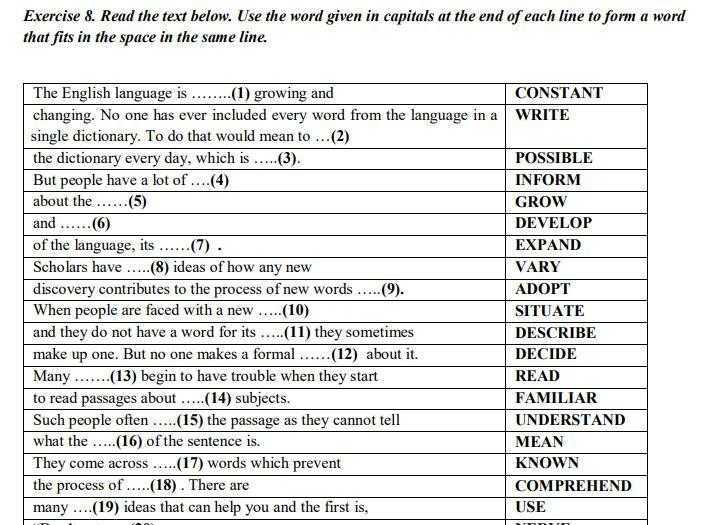
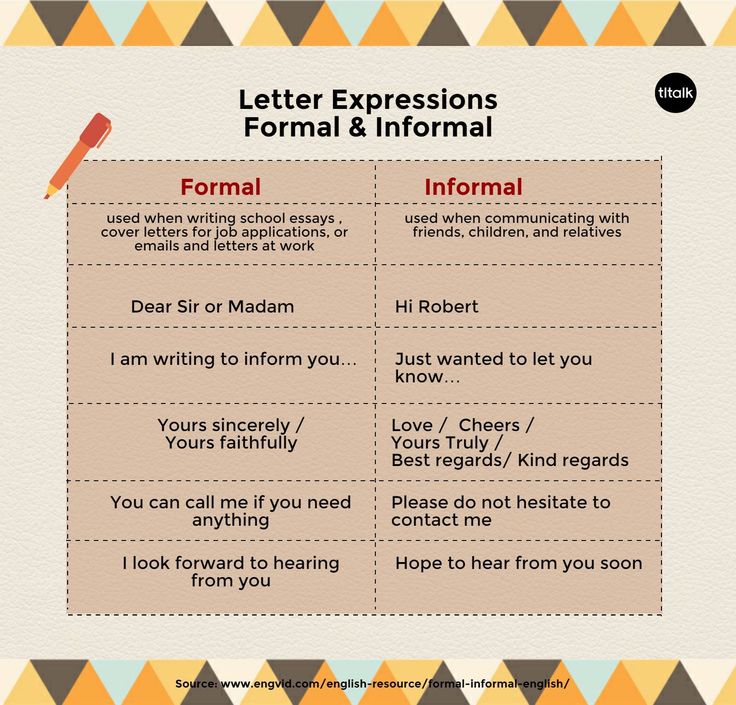
How to form letters
Form Letters Properly with These 9 Helpful Tips
Learning proper letter formation is more important than you think! Kids need to form letters properly from the start in order to prevent bad habits and avoid messy writing as they get older.
Children should learn how to form letters and numbers properly when they first begin pre-writing and writing.
Using a proper technique makes writing more efficient and prevents fatigue. This also helps prevent messy handwriting as kids get older… when they have to write smaller and faster.
A friend was recently chatting with me about her Kindergarten daughter’s virtual learning. During our conversation, she shared,
“I’m worried she’s not going to learn to form letters and numbers correctly! How do I know what’s right?! Her teacher can’t see what she’s doing and I don’t know how to help her!”
I LOVED that she recognized the importance of using correct letter and number formation with her daughter!
Why Learning to Form Letters Properly is Important (and Numbers, too!)Kids need to learn how to form letters properly to prevent sloppy writing when they start to write faster when they get older.
I’ve evaluated several 5th and 6th graders for school-based occupational therapy due to sloppy handwriting.
Teachers couldn’t read the writing on their assignments and tests. Worse, even the students had trouble reading their own writing!
Most of these students that I evaluated grasped the pencil correctly and had good motor and perceptual skills. Their sensory processing abilities were also normal.
The only problem: a LARGE majority of their letters were formed incorrectly. These students never learned to form letters properly.
That was the only problem!
They wrote from the bottom up, segmented letters, and/or made clockwise movements.
As students progress through each grade, they start naturally increasing the speed of their writing. When they have to write faster – in order to take notes and complete assignments – their writing became much sloppier. And much harder to read.
With these kiddos, they either had to learn cursive or they had to type. It was too late to re-teach them how to form letters properly… in order for their faster-paced writing to be legible.
It was too late to re-teach them how to form letters properly… in order for their faster-paced writing to be legible.
When children are learning to form letters and numbers, there are some things to keep in mind. And, there are some special tricks to help!
1. Check for “Pre-Writing Skills”- Children should be able to copy pre-writing strokes from a model (not imitate what another person has demonstrated for them.)
- The strokes / shapes I check for (some should be mastered in the toddler / preschool years): vertical and horizontal lines, a circle, an intersecting line (+), diagonal lines (slanting each direction), an X, a square and a triangle.
- Can they hold a pencil correctly with their thumb, index and middle fingers?
Before beginning writing instruction, make sure that children understand position words and directionality terms. Practice understanding these terms on and off their body
Practice understanding these terms on and off their body
- Top, bottom, middle
- Left, right
- Up, down
- Big, little (or tall, short)
- Clockwise, counterclockwise
My favorite position for kiddos to start is standing at a vertical surface. This helps them see what they’re doing and they can better understand concepts such as up / down.
- Stand at a wall or door with paper taped to it (largest piece of paper you have!)
- Use window crayons at a glass door or window
- Stand at an easel
- Stand at a chalkboard or a chalkboard wall
When sitting for handwriting, make sure that your students are using the Correct Sitting Posture at their desk. (In addition to sitting posture, the post gives tips on proper desk and chair size.)
4. Practice first WITHOUT Writing Lines- This is important for kiddos just learning… they need to focus on the correct motion of each letter and not worry about the lines.
 This detail can be addressed later.
This detail can be addressed later. - If your school’s program comes with lined paper for learning, please have a blank, plain piece of paper as well for practicing.
- Chalk, small crayons or dry erase crayons give more feedback for the hands. This helps increase motor memory when learning letter formation.
- Avoid using markers if possible – they are too slippery and don’t give adequate feedback to the hands as previously mentioned.
- If more feedback for the hands is desired, there are weighted tools or vibrating tools available. You can also use more chunky or thick writing tools.
Follow your school’s handwriting program and use the verbal cues provided for each letter.
- Programs SHOULD encourage forming letters from the top-down for all tall letters (b, f, h, k, l, t) and for #’s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
 Use a top to bottom motion (with an upward re-trace on some such as ‘m’ or ‘p’) for short letters (i, j, m, n, p, r, u, v, w, x, y, z)
Use a top to bottom motion (with an upward re-trace on some such as ‘m’ or ‘p’) for short letters (i, j, m, n, p, r, u, v, w, x, y, z) - Using a counterclockwise direction for letters with curves is really important (a, c, d, g, o, q, and the top part of ‘s’) as well as numbers 8 and 9. I often have kids practice large counterclockwise circles in the air to get their shoulder and arm used to moving in that direction.
- (It’s important to learn to form ‘e’ in one motion without picking up the pencil.)
- Show children how to form the letter first (while using the appropriate verbal cues.)
- Then, practice sky writing (or air writing.) They point their finger to “draw” the letter in the air. Using the shoulder muscles activates a larger area of the brain to help improve motor memory.
- I personally avoid having children trace letters when first learning. They tend to just cover up what they see and often don’t form the letter or number correctly.

- Tracing is a great warm-up activity on anything except letters and numbers. This article from the learning professor (Dr. Jenni Jacobs) supports my thoughts and further explains this!
[Affiliate links are used below for your convenience. There’s no additional cost for you. If you choose to click on an Amazon link and make a purchase, Develop Learn Grow may earn a small commission.]
8. Use Multi-Sensory Techniques during Letter and Number Formation- Write in a sand or salt tray using the finger.
- Use the finger to write in finger paint or shaving cream (with or without sand / salt.)
- Create a sensory bag (place gel, paint, or any condiment or puree into a Ziploc bag.) Place it on the table or *tape to a vertical surface such as a window or glass door!
- Practice with chalk on a chalkboard. Trace with a small, wet sponge (1/2 inch.)
- Put plain paper over a sheet of sandpaper or over a bumpy craft screen (like this one on Amazon).
 Use a pencil to write on the sandpaper or a crayon to write on the screen.
Use a pencil to write on the sandpaper or a crayon to write on the screen. - MY FAVORITE trick: have the children practice on plain paper with their eyes closed!
- This is the best way to check to see if “their hand can remember how to make the letter!”
- Without visual feedback, it shows that the muscles remember which way to move to form the letter or number.
- Only 5-10 minutes of practice per day, no more than 15 minutes. The focus should only be on one or two letters at a time.
- You can check the letter learned during a previous day, before moving onto a new one.
If your school doesn’t have a designated handwriting program, I highly recommend Handwriting Without Tears. It’s a program I’ve used very frequently as a pediatric occupational therapist.
It’s a program I’ve used very frequently as a pediatric occupational therapist.
And if you use another program, the supplies listed below (special pencils, crayons, etc) can be used to supplement your program.
The program was developed by an OT, Jan Olsen. Over the years, her writing program has evolved into a company, Learning Without Tears.
Jan Olsen’s Handwriting Without Tears program offers a fun and simplified approach to learning how to form letters and numbers. Booklets and hands on manipulatives can be found on Amazon (links provided below for your convenience.)
Form Letters Properly with Handwriting Without Tears Books (Available on Amazon)
The green My First School Book can be used in preschool or for kiddos who need additional fine motor practice. It includes pre-readiness tasks such as grasping, coloring, drawing, counting, numbers and shapes.
The purple Kick Start Kindergarten Book covers capital and lowercase letters. It bridges the Pre-K program. Use this for transitional kindergarten, Jr. kindergarten, or second year pre-K.
Use this for transitional kindergarten, Jr. kindergarten, or second year pre-K.
Letters and Numbers for Me Book is the orange book used for Kindergarten printing (student edition.)
The yellow My Printing Book is for first grade. Groups of the books can be purchased on Amazon for a discount.
Handwriting Without Tears Tools and Supplies (Available on Amazon)
Even if you don’t use the Handwriting Without Tears books, these are helpful supplies for little hands who are learning to write!
My favorite Handwriting Without Tears tools are included in the beginner kit which can be found here on Amazon.
In the kit, the chalkboard provides great feedback for the hands. The small sponge erasers help with grasp development and visual motor integration.
HWT pencils are appropriate for small hands. The flip crayons are excellent for improving in-hand manipulation / finger dexterity. (These each can be found separately from the kit.)
I have used and loved all of these supplies (and still have them in my supply stash!) There are also packs of specialized double line paper for kiddos who have trouble with three-lined paper.
Jan Olsen created some great songs that accompany the writing program. The entire CD of songs can be found for free on this YouTube link!
She also offers books for learning cursive writing. I’ve also used this for many kiddos who needed a simplified motor approach.
If your school already has a program, share this with someone you know who may need this info!
- Development of Pencil Grasp, How to Promote a Functional Grasp with 5 Types of Activities – this post also shows images of pencil grasp development
- Art Projects for Kids – several fun, relaxing and creative activities that support visual motor skills needed for writing
- An Easy Visual Motor Activity Using Magnets – fun activity to work on hand awareness, grasping, and coordination for writing – minimal DIY materials, many options!
For More Support with Writing / Posture / Core Stability for School Tasks, Check Out:
Classroom Exercise Program – 8 Week Brain Break Series, $12. 80
80Use these specific occupational therapy exercises to improve:
Attention… focus… core stability… crossing midline… sensory processing… visual development… & more… Click for more info!
Letter Formation Activities and Tools That Work
If there is one thing for sure, teaching letter formation to kids can be tricky. There’s a lot of reasons why writing letters is tricky for kids. We’ll cover all of the reasons why the letter formation aspect of handwriting can be so difficult below. Be sure to check out all of the letter formation activities here. You’ll find pediatric occupational therapy activities to use in OT interventions, as well as activities to teach letters that use a hands-on and sensory approach to learning letters. You’ll also find resources on letter order, and information on teaching letters based on child development.
Letter Formation
Handwriting, as we know, is an incredibly complex process. There is a lot that goes into handwriting, and letter formation is just one piece of the puzzle.
- Letter formation refers to several aspects of writing a letter of the alphabet: placement of the pencil when writing a letter (starting at the correct spot, as in top or bottom of the writing space).
- Moving the pencil in the correct direction to make parts of the letter.
- Placing the parts of the letter in the appropriate spots (intersecting lines or joined pencil strokes)
Why is letter formation important?
When letters are not formed correctly, handwriting suffers. You will see handwriting problems when letter formation isn’t a focus. Letter formation problems lead to poor handwriting that is sloppy and hard to read. Let’s break down common poor handwriting issues. We’ll go over how learning proper letter formation can impact legibility.
Writing Letters Incorrectly– A big piece of letter formation is learning correctly from the get-go. When a child learns an incorrect letter formation strategy, that can be hard to correct without practice. You might see kids pick up a pencil and trace letters, but they are segmentally forming the letters. They are marking lines in the incorrect order, pushing the pencil when they should be pulling the pencil, or starting at the bottom rather than the top.
You might see kids pick up a pencil and trace letters, but they are segmentally forming the letters. They are marking lines in the incorrect order, pushing the pencil when they should be pulling the pencil, or starting at the bottom rather than the top.
Kids that are handed letter formation worksheets without prompts, cues, models, and correct formation practice, will many times, trace or copy letters using segmented lines that start at incorrect places, and that can be a hard habit to break.
Forming Letters from Bottom to Top– There’s not a letter in the alphabet that starts at the baseline and ends on the top line. When we write, we start at the top and move the pencil to the base line, or below the baseline.
When kids start the letters at the bottom, they will run into legibility and efficiency issues. It’s harder to move the pencil on to the next letter with the bottom-to-top formation. And, when kids then need to keep up in writing tasks, (beginning as soon as first grade as they copy words and sentences from a model), they will lose the legibility piece.
Segmental Letter Formation– Letters are formed with a specific order. Capital A starts at the top line and slants down and to the left. Then, you jump back to the top starting point and slant down and to the right. Then, you jump to the middle line and go across toward the right. Sometimes, children start forming letters segmentally, so that they draw part of the letter, like the first slant of the A and then mark the middle line before marking the second slant.
There is a reason for the specific order of the lines when forming letters. Kids that are handed handwriting worksheets without specific directions for proper letter formation will create their own motor plan for making letters that might not be correct. This can be hard to “break” without practice. Segmental letter formation can lead to sloppy handwriting further down the road and trouble with handwriting efficiency.
Trouble with Diagonal Lines– Many times, you see young students write letters with diagonal lines that are not quite diagonal.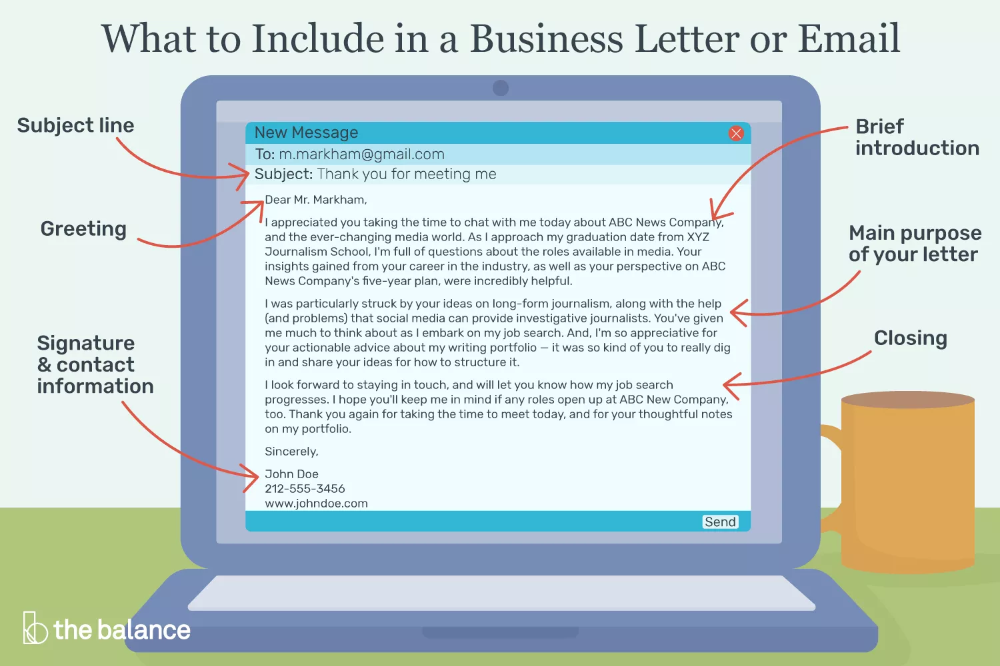 Letters like A, K, M, N, R, V, W, X, Y, Z and lowercase letters k, v, w, x, y, z all have diagonal lines. That slanted line is actually one of the later pre-writing strokes to form. So, when you see preschool, pre-K, and kindergarten writing letters, it’s simply too soon developmentally. Sure, some kids will be fine and learn to write letters at this age, but many others will struggle down the road with handwriting, reading, and learning. Here is some important information about pre-writing lines. Notice the age that kids typically develop the ability to form the lines of the pre-writing forms. It’s much later than preschool, pre-K, and even kindergarten!
Letters like A, K, M, N, R, V, W, X, Y, Z and lowercase letters k, v, w, x, y, z all have diagonal lines. That slanted line is actually one of the later pre-writing strokes to form. So, when you see preschool, pre-K, and kindergarten writing letters, it’s simply too soon developmentally. Sure, some kids will be fine and learn to write letters at this age, but many others will struggle down the road with handwriting, reading, and learning. Here is some important information about pre-writing lines. Notice the age that kids typically develop the ability to form the lines of the pre-writing forms. It’s much later than preschool, pre-K, and even kindergarten!
The problem is that with the fast-paced classroom curriculum, sometimes this early educational periods are the only time that children are truly taught proper letter writing. In most cases, they are simply “reviewing” letter formation in first grade. Kids then have established a poor letter formation without the opportunity to practice when their fine motor skills, hands, and visual motor skills are ready.
Letter formation and occupational therapy
Occupational therapists are often called into screen for or assess a student when they have letter formation issues, along with other aspects of handwriting: poor placement on the lines, an inefficient pencil grasp, visual perceptual skills problems reflected in learning or slow, awkward handwriting.
By working on letter formation, therapists can help kids with therapeutic practice and strategies in OT that address underlying issues like visual perceptual issues, visual motor concerns, fine motor needs, or gross motor, core stabilities issues.
Other common letter formation issues that occupational therapists address:
- Forming the letter within the borders of the line or given writing space
- Marking the pencil lines in the right direction (without reversal)
- Speed of writing (student can’t keep up with age-appropriate writing demands
- Poor legibility
How to work on letter formation
To work on letter formation, teaching the alphabet in a specific order is key! In fact, teaching kids to write in alphabetical order simply isn’t developmental. Here’s the thing: think about the letters of the alphabet. The specific pencil strokes go in so many different directions! You’ve got letters that start at the top followed by a letter that pulls the pencil in toward the hand, followed by letters that have diagonals and jump/hop moves, changes in direction. If you teach kids to write letters in alphabetical order, kids will use so many different movements.
Here’s the thing: think about the letters of the alphabet. The specific pencil strokes go in so many different directions! You’ve got letters that start at the top followed by a letter that pulls the pencil in toward the hand, followed by letters that have diagonals and jump/hop moves, changes in direction. If you teach kids to write letters in alphabetical order, kids will use so many different movements.
Why NOT teach letters in an order that makes sense?
Occupational therapists focus on development. We focus on building skills in an order that makes sense according to a child’s typically developing progression. And when there are delays or non-typical development, we know what to work on next. We know where to focus efforts on accommodating for specific skills. We can then help kids achieve age-appropriate goals so that they can be more independent and accomplish tasks that are appropriate for their age.
Order to Teach Letters
Let’s get specific about the best order to teach writing letters. Notice I mentioned “writing letters”. Here’s the thing: letter recognition should be taught in a specific order. Letter sounds should be taught in a specific order. Awareness of upper case and lower case can be taught in a different order.
Notice I mentioned “writing letters”. Here’s the thing: letter recognition should be taught in a specific order. Letter sounds should be taught in a specific order. Awareness of upper case and lower case can be taught in a different order.
Some preschools teach a letter of the week approach and teach sounds and awareness in alphabetical order.
Many schools follow a writing curriculum that teaches letters in a specific order determined by that curriculum.
Here is the occupational therapists’ take on the best order to teach letters:
Letter order matters– Teaching letter formation in a specific order based on development is essential for pencil control, motor planning, eye-hand coordination, efficiency (writing speed), and accuracy (placement of letters on the lines). Why does letter order matter? Let’s talk about that…
Teach uppercase letter writing first– This is important: Start with upper case letters when teaching kids to write letters. Now, this might go against what some teachers have been taught. This might be a conversation for debate among educators. But, hear me out; When kids are taught to write upper case letters first, they are learning letters in an order that makes sense developmentally. Here are reasons to teach uppercase letter formation before lowercase letter formation:
Now, this might go against what some teachers have been taught. This might be a conversation for debate among educators. But, hear me out; When kids are taught to write upper case letters first, they are learning letters in an order that makes sense developmentally. Here are reasons to teach uppercase letter formation before lowercase letter formation:
- Uppercase letters all start at the top line and go to the bottom line. This makes it easier for kids to know where their pencil marks start. There is no middle line to worry about with most upper case letters. There are only a few uppercase letters that contain a middle line component, and it is never the starting point of the pencil when forming that letter. Upper case letters that contain a middle line portion include: A, B, E, F, G, H, K, P, R, S, Y.
2. Another reason to start with uppercase letters is that there is little opportunity to reverse upper case letters. With the lowercase letters, there are (and will be) reversals of letters b, d, g, q, and others. By starting with the uppercase letters, kids can learn the motor plan needed for formation without the error of reversals to contend with.
By starting with the uppercase letters, kids can learn the motor plan needed for formation without the error of reversals to contend with.
3. Still another reason to teach upper case letter formation before lower case letters is that many of the uppercase letters transfer to the same lowercase letter in a similar motor plan. The only difference being that the letters are smaller. Uppercase letters that transition to a same or similar motor plan for lowercase letters include: C, K, O, P, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z.
4. Still one MORE reason to start by teaching formation of uppercase letters before lowercase letters is the starting points. Kids can easily know where to start uppercase letters because there are only two places where the pencil starts for uppercase letters. The pencil mark starts at either the top left corner or the top middle space. Lowercase letters start in seven different starting points (a, b, e, f, i, l, m)
Top left corner starters: B, D, E, F, H, K, L, M, N, P, R, T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z
Top middle starters: C, G, I, J, O, Q, S
Therapists recommend teaching kids to write the upper case letters before the lowercase letters for developmental reasons, but kids should be taught that there are corresponding upper/lowercase letters. This awareness is necessary, too! We are just talking about actually teaching the letter formation here.
This awareness is necessary, too! We are just talking about actually teaching the letter formation here.
Consider development– Letters have curves, back strokes, hopping lines, diagonals, curves…there is a lot to consider just with letter formation, and not considering letter size and spatial awareness. Asking kids to form diagonal lines before they are ready is simply too difficult. When we consider that children are developmentally able to form strait lines down and horizontal lines across before other diagonals, we set them up for success in handwriting. Here is a free PDF explaining developmental progression of pre-writing strokes. These pre-writing strokes are the very lines and pencil strokes that make up letters.
Teach letters in sets- Taking what we know about pre-writing lines, development of fine motor skills and visual motor skill development, we can use that knowledge to teach children letters in a way that make sense. Start by teaching letters that contain the same pencil strokes, such as all vertical and horizontal lines. Then, move on to letters that contain curved lines, finally, teach letters that contain diagonals. Then, teach formation of lowercase letters. Make the letter formation easy for kids by building off what they practice.
Then, move on to letters that contain curved lines, finally, teach letters that contain diagonals. Then, teach formation of lowercase letters. Make the letter formation easy for kids by building off what they practice.
Here is the order that I teach letters in handwriting
This letter order focuses on teaching handwriting based on development. The order is loosely based on Handwriting Without Tears (Learning without Tears) order for teaching letter formation, but I like to break down that list into smaller groups, and build letter formation concepts off previously learned motor planning. The Learning Without Tears program teaches students about frog jump letters, or letters that move the pencil and then jump to a different spot. That is a great visual and verbal cue for students to use. However, I like to focus on developmental strokes as a priority: those vertical and horizontal lines that transfer to different letters.
For example, teaching upper case F before E considers that the child has practiced a motor plan for the parts of a letter F (vertical line down, hop back to top, short line across the top, hop to middle line, short line across the middle. Then, to make the uppercase E, the child needs to replicate that same motor plan but add only a line at the baseline.
Then, to make the uppercase E, the child needs to replicate that same motor plan but add only a line at the baseline.
This order to teach letters is one that I’ve used throughout my career as a pediatric occupational therapist:
- Group together strait line uppercase letters first: L, F, E, H, T, I
With this order, I teach strait line letters that start in the upper left hand corner first, followed by strait line letters that start in the top-middle. This progression transfers nicely to other groups of letters that all start at the top-middle…)
2. Next, teach strait line/curved letters: D, B, P, U, J
These letters contain a curved portion that transitions nicely to the next group of letters. Including J in this group segues into the next group.
3. Third, teach the curved line uppercase letters: C, O, G, Q, S
These letters all start at the top-middle. This allows kids to think about moving their pencil in a push fashion, as they move the pencil in a different direction compared to previous letters.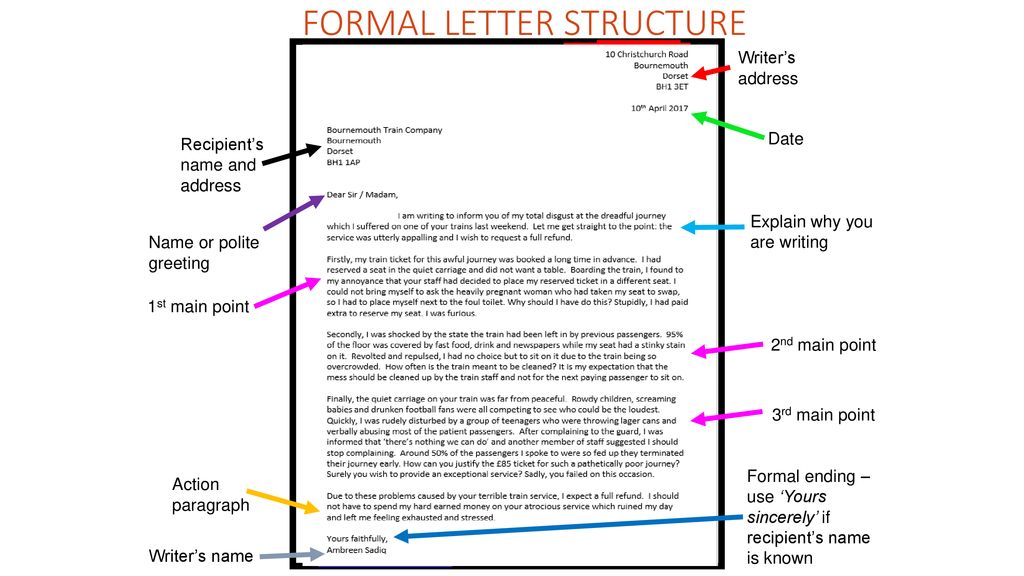 For right-handed writers, the pencil will now move away from the palm. For left-handed writers, the pencil will now move toward the palm. This group transitions nicely to the next set, the diagonals, which challenge pencil strokes by another different motor planning pattern.
For right-handed writers, the pencil will now move away from the palm. For left-handed writers, the pencil will now move toward the palm. This group transitions nicely to the next set, the diagonals, which challenge pencil strokes by another different motor planning pattern.
4. Fourth, teach diagonal line letters: R, A, K, M, N, V, W, X, Y, Z
Teaching the diagonals last allows for more progression on those developmental strokes that we talked about previously.
Next, teach lowercase letters in this order:
- Teach formation of strait line lowercase letters: l, t, i
2. Next, teach formation of letters that are the same as their uppercase letters: c, k, o, p, s, v, u, w, x, z
3. Next, teach formation of strait line/bump lowercase letters: h, n, m, r, b
This set uses strait lines and transitions well to the next group, which are curved line, magic c letters.
4. Fourth, teach formation of curved lowercase letters: a, d, g, q
Teaching this set of letters focuses on the “magic c” that forms the letters. Here, I review letter c and show how it is part of the other letters.
5. Teach formation of the tricky start letters: e, f, j
These letters are commonly used, but start in a tricky place and challenge the movement of the pencil.
6. Finally, teach formation of diagonal lowercase letters: k, y
Lowercase letters are broken down into smaller groups, so that focus can be done on placement on the lines, and spatial awareness. These variants are another reason why starting with uppercase letters first is easier for children to progress. How many different line combinations there are for lowercase letters compared to their uppercase companions!?
There are many different ways that letters could be grouped together effectively in teaching letter formation. The key is to use the terminology that works based on the individual child’s needs and skills and then use it consistently.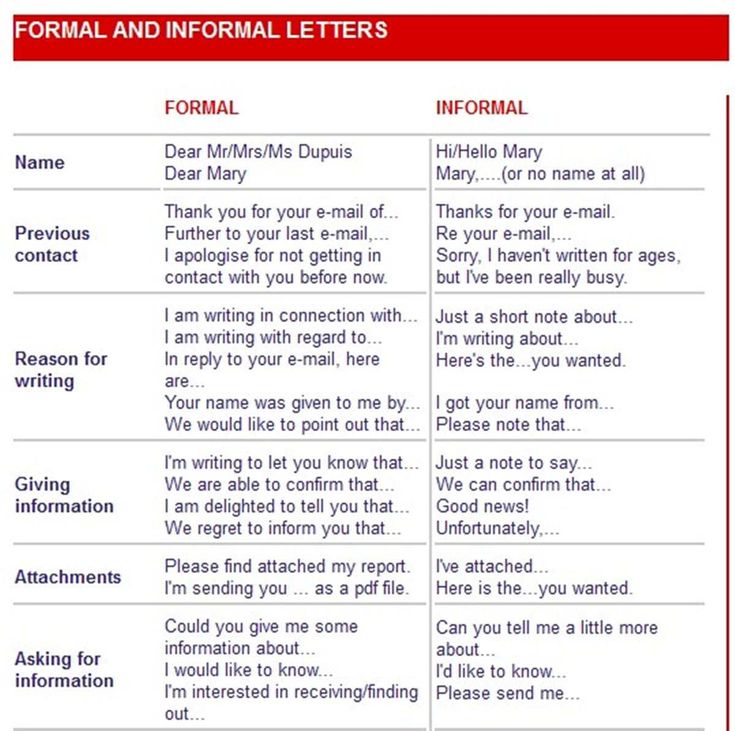
Current research on letter formation
Current research shows us the importance of proper letter formation and practicing handwriting skills for carryover and legibility.
This paper on interventions for letter formation covers strategies for those with intellectual challenges. The study looked at the use of direct instruction with visual and verbal modeling for how to write each letter, with feedback and correction during practice.
Important to the teaching and follow-through of letter formation instruction is the awareness of letters. This study addressed how to teach letter knowledge to impact writing skills, specifically the knowledge of the names, sounds, and symbols of the letters of the alphabet or alphabetic knowledge as an essential building block for learning to read and write.
The study used brief, explicit letter formation lessons included strategies such as multi-sensory writing strategies (see below in this article for more ideas).
• using a transparency and marker to trace over the letter as it is identified in enlarged print
from children’s books
• writing the letters on small white boards as the teacher dictates
• producing the letter form with clay, pipe cleaners, wiki sticks
These appropriately brief lessons also allow time for students to participate in additional meaningful literacy and content area experiences.
These multisensory letter formation strategies can include letter formation practice, and alphabet knowledge instruction through the use of multiple distributed instructional cycles. The study describes one letter a week learning is not enough practice and that young children will not sufficiently learn and use the alphabet letters from 1 week-long exposure to each letter or from only one complete cycle through the alphabet.
Rather, children learn letter formation best through frequent exposure and
repetition to the letters.
Finally, the paper describes the use of flexible instruction of letters with extra focus on letters that are problematic for students to learn often due to less frequent exposure or use in oral or written language. Rather than spending equal time on teaching each letter, more time and instruction is spent teaching certain letters or letter groups.
Determining the time and focus needed to teach letters, the following factors should be taken into consideration: Letters that require more time spent on teaching letter formation include:
(1) Letters located at the beginning and end of the alphabet are learned more easily than letters in the middle of the alphabet.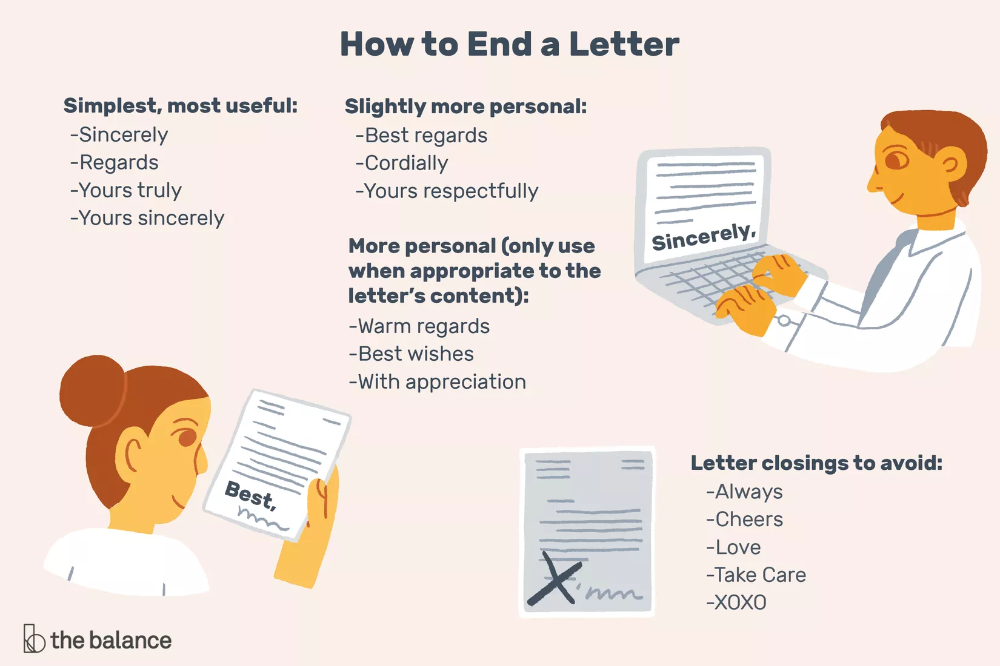
(2) If a letter’s shape or form is distinctive from other letter shapes or
forms, then letter discrimination is easier for young students than when letter forms or shapes share similar distinctive features.
(4) Differential rates of exposure to the letters, such as the letters found in a student’s own name or alphabet letters that occur more frequently in children’s
books and in printed materials in the child’s environment, can also render the acquisition of letter knowledge more or less difficult for young learners
H. (2015). Handwriting in early childhood education: Current research and future implications. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy, 15(1), 97-118. Engel, C., Lillie, K., Zurawski, S
Cursive letter Formation
When teaching children to write cursive letters, forming lines correctly is important for carryover and legibility. You’ll find many of our cursive handwriting resources in one place under How to teach cursive handwriting. Other important techniques for cursive letter formation include these strategies:
Other important techniques for cursive letter formation include these strategies:
- Left-handed cursive writing
- Positioning for cursive handwriting
- Pre-cursive activities
Cursive Letter order
Teaching cursive letter formation requires a different order to teach letters. Check out this resource for cursive letter order based on pencil control and establishing a motor plan for smooth cursive lines. You can print off a PDF of the cursive letter order, too.
Letter Formation Activities
Here, you’ll find creative ways to teach handwriting and how to write letters in creative ways. These are writing tips to teach letters as part of a handwriting curriculum based on an individualized approach to handwriting. We’ve shared a lot of fun handwriting activities here on the blog. Check out some of our favorites!
Here are more tips for teaching kids to write. This is a good read because we talk about why starting letters at the top is important as well as the developmental benefit of teaching upper case letters before teaching lowercase letters. So often, we see kids learn uppercase and lowercase letters at the same time. In actuality, kids are developmentally capable of learning upper case letters first due to the consistent starting point (upper case letters all start at the top!). Read more about this by clicking the link above.
So often, we see kids learn uppercase and lowercase letters at the same time. In actuality, kids are developmentally capable of learning upper case letters first due to the consistent starting point (upper case letters all start at the top!). Read more about this by clicking the link above.
Handwriting strategies that improve pencil control, specifically changes in direction improve legibility. This quick activity can help kids work on the pencil control needed for writing letters. Printed letters have many direction changes. Controlled pencil strokes can be a big help in legible handwriting.
These fun handwriting activities don’t involve a pencil. For some kids, writing is a hassle and they absolutely HATE to write. Those kiddos will love these writing activities.
Use a timer to work on letter formation, while focusing on specific details such as line accuracy.
Use the tips in our handwriting club to work on letter formation, placement, and accuracy along with the fun of a group.
Multi Sensory Letter Formation
Kids can practice letter formation by sliding a sheet of paper into a plastic gallon-sized bag and having kids write on top of letters with colored dry erase markers. Use a small bit of paper towel to erase the letters in the correct formation for another practice run.
Finger tracing in letter formation
Many of the handwriting activities below offer the opportunity for practicing letter formation using finger tracing. The techniques can be used in sensory bins, in sensory bags, on sandpaper, or on textured surfaces.
Finger tracing is a great strategy for early writers, for teaching pre-writing lines and shapes in preschool and toddler years, and for encouraging carryover of diagonal lines, jumping lines, and curves needed for form letters.
Try a few of these finger tracing techniques to incorporate the tactile system into letter formation:
- Trace letters in a sensory bin using dry rice, sand, or shaving cream
- Finger trace letters on sandpaper
- Finger trace letters using a sensory bag (details to make this tool below)
- Start with air writing letters
- Draw a letter on the palm of the child’s hand.
 The student then needs to finger draw the same letter on the palm of their hand.
The student then needs to finger draw the same letter on the palm of their hand. - Finger trace letters on one another’s back
- Draw letters with glue on paper. Students can finger trace the dry glue letters.
Multi-sensory handwriting strategies use the senses and kinesthetic feedback to help kids form a motor plan to form letters. Multi-sensory writing includes sensory writing trays, writing in shaving cream, forming letters with play dough. And that’s just the beginning.
Try these messy, sensory writing ideas:
- We talked above about teaching handwriting in letters groups because kids can build a motor plan for sets of letters. Using markers to work on these similar pencil strokes is a food way to establish this skill and carry over formation of those sets of letters.
2. Fill a low tray such as the lid of a food storage container with dish soap and ask students to write letters using their index finger. This is a great fine motor activity as well as a multi-sensory strategy for writing.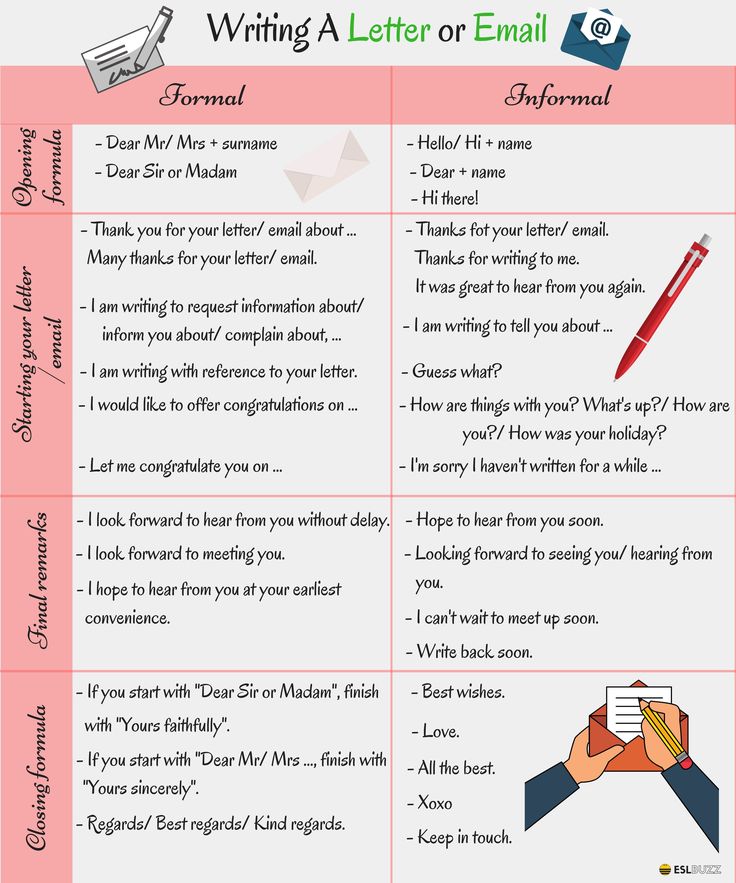
3. Offering a resistive surface provides kinesthetic feedback when learning letters. Use a sheet of sandpaper under paper to work on letter formation of the alphabet, especially when practicing high-frequency letters or letters that are commonly reversed.
4. Slime and Letter Beads- Work on letter formation using slime and letter beads! Kids can find the beads and then practice writing that letter.
5. This fizzy sensory letter activity uses DIY baking soda play dough and a chemical reaction to work on letters that kids will love. Form the letters with dough and then paint them with vinegar in correct formation to practice while enjoying the sensory feedback.
6. Letter cookie cutters are a great way to practice letter formation.
7. Here is an easy writing tray using only colored rice and a colorful background. Kids can work on finger isolation and separation of the sides of the hand by working letters with their index finger.
8. Be sure to check out all of these writing tray ideas, too.
9. Create a sensory memory game that also allows kids to trace letters on the bottom of the tray. It’s a fun way to practice letters with tactile feedback.
10. Take letter learning outdoors with this nature letter formation activity. It’s a hands-on approach to forming letters.
11. Use these approaches to forming lowercase letters.
12. These easy tips to teach kids how to write use fun and easy sensory activities that teach alphabet letter formation.
13. Teach letters with resistive feedback using pushpins and a recycled container.
14. Another hands-on approach with fine motor work is this pegboard letter activity.
15. Cotton Swab Letters– Use cotton swabs with colorful sensory additions to work on letter formation.
16. Teach letters in teletherapy with this interactive occupational therapy slide deck that helps kids with letter formation through gross motor, fine motor, and sensory activities.
17. Use this occupational therapy slide deck to work on strait line letters with kids. Use the slides as an outline for occupational therapy interventions in therapy sessions, while working on letter formation.
Use the slides as an outline for occupational therapy interventions in therapy sessions, while working on letter formation.
18. Our alphabet exercise slide deck offers kids a chance to move with letter-themed gross motor exercises AND work on letter formation by moving the interactive portion of these free Google slide deck. This OT resource is perfect for virtual therapy sessions.
19. This Scribble Day OT slide deck is perfect for a fun occupational therapy teletherapy session. Work through the slides and address letter formation as well as other areas including fine and gross motor activities, motor planning, and more.
20. These monster theme slides are great for occupational therapy sessions because they use a fun theme to work on letter formation as well as other underlying areas that impact handwriting.
21. Use this space theme OT slide deck to work on letter formation using interactive slides that help kids by adding movement in a digital format. Perfect for occupational therapy virtual sessions.
22. Another way to work on the motor planning needed for handwriting is to use various mediums for writing, such as carpet squares. We used small carpet fragments and chalk to write letters.
23. Slime Writing Tray- Kids that like playing with slime will love “writing” in it! Fill a low tray with watered-down slime. We used the eraser end of a pencil to form letters but you could use a fingertip too. It’s a sensory writing activity that kids can’t resist!
24. This handwriting trick uses a foam sheet to work on pencil pressure when writing letters, but it offers a great tactile feedback through the hands that allow kids to build a motor plan when working on letter formation. This is a great way to use sensory input to help kids with learning to write letters.
25. Kids often benefit from a visual cue when it comes to letter formation, especially with letters that are commonly reversed. This DIY letter strip is great because it sits right on the student’s desk and can be close to the writing task, requiring less visual shift, and less opportunities for the student to lose visual attention as a result of visual perceptual or visual motor concerns.
26. Visual spatial relations impact handwriting because letter formation depends on placement between lines, letter sizing, and accuracy of letter formation in a given space. This resource will give you tips and strategies to impact visual spatial skills in a way that makes a huge difference in legibility of written work.
27. These LEGO letter stamps are a fantastically sensory and motor activity that allows kids to focus on letter parts that make up each letter while working on fine motor work in a way that is fun and builds accuracy with letter accuracy and awareness. A GREAT warm-up activity to handwriting!
28. Adding gross motor, motor planning, coordination, bilateral coordination, and crossing midline activities to letter learning is priceless! These letter exercises combine movement with letter awareness and learning. Use these letter exercises as a warm-up or cooldown to therapy sessions. Or, use them as a classroom or home learning brain break activity!
29. This letter puzzle activity builds fine motor skills which is essential for pencil control, hand strength, and dexterity needed for manipulating a pencil so kids can accurately form letters. This activity is a powerful sensory and motor activity designed to help kids with letter formation and accuracy.
This letter puzzle activity builds fine motor skills which is essential for pencil control, hand strength, and dexterity needed for manipulating a pencil so kids can accurately form letters. This activity is a powerful sensory and motor activity designed to help kids with letter formation and accuracy.
30. Another amazing fine motor activity for building pencil control and coordination, this in-hand manipulation bead and puzzle activity allows kids to partner letter formation with fine motor skills.
33. High-Contrast Letter Formation– Use used coffee grounds for a high-contrast writing tray that works on letter formation. This is a great activity for practicing commonly reversed letters.
34. Letter Formation Resistive Surface– Use a recycled material to work on letter formation with a resistive surface, so that kids gain a motor plan for letter formation.
35. Tracing Letters: Letter Formation Handwriting Practice with Chalk– Use sidewalk chalk and outdoor movement activity to work on letter formation with a rainbow writing activity.
36. Here are more sensory writing activities that cover a variety of sensory strategies.
37. Use this color-changing writing activity to work on letter formation.
38. Sensory Letter Formation Practice– Practice letter formation with a mess-free sensory activity that provides feedback while helping kids develop a motor plan for letter formation.
39. Tracing Lines with a DIY Light Box– Tracing letters has it’s time and place! Using a DIY light box and materials found in the home, kids can work on letter formation and accuracy of pencil control.
40. Letter formation manipulatives for the light table– Explore parts of letters with sensory manipulatives.
41. Nature letter formation activity– Get outdoors to work on letter formation and handwriting.
42. These 10 fun ways to teach letter formation are creative ways to work on writing letters, using various strategies including kinesthetic learning, multi-sensory strategies, and visual prompts.
43. Cursive writing doesn’t mean copying the same letter over and over again. Practice cursive writing strokes with this glitter glue multi-sensory writing strategy for teaching the bumps and re-trace needed for cursive letters.
Cursive writing doesn’t mean copying the same letter over and over again. Practice cursive writing strokes with this glitter glue multi-sensory writing strategy for teaching the bumps and re-trace needed for cursive letters.
Letter formation with practice
While sensory motor letter formation is a key component, research tells us that therapeutic practive is essential to learning letter formation. This is the way that therapists use skilled interventions to work on letter formation: by offering strategies, accommodations based on individual needs of the child, verbal and physical prompts based on skilled analysis, and a just right challenge to build skills while offerning an oppourtunity to practice writing letters.
Below, you will fine practice activities that can be used to practice letter formation.
- Use these motivating handwriting practice activities to work on letter formation using therapeutic practice, so kids get time to write and learn letter formation with trials that build accuracy in letter formation.
 These activities are designed to be meaningful and motivating.
These activities are designed to be meaningful and motivating. - These Roll and Write Play Dough Mat Writing Prompts combine fine motor work with handwriting. Kids will love these writing prompt sheets that allow them to work on letter formation with therapeutic practice time so that they can carryover the skills they’ve learned. The play dough mat portion offers a great warm up for the hands so they are ready to write and move that pencil.
- Practice is essential if letter formation is going to “stick”! These tips for practicing handwriting are fun and list format so it’s easy for kids to write a quick list while practicing essential letter formation skills.
4. Use graph paper to teach spacing and letter placement. Letter formation requires accurate placement within a given area on the page and graph paper helps kids to practice this placement so they can carry the skill over to paper of all types.
5. Practicing letters doesn’t need to be boring. Use a creative writing journal that combines creative letter drawing and formation using materials like yarn, play dough, wikki sticks, etc. Kids can practice writing on the lines. This journal was designed for cursive letter formation but could be used with printed letters as well.
Use a creative writing journal that combines creative letter drawing and formation using materials like yarn, play dough, wikki sticks, etc. Kids can practice writing on the lines. This journal was designed for cursive letter formation but could be used with printed letters as well.
6. Write on the window using regular notebook paper for a movement-based letter writing activity that practices formation and accuracy while focusing on the motor components of the shoulder, forearm, and wrist.
Cursive letter formation
You will find tons of creative writing activities designed around teaching cursive here on this website. Cursive letter formation ideas can use all of the handwriting strategies and tips listed above, but you can focus on the smooth writing strokes, retracing lines, and connecting lines that cursive requires with some out-of-the box activities.
Check out some of the cursive letter formation ideas below:
- How to teach cursive handwriting– START HERE for a step-by-step guide to teaching cursive.
 You’ll find everything you need in one place, or check out the list below…
You’ll find everything you need in one place, or check out the list below…
2. Positioning When Writing in Cursive– Positioning in handwriting is SO important. In fact, positioning is the place to start when it comes to teaching kids to write letters.
3. Cursive Writing Lesson Plan– Work on cursive writing with a planned, set of strategies.
4. Gross Motor Cursive Exercises– Kids can work on bilateral coordination, crossing midline, and motor planning skills so they are able to hold their paper while writing, use smooth writing strokes, and form letters.
5. Pre-Cursive Activities– Handwriting doesn’t need to be boring! Use these fun cursive lines to work on smooth pencil strokes, while introducing loops, curves, and swoops.
6. Cursive Letter Formation: Wave Letters– Cursive letters can be grouped into sets so kids can work on specific letters that contain similar pencil strokes. The “wave” letters are one cursive letter family to start with.
7. Creative Ways to Practice Cursive
8. Cursive Writing Self-Assessment
Cursive Writing Self-Assessment
9. Conquering Cursive Letter Connectors
10. Left-handed Cursive Writing Tips and Tricks
11. Cursive Writing Rhythm
12. Cursive Writing Slant
13. How to Teach Cursive Letter Identification
14. Pencil Grasp in Cursive Writing
15. MORE Creative Ways to Practice Cursive Writing
16. How to Teach Cursive Writing Speed
17. Tips for Teaching Cursive in the Classroom
18. Cursive Pre-Writing Lines Watercolor Resist Activity
19. Cursive Writing Starting Lines
20. Cursive Letter Writing Activity
21. Diagnosing Cursive Problems with a Cursive Handwriting Assessment Checklist
22. Cursive Writing Tips and Cursive Certificate of Completion
23. Free Cursive Letter Flashcards
24. Cursive Letter Formation: Bump Letters
25. Cursive Letter Formation: Tree Letters
26. DIY Cursive Activity Beads
27. Cursive Letter Slime
28. Uppercase Cursive Letter Guide
29. The Research on Cursive Writing
The Research on Cursive Writing
30. Cursive Loop Letter
31. How to Teach Cursive Tow Rope Letter
32. Some cursive letters require re-tracing back over the lines. If those lines are sloppy, the letter can look illegible, Try this strategy for teaching re-trace in forming cursive letters c, d, a, g, o, and q. Using a dry erase marker to work on letter formation can be used with any cursive letter or printed letters too.
Free Letter Formation Worksheets
Want to put the occupational therapy interventions and tips that you’ve read here into practice, so kids learn letters based on development, motor skills, and motivating activities?
Enter your email address below to grab the FREE handwriting resource for handwriting resources to use in working on letter formation with kids. You’ll find uppercase and lowercase letter writing worksheets, as well as a list of extension ideas so you can use these worksheets with sensory activities, and take letter formation from dull and boring rote practice, to meaningful, motivating, and fun!
Add your email below and these free handwriting worksheets will arrive in your inbox shortly!
Colleen Beck, OTR/L is an occupational therapist with 20+ years experience, graduating from the University of Pittsburgh in 2000. Colleen created The OT Toolbox to inspire therapists, teachers, and parents with easy and fun tools to help children thrive. As the creator, author, and owner of the website and its social media channels, Colleen strives to empower those serving kids of all levels and needs. Want to collaborate? Send an email to [email protected].
Colleen created The OT Toolbox to inspire therapists, teachers, and parents with easy and fun tools to help children thrive. As the creator, author, and owner of the website and its social media channels, Colleen strives to empower those serving kids of all levels and needs. Want to collaborate? Send an email to [email protected].
Compose a word from a word or given letters online
In everyday life, we sometimes face the task of compiling a new word from predetermined letters or a finished word . For the most part, these are people who are fond of board or online games with words. The main games include:
1. Typesetter - two or more participants choose a word (preferably a long one) from which you want to make new words that exist in the Russian language. The one who finds the maximum number of such words wins. In addition, it is necessary to initially determine which parts of speech (noun, adjective, etc.), case (usually nominative), number (singular or plural), as well as proper or common nouns can be used (names of countries, mountains, rivers, etc. .). For example, to compose words from the letters that make up the word "PLANT". We get more than 50 words of different lengths ("STORK", "SATIN", "FRICTION", "INTEREST", etc.).
.). For example, to compose words from the letters that make up the word "PLANT". We get more than 50 words of different lengths ("STORK", "SATIN", "FRICTION", "INTEREST", etc.).
2. An anagram for a word or from letters - for this we have created a special section on the site dedicated to solving and compiling anagrams online . Please note that in most cases it is customary to call an anagram not only the composition of a word from a word, but also the composition of a word from given letters. Therefore, both sections of the site will be useful to you in your work. Evaluate the possibilities of each direction and the specifics of the work.
3. Leapfrog - the presenter mixes the letters in the original word and the participants begin to guess it. Whoever is first wins. For example, we mix the letters in the word "PROGRAM", get "GMORAMPAR" and wait for the winner!
4. Four pictures one word - there are 4 pictures on the slide that have something in common. The task is to find this zest. As hints, a set of letters can be given, where extra letters will eventually remain, since the length of the word is determined initially.
The task is to find this zest. As hints, a set of letters can be given, where extra letters will eventually remain, since the length of the word is determined initially.
The PoiskSlova.com service allows you to compose words from a word or given letters in a matter of seconds. We have added a lot of filters to work in the "Search Options" block. They allow you to show only words with a definition, set the length of the word, and also make it possible to use the same letter several times.
Consider an example. Enter the search query: "EKALRAM". We display ALL words, use the letters ONCE, the length of the word is ANY. We get 232 words.
Refine your search by showing words ONLY with a definition. Total 43 words.
Compose a word from the given letters using ALL letters without repetition. Let's get an anagram from the letters: "CARAMEL".
The system allows you to group the results by any parameters, which is convenient in solving individual problems. Especially when the whole process of composing a word from letters takes place online, and not manually.
Especially when the whole process of composing a word from letters takes place online, and not manually.
In addition, the project implemented: "Rubricator of words of the Russian language" , "Words starting with letters ..." , "Words ending with letters ..." , "Words containing a sequence of letters ", "Search for words by mask and definition" , collected together the explanatory dictionary of the Russian language named after S.I. Ozhegov, edited by D.N. Ushakov, the dictionary of the living Great Russian language by V.I. Dahl, professional dictionaries.
We tried to create a resource that meets the requirements of users and we ask you to share the link in social networks, forums and recommend the site to friends and family. We wish you good mood and success in your work!
Teaching a child to read syllables easily. 5 funny games
Teach your child to read by syllables, but nothing works? Do you repeat 10 times, but after a couple of seconds he forgets everything, and all your attempts end in screams and tears? Of course, school is coming soon and a slight panic seizes you, but relax and don't worry. Maybe your child is just not ready yet, or maybe you started wrong. Stay with us and find out everything.
Maybe your child is just not ready yet, or maybe you started wrong. Stay with us and find out everything.
How to teach a child to read in syllables so that he likes it?
If your child already knows the letters but does not want to learn to read by syllables, most likely you simply did not explain why he needs it. Arguments like “to learn to read”, “to do well in school and be no worse than others” do not work. The child needs to understand why he is doing this at the moment? That is, you must “sell” him the idea of learning to read in syllables so that he wants it himself and is still satisfied.
How to do it?
Start with what your child is interested in. For example, while walking around the city, draw his attention to the poster of a cinema or circus and ask: “Are you interested in knowing which cartoon will be shown in the cinema? Let's honor." Or here is another good example: “Ice cream, what flavor would you like? Let's read what they offer here? Of course, the child will say that he cannot read and ask you to help him.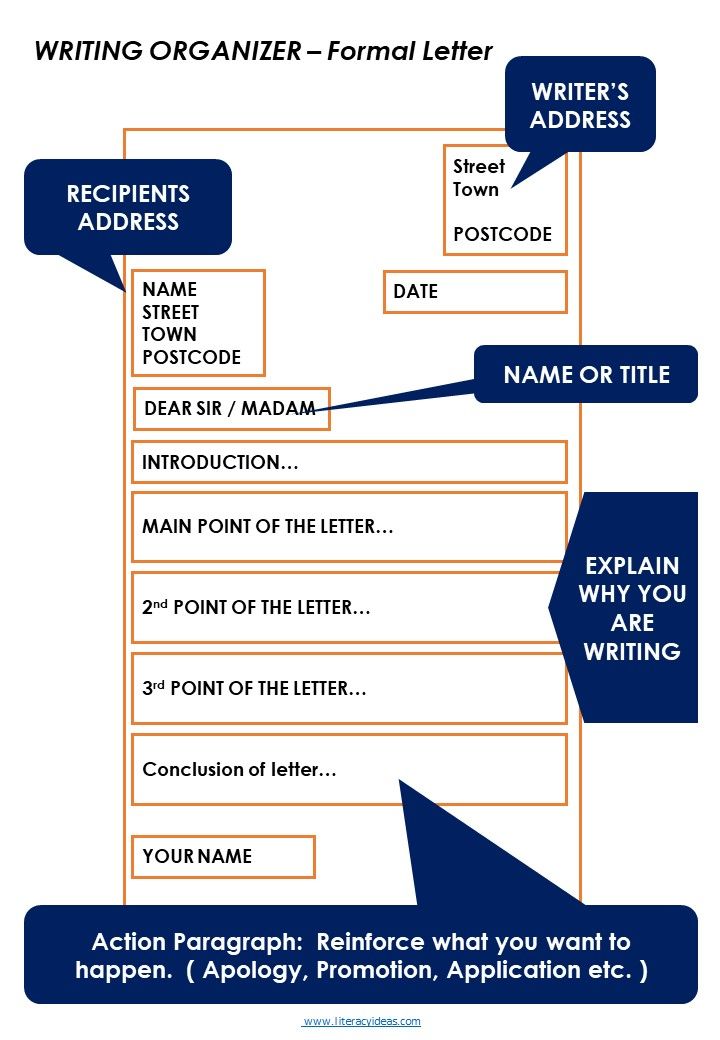 Then you explain to him why you need to be able to read and what is the use of this.
Then you explain to him why you need to be able to read and what is the use of this.
The idea is "sold" - you can start learning!
If your child does not yet know the whole alphabet, then at the same time as learning the letters, you can start making small words out of them. Did the child learn two or three letters? For example "M", "U", "I". Excellent! Fold them immediately into the word "MEW" and ask the child who does this. Then ask him to repeat after you syllable by syllable: “meow”, pausing after the first syllable.
Thanks to this approach, it will be easier for the child to read longer words in syllables in the future.
5 fun exercises to teach children to read by syllables
The first rule that all parents should remember before starting anything to teach their child up to 7 years old is no coercion, always translate everything into a game. Then your child will be happy to participate in the process, and you will see the result faster.
Therefore, all the exercises that we have selected for you are in the form of a game.
Surprise eggs
Take some plastic Kinder Surprise eggs and small cardboard cards with letters. Think of a game scenario. For example, put the letters in the eggs that make up the name of the child's favorite cartoon character according to the principle - one egg - one letter. Then call the child and say that you need to find the name of the hero, otherwise he is lost and cannot find his way home. Then begin to open the eggs together and fold the name in such a way that there is a small distance between the syllables, for example "BIN-GO". As soon as you add up the name, ask the child to read it in syllables and call the hero so that he can find his way home.
When the child manages to name all the characters, you can give him the toy characters he called (if there are such toys at home) or turn on your favorite cartoon.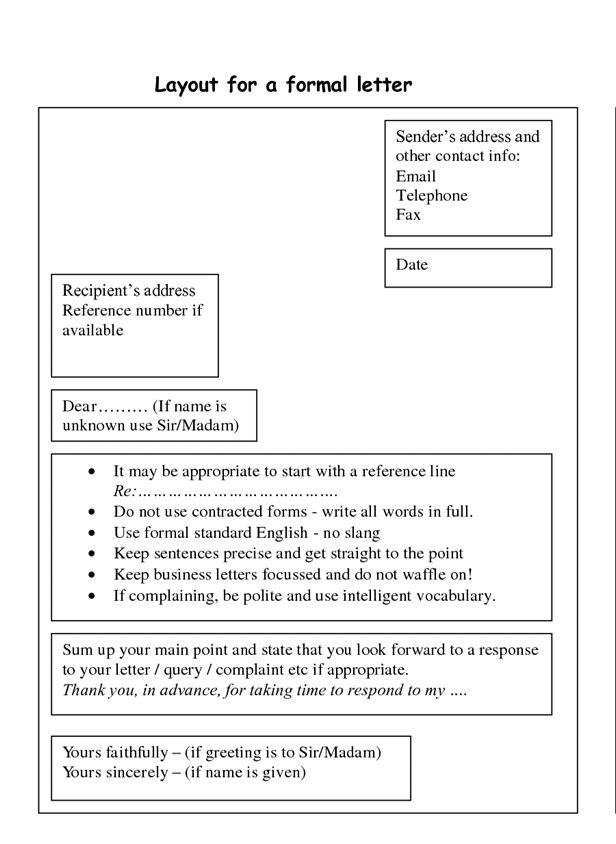
Find a double
Take blocks with letters and together with your child make a syllable out of two letters. For example, let there be a syllable "BA". Say the syllable several times so that the child remembers it. Then ask him to find the familiar syllable "BA" on the pages of any book.
Of course, it may not work the first time. But nothing, praise the child for every syllable found and say that this is just a game and in case of failure you should not be upset.
This exercise develops visual memory well and helps the child get used to syllables.
Let's be friends
What could be more boring than just combining vowels and consonants into syllables? Another thing is to teach letters to be friends so that they make up words. You will need a metal board and letters on magnets. Arrange the letters on the right and left in this order:
Then tell the child that the letters quarreled and they need to be connected and made friends. Move together the letter "A" to "U" and read what happened - "AU". So the child will understand that connecting letters into syllables is fun and will begin to connect syllables into words with pleasure.
Move together the letter "A" to "U" and read what happened - "AU". So the child will understand that connecting letters into syllables is fun and will begin to connect syllables into words with pleasure.
⠀
Also learn to read by syllables with our free games.
Pick me up
In this exercise you will have to get a little creative. Take an A4 sheet and draw a dog on it. Sign the word “SO-BA-KA” under the drawing by syllables. Then take scissors and cut vertically so that you get three equal parts with pattern elements and syllables. Ask the child to read each syllable separately, and then ask the dog to collect and read the word syllable by syllable.
If you have no time to draw yourself, look for similar puzzles in the store.
This fun exercise will quickly help your child learn to read long words.
Transformer Word
Blocks or cards with letters are suitable for this exercise. For example, put together the already familiar word “SO-BA-KA” with your child. Read it syllable by syllable and disassemble it into individual letters. Say: “And now you will see how much our “DOG” can give us new words! Let's watch?".
For example, put together the already familiar word “SO-BA-KA” with your child. Read it syllable by syllable and disassemble it into individual letters. Say: “And now you will see how much our “DOG” can give us new words! Let's watch?".
Then, from individual letters, make up new words: "JUICE", "TANK", "BOK", "KO-SA". Make up words in turn, ask the child to read each syllable by syllable and explain the meaning of what they read.
This exercise allows you to learn to read several words from already familiar syllables in one session.
Practice with your child every day for 10-15 minutes and in a couple of weeks you will see the first results. Your child will learn to combine letters into syllables and will already be able to read small words in syllables. And most importantly, he will do it with great enthusiasm and pleasure, because the whole learning process is an exciting game.