How to write abc for kindergarten
Browse Writing Letter Educational Resources
Entire LibraryPrintable WorksheetsGamesGuided LessonsLesson PlansHands-on ActivitiesInteractive StoriesOnline ExercisesPrintable WorkbooksScience ProjectsSong Videos
408 filtered results
408 filtered results
Writing Letters
Sort byPopularityMost RecentTitleRelevance
-
Filter Results
- clear all filters
By Grade
- Preschool
- Kindergarten
- 1st grade
- 2nd grade
- 3rd grade
- 4th grade
- 5th grade
- 6th grade
- 7th grade
- 8th grade
By Subject
- Coding
- Fine arts
- Foreign language
- Math
Reading & Writing
- Leveled Books
Reading
Early Literacy
- Concepts of Print
- Early Writing Practice
Writing Letters
- Writing Names
- Picture Comprehension
- Communicating Through Symbols
- Alphabet
- Reading Comprehension Strategies
- Reading Genres and Types
- Writing
- Grammar
- Science
- Social emotional
- Social studies
- Typing
By Topic
- Arts & crafts
- Coloring
- Holidays
- Offline games
- Seasonal
By Standard
- Common Core
Short A 1
Guided Lesson
Short A 1
Bag, cat and cap are all examples of short A words that kindergarteners will be learning to read this year. You can support this learning with a guided exploration of the short A sound. Kids will be taught how to identify the short A within text, in addition to the corresponding sound. Check out our short A printables for more phonics practice.
Kindergarten
Reading & Writing
Guided Lesson
Search Writing Letter Educational Resources
Young students can train their hands and fine motor skills with support from the Learning Library's tools on writing letters. The ABCs are broken down into simple steps so kindergartners learn to build letters line by line. There is a large supply of tracing assignments, lessons on letter sounds, and much more that familiarize kids with the 26 little letters that create a robust language.
Simple as ABC: Writing Letter Resources
In preschool through first grade, young students learn their ABCs, the building blocks to the world's greatest novels, moving speeches and profound poetry. It all starts with mastering each letter, its sound and shape. The Learning Library provides alphabet writing resources for new students to practice this powerful fundamental.
It all starts with mastering each letter, its sound and shape. The Learning Library provides alphabet writing resources for new students to practice this powerful fundamental.
Handwriting may be a dying art form now that keyboards have largely replaced pencils. But there are still many instances where penning words down occurs, like when filling out a doctor form or writing a personal letter. Recognizing letter shapes is essential for reading, too. Education.com provides printable worksheets and teacher-created lesson plans that teach specific letters, such as Practicing P and Z is for Zookeeper. A preparatory lesson plan, Get Ready to Write! trains students' hand coordination and finger strength by instructing them to write different lines that commonly appear in letters.
Kids can leave the pencil and eraser at home and practice letter writing digitally with the resource center's online games that include a look at short A, E and U. An active hands-on activity, Fine Motor Practice, includes different exercise stations that smooths small-scale coordination capabilities, such as stringing beads and cutting paper with scissors. Guided lessons and printable workbooks on writing the alphabet can also be accessed in the library. Students will be masters of the alphabet—from A to Z—with Education.com's writing letter resources.
Guided lessons and printable workbooks on writing the alphabet can also be accessed in the library. Students will be masters of the alphabet—from A to Z—with Education.com's writing letter resources.
At What Age Should a Child Know the Alphabet?
As children grow, they naturally hit learning milestones. One of the most critical educational milestones a child must reach is learning the alphabet, which prepares them for reading and writing.
But at what age should a child know the alphabet?
In this article, you will learn at what age a child should know how to recite the alphabet, recognize and write individual letters, learn letter sounds, and eventually learn how to read. Read on to make sure your little one is on the right track!
At What Age Should a Child Know the Alphabet?
Recitation
Typically, by the age of three, children should be able to recite the alphabet. However, every child is different. Some toddlers may learn in their twos, and others might not pick it up until the late threes.
Children generally learn how to recite the alphabet through repetition. If you sing the ABC song to your kids often, they are more likely to pick it up quicker, just as they would any song.
Recognition
Most children can recognize letters between the ages of three and four. Most kids will recognize the letters in their name first.
For example, a boy named Jace will probably be able to remember what the letter “J” looks like as well as recognize most other letters in his name. Similar to alphabet recitation, use repetition to teach your children about recognizing individual letters. You may ask them, “What letter is that?” whenever you see an isolated letter.
Writing
By ages four to five, children will start writing letters. Children will learn to write the alphabet in preschool and kindergarten, but it may be beneficial to have your child practice writing his/her letters at home. Most children at this age know that written symbols represent messages and may be interested in writing on their own. One of the easiest ways children learn how to write letters is to begin tracing them.
One of the easiest ways children learn how to write letters is to begin tracing them.
Additionally, teaching your child how to write his/her name is an important step that will ultimately help them become familiar with writing the rest of the alphabet.
Sounds
By five years old, children will start to associate letters with their accompanying sounds, otherwise known as phonics. In other words, around the age of five, children should be able to reason that the word “book” starts with the letter B.
Children begin learning phonics in kindergarten, which is a vital step to decoding written text and begin reading.
Reading
By six years old, first graders should be able to read words aloud with ease. For the most part, children can recognize sight words and their names. Moreover, children can decode some words by sounding out their letter combinations.
By second grade, a child should be able to sound-out a simple book. By the third grade, your child should be able to read independently and fluently. By this point, your child should be a master of the alphabet and is ready to master the art of reading!
By this point, your child should be a master of the alphabet and is ready to master the art of reading!
What If Your Child Isn’t Learning at the Rate S/He Should?
It’s important to remember that every child is different and may learn at a different rate. If your child isn’t learning the alphabet at the pace s/he should, one reason may be because s/he isn’t interested or is simply undergoing a minor setback.
However, if your child is falling severely behind, it’s important to find out if your child truly has a problem learning or if it is nothing to worry about. Therefore, work one-on-one with your child to determine if there is a problem. For example, practice reading and writing with your child. If s/he is having a hard time comprehending the instruction or if it’s taking him/her an abnormally long time to do the task, consider talking with your child’s teacher about it.
In the end, if you suspect your child might have a reading or learning disability, discuss it with a doctor.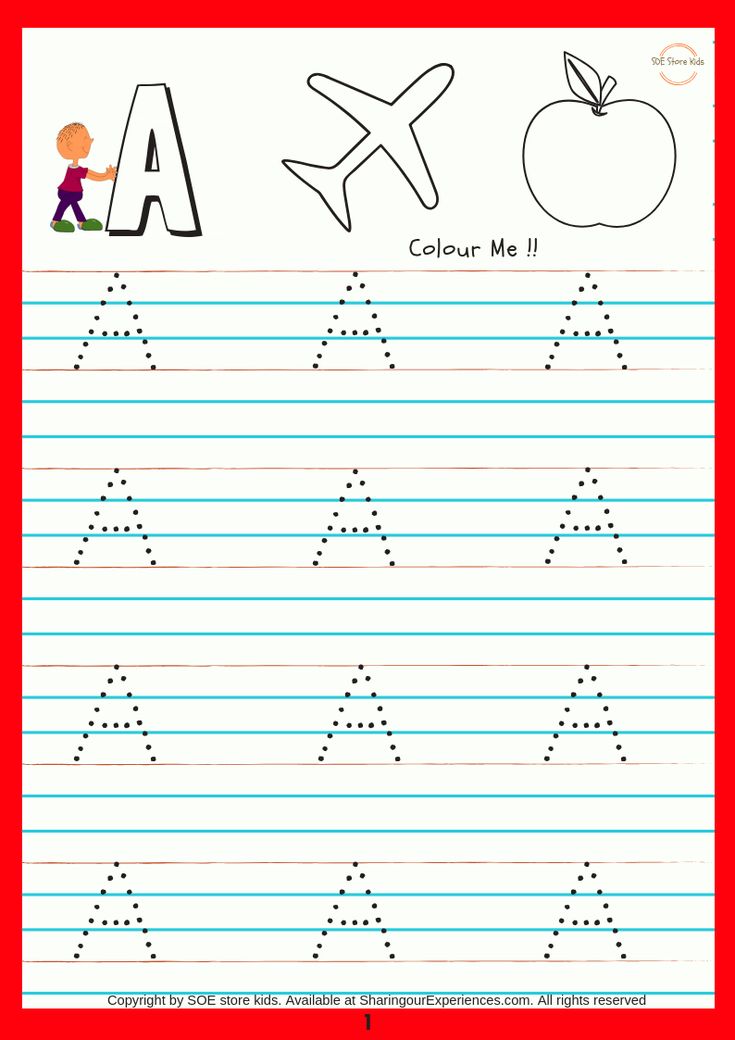 If your child is truly suffering from a reading disability, it can cause him/her to fall behind in his/her education. The sooner you seek help, the sooner you will be able to find a solution that works for your precious little one!
If your child is truly suffering from a reading disability, it can cause him/her to fall behind in his/her education. The sooner you seek help, the sooner you will be able to find a solution that works for your precious little one!
Learn the Alphabet at a Top-Tier School!
So at what age should a child know the alphabet? Learning the alphabet is an ongoing process. That being said, it’s crucial to enroll your little one in a school that will not only teach him/her but also helps develop in him/her a love of learning.
Smaller Scholars Montessori Academy helps children become more confident, creative, and independent through the acclaimed Montessori experience. You can enroll your child in the toddler program, which is for kids between the ages of eighteen months and three years, or in the primary program, for children between three and six years. In both programs, children have a rich classroom environment in which they are encouraged to explore, learn, and thrive. Then, as children grow older, they can explore the elementary program for kids up to twelve years old.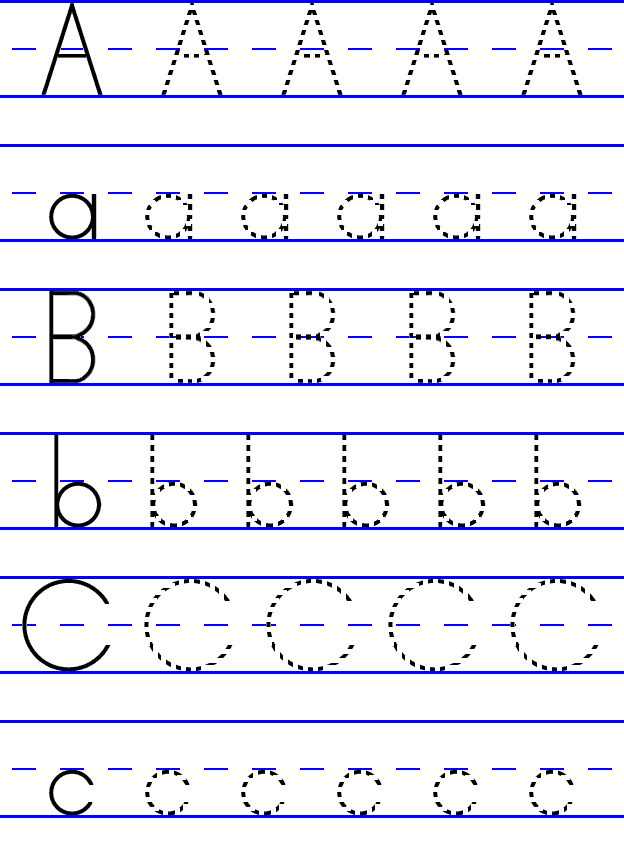
What are you waiting for? Ensure your child learns the alphabet and how to read by enrolling your child in Smaller Scholars Montessori Academy! Contact them to learn more.
Alfavit kindergarten - vitamin and mineral complex for children from 3 to 7 years old
contains 13 vitamins and 9 minerals. Dosages correspond to the established in the Russian Federation, physiological norms for the consumption of vitamins and minerals.
The complex reliably provides the child with useful substances necessary for his development. Taking into account the Russian natural and social conditions, the composition includes iron, selenium and iodine, as well as calcium, which is necessary for the child in growth period. The compatibility of components and the absence of artificial colors reduces the risk of allergic reactions. reactions.
Iron+ Tablet #1
pink
(cherry)
| Vitamins | | % off RUSP * |
|---|---|---|
| C | 20 mg | 40 |
| B1 | 0. 72 mg 72 mg | 80 |
| Beta-carotene | 0.9 mg | - |
| Folic acid | 80 mcg | 40 |
| Minerals | ||
| Iron | 8 mg | 80 |
| Copper | 0.48 mg | 80 |
Antioxidants+ Tablet #2
orange
(orange)
| Vitamins | | % off RUSP * |
|---|---|---|
| C | 20 mg | 40 |
| Nicotinamide (PP) | 7.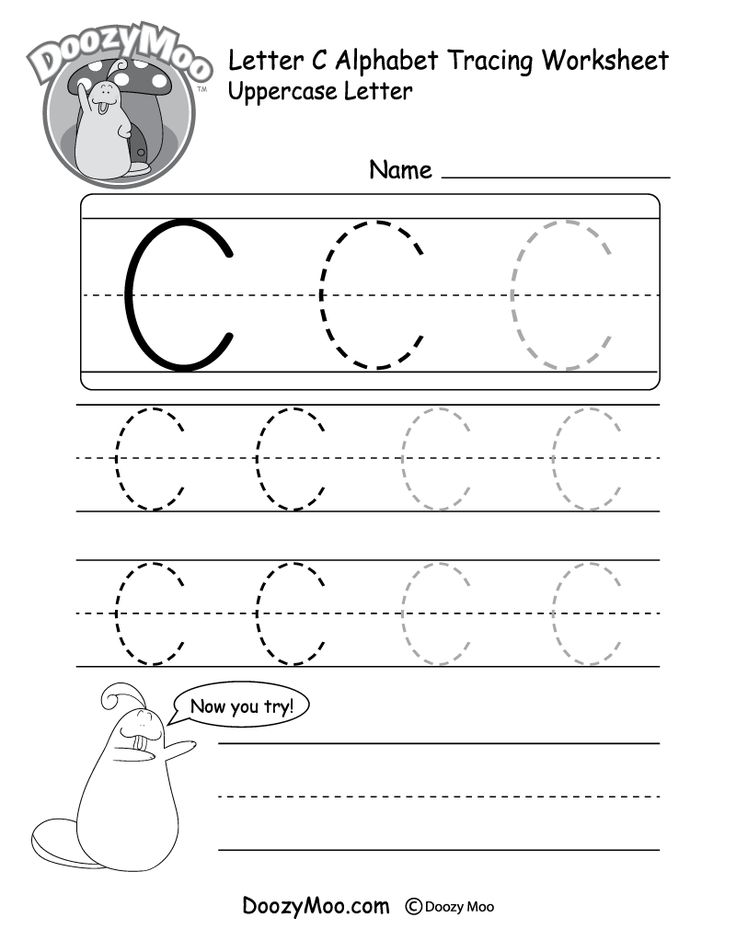 15 mg 15 mg | 65 |
| E | 4.9 mg | 70 |
| B2 | 0.8 mg | 80 |
| B6 | 0.96 mg | 80 |
| Beta-carotene | 0.9 mg | - |
| Minerals | ||
| Magnesium | 30 mg | 15 |
| Zinc | 4.8 mg | 60 |
| Manganese | 0. 5 mg 5 mg | - |
| Iodine | 50 mcg | 50 |
| Selenium | 20 mcg | 100 |
Calcium-D3+ Tablet #3
light yellow
(vanilla)
| Vitamins | | % off RUSP * |
|---|---|---|
| Pantothenic acid | 2.4 mg | 80 |
| Folic acid | 80 mcg | 40 |
| B12 | 1. 05 mcg 05 mcg | 70 |
| D3 | 2.5 mcg | 25 |
| K1 | 25 mcg | 45.5 |
| Biotin (H) | 10.5 mcg | 70 |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 135 mg | 15 |
| Chrome | 10.5 mcg | 70 |
*– According to MP 2.3.1.2432-08 "Norms of physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population Russian Federation".
**- Nutrition information of the product is determined by calculation by the average value of the content of biologically active substance in product.
How to take
Daily dose - 3 chewable tablets of different colors. Giving a child a pill with a gap in time: for example, in the morning, afternoon and evening, you will make vitamin prophylaxis more effective. The order in which the pills are taken during the day is not important.
Admission procedure
tablets unimportant
Interval
between appointments
4-6 hours
During this time, the vitamins and minerals that are part of one tablet will be completely absorbed and will not interact with the next components.
Twice a day
For example, one tablet in the morning
and two in the evening or vice versa -
the effect will be higher than with
taking a single tablet
complex.
Three times a day
get the most out of it
from taking ALFAVIT -
it will be 30-50% more,
than from taking the traditional
vitamin and mineral
complex.
Remember that the degree of lack of vitamins and minerals is an individual indicator. Typically, to solve problems and eliminate the lack of useful substances in the body, it is necessary to conduct 2-3 courses, with an interval 10-15 days between them.
60 chewable tablets
in blister packs
Indications
for use
as an additional source of vitamins and minerals (macro- and microelements) for children from 3 up to 7 years old.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to the components, hyperthyroidism.
Before use, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Not a drug. SGR No. RU.77.99.88.003.R.000440.02.20 dated February 18, 2020
Additional
information
In the conditions of modern life with its loads and stresses, complex ecological the health situation must be taken care of very carefully, especially when it comes to a child. A fragile body needs reliable protection. And here the parents have a question: what complex vitamins for children to choose? The range of pharmacies is large, which makes you a little confused: how choose the right children's vitamins? Firstly, it is worth discussing this issue with a pediatrician, and secondly, get as much information as you can.
Vitamins for children are divided into several groups according to their composition and dosages, depending on age. Conventionally, they can be classified as follows:
Conventionally, they can be classified as follows:
- vitamins for children from 1 to 3 years old,
- for children 3-7 years old,
- for older children.
ALFAVIT Kindergarten belongs to the second category. It contains vitamins and minerals that take into account the rapid development of the child after 3 years, changes in his environment, contact with large groups of other children (which sometimes becomes stressful for the child and leads to a weakening immunity). Useful substances help to grow and develop harmoniously, help to adapt to increased stress - emotional and mental.
Even if a child knows about the benefits of vitamins, it is often very difficult to get them to accept. Therefore ALFAVIT Kindergarten is produced in the form of fruit-flavored tablets. They don't need swallow, or you can eat like delicious fruit candies. This method is very popular with children.
This method is very popular with children.
"The ABC of fire safety" was studied by pupils of the kindergarten "Bear cub" - News
Government of the Russian Federation
GI websites by county Portal EMERCOM of Russia
Version for the visually impaired
Search
close Expand filters Searchwhole phrase
single words
Publication not earlier than
Publication no later than
Partition type Whole siteHeadquartersActivitiesDocumentsPress centerNewsNews
Sort by relevance date descending date ascending
Collapse filters-
Head office
Central Federal District
- Moscow
- Belgorod region
- Bryansk region
- Vladimir region
- Voronezh region
- Ivanovo region
- Kaluga region
- Kostroma region
- Kursk region
- Lipetsk region
- Moscow region
- Oryol region
- Ryazan region
- Smolensk region
- Tambov region
- Tver region
- Tula region
- Yaroslavl region
Privolzhsky Federal District
- Republic of Bashkortostan
- Republic of Mari El
- Republic of Mordovia
- Republic of Tatarstan
- Udmurt Republic
- Chuvash Republic
- Kirov region
- Nizhny Novgorod Region
- Orenburg region
- Penza region
- Perm region
- Samara region
- Saratov region
- Ulyanovsk region
Northwestern Federal District
- Republic of Karelia
- Republic of Komi
- Arkhangelsk region
- Vologda region
- Kaliningrad region
- Leningrad region
- Murmansk region
- Novgorod region
- Pskov region
- St.
 Petersburg
Petersburg - Nenets Autonomous District
Southern Federal District
- Republic of Adygea
- Republic of Kalmykia
- Krasnodar Territory
- Astrakhan region
- Volgograd region
- Rostov region
- Republic of Crimea
- Sevastopol
North Caucasian Federal District
- Republic of Dagestan
- Republic of Ingushetia
- Kabardino-Balkar Republic
- Karachay-Cherkess Republic
- Republic of North Ossetia - Alania
- Stavropol Territory
- Chechen Republic
Ural Federal District
- Kurgan Region
- Sverdlovsk region
- Tyumen region
- Chelyabinsk region
- Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District
- Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug
Siberian Federal District
- Republic of Altai
- Tyva Republic
- Republic of Khakassia
- Altai Territory
- Krasnoyarsk Territory
- Irkutsk region
- Kemerovo region - Kuzbass
- Novosibirsk region
- Omsk region
- Tomsk region
Far Eastern Federal District
- Republic of Buryatia
- Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
- Primorsky Krai
- Khabarovsk Territory
- Amur Region
- Kamchatka Territory
- Magadan region
- Sakhalin Region
- Trans-Baikal Territory
- Jewish Autonomous Region
- Chukotka AO
September 11, 2022, 08:24
Download original
As part of the project "ABC of fire safety", a preventive event was held in the kindergarten "Bear cub" in the city of Tambov.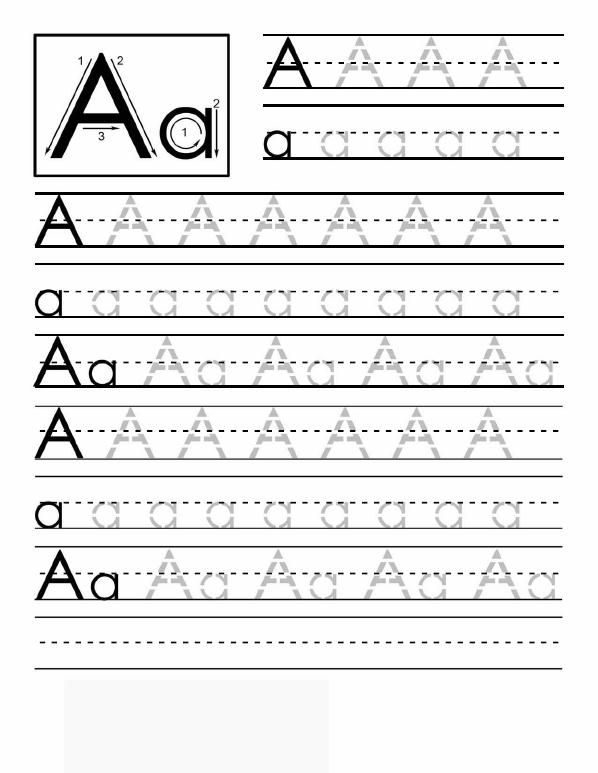
Kindergarten pupils and staff worked out practical actions according to the evacuation plan. In a matter of minutes after the fire alarm went off, they left the building in an organized manner and without panic.
Deputy Chairman of the Council of the Tambov regional branch of the VDPO conducted a lesson with preschoolers. Children learned about the dangers that can occur as a result of careless handling of fire, why playing with matches is dangerous, and why it is impossible to turn on household electrical appliances without the permission of adults. During the lesson, the children watched preventive cartoons, participated in competitions. The children prepared their homework in advance - drawings and crafts that they made together with their parents for the regional family competition "Safety through the eyes of children."
The ABC of Fire Safety project is implemented by the Tambov regional branch of VDPO in preschool institutions of the region and teaches not only children, but also adults how to act in an unforeseen situation in order to save not only their own lives, but also the lives of other people.