Pre k sight words activities
25 low-prep sight word activities
This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Today I’m sharing some simple sight word activities that you can prepare in minutes!
(This post contains affiliate links.)
So what are sight words, anyway?
Some people will tell you that sight words are words that kids can’t sound out; they just have to learn them by sight. Others tell you that sight words are the high frequency words: the words that kids encounter the most when they read.
But researchers tell us that sight words are words we recognize automatically without needing to sound out or guess.
The real question is … how can we turn high frequency words INTO sight words?
The number one thing to do is to teach each word explicitly. That’s why I created my set of sight word lessons with decodable books.
Once you’ve taught the words with attention to the spelling patterns (these sight word worksheets are also great for this), you’re ready for these low prep sight word activities that you can put together in under 15 minutes!
1- It takes just 5 minutes to set up Sight Word Sticky Note Match. Just write the words on sticky notes and have your child cover the words on a dry erase board!
2 – Grab your alphabet stamps and some play dough for this simple sight word activity.
3 – Write the words on sticky notes. Then have your child write them in sand.
4 – Teach sight word songs. We are big fans of the collection of the sight word DVD’s and CD’s from Heidisongs. Listen to them as you’re driving to school or during transitions in the classroom.
THE BEST SIGHT WORD WORKSHEETS
Sight Word Worksheets – Based on the science of reading!
$15.00
Just say no to busywork! These high frequency word worksheets are the real deal. They’ll help your students connect the sounds to the letters and finally master those sight words!
Buy Now
5 – Write the words on sticky notes. Then have your child swat each sight word with a fly swatter as you name it!
6 –Do fun actions with your sight words with This Reading Mama’s free action cards.
7 – Write sight words in play dough with a stick or wooden skewer.
8 – Try chanting sight words in a variety of different ways – like a robot, a cheerleader, and more! You can get free sight word chants on TPT here.
HANDS-ON PRACTICE FOR SIGHT WORDS
High Frequency Word Practice Mats – 240 words!
$24.00
Teachers love our practice mats because they’re low-prep and effective. Kids love them because they’re engaging and hands-on!
Buy Now
9 – Make a sight word memory game. Just write each sight word on two different index cards. Then turn the cards over and invite your child to find the matches.
10 – Print these free sight word cards and build the words with letter tiles. When you join This Reading Mama’s free email list, you’ll get lots of free sight word cards! Learn more here.
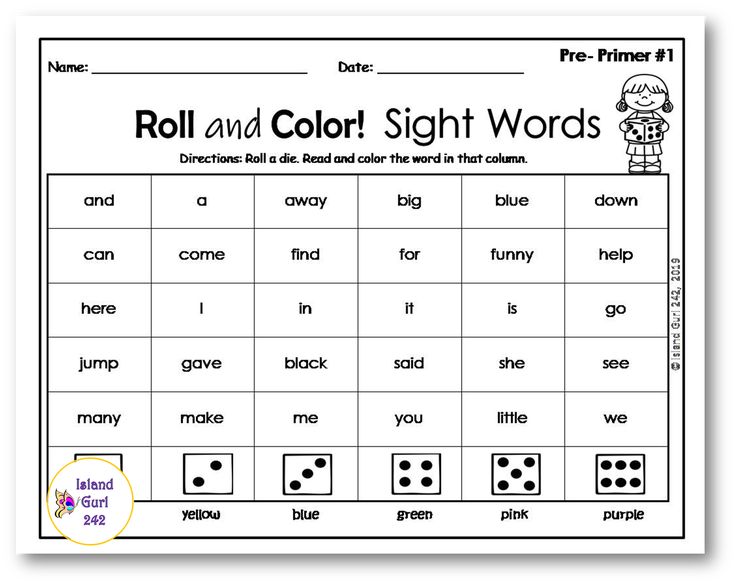
11- Learning is always more fun with dice! Grab these free rainbow roll & write pages for a variety of sight words. Kids roll a die, check the key at the top of the page, and write the word in a particular color.
Kids roll a die, check the key at the top of the page, and write the word in a particular color.
12 – This is such a creative way to practice writing sight words! Find the words with a magnifying glass and write them on the lines. Get the freebie here.
13 – Are you students learning beginning sight words? Print and play sight word blackout.
14 – Simply write your child’s sight words on a piece of paper and have him stamp them with alphabet stamps.
15. Grab the play dough, a sheet protector, and a dry erase marker. Your child can build the word with play dough and write it on the lines below. Get the freebie here.
16 – Grab these free color-by-sight-word pages.
17 – Get some colorful craft sticks and write the words with a permanent marker for some simple sight word puzzles.
18- Sight Word Showdown is both simple and genius! Just grab a stack of index cards and write each word twice. Then follow the directions in this post.
Then follow the directions in this post.
19 – Write sight words in muffin tin liners and play a simple game of Three in a Row.
20 – Bury magnetic letters in a sensory material. Have children dig out the letters to build words.
21 – Make a sight word parking lot. Draw tiny parking spots on a piece of poster board, and write a sight word in each one. As you name the words, have your child park a toy car in each spot. Learn more here.
22- Practice writing sight words using a dry erase marker on a dry erase board.
23- Write sight words on craft sticks and provide some magnetic letters for this portable sight word activity.
24 – Where’s the bear? Write the words on paper cups and hide a small bear or other tiny object. Your child guesses where the bear is hiding by naming the word on the cup.
25 – Go on a simple sight word hunt by matching the sticky note sight words to the words on a clip board.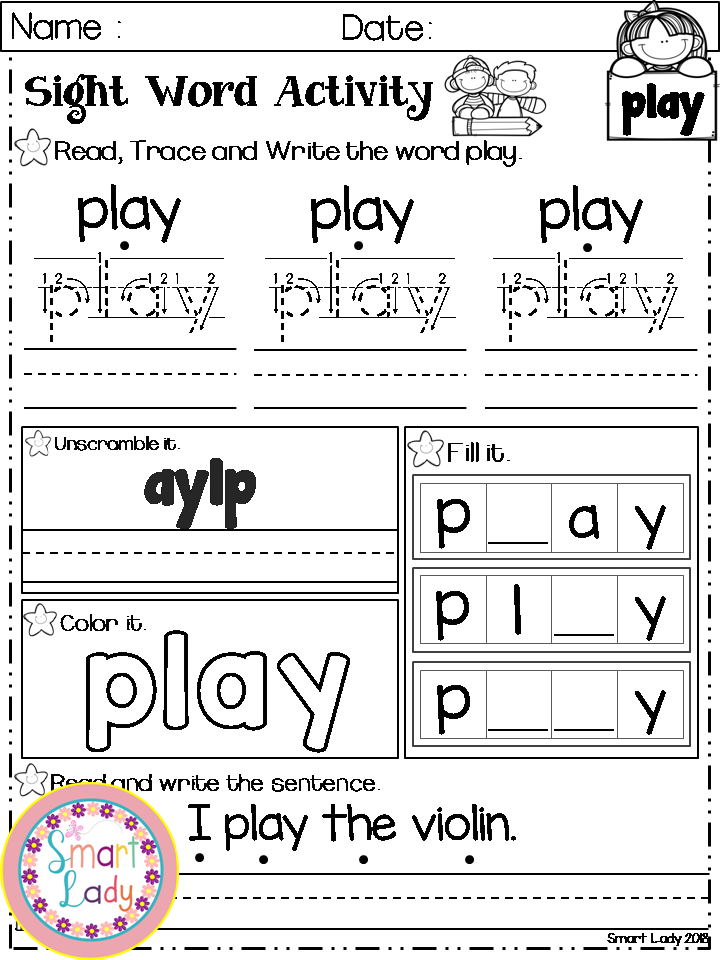 (This one’s a favorite at our house.)
(This one’s a favorite at our house.)
And there you have it! 25 low-prep ways to practice sight words!
YOU’LL LOVE OUR EDITABLE SIGHT WORD GAMES
Editable Reading Games for Every Season – MEGA PACK!
$24.00
Your students will ASK to practice their sight words when you start using this versatile set of sight word games! Simply type up to 12 words, and they’ll autofill into the 150 seasonal games.
Buy Now
Free Reading Printables for Pre-K-3rd Grade
Join our email list and get this sample pack of time-saving resources from our membership site! You'll get phonemic awareness, phonics, and reading comprehension resources ... all free!
Free Printable Pre-K Sight Word Worksheets
Need more opportunities for your pre-k students to practice sight words? These free printable pre-primer sight words worksheets are a fun and effective way for your pre-k students to master their word list!
Pre-K Sight Word Worksheets
In pre-k, students begin working on learning sight words. The Dolch pre-primer sight words list is the perfect place for young readers to start working on words. These free sight word printable worksheets will give your pre-k, preschool, and even kindergarten students many meaningful opportunities to practice and work on these high frequency words.
The Dolch pre-primer sight words list is the perfect place for young readers to start working on words. These free sight word printable worksheets will give your pre-k, preschool, and even kindergarten students many meaningful opportunities to practice and work on these high frequency words.
Your students will get to work with each of the 40 pre-primer words on the Dolch sight word list in 7 different ways on each worksheet. These 7 activities will help students identify, read, spell, build, and write the words. Since each sight word worksheet focuses only on one word, your students can hone in on learning that word without getting confused.
These worksheets not only offer free sight word practice for students, but they also offer a no-prep option for teachers. Simply print and go, that’s it! These pre-k sight word worksheets can also be uploaded as a digital activity if you are using Google Classroom, Seesaw, or another digital learning platform.
Add these no-prep worksheets to your morning tubs, literacy lessons, early finisher activities, or as an independent sight word activity.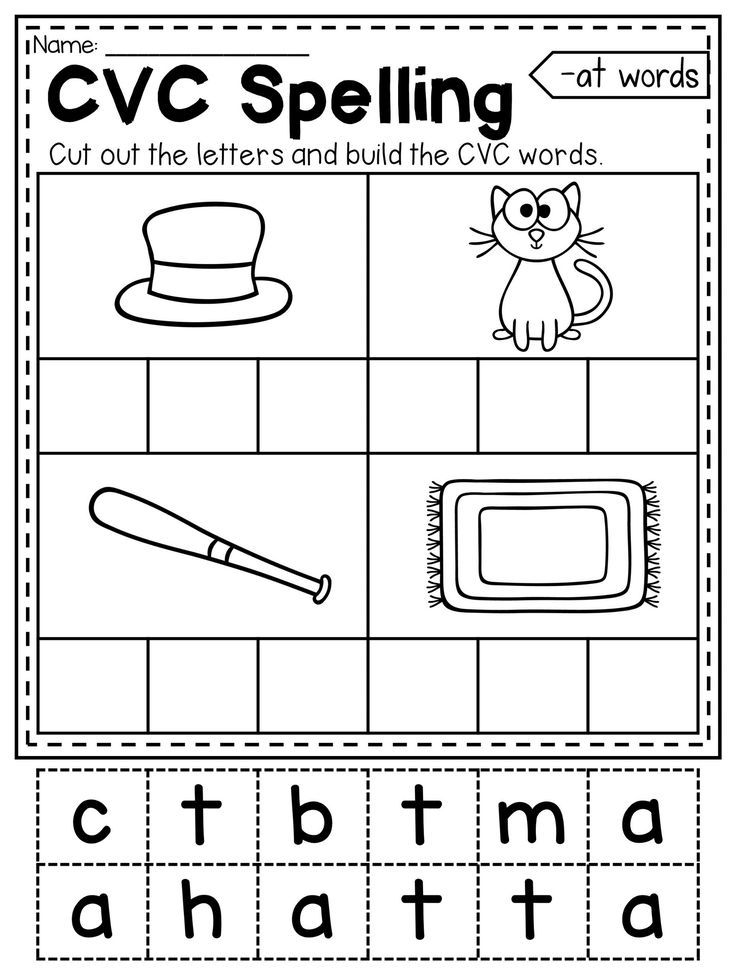 The directions are the same for each sight word, so your students will know exactly what to do and can complete them with success.
The directions are the same for each sight word, so your students will know exactly what to do and can complete them with success.
No-Prep Sight Word Worksheets
These free printable worksheets are fun, effective, and best of all…no-prep! To get these ready for your students, simply print and go. No cutting, stapling, or laminating required. The sight word worksheets come in black and white, so you can use them even if you don’t have access to colored copies.
If you want to plan ahead and save time down the road, you can print multiple words at once and store them in file folders or colorful trays for easy grab-and-go access.
Additionally, if you are using them digitally, you can upload the PDF into your learning platform ahead of time with the words you want your students to work on. Another option is to have the students complete the worksheet and submit a picture to your learning platform.
Differentiated Pre-Primer Sight Word Activities
These pre-k sight word worksheets are very versatile and can be used in a variety of ways, making differentiation a breeze. There are 40 pre-primer words included. You can easily use these worksheets for pre-k and preschool sight word work and kindergarten sight word work. Depending on the needs of your students, you can assign the word or words they need the most practice with to achieve mastery.
There are 40 pre-primer words included. You can easily use these worksheets for pre-k and preschool sight word work and kindergarten sight word work. Depending on the needs of your students, you can assign the word or words they need the most practice with to achieve mastery.
Here are a few ways in which you can utilize these sight word worksheets:
- Complete a worksheet for the word of the week.
- Revisit common words students struggle with,
- Assign certain words to small groups depending on level.
- Spiral review words throughout the year.
- Assign more challenging words to students who are ready.
- Have students work on reading fluency by completing a worksheet and then read a leveled reader focusing on that word.
Each sight word worksheet follows the same pattern of activities to read the word and write the word, so you only need to teach students how to use it one time and they’ll be set to successfully complete the rest of the word work worksheets.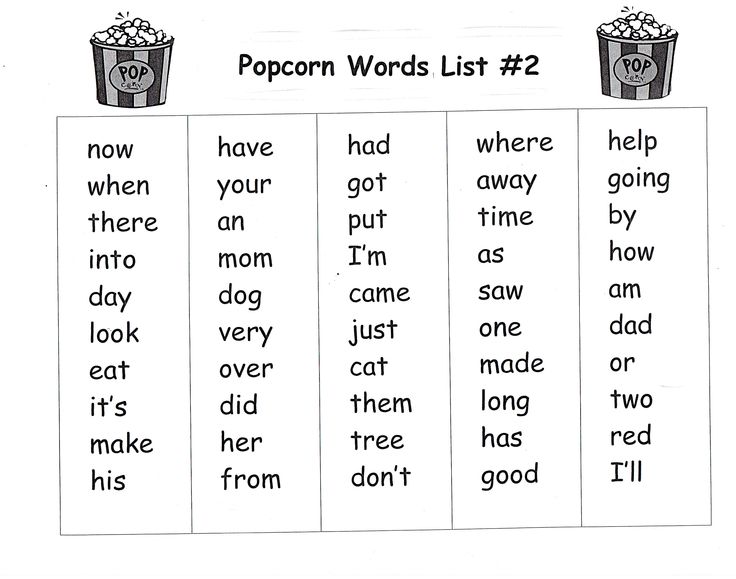
These pre-primer sight word worksheets make practice more fun, engaging, and hands-on than other types of activities, such as flash cards or rote memorization drills.
To make learning sight words even more fun for your students, you can let them complete the worksheets using colored pencils, crayons, or markers! They’ll love it!
Implementing the Sight Word Worksheets
To implement the free printable pre-k sight word worksheets, students will first read the focus sight word at the top of the page. Next, they’ll work on tracing the word, following the arrows to ensure proper writing technique and directionality. Then they will write the word independently on the line.
Students get to become artists for the next activity as they decorate the word written in bubble letters. If you wanted to encourage direction following, you could give students specific directions, such as, “Give the first letter big blue polka dots.”
They also get to be word detectives by finding and circling the sight words hidden in the word search. To make this more fun, you can give students magnifying glasses and highlighters to find and circle the words.
To make this more fun, you can give students magnifying glasses and highlighters to find and circle the words.
After that, the students will look at the letters of the alphabet and color in the letters that spell the sight word. Finally, they will fill in the missing letters in the words at the bottom of the worksheet to spell the word correctly.
In just one no-prep worksheet, students are getting a ton of meaningful practice and word work opportunities.
These sight word worksheets are perfect for practicing pre-primer sight words in any pre-k classroom! They’ll become sight word reading rockstars in no time after completing these fun sight word activities!
Click the button below to get the Pre-K Sight Word Worksheets for your students! I hope you enjoy them!
Do you need these sight word worksheets for other levels? Get them below!
These sight word worksheets pair perfectly with our Superhero Sight Word Mats for Google Slides and Seesaw! Use the mats online and then add the worksheets for extra practice!
Here are some more sight word activities!
Editable Sight Word Activities
Editable Sight Word Games Bundle
Paperless Superhero Sight Word Mats
Free Printables Page
Special Education Terms You Need to Know
Reading special education records or documents can be difficult! Sometimes it may seem like you are trying to understand a new language. Below is a list of some abbreviations and terms. We hope this will help you better understand your child's records.
Below is a list of some abbreviations and terms. We hope this will help you better understand your child's records.
Print This Publication
Making sense of special education records or documents can be tricky! Sometimes it may seem that they are written in another language. Below is a list of some abbreviations and terms. We hope this will help you better understand your child's notes.
If you have questions or need more information, you can visit our website at www.disabilityrightsca.org anytime or call 1-800-776-5746 (TTY: 1-800-7195798 ), from Monday to Friday, from 9:00 to 16:00.
Top 6 terms to remember
Plan 504: Section 504 is a law that requires schools to provide students with disabilities equal access to education as all students. A 504 plan is a plan that describes the services, aids, and accommodations that schools will need to provide to a student to ensure that the student has access to education on an equal basis with everyone.
FAPE: Qualified Free Public Education. Students with disabilities should receive a public education free of charge to the student and family that will enable them to excel.
Students with disabilities should receive a public education free of charge to the student and family that will enable them to excel.
IDEA: Persons with Disabilities Education Act. Federal Education Act for students who fall under one of the 13 qualifying categories of disabilities and need specialized support to complete the required education. Specialized supports and services are described in the student's Individualized Education Program (IEP).
IEP: Individual Education Program. A plan for students who qualify for a special education program. The plan describes the student's current academic performance, development goals, and the services that will be provided to support the student's studies.
The plan should be updated at least once a year.
LRE: Least Restrictive Environment. A student with a disability should be educated with non-disabled peers to the maximum extent possible for that individual student.
SWD: Student with a disability.
Agencies to Know About
CSS: California Children's Services Program. Provides students with some medical therapies, usually outside school hours. CSS often has facilities on school grounds.
CDE: California Department of Education. The state body supervising public education. It handles issues such as funding, testing, and holding local educational institutions (such as school districts) accountable for student achievement. CDE also accepts compliance complaints.
CTC: Teacher Attestation Commission. Allows anyone to find teacher certification data online or file a complaint. CTC also provides guidance on how to pass the appropriate certification for positions that require a specific certification.
DDS: California Department of Developmental Welfare Services. Oversees the coordination and delivery of services to California residents with developmental disabilities.
DOR: Department of Rehabilitation. Can be attracted upon reaching the transitional age (16 years and older). DOR helps Californians with disabilities find and keep jobs and ensure they have the greatest possible equality of opportunity and ability to live independently.
DOR helps Californians with disabilities find and keep jobs and ensure they have the greatest possible equality of opportunity and ability to live independently.
DSS: California Department of Human Services. The state agency that oversees social assistance programs such as cash assistance, adult services, and CalFresh (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program).
OAH: Office of Administrative Hearings. A public authority that receives complaints within the framework of the procedures provided for by law.
OCR: Office of Civil Rights. A federal agency that can receive civil rights complaints, including complaints alleging discrimination based on disability.
OCRA: Office of Client Advocacy. The California Disability Legal and Assistance Center (DRC) program, developed with the California Department of Developmental Disabilities Social Services (DDS) to provide free legal information, advice, and representation to regional center consumers.
PTI: Parent Education and Information Centers. Provide support services for children or youth with disabilities and their families. Services may include helping parents or guardians to participate effectively in a child's education, or working with families of people with disabilities from birth to age 26.
Provide support services for children or youth with disabilities and their families. Services may include helping parents or guardians to participate effectively in a child's education, or working with families of people with disabilities from birth to age 26.
Regional Centers: Managed by the California Department of Developmental Disabilities Social Services (DDS). A network of 21 district-level agencies that assess, determine eligibility for services, and offer individualized assistance to people with developmental disabilities.
SCDD: State Council on Developmental Disabilities. An independent government agency that ensures that people with developmental disabilities and their families get the services and support they need.
Tests and assessments
BASC: Behavior Assessment System for Children. A test in which the teacher and parents answer a series of questions about the student's behavior.
CAA: California Alternative Assessment
CAS: Cognitive Assessment System. A test that allows you to evaluate the cognitive processes of the student.
A test that allows you to evaluate the cognitive processes of the student.
CCSS
CELDT California English Language Proficiency Test. English proficiency test, which has now been replaced by ELPAC.
Vision Development Assessment: This is the name of the assessment to be done before an IEP team meeting (?) to determine if a student needs therapy to improve their vision.
DRA: Diagnostic Reading Assessment
ELPAC: California English Proficiency Assessment, replaced CELDT. This is a test used in California to assess students' English proficiency.
FBA: Functional Behavior Assessment. It is sometimes referred to as the Functional Analysis Assessment. This is a test used to determine the function of a student's behavior.
NAR: Nursing Assessment Report
SBAC: More Automated Objective Assessment Consortium. These are the standardized tests used in California.
WIAT: Wechsler Individual Achievement Test, third edition. A test to determine the academic performance of a student.
WJ-IV: Woodcock-Johnson Achievement Test, fourth edition. Another test to determine the academic performance of a student.
WISC-V: IQ test to assess a student's cognitive abilities. Wexler scale for assessing the mental abilities of children, fifth edition.
Law and Legal Terms
ADA: Americans with Disabilities Rights Act. A law that provides protection for students with disabilities in public schools, day care, recreation programs, and vocational training or residential employment. It also sets out the requirements for reasonable aids for students with disabilities who meet the requirements of a special education program to perform essential functions.
ADR: Alternative Dispute Resolution. Dispute resolution process with the school district, which does not involve going to court and may involve a mediator.
ALJ: Administrative Law Judge. Oversees hearings conducted by the Office of Administrative Hearings.
Compliance Complaint: A less formal complaint process through the California Department of Education.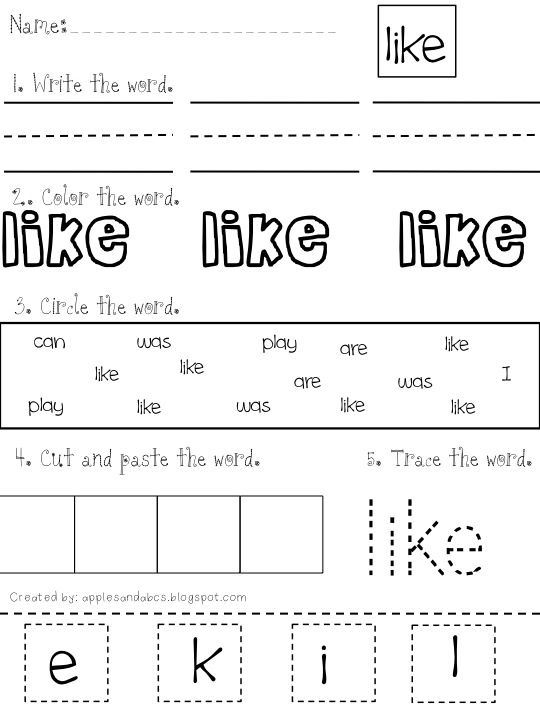 Allows a parent to report that the school is not following the Special Education Act and is not enforcing the IEP. The California Department of Education (CDE) may investigate and, if it is found that the school district is not in compliance with the IEP or the Special Education Act, issue a Corrective Action Order.
Allows a parent to report that the school is not following the Special Education Act and is not enforcing the IEP. The California Department of Education (CDE) may investigate and, if it is found that the school district is not in compliance with the IEP or the Special Education Act, issue a Corrective Action Order.
CPRA: California Public Records Act. Allows members of the public to request information from government agencies, including school districts. For example, information such as school district policies, school documents, and data.
Statutory Procedures: A procedural safeguard that gives guardians and local educational institutions the opportunity to formally disagree with a proposal to provide an appropriate free public education and submit the disagreement to an ALJ.
ESSA: Every Student Success Act. The federal law that replaced the No Child Left Behind Act.
FERPA: Federal Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act. Gives parents and students some control over the disclosure of education records, provides parental access, and allows them to view such records. It also provides for a procedure for changing the content of records.
It also provides for a procedure for changing the content of records.
Mediation: A formal meeting between two parties to try to resolve a dispute before a hearing through legal procedures. Often includes an independent mediator, usually an ALJ, who assists the parties by acting as mediator.
Mediated dispute resolution: An agreement between the parties resulting from a mediation procedure or procedures.
NDA: Confidentiality Agreement. Dispute resolution with the school district may require the guardian or student to sign a confidentiality agreement that states that certain information may not be disclosed to other persons or entities.
Procedural safeguards: Rules or procedures designed to protect the rights of students with disabilities and their parents, and how disputes between parties are resolved.
Section 504: Section 504 of the Rehabilitation of the Disabled Act 1973. A federal law that prevents discrimination against all people with disabilities in one or more important areas of life and provides aids to remove discriminatory barriers.
Special Education Terms
ABA: Applied Behavior Analysis. ABA is a data-driven intervention that helps shape student behavior.
Aids: Listed on the Special Considerations pages of the IEP. Aids do not change or lower expectations or standards; rather, they provide additional support: providing the most convenient places, extra time, etc., which help students with disabilities access learning and materials on an equal basis with others.
ADL: Self-service activities. Often mentioned in evaluation. Includes activities such as dressing, going to the toilet, and eating.
Annual IEP: IEP meetings for a student using the IEP must be held at least once a year to assess the student's progress towards goals, determine appropriate placement, review aids provided, and propose new related services.
APE: Adaptive Physical Education. Typically, this is a group related service that offers a modified physical education curriculum to students with disabilities.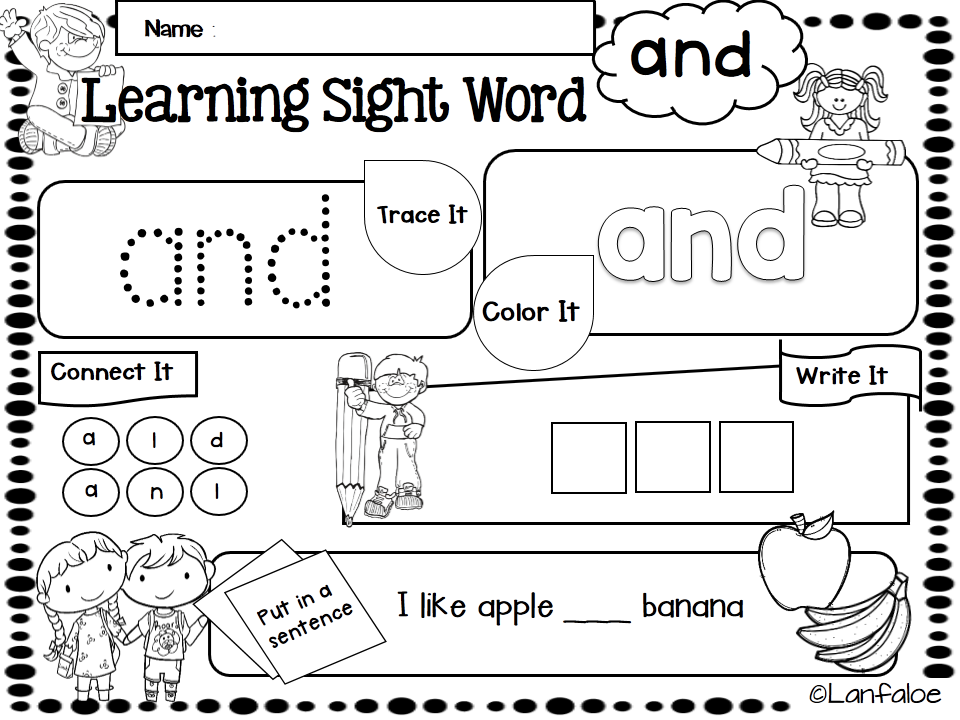
Articulation: Formation of sounds during speech; most likely to be considered in relation to how clear and understandable the student's speech is.
ASL: American Sign Language
AT: Rehabilitation aids. High-tech or low-tech devices used to provide a student with a disability with access to classes.
Auditory: Associated with the perception and interpretation of sounds
AUT: An abbreviation for the word "autism", which is used to indicate compliance with the requirements of the federal special education program.
Baseline: A short-term learning goal that defines the path to the achievement of the annual goal.
BIP: Behavior Intervention Plan. Also referred to as a behavior maintenance plan or a behavior plan. A formal, written plan that identifies a student's problem behavior, the reasons for that behavior, and strategies or supports to help the student.
Mixed groups for preschoolers: A variant of the formation of correctional groups, which implies the presence of both a general practice preschool teacher and a correctional preschool teacher who conduct classes with children together.
BSR: Behavior Correction Educational Resources. Training and support for teaching staff as needed.
CAPD: Central auditory processing disorder. A special type of audiological testing usually given to children over the age of 10.
CBI: Area based training. As a rule, the territorial principle is important to consider when a student transitions into adulthood. Area-Based Learning (CBI) provides hands-on learning for students who need to learn functional and self-care skills.
CCTE: Vocational education. The emphasis in this form of education is on "hands-on" skill acquisition, which should help students prepare for employment after high school.
Teacher collaboration: May refer to situations where a special education teacher and a general practitioner teacher are teaching a class together.
Comprehension: How words, phrases, sentences and paragraphs mean to the student. Does the student understand how to read them?
Compensatory Education/Services: Describes services that were not provided according to the IEP and must now be provided ex post; sometimes cited as part of corrective action, or if the legal process for a complaint ends in the student's favor.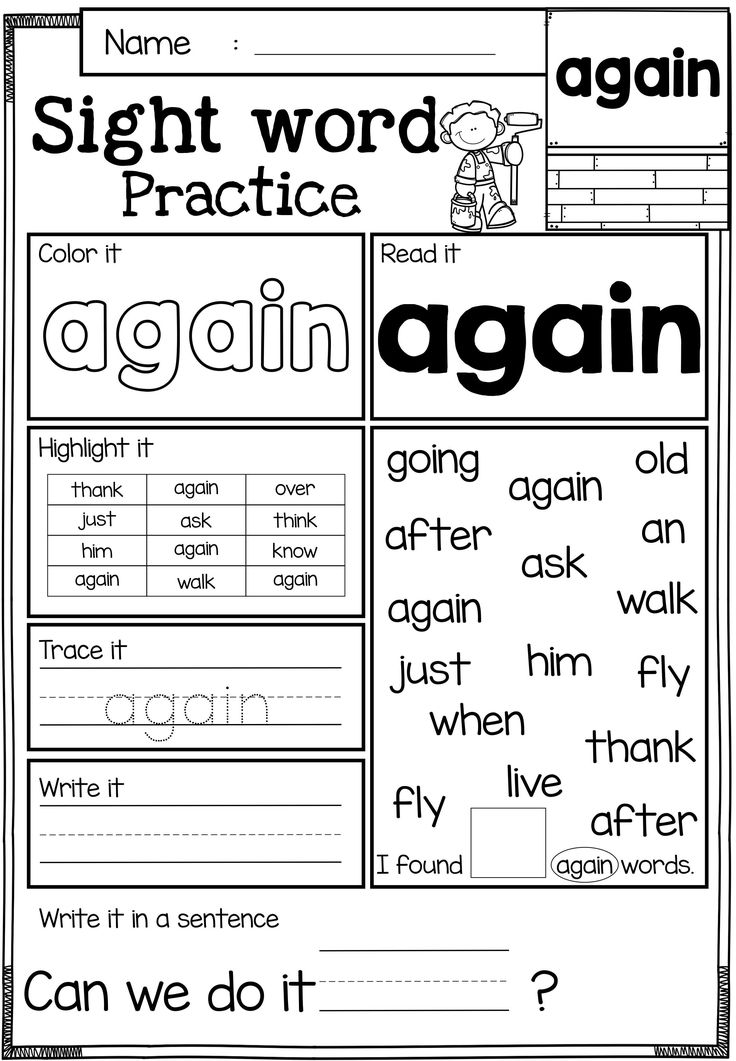
Documentation Package: Student with a disability, including initial determination of IEP eligibility, all grades, all subsequent IEPs, etc.
Corrective Action: This term describes the local authority's instructions to be followed. For example, to resolve a complaint that a district has been found to be non-compliant, the district may have to provide training and documentation to prove that the employee's training was provided.
COTA: Certified Occupational Therapy Assistant
Personnel: See application package. The personal file also includes all information about the student's general education and enrollment.
D/HH: Abbreviation for "deafness/hard of hearing", which is used to indicate compliance with the requirements of the federal special education program.
DB: An abbreviation for "deaf-blind", which is used to indicate compliance with the requirements of the federal special education program.
DD: An abbreviation for "developmental delay", which is used to indicate compliance with the requirements of the federal special education program.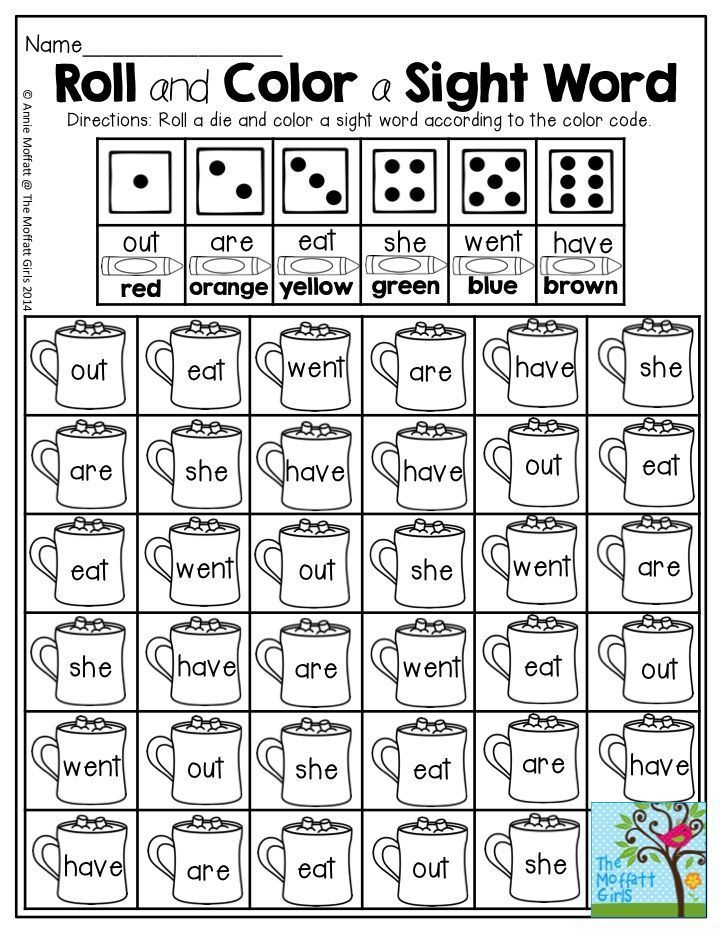
Decoding: Learner's Sound Letter Competence; how clearly the student pronounces the words.
Diploma Aimed: Indicates that the student is committed to graduating on time with a high school diploma. All students are considered eligible for a diploma, UNLESS the IEP states otherwise. The decision to recognize a student as not aimed at obtaining a certificate is made no earlier than the 7th grade.
Discrepancy pattern: A possible way to conclude that a child has a learning disability. A violation is ascertained if the indicators of the student's intellectual activity are 1.5 standard deviations higher than his results in the performance test.
Fluency disorder: Related to stuttering.
Dysgraphia: A disorder that causes difficulty in writing words.
Dyslexia: A disorder that causes difficulty in reading.
Dysphagia: A disorder that causes difficulty in swallowing.
Dyspraxia: Developmental disorder of motor coordination.
ECSE: Early Childhood Special Education. Program for infants, toddlers and preschoolers with disabilities.
Program for infants, toddlers and preschoolers with disabilities.
ED: An abbreviation for "emotional disorder", which is used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program.
Special education teacher: An educator who has been certified and can provide special education services.
EL: English learner.
ELA: English Literature.
ELST: Teacher who helps English learners.
ERMHS: Educational Mental Health Services. Certain mental health services provided to special education students who have social and emotional needs that affect their ability to learn.
ESY: Extended academic year. Specialized education or related services that are part of a child's IEP and are usually provided outside the school year. Students who qualify for the ESY program are those who are enrolled in an IEP and who have a disability that is likely to persist for a long time. Students will also be required to demonstrate that failure to provide such services to them during the school holidays may result in loss of skills and that their ability to relearn lost skills is limited, so that a student with a disability is likely to be able to develop independent living skills without resorting to to ESY services is excluded and insignificant.
Executive function: The student's ability to choose and control his or her behavior in order to achieve a specific goal. Requires simultaneous and complex work of thinking and working memory.
Expressive speech: presentation of ideas. These can be gestures, signs, facial expressions and speech.
Fine motor skills: Associated with precise movements of the hands and fingers. For example, students use fine motor skills to write and fasten clothes.
Behavior function: Describes why a student may behave badly. Generally, bad behavior falls into one (or more) of 4 categories: Gaining access to a desired object/activity; The desire to run away; Attracting the attention of another person; and Influx of sensory signals.
Goal: An individual measurable outcome that allows a student with a disability to focus on an area of interest; it is usually written on the IEP; problems in this area are expected to be resolved within a year. Goals should follow the SMART model: be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and fit into certain time frames.
Gross motor skills: Associated with large muscles (ie movement and coordination).
HSDP: High School Diploma Program
IAES: Temporary Alternative Educational Environment. During periods of extended suspension, a student may receive education and services in a temporary alternative educational environment, in a location that is different from where the student normally receives education and services.
ID: An abbreviation for "intellectual disability" used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program.
IEE: Independent Evaluation of Educational Quality. An IEE is an assessment conducted by an individual who is not employed by the school district. Parents and guardians may obtain an IEE at the district's expense if they disagree with the findings or recommendations of the District's Special Education Assessment.
IEP Amendments: When changing the annual IEP to update part of the IEP. Holding an IEP review meeting does not relieve the local school of its responsibility to review the IEP annually.
IFSP: Individualized Family Services Plan. It describes the early childhood intervention services that the child will receive through the regional center until he/she is 3 years old.
IPP: Individual Program Plan. It describes the non-educational goals and services available through the Regional Center for Persons with Disabilities.
ITP: Individual Transition Plan. A written plan to assist in the student's transition from school to life after graduation. Should include goals, timelines and people who are responsible for achieving the goals.
LEA: Local educational institution. A community board of education or other government agency that operates public elementary or high schools in a city or county.
Low Prevalence: Rare disability. Examples include, but are not limited to, deafness and blindness.
Inclusion: Some staff still use the term to refer to "inclusion", or use it to say that a student with a disability is spending time in a mainstream environment.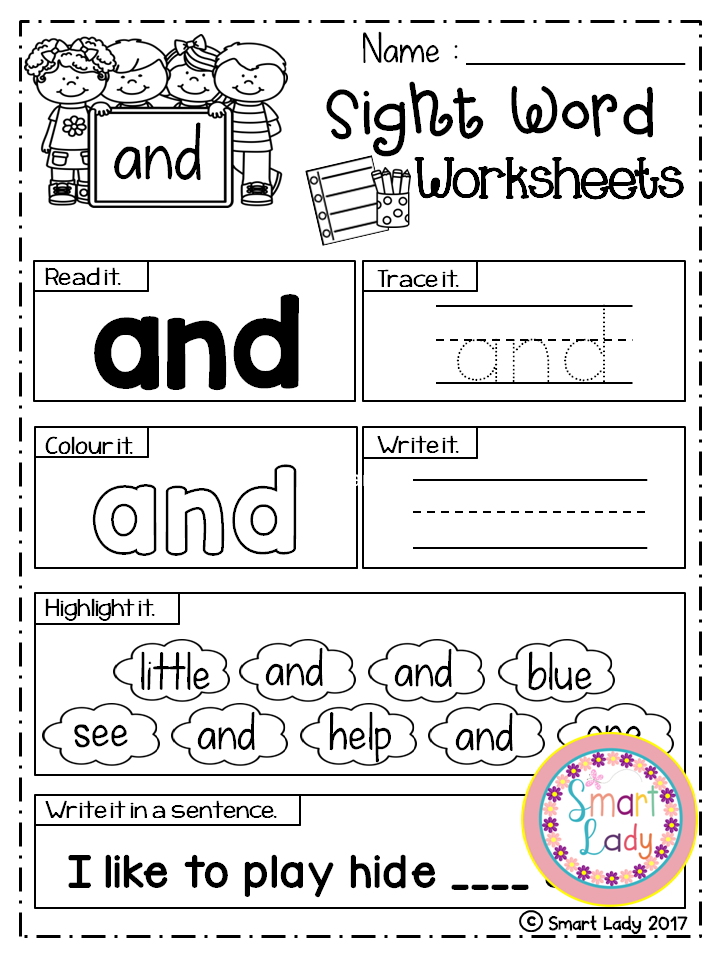
Manifestation Detection: An important meeting to be held if a student with a disability has been suspended for more than 10 days in a single school year OR if the student is recommended to be expelled. During this meeting, the school should check to see if the behavior was caused by the student's disability.
MD: An abbreviation for "complex defect", which is used to indicate compliance with the requirements of the federal special education program.
Adaptation: A situation in which the nature of the instruction or materials provided to a student with a disability differs from the curriculum provided to peers of the same age.
MPC: Formerly referred to as "handicapped" classrooms. This is a separate classroom for students with medical or physical disabilities.
MT: Music Therapist. Uses music for medicinal purposes as an accompanying service.
NPA: Non-Profit Organization. A non-school district organization that provides educational services to students with disabilities. Must be certified by the California Department of Education (CDE).
Must be certified by the California Department of Education (CDE).
NPS: Private school. The school with which the school district enters into a contract to provide educational services and support for students with disabilities. Must be certified by the California Department of Education (CDE).
OHI: An abbreviation for "Other Health Disabilities", which is used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program.
OI: Abbreviation for "orthopedic impairment" used to indicate compliance with the requirements of the federal special education program.
Olfactory: Pertaining to the ability to smell.
OT: Occupational Therapist or Occupational Therapy.
Rate of speech: How fast the person speaks.
PBIS: Intervention and maintenance of positive behaviour. An intervention program that focuses on encouraging the student's desired behavior.
PK or Pre-K: Preschool
Pragmatics: Using language to perform functions such as asking for information or greeting.
Pre-job skills: Skills that a person will need to be ready for a job. These may be "interpersonal skills" such as communication skills and appropriate behaviour. It can also be the development of a "work ethic", such as perseverance, the ability to ask for clarification and accept constructive criticism.
Pro-ACT: Training in professional crisis management skills. A training program designed to enable educators, paraprofessionals, and related service providers (and other facility personnel) to intervene when students exhibit behavior that could endanger themselves or others. The focus is on de-escalation; physical intervention is used as a last resort. General training program for restriction and/or isolation.
Progress Report: At least as often as peers of the same age receive a report card, a student with a disability has the right to receive a report on their progress towards their IEP goals. Sometimes called "annotated targets".
Prompt: The prompt is used to indicate the level of direction given to the student; it is usually listed in the goals or objectives of the IEP. Includes physical, verbal, gestural and visual cues.
Includes physical, verbal, gestural and visual cues.
Proprioception: How our brain processes body movements and position in space.
Prosody: Tempo and intonation of language and sounds.
PT: Physiotherapist or Physical Therapy
PWN: Prior Written Notice. In certain situations, the school district is required to provide prior written notice; for example: if the district refuses to take the action requested by the parent, if the district wants to change the placement or category of a student with a disability, or if it plans to evaluate a student with a disability.
Receptive speech: The ability to hear sounds and translate them into meaningful ideas. Also includes the ability to interpret the gestures and facial expressions of other people.
Recovery: The amount of time required to recover a lost skill. See regression.
Rehabilitation: An associated service that may be offered as part of FAPE.
Regression: Loss of critical skills for students with disabilities during a natural break in the school year.
See recovery.
Related Services: Services that may be needed to help a student with a disability achieve IEP goals. Examples: speech therapy or occupational therapy.
RSP: Methodist
RTI: Intervention Response. A general education program that aims to provide high quality education and screen every child for proper access to the curriculum.
SAI: Specialized Academic Education
SCERTS: Social Communication/Emotion Regulation/Interaction Support. An integrated educational approach to address the major challenges faced by children on the autism spectrum; the focus is on building social communication, regulating emotions, and supporting interaction.
SCIA: Special Circumstances Education Assistant. A term used by some school districts to describe an individual learning assistant.
SEA: Special Education Assistant
Independent Decision Making: Emphasis is placed on the fact that a student with a disability makes a significant contribution and has the right to choose in making decisions that directly affect them. This approach takes into account things like personal preferences, balance of power, things you don't like, goals, and circle of support.
This approach takes into account things like personal preferences, balance of power, things you don't like, goals, and circle of support.
SELPA: Special Education Local Plan Area
SESA: Special Education Administrator
SET: Special Education Technician
SLD: An abbreviation for Specific Learning Disabilities, which is used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program, sometimes also referred to as "LD" for Learning Disabilities.
SLI: An abbreviation for Speech Language Impairment, which is used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program.
SLP: Speech therapist
SST: Student Task Force. A process in which educators and parents meet to discuss why a student is not making progress in the overall curriculum and to discuss techniques or strategies that can be applied. Sometimes such a meeting may occur before the issuance of a referral for special education, but this is not necessary. If you suspect that your child may have a disability, you should submit a request for assessments for placement in a special education program.
TBI: Abbreviation for traumatic brain injury, which is used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program.
TK: Transition Kindergarten
Transition: Refers to the process of transition from secondary education to adulthood. The school district must develop an ITP to help students using the IEP through this process.
It should begin when the student is between 14 and 16 years old.
Triennial IEP: May also be referred to as Triennial Evaluation or Triennial Review. A reassessment every three years to determine if the student is eligible for special education services in all areas of suspected disability.
Vestibular: Related to how our brain controls balance and orientation.
VI: Abbreviation for visual impairment, which is used to indicate eligibility for the federal special education program
Visual: Pertaining to sight and the processing/interpretation of what is seen.
Skills: Actions and concepts that keep a job. Often associated with transition.
Often associated with transition.
VT: Vision Improvement Therapy
Disclaimer: This publication is legal information only and does not constitute legal advice regarding your individual situation. It is current as of the date of publication. We try to update our content regularly. However, laws change regularly. If you want to make sure the law hasn't changed, contact the DRC or another legal office.
Izvestiya VSPU - Error
Journal archive
2010
- 4 (48)
- 5 (49)
- 6 (50)
- 7 (51)
- 4 (52)
- 9 (53)
- 10 (54)
2011
- 1 (55)
- 2 (56)
- 3 (57)
- 4 (58)
- 5 (59)
- 6 (60)
- 7 (61)
- 8 (62)
- 9 (63)
- 10 (64)
2012
- 1 (65)
- 2 (66)
- 3 (67)
- 4 (68)
- 5 (69)
- 6 (70)
- 7 (71)
- 8 (72)
- 9 (73)
- 10 (74)
- 11 (75)
2013
- 1 (76)
- 2 (77)
- 3 (78)
- 4 (79)
- 5 (80)
- 6 (81)
- 7 (82)
- 8 (83)
- 9 (84)
- 10 (85)
2014
- 1 (86)
- 2 (87)
- 3 (88)
- 4 (89)
- 5 (90)
- 6 (91)
- 7 (92)
- 8 (93)
- 9 (94)
- 10 (95)
2015
- 196)
- 2 (97)
- 3 (98)
- 4 (99)
- 5 (100)
- 6 (101)
- 7 (102)
- 8 (103)
- 9-10 (104)
2016
- 1 (105)
- 2 (106)
- 3 (107)
- 4 (108)
- 5 (109)
- 6 (110)
- 7 (111)
- 8 (112)
- 9-10 (113)
2017
- 1 (114)
- 2 (115)
- 3 (116)
- 4 (117)
- 5 (118)
- 6 (119)
- 7 (120)
- 8 (121)
- 9 (122)
- 10 (123)
2018
- 1 (124)
- 2 (125)
- 3 (126)
- 4 (127)
- 5 (128)
- 6 (129)
- 7 (130)
- 8 (131)
- 9 (132)
- 10 (133)
2019
- 1 (134)
- 2 (135)
- 3 (136)
- 4 (137)
- 5 (138)
- 6 (139)
- 7 (140)
- 8 (141)
- 9 (142)
- 10 (143)
Founder:
Volgograd State Socio-Pedagogical University (400066,
Lenina Ave.