Kindergarten math topics
Math concepts your children will learn in Kindergarten
In a preschool math class, children will learn basic concepts such as numbers, shapes, and measurements. They will also begin to develop problem-solving skills and an understanding of basic mathematical operations. But, what will they learn in Kindergarten?
Understanding what your kiddos will learn in Kindergarten is important so you can support their learning at home. Or, if your kiddos are homeschooled, you may be wondering which skills they will need to learn in their Kindergarten year. So, here are the essential math concepts taught at the Kindergarten level.
My top teacher tip for math with young children? Keep it fun! It’s extremely important that learning math is a positive experience. This encourages enthusiasm for math (and helps prevent math anxiety later in life).
Math concepts your children will learn in KindergartenKindergarten math concepts: What will they learn?
During their preschool years, children will have learned basic concepts such as numbers, shapes, and measurements. They will also have begun to develop problem-solving skills and an understanding of basic mathematical operations. These early math concepts helped prepare them for Kindergarten, where basic math concepts are explored at a deeper level.
Here’s a look at the BC Kindergarten math curriculum, so you have an idea of what they learn.
By practicing important math skills early on, and working to reinforce concepts throughout their Kindergarten year, your child will be better equipped to succeed in school and in life. This is just one of the 10 important reasons that Allison Master, PhD, finds math important.
Why is Kindergarten math important?
Kindergarten math concepts are important because they help children develop strong mathematics foundations. These foundations will be necessary as they begin to learn more advanced mathematics concepts later in school. Additionally, Kindergarten math can help children develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills.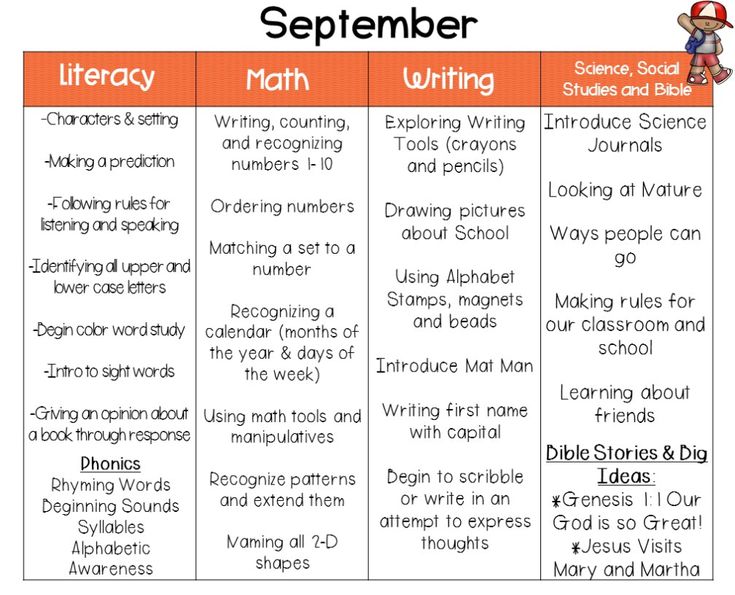 By learning how to count, identify patterns, and solve simple problems, children can begin to develop the mathematical skills they need to be successful in school and in life.
By learning how to count, identify patterns, and solve simple problems, children can begin to develop the mathematical skills they need to be successful in school and in life.
The basics: Numbers, shapes, and measurements
Pre-school math typically covers the basics of numbers, shapes, measurements, and the likeliness of events. Children learn to identify, count, and manipulate numbers 1-10, as well as to recognize common shapes such as circles, squares, and triangles. They also begin to develop an understanding of basic measurements such as length, width, and height.
These concepts lay the foundation for more advanced mathematics concepts that children will learn in school. Math in the early years also covers how to understand time, money, and patterns among other important math skills! Additionally, by understanding the basics of numbers, shapes, and measurements, children can begin to develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
Why learning basic math concepts is important for your child
I may have hinted at this once or twice, but Kindergarten math is important for your child because it helps them develop strong mathematics foundations. After all, math is all around us! Regardless of how we feel amount math (trust me – I didn’t start enjoying it until teacher’s college!), we use fundamental mathematical concepts every single day.
After all, math is all around us! Regardless of how we feel amount math (trust me – I didn’t start enjoying it until teacher’s college!), we use fundamental mathematical concepts every single day.
Hint: Have you ever bought groceries, planned an exciting trip, or watched a sports game? They all use basic math skills!
The foundations learned in Kindergarten will be necessary as they begin to learn more advanced mathematics concepts in their elementary school education. Additionally, math can help children develop problem-solving, critical thinking, and reasoning skills. By learning how to count, identify patterns, complete simple addition, and solve simple problems, children can begin to develop the skills they need to be successful in school and in life.
Problem-solving skills: Developing a logical mindset
One of the most important skills that children can develop through the Kindergarten math curriculum is problem-solving. By learning how to identify patterns and solve simple problems, children can begin to develop a logical mindset. This is important for young learners because it helps increase academic performance, confidence, creativity, and self-esteem, according to Mrs. Meyer’s Learning Lab.
By learning how to identify patterns and solve simple problems, children can begin to develop a logical mindset. This is important for young learners because it helps increase academic performance, confidence, creativity, and self-esteem, according to Mrs. Meyer’s Learning Lab.
The skills learned in Kindergarten will be essential as they encounter more complex mathematical problems later in life. Having a strong foundation in mathematics will therefore help them learn other math skills down the road. Additionally, problem-solving skills can help children develop critical thinking skills. By learning how to break down problems and find solutions, children can begin to think more critically about the world around them (while getting more resilient in their learning, too!).
Math concepts your children will learn in KindergartenNumber sense: Understanding quantity and value
Another important part of Kindergarten math is developing number sense. This involves understanding quantity and value. If I were to say it in teacher talk, I would say they learn ‘one-to-one correspondence’ – Basically, this number concept teaches that a
number has a corresponding value (for example, one object = 1).
If I were to say it in teacher talk, I would say they learn ‘one-to-one correspondence’ – Basically, this number concept teaches that a
number has a corresponding value (for example, one object = 1).
Children also learn to identify and count numbers while developing their rote counting abilities. Rote counting is the ability to memorize numbers and repeat them (displayed by counting 1-10 in sequential order).
Addition and subtraction are other abilities your kiddos will practice in Kindergarten. At this age, the number manipulation is pretty basic. Stick with numbers under 10! For example, you could ask your child questions like “You have two apples and add three more. How many apples do you have in total?” At this age, using manipulatives (real objects) is super important. By using objects, you can help children understand the very abstract concept of counting. If you don’t have apples, use wooden blocks! (Or whatever else is available).
Patterns: Recognizing and creating order
Pattern recognition is another important part of Kindergarten math. By learning to identify patterns, children can begin to develop a sense of order. This lets them organize information in a logical way while learning to identify different shapes and sort objects. Plus, pattern identification is important for more than just math – This is also a foundational skill for reading (rhyming, predicting text) and music, among other subjects!
Measurements: Understanding size, weight, and capacity
Measurements are a part of our daily life. From weighing out our groceries to picking the correct size of clothing while shopping, we rely on these concepts a lot. Children learn to understand basic concepts such as length, width, and height. Understanding physical objects is a skill that they will continue to explore throughout their elementary experience (and high school, too!). So, enhancing the child’s understanding of measurement at a young age is a foundational skill, too.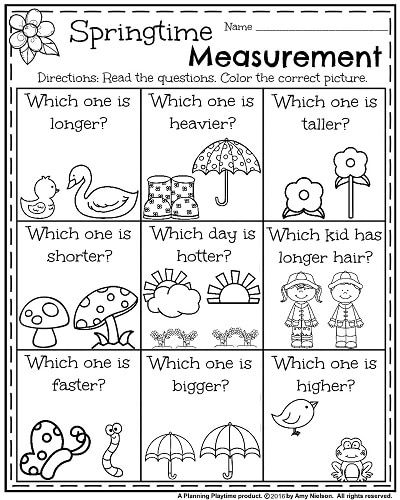
Geometry: Understanding basic shapes
Children will also learn to identify and understand basic geometric shapes such as squares, circles, and triangles. Since shapes are all around us and are more concrete than abstract concepts like numbers, this can easily be practiced day to day. In everyday interactions, this might look like recognizing different objects as shapes. Ask your child questions like “what shape is this ball?” to help them practice this. At this age, it’s all about keeping it fun!
Mathematical operations: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
Mathematical operations are first taught at the pre-K level, starting with basic math activities and easy math concepts. In Kindergarten, children will learn to understand and perform basic operations such as addition and subtraction. In the early years of elementary school, they will begin exploring more complicated concepts, like multiplication and division.
A big part of this stage is developing the appropriate language (more than, less than, how many in total).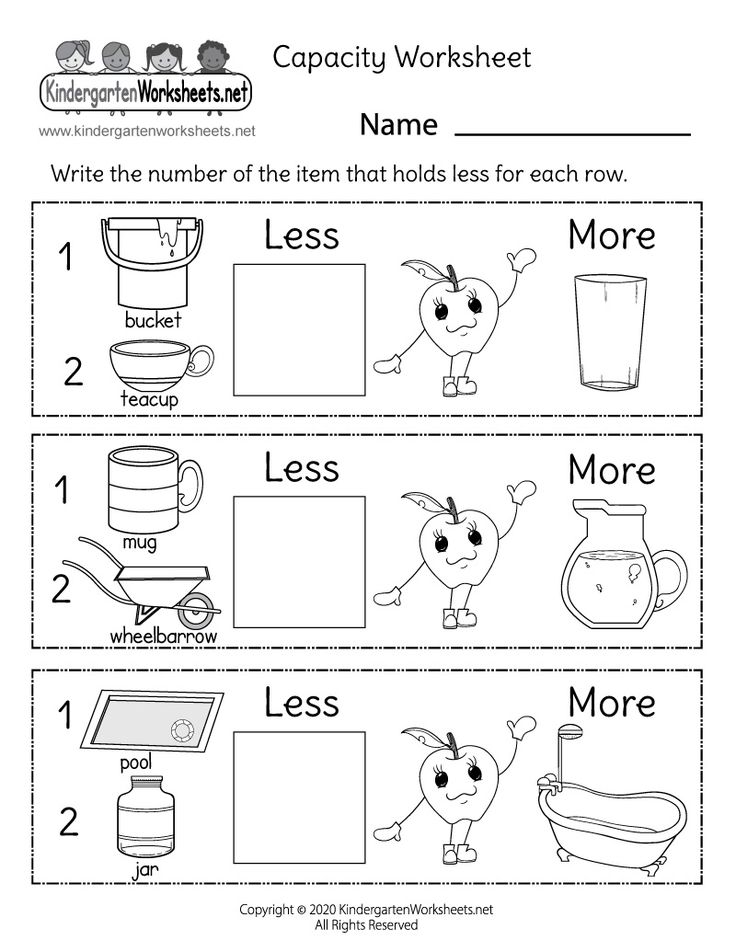 As they practice counting and become confident at it, you can start incorporating basic addition into daily routines. Again, use manipulatives (hands-on activities) as much as you can and keep it fun!
As they practice counting and become confident at it, you can start incorporating basic addition into daily routines. Again, use manipulatives (hands-on activities) as much as you can and keep it fun!
They will also practice skip counting, which is basically counting in groups, like counting by 2’s or 5’s. Not only is this a basic part of adding and subtracting, but it’s a foundational skill for multiplication down the road.
They are also ready to write numbers at this stage, which helps with number recognition. You can practice this skill through fun activities like making numbers from play do then writing them down.
Putting it all together: Using math in everyday life
Kindergarten-aged kids are learning so much. In order to keep it fun and exciting, it’s important to make practicing math a part of their daily routine. Just like it takes a ton of practice to read, write, and speak, Kindergarten math skills require a lot of repetition!
If you consistently make math a part of your everyday life, it won’t feel like such a daunting task for your kiddos. Number sense doesn’t need to be taught in worksheets and by rote memorization. Children learn best when they’re having fun, anyway! Judy Willis did a pretty cool study on the neuroscience behind this – Read it here!
Number sense doesn’t need to be taught in worksheets and by rote memorization. Children learn best when they’re having fun, anyway! Judy Willis did a pretty cool study on the neuroscience behind this – Read it here!
Conclusion
Kindergarten math concepts are important because they help children practice many skills that are a part of early child development. Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are among the most important of these! The basics of numbers, shapes, and measurements also lay the foundation for more complex mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. By understanding and using math in everyday life, children can develop a better understanding of the world around them.
By encouraging children to practice their skills through fun math activities, children understand big ideas in a way that makes sense to them. If you are working with young children, it’s important to look for fun ways to teach math – You could sing songs or play games, for example. This keeps learning fun and helps children understand the world around them through play.
This keeps learning fun and helps children understand the world around them through play.
In Kindergarten, you can expect that your children will learn the basics of addition and subtraction, how to recognize shapes, how to count and manipulate small numbers, the basics of financial literacy and telling time, how to predict the likelihood of future events, and basic graphing (among other skills).
In conclusion, Kindergarten math is essential in preparing children for kindergarten and beyond. By teaching them the basics of numbers, shapes, and measurements, they will be better equipped to understand more advanced concepts that they will encounter in school and in life.
BTW, if you’re working on learning math and money, we’ve created some free worksheets. Get them here!
Other posts about math
Looking for another math-related post? You may enjoy one of the articles below!
- Easy DIY kindergarten sorting activities
- Kindergarten math word problems
- Free number tracing worksheets (Numbers 1-10)
- Tally mark worksheets (with free printable!)
- Ways to teach preschool math in nature (with free printable)
- 10 Nature counting activities for preschoolers
- Simple sorting activities for preschoolers
Kindergarten Online Math Lesson Plans
View Our Lesson Demos!
The Time4Learning kindergarten math lessons put a fun spin on learning important foundational skills for the youngest of students. In addition to engaging, interactive activities that teach the lessons, each of the chapters features an overarching theme such as safari, playtime, and cooking.
In addition to engaging, interactive activities that teach the lessons, each of the chapters features an overarching theme such as safari, playtime, and cooking.
This page provides information on what kindergarten math a student should know, math objectives for the year, and why Time4Learning is the best choice to help your child reach all of the kindergarten math goals and objectives.
What Math Should a Kindergarten Student Know?
Kindergarten math is all about becoming familiar with the basics and setting a solid foundation. Students will learn to count and recognize numbers, identify shapes and their attributes, add and subtract numbers, and complete patterns.
Below are some of the other skills that a student should know in kindergarten math.
- Create, describe and compare 2-D and 3-D shapes
- Compare groups using the terms greater, less, fewer, more
- Use tally charts and picture graphs to represent numbers
- Recognize that larger numbers are made up of smaller numbers
- Order events in a sequence
Kindergarten Math Objectives
For most students, kindergarten is their first official year of schooling.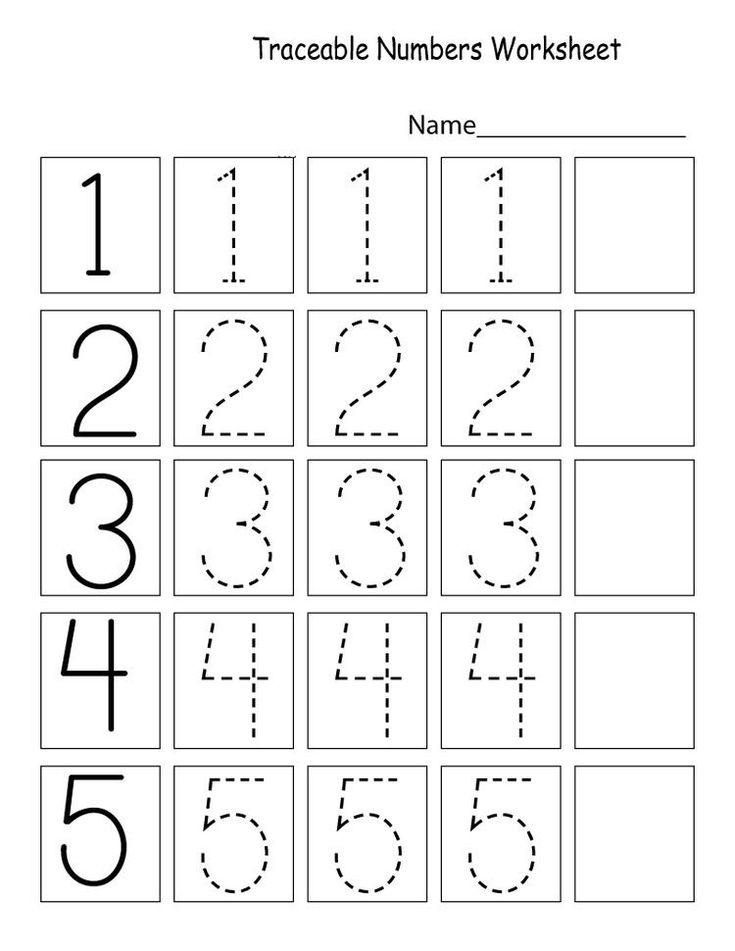 Gaining a solid understanding of basic concepts now, will help them feel confident and prepared as they learn new math skills in the years to come. That’s why it’s so important that students use a comprehensive curriculum, like Time4Learning, to help them master these concepts and reach all their kindergarten math goals and objectives.
Gaining a solid understanding of basic concepts now, will help them feel confident and prepared as they learn new math skills in the years to come. That’s why it’s so important that students use a comprehensive curriculum, like Time4Learning, to help them master these concepts and reach all their kindergarten math goals and objectives.
Below are some of the math objectives a kindergarten math curriculum should help your child achieve.
- Count objects up to 20
- Use an analog and digital clock to identify time to the nearest hour
- Identify pennies, nickels, dimes, and quarters and know their value
- Compare the length and weight of objects
- Explore properties of addition and subtraction
Time4Learning’s Kindergarten Math Lesson Plans
Chapter 1: “Tutorial”
Lesson 1: Tutorial –
1 ActivityFunctionality of buttons and interactions, and practice questions from lessons based on objectives.
Chapter 2: “Under the Sea”
Lesson 1: Adventures Under the Sea –
4 ActivitiesRecognize likenesses and differences between pairs of items.
Lesson 2: Searchers of the Sunken Ship –
4 ActivitiesSort objects by appearance (e.g., color, size, and shape). Recognize items that are the same and different. Extend and identify a repeating pattern.
Lesson 3: Sea Sorting –
4 ActivitiesSort representations of living things by appearance. Create items with given attributes. Recognize one-to-one correspondence.
Lesson 4: Fantastic Fish –
4 ActivitiesAlign sorted objects to determine whether a one-to-one match exists. Determine which set has more or fewer members when a one-to-one match does not exist. Create and interpret picture-graph displays.
Lesson 5: Sea Symphony –
4 ActivitiesCopy, continue, and complete patterns involving two attributes.
Chapter Test: Under the Sea
Chapter 3: “Playtime in the Park”
Lesson 1: Moose Park Footrace –
4 ActivitiesUse positional words to describe vertical and horizontal relationships. Recognize that more than one term may be appropriately used to describe a positional relationship. Create a positional relationship by following directions.
Lesson 2: Digby Hide-and-Seek –
4 ActivitiesUse positional words to direct investigations that occur in different locations. Use positional words to describe locations.
Lesson 3: A New View –
4 ActivitiesRecognize that vertical and horizontal relationships are often determined by point of view. Recognize that individual items may each appear different from different perspectives.
Lesson 4: Shape Hunt –
4 ActivitiesInvestigate the features of a circle, triangle, square, and rectangle, and identify their presence in contextual settings. Identify likenesses and differences between pairs of shapes. Construct shapes.
Identify likenesses and differences between pairs of shapes. Construct shapes.
Lesson 5: Shapes, Shapes, Everywhere –
17 ActivitiesAnalyze, compare, create, and compose two- and three-dimensional shapes, in different sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their similarities, differences, parts, and other attributes.
Lesson 6: Photo Finish –
8 ActivitiesConstruct and/or complete simple scenes formed with plane figures. Construct, complete, and describe patterns formed with plane figures.
Chapter Test: Playtime in the Park
Chapter 4: “Let’s Go On a Safari”
Lesson 1: Jungle Safari –
6 ActivitiesRecognize that objects can be counted and represented by numerals. Recognize that cardinal numbers represent a quantity (numbers 1-5). Read and represent numbers 1-5. Recognize that different arrangements represent the same quantity (numbers 1-5).
Lesson 2: Safari Tales –
6 ActivitiesCompare groups to determine more/greater/less/fewer. Use one-to-one correspondence when comparing sets. Recognize the concept of zero as representing an empty set. Construct and interpret picture graphs.
Use one-to-one correspondence when comparing sets. Recognize the concept of zero as representing an empty set. Construct and interpret picture graphs.
Lesson 3: Wild Animals –
10 ActivitiesRecognize that objects can be counted and represented by numerals (0-20). Recognize that cardinal numbers represent a quantity (numbers 0-20). Read, write, and represent numbers 0-20. Recognize that different arrangements represent the same quantity (numbers 0-20).
Lesson 4: Sounds Wild! –
8 ActivitiesUse one-to-one correspondence to represent and compare quantities of 0-10. Use tally charts and picture graphs to represent 0-10. Recognize sequence of numbers on a number line. Describe position in a sequence of whole numbers on a number line up to 10.
Lesson 5: Animal Keeper at Work –
10 ActivitiesRecognize that larger numbers are formed from combinations of smaller numbers. Explore addition models. Recognize that smaller numbers are formed by taking apart sets.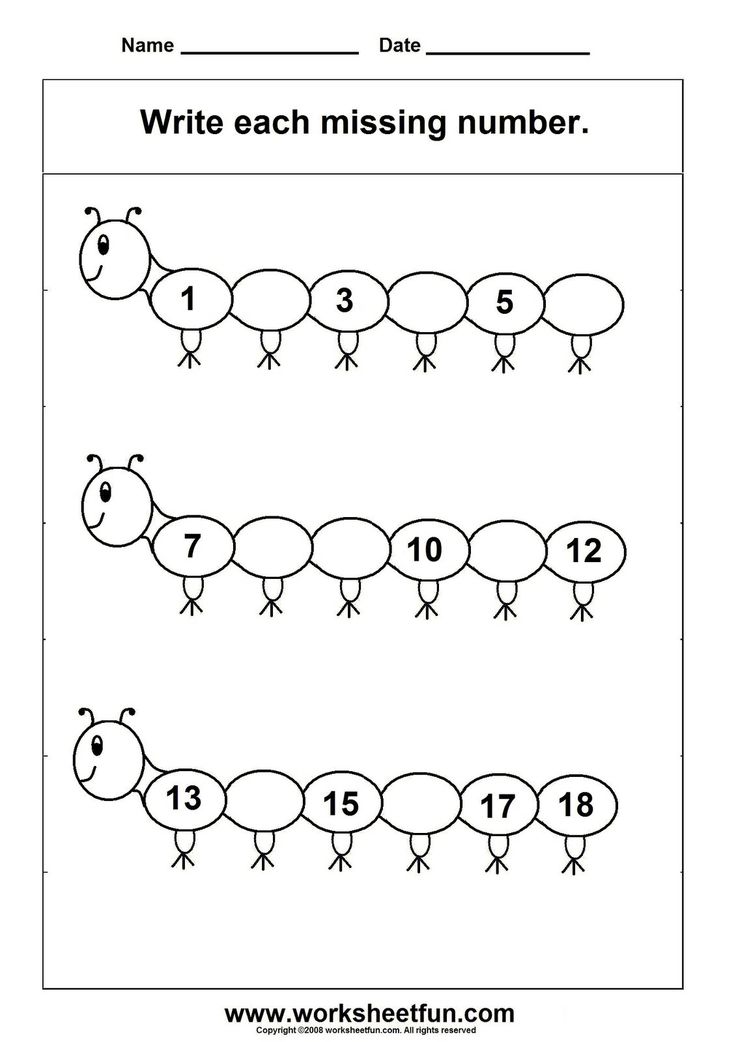 Informally explore subtraction models.
Informally explore subtraction models.
Chapter Test: Let’s Go On a Safari
Chapter 5: “What’s Cooking?”
Lesson 1: Snack Time –
9 ActivitiesUse a calendar as a tool to identify months, days, and dates. Use a calendar as a tool to identify today, yesterday, and tomorrow. Identify parts of a day (morning, afternoon, evening). Use an analog clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Use a digital clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Order events in a sequence. Identify temperature using a thermometer.
Lesson 2: Harriets Piggy Bank –
5 ActivitiesIdentify penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Identify value of penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Combine coins to make values up to 10 cents.
Lesson 3: Tasty Treats –
6 ActivitiesCompare the length of objects. Identify and correct common errors in linear measurement. Estimate and measure length using nonstandard units. Measure length using standard units.
Lesson 4: Sharing Snacks –
4 ActivitiesSeparate items into equal parts through an active comparison of their length. Informally explore commonly used fractional parts of a whole (fourths, thirds, halves).
Lesson 5: Measurement Matters –
6 ActivitiesCompare the weight of objects. Compare the capacity of objects. Recognize tools of measurement. Informally explore the concept of area.
Lesson 6: Writers Corner –
1 ActivityUse a calendar as a tool to identify months, days, and dates. Use a calendar as a tool to identify today, yesterday, and tomorrow. Identify parts of a day (morning, afternoon, evening). Use an analog clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Use a digital clock to identify time to the nearest hour. Order events in a sequence. Identify temperature using a thermometer. Identify penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Identify value of penny, nickel, dime, quarter. Combine coins to make values up to ten cents. Compare the length of objects. Identify and correct common errors in linear measurement. Estimate and measure length using nonstandard units. Measure length using standard units. Separate items into equal parts through an active comparison of their length. Informally explore commonly used fractional parts of a whole (quarters, thirds, halves). Compare the weight of objects. Compare the capacity of objects. Recognize tools of measurement. Informally explore the concept of area.
Compare the length of objects. Identify and correct common errors in linear measurement. Estimate and measure length using nonstandard units. Measure length using standard units. Separate items into equal parts through an active comparison of their length. Informally explore commonly used fractional parts of a whole (quarters, thirds, halves). Compare the weight of objects. Compare the capacity of objects. Recognize tools of measurement. Informally explore the concept of area.
Chapter Test: What’s Cooking?
Chapter 6: “Numbers in the Neighborhood”
Lesson 1: Number Sense Center –
7 ActivitiesRead and represent numbers 11-20. Recognize that larger numbers are formed from combinations of smaller numbers (11-20). Demonstrate understanding of conservation of number (recognizing that size does not affect number). Explore numbers 0-100. Explore number patterns, counting by 1s, 2s, 5s, and 10s.
Lesson 2: Graphing Data Drive –
5 ActivitiesUse data to create picture graphs. Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems.
Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems.
Lesson 3: Probability Place –
4 ActivitiesUnderstand basic concepts of chance and probability. Describe events as likely or unlikely.
Lesson 4: Addition Avenue –
10 ActivitiesRecognize that larger numbers are formed from combinations of smaller numbers. Explore addition models. Explore properties of addition. Use addition number sentences to record the combining of sets. Solve addition number sentences.
Lesson 5: Subtraction Street –
6 ActivitiesExplore subtraction models. Explore properties of subtraction. Use number sentences to record subtraction. Solve subtraction number sentences.
Lesson 6: Writers Corner –
1 ActivityUse data to create picture graphs. Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems. Use data to create picture graphs. Use data to create bar graphs. Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems. Understand basic concepts of chance and probability. Describe events as likely or unlikely. Explore addition models. Explore properties of addition. Use addition number sentences to record the combing of sets. Solve addition number sentences. Explore subtraction models. Explore properties of subtraction. Use number sentences to record subtraction. Solve subtraction number sentences.
Interpret data from graphs and use it to solve problems. Understand basic concepts of chance and probability. Describe events as likely or unlikely. Explore addition models. Explore properties of addition. Use addition number sentences to record the combing of sets. Solve addition number sentences. Explore subtraction models. Explore properties of subtraction. Use number sentences to record subtraction. Solve subtraction number sentences.
Chapter Test: Numbers in the Neighborhood
Scope & Sequence Copyright © 2023 Edgenuity, Inc. All rights reserved.
Why Choose Time4Learning Kindergarten Math Homeschool Curriculum
Setting up students for success in math or any other subject starts as early as kindergarten. Helping them master counting, shapes, basic addition and subtraction will have a big impact on their performance in later years.
Time4Learning’s kindergarten math curriculum uses bright, colorful and engaging activities to make math fun and enjoyable for the little ones. Students are able to log in on their time and progress at their own pace. The curriculum is simple to follow and material is presented in a suggested sequence that builds on itself.
Students are able to log in on their time and progress at their own pace. The curriculum is simple to follow and material is presented in a suggested sequence that builds on itself.
Parents have access to lesson plans, student planners, and plenty of resources to make homeschooling simple. In addition, our automated grading and recordkeeping system keeps track of all of your child’s work and makes it simple to print reports and create homeschool portfolios. And if you plan on using the kindergarten math curriculum as a supplement, you will have full access to these features as well.
Interested in other kindergarten subjects? Learn more about our online kindergarten curriculum, designed to teach your student their fundamental concepts.
lessons, presentations, class notes, planning, electives, knowledge assessment
Publish and download methodological developments for a preschool kindergarten teacher in mathematics in preschool education. Publication of interesting and necessary materials for a teacher on teaching children mathematics in a preschool educational institution with a free certificate of publication in the media.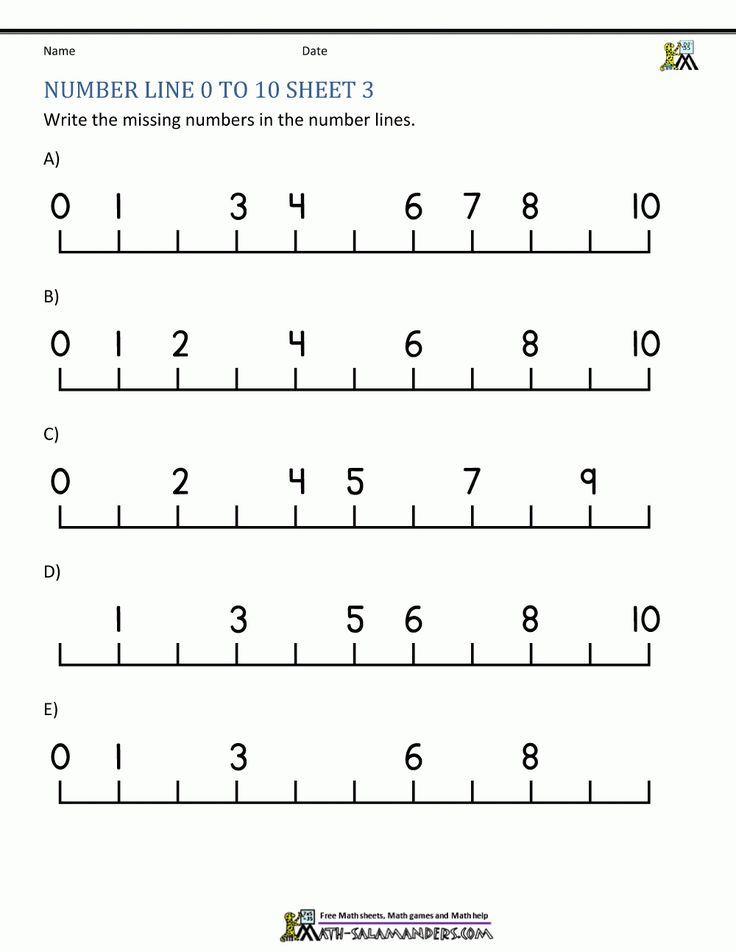
The section of mathematics in preschool education in kindergarten contains:
- NOD in the senior group
- Development of logical thinking of preschool children
- Kindergarten Mathematics Presentations
- Synopsis of the open GCD in the middle group according to FEMP
- Abstracts of classes in mathematics in kindergarten
- Mathematical leisure
- Lesson in mathematics in the 2nd junior group
- Abstract of a lesson for children with disabilities in mathematics
- Synopsis of GCD for FEMP
- Journey to the Land of Mathematics
- Abstract of the sensory class
- Abstract of the integrated lesson in mathematics
- Lesson on FEMP in the 2nd junior group
- Consultation for the educator
- Summary of the lesson on the formation of FEMP
- Summary of the final lesson on the formation of elementary mathematical representations
- Construct for the formation of mathematical representations
- Graphic dictations in the formation of visual-motor coordination
- Interactive Math Game
- Mathematical game library
- Summary of GCD in mathematics in the middle group using innovative technologies
- Methodical development of a lesson on the development of mathematical and sensory abilities in children
- Technological map of GCD for FEMP in the senior group
- Synopsis of OOD on the development of quantitative representations in children
- The development of mathematical abilities in children through play activities in the context of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard DO
The development of speech, logic and mathematics can be carried out in a playful way and perceived by the baby as a fun pastime.
Mathematics in kindergarten begins in the second junior group, where they begin to carry out special work on the formation of elementary mathematical representations.
The development of mathematics by preschoolers plays an important role not only in preparing for school life, but also for the formation of logical thinking skills, the development of intelligence and understanding. Mathematics for preschoolers is usually included in the traditional developmental curriculum in kindergarten.
Here you will find lessons, notes, tests, presentations, plans, activities and other useful materials for the work of the teacher and the education of the student.
Synopsis of OOD on FEMP for children of senior preschool age "Flower-Semitsvetik"
Synopsis of OOD on FEMP in the senior group on the topic "Flower - seven-color" Tasks: Improve counting skills within 10. Compare objects by length. Improve knowledge of geometric shapes. Develop the ability to navigate in space. For ...
Develop the ability to navigate in space. For ...
44 0 02/21/2023
Synopsis of OOD on FEMP for children of senior preschool age "Geometric shapes"
Synopsis of GCD on FEMP for children of senior preschool age. The purpose of this abstract: to develop the ability of children to independently perform mathematical tasks. Tasks: Consolidate and generalize knowledge about geometric shapes (circle, square, triangle, rectangle ...
16 0 02/21/2023
Summary of the final lesson on FEMP in the middle group "In Search of Treasures"
Purpose. Clarification of the knowledge, ideas, skills that they received in the classroom in mathematics. Tasks: 1. To consolidate the skills of quantitative and ordinal counting within 5, correlating the numbers 1-5 with the number of objects; ideas about geometer . ..
..
25 0 02/21/2023
Summary of the lesson on FEMP in the preparatory group Topic: "Journey to mathematics"
Purpose: Formation of elementary mathematical representations. Tasks Tutorials: • To consolidate the ability of children to count from 1 to 10 in forward and reverse order, the ability to name the number preceding and following the named number. • Consolidate knowledge d ...
32 0 02/20/2023
Abstract of the lesson in mathematics "Journey through Grandma's tales"
A lesson in mathematics for children of the senior group based on the didactic set "Grandmother's Tales", using a set of Gyenesh blocks, Kuizner's sticks. They learned to divide the square into 4 equal parts, fixed the ordinal score.
17 0 02/20/2023
Journey to Queen Math
Purpose: creation of favorable conditions for the formation of elementary mathematical representations of preschoolers. Tasks: Educational: to form the skills of computational activity; exercise children in forward and backward counting within 10; fasten ...
Tasks: Educational: to form the skills of computational activity; exercise children in forward and backward counting within 10; fasten ...
22 0 02/20/2023
fun math
FEMPE lesson in the senior group. 1. Stimulate the development of mental abilities, curiosity, cognition. 2. Develop the ability to clearly and quickly answer questions. Improve knowledge of forward and backward counting, about ordinal ...
31 0 02/20/2023
GCD for FEMP "Comparison of objects by size" (senior preschool age)
This GCD is intended for children of senior preschool age, content is focused on the theme of the week: "Defender of the Fatherland Day". Purpose: To form the ability of children to compare objects by size. GCD very informative, full of various games ...
33 0 02/20/2023
Advice for parents: "We play mathematicians with children"
Mathematics in everyday home life invades everywhere. It is important to unobtrusively, in a playful way, draw the child's attention to such objects that under normal conditions do not interest him. They can be included in the game space.
It is important to unobtrusively, in a playful way, draw the child's attention to such objects that under normal conditions do not interest him. They can be included in the game space.
23 0 02/20/2023
Formation of mathematical abilities of preschoolers
Nowadays, in the age of "computers", mathematics is needed to some extent by a huge number of people of various professions, not only mathematicians. The special role of mathematics is in mental education, in the development of intellect. Late formation of logical structures ...
10 0 02/20/2023
Abstract of the lesson in the senior group on cognitive development on the topic: "In the autumn forest"
-Clarify and expand children's knowledge about the autumn season; -Activate the vocabulary of children on the topic of the lesson; - To develop the cognitive interest of children, their attention and memory; -To instill in children a respect for nature; -Creation of emotional comfort . ..
..
13 0 02/20/2023
Formation of mathematical representations in children 3-4 years old through didactic games
Sensory education has a great influence on the development of the child's perception and the formation of his ideas about the external properties of objects: their shape, color, size, position in space, taste, and so on. It is from the perception of objects and phenomena about ...
72 0 02/16/2023
Game "Name the differences"
Educator: Guys, look at the table. This is where the money is. Look carefully and say how they are similar and how they are different. Children are offered toy coins and banknotes of the Bank of Russia. Children name the similarities and differences between coins and banknotes. 1. Than n ...
23 0 02/16/2023
Organized activity of children "Journey to the country of Mathematics.
 "
" Group: senior group "A" - "Why" ODD theme: "Journey to the country of mathematics" Goal: Creating favorable conditions for consolidating elementary mathematical concepts of preschoolers Tasks: Learning tasks: • Form skills at ...
19 0 02/15/2023
Didactic game "Name the figure"
Program content To teach children to single out individual objects from a group and make a group of individual objects - Establish relationships between the concepts of "one", "many". - Use the words many, one, none. - Co ...
25 0 02/15/2023
Didactic game "Many, one"
To teach children to single out individual items from a group and make a group of individual items - Establish relationships between the concepts of "one", "many". - Use the words many, one, not ONE. - Coordinate the numeral odi . ..
..
33 0 02/15/2023
abstract
• Teach children to navigate in space: near, under, behind, on a chair. To consolidate the ability to compare objects by size, length, width, height. Fix the idea of dividing the whole into equal parts, geometric shapes. • Fix numbers and ordinal ...
33 0 02/15/2023
frog house
Continue to nurture responsiveness in children, arouse a desire to help a toy character. To consolidate the skills of distinguishing geometric shapes: circle, triangle, square; improve the ability to recognize geometric shapes by touch; Develop skills b ...
182 1 02/14/2023
"Garden. Vegetables"
Continue to teach understanding of quantitative relationships between objects; establish causal relationships between the state of the plant and environmental conditions: To consolidate the skills of forward and backward counting within 10; knowledge of geometric functions . ..
..
53 0 02/14/2023
Synopsis of GCD on FEMP in the younger group
Summary of GCD on FEMP in the younger group Theme: "Pets". Purpose: to consolidate the knowledge of children of the number 1, to introduce the number 2. Tasks: -to form the ability to distinguish objects by quantity, designate them with words: one, two, the same, equally, fixed ...
65 0 1 02/14/2023
Mathematics in DOW. Formation of elementary mathematical representations.
Abstracts of GCD with children of the middle group (4-5 years old) on the formation of elementary mathematical concepts in kindergarten.
Author's lessons in mathematics for younger preschoolers. This material on FEMP will be useful for teachers of preschool institutions working with younger preschoolers.
Formation in a game form of elementary mathematical representations in children when comparing objects, groups of objects by size and quantity.
Summary of directly educational activities in mathematics in the middle group. Topic: Visiting forest dwellers.
Summaries of classes on the formation of elementary mathematical representations in the preparatory group (children aged 6–7 years).
Autumn. Classes on the formation of elementary mathematical representations for preschoolers in kindergarten. Autumn classes in mathematics at the preschool educational institution.
Notes on the formation of elementary mathematical representations for children 4-5 years old, middle group preschool. For kindergarten teachers.
Summary of leisure activities for the preparatory group in kindergarten, dedicated to professions "Does everyone need mathematics?".
Summaries of classes on the formation of elementary mathematical representations in the senior group, children 5-6 years old.
Summary of the open GCD in mathematics in the middle group on the topic "Teremok in a new way." Summary of lessons on lego construction in kindergarten.
Count within 10 for preschool children in kindergarten. How to teach a child to count within 10.
Numbers 1 to 10 for preschoolers. Summary of the lesson on FEMP (mathematics) in the preparatory group "From 1 to 10".
Number and number 0 for preschoolers. Number 0 for children. Purpose: To introduce the meaning and method of obtaining the number zero.
The number and number 7 for preschoolers. Number 7 for children. Summary of GCD in mathematics in the senior group "Consolidating the number and number 7."
Number and number 3 for preschoolers. Abstract of the FEMP lesson on teaching children to count up to 3 children of the second junior group.
A lesson on raising interest in mathematics among preschoolers. Purpose: to cultivate interest in mathematics, to develop the processes of logical thinking, visual and auditory perception, voluntary attention.
Purpose: To introduce children to the shape - circle, size, color. Tasks: To teach the ability to focus on
Math lesson for preschoolers: getting to know the geometric figure - Circle. Acquaintance of children with radius, diameter, compass.
Game-lesson: the formation of elementary mathematical representations based on the fairy tale by V. Suteev "Under the Mushroom".
Subject: Journey through the island of mathematics in search of the Golden Key. Integration of educational areas: cognitive
Purpose: Development of cognitive activity. Tasks: Cognitive development: - Formation of the ability to recreate an object of a complex shape,
Program content: fix forward and backward counting within 20, in the ability to distinguish0003
Summary of GCD on FEMP in the 2nd junior group using Gyenesh blocks and sticks
Summary of GCD in mathematics for children of senior preschool age “Spring is coming red ...” (show for parents).
Dudina Nadezhda Alexandrovna educator of the first qualification category GBOU secondary school No.