Learn about ducks
Duck Facts for Kids - Information about Ducks
This educational video for kids will help your children learn about ducks as well as showing some interesting duck facts for kids. We also included duck sounds, HD footage of a mallard duck, ducks quaking, duck true facts and cute ducklings.
We would like your children to learn about ducklings in an interesting and fun way. The information about ducks is presented in a clear and interesting way. This video can be used in kindergartens and schools to teach toddlers and children the duct facts.
Information about ducks
Where do ducks live?
- Ducks are found in wetlands, marshes, ponds, rivers, lakes and oceans. Because they simply love the water.
What do ducks eat?
- Ducks are omnivores. They eat water plants, worms, grain, seeds, nuts, fruit, insects, water plants and even small fish. They even eat bread.
Can ducks fly?
- Ducks can fly. They fly in a “V” shape.
This makes flying easier for them.
How long do ducks live?
- Ducks can live from 2 – 20 years. Wild ducks live longer than domestic ducks.
What is a male duck called?
- An adult male duck is called a drake.
What is a female duck called?
- An adult female duck is known as a hen or a duck.
What is the scientific name of a mallard duck?
- The scientific name of a mallard duck is Anas platyrhynchos.
Is duck a bird?
- Ducks are birds. They are related to Geese and Swans.
More interesting duck facts
- Ducks are smaller than their relatives. They also have shorter necks and wings and a stout body.
- Ducks are also called ‘Waterfowl.’
- Ducks are found everywhere in the world except Antarctica. It is too cold for them there.
- Ducks have been domesticated as pets and farm animals for more than 500 years.
- They are curious and friendly animals.

- Baby ducks ae called ducklings.
- Ducks have many economic uses. Their feathers are used in many products such as pillows.
- People raise the white Pekin duck for its eggs and meat.
- All ducks have highly waterproof feathers.
- Ducks have very good vision and they can see in color.
- Some species of ducks migrate or travel long distances every year to breed.
- Usually, they travel to warmer areas or where the water does not freeze.
- There they can rest and raise their young. The distance may be thousands of kilometers away.
- Not all ducks are yellow, and not all ducks quack.
- A male duck typically has a green head, white neckband, and grayish body.
- A female duck is typically are brownish in color. In general, male ducks are more colorful than females.
Please have a look our farm animals page for more educational videos of the animals of the farm.
Sources:
http://www.coolkidfacts. com/duck-facts-for-kids/
com/duck-facts-for-kids/
https://animalcorner.co.uk/animals/ducks/
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefacts/animals/duck.html
http://easyscienceforkids.com/all-about-ducks/
Warning: A non-numeric value encountered in /homepages/0/d630541942/htdocs/clickandbuilds/Kiddopedia/wp-content/themes/Newspaper/includes/wp_booster/td_block.php on line 326
Key Information, Facts & Pictures Of Ducks
Image Source
Ducks are birds. Ducks are also called ‘Waterfowl’ because they are normally found in places where there is water like ponds, streams and rivers.
Ducks are related to Geese and Swans in the Anatidae family. Ducks are sometimes confused with several types of unrelated water birds with similar forms, such as loons (an aquatic bird found in many parts of North America and northern Europe) or grebes (freshwater diving birds) and coots (medium-sized water birds which are members of the Rail Bird family).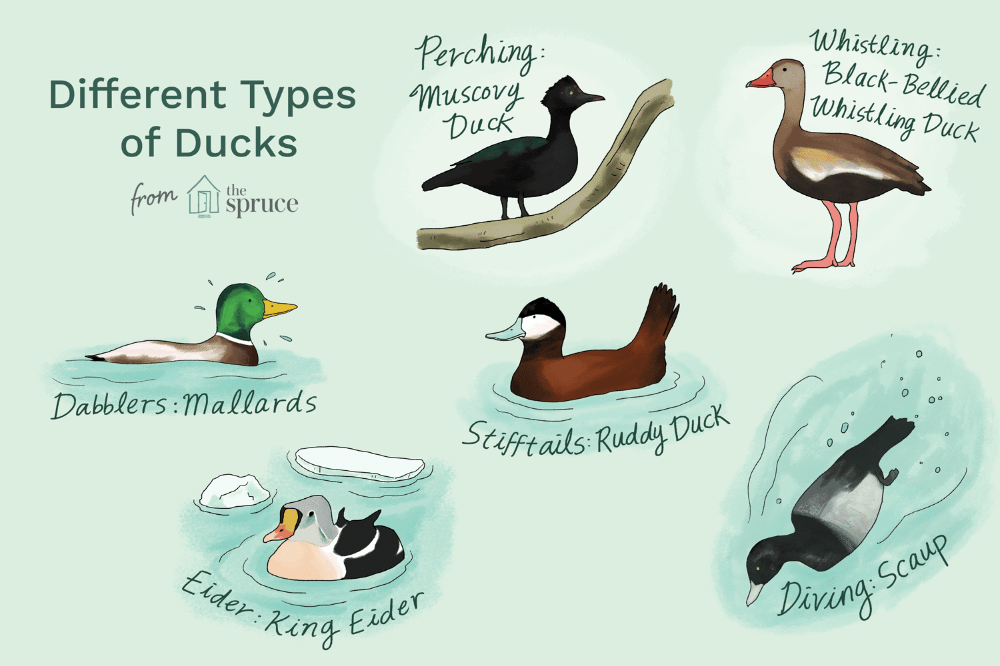
Duck Characteristics
Ducks are smaller than than their relatives (swans and geese). Ducks also have shorter necks and wings and a stout body.
A female duck is called a ‘hen’, they are identified by their very-dull, brown feathers. The females have dull-brown feathers so that they can hide from enemies and predators. They can also camouflage themselves in their nests and also protect their young.
A male duck is called a ‘drake’, you can identify the male duck by its brightly colored feathers. They use these colored feathers to attract the female ducks for mating. Here is a beautifully colored Drake with a purple plumage, shiny green head coloring, silvery white body and grey wings with blue markings.
The males use their colorful plumage to attract females. However, they will lose or molt their colorful feathers when the females are busy hatching the eggs. The males will now look like the female in color and will be unable to fly temporarily. They will molt again in early Autumn and get back their colorful feathers and be able to fly again. The females also molt. They replace all their feathers and get new ones after their ducklings are hatched.
They will molt again in early Autumn and get back their colorful feathers and be able to fly again. The females also molt. They replace all their feathers and get new ones after their ducklings are hatched.
Ducks have webbed feet, which are designed for swimming. Their webbed feet act like paddles for the ducks. The reason ducks can swim in cold water is their amazing circulatory system. Their blood vessels are laid out very close to each other in their legs and feet in a network that allows the warm and cool blood to exchange heat.
This allows the warm blood going from the body into the feet to warm the cooler blood re-entering the body from the feet, and the blood going to the feet is cooled enough that the cold does not bother the duck. Thus the duck’s feet are able to tolerate the cold and not bother them. All birds have this circulatory system in their legs and feet.
A duck has water-proof feathers. There is a special gland called the ‘Preen Gland’ near the ducks tail. This tiny gland produces oil which the duck uses to coat its feathers.
This tiny gland produces oil which the duck uses to coat its feathers.
The duck picks up the oil with its head and beak, and then smears it all over its body to make the outer feathers waterproof. Without this protective barrier, a ducks feathers would become water-logged and because they spend their whole lives around and in water, this water-proof barrier is extremely important. Beneath the water-proof coat are fluffy and soft feathers which keep the duck warm.
The ducks mouth is called a beak or bill. It is usually broad and flat and has rows of fine notches along the edge called ‘lamellae’. The lamellae helps the duck to grip its food so that it will not slip off.
However, ducks beak comes in different shapes and sizes. The shape of the beak and body determines how the duck will hunt for its food.
Duck Behaviour
Ducks keep clean by preening themselves. Ducks do this by putting their heads in funny positions and putting their beaks into their body.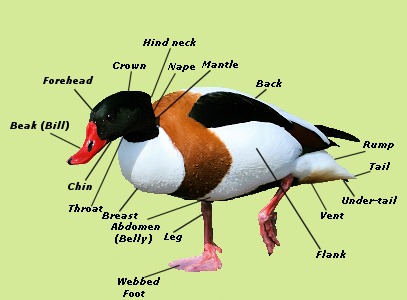 Ducks preen themselves very often. Preening also removes parasites, removes scales which cover newly sprouting feathers and also involves the removal of spreading oil over clean feathers.
Ducks preen themselves very often. Preening also removes parasites, removes scales which cover newly sprouting feathers and also involves the removal of spreading oil over clean feathers.
Duck Habitats
Many species of duck are temporarily flightless while moulting. Ducks seek out protected habitats with a good food supply during this period. They usually moult before migrating.
Ducks are found in wetlands, marshes, ponds, rivers, lakes and oceans. This is because ducks love the water. Some species of ducks migrate or travel longs distances every year to breed. Ducks usually travel to warmer areas or where the water does not freeze so that they can rest and raise their young. The distance may be thousands of miles away. Ducks are found everywhere in the world except the Antartica which is too cold for them.
Duck Life Span
Ducks can live from 2 – 20 years, depending on species and whether they are wild ducks or ducks in captivity. Its a fact that a wild duck can live 20 years or more. Domestic ducks typically live 10 – 15 years in captivity. The world record is a Mallard Drake that lived to a ripe old age of 27 years.
Domestic ducks typically live 10 – 15 years in captivity. The world record is a Mallard Drake that lived to a ripe old age of 27 years.
Ducks and their feeding habits
Shovelers – these ducks have broad beaks and sift their food for insects, nails and seed from the mud.
Diving ducks and Sea ducks forage deep underwater. To be able to submerge more easily, the diving ducks are heavier than dabbling ducks and therefore have more difficulty taking off to fly. These ducks have long and narrow beaks. Their narrow beaks are also covered will saw-like edges which help them to grab fish.
Dabbling ducks feed on the surface of water or on land, or as deep as they can reach by up-ending without completely submerging. Their beaks are broad and short. Dabbling ducks have tiny rows of plates along the inside of the beak called ‘lamellae’ like a whales baleen.
These let them filter water out of the side of their beaks and keep food inside. Dabbling ducks eat plants, seeds, grasses and other small insects and animals that they find on or under the water. Usually they stick their tails in the air and stretch their heads into the water to reach their food.
Dabbling ducks eat plants, seeds, grasses and other small insects and animals that they find on or under the water. Usually they stick their tails in the air and stretch their heads into the water to reach their food.
Dabblers usually have shiny colored patches on their wings. The domestic ducks are dabblers too. They are descendants of the Mallards. Dabbling ducks take off from the water in quick jumps. Ducks with longer necks dive with their head down into the shallow water and pick up their food.
Duck Reproduction
Ducks usually look for a mate or partner in winter. Male ducks will attract the female ducks with their colorful plumage or feathers. The female ducks will then lead the male ducks to their breeding ground in spring. The breeding ground will usually be the place where the female duck was hatched. The female duck builds her nest with grass or reeds or even in a hole in a tree.
The male duck will guard their territory by chasing away other couples. Once the female lays 5 – 12 eggs, she will sit on her eggs to keep them warm so that they can hatch into ducklings. The male ducks on the other hand, will be with the other male ducks.
The male ducks on the other hand, will be with the other male ducks.
The eggs will hatch within 28 days normally, except for the Muscovy duck which takes about 35 days to hatch.The mother duck will keep her brood of ducklings together to protect them from predators. Animals like the raccoon, turtles, hawks, large fish and snakes are a ducks main predators and they will eat the ducklings. Ducklings are able to fly within 5 – 8 weeks. Their feathers develop very fast.
When the young are ready to fly, all the ducks will gather in flocks on large lakes, marshes or the ocean to migrate to their wintering home. When the ducks fly, they usually do so in a ‘V-shaped’ or a long line.
Interesting Duck Facts
A hen makes a loud QUACK sound while the drake has a raspy, muffled call.
Touching a duckling does not prevent the mother duck from taking care of it. It is however best to leave ducklings alone so as not to scare the mother duck away or accidentally injure them.
Ducks sleep with half their brains awake. Ducks are more likely to sleep with one eye open when they are located on the edge of sleeping groups. Ducks can detect predators in less than a second.
Duck eggshells have tiny holes (pores) that allow it to breathe. A hen’s eggs can have 7500 pores, most found at the blunt end of the egg. Respiratory gasses as well as water vapour travel through these pores allowing the egg to breathe.
Baby ducks are precocial meaning they are born with their eyes wide open, with a warm layer of down and are not fully dependant on their parents for food. Ducklings are ready to leave the nest within hours of hatching.
A ‘clutch’ is the total number of eggs laid by one bird during one nesting session. Clutch size affected by hereditary and environmental factors. When food is abundant, birds lay more eggs.
A brood is the total number of hatchlings, or ducklings in a clutch.
Ducks have very good vision and they see in color.

Learn how to keep ducks at home
What is a female duck called?
A female duck is called a ‘hen’, they are identified by their very-dull, brown feathers. The females have dull-brown feathers so that they can hide from enemies and predators. They can also camouflage themselves in their nests and also protect their young.
What are baby ducks called?
A baby duck is called a duckling. A group of ducklings is called a brood.
Where do ducks sleep?
Most species of Duck sleep floating on water. Some ducks such as mallards can roost on lands or water.
Ducks, interesting information about ducks
Mandarin duck
Duck is one of the most popular birds in the household of many countries. In addition, there are huge populations of wild ducks in the world.
- Duck meat is popular with culinary experts almost all over the world. The only region where domestic ducks are almost never bred is the countries of South and Central America.

- Once, back in 1992, during a storm, several containers filled with plastic ducks were washed off the deck of a merchant ship. In total, about 30 thousand toys were lost, and then they were found in different parts of the world for several years. But every cloud has a silver lining - thanks to these findings, scientists managed to learn a lot about ocean currents.
- During migration, ducks sometimes fly 400-500 kilometers a day.
- Ducks have three eyelids. One for blinking, one for eye protection, and one for sleep. Owls do the same, by the way.
- Normally, ducks fly at an average speed, but researchers once recorded a wild duck flying at a speed of 170 km/h. She was flying in front of a small plane, and was apparently terrified to death, which gave her strength.
- These birds do not often rise to a height of more than a kilometer, however, they are capable of it. Once in the USA, the plane collided with a duck at an altitude of 6.5 kilometers.

- Most ducks, except Muscovy, are descended from wild mallard ducks. It is believed that among the ancestors of musky ducks there are turkeys.
- Ducks have 80 chromosomes.
- Judging by the discovered archaeological finds, about 5000 years ago in ancient Mesopotamia, people had already domesticated ducks and were breeding them with might and main.
- During molting, these birds stop laying eggs.
- Of the more than 110 duck species in the world, more than 30 are found in Russia.
- Three-quarters of all domestic ducks (about 2 million) are raised annually in China.
- Contrary to popular myth, duck quacks do have an echo under certain conditions. But in most cases there really is no echo, that's a fact.
- Drakes do not know how to quack at all - only females of these birds can reproduce this sound.
- There are more vertebrae in the neck of a duck than in the neck of a giraffe.
- An adult duck can lay up to 240-260 eggs in a year.

- The most common today is the Peking duck, which is native to China. The weight of a duckling at the age of 60 days is 2.5 kg
- The second most popular is the Indian (musk breed). A feature of the indo is also the fact that when swimming on a frosty day, there is a high risk of getting frostbite. This breed is afraid of the cold. When kept at home in winter, they build a warm house for her.
- Cases have been recorded when ducks floating on the surface of the reservoir became victims of large pikes.
- Duck feathers cannot be wetted because they are covered with a special fatty layer. This secret is produced by glands near the base of the tail feathers, and ducks apply it with their beak to the whole body.
- The legs of these birds are unable to feel the cold, as they do not have blood vessels and nerve endings.
- During the annual molt, ducks lose their ability to fly because they lose a lot of feathers.
- Moving on land, these birds clumsily roll from side to side because of their short and, moreover, widely spaced legs.

- Everyone knows that ducks sometimes dive under water in search of food, but few people know that the depth of their immersion can be 5-6 meters.
- Having eaten, they swallow stones and clay. This helps them digest food more efficiently.
- Baby ducklings actually think of the first creature they see when they get out of the egg as their mother. Moreover, this creature may turn out to be, for example, a person or a domestic cat - ducklings do not care.
Information source http://npc-news.ru/?p=21110 Ducks, interesting and unusual facts about ducks.
DUCKS, a group of genera of webbed-footed water birds belonging to the family Anatidae, which also includes geese and swans. Ducks differ from them in their relatively small size, short legs and neck, somewhat flattened body, and usually unequal plumage coloration in males and females. Like geese, swans, and flamingos, ducks along the edges of their beaks, on their inner side, have transverse tooth-like ridges - plates - for straining food particles from silt or water.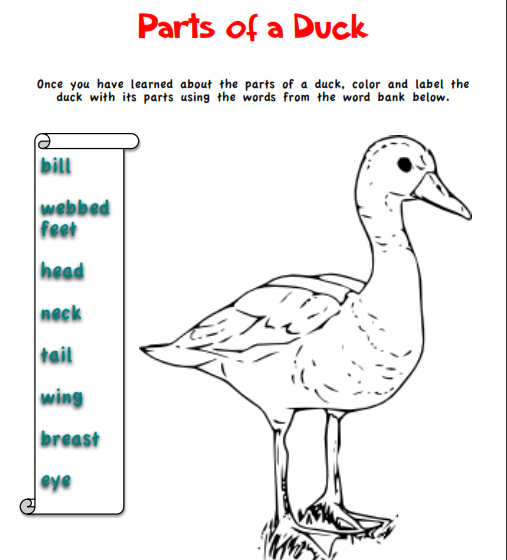 Numerous species of ducks are found in freshwater bodies of water and seas around the world.
Numerous species of ducks are found in freshwater bodies of water and seas around the world.
Bookmark this page for yourself:
No comments allowed.
Blog about ducks - interesting and useful information for beginners
Secrets of keeping and feeding indoutok
Indian ducks are of particular interest today for lovers of exotic poultry. And the question arises, how to contain them? Read about it with us!
The most popular breeds of domestic ducks
Along with geese, ducks are an excellent source of eggs and meat. But what breed to choose for the household? Find out about the most popular now!
Hybrid Moulard ducks - a find of a modern farmer
Many owners of personal plots are interested in who are mulard ducks? They appeared just a few years ago. Read more right now!
River feathered beauty - gray duck
Have you observed gray duck in nature? Are you curious to know what her appearance, habits and features are? Then find out all the details in this article!
Indian runner - the fastest duck on the farm
Indian runner duck is distinguished by its briskness and ability to rush all year round. Want to know more about the fastest bird? Details are on our website!
Want to know more about the fastest bird? Details are on our website!
Bashkir ducks - find a good owner
Bashkir ducks are the best choice for home meat and egg poultry farming. If you have not heard of this breed, then learn about it now!
River quiet and wonderful divers - wild diving ducks!
Did you know that diving ducks almost never come out to live on land and can spend their whole life on the water? Read more about these wild birds now!
Muscovy duck in the yard: the secrets of breeding and keeping
Muscovy duck is a favorite bird of many breeders. She is not whimsical in food and is quite calm. How to breed and keep this duck? More on this later!
Orderlies for rivers and lakes - wild ducks
What are the types of wild ducks? What do birds eat in nature and how to feed them at home? About this and much more. read on our website!
Pintail Duck - the hunter's coveted trophy
The pintail duck is without exaggeration one of the most beautiful ducks in the world. According to experts, hunting for this duck is very difficult. Why? Learn from us.
According to experts, hunting for this duck is very difficult. Why? Learn from us.
River beauty - shovel duck
The broad-nosed duck is a river breed of birds that beckons with its beauty. Why did she get such a name, where does she live and how does she live? Read now!
Whistler, sviyaga or simply sviyaga duck
The wigeon duck is one of the most famous northern birds of Russia. This taiga duck gets along well in the tundra zone and northern forest-steppes. Read about it with us.
Peganka - an unusual piebald duck
Unusual waterfowl shelduck because of its bright plumage is a valuable trophy for hunters. You can learn more about it on our website!
Correctly trimming the wings of flying ducks
Hunters clip the wings of decoy ducks. But with almost the same methods, you can carry out the procedure with poultry. How? Read on.
Sad scoter with white eyes
A gloomy bird with heavy eyes - this is the first impression if you look at the scoter duck. What does she look like and where does she live? Learn from us!
What does she look like and where does she live? Learn from us!
Domestic ducks are animals without which it is difficult to imagine any poultry yard. About the history of the origin of ducks, as well as a description of their appearance and conditions of detention, read further in our section.
Origin
The forerunner of the domestic duck is the wild mallard. Historical data on the domestication of this bird species differ depending on the region of habitat. Even in ancient Rome, eggs of mallard ducks were laid on domestic chickens in order to hatch a chick accustomed to humans and captivity. In Rome, special yards were created and actively operated, in which domestic ducks were kept. The scientist and business executive Colummela reported about this in the first century BC in his notes.
But in China, birds were tamed much earlier, and it was the Chinese who were the first to come up with a semblance of an incubator. Duck eggs were placed in warm chaff, and egg baskets were then left in warm rooms. After the allotted time, the breeders received domestic chicks, which continued to grow and breed in captivity. For example, the American Indians domesticated the warty duck, and then the bird was brought to Europe. Since then, active breeding of ducks began throughout the mainland.
After the allotted time, the breeders received domestic chicks, which continued to grow and breed in captivity. For example, the American Indians domesticated the warty duck, and then the bird was brought to Europe. Since then, active breeding of ducks began throughout the mainland.
Appearance
All breeds of ducks are outwardly similar to each other, they differ only in color and size, as well as in certain habits and skills. In general, the weight of an adult reaches one and a half kilograms, depending on the breed and diet, it can be more. The body length of the bird is about 60 cm, moreover, wild birds are naturally smaller and thinner than domestic relatives. The wings are wide, with long feathers.
Ducks have a powerful long beak (grey or black) and a short neck. Yellow or gray webbed feet designed for swimming. Ducks are excellent divers, they love water very much and immediately go to splash in it if they see a container of water or a river nearby. They walk, waddling, and swim much better than they maneuver on land.