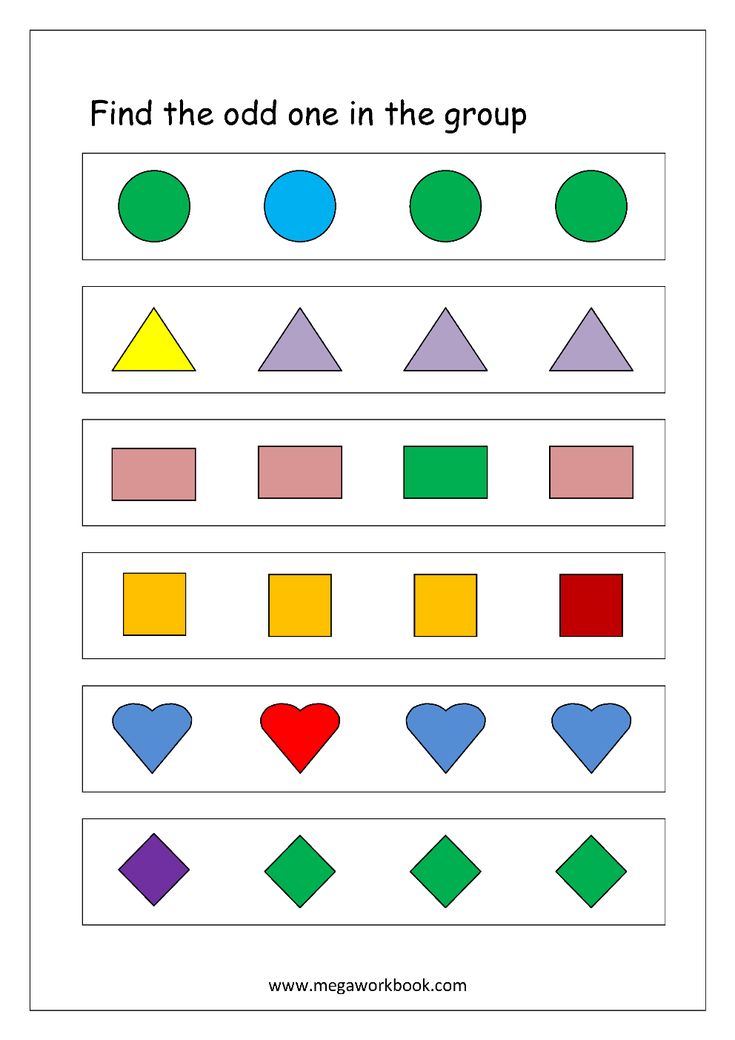
Learning shapes in kindergarten
25 Creative Activities and Ideas For Learning Shapes
Learning shapes is one of the earliest concepts we teach kids. This readies them for geometry in the years ahead, but it’s also an important skill for learning how to write and draw. We’ve rounded up our favorite activities for learning shapes, both 2-D and 3-D. They all work well in the classroom or at home.
1. Start with an anchor chart
Colorful anchor charts like these are terrific reference tools for kids learning shapes. Have kids help you come up with examples for each one.
Learn more: A Spoonful of Learning/Kindergarten Kindergarten
2. Sort items by shape
Collect items from around the classroom or house, then sort them by their shapes. This is a fun way for kids to realize that the world around them is full of circles, squares, triangles, and more.
Learn more: Busy Toddler/Shape-Sorting
3. Snack on some shapes
Everyone loves a learning activity you can eat! Some food items are already the perfect shape; for others, you’ll have to get a little creative.
ADVERTISEMENT
Learn more: Chieu Anh Urban
4. Print with shape blocks
Grab your shape blocks and some washable paint, then stamp shapes to form a design or picture.
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
5. Go on a shape hunt
These “magnifying glasses” make an adventure of learning shapes! Tip: Laminate them for long-term use.
Learn more: Nurture Store UK
6. Hop along a shape maze
Use sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun
7. Assemble a truck from shapes
Cut out a variety of shapes (excellent scissors skills practice!), then assemble a series of trucks and other vehicles.
Learn more: Little Family Fun
8.
 Stretch out shapes on geoboards
Stretch out shapes on geoboards
Teachers and kids love geoboards, and they’re a great tool for learning shapes. Give students example cards to follow, or ask them to figure out the method on their own.
Learn more: Mrs. Jones’ Creation Station
9. Drive on shaped roads
Use these free printable road mats to work on shapes. Bonus: Make your own road shapes from sentence strips!
Learn more: PK Preschool Mom
10. Find shapes in nature
Take your shape hunt outside and look for circles, rectangles, and more in nature. For another fun activity, gather items and use them to make shapes too.
Learn more: Nurture Store UK
11. Put together craft stick shapes
Add Velcro dots to the ends of wood craft sticks for quick and easy math toys. Write the names of each shape on the sticks for a self-correcting center activity.
Learn more: Surviving a Teacher’s Salary
12.
 Blow 3-D shape bubbles
Blow 3-D shape bubblesThis is a STEM activity that’s sure to fascinate everyone. Make 3-D shapes from straws and pipe cleaners, then dip them in a bubble solution to create tensile bubbles. So cool!
Learn more: Babble Dabble Do
13. Prep a shape pizza
Cover a paper plate “pizza” with lots of shape toppings, then count the number of each. Simple, but lots of fun and very effective.
Learn more: Mrs. Thompson’s Treasures
14. Construct shapes from toothpicks and Play-Doh
This is an excellent STEM challenge: how many shapes can you make using toothpicks and Play-Doh? Marshmallows work well for this activity too.
Learn more: Childhood 101
15. Outline shapes with stickers
Kids adore stickers, so they’ll enjoy filling in the outlines of the shapes they’re learning. They won’t realize it, but this gives them fine motor skills practice too!
Learn more: Busy Toddler/Sticker Shapes
16.
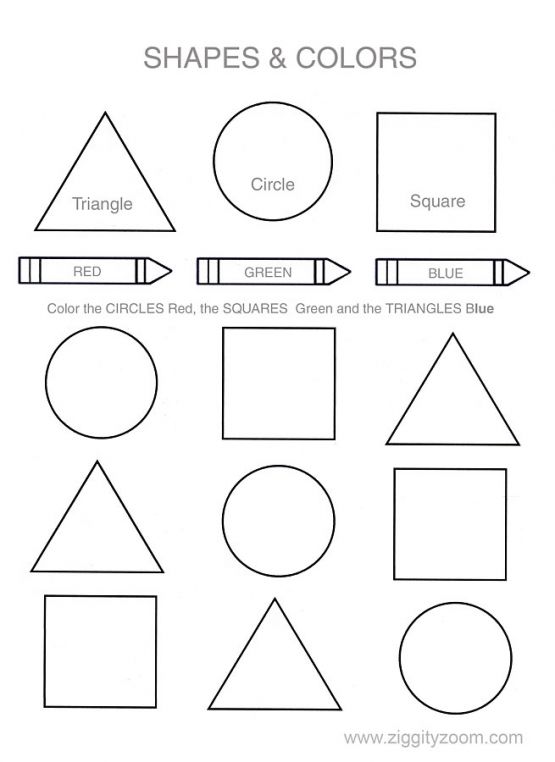 Lace shapes
Lace shapesLacing cards have long been a classic, but we really like this version that uses drinking straws. Just cut them into pieces and glue them along the edges of the cards.
Learn more: Planning Playtime
17. Make shapes with LEGO bricks
LEGO math is always a winner! This activity also makes a good STEM challenge. Can your students figure out how to make a circle from straight-sided blocks?
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
18. Categorize shapes by their attributes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like, “The shape in this bag has 4 sides. What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
19. Count and graph shapes
These free printable worksheets challenge kids to identify shapes, then count and graph them. Lots of math skills, all in one!
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
20.
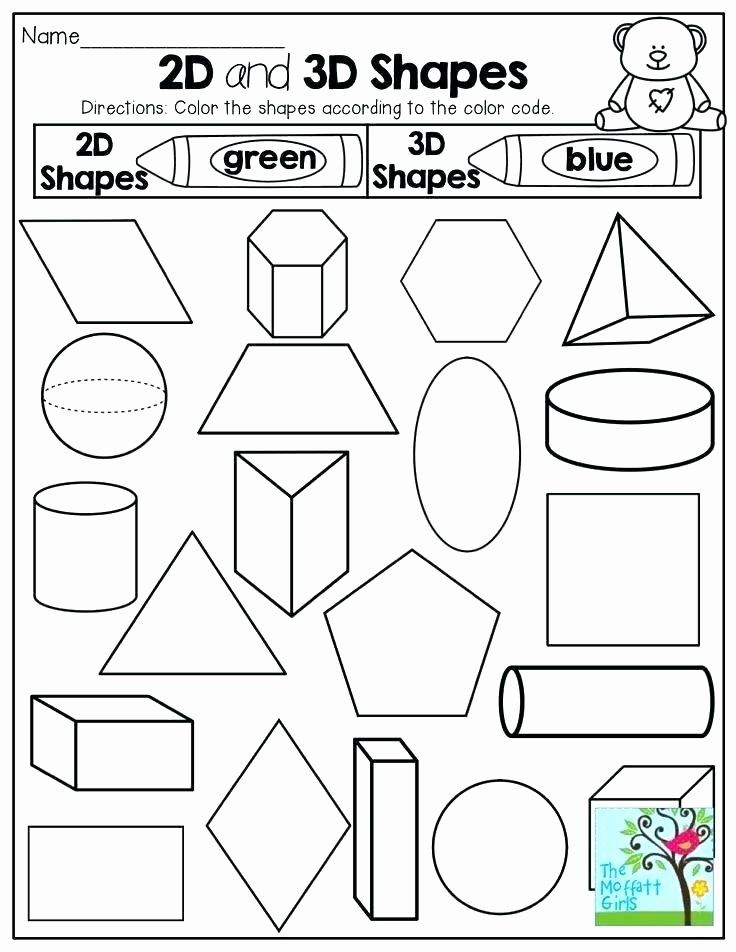 Create a shape monster
Create a shape monster
Add arms, legs, and faces to create cheery (or scary) shape monsters! These make for a fun classroom display.
Learn more: Fantastic Fun and Learning
21. Sift through rice for shapes
Sure, kids can identify their shapes by sight, but what about by touch? Bury blocks in a bowl of rice or sand, then have kids dig them out and guess the shape without seeing them first.
Learn more: Fun With Mama
22. Craft an ice cream cone
Ice cream cones are made up of several shapes. Encourage kids to see how many different ways they can make a sphere of “ice cream.”
Learn more: Extremely Good Parenting
23. Ask “What does the shape say?”
If you don’t mind the risk of getting that song stuck in your kids’ heads, this is such a neat way to combine writing and math.
Learn more: Around the Kampfire
24. Piece together shape puzzles
Use wood craft sticks to make simple puzzles for kids who are learning their shapes. These are inexpensive enough that you can make full sets for each of your students.
These are inexpensive enough that you can make full sets for each of your students.
Learn more: Toddler at Play
25. Feed a shape monster
Turn paper bags into shape-eating monsters, then let kids fill their hungry bellies!
Learn more: Teach Pre-K
From teaching shapes to long division and everything in between, these are the 25 Must-Have Elementary Classroom Math Supplies You Can Count On.
Plus, 22 Active Math Games and Activities For Kids Who Love to Move.
Fun and Engaging 2D Shape Activities
One of the very first math lessons we teach in kindergarten is two-dimensional shapes! There are so many ways you can introduce shapes while also engaging your students in fun, hands-on activities. I think one of my favorite things about teaching shapes is that the students don’t even realize they are learning! They get to build, sort, and manipulate shapes in many ways, which leads to high engagement. Read on for my favorite kindergarten-approved 2D shape activities that your students will love!
Read on for my favorite kindergarten-approved 2D shape activities that your students will love!
Activities for Teaching 2D Shapes
Since shapes are all around us, chances are that many of our students will enter kindergarten with a basic knowledge of shape names. It also doesn’t take too long to fill in the missing shape names that our students haven’t quite mastered. After that, the goal is for our students to describe, build, and even manipulate two-dimensional shapes. This is where some additional shape practice activities can come in handy!
Introducing Shape Names and Attributes
The first step in teaching students shapes is to make sure they know all of the 2D shape names and their unique attributes. I have found that all students benefit from an introduction (or reintroduction) to the shape names and attributes before we move on to other 2D shape activities.
I love introducing and reviewing shapes with these 2D Shapes Poems! These poems are catchy and help students learn about each shape’s attributes as well as relate them to real-world objects that they already know.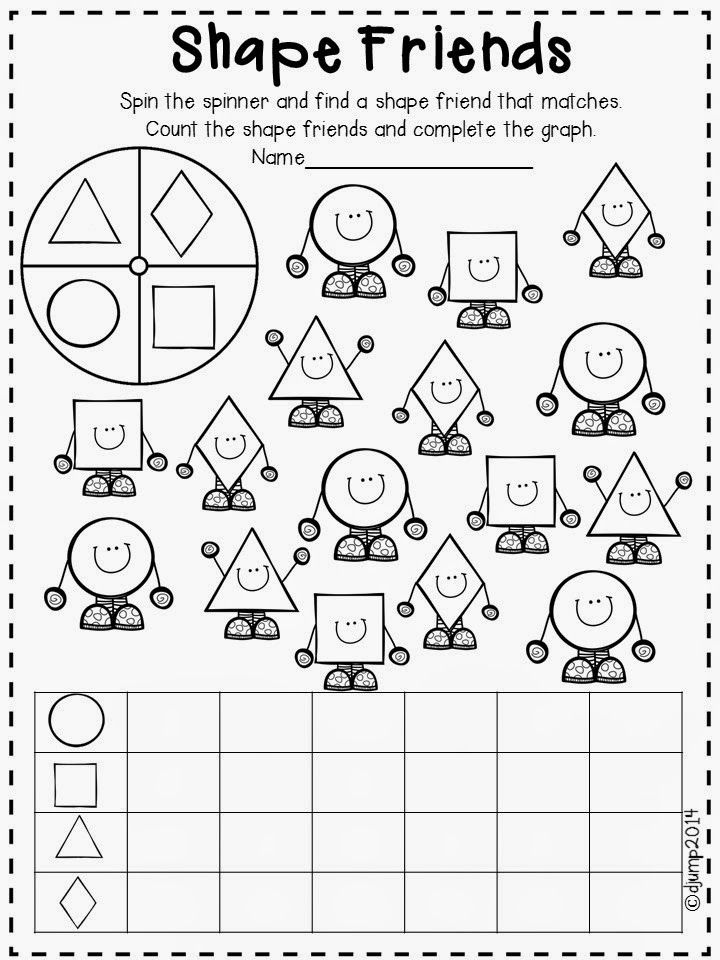 Before you know it, your students will look at a stop sign and say, “Hey, that’s an octagon!” 🙂 #proudteachermoment
Before you know it, your students will look at a stop sign and say, “Hey, that’s an octagon!” 🙂 #proudteachermoment
I introduce the shapes one at a time which prevents overwhelm and allows the students to focus on that shape and its unique attributes. We practice one shape each day until all of them have been added to our shape wall!
Identifying and Describing Shapes
After plenty of time has been spent pronouncing the shape names and discussing the shape attributes, it is time for students to put that knowledge into practice. They are now ready to identify shapes in different contexts and describe them in their own words! As with any new concept, it’s important to keep young learners engaged by using a variety of activities when practicing the same skill multiple times, such as identifying and describing shapes.
Shape Bingo is a fun way to add repetition to your 2D shape practice because students will want to play this game over and over again! I love to play this game in small groups, so we can quickly review the shape names and attributes as we draw each card. For an added challenge, you could pull a card and keep it hidden from the students. Then, give them clues about the shape by describing its unique attributes so that the students can guess the correct shape before placing their bingo markers.
For an added challenge, you could pull a card and keep it hidden from the students. Then, give them clues about the shape by describing its unique attributes so that the students can guess the correct shape before placing their bingo markers.
I also love to encourage students to identify shapes in the world around them. One way to practice this skill is with a shape sort, where students can identify and sort a variety of real-world objects based on shape. This 2D shape sort is a very fun center activity that gets students excited to look for shapes all around them. It’s so fun to hear students point out the shapes they see as they walk down the hall!
Here are several more 2D shape activity ideas that will keep your students engaged as they practice identifying and describing shapes in multiple ways:
- Play a shape game where students draw a shape out of a bucket and say its name and whether it has curved or straight lines
- Play “I Spy” where students must find real-world objects that match a specific shape
- Go outside on a nature hunt and see what you can find in each shape
- Do a shape show-and-tell
Making Shapes
After students have a good understanding of shape names and their attributes, they are ready to start building shapes on their own! There are many ways to provide individualized opportunities for shape building, based on the fine motor skills of your students. Some students might form shapes using craft sticks while other students might be ready to trace shapes with a highlighter.
Some students might form shapes using craft sticks while other students might be ready to trace shapes with a highlighter.
In the kindergarten classroom, it’s important to include fine motor practice anywhere we can. Two-dimensional shape building practice is the perfect time to strengthen hand-eye coordination and writing skills! Here are some additional ways to practice forming and writing shapes:
- Practice drawing shapes in the air
- Highlight shapes
- Trace shapes with a writing utensil
- Practice making shapes with sensory materials, such as in sensory trays filled with beads, cereal, rice, etc.
- Trace over shapes with little cars or something similar
- Form shapes with playdough (Check out this playdough mat freebie)
- Form shapes with craft supplies, such as pom-poms, craft sticks, pipe cleaners, etc.
Working With Shapes
Once students have had plenty of time to form shapes using their knowledge of shape names and attributes, they’re ready for the next step: Working with shapes.
When students are given plenty of opportunities to manipulate and work with shapes in various ways, it deepens their understanding of two-dimensional shapes and prepares them for future math concepts.
One of my favorite 2D shape activities is this shape-building activity, where students can see the relationship between shapes as they use pattern blocks to create a larger shape. I love how this activity encourages students to see how shapes are related to each other.
Here are some of my other favorite ways to help students build on their budding knowledge of 2D shapes:
- Sort shapes by attributes, size, color, etc.
- Build with shapes
- See what they can build using only one shape
- Do art projects using a variety of shapes
- Build their name with shapes
- Make a shape book
Using 2D Shape Activities for Centers
Many of the activities I mentioned above would be perfect for math centers in your kindergarten classroom.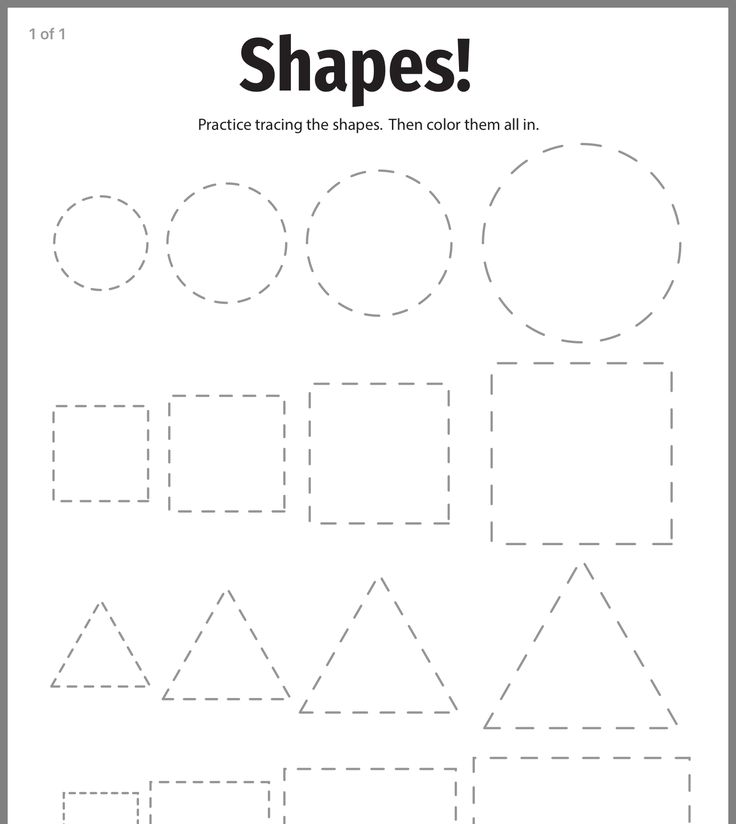 In fact, I have compiled my ten favorites into a collection of 2D Shapes Centers and Activities! These activities include practice opportunities for 12 different two-dimensional shapes. These shape centers are perfect for kindergarten, Pre-K, and preschool!
In fact, I have compiled my ten favorites into a collection of 2D Shapes Centers and Activities! These activities include practice opportunities for 12 different two-dimensional shapes. These shape centers are perfect for kindergarten, Pre-K, and preschool!
2D Shapes Centers and Activities
$5.00
These 2D shapes centers and activities are full of learning and fun for your preschool and kindergarten students. You can use these activities as you introduce the 2D shapes to your class, or spread them out throughout the year in your math centers. Some centers are also in black and white to be printed on colored paper.
Shop Now
Save These 2D Shape Activities
Be sure to save this post to your favorite classroom board on Pinterest so that you can refer back to these ideas later!
Learning Geometric Shapes: Games for Preschoolers
One of the important aspects of the development of mathematical concepts in preschoolers is the study of the basics of geometry.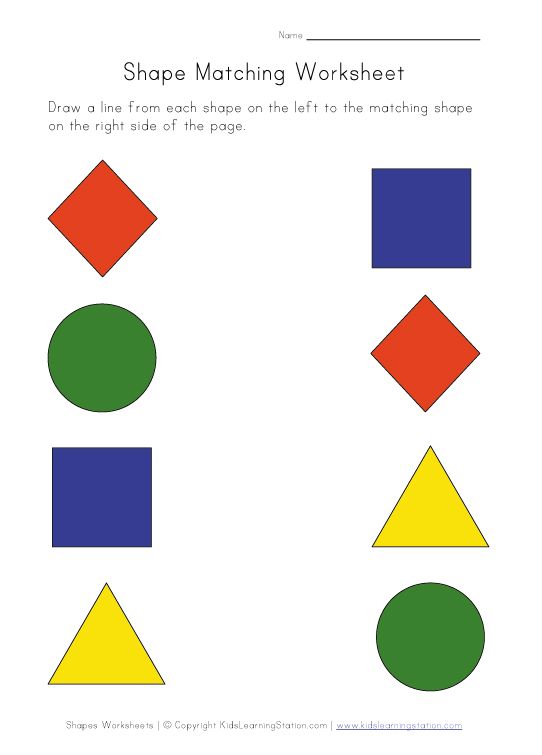 In the course of acquaintance with geometric shapes, the child acquires new knowledge about the properties of objects (shape) and develops logical thinking. In this article, we will talk about how to help a preschooler remember geometric shapes, how to properly organize games for teaching geometry, and what materials and aids can be used to develop a child’s mathematical abilities.
In the course of acquaintance with geometric shapes, the child acquires new knowledge about the properties of objects (shape) and develops logical thinking. In this article, we will talk about how to help a preschooler remember geometric shapes, how to properly organize games for teaching geometry, and what materials and aids can be used to develop a child’s mathematical abilities.
At what age can one start learning geometric shapes?
Many parents are wondering if young children need to get acquainted with geometric shapes. Experts believe that it is optimal to start classes in a playful, relaxed form from the age of 1.5. Until this age, it is appropriate to pronounce to the child the names of the shapes of objects that the baby meets in real life (for example, “round plate”, “square table”).
Introducing the child to geometric shapes, be guided by his reaction. If your baby started to show interest in them at an early age (by playing with the sorter or looking at pictures), encourage his curiosity.

At the age of 2, the baby should be able to distinguish between:
- Circle;
- Square;
- Triangle.
By the age of 3 you can add:
- Oval;
- Rhombus;
- Rectangle.
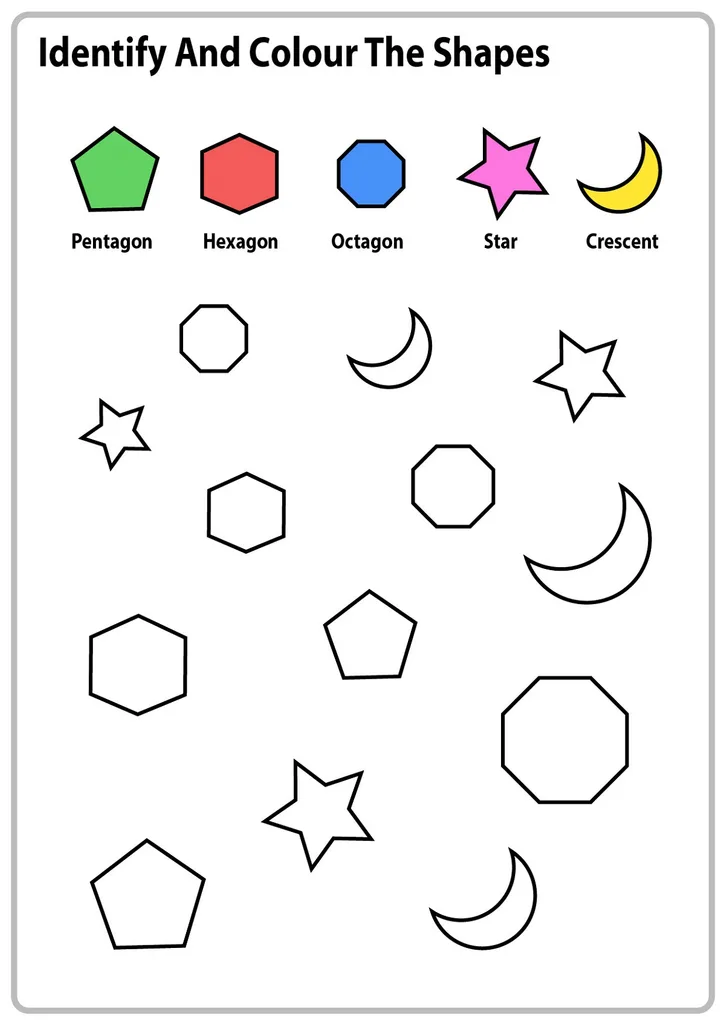
At an older age, a child can memorize such shapes as a trapezoid, a pentagon, a hexagon, a star, a semicircle. Also, children visiting the Constellation Montessori Center get acquainted with geometric bodies with interest.
How can I help my child remember geometric shapes?
Teaching a child geometric shapes should take place in stages. You need to start new figures only after the baby remembers the previous ones. The circle is the simplest shape. Show your child round objects, feel them, let the baby run his finger over them. You can also make an application from circles, mold a circle from plasticine. The more sensations associated with the concept being studied, the child receives, the better the baby will remember it.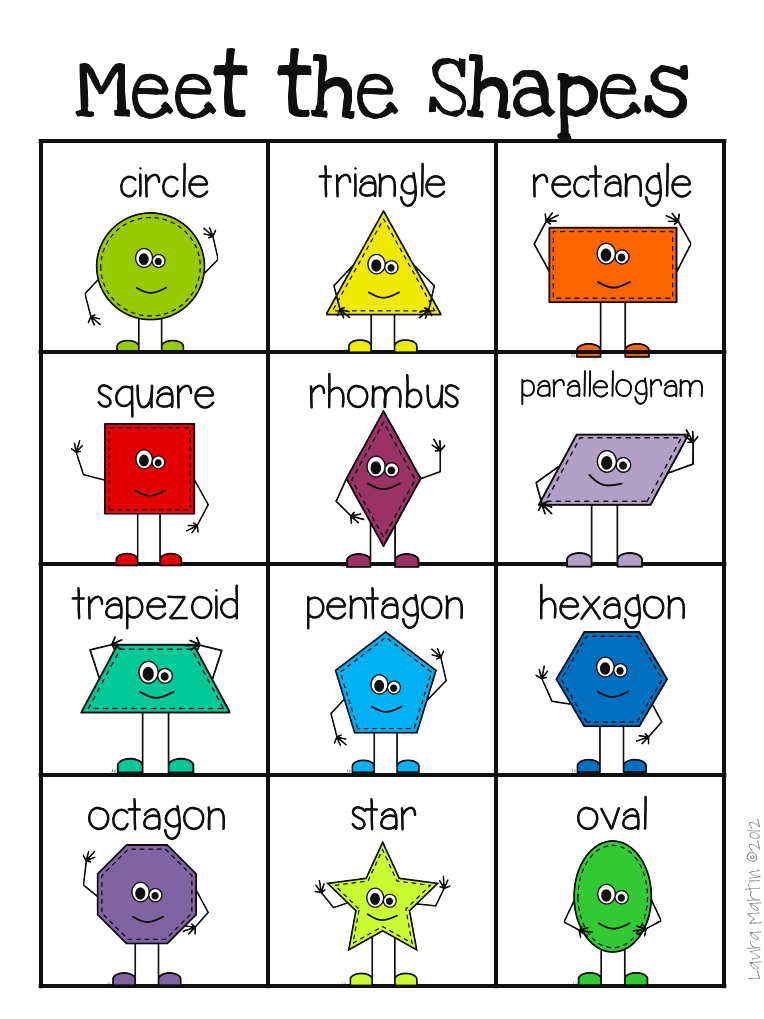
Three-dimensional figures can be used to get acquainted with the forms. It can be made by a designer, a sorter, lacing, frame inserts. Since at an early age the visual-effective type of thinking is most developed, various actions with figures will help to remember them better.
How children of different ages perceive geometric figures
The operations that a child can perform with geometric figures and how he perceives shapes depend on the age of the baby. In accordance with age characteristics, the following stages of training can be distinguished:
- In the second year of life, the baby is able to visually recognize familiar figures and sort objects according to shape.
- At 2 years old, a child can find the desired shape among a number of other geometric shapes.
- By the age of 3, babies can name shapes.
- At the age of 4, a child is able to correlate three-dimensional figures with a flat image.
- At senior preschool age (and sometimes even earlier) you can start studying geometric bodies (ball, cube, pyramid). Also at this age, the child can analyze complex pictures consisting of many shapes.
Regardless of the child's age, try to pay attention to the shapes of the surrounding objects and compare them with known geometric shapes. This can be done at home and on the go.
Games for learning geometric shapes
For a child to be interested, learning geometric shapes should take place in a playful way. You should also select bright and colorful materials for classes (you can buy them in a store or do it yourself). Here are some examples of games and tutorials for learning geometric shapes:
- Sorting. Games with a sorter can be started from the age of 1. Invite the child to find its window for the figure. So the child will not only memorize geometric shapes, but also develop fine motor skills, thinking and spatial representations, because in order for the part to fall into the hole, you need to turn it at the right angle.
 You can also sort any other items, such as building blocks, Gyenesch blocks, or counting material.
You can also sort any other items, such as building blocks, Gyenesch blocks, or counting material. - Insert frames. In fact, this manual is similar to a sorter. For each geometric figure, you need to find its place.
- Geometric lotto. To play, you will need a field with the image of geometric shapes and handout cards with each figure separately. A child can take small cards out of a chest or bag, and then look for their place on the playing field. This game also perfectly trains the attention of the baby.
- Geometric appliqué. Cut out various geometric shapes from paper and, together with your child, make a picture out of them (for example, you can make a Christmas tree from triangles, a house from a square and a triangle).
- Drawing (including stencils).
- Modeling.
- Laying out figures from counting sticks.
- Geometric mosaic.
- Laces with geometric shapes.
- Card games.

- Guess by touch.
- Active games. Draw geometric shapes on the pavement with chalk. Ask the child to imagine that the figures are houses that you need to run into on a signal. Next, you name a geometric figure, and the child runs to it.
In addition, educational cartoons can be used to study geometric shapes. Here is one of them:
Conclusions
Learning the basics of geometry at preschool age is an important part of developing a child's mathematical and sensory representations. Acquaintance with the figures should occur gradually (first, simple figures - a circle, a square, a triangle). To keep your child interested, study geometric shapes in a playful way. Your assistants in this can be such educational aids as insert frames, mosaics, lotto, sorters, sets of geometric shapes and bodies, stencils. You can also study geometric shapes on the street: just talk to your child about what you see around and what shapes these objects look like. Then the kid will definitely learn to distinguish geometric shapes and remember their names.
You can also study geometric shapes on the street: just talk to your child about what you see around and what shapes these objects look like. Then the kid will definitely learn to distinguish geometric shapes and remember their names.
Conclusion
Montessori environment has been specially created for the comprehensive and harmonious development of each child in the children's center "Constellation". In the process of free work in it, children not only get acquainted with the basics of geometry, but also develop their cognitive processes, fine motor skills, learn to write, read, and count. In addition, the Montessori environment gives the child the opportunity to fully demonstrate independence and responsibility. We will be glad to see you and your baby at our center!
Prepared by a Montessori teacher
Malysheva Evgenia
Geometric figures in the lesson in the middle, older and younger groups
Children have the ability to distinguish the shapes of objects almost from birth.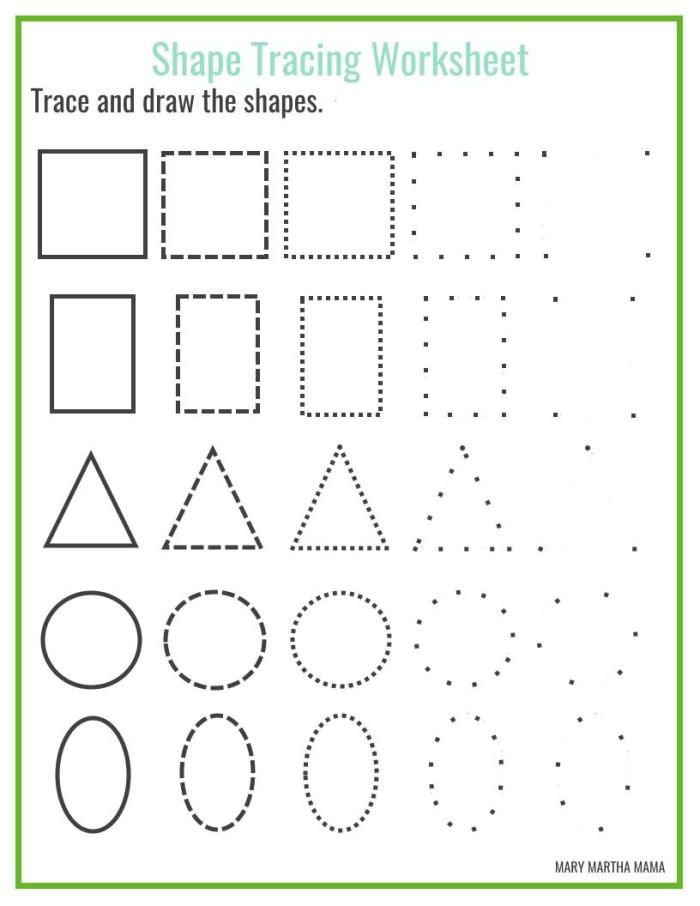 When studying geometric shapes, the lesson in the middle group should be built using a variety of methods of working with children. The more exciting the games and conversations are, the more firmly the children will master the initial concepts of geometry.
When studying geometric shapes, the lesson in the middle group should be built using a variety of methods of working with children. The more exciting the games and conversations are, the more firmly the children will master the initial concepts of geometry.
At what age can one start studying geometric shapes
A child's knowledge of the world around him begins with his perception of objects and phenomena. At the youngest age, babies are not yet able to understand the shape of an object separately from itself. In fact, they get to know them using various senses: not only with the help of sight, but also by touch, as well as by pronouncing various words.
Study kit
Comparison plays an important role in this process. Seeing a new object, the baby can determine if it is similar to others already known to him.
In the process of his development, the child perceives the geometric shape of objects in different ways. Young children see and feel them as a whole, without highlighting the form.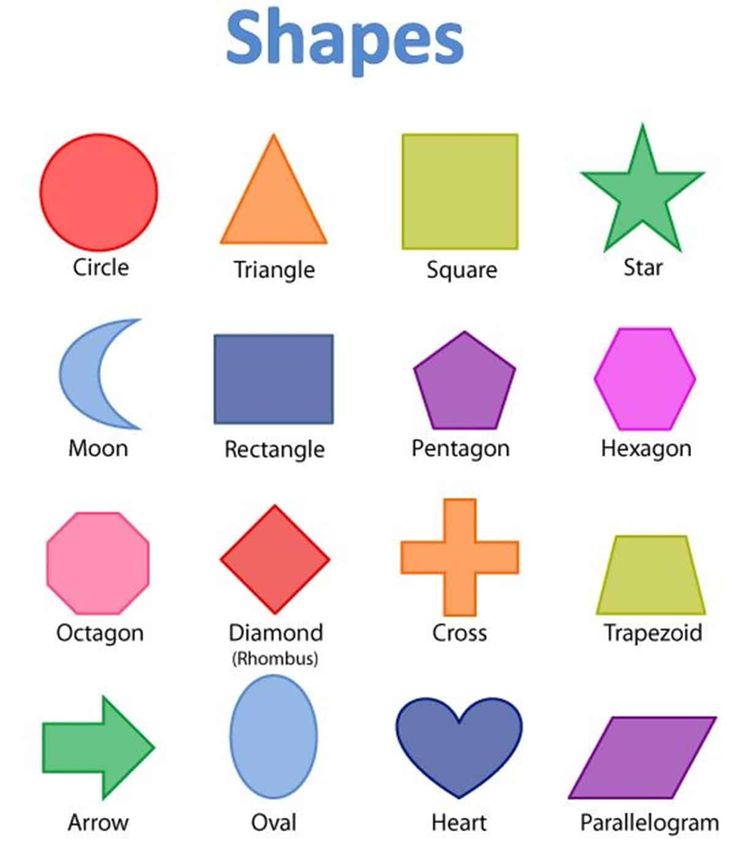 That is, each ball is not a ball for them, but a special object.
That is, each ball is not a ball for them, but a special object.
At an older age, the baby can already compare objects, determining their similarity or difference. Gradually, he learns to highlight the elements of the form properly. At senior preschool age, he already understands what a geometric figure is and what properties it has.
However, the development of geometric perception and thinking does not occur automatically, but in the learning process.
It is important to note that the acquisition of initial geometric knowledge and learning to count is of an introductory nature. At the same time, there is no systematic study of geometric knowledge. No precise definitions are being considered at this time.
Important! In the process of learning, children learn to recognize and study figures, draw them, describe them in Russian.
Learning geometric shapes with kids in preschool
While studying geometric concepts in parallel, children also receive other knowledge and skills:
- they learn to think logically;
- get the opportunity to develop knowledge of the Russian language;
- improves the perception of space, the ability to navigate in it;
- children develop fine motor skills;
- intellectual qualities develop: the ability to make comparisons, analyze, generalize.

Please note! When teaching in kindergarten, the development of geometric concepts is not singled out as a separate topic, but occurs in combination with other topics.
Children learn geometry
Learn colors and shapes for children from 2 years old
Teaching geometry should start with the simplest shapes, more complex ones are best left for subsequent years. It is believed that on a subconscious level, children are able to perceive the form already six months after birth. At this time, the main way of learning is mentioning during the story. Showing pictures, you can casually notice that the objects depicted on it have a certain shape.
When learning, you need to take into account that babies are still able to learn to distinguish between the simplest ones: a circle, a square and a triangle.
Please note! Study in a year, two or three should be easy and fun. For mastering it is convenient to use volumetric figures. Studying, for example, a circle, one can imagine that he came to visit the baby. You can trace a circle around the contour with the child's finger. You can make such an application by decorating with eyes and nose.
Studying, for example, a circle, one can imagine that he came to visit the baby. You can trace a circle around the contour with the child's finger. You can make such an application by decorating with eyes and nose.
The child can play with this item: make a tower by putting one on top of the other, throw it aside or put it in a box.
This complex approach in a project dedicated to the study of geometric objects is very effective for toddlers, but at a younger age it can be considered the main way to learn shapes.
Under two years of age, the following can be used:
- children's ability to compare objects;
- apply a children's educational set, where you need to choose a hole that is suitable in shape and size for the figure.
A 2-year-old child is able to choose the right shape from the set.
When teaching figures for children of 3 years old, they can already show the one that was named by the teacher.
Learning figures for children 3 years old
When teaching children geometric shapes, it is important to consolidate their familiarity with the material that they have learned earlier. You need to continue studying and move on to those that are more difficult to understand - this is an oval, rhombus and rectangle.
When teaching toddlers, you can show children patterns of figures, letters of the alphabet and match them with other objects in shape and size.
Important! On a walk, children are told about the objects they see with a mention of their shape and the simplest geometric properties.
An important role when learning geometric shapes with kids is played by creative activities when kids draw or sculpt samples, put them together from a given set of components.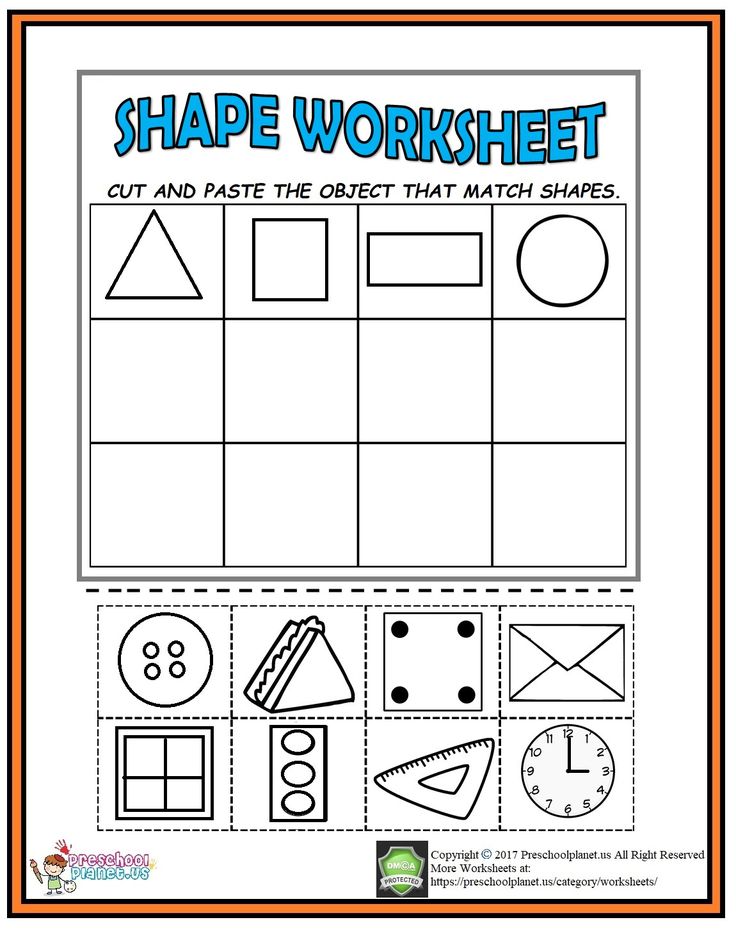
Based on the cards with the image of complex objects, the child is asked to tell about the components in the form of certain figures.
Child education poster
Geometric figures in the senior group
At this time, the lessons move on to the consideration of new, more difficult to understand figures, repeating those that they should have known before.
At the age of five, children are invited to consider and talk about their common and different properties. For example, they ask questions about where open figures have corners, and in what cases they do not.
They try to teach children to analyze the complex forms of real objects, to find elements in them that have the form of simple figures. They learn about more complex shapes, such as the cone.
Geometric figures in the preparatory group
At this age, children have already mastered the basics of understanding the shapes of objects. At this stage, it is important to develop knowledge, to make it more systematic.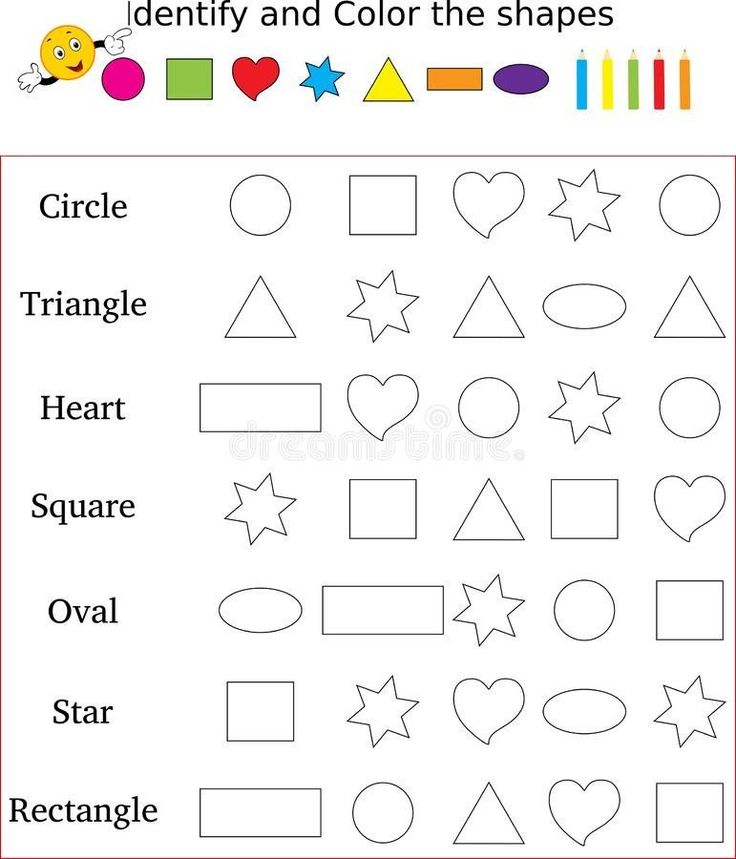 At this age, the basis for school education is created for kids.
At this age, the basis for school education is created for kids.
Please note! Children in the preparatory group, introducing polygons, are told about their sides and angles, taught to find the desired figure from the description.
Here is an example of an educational game that can be included in the lesson outline and used for teaching. Children are given a set of figures. The player lays out one of them. Another should put next to one that differs in only one feature. For example, if one proposes a large blue square, then another may lay out a small blue square, a large yellow square, or a large blue circle.
The teacher tells the children about the figures
Tasks and exercises for studying geometric shapes
To organize the process of teaching kids about FEMP geometric knowledge, special methods of work are used.
In this case, you can use the following tasks or exercises:
- Children are offered posters on which tables with square cells are drawn.
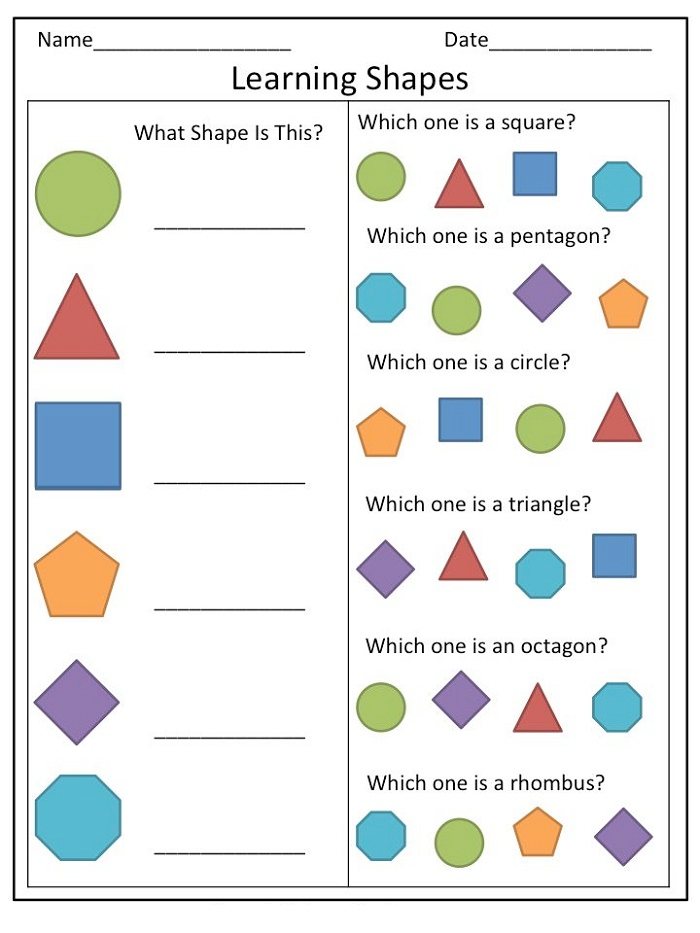 They can have different sizes and be shaded. Kids are asked to determine where there are more squares, to compare their size.
They can have different sizes and be shaded. Kids are asked to determine where there are more squares, to compare their size. - The picture shows a caterpillar made up of green circles. Two legs come out of each. Children are offered posters showing caterpillars of different lengths in order to compare them and determine which ones are tall or short, long or short.
- A large number of simple geometric shapes are drawn on the poster in the form of contours. At the same time, figures of the same type have the same color, and different ones differ in their color. Children are offered to divide the drawn figures into groups. This can be done verbally or by cutting them out and putting them into several piles.
- Children at preschool age need to be educated to understand the basics of mathematics — the relationship between figures and numbers. To better master it, children are shown drawings where several squares are shown side by side, in the other part of the circle, in the third - triangles.
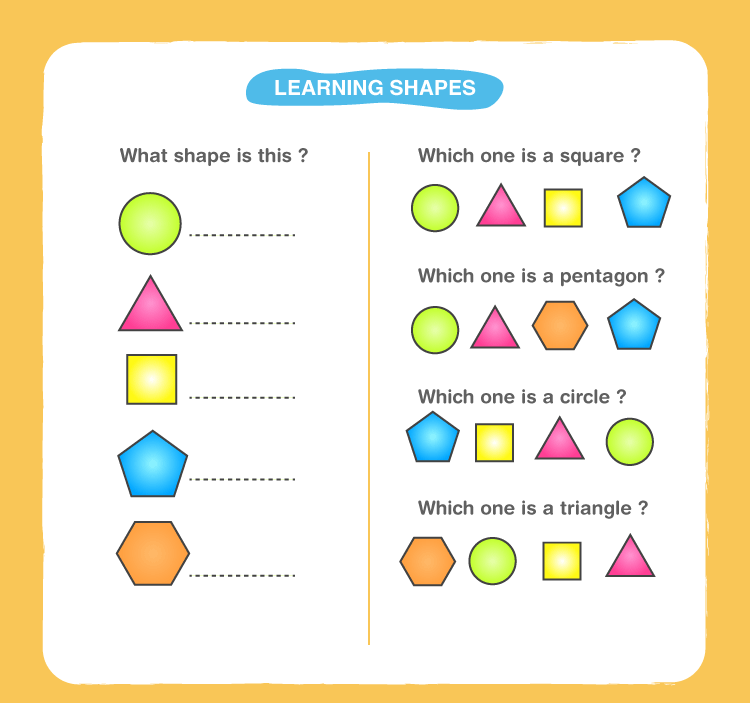 In the form of a task, they are offered to count them. They also draw simple addition and subtraction examples to learn counting. For example: two circles, a plus sign, two squares, an equals sign, then draw two circles and two squares in a row.
In the form of a task, they are offered to count them. They also draw simple addition and subtraction examples to learn counting. For example: two circles, a plus sign, two squares, an equals sign, then draw two circles and two squares in a row. - Using checkered paper, they offer to draw figures according to the parameters set by the teacher.
- You can use stripes of different colors and lengths, but the same width, to help your little ones learn the concepts of "more" or "less". By superimposing stripes, you can determine which of them will be longer and which will be shorter.
Preschoolers can build more complex figures from a given set of elementary ones. For example, the Tangram game can be used for this purpose. In it, the square is cut into several pieces, from which it is necessary to add the given complex figures.
Toddlers learn to recognize shapes
The following methods can also be applied to children: