Teaching to share
Tips for teaching children to share
Sharing (or, more precisely, the lack thereof) is a common topic among parents and educators of young children.
Reading different Facebook groups, you’ll often find posts about children who won’t share and caregivers questioning how to help them. The advice given on those boards can vary widely from buying numerous copies of the same toy so everyone has one, to using a timer to set the amount of time a child can use a toy.
But what is sharing at its core and why do we ask young children to do it?
Developmental readiness for sharing
Sharing teaches cooperation, collaboration, and teamwork. Sharing with friends and family can increase the unity and bond you feel with them. Many acts of kindness involve sharing — of time, money, or resources. Personally, sharing can make us happier and live longer.
The ability to share is a developmental milestone. Just like you wouldn’t expect a 3-month-old to walk or a 2-year-old to read, you can’t expect your child to share until they are developmentally ready to share. I know, I know… somewhere out there is a parent or educator who is saying, but my child COULD read at 2 years old! However, just like any other milestone, there is an age range, but most children will not even begin to understand the concept of sharing until they are able to understand that others have a different point of view from theirs.
Consider the stages of children’s psychosocial development (psychosocial relates to one’s psychological development in, and interaction with, a social environment; in other words, how a child grows and relates to the society around him). Young children are naturally very egocentric. They have difficulty seeing anything outside their own point of view.
Egocentrism is very different than egotism. The egotist believes that she or he is superior to others. Egocentricity in young children is a developmental stage. They are egocentric not because they are selfish or self-centered, but because they are incapable of seeing things from another’s perspective.
Many researchers — for example, Piaget and Erikson — have shown this to be true. They have proven that during the ages of approximately 2 – 7 years old, children are slowly learning to understand that others have different thoughts, perspectives, and ideas than their own. During this period children will be resistant to parents and other caregivers asking them to share because they are only just beginning to understand the concept.
Is that to say that we shouldn’t ask our children to be giving with others? Should we not ask them to share their toys? No. Just like any other skill, sharing takes practice, time, and positive reinforcement. There are many things adults can do to help a child learn to share.
Tips for teaching sharing
1. Sharing is not just about objects
Sharing is not just about sharing your physical belongings. It’s not just about those favorite blocks or doll. Sharing is also about sharing time, turns, and themselves. Young children are just beginning to learn to take turns, to wait until daddy finishes the dishes to read a book or to share their time helping a grumpy friend feel better.
It’s very helpful for adults to model and encourage sharing of all kinds. So whether you are making soup to take to your sick neighbor or waiting in line at the grocery store, these are opportunities for you to teach your child about sharing in a natural way.
2. Teach the language of sharing
Early on, it’s important that your child hears the language of sharing. For example, I’ve worked with children in a multi-age environment. I had an infant and several toddlers, along with slightly older preschoolers together in my program. The infant’s needs often took precedence over many of the older children’s needs. When an infant needs to be fed or held or changed it’s obviously important to take care of those needs quickly.
Inevitably, the needs of the baby coincided with the toddlers’ and preschoolers’ needs. So, while I was feeding the baby, I would be talking to the other children, saying things like:
- “I know how frustrating it can be to wait, but right now it’s the baby’s turn.
 Soon it’ll be your turn.”
Soon it’ll be your turn.” - “Can you help me with the baby by bringing me the wipes? Wow! What a good helper you are.”
- “Can you sing the baby a song while I’m changing her diaper? She’s not very happy right now.”
Give the children words for their feelings, frustrations, and actions. Praising their ability to share (whether it be sharing their time, their feelings, their toys, etc.) gives them the confidence to try it again.
I also made it a point to talk out loud to the baby when it wasn’t her turn. For example, when I was in the middle of serving lunch to 5 hungry children and the baby became fussy and cried, I would say, “just a minute, baby! Right now it’s their turn, but next it’ll be your turn,” or “hold on, baby, I just need to serve everyone their lunch and then it’ll be your turn.” This wasn’t really for the baby’s sake; it provided the older children with the language of taking turns. It allowed them to internalize the fact that they were all taking turns and sharing.
3. Play cooperative games
Playing cooperative games with your child is a great way to reinforce the concept of sharing in a fun, relaxed environment. Taking turns while playing a board game or putting together a puzzle can give children practice sharing with others. Even informal games you play with your toddler or preschooler such as rolling a ball back and forth across the room or taking turns adding a block to a tower can give your child another way to practice sharing.
4. Allow your child to not share in some cases
There are times when it’s perfectly okay for your child not to share. In these situations, it’s important for you to set up your child for success. For example, your friend is coming over to your house with her children. You know there are toys that are very special to your child. Make sure to put away the toys that are very special to your child so that they aren’t an issue or allow your child to put things in their room that they don’t choose to share and shut the door. Giving your child the space to keep certain things for themselves may help them be more willing to share their other toys.
Giving your child the space to keep certain things for themselves may help them be more willing to share their other toys.
5. Set your child up for success
Plan ahead and prepare your child for whatever situation is coming. Explain what will be happening in simple terms. For example, “Daddy’s friend Max and his kids are coming over this afternoon. When they get here they are going to play with you! How fun it will be to play together with your toys! I know that some toys like your teddy bear are very special to you. What do you think about putting Teddy away while your friends are here so he’ll be safe in your room?”
6. Positive reinforcement and direction
Just like with any other skill your child is learning, it’s important for you to be patient and offer positive reinforcement as your child learns to share. I know it can be embarrassing when your child loudly refuses to share their sand toys at the park or when your preschooler hoards all of the Legos at the table. Instead of escalating the situation and trying to force your child to share, diffuse the situation by bringing out something they can do cooperatively such as play dough or coloring. Change up the environment by bringing them outside. And remember, once your child is sharing, offer praise for their efforts!
Instead of escalating the situation and trying to force your child to share, diffuse the situation by bringing out something they can do cooperatively such as play dough or coloring. Change up the environment by bringing them outside. And remember, once your child is sharing, offer praise for their efforts!
In-class or home techniques to try
Here are some tried and true techniques that have been used by preschool educators for decades:
1. Have multiple of favorite toys
While this may be more practical in a group care setting, having multiples of favorite toys can take the pressure off. However, this doesn’t always work. Toddlers and preschoolers are unpredictable. They still, somehow, often fixate on “the one” even when all of the toys are identical. I’ve dealt with arguments over a specific yellow chair (when all the other chairs were also yellow) or the red playground ball (when all the other balls were also red).
2. Use a timer to take turns
Some educators set a timer for turn-taking. They will give each child a certain amount of minutes before they need to stop and give the toy to the next friend. This can be helpful because it takes out the adult element. The timer is to blame for your turn being over. However, a pitfall with this technique is that it stops a child mid-play which can be upsetting.
They will give each child a certain amount of minutes before they need to stop and give the toy to the next friend. This can be helpful because it takes out the adult element. The timer is to blame for your turn being over. However, a pitfall with this technique is that it stops a child mid-play which can be upsetting.
3. Allow children to play with a toy until they’re done and then share
In my program, this was the method I used most often. All of the children knew that if you chose a toy it was okay to play with it until you were done and then it was the next person’s turn. It wasn’t okay to hoard all of a certain type of toy and it wasn’t okay just to carry that toy around or hide it when you weren’t using it, but if you were actively using that toy, it was yours until you were done.
Through the years, I found that this technique took a lot of pressure off of me and the children. When they had control of the situation, they often shared more quickly and effortlessly than any time I asked them to share. The others learned that everyone who wanted a turn would get one. Obviously, this didn’t work smoothly all of the time. Toddlers and preschoolers aren’t known for their patience and understanding. I had some crying tantrums and frustrated children, but no method works smoothly for every child.
The others learned that everyone who wanted a turn would get one. Obviously, this didn’t work smoothly all of the time. Toddlers and preschoolers aren’t known for their patience and understanding. I had some crying tantrums and frustrated children, but no method works smoothly for every child.
4. Make a list
Allow children to set up a schedule of their own. I saw in another program recently where an educator had a clipboard and a paper/pencil. When there was a particular thing many children wanted to use, they were responsible for putting their name (or their letter or their shape or however they could mark their spot) onto the list. The child playing would check the list when they were done and the next person took a turn. This turns control over to the children and allows everyone to be listened to and get a turn. It also has the added benefit of sneaking in some purposeful, meaningful writing.
The road to teaching a child to share is a marathon, not a sprint. It’ll take time, but through positive reinforcement, modeling, and patience, your child will be well on their way!
How to teach your child to share
In this article
- Why does my preschooler find it hard to share?
- How can I teach my preschooler to share?
It’s perfectly normal for your preschooler to find the idea of sharing tricky. Children generally understand the concept of sharing at about age three. But it will take a while longer before they’re prepared to do it (Zero to Three nd). You can encourage your child to share by setting a good example and by teaching them to problem-solve. Read on for more tips.
Children generally understand the concept of sharing at about age three. But it will take a while longer before they’re prepared to do it (Zero to Three nd). You can encourage your child to share by setting a good example and by teaching them to problem-solve. Read on for more tips.
Why does my preschooler find it hard to share?
Although your child is starting to develop empathy, and knows that they need to take turns, they aren’t mature enough yet to resist all of their impulses. Most three-year-olds and four-year-olds put their own needs first, and can get upset when the needs of others get in the way (Zero to Three nd).
Your child may not understand enough to realise that even if they don’t have a toy now, it’ll be their turn soon. So don’t be surprised when you see them grab a truck from a friend, or refuse to let their sibling look at their favourite book.
Beneath the surface, though, your little one’s sharing skills are maturing. This is partly because they love getting praise from you and other trusted adults. They may enjoy drawing pictures for teachers, making presents for you and sharing snacks with their friends. You can sow the seeds of generosity by gently encouraging your child to share.
This is partly because they love getting praise from you and other trusted adults. They may enjoy drawing pictures for teachers, making presents for you and sharing snacks with their friends. You can sow the seeds of generosity by gently encouraging your child to share.
How can I teach my preschooler to share?
Set a good example
You are your child’s greatest role model when it comes to sharing. Let them see you give and take, compromise, and share with others in everyday life.
Teach your child cooperative games in which they have to work together with others, rather than competitive games which focus on winning. You could try doing a jigsaw puzzle together, taking turns to add pieces. Or you could blow up a balloon and play balloon tennis.
Share projects, too: water the plants, tidy up toys, or unpack the shopping together.
As far as you can, try to model and point out sharing and turn-taking in family life.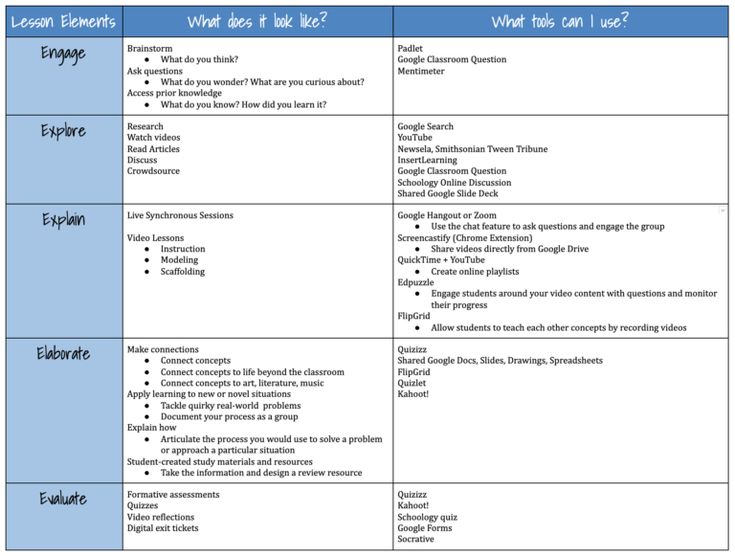 When you and your partner share food together, point out how nice it is to your preschooler and ask if they would like to share too. If you notice another child or sibling sharing, praising their behaviour in front of your little one will encourage them to do the same (Pathways nd).
When you and your partner share food together, point out how nice it is to your preschooler and ask if they would like to share too. If you notice another child or sibling sharing, praising their behaviour in front of your little one will encourage them to do the same (Pathways nd).
Talk about sharing
If your preschooler has a play date planned, have a chat with them beforehand about how important it is to share. Let them know that it’s normal to play with a friend’s toys if you go to their house, and vice versa. It may seem obvious to you, but it won’t be to your little one!
Where possible, encourage your preschooler to put themselves in their friend’s position: "If you went to Addy’s house and he didn’t let you play with any of his toys, how would you feel?". (Pathways nd)
If your child squabbles with a friend about a toy, try to intervene before things become too heated, and explain that each of them will have a turn (Pathways nd).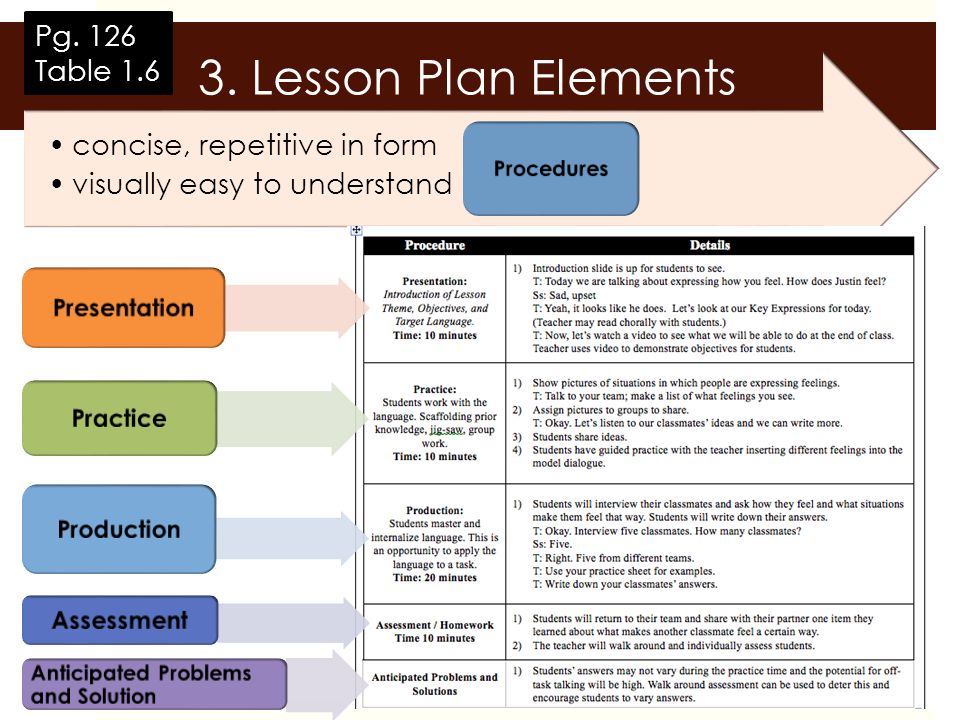 If either child starts having a full-blown tantrum, try to remove your child from the area until things have calmed down.
If either child starts having a full-blown tantrum, try to remove your child from the area until things have calmed down.
Once both children are ready to listen, discuss the situation with them in a thoughtful and compassionate way. The discussion only needs to be a minute long as children have short attention spans at this age. You can then quickly move the discussion towards a plan, "So, Ben is going to play with it for the first two minutes, then it will be your turn to play with it for the next two minutes."
If your child's friend is holding a toy back, explain how they may be feeling. For instance: "Josh really likes that toy, and he doesn't want anyone to play with it right now. Can you find something else to play with?"
Help your preschooler put their own feelings into words, too. You may need to give them the words, for example by saying, "It sounds like you feel cross", or "You’re looking a bit disappointed". This also reassures your child that you understand how they might be feeling (Zero to Three nd).
Don't punish but do step in
It can be embarrassing to see your child snatching a teddy from their friend, or throwing a tantrum because their turn with the trucks has ended. But if you tell your child that they’re selfish, or force them to hand over a prized possession of theirs, they may get the message that sharing has negative consequences.
When children feel ashamed or embarrassed, they sometimes become defensive, which makes it much more difficult for them to learn new skills. So give your child some leeway, and acknowledge that they’re probably not being deliberately mean or rude by refusing to share.
Keep in mind that it's natural for your child to want to keep some items to themselves, as they develop a sense of what it means to own something. Rest assured that as they mature, they’ll learn that sharing with friends is much more fun than playing alone.
Teach your child to problem-solve
Encourage your child and their playmate to think up ways themselves of sharing toys. For example, ask: "We only have one truck, how do you think we can all play with it?". You may be surprised at their suggestions! Giving your little one opportunities to be kind and generous will encourage them to do it more often (Zero to Three nd).
For example, ask: "We only have one truck, how do you think we can all play with it?". You may be surprised at their suggestions! Giving your little one opportunities to be kind and generous will encourage them to do it more often (Zero to Three nd).
Respect your child’s possessions
If your preschooler feels that their clothes, books and toys may be lost or damaged, they’ll be less willing to share them. So ask permission before you let their sibling or friend borrow their crayons, and give them the option of saying no.
Make sure that siblings and friends respect your child’s things too, by encouraging them to ask if they can use them and making sure they take care of them.
Reassure your little one that sharing isn't the same as giving away, and point out that if they share their toys with friends, their friends will want to share back.
Before a play date, ask your child if there's anything they’d rather not share, and help them find a safe place to put their special toys (Pathways nd). Then ask them to think about things that would be fun for them and their guest to play with together, such as walkie-talkies, art and craft supplies, or a bat and ball. Ask their friend to bring along a few toys too, so your child isn’t the only one sharing.
Then ask them to think about things that would be fun for them and their guest to play with together, such as walkie-talkies, art and craft supplies, or a bat and ball. Ask their friend to bring along a few toys too, so your child isn’t the only one sharing.
Learn more about when your child will start to show empathy for other people’s feelings, and find out when to teach them about respect.
More on preschooler behaviour:
- What to do if your little one has got into the habit of biting their nails
- How to put a stop to teasing
- What to do when your child has a meltdown
- Tips on developing your child's social skills through active play
References
Pathways. nd. Getting Preschoolers to Share… How Do You Do It? www.pathways.org [Accessed June 2021]
Zero to Three. nd. Helping Young Children With Sharing www.zerotothree.org [Accessed June 2021]
Show references Hide references
90,000 Should a child be taught to share?Author of article Kravtsova Elena Mikhailovna
7922 views
September 15, 2021
Just now your child was peacefully playing with another kid in the sandbox, and you were enjoying a warm day, rare for late autumn, when suddenly his bitter cry cuts the air. What happened? It turns out that the boy with whom they just made Easter cakes took his favorite scoop. The mother of the “opponent” persuades your sobbing child: “Well, for a minute, what are you sorry for?”. Familiar?
What happened? It turns out that the boy with whom they just made Easter cakes took his favorite scoop. The mother of the “opponent” persuades your sobbing child: “Well, for a minute, what are you sorry for?”. Familiar?
About whether it is necessary to teach the baby to share, we talked with a child psychologist Elena Mikhailovna Kravtsova .
Where does what come from?
At about 1.5 years old, many children shock their parents for the first time with their stinginess, they do not want to share with anyone. If they try to take away a toy, kids fight, scream or silently run away from peers who encroach on their property. Why is this happening?
The fact is that babies do not have an idea of \u200b\u200btime, so the argument “another child will play and give it back” does not work. For a baby, there is only “here and now”, and if someone takes his car, for a small owner it is “forever”.
This is normal!
Unwillingness to share is a sign of the normal development of the child. Children have different temperaments, so for some it will be stronger, for others it will be weaker. In any case, we must remember that “no” uttered by a child is a way to “defend” one’s independence, to declare oneself as a person. What adults might describe as greed is actually a normal sense of ownership. The kid begins to realize that he is a separate person and there is something in the world that belongs only to him. Children perceive their things as part of themselves. Therefore, the reluctance to share is just a completely desirable phenomenon in childhood.
Children have different temperaments, so for some it will be stronger, for others it will be weaker. In any case, we must remember that “no” uttered by a child is a way to “defend” one’s independence, to declare oneself as a person. What adults might describe as greed is actually a normal sense of ownership. The kid begins to realize that he is a separate person and there is something in the world that belongs only to him. Children perceive their things as part of themselves. Therefore, the reluctance to share is just a completely desirable phenomenon in childhood.
We respect the word "no" spoken by a child
Learning to say “no” is like learning to feel important. This ability is the key to high self-esteem and self-respect. All this develops only when others respect the feelings and interests of the child, do not try to “break” him.
What should parents do?
The main thing that can be advised is not to force children to share. It is better to calmly explain to the surrounding children that your baby has not played enough himself yet and is not ready to give his car or doll.
In no case should you insult or ridicule the little "miser", and even more so - take away his toy and give it to another child, even if it is a brother or sister. Remember: the more adults "pressure" on the baby, the less he wants to share.
The wisest parental tactic during this period is to be sympathetic to the feelings of the child, while explaining to him what others are experiencing. “Vitya so wants to drive your truck, he probably never saw such a car. He'll be so upset if he doesn't get to play with that truck. Look how upset he is already."
The main task of parents is to gently, without violence, awaken a sense of empathy in the baby, make him want to share and make sure that his own interests are not infringed. If the baby refuses to empathize, do not insist. He's just not ready for this yet.
Be on the child's side
If another child's mother insists that your child share a toy, you should be politely firm. You can answer like this: “Unfortunately, my baby is not yet ready to share, he himself has not yet played enough. ” And at the same time, you need to keep the thought in your head: “This is his full right.”
” And at the same time, you need to keep the thought in your head: “This is his full right.”
What if a child gives even what he needs?
It all depends on the specific situation. Some babies are so peaceful and social that it is more important for them to share and see how the other plays than to stubbornly take away their toys. If a child gives everything in a row because this is his game, he sees what will come of it - that's okay. But if the baby gives away his toys with fear, while crying bitterly and tormented, he needs help.
Important!
Remember: the period of "greed" is short-lived. Growing up, the child will understand that his things do not cease to belong to him if they were used by other children. And learn to experience the joy of their own generosity.
Author of the article Kravtsova Elena Mikhailovna
Psychologist, child and adolescent
All expert articles
Articles about child nutrition, development and health
- All articles
- Food
- Health
- Development
- A family
Child's age
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
808 views
How to teach your child to fall asleep on their own
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
239 views
How to teach a child to crawl
Starting complementary foods Dry cereals - a triple benefit in every spoonThe benefits of ripe fruit in juices Fruit pieces from natural fruits and berriesDo babies really need cow's milk?Video: Baby milkshakes, is it possible?Do children need probioticsHow to wean a child from night feeding?How to choose a high chair
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
559 views
When babies start holding their heads on their own
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
400 views
How to teach a child to eat with a spoon on his own: games and discipline
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
471 views
One, but a long one: when a child switches to one nap
How much sleep a child should have Video: how to dress your child for a walkVideo: How to choose the right first shoes for your baby Colic in newborns: how to helpHow to prepare for conception
Login or register to save articles and products to favorites
Development
9588 views
Teaching your baby to wash their hands
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
795 views
How to wean a child from sucking on a pacifier
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
3877 views
Why does a child suck his thumb and how to wean him
Login or register to save articles and products to your favorites
Development
19258 views
12 questions about children's whims: psychologist Elena Kravtsova answers
Active and hyperactive: what's the difference? Self-care skills: what and when?
Showing 9 of 103 articles
Load more
We use cookies to make sure our website works properly, personalize advertisements and other content, provide functionality social networks and analyze network traffic.