Math games table
Multiplication Tables with times tables games
At Timestables.com you can easily practice all of your tables. The arithmetic problems are clear and simple so you can immediately get started on practicing your tables. Select one of the multiplication table you wish to practice from the list below and show what you can do on the speed test or printout great worksheets.
Choose the table you want to practice from the following. First you can practice the multiplication facts in sequence and once you have got the hang of that you can practice all the sums in random order for each table. If you have forgotten any answers, just go back to the 'all tables in sequence' page and practice them again thoroughly before trying again.
Once you have got the hang of a number of tables you can select the speed test and choose the tables you want to practice getting quicker at. If you make a mistake, you came see what the right answer is at the end of the test. This will help you learn all of your tables.
The speed test is good practice for getting your tables diploma. On the tables diploma the questions are a bit quicker than on the speed test, but if you get all of them right you will get your tables diploma. There are two tables diplomas. The little diploma is made up of 30 questions. Your little diploma shows you can do the 1,2,3,4,5 and 10 times tables. For the big tables diploma you are given 40 questions which include all the tables from 1 to 12.
Learn the multiplication tables in an interactive way with the free math multiplication learning games for 2rd, 3th, 4th and 5th grade. The game element in the times tables games make it even more fun learn.
Practice your multiplication tables
Here you can find additional information about practicing multiplication tables at primary school. The 1 times table, 2 times table, 3 times table, 4 times table, 5 times table and 10 times table are the first times tables to be learned. The 6 times table, 7 times table, 8 times table, 9 times table, 11 times table, 12 times table and of course all the tables in random order are the next step.
Not every child finds it easy to learn all the tables, so it is a good idea to keep on practicing them regularly after you learned them. There are a few tricks which make it easier to learn the tables and continue to master them, such as putting the smallest number first, which makes it easier for many children to answer correctly. For example 4 x 9 is easier to work out than 9 x 4. Switching the multiplication sum around makes it easier to answer. What also often helps is to use the tables you know well for answering the sums in the more difficult tables. One example of this is 6 x 7, which is often said to be tricky. If you do 5 x 7 first and then add 1 x 7 it is suddenly easier to answer. You can do this the other way round too. For instance with 4 x 7 you can do 5 x 7 first then subtract 1 x 7.
Why do we put so much effort into learning tables? Well, the multiplication tables keep on coming up in the next primary school years and even when you're at secondary school. You don't see them as tables, but as part of bigger mathematical problems. And it isn't only at school, but in your everyday life it is useful to know your times tables well so you can quickly work things out, for instance when you are buying or selling vegetables on the market. If you have any questions, comments or ideas for Timestables.com, please use our contact form. We'd be glad to hear from you.
And it isn't only at school, but in your everyday life it is useful to know your times tables well so you can quickly work things out, for instance when you are buying or selling vegetables on the market. If you have any questions, comments or ideas for Timestables.com, please use our contact form. We'd be glad to hear from you.
The 5-step plan
Learn the times tables with the 5-step plan. We developed an innovative five step plan to help pupils learn the times tables in an effective and efficient way. This method has been tested at several schools and is recommended by teachers.
The steps are:
- Step 1a: View, read aloud and repeat. To get familiar with the table.
- Step 1b: Fill in your times tables answers in sequence and check if you got them all right.
- Step 2: Drag the correct answers to the questions.
- Step 3: Fill in your answers for the mixed questions and check if you got them all right.
- Step 4: Multiple choice questions will help you to improve by looking at the questions in a different way.
- Step 5: Proof your knowledge and get the diploma.
When you finished the 5 steps you can play the memory game or exercise with the worksheet. Other way to train more are with the tempo test, the 1 minute test or to play the times tables games.
We advise to exercise daily for 15 minutes for maximum result.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I learn my times tables fast?
Learn them in chunks. Start with the easy times tables like 10, 2, and 5. Use methods like skip counting, adding and exercising daily for 15 minutes for a maximum long-term result.
What is the hardest times table in the world?
The 7 times table is the hardest to learn because 7 is a prime number, and so the last digit does not repeat itself until 10 times 7. The hardest times table question is 6 times 8.
Which times table is the easiest?
The 10 times table is one of the easiest to learn. For a start, numbers in the 10 times table always end in a 0. And then the 5 and the 2 multiplication tables are also one of the easiest.
And then the 5 and the 2 multiplication tables are also one of the easiest.
Practice your time tables online
Multiplication tables are important and there are not many places where you can learn them quickly and easily, so we have come up with Timestables.com! Practicing your tables online is really easy at Timestables.com. The multiplication games are clear and simple so you can get started right away. Click on one of the tables to get started right away. Fill in the answers in the lines and when you've finished, click on 'check'. You will see right away which answers are correct and which are incorrect. You can also practice different times tables in one exercise so you can test whether you know them all.
You can also practice the tables interactively with the free multiplication games. On the multiplication games page we now have an answer-dragging game and a table balloons game.
Multiplication tables form the basis for the calculations that you do in the following years, so it’s important that you fully understand them.
Do you want to practice more math? Go to Mathdiploma.com - Here you can practice addition, subtraction, multiplying, dividing and a lot more!
We also have a fraction website! On Fractionsweb.com are lots of exercices about simplifying, adding, subtracting, dividing and multiplying fractions. There are fraction games, worksheets and 5-step plans!
All Games | Maths Chase
All Games | Maths ChaseMulti Select - Click to select multiple question types in the same game!
Global Game Settings
These settings will apply to all games linked from this page.
Multi Game Select [active]
Times Tables
- 2 Times Table
- 3 Times Table
- 4 Times Table
- 5 Times Table
- 6 Times Table
- 7 Times Table
- 8 Times Table
- 9 Times Table
- 10 Times Table
- 11 Times Table
- 12 Times Table
Addition
- Adding 1
- Adding 2
- Adding 3
- Adding 4
- Adding 5
- Adding 6
- Adding 7
- Adding 8
- Adding 9
- Adding 10
- Adding Doubles (to 10)
Subtraction
- Subtract 1
- Subtract 2
- Subtract 3
- Subtract 4
- Subtract 5
- Subtract 6
- Subtract 7
- Subtract 8
- Subtract 9
- Subtract 10
Division
- Divide by 1
- Divide by 2
- Divide by 3
- Divide by 4
- Divide by 5
- Divide by 6
- Divide by 7
- Divide by 8
- Divide by 9
- Divide by 10
Odd or Even
- Odd/Even (up to 10)
- Odd/Even (up to 100)
- Odd/Even (up to 1000)
Sequences
- Sequences (in 1s)
- Sequences (in 2s)
- Sequences (in 3s)
- Sequences (in 4s)
- Sequences (in 5s)
- Sequences (in 6s)
- Sequences (in 7s)
- Sequences (in 8s)
- Sequences (in 9s)
- Sequences (in 10s)
- Sequences (in 11s)
- Sequences (in 12s)
Prime Numbers
- Is it Prime? (up to 20)
- Is it Prime? (up to 100)
- Is it Prime? (up to 1000)
Place Value
- Place Value - Tens and Ones
- Place Value - Hundreds, Tens, and Ones
- Place Value - Up to Thousands
- Place Value - Tens and Ones
- Place Value - Hundreds, Tens, and Ones
- Place Value - Up to Thousands_
Round table “Mathematics is around us.
 Intellectual development of preschoolers through logical and mathematical games» | Preschool education
Intellectual development of preschoolers through logical and mathematical games» | Preschool education Round table “Mathematics is around us. Intellectual development of preschool children through logical and mathematical games”
Author: Senatorova Svetlana Vasilievna
Organization: MBDOU kindergarten “Rainbow”
Settlement: Penza region, Sosnovoborsky district, p.g.t. Sosnovoborsk
Purpose:
- Development of creative activity and initiative of teachers;
- Increasing the interest of teachers in expanding their knowledge of logical and mathematical games;
- Presentation of new logic games with children to enhance knowledge in mathematics.
Good afternoon, dear colleagues. Today we will talk about mathematics and the importance of logic games in preparation for school. First, let's remember: where did the science " Mathematics " originate?
Question: the birthplace of mathematics? nine0012
Ancient India. It was in archaic India that the science of numbers took shape, and then spread throughout the world, in the form of ordinary applied mathematics and as a higher philosophical doctrine.
It was in archaic India that the science of numbers took shape, and then spread throughout the world, in the form of ordinary applied mathematics and as a higher philosophical doctrine.
The scientific achievements of Indian mathematics are wide and varied. Already in ancient times, Indian scientists, on their own, in many respects, original path of development, reached a high level of mathematical knowledge. In the 1st millennium A.D. Indian scientists raised ancient mathematics to a new, higher level. They invented the decimal positional notation system familiar to us, proposed symbols for 10 digits, which, with some changes, are used everywhere today, laid the foundations of arithmetic, combinatorics, and various numerical methods, including trigonometric calculations. nine0005
Mathematics as a science was born in Greece. In the contemporary countries of Hellas, mathematics was used either for everyday needs (calculations, measurements), or, conversely, for magical rituals aimed at finding out the will of the gods (astrology, numerology, etc. ). The Greeks approached the matter from a different angle: they put forward the thesis "Numbers rule the world." Or, as Galileo formulated the same idea two thousand years later: "the book of nature is written in the language of mathematics."
). The Greeks approached the matter from a different angle: they put forward the thesis "Numbers rule the world." Or, as Galileo formulated the same idea two thousand years later: "the book of nature is written in the language of mathematics."
Question: name the great mathematicians of antiquity? nine0012
Pythagoras was born in Sidon, Phoenicia, about 570 BC. At a young age, Pythagoras went to Egypt to gain wisdom and secret knowledge from the Egyptian priests. Diogenes and Porphyry write that the Samian tyrant Polycrates supplied Pythagoras with a letter of recommendation to Pharaoh Amasis, thanks to which he was admitted to study and initiated into the sacraments forbidden to other strangers
Archimedes - an ancient Greek scientist, mathematician and mechanic from Syracuse. He developed methods for finding surface areas and volumes of various figures and bodies. His mathematical works were far ahead of their time and were correctly evaluated only in the era of the creation of differential and integral calculus. Archimedes is a pioneer of mathematical physics, one of the creators of mechanics as a science. Mathematics in his works is systematically applied to the study of problems of natural science and technology. Archimedes owns various technical inventions
Archimedes is a pioneer of mathematical physics, one of the creators of mechanics as a science. Mathematics in his works is systematically applied to the study of problems of natural science and technology. Archimedes owns various technical inventions
Question: what is mathematics?
What is mathematics? Mathematics (Greek mathematike, from máthema - knowledge, science), the science of quantitative relations and spatial forms of the real world.
What is logic? Logic is the science of the forms and laws of correct human thinking
Question: in what kind of activity will a child learn this science better?
The well-known psychologist L. S. Vygotsky said: “Scientific concepts are not assimilated and not memorized by a child, are not taken by memory, but arise and add up with the help of the greatest tension of all the activity of his own thought”
The game is the leading activity of a preschooler, and it is in it that the most important personal and mental neoplasms necessary for successful schooling should be formed. As V. A. Sukhomlinsky said, “There is no, and cannot be, full-fledged mental development without play. Play is a huge bright window through which a life-giving stream of ideas , concepts flows into the child's spiritual world. Play is the spark that ignites the flame of inquisitiveness and curiosity.”
As V. A. Sukhomlinsky said, “There is no, and cannot be, full-fledged mental development without play. Play is a huge bright window through which a life-giving stream of ideas , concepts flows into the child's spiritual world. Play is the spark that ignites the flame of inquisitiveness and curiosity.”
Watching the game, you can tell a lot about the level of development of the child as a whole. Each game is a communication of the child with others. In logical games, conscious discipline is brought up, the child is taught to follow the rules, justice, the ability to control his actions, rejoice at the successes of others, endure his failures. If the child is passive, does not show interest in games, if they are stereotyped and primitive in content, this is a serious signal of trouble in the development of the child.
In order for a child to be smart, cheerful, friendly and self-confident, it is not necessary for him to give a lecture on this topic (and this is not effective), you just need to play games that are useful for his age.
We are all interested in that children study well and as quickly as possible acquire a greater amount of knowledge. In this regard, the question arises: is it possible to accelerate cognition? The answer to this question is in the affirmative. But this cannot be achieved by hammering large portions of educational material into the heads of children from the outside, based on one memory. This can achieve the opposite, very negative result. nine0005
Therefore, the only correct way leading to the acceleration of cognition consists in the application of teaching methods that contribute to the acceleration of intellectual development (of course, without prejudice to physical development, but in harmonious unity with it). Education of preschoolers, based on the use of special logic games - puzzles, refers to such methods.
Question: how to convince a child to follow your example?
One of the ways out is to engage in creativity and play with him. It is worth taking a number of steps, thanks to which classes with a child will become a discovery not only for him, but also for you. nine0005
It is worth taking a number of steps, thanks to which classes with a child will become a discovery not only for him, but also for you. nine0005
Become a child again. Do you remember what you liked to do as a child? Who supported you in your endeavors, and who dissuaded you? Remember how you felt when you played, giving free rein to your imagination? Imagine that you are five years old again.
Question: Does mathematics occur in everyday life, and if so, how can it be used to develop children's mathematical abilities?
Mathematics is found everywhere in everyday home life. It is important to unobtrusively, in a playful way, draw the child's attention to such objects that under normal conditions do not interest him. They can be included in the play space. In the game, the child begins to solve learning problems imperceptibly. nine0005
Question: What didactic games can be offered to children?
D / game "The fourth is superfluous"
Purpose : consolidation of knowledge about the seasons, their signs, the development of logic.
Material : 4 round cards representing the seasons, 16 square cards representing the seasons.
Content: children are invited to look at the symbolic pictures of the seasons, define their name and order. Then the teacher places opposite the cards with the image of signs and phenomena of each season.
Children are asked to find the extra picture in each row and explain their choice.
An interesting game with figures for children 48 geometric figures are characterized by four features: shape , color, size, thickness.
Games with figures of Gyenesh are varied and are not limited to variants. It should be noted that in the set there is not a single exactly the same figure. Gyenes logic blocks are a kind of unique constructor for the development of analytical skills in children with the help of a variety of interesting educational games. With the help of these games, children train memory, attention and perception, learn to analyze information .
With the help of these games, children train memory, attention and perception, learn to analyze information .
Geometric figures in the set differ in the following properties:
- Form . Volumetric geometric figures in circle shape , square, triangle and rectangle. nine0005
- Bloom. These figures are painted in three primary colors - red, yellow and blue.
- Fitted. Big and small.
- Thickness. Thick and thin.
Therefore, each geometric figure in the set is characterized by four features: shape , color, size and thickness. Children often come up with games on their own. For example, “composing a chain” according to the rules: so that there are no identical shapes and the color of figures or the same size, etc.
D/game "Chain or train".
- alternating parts according to a certain feature .
For example,
- by color : blue, yellow, blue, yellow…
- by size : small, large, small, large…
- by square: 90, square: 90,011 , circle…
Comparative analysis method
Comparative analysis is a method of object analysis, which compares the new state of the object with the old one. ("What's Changed", "Spot the Differences")
Think and answer games.
Purpose : children's exercise in determining the seniority of people relative to each other; developing a sense of respect for the elderly. Development of logical thinking.
Material : pictures of people of different sex and age .
Content: the teacher puts 6 pictures of people in a row and asks the children to arrange them from the youngest to the oldest correctly. nine0005
Game "Euler Circles" or "Games with hoops" precedes the formation of one of the most important general educational skills - the ability to classify an object and develops the logical thinking of preschoolers. Children learn to classify objects according to 2 and 3 properties (color, size, shape , place them in 4 and 8 areas obtained from the intersection of 2 and 3 circles.
Children learn to classify objects according to 2 and 3 properties (color, size, shape , place them in 4 and 8 areas obtained from the intersection of 2 and 3 circles.
Modeling and construction is one of the means of knowing reality.
D / games "Collect - ka"
Purpose : fixing the names and order of the days of the week, fixing the ordinal number and numbers indicating the days of the week; development of visual perception of the whole.
Material : cards (7 pieces, divided into three parts (number - number - name of the day of the week) according to the type of puzzles).
Kuizener's sticks - set multi-colored sticks in different sizes , with the help of which children develop ideas about the number , the basics of counting, the ability to measure objects . Preschoolers quickly remember the composition of numbers, understand the essence of arithmetic operations.
Preschoolers quickly remember the composition of numbers, understand the essence of arithmetic operations.
Crosswords, puzzles.
Tasks : "What is round in nature?" (sun, moon, orange, apple, watermelon, tomato...).
"What is yellow in nature?"
(dandelion, lemon, pear, autumn leaves, water lilies, chicken….). nine0005
"When does this happen?" (winter, summer, spring, autumn)
Solving logic problems.
Logical tasks, exercises, puzzles contribute to the development of logical thinking and intelligence. For example: Which figure is superfluous? Why? How is one picture different from another? What figure is missing? And tasks, for example: Dunno, Pinocchio and Winnie the Pooh gathered for a walk and took a banana, a tomato, an orange with them on the road. What did each of them take? If Dunno took not round, but Winnie the Pooh - not red? nine0005
Question: what logic games can be offered to children in their free time?
Came to the group after a walk. You can offer logic puzzles:
You can offer logic puzzles:
1. The children made a snowman. After a walk on the radiator, 8 wet mittens dried. How many children were there?
2. 8 squirrel tails looked out from the hollow. How many squirrels were in the hollow?
Z. Grandfather, grandmother, granddaughter, a bug, a cat and a mouse pulled out a turnip. How many eyes saw the turnip?
4. The log was cut into three pieces. How many cuts were made? nine0005
5. 8 cat paws can be seen from under the gate. How many cats are in the yard?
“Who has more...”
.. .paws - a cat or a parrot?
. . .tails - a dog or a frog?
. . .ears - in a mouse or a pig?
. .. eye - a snake or a crocodile?
"Which number did I miss?"
An adult calls a series of numbers at a fast pace from 1 to 20, from 7 to 16.
One of the numbers is skipped. The child needs to name the missed. nine0005
"What's higher?"
House or fence?
Elephant or crocodile?
Table or chair?
Slide or sandbox?
Truck or car?
"Who else?"
What is more in the flower bed - flowers or tulips?
Who has more animals or bears in the zoo?
What is more in the apartment - furniture or chairs?
Say the number.
Name a number from 3 to 7, from 9to 12, from l4 to 5.
What number comes before 16?
What number comes after 8?
If you add 1 to my number, you get 10. What number did I have in mind?
I added 1 to the number Z and subtracted 1. How much did it become?
Look around.
What is rectangular?
What is round?
What is triangular?
Group games:
You can involve your child in the following game exercises between activities. nine0005
Which one?
There are toys on the shelf. Who is first? Third?
Who stands between the second and fourth? Who is second from the right? Who is the tallest?
Who is the shortest? If we rotate them so that they look to the right side, who will be the first now? Fifth?
"Playing with sticks".
You can play with counting sticks, matches or toothpicks, after breaking off the heads with sulfur from the matches. Post a figure like mine. nine0005
Post a figure like mine. nine0005
Move two sticks so that five equal squares are formed.
Remove two sticks to make four identical squares.
Lay out the same figure.
How many squares have I laid out now? (Four.) Remove one match to make three.
Number composition games.
One of the most difficult and important topics in mathematics is the composition of a number from two smaller numbers. You can consolidate knowledge on this topic in a playful way. nine0005
Nut exercise.
Take six nuts. Hold two in one hand and four in the other. Task options: 3 and 3, 1 and 5. Show the child how many nuts are in one hand, let him guess how many are in the other. Cover a few nuts with a glass. How much is visible? How much is in a glass?
Nikitin's Squares.
For the development of logical thinking, it is very useful to offer children various puzzles, for example, the games "Tangram", "Mongolian game". You can buy "Nikitin Squares", they come in different levels of complexity, you can make them yourself. To do this, cut out a square with a side of at least 10 cm, cut it into several parts, and then fold it into a whole together with the child. nine0005
You can buy "Nikitin Squares", they come in different levels of complexity, you can make them yourself. To do this, cut out a square with a side of at least 10 cm, cut it into several parts, and then fold it into a whole together with the child. nine0005
Question: What games and exercises can parents offer to develop their children's mathematical abilities at home?
On a walk:
- Spending time in nature, we can practice with children in ordinal and quantitative counting, in comparing objects (more - less, in recognizing geometric shapes and figures.
What can be counted on anything: benches, and trees, and bushes, and petals on a flower, and swings on playgrounds, and steps on stairs, and shovels in a sandbox, and much more.0005
Children will find it interesting not just to count objects, but to complete interesting tasks. For example: find two identical flowers, find objects that are square or triangular in shape, find the tallest tree in the area, find the thickest trunk of a tree in the park, find an object of the same height or width in the playground.
It is possible to measure the height and width of various objects using a conventional measure. For example, using the steps of an adult and a child, measure the perimeter of the sandbox.
Children will enjoy drawing various geometric shapes on the sand or snow. nine0005
In the store:
Where can you find the largest number of numbers and numbers? Well, of course, in the store. And not only numbers, but also concepts : more - less, lighter - heavier, thinner - thicker, more expensive - cheaper, and others can be mastered with a preschooler in a store.
The kid will like to put vegetables and fruits in a bag according to the rules set by adults. For example: “Katya, let's buy three lemons. Please put them in a bag" , "Vova, we need two carrots: one large and the other small" .
In the fruit and vegetable section of the store, the child will practice distinguishing shapes. Offer to find fruits (vegetables) that are round or oval in shape.
Before the next visit to the hypermarket, you can plan a route with your child in advance. You will move around the store according to the plan, move in a given direction, turning in accordance with the map. This will help improve the child's ability to navigate in the surrounding space. nine0005
In the store, a child can weigh food on a scale with the help of an adult.
While eating:
Children will enjoy doing "math operations" during meals.
After eating one slice of orange out of three on the plate, having carried out “subtraction”, calculate how much is left.
Comparing the ratio of children and cups, plates and spoons, come to the conclusion that their number is the same or equal, but there are different numbers of children and napkin holders. nine0005
You can fill one cup to the brim and the other half a cup and compare where there is more water.
Children will enjoy counting how many full cups a bag of yogurt (juice) can be poured into.
During labor assignments:
During labor assignments, the child can also practice counting, learn to create sets (groups of objects), from elements of different quality (objects of different colors, sizes, shapes, purposes, compare 9 of them0005
Count the number of flowers to be watered, the number of ficus leaves to be wiped, the number of toys, shelves and any other items.
When sorting toys on the shelves, you can give the task to place all the animals on the top shelf, dolls on the middle shelf, and put boxes with play materials on the bottom shelf.
In the boys' play corner, you can arrange the cars according to size: on the top shelf - only small ones, on the middle one - more, on the bottom - large ones. nine0005
To form an idea of equality: it is not difficult to determine the equal number in groups if you invite the child to put the same number of items on the bottom shelf as on the top.
In the kitchen while cooking:
Cooking lessons can be great math helpers. Children love to help in the kitchen.
Children love to help in the kitchen.
The child can be involved in the preparation of pastries, soups, salads. Fulfilling all the prescriptions of the culinary recipe, familiarization with the numbers, quantity, shape of objects will happen for the child by itself. nine0005
When cutting food, a child can learn division skills. Having easily mastered the concepts of part and whole, it will be easy to move on to understanding the topic of “fractions”.
In the process of cooking, the child must get acquainted with measuring units: milliliter and liter, gram and kilogram.
Children love to cut out curly cookies with different cutters: round, triangular, square and more.
It is important for adults to instill in a child an interest in logic games and in the learning process in general. These games should enter the child's life not as a monotonous theory consisting of mere examples and problems, but as a special world of mathematical phenomena. nine0005
Children who have extensive playing practice in their preschool years, in contrast to those who play little, adapt more successfully at school, adults cope better with life's problems.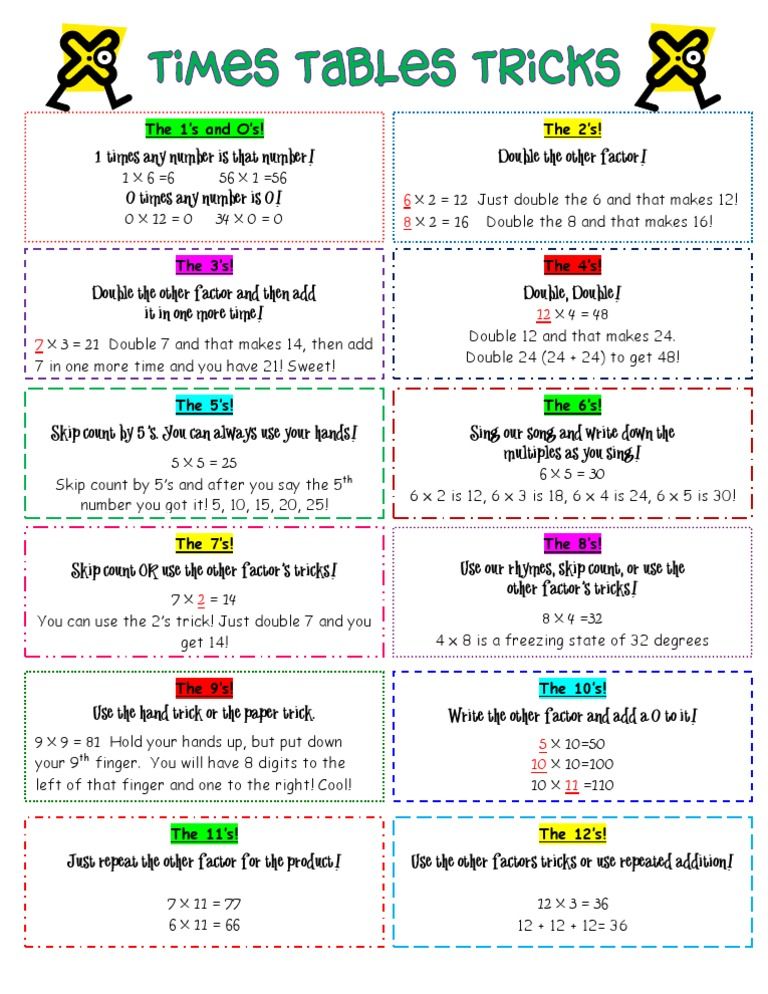 Playing logic games, the child satisfies the important need to be like an adult, freely express his desires, embody fantasies. Only thanks to logic games do they feel real inner freedom from the position of their dependence in the world of adults with numerous social norms and rules, which in the real world are far from being subject to everything, but in the world of game roles and relationships become available. nine0005
Playing logic games, the child satisfies the important need to be like an adult, freely express his desires, embody fantasies. Only thanks to logic games do they feel real inner freedom from the position of their dependence in the world of adults with numerous social norms and rules, which in the real world are far from being subject to everything, but in the world of game roles and relationships become available. nine0005
Mathematics is around us. The main thing is to be attentive and creative in the process of teaching children. When a child understands that mathematics is everywhere and realizes its role in everyday life, then learning will bring more benefits than a boring class at the desk.
Real math with practical application is what a preschooler needs.
Literature:
- Novikova V. P., Tikhonova L. I. “Developing games and exercises with Kuizener's sticks. To work with children aged 3-7. "MOSAIC-SYNTHESIS", 2008
- Kolman E. "The History of Mathematics in Antiquity".
- Mikhailova Z. A. Nosova E. A. Logical and mathematical development of preschoolers. Games with Gyenesh logic blocks and colored sticks" Detstvo-Press, 2019
VP Novikova Mathematical games in kindergarten and elementary school. Collection of games for children 5-7 years old. "MOSAIC-SINTEZ", 2011
Applications:
- file1.pptx.zip.. 4.8 MB
- file0.docx.. 33.0 KB nine0513
- figure ::= ellipse | rhombus | "snot"
- color ::= red | green | purple
- fill ::= white | striped | solid
- count ::= 1 | 2 | 3
Published: 11/29/2019
Mathematics and the game "Set" / Sudo Null IT News
Whoever finds a "set" here will get a chocolate bar from me.
Set is a brilliant game that we played 5 years ago. Screams, screams, photographing combinations.
The rules of the game say it was invented in 1991 by geneticist Marsha Falco, while making notes during a 1974 study of epilepsy in German Shepherds. For those whose brains are exhausted enough by mathematics, after a while there is a suspicion that there are some echoes here with planimetry and drawing lines through points. (For given two cards, there is one and only one card that is in the same set with them.)
(For given two cards, there is one and only one card that is in the same set with them.)
Marsha Falco seems to be asking, "Well, didn't you find the 'set'?"
Remembering the rules
Set is a card game. All cards have four parameters, each of which takes three values (total 3 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 81 cards).
The types and values of the parameters are:
The object of the game is to find special combinations of three cards. Three cards are called a “set” if, for each of the four attributes, the cards are either all the same, or all are different.
In other words, three cards will not make a set if two cards have one parameter value and the third card has a different one. It can be seen that for any two cards there will always be a third (moreover, the only one) with which they will be a set. nine0005
It can be seen that for any two cards there will always be a third (moreover, the only one) with which they will be a set. nine0005
Game progress: The host lays out 12 cards on the table. When someone finds a set, they shout "Set!" and then calmly takes the constituent cards of the set. If there is no set in the laid out cards (most likely, it just seems that there is not), the host lays out three more cards.
The maximum number of cards without a set is 20. The round continues until the deck runs out. The one with the most sets wins.
Mathematicians fussed and presented a combination of 20 cards. Who considers himself Chuck Norris can forget this picture and try to assemble "solitaire" without a set on his own. nine0537 Or check, what if there is still a “set” here?
20 cards without a set
It is convenient to check that there is no “set by color”.
The same cards, but the location shows that it carried sets according to the "fill" parameter.
Learn more