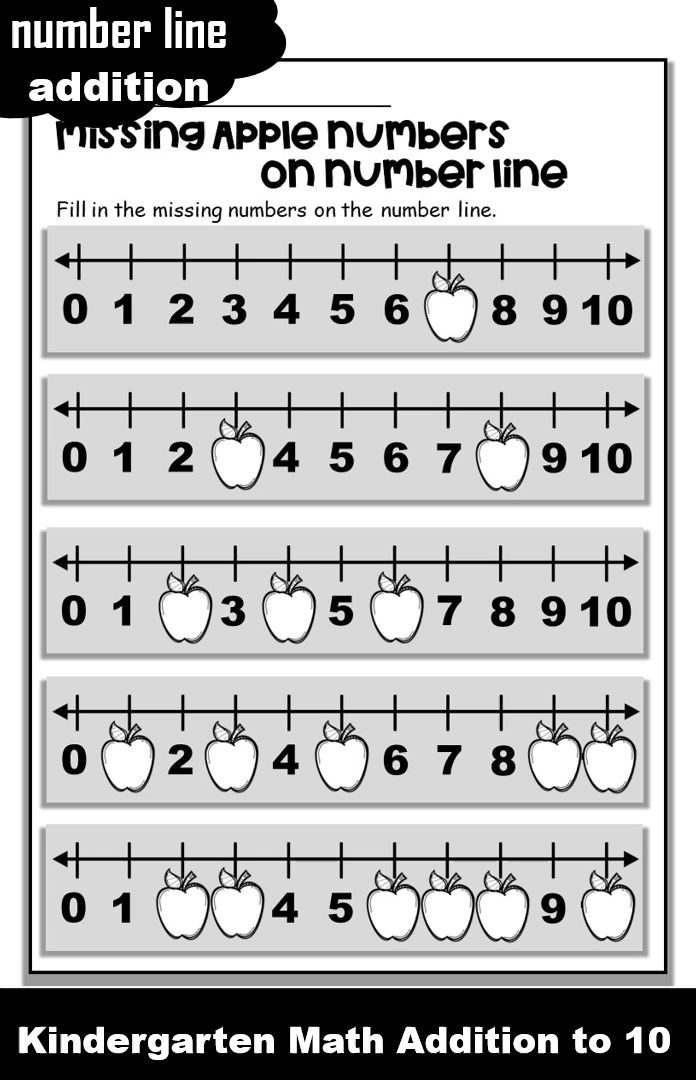
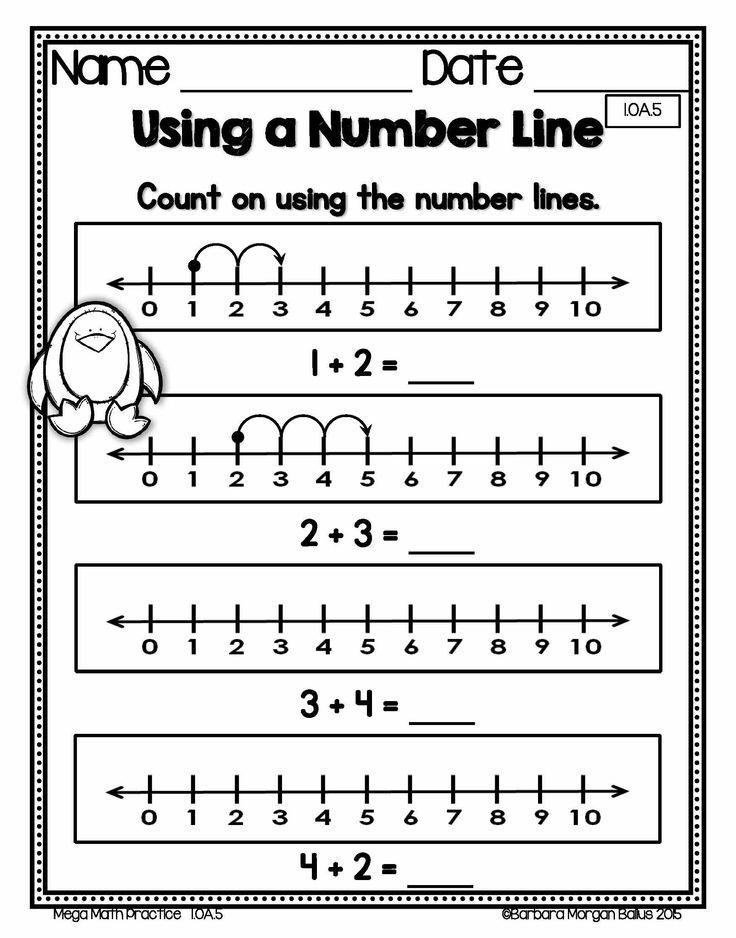
Number line activities kindergarten
25 Fun Number Line Activities for Your Little Learners
// by Eileen Zajac
Teaching number lines to students in a way that they can both visually and physically represent them will be important for the entirety of their use of math. Teaching students at a young age to think mathematically will foster a variety of personality traits that will be followed by students throughout their math journey. A strong foundation of understanding and visualizing numbers can easily be taught. Our experts have come up with 25 unique, engaging, and overall fun activities that your students will love!
1. Hop Along the Bunny Line
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Andrea Powell (@powellinprimary)
Whether it's Easter or you've been reading a Rabbit book like this one, your students will love creating this number line. Bringing hands-on activities into your math stations will not only keep students engaged, but will also help keep the teacher table focused and undistracted.
Learn more: Powell in Primary
2. Guess My Number
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Alessia Albanese (@mrsalbanesesclass)
This can definitely be purchased but can also easily be made by a crafty elementary math teacher. Whether you're planning to use it as a math center rotation or as a fun math competition, students will be totally engaged with this super fun activity.
Learn more: Mrs. Albanese's Class
3. Outside Number Line Fun
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by 5th and 6th Grade Math Teacher (@mathwithmsmatherson)
This low prep resource is perfect for those days that students are just a little stir crazy inside the classroom. This engaging activity can honestly be used with a variety of classes, just draw different number lines using sidewalk chalk.
This engaging activity can honestly be used with a variety of classes, just draw different number lines using sidewalk chalk.
Learn more: Math With Ms. Matherson
4. Tape Me Up - Number Line for Visual Kinesthetic Learners
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by FPCS ARMSTRONG (@fpcsarmstrong)
Sometimes teaching challenging math concepts to visual kinesthetic learners can be very difficult. Making math tech connections can sometimes cause issues for this special group of kiddos. Come out of the tech world for a bit and use this simple math number line in your classroom!
Learn more: FPCS Armstrong
5. Simplify Math Digital Resource
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Simplifying School (@simplifying_school)
Digital activities can enhance student learning in a variety of ways. Working at math centers using chrome books, or during distance learning. These math number lines are a great addition to any learning strategy.
Learn more: Simplifying School
6. Stick My Number
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Ms. Badial 📚✏️ (@msbadialteaches)
A perfect activity for toddlers and older kids alike, this interactive activity will build math skills in even our youngest learners while also being fun and engaging. An ideal resource for those mamas looking for a simple idea that can spark love and understanding of math.
Learn more: Ms. Badial Teaches
7. Read Aloud and Count
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by MathArt (@mathartma)
Bringing literacy across the curriculum will provide students with a different range of strategies that they'll need throughout life. Reading a book like Veggies with Wedgies will be both engaging for students and a great resource for number line math lessons. Count the veggies you see in the story and tape them to the number line!
Learn more: Math Art Ma
8. Number Line in Nature
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by SKIPS Pre-School (@skipspreschool)
If your kids are just starting to count or they're already using 2-digit numbers, this is a great activity for them. Used with both homeschool preschool and school-aged children, this is a great visual representation that will get your students outdoors and crafty!
Used with both homeschool preschool and school-aged children, this is a great visual representation that will get your students outdoors and crafty!
Learn more: Skips Preschool
9. Make It A Match
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Genius Teachers- Quiz App (@geniusteachers)
Finding different ways to engage our soccer-loving kids can be a bit difficult. Using different number lines on soccer fields can be a great visual for your students. Add this to your collection of activities while teaching number lines to higher-grade students.
Learn more: Genius Teachers
10. Subtracting
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Mrs Mactivity 🍎 Educator (@mrsmactivity)
Subtracting can be a difficult concept for many students. With this number line activity, not only will your students have an easier time grasping the idea, but teachers will also have an easier time assessing student understanding. Using hands-on subtraction activities in the classroom can seriously help students in the long run.
With this number line activity, not only will your students have an easier time grasping the idea, but teachers will also have an easier time assessing student understanding. Using hands-on subtraction activities in the classroom can seriously help students in the long run.
Learn more: Mrs. Mactivity
11. Ocean Themed Number Line
Visual tools along with hands-on activities have been proven to help students understand different math concepts. This super cute ocean-themed activity is not only easy to make but also super exciting for students to use. Also enhancing motor skills by using the craft sticks.
Learn more: Stephanie Trapp
12. Understanding Fractions - Christmas Style
Give students a better understanding of fractions this year, with this engaging and themed fraction number line. Although this might be a bit more prep for teachers, providing daily activities to engrain fraction strategies into students' brains will not disappoint.
Learn more: Math in Demand
13. Paper Strip Number Line
Lead students in an activity to make a number line out of a sheet of paper. Teaching tools like this are extremely simple to teach but will help students to create their own number lines in an emergency or at home. It's also an engaging hands-on activity that students will love.
It's also an engaging hands-on activity that students will love.
Learn more: ICEVI Math Made Easy
14. Recognizing Numbers
Fun math games that teach students to recognize different numbers on a number line are a dime a dozen, but this one is great for the teacher too! Assess and understand where students are thriving and where they're being challenged in their comprehension.
Learn more: Kids Jump
15. Teaching Fractions On A Number Line
Finding helpful resources to teach and engrain fractions into your student's brains can be a daunting task.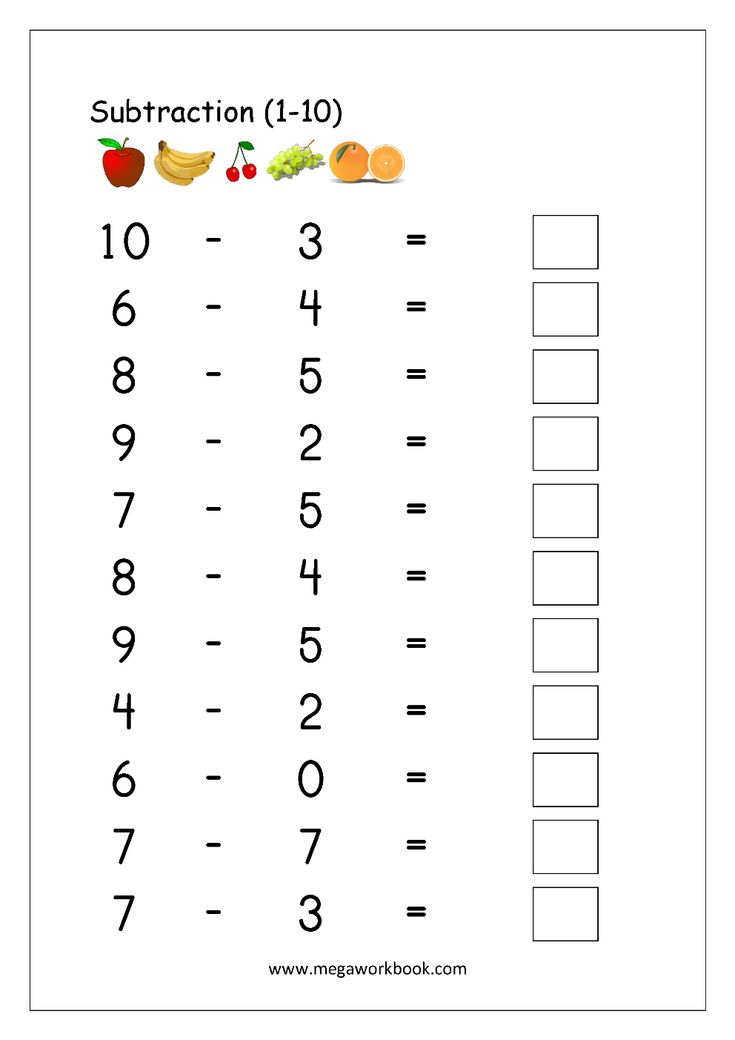 This is a great scaffold for math centers and teaching students who are quite grasping the content. An intricate math tool that will strongly benefit your students.
This is a great scaffold for math centers and teaching students who are quite grasping the content. An intricate math tool that will strongly benefit your students.
Learn more: Living With Lina
16. Digital Fraction Number Line
During a time of distance learning and classroom technology constantly changing and climbing, having a few different resource types throughout your lessons is super important for teachers. Using digital fraction activities not only gives students extra manipulative but also some technology use!
Learn more: Easy Teaching
17. Dice and Butterflies
Finding fun games to bring into your math center rotation is never easy. This activity can easily be used at home and in the classroom. Your students will love being active learners by rolling the dice and marking the number on the number line.
Your students will love being active learners by rolling the dice and marking the number on the number line.
Learn more: Fun Learning for Kids
18. Human Number Line
Making a human number line in the classroom can be a super fun and engaging math game. Whether you draw numbers on paper or have students wear them on their shirts, it can be super exciting to make human math games!
Learn more: Peppy Zesty Teacherista
19. Puzzle Number Lines
These fun puzzle pieces are a perfect addition to your next adding or subtracting number line lesson. Whether it be math stations or whole-group activities, these number lines are a great way to have students focus on their independent practice.
Learn more: Elementary Nest
20. Gobble into Numbers
This wonderful Thanksgiving activity will be a great way to enhance students learning and understanding of the number line. Throwing the dice never fails for our littlest learners. Don't let this game get away, it's easy to make and super cute to play!
Throwing the dice never fails for our littlest learners. Don't let this game get away, it's easy to make and super cute to play!
Learn more: One Sharp Bunch
21. Pipe Cleaner Number Line
Using a pipe cleaner and a hand full of beads is always a good time in the classroom. This easy pipe cleaner activity can be used as both a math lesson and a great skills motor math game. You will be shocked at your student's patience during this activity.
Learn more: More Time to Teach
22. Dominos Number Building
Counting with dominos is a fun math game that can be used throughout math centers, at home, or as a whole class activity. Having students work collaboratively on this will be even more beneficial for their learning outcomes.
Learn more: Busy Toddler
23. PlayDough and Flowers
Being a bit more of an intense prep of a number line activity, this is perfect for a rainy day or a day that you have a big math block. Students will not only love to show off their creations but they'll also have a blast making them! It's a perfect informal project-based assessment activity.
Students will not only love to show off their creations but they'll also have a blast making them! It's a perfect informal project-based assessment activity.
Learn more: Learning 4 Kids
24. Lego Man Counting
Have students bring in their favorite action figures or Lego men for this fun math activity. Students will love to be able to bring their friends from home into the classroom and use them in a math lesson!
Learn more: Play Ideas
25. Friday Game Day
I love to have one of my math stations a game on Fridays. My students loved this number line game! It was easy to get to and easy to understand. I also love hearing my kiddos when they do well and when they do not do so well.
Learn more: Gizmos
Related posts:
Category: Classroom Ideas
18 Number Line Activities You'll Want to Try in Your Classroom
Number lines are a reliable method teachers have been using for ages to teach number sense, arithmetic, and all sorts of other math skills.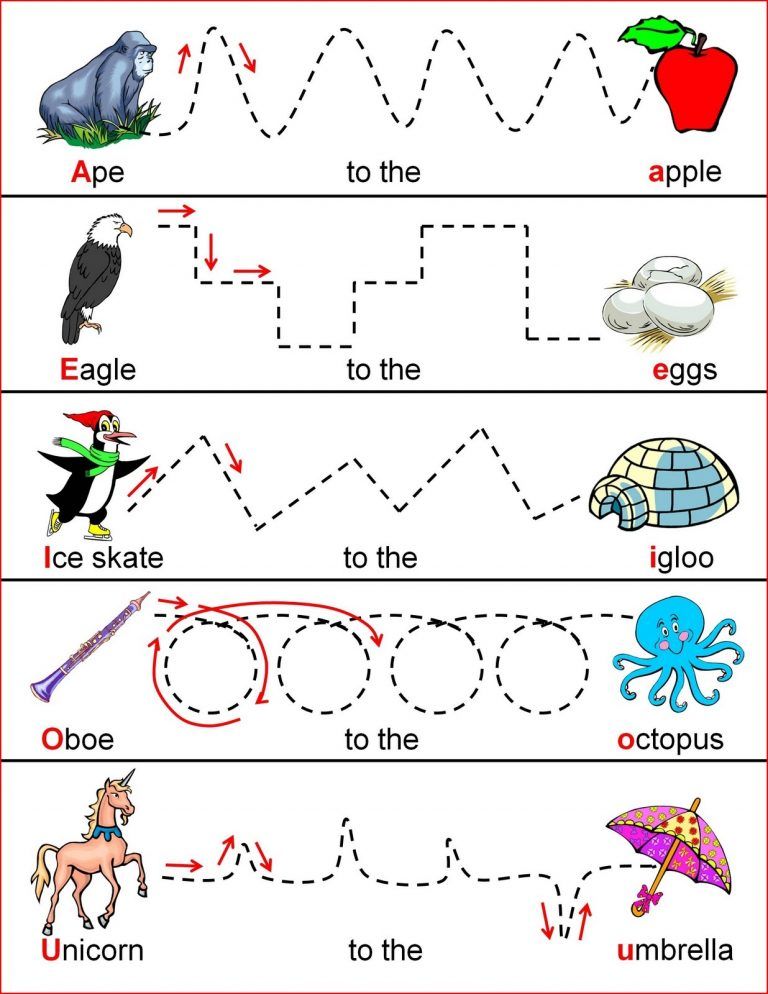 This collection of number line activities works with littles and not-so littles, as they learn the concepts they need to be successful at math. Pick a few to try today!
This collection of number line activities works with littles and not-so littles, as they learn the concepts they need to be successful at math. Pick a few to try today!
1. Use sticky notes to line up numbers.
Write numbers on sticky notes and ask kids to place them in order on the number line. This simple idea is perfect for little ones first learning to sequence numbers. But number line activities are useful for older students too; try this same exercise with fractions, decimals, or negative numbers. (We love sticky notes in the classroom!)
Learn more: Busy Toddler
2. Build a life-size number line.
A life-size number line in your classroom allows you to do all sorts of active math games and practice. Kids will get even more out of number line activities when they become the numbers! (Pro tip: Carpet spots are fantastic for this project.)
Learn more: School Is a Happy Place
3. Line up your shoes.
Here’s one of those number line activities just made for your life-size line! Have the class count and line up their shoes, or workbooks, or crayons. The possibilities are endless.
ADVERTISEMENT
Learn more: Days With Grey
4. Paint a dotted number line.
Kids use cotton swabs and paint to represent the value of each number on a line, helping them visualize what each number means. They can see how numbers grow in size from left to right.
Learn more: A Pinch of Kinder
5. Go vertical for number line activities.
Most number lines used in the classroom are horizontal, but vertical lines can help give kids better number sense. Since we associate “up” with “greater,” a vertical number line makes that concept easier to grasp.
Learn more: Mr. Elementary Math
6. Match dominoes to the numbers.
Kids count the dots on dominoes, or add the two numbers they see to get the sum, and place them by the corresponding number on the line. You could do this with subtraction, too.
You could do this with subtraction, too.
Learn more: Busy Toddler
7. Build a number line with LEGO bricks.
Playing with LEGO bricks is learning? Who knew! We love this idea for practicing counting on using a LEGO minifig and dice.
Learn more: Gluesticks & Giggles/Instagram
8. Hop and drop along the line.
Here’s a number line activity that’s sure to get kids giggling. Challenge them to carry a ball along the line and drop it on a specific number—without using their hands! They can hold it between their knees, under their neck, or any way they choose. Their antics will make you laugh, but they’ll be learning all the while.
Learn more: Teach Me Mommy
9. Turn a zipper bag into a number line slider.
Well, how ingenious is this idea? Write a number line across the top of a zipper bag with a slider. Then insert a math fact to practice and slide along to find the answer. So fun!
So fun!
Learn more: Hefty
10. Plant a number line garden.
Turn cupcake wrappers and craft sticks into numbered flowers, and “plant” them in a cardboard tube number line. (A pool noodle would also be fun for a number line garden.)
Learn more: 123Homeschool4Me
11. Use clothespins for number line activities.
Pick up a bag of clothespins at the dollar store (you know you’re shopping there for teacher supplies anyway) and write numbers on them with a Sharpie. Then create individual number line manipulatives from paint stirrer sticks. Simple and cheap!
Learn more: Fantastic Fun and Learning
12. Craft a number line bookmark.
Hit the link below for the free printable and print these bookmarks out on card stock. (Laminate if you like.) Then punch holes at the top and bottom, slide a bead onto a pipe cleaner, and attach it as shown. Kids now have a handy bookmark to help them with number line activities.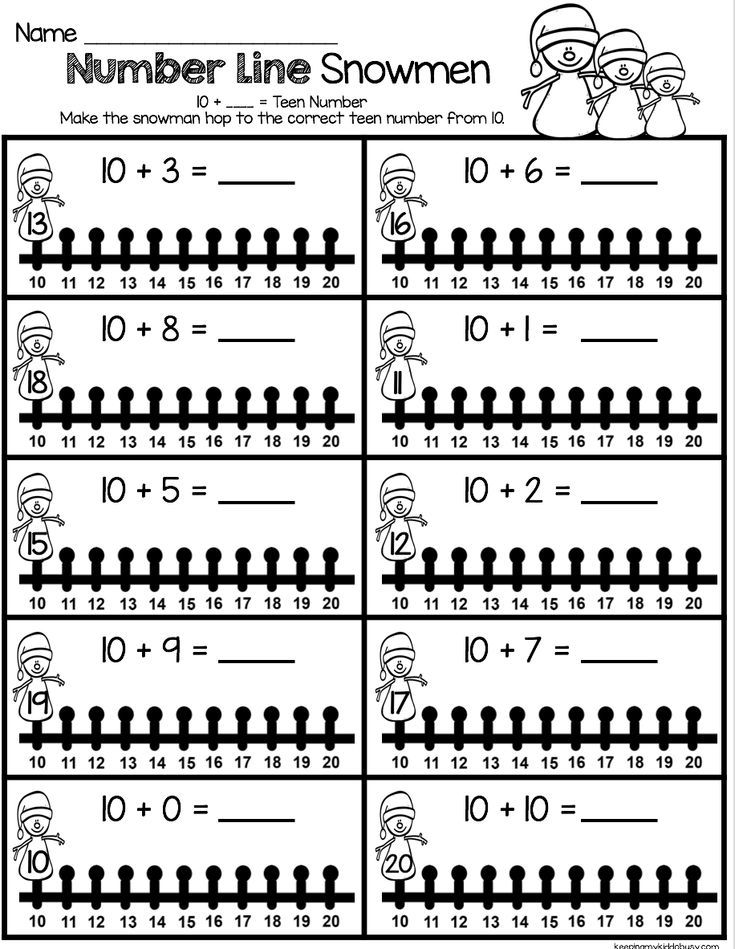
Learn more: Highland Heritage Homeschool
13. Tell the story of the “naughty numbers.”
If your students sometimes have trouble remembering which directions the written numerals should face (hello, backwards 3 that looks like capital E!), the story of the naughty numbers may help. Hit the link below to hear the tale and learn how it works.
Learn more: The First Grade Parade
14. Teach rounding with number lines.
Number line activities are handy for more advanced students, too. They’re ideal for learning about the concept of rounding numbers. Use a clever anchor chart like this one to show kids how it works.
Learn more: Crafting Connections
15. Send messages in secret code.
Assign each number on the line a letter (mix them up to make it more challenging). Then, craft your message using arithmetic problems for students to solve. Kids figure out the answers, find the corresponding letters, and spell out your message (which hopefully does not self-destruct!).
Learn more: Creative Family Fun
16. Drive along to learn fractions.
Understanding equivalent fractions can be a challenge, but number line activities can help. In this one, drive a toy car along the lines and use equivalent fractions to prove your answer. See how it works at the link below.
Learn more: Beyond Traditional Math
17. Use a number line to understand improper fractions.
Improper fractions can be a bit tricky, but number line activities make them easier to understand. Get this free printable cut-and-paste activity at the link below.
Learn more: Math Tech Connections
18. Put decimals on the line.
Fractions and decimals go hand in hand, and both are easier with number lines. Get free printable worksheets at the link below and learn how to use number lines with decimals.
Learn more: Math Geek Mama
Number lines are terrific for estimation, too.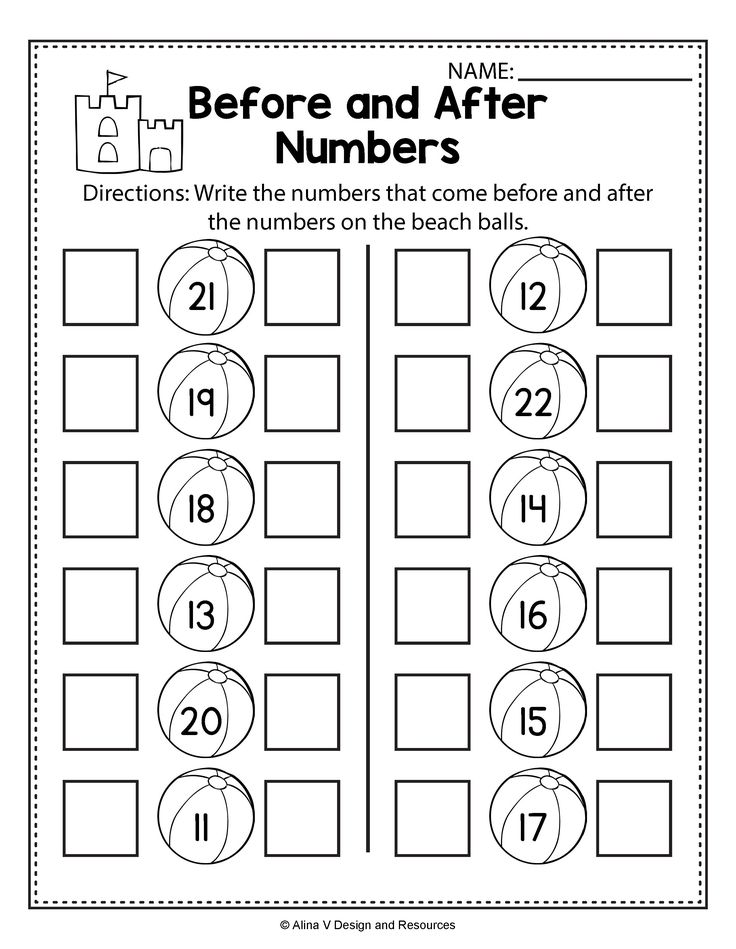 Find 18 estimation activities for your classroom here.
Find 18 estimation activities for your classroom here.
10 frames are another incredibly useful math tool. Here are some fantastic and fun 10 Frame Activities you’ll want to try next.
Content-methodical lines of the course of mathematics "Learning to learn" for grades 5-6 authors G.V. Dorofeeva, L.G. Peterson
- Introductory consultation
- Didactic system of the activity method of teaching “School 2000…”
- Content and methodological lines of the mathematics course "Learning to learn" for grades 5-6
- Activity Method Technology Implementation Levels
- Monthly consultations
mathematics course "Learning to learn" for grades 5-6
authors G.V. Dorofeeva, L.G. Peterson
Number line
The number line is built on the basis of counting objects (set elements) and measuring quantities.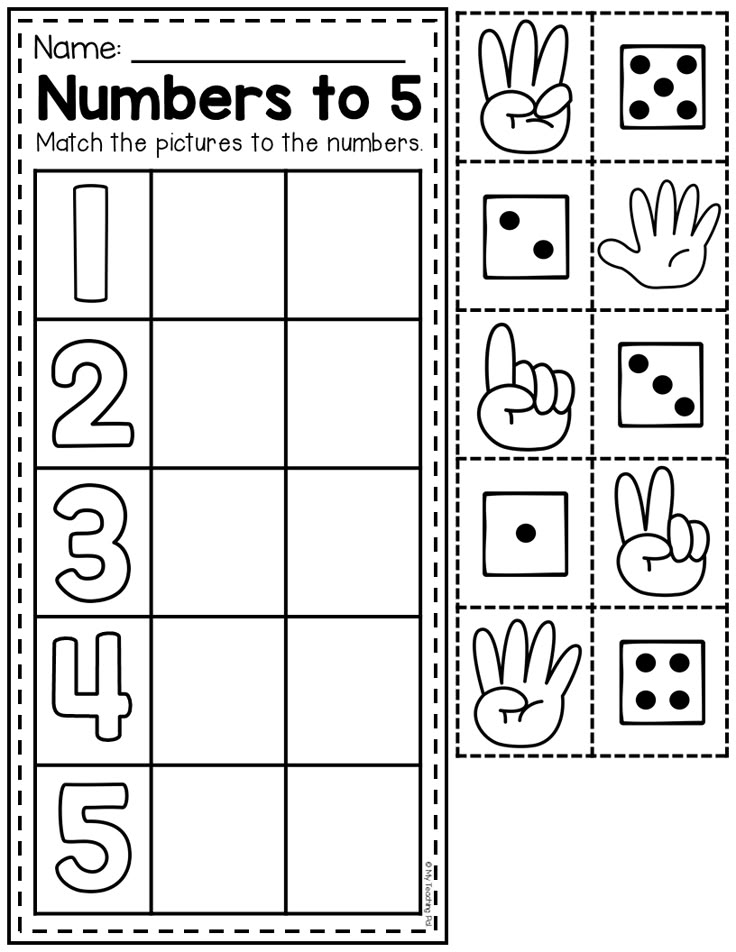 The concepts of set and magnitude lead students from different sides to the concept of a number: on the one hand, a natural number, and on the other, a positive real number. This reflects the dual nature of number, and in a deeper aspect, the dual nature of the infinite systems with which mathematics deals: discrete, countable infinity and continual infinity. The measurement of magnitudes connects natural numbers with real ones, therefore, the number line receives its further development in the transition from elementary school to the middle school as an infinitely precise process of measuring magnitudes.
The concepts of set and magnitude lead students from different sides to the concept of a number: on the one hand, a natural number, and on the other, a positive real number. This reflects the dual nature of number, and in a deeper aspect, the dual nature of the infinite systems with which mathematics deals: discrete, countable infinity and continual infinity. The measurement of magnitudes connects natural numbers with real ones, therefore, the number line receives its further development in the transition from elementary school to the middle school as an infinitely precise process of measuring magnitudes.
In elementary school, within the framework of the number line, students learn the meaning of the concept of a natural number and zero, the principles of writing and comparing non-negative integers, the meaning and properties of arithmetic operations, the relationship between them, methods of oral and written calculations, estimates, evaluation and verification of the results of arithmetic operations , dependencies between their components and results, ways to find unknown components.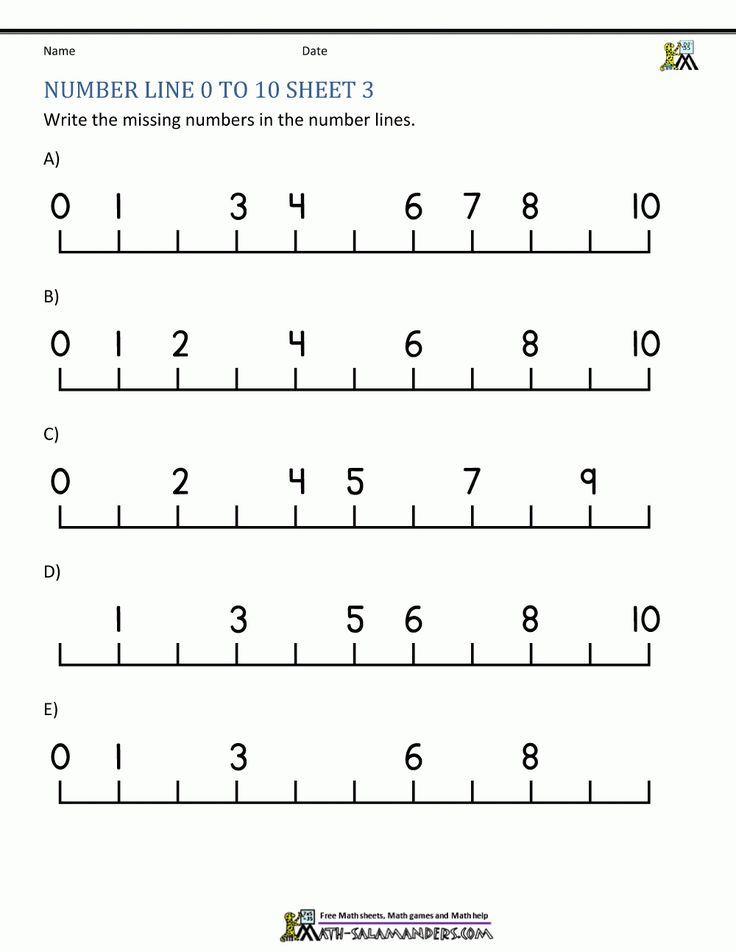 On the other hand, they get acquainted with various quantities and the general principle of their measurement, learn to perform actions with the values \u200b\u200bof quantities (named numbers).
On the other hand, they get acquainted with various quantities and the general principle of their measurement, learn to perform actions with the values \u200b\u200bof quantities (named numbers).
The use of the activity method of teaching made it possible not only to preserve in full the content of the traditional elementary school mathematics curriculum, but also to enrich it, taking into account the sensitive periods of children's development. So, in the 3rd grade, they study with interest numbering and actions with non-negative integers within 12 digits, in the 4th grade - fractions, addition and subtraction of fractions with the same denominators, mixed numbers, that is, topics that were traditionally studied in the 5th grade, but children were not interested.
In grade 5, the number line continues with the study of ordinary and decimal fractions, and in grade 6 - rational numbers. In conclusion, children's knowledge of numbers is systematized, children get acquainted with the history of the development of the concept of number and with the method of expanding numerical sets.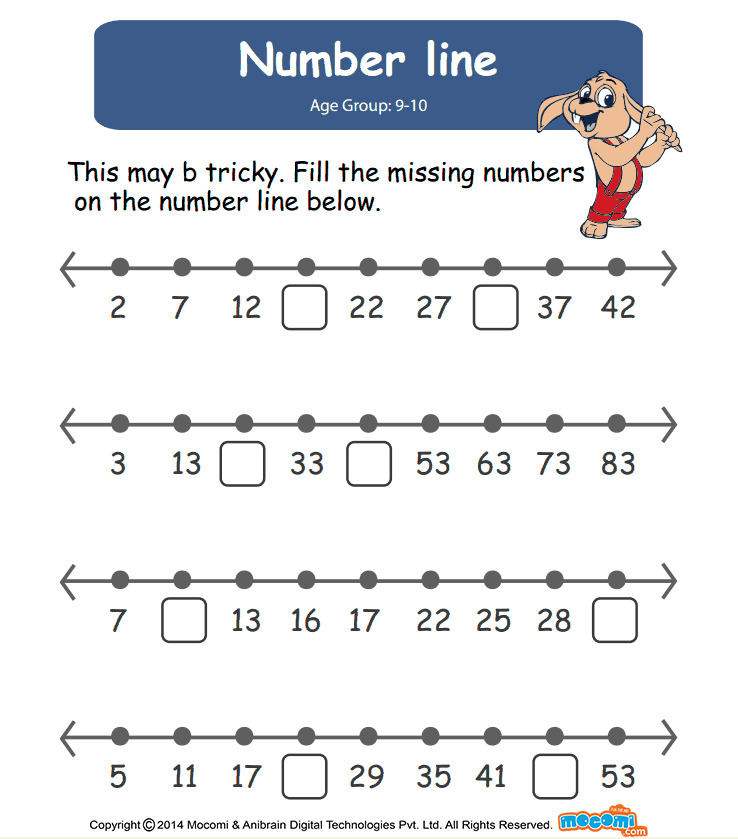 The problem of the insufficiency of the studied numbers for measuring quantities (for example, the length of the diagonal of a square with side 1) is posed.
The problem of the insufficiency of the studied numbers for measuring quantities (for example, the length of the diagonal of a square with side 1) is posed.
The number line, having its own tasks and specifics, nevertheless, is closely intertwined with all other content and methodological lines of the course. So, when constructing algorithms for actions on numbers and studying their properties, various graphical models are used. Actively included in the educational process as an object of study and as a means of teaching such concepts as a set (at first - a "bag", a group of objects), a part and a whole, an operation and an algorithm, which then become the basis for the formation of strong computational skills and learning in children their solution of equations and word problems.
Algebraic line
The development of the algebraic line is inextricably linked with the numerical one, in many ways complements it and provides a better understanding and assimilation of the material being studied, and also increases the level of generalization of the knowledge acquired by children. Students, starting from grade 1, write down expressions and properties of numbers using alphabetic symbols, which helps them structure the material being studied, identify similarities and differences, and analogies of objects. For example, when solving equations, from the fact that A + X \u003d B it follows that X \u003d B - A (for sets), and from the fact that a + x \u003d b it follows that x \u003d b - a (for quantities). In both cases, the decision is justified by the fact that we are looking for an unknown part, so we subtract the other part from the whole.
Students, starting from grade 1, write down expressions and properties of numbers using alphabetic symbols, which helps them structure the material being studied, identify similarities and differences, and analogies of objects. For example, when solving equations, from the fact that A + X \u003d B it follows that X \u003d B - A (for sets), and from the fact that a + x \u003d b it follows that x \u003d b - a (for quantities). In both cases, the decision is justified by the fact that we are looking for an unknown part, so we subtract the other part from the whole.
As a rule, writing down the general properties of operations on sets and quantities overtakes the corresponding skills of students in performing similar operations on numbers. This makes it possible to create a general framework for each of these operations, which then, as new classes of numbers are introduced, operations on numbers and the properties of these operations fit. This gives a theoretically generalized method of orientation in the doctrines of sets, magnitudes, and numbers, which then makes it possible to solve vast classes of specific problems.
In grades 5-6, students move up to the next level by learning to use letter notation to prove general statements. This allows them to carry out a logical proof of the properties and signs of divisibility, the properties of proportions, etc. Thus, high-quality preparation of children for the study of program material in algebra in grades 7–9 is ensured.
Geometric line
When studying geometric line in elementary school, students get acquainted with such geometric shapes as a square, rectangle, triangle, circle, the simplest spatial images: cube, parallelepiped, cylinder, pyramid, ball, cone, as well as more abstract concepts point, straight and curved line, ray, segment and polyline, angle and polygon, area and border, circle and circle, etc., which are used to solve a variety of practical problems. For example, segment diagrams serve as graphical models of word problems, circles are used to build pie charts, etc.
Cutting figures into parts and composing new figures from the resulting parts, drawing figures, gluing models according to their scans develops children's spatial representations, imagination, speech, combinatorial abilities and at the same time forms practical skills in working with basic measuring and drawing tools (ruler, square, compass, protractor).
The stock of geometric ideas and skills that students have accumulated by grades 3-4 allows them to set a new, much deeper and more exciting goal: the study and discovery of the properties of geometric shapes. With the help of constructions and measurements, they reveal various geometric patterns (for example, the property of the angles of a triangle, the properties of adjacent and vertical angles, inscribed and central angles, etc.), which they formulate as an assumption, a hypothesis.
This work continues in grades 5-6: students explore and discover various properties of a triangle and a rectangle, a parallelogram and a trapezoid, a circle and a circle, etc. At the same time, not only flat, but also spatial figures are considered - a ball, a sphere, cylinder, cone, pyramid, polyhedra. This helps them, on the one hand, to discover the beauty of geometric facts, and on the other hand, to realize the need for their logical substantiation, proof, which prepares them to study the systematic course of geometry in 7–9classes. E.S. Smirnova “Geometric line in mathematics textbooks for grades 5–6 G.V. Dorofeeva, L.G. Peterson" .
At the same time, not only flat, but also spatial figures are considered - a ball, a sphere, cylinder, cone, pyramid, polyhedra. This helps them, on the one hand, to discover the beauty of geometric facts, and on the other hand, to realize the need for their logical substantiation, proof, which prepares them to study the systematic course of geometry in 7–9classes. E.S. Smirnova “Geometric line in mathematics textbooks for grades 5–6 G.V. Dorofeeva, L.G. Peterson" .
Functional line
Functional line is built around the concept of the functional dependence of quantities, which is an intermediate model between reality and the general concept of a function, and thus serves as a source of the concept of functions in the upper grades. Students observe the interconnected change of various quantities, get acquainted with the concept of a variable quantity, and by grade 4 gain significant experience in fixing dependencies between quantities using tables, diagrams, graphs (movements) and simple formulas. So, students build and use formulas for solving practical problems: area of a rectangle S = a • b, volume of a rectangular parallelepiped V = a • b • c, path s = = v • t, cost C = a • x, work A = w • t, etc. When studying various dependencies, children identify and fix their general properties in mathematical language, which creates the basis for building a general concept of a function in high school, understanding the expediency of its introduction and practical significance.
So, students build and use formulas for solving practical problems: area of a rectangle S = a • b, volume of a rectangular parallelepiped V = a • b • c, path s = = v • t, cost C = a • x, work A = w • t, etc. When studying various dependencies, children identify and fix their general properties in mathematical language, which creates the basis for building a general concept of a function in high school, understanding the expediency of its introduction and practical significance.
Call appearance
Quite serious attention is paid in the course to the development of the logic line in the study of arithmetic, algebraic and geometric questions of the program. All tasks of the course of mathematics "Learning to learn" require students to perform logical operations (analysis, synthesis, comparison, generalization, analogy, classification), contribute to the development of cognitive processes: imagination, memory, speech, logical thinking.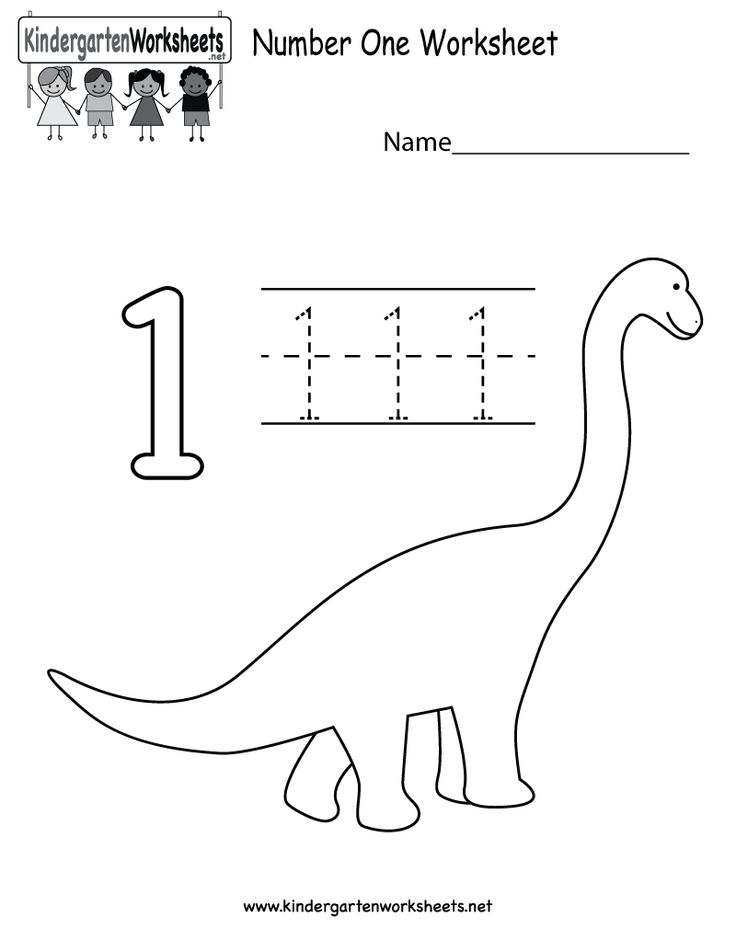
In elementary school, as part of the study of the logic line, students master the mathematical language, learn to read mathematical text, use mathematical terms to describe the phenomena of the world around them. In the process of calculations, solving problems, equations, geometric constructions, they check the truth of statements, build their judgments in mathematical language and justify them based on an agreed method of action (standard). Already in the 3rd grade, students get acquainted with the language of sets, various types of statements (private, general, about existence), with complex statements with the unions “and” and “or”, gain experience in proving and refuting them.
On this basis, in grades 5-6, the logical line unfolds into a chain of interrelated questions: mathematical language - statements - proof - methods of proof - definitions - equivalent sentences - negation - logical consequence - theorem, etc. Thus, students get the opportunity to fully prepare for the study of mathematics in high school and for solving various life problems of a logical nature.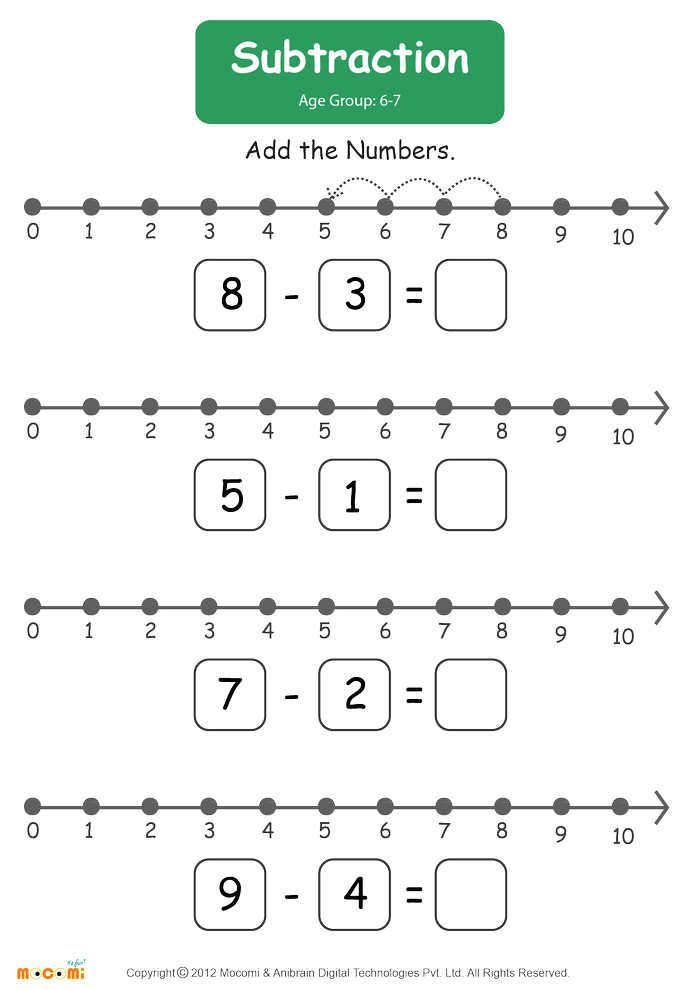
Data analysis line
Data analysis line purposefully forms students' information literacy, the ability to independently obtain information - from observations, reference books, encyclopedias, Internet sources, conversations; work with the information received: analyze, systematize and present in the form of diagrams, tables, abstracts, diagrams and graphs; draw conclusions; identify patterns and significant features; carry out the classification; carry out a systematic search of options; build and execute algorithms.
Already in elementary school, students get acquainted with the tree of possibilities, with different types of programs: linear, branched, cyclic. The systematic construction and use of algorithms to justify their actions and self-check the results helps to more successfully study many traditionally difficult issues of the program (for example, the order of actions in expressions, actions with multi-digit numbers, etc. ).
).
In grades 5–6, this work continues, and information skills are formed both in the classroom and in extracurricular project activities, circle work, when creating your own information objects: presentations, collections of tasks and examples, wall newspapers and information sheets, etc. . During this activity, students master the basics of computer literacy and computer skills necessary for schooling and modern life.
Simulation line
Within the framework of modeling line (text problem lines), students master all types of mathematical activities, realize the practical significance of mathematical knowledge, they form universal learning activities, develop thinking, imagination, speech.
The knowledge acquired by children in the study of various sections of the course finds practical application in solving word problems. In elementary school, students get acquainted with the solution of simple and compound text problems on the meaning of arithmetic operations, difference and multiple comparisons (containing the relations “more by . .., in ...”, “less by ..., in ...”), on the dependence of values of the form a = bc (path, speed, time; cost, price, quantity of goods; work, productivity, work time, etc.). A feature of the course is that after systematically working out a small number of basic types of tasks, students are offered a wide range of various structures consisting of basic elements, but containing some novelty, which develops their ability to act in a non-standard situation.
.., in ...”, “less by ..., in ...”), on the dependence of values of the form a = bc (path, speed, time; cost, price, quantity of goods; work, productivity, work time, etc.). A feature of the course is that after systematically working out a small number of basic types of tasks, students are offered a wide range of various structures consisting of basic elements, but containing some novelty, which develops their ability to act in a non-standard situation.
The system for selecting and arranging problems creates an opportunity to compare them, identify similarities and differences, and relationships between them (mutually inverse problems, problems with the same mathematical model, etc.). Particular attention is paid to teaching independent analysis of text problems. Students identify the quantities referred to in the problem, establish relationships between them, make condition models using diagrams and tables, draw up and implement a solution plan, justifying each step.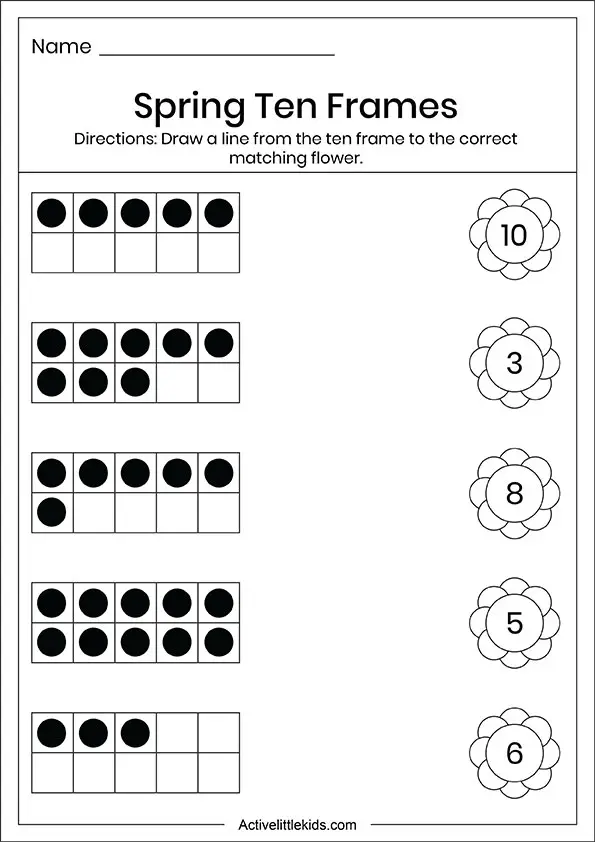 They learn to give a complete answer to the question of the problem, find various ways to solve them and choose the most rational ones, independently compose tasks according to a given model (expression, scheme, table), while using the language and tools that are accepted in high school.
They learn to give a complete answer to the question of the problem, find various ways to solve them and choose the most rational ones, independently compose tasks according to a given model (expression, scheme, table), while using the language and tools that are accepted in high school.
The modeling line is constructed in such a way as to ensure, on the one hand, that students learn the learned methods of action in all other lines, and on the other hand, create conditions for their systematization, and on this basis, reveal the role and significance of mathematics in the development of culture. This is facilitated by specially developed methods, as well as the literal notation of expressions for problems and the properties of operations on numbers, which already in elementary school make it possible to identify the commonality of text problems with outwardly different plots, but a single mathematical content. So, in the 3rd grade, students identify four types of simple tasks, the methods for solving which are well known to them: 1) a + b = c; 2) a • b = c; 3) difference comparison; 4) multiple comparison.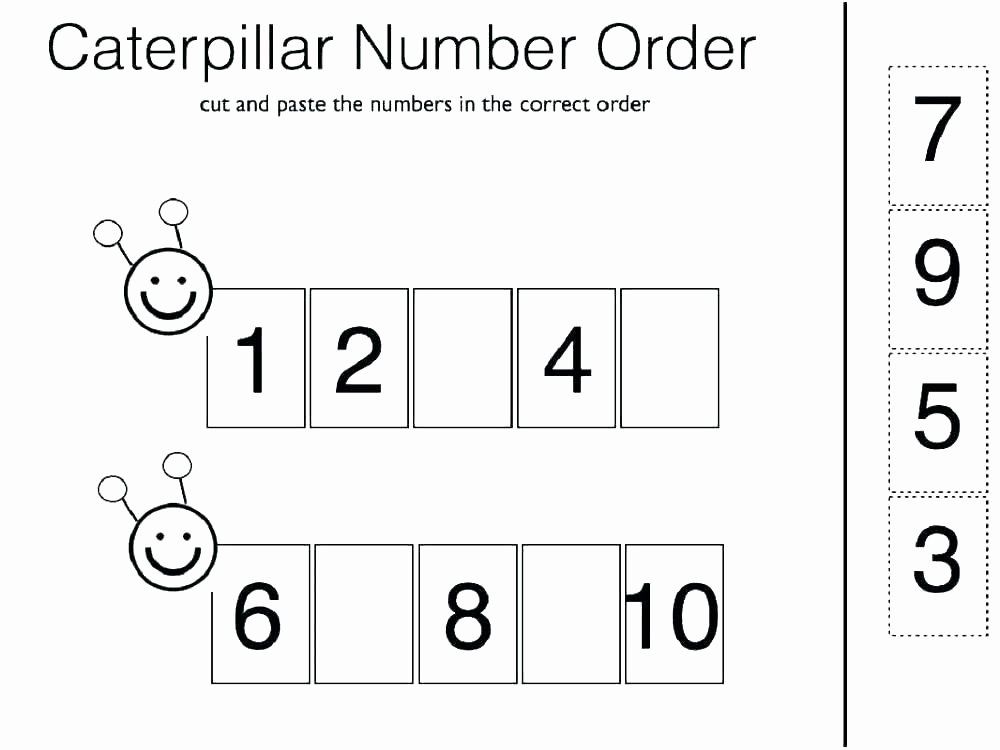 At the same time, tasks for finding the part and the whole (1) are modeled using graphical diagrams, tasks for the relationship of quantities of the form a • b = c (2) - using tables, and tasks for difference and multiple comparison - using the rules, respectively, of difference and multiple comparison, finding a larger number by a smaller one and a difference (multiple), finding a smaller number by a larger one and a difference (multiple). And the solution of any compound problem is presented as a program of actions, each operation in which is the solution of one of these four types of simple problems well mastered by students.
At the same time, tasks for finding the part and the whole (1) are modeled using graphical diagrams, tasks for the relationship of quantities of the form a • b = c (2) - using tables, and tasks for difference and multiple comparison - using the rules, respectively, of difference and multiple comparison, finding a larger number by a smaller one and a difference (multiple), finding a smaller number by a larger one and a difference (multiple). And the solution of any compound problem is presented as a program of actions, each operation in which is the solution of one of these four types of simple problems well mastered by students.
Mastering the general methods of constructing a plan for solving compound problems (analytical, synthetic, analytical-synthetic) "puts things in order" in the thinking of children and thereby reduces the time for their study. In the free time, children get acquainted with new types of tasks - tasks for fractions (three types) and for the simultaneous uniform movement of two objects (four types), they form an idea of \u200b\u200bpercentage, which creates a solid basis for the successful mastering of these traditionally difficult sections of the program 5 –6 classes, and in general, for mastering the general method of mathematical modeling.
Summing up, we can say, that the basis of the continuous course of mathematics "Learning to learn" of the "School 2000" program in grades 5-6 is the content and methodological lines traditional for the school mathematics course. However, other principles for constructing the program, new didactic and technological approaches make it possible to include new topics and sections in the content of the program, to give the learning process an incomparably greater depth and bring it into line with the new goals and objectives of education established by the Federal State Educational Standard.
Printable version
Kindergarten team is glad to welcome you to our website! Main page
Kindergarten No. 133 is a participant of the governor's project "We decide together!"
Information Organization Link: https://mdou133.edu.yar.ru/svedeniya_obrazovatelnoy_organizatsii/osnovnie_svedeniya. html [email protected]
html [email protected]
Phone: Head 57-94-14, Senior Nurse 57-97-44, Accounts Department 57-93-83
901 Federal hotline number 00135
901 -3006-003, the call is free.
is free social-informational, legal, psychological, humanitarian aid.
The family line is open 24/7, 24/7.
About the activities of MDOU "Kindergarten No. 133"
during the unfavorable epidemiological period
Dear parents!
(legal representatives)
Currently, MDOU “Kindergarten No. 133”
is determined by the following documents:
- 9023 SAD ” April 2022 "On the removal of part of the restrictive and preventive measures in connection with the spread of coronavirus infection caused by virus SARS - COV -2 " - Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated 06. 30.2020 N 16
30.2020 N 16
Currently admission to MDOU" Kindergarten No. 133 "
Visits by parents (legal representatives) of the preschool educational institution are limited
We kindly ask you to use boot covers to visit the preschool building.
From 09/01/2020 until the end of the unfavorable epidemiological period, a certain activity regulation is in force at the Kindergarten No. 133.
Parents (legal representatives) of the child inform the head of the institution in advance about the child's departure to the preschool educational institution, the time of the child's arrival and departure is determined.
Parents should familiarize with the amended regulations for the activities of preschool educational institutions dated 01/11/2021 during an unfavorable epidemiological situation and the working hours of the preschool educational institution.
In the morning, a medical worker receives children strictly in accordance with the list through the central entrance of preschool educational institution with mandatory thermometry.
Answers to your questions about the work of preschool educational institutions in an unfavorable epidemiological period and distance learning for pupils can be obtained by calling (4852) 57-94-14.
Documents on measures to prevent coronavirus infection:
Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation No. 16 dated June 30, 2020 "On Approval of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules SP 3.1/2.4.3598-20" Sanitary and Epidemiological Requirements for the Device, the content and organization of the work of educational organizations and other social infrastructure facilities for children and youth in the context of the spread of a new coronavirus infection (COVID-19)»
Decree of the Governor of YaO No. 47 dated March 18, 2020 "On measures to prevent the importation into the territory of the Yaroslavl region of a new coronavirus infection and its spread"
Decree of the Governor of YaO No. welfare of the population and amending the Decree of the Governor of the region dated 18. 03.2020 No. 47 "
Decree of the Government of the YaO No. 304-p dated 04.09.2020 "On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the region dated 03.04.2020 No. 302-p and supplementing the list of non-food products essentials"
Decree of the Governor of the YaO No. 109 dated 05/08/2020 "On Amendments to the Decrees of the Governor of the Region No. 47 dated 18.03.2020 and No. 80 dated 03.04.2020"
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation V.V. On determining the procedure for extending measures to ensure the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in connection with the spread of the new coronavirus infection COVID-19"
Decree of the Government of the YaO "On the work of organizations and individual entrepreneurs in the period from May 12 to May 15"
Decree of the Government of the YaO No. 418-p "On the work of organizations and individual entrepreneurs in the period from May 16 to May 22"
Decree of the Governor of the YaO No. 04/03/2020 No. 80"
04/03/2020 No. 80"
Resolution of the Government of YaO No. 465-p of 05/29/2020 "On Amendments to the Resolution of the Regional Government of 05/15/2020 No. 418-p"
THANK YOU FOR YOUR UNDERSTANDING!
HEALTH AND PATIENCE TO ALL!
“Together against corruption!” Social Anti-Corruption Advertising
Video -1 video -2 -2
pupils and students of educational institutions of the city of Yaroslavl
Combine Social Power Plant
Related
Answers to the most frequently asked questions in the system of personalized additional education are available at the following link
https://www.yarregion.ru/depts/dobr/Pages/sertifikaty_dopObr.aspx
How to enroll in an additional education program?
Portal of personified additional education of the Yaroslavl region
so that you can quickly track the procedure for recording and training in institutions that implement additional education programs, please read the review of the functionality of the child’s personal account (certificate) and with the instruction "How to sign up for a group on selected program.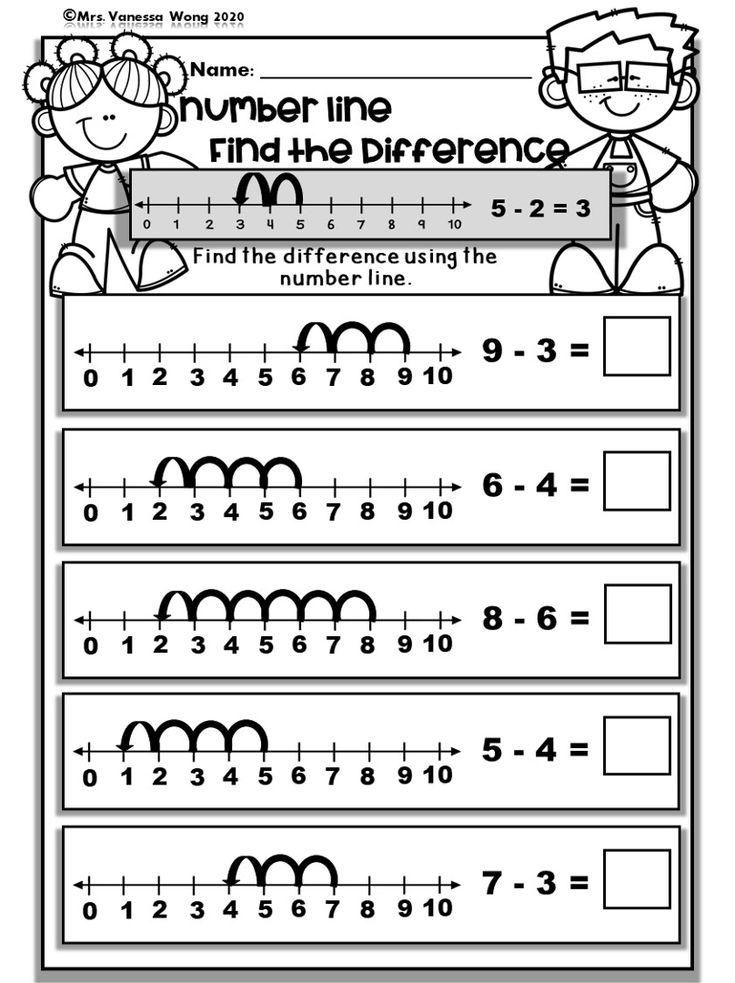
Every day we are happy to meet our pupils,
telling parents and children: "Smile! You came to kindergarten!"
"MDOU" Kindergarten No. 133 "
- this is a source of heat, joy and knowledge for children,
- this is the Commonwealth of teachers and parents in the education and development of preschool children,
is the mission of the three P's: to understand, accept and help the child.
- works according to the principle: "Success in childhood determines success in life!"
Status priority
Status: municipal preschool educational institution "Kindergarten No. 133" with combined groups.
The principles of preschool education that underlie the work of our institution are fully consistent with the principles of the Federal State Educational Standard:
1. Full living by the child of all stages of childhood (infant, early and preschool age), enrichment (amplification) of child development.
Full living by the child of all stages of childhood (infant, early and preschool age), enrichment (amplification) of child development.
2. Building educational activities based on the individual characteristics of each child, in which the child himself becomes active in choosing the content of his education, becomes the subject of education.
3. Assistance and cooperation of children and adults, recognition of the child as a full-fledged participant ( subject ) educational relations.
4. Support for children's initiative in various activities.
5. Collaboration of the preschool educational institution with the family.
6. Introducing children to socio-cultural norms, traditions of the family, society, state.
7. Formation of cognitive interests and cognitive actions of the child in various activities.
8. Age appropriateness of preschool education (correspondence of conditions, requirements, methods to age and developmental characteristics).