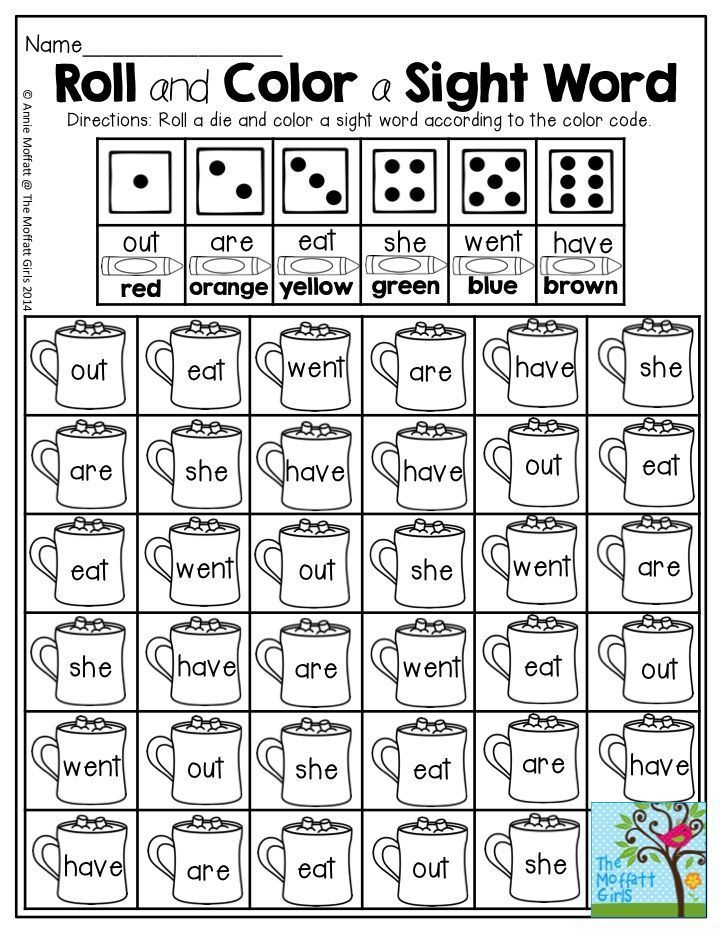
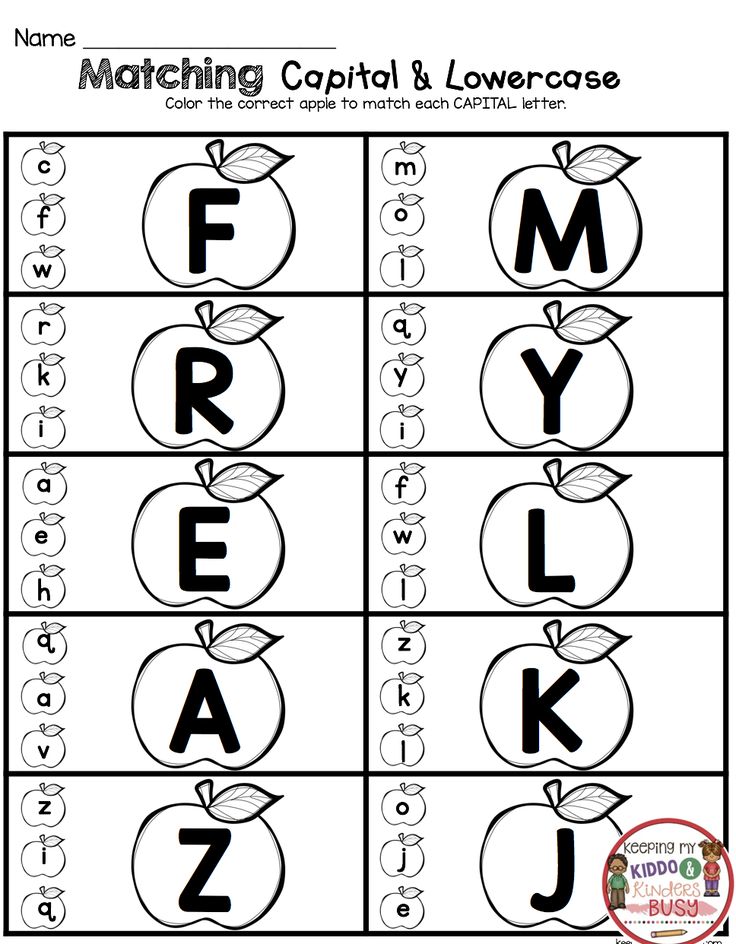
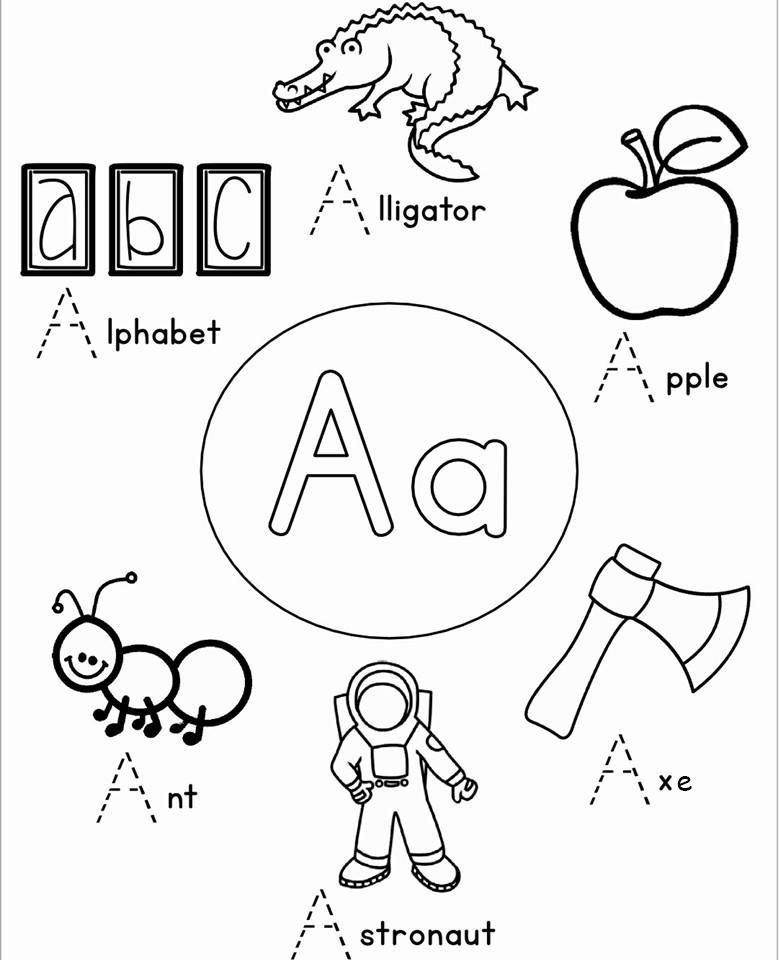
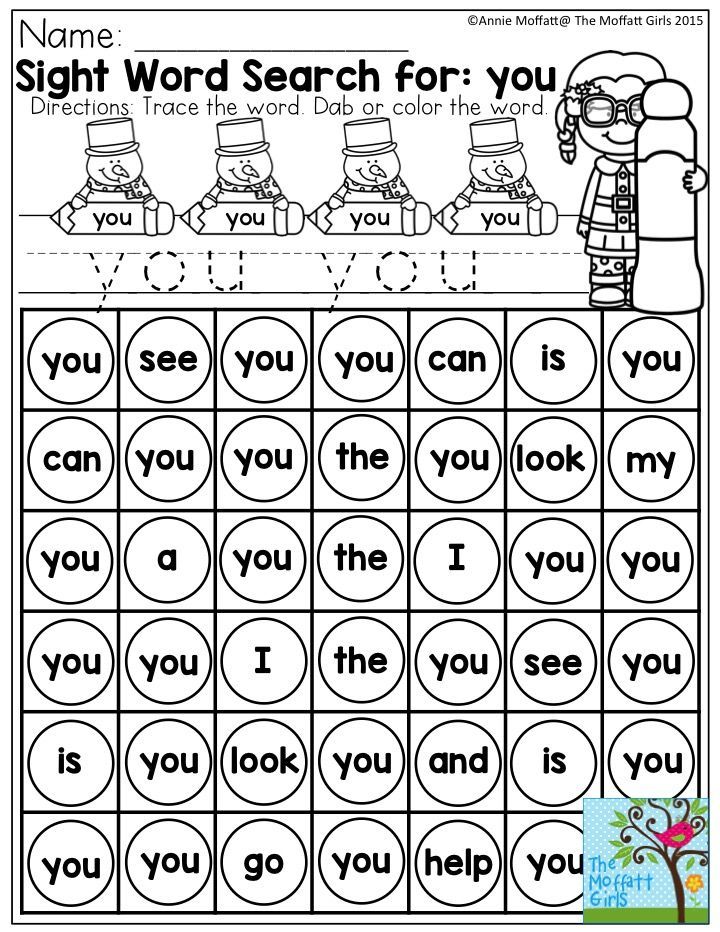
Preschool sight words activities
48 Fun Sight Word Activities That Work
Teachers are always on the hunt for great sight word activities. Sight words are any words readers recognize automatically “by sight”—for fluent readers, that’s almost all words! High-frequency words, the most commonly occurring words in written English like those on the Dolch list, are often thought of as the most crucial sight words.
It’s a myth that blindly memorizing every letter in a sight word is the only way to learn it. The science of reading tells us that linking sounds and letters is the most effective way for kids’ brains to learn any word. Many common words are easy to tackle using beginning phonics skills (like “at,” “can,” “him,” etc.), so staying true to a strong phonics curriculum is one way to support kids’ sight word learning. Even irregularly spelled words have decodable parts, e.g., kids can use the sounds of “s” and “d” to help with “said,” even if the “ai” is unexpected. Experts often call these words “heart words” to call out for kids that they should learn the unexpected word parts “by heart.
” (If all this is unfamiliar to you, it can feel overwhelming, but you’ve got this! Check out teaching guru Jillian Starr’s explanation for more help.)
Check out these low-prep and engaging sight word activities for both teaching and practicing words.
1. Map it and drive it
This is a genius way to introduce words with appealing materials: Say the word, represent each sound with a LEGO brick, write letters for each sound, and “drive” to read it.
Source: @droppinknowledgewithheidi
2. Smush play dough for each sound
Set up a routine that works for any word. Play dough squishing for each sound is the ultimate multi-sensory component.
ADVERTISEMENT
Source: @playdough3plato
3. Map words with a magnet wand
It is so super-satisfying to drag those magnetic dots around! Watch the video below for lots of tips on introducing a word using this process.
Source: @warriorsforliteracy
4.
 Make a mini book
Make a mini book
Lots of handy info in one place for your little learners.
Source: @hughesheartforfirst
5. Tap it, pop it, learn it!
Hardwire those words in kids’ brains with this comprehensive word intro routine. (You had us with the pop its!)
Source: @hellojenjones
6. Find and swat words
An oldie but such a goodie. Find a word in an array and WHACK! Swat it with a fly swatter!
Source: @kids_play_learn_laugh
7. Flip word pancakes
Serve up sight word pancakes while practicing spelling them aloud.
Source: @bee_happy_teaching
8. Wear heart word bracelets
Make kids feel like sight word VIPs.
Source: @teachingmoore
9. Search for sight word balls
Write sight words on ball pit balls with a chalk marker or dry-erase marker. Kids can race around hunting for balls to read and toss in a basket, or hunt through a big tub of balls for a certain word.
Source: @preschoolforyou
10.
 Start a sight word band
Start a sight word bandLoud but oh-so-fun! Feel the rhythm while tapping and reading sight words stuck to homemade percussion instruments.
Source: @earlyyears_withmrsg
11. Drive on a sight word path
This is one of many fun ways to use magnetic tiles for learning! Kids love “knocking down” word tiles with a toy car as they read each one.
Source: @travisntyler
12. Use sticky notes to inspire sight word sentences
Have kids stick words on items that give them ideas for sentences. “My Mom said to wear a helmet!” = so good!
Source: @kinneypodlearning
13. Write words on a sensory bag
So easy: Fill a zip-top bag with a small amount of kid-safe paint, seal well, and have kids practice “writing” sight words with their finger or a cotton swab.
Source: @makeitmultisensory
14. Wear a sight word crown
Wear your word proudly and practice reading others’ words. Fun in person or virtually.
Source: @mrsjonescreationstation
15. Play a magnetic-tile board game
We love new ideas for ways to use magnetic tiles for sight word activities. Easy to set up and fun to play.
Source: @twotolove_bairantwins
16. Spell words to a familiar tune
Get sight words stuck in everyone’s head, in a good way. We’d add a line for chanting the sounds in the word!
Source: @saysbre
17. Feed a word monster
Nom, nom, nom.
Source: @ecplayandlearn
18. Search for the pom-pom under sight word cups
Read all the words as you try to find the cup that hides the prize.
Source: @la.la.learning
19. Play sight word KABOOM
This classroom classic is perfect for sight words. If you need a refresher on the rules, Jillian Starr covers them.
Source: @essentiallykinder
20. Roll and write words
Roll, write, repeat.
Source: @mylittlepandamonium
21. Write words with rainbow colors
Bonus points for aromatic markers.
Source: @mylittlepandamonium
22. Trace words with flashlights
Stock up on batteries because kids never get tired of this!
Source: @giggleswithgerg
23. Find words in plastic eggs
Give kids a checklist of words to find as they open each egg.
Source: @blooming_tots1
24. Spy words around the classroom
Just add a magnifying glass and clipboard to make kids feel like supersleuths!
Source: @readingcorneronline
25. Find words in the morning message
Don’t forget about old standbys! This is one of our favorite ways to get kids to recognize sight words in connected text.
Source: @tales_of_a_kinder_classroom
26. Build words with bricks
Such a great use of extra building bricks!
Source: @raysinkinder
27. Write words in sand
Easy-peasy to set up and keep neat if you use plastic pencil boxes.
Source: @teacherhacks
28. Spell words on a construction site
Bulldozing over each word to read it is the best part!
Source: @planningplaytime
29.
 Spell words with toy cars
Spell words with toy carsDrive on over!
Source: @lozlovesprep
30. Park in a sight word “parking lot”
This one is easy to modify based on whatever toys are available in the classroom or at home.
Source: @msbendersclassroom
31. “Plant” words in play dough
Watch those reading skills grow!
Source: @planningplaytime
32. Build words in a sensory tub
Because spelling is just more fun when your hands are covered in beans!
Source: @coffeeandspitup
33. Write words on a magnetic drawing board
That eraser track makes for a perfect word card holder!
Source: @moffattgirls
34. Or write words on the window!
Everyone wants a turn to write on the window!
Source: @kindergarten_matters
35. Shhh! Discover words written in invisible ink
Write words in white crayon and reveal them with watercolors on top!
Source: @teachstarter
36.
 Dot-paint words with a cotton swab
Dot-paint words with a cotton swabCalming and effective.
Source: @sightwordactivities
37. “Type” words on a keyboard
Busy day at the sight word office! Use a keyboard cover or any old keyboard.
Source: @lifebetweensummers
38. Read words before heading through the door
The line leader can double as the word pointer during transitions.
Source: @ms.rowekinder
39. Read the word the teacher’s wearing!
Wait, is there something on my shirt?
Source: @theprimarypartner
40. Take a sight word cakewalk
Choose a winning word when the music stops!
Source: @joyfulinkinder
41. Play sight word hopscotch
If you can’t get outdoors, tape on the floor works just as well.
Source: @wheretheliteracygrows
42. Play tic-tac-toe
I’ll be team “the.”
Source: @create_n_teach
43. Go sight word bowling
No bowling pins? Use half-filled plastic water bottles instead.
Source: @thecreativeteacher_
44. Ready, aim, read
Just throw a beanbag at a word target if foam darts are a no-go.
Source: @laurens_lil_learners
45. Play muffin tin ball toss
Toss and read. It’s easy to use colored muffin cups to prep different sets of words.
Source: @homeschooling_fun_with_lynda
46. DIY sentence flash cards
Authentic use of words in context for the win.
Source: @teachertipsandtales
47. Play sight word checkers
King me! If kids don’t have a partner available, they can “play” with a stuffed animal and get double practice.
Source: @sightwordactivities
48. Play sight word Guess Who?
Set up this game once and use it forever.
Source: @lessons_and_lattes
We’d love to hear—what are your favorite sight word activities? Share in the comments below.
Want more articles like this? Be sure to sign up for our newsletters.
Plus, what are sight words?
14 Fun Sight Word Activities and Games (Printables Included!)
Are you looking for fun sight word activities and sight word games that you can do in the classroom with your pre-k or kindergarten students? Or maybe you are looking for something different to send home for homework with your children?
Whether you use the Dolch sight words, the Fry sight words, or another list, we have some options to make this part of your ELA curriculum a whole lot more fun!
Sight Word Games
Sight word games make learning all those words that early readers need to recognize a whole lot easier and a lot more fun too. So we did a deep dive into the world of sight words to come up with some games that would help kids remember the most common sight words and make teachers’ lives easier too!
So we did a deep dive into the world of sight words to come up with some games that would help kids remember the most common sight words and make teachers’ lives easier too!
Many of these games are printable, so you can easily use them in the classroom — but there are virtual options too!
How to Play the BOOM Sight Word Game
To kick things off, teacher @misslearningbee shared this sight word game with Teach Starter, and we were instantly hooked not only because it is super easy to set up, but because it has already been tried and tested, and her kids just love it! The best thing about this game is that you can easily differentiate but keep each sight word level together using some rubber bands. Here’s what you need to know:
- Write the chosen sight words on colorful craft sticks.
- Write the word BOOM on a few sticks — this is the key to making this game fun!
- Pair students off to work together (or create small groups!), and set a timer for your desired time.
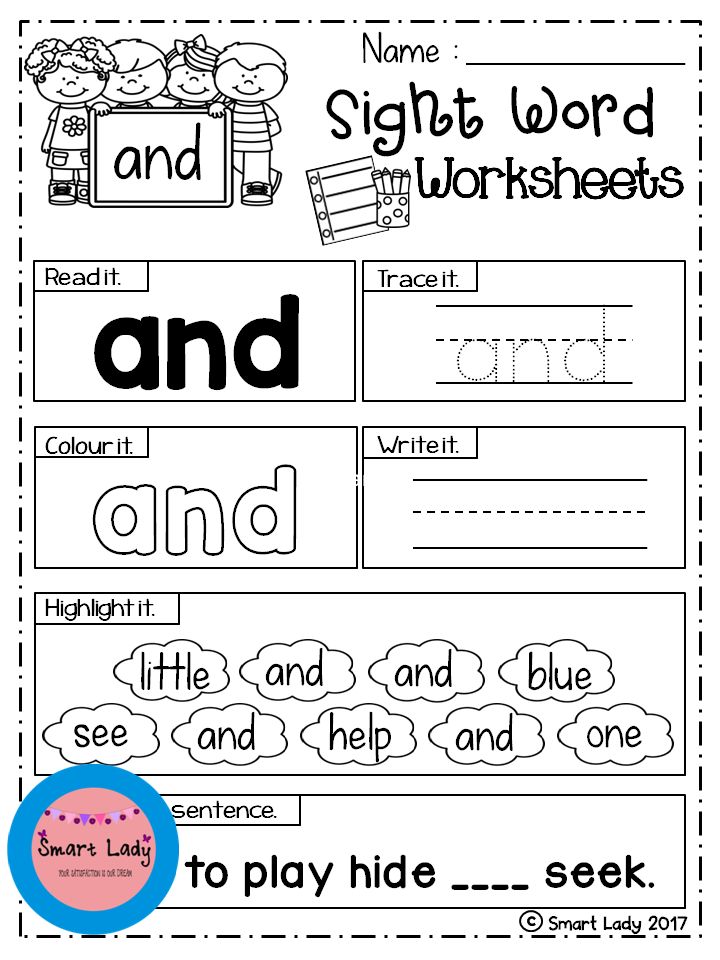
- Place the sticks in a cup with the word side down.
- Students should then take turns passing the cup, pulling out a stick, and reading the word.
- If they read the word correctly, they get to keep the stick!
- If they pull out a BOOM stick, the other player gets all of their sticks. If they’re in larger groups, the student gives their sticks to their partner or person to their right.
- At the end of the time limit, the person with the most sticks wins!
As an extension or alternative to using Boom sticks as a sight word game, you could do rhyming words, or students could put the words into a sentence. Other ideas include:
- parts of speech
- describing words
- numbers
- addition/subtraction problems.
Sight Word Hopscotch Game
Inspired by hopscotch, this sight word game is an active one that will help them get the wiggles out.
Find a tiled area and write one sight word on each tile with three different colors.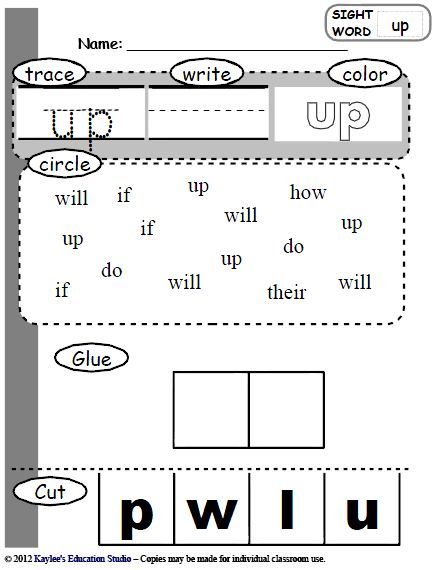 Children then pick a color, and by hopping only on that color sight word, they can get home. They must say each sight word as they hop on it to get to the end.
Children then pick a color, and by hopping only on that color sight word, they can get home. They must say each sight word as they hop on it to get to the end.
Sight Word Fishing Game
It looks basic, but children in my class loved this game — it’s sight word fishing!
Attach paper clips to sight word flashcards, and create a fishing rod with a magnet at the end of the string. In a small group, children take turns trying to fish out a sight word. If they can successfully fish the sight word and say the sight word, they get to keep that flashcard. The child with the most sight word flashcards at the end wins!
Bowling for Sight Words
Pick up a cheap plastic ten-pin bowling set from your local dollar store. Using some sight word flashcards, place a hole punch in the corner, and attach one word to each pin using a rubber band.
Students try and hit as many pins over as they can, then correctly say each of the sight words they knocked over in order to add to their overall score!
Sight Word Popcorn
Print out sight word flashcards on yellow paper and scrunch up just like popcorn. Have students pick a piece of popcorn and read the sight word. If they get it correct they get to keep that piece of popcorn. Who can fill their popcorn bucket first?
Have students pick a piece of popcorn and read the sight word. If they get it correct they get to keep that piece of popcorn. Who can fill their popcorn bucket first?
Printable Sight Word Games
If you are looking for another sight word game that you can play in your reading centers or to send home for some fun sight word practice, we’ve got you covered! Here are some of our sight word games. Although we have used the Dolch Sight Words list of words, you can use the editable version when available to suit the sight words that you may use at your school.
Fishy Find Sight Word Game
For this version of a fishing sight word game, we’ve created the fish you’ll need to get started! Just follow the instructions below!
- Set up a station with a large bowl.
- Attach metal paper clips onto the creatures and attach a magnet to a stick and string.
- To help build word recognition, students need to lower their fishing rod into the bowl, then read the word on the fish they have caught, and then place them in a pile.
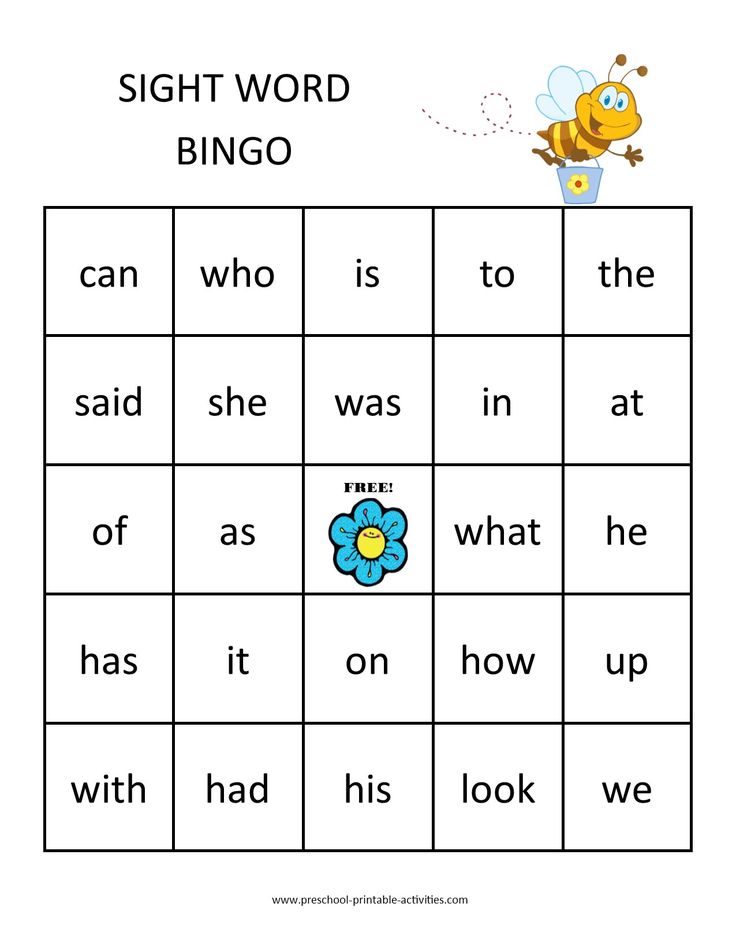
Sight Word Bingo
There was a game to play with sight words, and Bingo was its name-o! (Sorry, we had to!).
This printable sight word game takes classic Bingo and adds the first 100 words on the Fry Sight Words list to make a game the whole class can play! Print them out on sturdy cardstock, and you’ll be able to use the bingo cards, again and again, to help your early readers really nail those crucial words.
Available as a Powerpoint or in Google slides, this is also a great sight word activity for virtual students. Get additional words:
teaching resource
Sight Word BINGO (Fry Word List 101-200)
Practice learning sight words 101-200 on the Fry Sight Word List with our set of 22 Sight Words Bingo cards.
42 pagesGrades: 1 - 2teaching resource
Sight Word BINGO (Fry Word List 201-300)
Practice learning sight words 201-300 on the Fry Sight Word List with our set of 22 Sight Words Bingo cards.
42 pagesGrades: 1 - 2Fun Sight Word Activities
Need other sight word activities that will get your preschoolers and kindergartners excited? These options are not necessarily game-like, but there’s still plenty of fun packed in.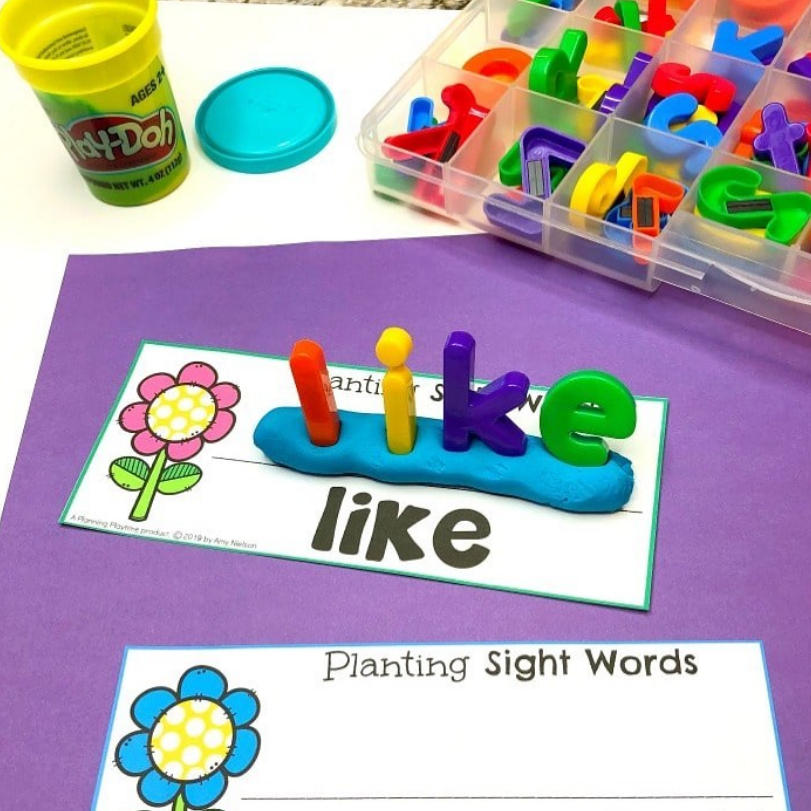
Let Students Write on Their Desks
What’s more fun for kids than the ability to write on the desk?
Use a window marker to write sight words on the desk (don’t worry, the writing comes off easily with a damp wipe). Have students pick three or four sight word flashcards suitable to their level, then have them copy each of the sight words on their desk.
Sand or Rice Writing
Fill a tray with sand or rice in a tray and have students pick sight word flashcards, then write that word in the sand or rice.
Place a sheet of colored paper on the bottom of the tray for a more visually appealing activity.
Sight Word Paper Cup Tower Building
Using paper cups, stick sight words to each cup using a glue stick. Children must correctly say the word on each cup before they can place it on their “sight word tower.” Challenge your students to find out who can correctly say all of the words and create the tallest tower! Bonus: This sight word activity also helps them build those engineering skills.
Play Dough Sight Word “Writing”
Who doesn’t love to play with play dough? Using sight word flashcards, have students pick a word and then create it using play dough. You can also print the sight word cards and send them home for parents to practice sight words at home with their children.
Mess-Free Paint Writing
Put some paint or cheap hair gel in a plastic zip-lock bag, have your students pick sight words, and then use a cotton swab or their finger to write the sight word! Easy-peasy lemon squeezy.
Scratch Paper Fun
Black paper that can be “scratched” to reveal rainbow-colored designs isn’t just good for art class. Encourage your students to write each sight word on the scratch paper to create a colorful list of sight words.
Magic Sight Words Activity
Using a white crayon, write some tricky sight words on a white piece of paper. Children then use watercolor paint to discover their magic words. Can they work out what the magic sight words are? Challenge students by writing a secret sight word message for them to discover!
Can they work out what the magic sight words are? Challenge students by writing a secret sight word message for them to discover!
Want more sight word fun? Check out our mini sight word books!
Program "STEM education for children of preschool and primary school age"
Explanatory note
The proposed program "STEM-EDUCATION OF PRESCHOOL AND PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN" is a partial modular program of preschool education aimed at developing intellectual abilities in the process of cognitive activity and involvement in scientific and technical creativity.
The program can also be successfully used in extracurricular activities within the framework of the main educational program of primary general education, and each of its sections - an educational module - can be used as an independent unit in the system of additional education.
The Law “On Education in the Russian Federation”, the federal state educational standard for preschool education, the state program of the Russian Federation “Development of Education” for 2018-2025 and the “Strategy for the Development of Education until 2025” set new targets for the development of the education system in the Russian Federation: creation mechanisms for its sustainable development, ensuring compliance with the challenges of the 21st century, the requirements of the innovative development of the economy, the modern needs of society and every citizen.
One of the trends in the development of modern education is its socio-cultural modernization. The focus of the methodology of socio-cultural construction of education as the leading social activity of society is the formation of civic identity, the formation of civil society, the strengthening of Russian statehood; development of individuality and competitiveness of the individual in a constantly changing world.
The concept of modern education is based on humanistic principles of education, which are based on the theory of "child-centrism" - the absolute value of childhood, when the idea of childhood should be at the center of any government decisions and political programs.
Hence the special status of preschool and primary levels of education, since it is during this period that the fundamental components of the formation of the child's personality and the foundations of cognitive development are laid.
GEF DO assumes the formation of cognitive interests and actions of preschoolers in various types of activities, and the primary education standard provides recognition of the decisive role of the content of education, ways of organizing educational activities and interaction of participants in the educational process to achieve the goals of personal, social and cognitive development of younger students.
Thus, at the present stage of development of education for children of preschool and primary school age, the emphasis is shifted to the development of the personality of the child in all its diversity: curiosity, purposefulness, independence, responsibility, creativity, ensuring successful socialization of the younger generation, increasing the competitiveness of the individual and, as a result , society and the state.
Modern education is more and more focused on the formation of key personal competencies, that is, skills directly related to the experience of their application in practical activities, which allow students to achieve results in uncertain, problematic situations, to solve problems independently or in cooperation with others, are aimed to improve the skills to operate with knowledge, to develop the intellectual abilities of children.
Currently, there is a wide variety of interpretations of the terms "intelligence" and "intellectual abilities" (G. Gardner, M. A. Kholodnaya, N. N. Moiseev). The most common is the concept of intelligence as "the ability to carry out the process of cognition and to effectively solve problems, the ability to plan, organize and control one's actions to achieve the goal."
Gardner, M. A. Kholodnaya, N. N. Moiseev). The most common is the concept of intelligence as "the ability to carry out the process of cognition and to effectively solve problems, the ability to plan, organize and control one's actions to achieve the goal."
Essential for understanding the intellect and intellectual abilities are such personality traits as the desire for new knowledge and deep understanding of everything that aroused interest; the ability to use existing experience and separate the main from the secondary; logic, criticality, breadth and creativity of thinking; the ability to generalize, abstract and find patterns; learnability.
In the modern world, the problem of becoming a creative person who is able to independently replenish knowledge, extract useful things, and realize their own goals and values in life is very urgent. This can be achieved through cognitive research activities, since the child's need for new experiences underlies the emergence and development of inexhaustible research activity aimed at understanding the world around. In the presented program, the emphasis is placed on cognitive research activities, which are aimed at obtaining new and objective knowledge.
In the presented program, the emphasis is placed on cognitive research activities, which are aimed at obtaining new and objective knowledge.
One of the significant areas of cognitive research activity is children's scientific and technical creativity, and one of the most innovative areas in this area is educational robotics, which combines classical approaches to studying the basics of technology and information modeling, programming, and information technology.
The comprehensive program "Development of educational robotics and continuous IT education in the Russian Federation" (No. 172-R of 01.10.2014) defined a number of tasks focused on preschool and primary levels of education. Among them:
- popularization of educational robotics and scientific and technical creativity as forms of leisure activities for students of preschool, general and additional education organizations;
- technical equipment of organizations of preschool, general and additional education of children, implementing programs to study the basics of robotics, mechatronics, IT and scientific and technical creativity of youth;
- improvement of the system of self-study in the implementation of programs of preschool, general and additional education for children;
- improving the efficiency of using interactive technologies and modern technical teaching aids;
- improvement of the mechanisms of public-private partnership in the system of preschool, general and additional education.

These tasks are designed to develop in a child such structural elements of information competence as the formation of information processing processes; formation of motivational motives and value orientations; understanding of the principles of operation, capabilities and limitations of technical devices designed for automated search and processing of information; communication skills, the ability to communicate; ability to analyze their own activities.
The essence of scientific and technical creativity lies in the application of scientific achievements to create technical products that meet specified requirements. The basic method of technical creativity is design, that is, the creation of a new one from a set of already existing, ready-made elements, although recently elements of design activity have been introduced into technical creativity.
There is a technological revolution going on right now. High-tech products and innovative technologies are becoming an integral part of modern society.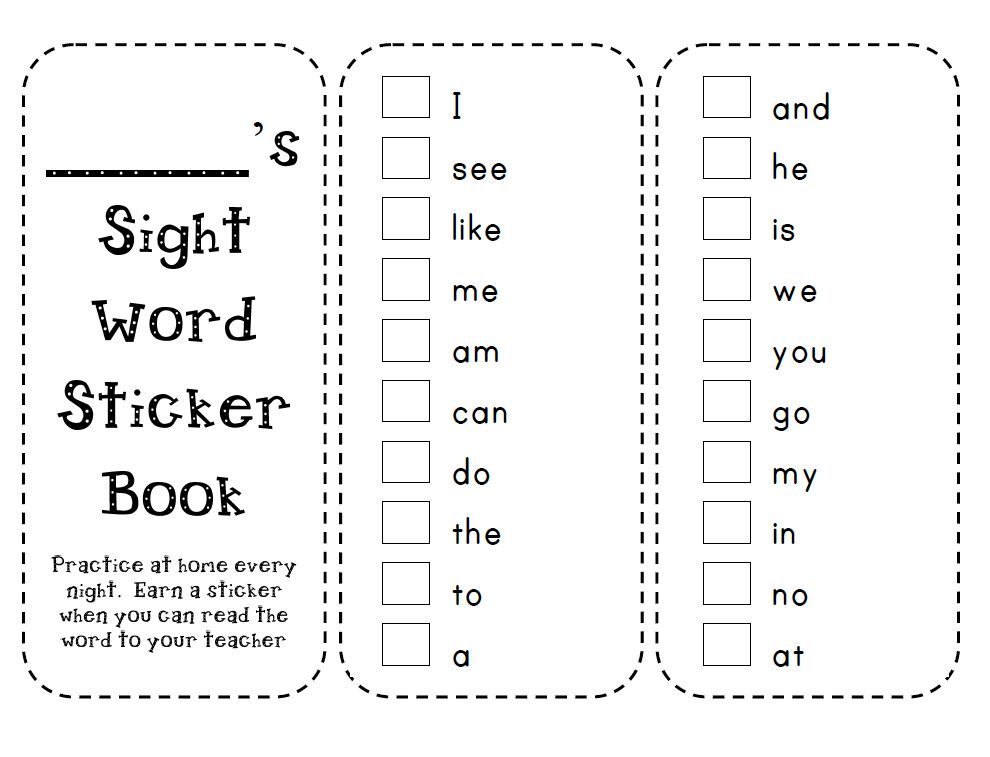 If in developed countries there are many regional and national projects to attract children to scientific and technical creativity, to increase its attractiveness and status, then in our country with the disappearance of the system of circles of young technicians, modellers and designers, children's technical creativity has declined. At present, the system of technical creativity of children of preschool and primary school age is being revived, taking into account the requirements of the time. There are investments in the creation of children's technology parks. New state educational standards require the introduction of modern technologies in the educational process. However, the designation of the problem does not say anything about how exactly the technical creativity of preschoolers and younger schoolchildren should develop.
If in developed countries there are many regional and national projects to attract children to scientific and technical creativity, to increase its attractiveness and status, then in our country with the disappearance of the system of circles of young technicians, modellers and designers, children's technical creativity has declined. At present, the system of technical creativity of children of preschool and primary school age is being revived, taking into account the requirements of the time. There are investments in the creation of children's technology parks. New state educational standards require the introduction of modern technologies in the educational process. However, the designation of the problem does not say anything about how exactly the technical creativity of preschoolers and younger schoolchildren should develop.
An attempt to develop intellectual abilities in regulated classes in kindergarten and lessons in elementary school is ineffective, since higher levels of competencies require independence, responsibility in solving non-standard tasks, which is poorly achievable within the traditional model of education. Only a fundamentally new construction of the educational environment, an integral part of which is the developing object-spatial environment, can answer this challenge.
Only a fundamentally new construction of the educational environment, an integral part of which is the developing object-spatial environment, can answer this challenge.
Therefore, the purpose of this partial modular educational program "STEM education of children of preschool and primary school age" is to develop the intellectual abilities of children of preschool and primary school age by means of STEM education.
If you decipher this abbreviation, you get the following: S - science, T - technology, E - engineering, M - mathematics: natural sciences, technology, engineering, mathematics.
That is why today the STEM system is developing as one of the main trends. STEM education is based on the application of an interdisciplinary and applied approach, as well as the integration of all four disciplines into a single scheme.
From the address of the President of the Russian Federation V.V. Putin to the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation on March 1, 2018: “Today, knowledge, technology, and competencies are the most important competitive advantage. This is the key to a real breakthrough, to improving the quality of life. In the shortest possible time, we need to develop an advanced legislative framework, remove all barriers to the development and widespread use of robotics, artificial intelligence, unmanned vehicles, e-commerce, and big data processing technologies.” These words actualize STEM education and emphasize its advantages, namely:
This is the key to a real breakthrough, to improving the quality of life. In the shortest possible time, we need to develop an advanced legislative framework, remove all barriers to the development and widespread use of robotics, artificial intelligence, unmanned vehicles, e-commerce, and big data processing technologies.” These words actualize STEM education and emphasize its advantages, namely:
- An integrated approach to solving modern problems based on the interpenetration of various areas of natural sciences, engineering creativity, mathematics, digital technologies, etc. This integration is based on the project method based on cognitive and artistic search and having a specific real product in as a result of activity.
- Adaptation of children, starting from preschool age, to the modern educational environment at all levels of education. In the context of the continuity of all levels of the educational system of the Russian Federation, all components of the educational environment - content, technology, subject-spatial content, material and technical support - are successive in the logic of age-related opportunities and content complication.

- The development of intellectual abilities in the process of cognitive research activities and involvement in scientific and technical creativity is aimed at developing not only competencies specific to these types of activities, but also a comfortable sense of self in the modern world, creating conditions for a high quality of life in the future.
- The development of critical thinking is seen as a three-stage process aimed at the formation of:
- skills to obtain the necessary information;
- skills to analyze it;
- skills to apply the received information in practice.
- The formation of teamwork skills in synthesis with the individualization of education lies in the ability to:
- combine individual intelligent algorithms to achieve common goals;
- negotiate, ask questions correctly, argue with logically substantiated facts, etc.,
that is, it forms a culture of discussion and the skill of "sublimated conclusion".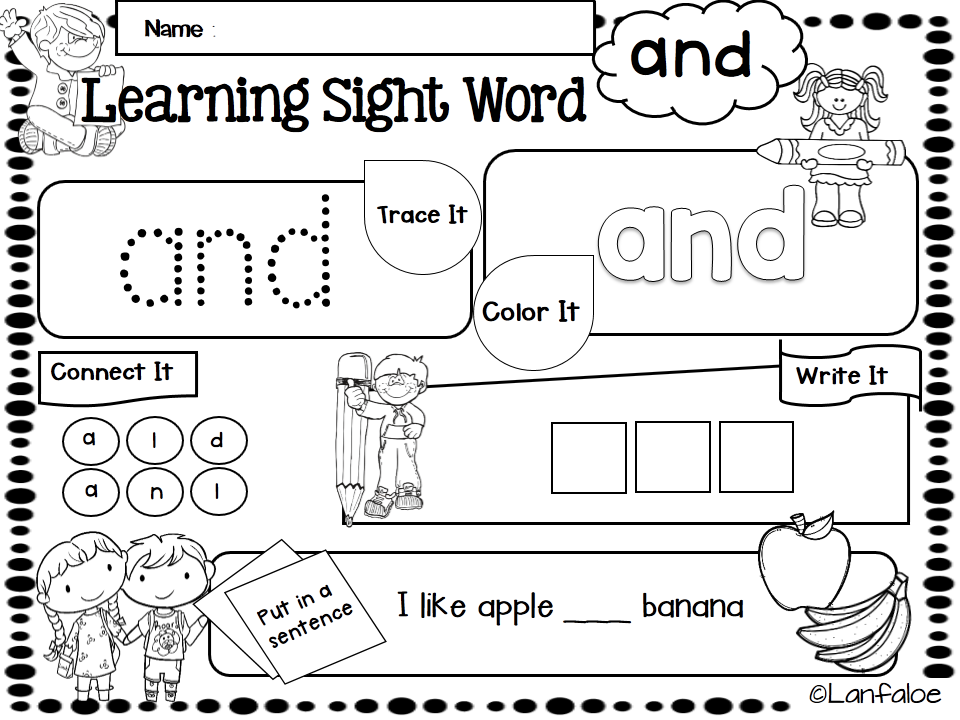 The overall positive result forms self-confidence and a sense of teamwork efficiency.
The overall positive result forms self-confidence and a sense of teamwork efficiency.
In addition, in the process of collective activity, a value attitude is brought up both to the process and to the results of labor, both of the general and of each participant.
- Primary propaedeutics of a number of professions and specialties of the 21st century, including: specialists in the field of information technology, including information security, who are able to work with a large amount of operational information; analysts, engineers and operators of electronic computing systems; specialists of engineering industries; specialists in the field of robotics, automation, nuclear physics, radiochemistry, safety and non-proliferation of nuclear materials; military professions where technical knowledge from different areas is required.
- Development of interest in technical creativity. STEM education is designed to revive the system of sections and circles of "young technicians", based on the natural interest of children in technical design and modeling.

It is important that these types of activities are based on the child's research experience acquired in kindergarten, so that the natural-science picture of the world is formed on the basis of a system-activity approach and is based on knowledge gained experimentally.
In this program, the child explores the world around him through play and experimentation with objects of animate and inanimate nature. Methodological materials provide a link between living beings and robots, motivating the child to move from the game and children's experiment through design and exciting technical and artistic creativity to the design and creation of robots - models resembling objects of the living world. The basics of programming and the use of sensors lead the child to desire to endow these creatures with sight, hearing and logic. This is a very exciting process that can become a motivational core until graduation and getting your favorite specialty: engineer, programmer, designer, scientist.
STEM thus becomes an addition to the compulsory part of the main educational program (BEP). In the main educational program for preschoolers, especially in the part developed by the participants in educational relations, the demanded content is mobile and dynamically implemented, which meets the interests and priorities of the modern preschooler.
STEM programs for elementary school students are focused on increasing their interest in regular lessons, where they receive basic knowledge from various fields of science and technology. In extracurricular activities, students apply the knowledge they have already acquired and supplement it with the skills obtained in experimental practice.
- Formation of the foundations of security, both one's own (in the process of interaction with the outside world) and the security of the environment, which directly depends on human activity, understanding technocratic risks, the impact of technological development on the environment and the state of the planet as a whole.
 Particularly relevant is the question of the possible impact of robotization on the fate of mankind.
Particularly relevant is the question of the possible impact of robotization on the fate of mankind. - Creation of conditions for the identification and further support of gifted children with extraordinary thinking and showing special abilities and desire for scientific and technical creativity.
Note that these advantages provide amplification of child development, “a necessary condition for the versatile upbringing of a child” (AV Zaporozhets). The significance of the richness of opportunities in the early stages of child development is especially great. This is a means of overcoming his one-sidedness, revealing inclinations and abilities. In accordance with the theory of A. V. Zaporozhets, the STEM education program involves the maximum enrichment of specific forms of children's activities: games, cognitive research, design, artistic and aesthetic, and also provides the opportunity for children to communicate productively with each other, with teachers and parents for a full-fledged development of the intellectual abilities of each child.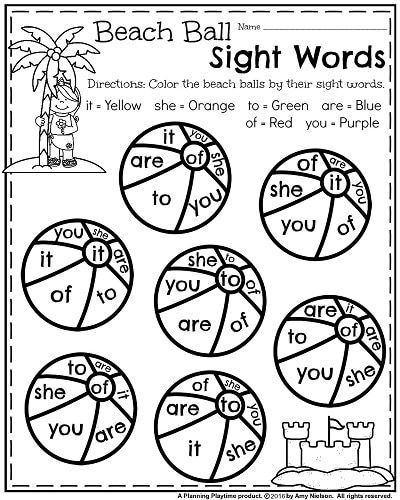
This partial modular program "STEM-EDUCATION OF PRESCHOOL AND PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN" determines the content and organization of the educational process for preschool children in the studio-circle, and junior school - in extracurricular activities. This content can also supplement the mandatory part of the main general education program.
Structural partial modular program "STEM-EDUCATION OF PRESCHOOL AND PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN" is presented in the integration of educational modules indicated in the diagram.
Implementation of educational modules in the priority activities of children of preschool and primary school age
- Game.
- Design.
- Cognitive and research activities.
- Educational activities.
- Various types of artistic and creative activities.
- Mastering XX technologies! century (elements of programming and digital technologies).
Each module is aimed at solving specific tasks, which, when integrated, ensure the implementation of the goals of STEM education: the development of intellectual abilities in the process of cognitive research activities and the involvement of preschool and primary school children in scientific and technical creativity.
The Program provides conditions for the development of intellectual abilities in accordance with the age and individual characteristics of the child. Starting with sensory perception through visual-figurative and verbal-logical thinking (“F. Froebel’s didactic system”, “Mathematical development”, “Experimenting with animate and inanimate nature”), the prerequisites are created for the scientific and technical creativity of children, during which they receive and apply the knowledge of algorithmization, design and programming and conduct project activities (“LEGO-construction”, “Animation studio “I create the world”, “Robotics”).
The activity of an adult is aimed at making the child accept the general scheme of action, feel the connection between educational modules, the meaning of each link in the general system of action, the hierarchy of secondary and main goals. In this case, the child acquires the ability to act "in the mind", which is the most important condition for the development of intellectual abilities.
The content of each module is divided into two parts: for preschool children and for younger students. Within each part, the content is differentiated, taking into account the specifics of the educational module and the age of the pupils.
Achievement of the set goals is carried out in activities specific for children of this age, such as playing, designing, cognitive and research activities (including scientific and technical creativity), various types of artistic and creative activities (design, creating cartoons, etc.) . These types of activities organically include the development of technologies of the XXI century (elements of programming and digital technologies).
Read full program...
Special preschool education
Qualification - Educator of preschool children with developmental disabilities and with safe development
Many of us remember our beloved kindergarten teacher, who every morning for many years took us from our mother's hands into his own. He taught us how to dress ourselves, how to use a spoon and fork, played games and made us laugh. And later, when we got older, he taught us to count and write. It was with his help that we clumsily spelled the word "MAMA" for the first time. He always empathized with our victories and failures.
He taught us how to dress ourselves, how to use a spoon and fork, played games and made us laugh. And later, when we got older, he taught us to count and write. It was with his help that we clumsily spelled the word "MAMA" for the first time. He always empathized with our victories and failures.
Implemented in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia dated October 27, 2014 No. 1354 "On approval of the federal state educational standard of secondary vocational education in the specialty 44.02.04 Special preschool education."
Field of professional activity of graduates:
- upbringing and education of preschool children with developmental disabilities and with safe development in educational institutions of various types and at home.
Professional activities:
-
organization of activities aimed at improving the health of the child and his physical development;
-
training and organization of various activities and communication of children with safe development;
-
training and organization of various activities and communication of children with disabilities;
-
interaction with parents, persons replacing them, and employees of the educational organization;
Objects of professional activity of graduates:
-
tasks, content, methods, means, forms of organization and the process of educating and educating preschool children with disabilities and with safe development;
-
tasks, content, methods, forms, means of organization and the process of interaction with colleagues and social partners (institutions, organizations) of education, culture, parents (persons replacing them) on the issues of education and upbringing of preschool children with disabilities and with safe development;
Personal qualities and abilities required in the profession:
-
the ability to empathize;
-
friendliness, sociability;
-
courtesy, courtesy;
-
love for children;
-
positivity;
-
great sense of responsibility;
-
ability to perform routine work;
-
accuracy and consistency in work;
-
good memory, ability to teach others;
-
grammatically correct speech;
-
the ability to care for others;
Description of profession
But an even greater responsibility falls on the educator if he works with "special" children who have speech, visual, motor or auditory developmental disorders. Such children and their parents are in dire need of the help of a highly qualified specialist. An educator working with children with disabilities is able to teach such children to serve themselves independently, move around in the surrounding space, speak correctly, and communicate with peers.
Such children and their parents are in dire need of the help of a highly qualified specialist. An educator working with children with disabilities is able to teach such children to serve themselves independently, move around in the surrounding space, speak correctly, and communicate with peers.
There are many noble professions. These are doctors, and rescuers, and the military, and policemen. But among them there is a profession that, without potions and injections, heals with a word, advice, smile, attention. This profession is for those who love children. Preschool education is carried out, as a rule, in kindergartens, boarding schools, polyclinics, correctional and rehabilitation centers, etc., but it can also be carried out at home in the family. The change in the demographic situation has led to the need for more kindergartens and, accordingly, for staff. Each child is a person with his own needs, beliefs, opportunities, abilities. Taking into account the fact that in Russia now more than a third of young families with a child are not provided with preschool institutions, preparing parents for the basics of family preschool education is becoming one of the most important tasks.
Raising a person in the full sense of the word means performing a miracle, and such miracles are performed daily, hourly, every minute by ordinary people, because the foundations of education are laid for the first years of life. It is important that at this stage there are qualified educators with the children.
Profile disciplines in your program:
Fundamentals of general and preschool pedagogy
Psychology
Age anatomy, physiology and hygiene
Fundamentals of correctional pedagogy and correctional psychology
Medical and biological foundations for the education and upbringing of children with disabilities
Theoretical and methodological foundations of physical education and development of children of early and preschool age
· Workshop on improving motor skills and abilities
Psychological and pedagogical foundations of the organization of preschool children
Theoretical and methodological foundations for the organization of various types of activities for children of early and preschool age
· Theoretical foundations and methods of mathematical development, children's literature of preschoolers, speech in children, musical education.