Reading goals for first grade
1st Grade Reading IEP Goals
This IEP goal bank is on first-grade reading prerequisite skills, including progress monitoring, data collection tools, worksheets, and lesson packs for all top nationally used IEP goals.
Best First Grade Reading IEP Goals
Free IEP goals and objectives for 1st grade reading that are focused on a learning progression for most common core clusters to build strong reading foundational skills for future grades.
MathELA
Kindergarten1st2nd3rd4th5th6th7th8th
First Grade Reading IEP Goals
L.1: Language
- L.1.1: Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking.
- L.1.1.A: Print all upper- and lowercase letters.
- L.1.1.B: Use common, proper, and possessive nouns.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Form the singular possessive
- Select the possessive noun that matches the picture
- Identify proper nouns
- Sort common and proper nouns
- L.
1.1.C: Use singular and plural nouns with matching verbs in basic sentences (e.g., He hops; We hop).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Complete the sentence with the best subject
- Complete the sentence with the best verb
- Irregular plurals: select the word that matches the picture
- Select the regular plurals word that matches the picture
- L.1.1.D: Use personal, possessive, and indefinite pronouns (e.g., I, me, my; they, them, their, anyone, everything).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Pronoun-verb agreement: Complete the sentence with the best subject
- Pronoun-verb agreement: Complete the sentence with the best verb
- Complete the sentence with the correct personal pronoun
- Choose between subject and object personal pronouns
- L.1.1.E: Use verbs to convey a sense of past, present, and future (e.g., Yesterday I walked home; Today I walk home; Tomorrow I will walk home).

- This goal covers the following objectives
- Place sentences with irregular verbs on a timeline
- Select the sentence that tells about the future
- Select the sentence that tells about the past
- Select the sentence that tells about the present
- L.1.1.F: Use frequently occurring adjectives.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Comparing: Pictures using adjectives
- Use sense words
- Use number words
- Compare pictures using adjectives
- L.1.1.G: Use frequently occurring conjunctions (e.g., and, but, or, so, because).
- L.1.1.H: Use determiners (e.g., articles, demonstratives).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Identify articles
- Identify articles
- Use the correct article: a or an
- Use the correct article: a or an
- L.1.1.I: Use frequently occurring prepositions (e.g., during, beyond, toward).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Select the best preposition to complete the sentence
- Select the best preposition to complete the sentence
- Select the best preposition to match the picture
- Select the best preposition to match the picture
- L.
 1.1.J: Produce and expand complete simple and compound declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences in response to prompts.
1.1.J: Produce and expand complete simple and compound declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences in response to prompts.- This goal covers the following objectives
- Unscramble the words to make a complete sentence
- Complete the sentence
- Determine the naming or action part of the sentence
- Statement, question, command, or exclamation
- L.1.2: Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing.
- L.1.2.A: Capitalize dates and names of people.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Capitalize days and months
- Capitalize the names of people and pets
- Capitalize the pronoun "I"
- Capitalize the first letter of a sentence
- L.1.2.B: Use end punctuation for sentences.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Statement, question, command, or exclamation
- Choose the right end mark
- Identify and use end marks
- Sentences: Answer is it a telling sentence or an asking sentence
- L.
 1.2.C: Use commas in dates and to separate single words in a series.
1.2.C: Use commas in dates and to separate single words in a series. - L.1.2.D: Use conventional spelling for words with common spelling patterns and for frequently occurring irregular words.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Irregular plurals: select the word that matches the picture
- Form regular plurals with -s and -es
- Use singular and plural nouns
- Select the regular plurals word that matches the picture
- L.1.2.E: Spell untaught words phonetically, drawing on phonemic awareness and spelling conventions.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Complete the word with the right digraph
- Complete the word to match the picture -ss, -ll, -ff, -zz, -ck
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Complete the word with the right final consonant blend
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Complete the word with initial consonant blend
- L.1.2.A: Capitalize dates and names of people.
- L.1.4: Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 1 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies.

- L.1.4.A: Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Context clues: Use context to identify the meaning of a word
- Multiple meaning words: Multiple meaning words with pictures
- Categories: Select which one is not like the others
- Sorting: Objects into categories
- L.1.4.B: Use frequently occurring affixes as a clue to the meaning of a word.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Understand words with prefixes and suffixes
- Use words with prefixes and suffixes
- Match the -ed and -ing sentences to the pictures
- Sentences: Answer is it a telling sentence or an asking sentence
- L.1.4.C: Identify frequently occurring root words (e.g., look) and their inflectional forms (e.g., looks, looked, looking).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Match the -ed and -ing sentences to the pictures
- Understand words with prefixes and suffixes
- Use words with prefixes and suffixes
- Context clues: Use context to identify the meaning of a word
- L.1.4.A: Use sentence-level context as a clue to the meaning of a word or phrase.
- L.
 1.5: With guidance and support from adults, demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
1.5: With guidance and support from adults, demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
- L.1.5.A: Sort words into categories (e.g., colors, clothing) to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Sort words into categories
- Categories: Select which one is not like the others
- Sorting: Objects into categories
- Use color words
- L.1.5.B: Define words by category and by one or more key attributes (e.g., a duck is a bird that swims; a tiger is a large cat with stripes).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Meaning: Find the words with related meanings
- Which word is not like the others?
- Match synonyms
- Meaning: Describe the difference between related words
- L.1.5.C: Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g., note places at home that are cozy).

- This goal covers the following objectives
- Select the best preposition to match the picture
- Identify adjectives
- Use sense words
- Use action verbs
- L.1.5.D: Distinguish shades of meaning among verbs differing in manner (e.g., look, peek, glance, stare, glare, scowl) and adjectives differing in intensity (e.g., large, gigantic) by defining or choosing them or by acting out the meanings.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Meaning: Order related words based on meaning
- Meaning: Describe the difference between related words
- Meaning: Find the words with related meanings
- Match synonyms
- L.1.5.A: Sort words into categories (e.g., colors, clothing) to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent.
- L.1.6: Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using frequently occurring conjunctions to signal simple relationships (e.g., because).
- L.1.6: Use words and phrases acquired through conversations.
 ..
..- This goal covers the following objectives
- Select the best preposition to complete the sentence
- Select the best preposition to match the picture
- Use sense words
- Meaning: Describe the difference between related words
- L.1.6: Use words and phrases acquired through conversations.
RF.1: Reading: Foundational Skills
- RF.1.1: Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print.
- RF.1.1.A: Recognize the distinguishing features of a sentence (e.g., first word, capitalization, ending punctuation).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Capitalize sentences and the pronoun "I"
- Unscramble the words to make a complete sentence
- Find the complete sentences
- Find the complete sentence
- RF.1.1: Demonstrate understanding of the organization and basic features of print.
- RF.1.1.A: Recognize the distinguishing features of a sentence (e.g., first word, capitalization, ending punctuation).
- RF.1.2: Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes).
- RF.
 1.2: Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes).
1.2: Demonstrate understanding of spoken words, syllables, and sounds (phonemes).- This goal covers the following objectives
- Put two syllables together to create a word: harder
- Determine which two words end with the same sound
- Determine which two words start with the same sound
- Syllables: Determine how many syllables does the word have
- RF.1.2.A: Distinguish long from short vowel sounds in spoken single-syllable words.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Use spelling patterns to sort long and short vowel words
- Sort short and long vowel words
- Sort short and long vowel words
- Choose the word that has a different vowel sound
- RF.1.2.B: Orally produce single-syllable words by blending sounds (phonemes), including consonant blends.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Fill in the missing consonant blend
- Blending and segmenting: Blend the sounds together to make a word
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Answer does the word end with a consonant blend
- Short a: Complete the short a word
- RF.
 1.2.C: Isolate and pronounce initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in spoken single-syllable words.
1.2.C: Isolate and pronounce initial, medial vowel, and final sounds (phonemes) in spoken single-syllable words.- This goal covers the following objectives
- Complete the vowel team words
- Complete the word with the right r-controlled vowel: ar, er, ir, or, ur
- Complete the word with the right digraph
- Choose the correct digraph
- RF.1.2.D: Segment spoken single-syllable words into their complete sequence of individual sounds (phonemes).
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Put the sounds in order
- Identify each sound in a word
- Blending and segmenting: Blend the sounds together to make a word
- Blending and segmenting: Blend the sounds together to make a word
- RF.
- RF.1.3: Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.
- RF.1.3: Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Complete the word with the right diphthong: oi, oy, ou, ow
- Complete the word with the right r-controlled vowel: ar, er, ir, or, ur
- Complete the sentence with the correct short vowel word
- Complete the word with the right short vowel
- RF.
 1.3.A: Know the spelling-sound correspondences for common consonant digraphs.
1.3.A: Know the spelling-sound correspondences for common consonant digraphs.- This goal covers the following objectives
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Sort by initial consonant blend or digraph
- Spell the digraph word
- Choose the correct digraph
- Complete the word to match the picture -ss, -ll, -ff, -zz, -ck
- RF.1.3.B: Decode regularly spelled one-syllable words.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Choose the diphthong word that matches the picture
- Choose the r-control word that matches the picture
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Does the word end with a consonant blend
- Consonant blends and digraphs: Determine if the word start with a consonant blend
- RF.1.3.C: Know final -e and common vowel team conventions for representing long vowel sounds.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Choose the vowel team sentence that matches the picture
- Complete the word with the right vowel team
- Complete the silent e words
- Use spelling patterns to sort long and short vowel words
- RF.
 1.3.D: Use knowledge that every syllable must have a vowel sound to determine the number of syllables in a printed word.
1.3.D: Use knowledge that every syllable must have a vowel sound to determine the number of syllables in a printed word.- This goal covers the following objectives
- Put two syllables together to create a word: harder
- Put two syllables together to create a word: easier
- Syllables: Determine how many syllables does the word have
- Consonants and vowels: Finding vowels in words
- RF.1.3.E: Decode two-syllable words following basic patterns by breaking the words into syllables.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Complete the sentence with a two-syllable word
- Complete the two-syllable words
- Put two syllables together to create a word: harder
- Put two syllables together to create a word: easier
- RF.1.3.F: Read words with inflectional endings.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- Match the -ed and -ing sentences to the pictures
- Complete the verb with the ending that you hear
- Select the sentence that tells about the past
- Select the sentence that tells about the present
- RF.
 1.3.G: Recognize and read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words.
1.3.G: Recognize and read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words.- This goal covers the following objectives
- Complete the sentence with the correct sight word
- Choose the sight word that you hear
- Choose the sight word that you hear
- Choose the two sight words that are the same
- RF.1.3: Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words.
- RF.1.4: Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension.
- RF.1.4: Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension.
- RF.1.4.A: Read grade-level text with purpose and understanding.
- This goal covers the following objectives
- What am I?
- Choose the vowel team sentence that matches the picture
- Complete the poem with a word that rhymes
- Complete the rhyme
- RF.1.4.B: Read grade-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings.
- RF.1.4.C: Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.

- This goal covers the following objectives
- Use sense words
- Use action verbs
- Complete the sentence with the correct sight word
- Complete the sentence with a two-syllable word
RL.1: Reading: Literature
- RL.1.1: Ask and answer questions about key details in a text.
- RL.1.2: Retell stories, including key details, and demonstrate understanding of their central message or lesson.
- RL.1.3: Describe characters, settings, and major events in a story, using key details.
- RL.1.4: Identify words and phrases in stories or poems that suggest feelings or appeal to the senses.
- RL.1.5: Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information, drawing on a wide reading of a range of text types.
- RL.1.6: Identify who is telling the story at various points in a text.
- RL.1.7: Use illustrations and details in a story to describe its characters, setting, or events.

- RL.1.9: Compare and contrast the adventures and experiences of characters in stories.
- RL.1.10: With prompting and support, read prose and poetry of appropriate complexity for grade 1.
RI.1: Reading: Informational Text
- RI.1.1: Ask and answer questions about key details in a text.
- RI.1.2: Identify the main topic and retell key details of a text.
- RI.1.3: Describe the connection between two individuals, events, ideas, or pieces of information in a text.
- RI.1.4: Ask and answer questions to help determine or clarify the meaning of words and phrases in a text.
- RI.1.5: Know and use various text features (e.g., headings, tables of contents, glossaries, electronic menus, icons) to locate key facts or information in a text.
- RI.1.6: Distinguish between information provided by pictures or other illustrations and information provided by the words in a text.
- RI.
 1.7: Use the illustrations and details in a text to describe its key ideas.
1.7: Use the illustrations and details in a text to describe its key ideas. - RI.1.8: Identify the reasons an author gives to support points in a text.
- RI.1.9: Identify basic similarities in and differences between two texts on the same topic (e.g., in illustrations, descriptions, or procedures).
- RI.1.10: With prompting and support, read informational texts appropriately complex for grade 1.
W.1: Writing
- W.1.1: Write opinion pieces in which they introduce the topic or name the book they are writing about, state an opinion, supply a reason for the opinion, and provide some sense of closure.
- W.1.2: Write informative/explanatory texts in which they name a topic, supply some facts about the topic, and provide some sense of closure.
- W.1.3: Write narratives in which they recount two or more appropriately sequenced events, include some details regarding what happened, use temporal words to signal event order, and provide some sense of closure.

- W.1.5: With guidance and support from adults, focus on a topic, respond to questions and suggestions from peers, and add details to strengthen writing as needed.
- W.1.6: With guidance and support from adults, use a variety of digital tools to produce and publish writing, including in collaboration with peers.
- W.1.7: Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., explore a number of "how-to" books on a given topic and use them to write a sequence of instructions).
- W.1.8: With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question.
Special education teachers determine what children need for smart iep goals and how best to align common core state standards. Thank you for letting us be part of your special education classsroom.
1st Grade / First grade ELA goals
Language Arts in First Grade
The following goals for reading and writing instruction have been taken directly from the Scarsdale Schools' curriculum.
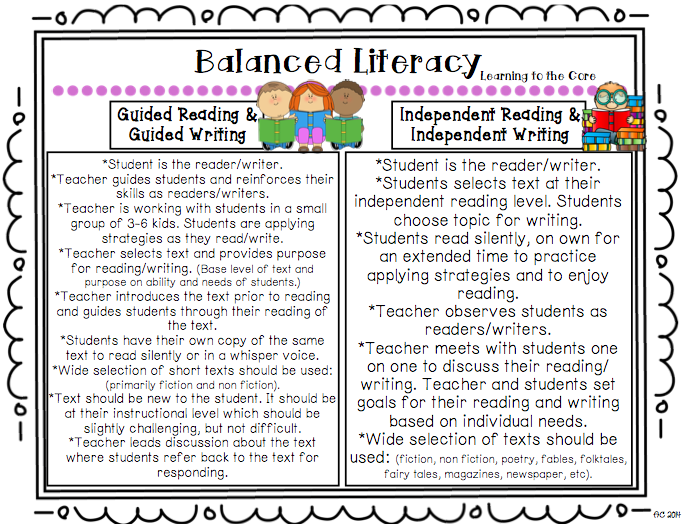
In our classroom, we work towards achieving reading goals through participation in lessons and activities planned using the TC Phonics Units of Study, Primary Concepts Sight Words, shared reading, read-alouds, guided reading groups and comprehension strategy lessons. Lessons are planned using the TC Units of Study in Reading.
Writing goals are addressed during our writing workshop which includes shared and guided writing activities, independent writing, conferences and author's circle. Lessons are planned using the TC Writing Units of Study. We also participate in Zaner-Bloser handwriting instruction and practice described on another page of our site.
First Grade Reading
Phonemic Awareness
• Count the number of syllables in a word
• Blend spoken sounds to form words, manipulating letters to represent each sound of most one-syllable words
• Segment spoken words into component sounds, manipulating letters to represent each sound of most one-syllable words
Decoding Including Phonics and Structural Analysis
• Identify and produce letter-sound correspondences, including consonants and short and long vowels
• Blend sounds using knowledge of letter-sound correspondences in order to decode unfamiliar, but decodable, one-syllable grade-level words
• Read common word families by blending the onset (/s/) and the rime (/it/, /at/) in grade-level words (s-it, s-at)
• Decode grade-level words using knowledge of root words, prefixes, suffixes, verb endings, plurals, contractions, and compounds
• Check accuracy of decoding by using context to monitor and self-correct
Print Awareness
• Identify parts of a book and their purposes, including author, illustrator, title page, table of contents, and chapter headings
Fluency
• Sight-read automatically grade-level common, high-frequency words
• Sight-read automatically grade-level irregularly spelled words
• Use punctuation clues to read connected text with expression, accuracy and fluency
• Read grade-level texts with decodable and irregularly spelled words with appropriate speed, accuracy and expression
Background Knowledge and Vocabulary Development
• Study antonyms, synonyms, and homonyms to learn new grade-level vocabulary
• Study categories of words (e. g., animals, place names) to learn new grade-level vocabulary
g., animals, place names) to learn new grade-level vocabulary
• Study root words, prefixes, suffixes, verb endings, and plural nouns to learn new grade-level vocabulary
• Connect words and ideas in books to prior knowledge
• Learn new words in context from reading books and other print sources
• Increase background knowledge by elaborating on and integrating new vocabulary and ideas from texts
• Learn the uses of a dictionary
Comprehension Strategies
• Read grade-level texts for different purposes
• Use comprehension strategies (predict/confirm, reread, self-correct) to clarify the meaning of text
• Work cooperatively with peers (partners or small groups) to comprehend text
• Use graphic or semantic organizers to organize and categorize information
• Ask questions in response to texts
• Answer questions (such as how? why? what if?) in response to texts
• Sequence events in retelling stories
• Summarize main ideas from informational texts
• Follow simple written instructions
• Use own perspectives and opinions to comprehend text
Motivation to Read
• Show interest in reading grade-level children’s texts from a variety of genres, such as stories, folktales, fairy tales, poems, and informational texts
• Read familiar grade-level texts for pleasure
• Show familiarity with title and author of grade-level books
First Grade Writing
Letters and Words
• Use lower case and upper case letters
• Use spaces between words
Capitalization
• Use capitals at the beginning of sentences, names and places, months, days of the week
Punctuation
• Use punctuation at the end of sentences
• Use periods consistently
• Begin to use exclamation points and question marks
• Begin to learn about the use of commas in dates, parts of informal letters
• Begin to learn about apostrophes in contractions
Grammar
• Use simple sentences
• Use transition words
• Use pronouns
• Match subjects with verbs
Spelling
• Write own first and last names correctly
• Use developing knowledge of letter-sound correspondence (e. g., sound spelling or invented spelling) to spell independently grade-level decodable words, including words in word families
g., sound spelling or invented spelling) to spell independently grade-level decodable words, including words in word families
• Represent most phonemes in invented spelling, although not necessarily with conventional spellings (e.g., /k/ /a/ /t/ for cat)
• Use conventional spelling to spell common grade-level irregularly spelled content and high-frequency words
• Spell correctly three- and four-letter short vowel words
• Understand the difference between conventional spelling, and sound or invented spelling
Composition
• Write stories and informational texts that establish a topic and use words that can be understood by others
• Write compositions and begin to use the writing process (e.g., prewriting, drafting, revising, proofreading, editing)
• Use conventional capitalization and punctuation to begin and end sentences
• Write compositions for various purposes and include text, illustrations, and other graphics
Motivation to Write
• Choose to write to communicate to others
• Choose to write for various purposes (e. g., tell stories, share information, give directions, write to a friend)
g., tell stories, share information, give directions, write to a friend)
• Share writing with others (e.g., participate in author’s circle)
summary of the lesson of literary reading in grade 1 | Outline of a reading lesson (Grade 1) on the topic:
SUMMARY OF THE READING LESSON 1 CLASS
Teacher of the 1st category
Chekanova Nina Trofimovna
TOPIC: Consolidation of the studied. The development of speech.
OBJECTIVES: 1. to continue working on the formation of fluent and conscious reading skills;
2. to teach children to analyze, generalize and highlight the main thing;
3. learn to build sentences from disparate words, text from sentences
4. teach children the "rules of friendly work" in the group
5. develop students' speech, thinking, enrich and activate students' vocabulary;
6. develop interest in reading
LESSON PROCESS:
I. Organizational moment
The long-awaited bell has been given.
The lesson is starting!
--Do you like reading lessons? What do you like about them?
II. Presentation of the topic and objectives of the lesson.
1). "Tell me, what do we learn in reading lessons?"
--That's right, today we will continue to learn to read expressively, fluently and try to increase the speed of reading.
But we will return to the definition of more specific goals of our work a little later. In the meantime...
--Guess which animal we are talking about?
This animal lives in the forest.
He is very careful…, quick-footed…, smart…, cunning…
Likes to hunt mice.
2). Fox enters.
--Who remembers me here?
Hello guys!
I'm so glad you're talking about me. I really love it when they talk about me, when they admire my beauty, my mind. But it is true: I am the smartest, dexterous, cunning, most beautiful.
Here is an envelope for you, it contains a task:
- Learn to solve riddles about me so as not to confuse me with other inhabitants of the forest
- Read stories about me
- Learn more about my habits
- And prepare me a present.
 I really love gifts.
I really love gifts.
And I will come for a gift tomorrow or the day after tomorrow. Goodbye!
III. Work with riddles (work in pairs)
1). -We carry out the first task of the Fox. Learning to solve riddles about the fox.
--Read the riddle. Underline the helper words that helped you solve the riddle.
--Agree who will read the riddle aloud and who will read the highlighted helper words.
(There are cards with riddles on each desk.)
The red-haired hostess came from the forest, Fluffy tail, golden fur,
Kur counted and took it with her. He lives in the forest, steals chickens in the village.
Get into the habit of a poultry house - expect trouble. Cunning cheat, red head,
Covers his tracks with his red tail. Fluffy tail is beautiful. And her name is…
Smaller than a tiger, bigger than a cat, Small in stature, long tail,
Above the ears are brush-horns. Gray coat, sharp teeth. (Mouse)
Gentle in appearance, but do not believe:
This beast is terrible in anger! (Lynx)
--Any riddles not about the fox? It can't be, because the fox said that we should learn to solve riddles about her.
--Ah, a swindler, and here she wanted to outwit!
2). Working with help words
(Write the words on the board.)
Red-haired hostess
Fluffy tail
Cunning cheat
Red tail
Golden fur
Red head
--Can you draw a fox from these words? (Then hang another drawing of a fox on the board)
--Which line of words did not participate in the drawing? Which line is missing and why? (it's about the character of the fox)
--How do you understand the meaning of the word "cheat"? (a rogue is a sly one)
3). Front work in a circle. Fox character.
(The teacher starts: he has a toy, says a word and passes it around in a circle or to the one who raised his hand)
--We talked about the appearance of the fox. Now let's find out what character the fox has and what habits it has.
What kind of fox? – dexterous = quirky, nimble, quick = quick, agile, resourceful, quick-witted, cunning = rogue, insidious, cunning, cautious
--If you find it difficult to choose words, you can use the hint: on the back of the word board, but try to explain meaning of the word.
4). Away from the word.
--Do you know why the fox is called a fox?
Choose a related word. How else can you say: fox ...
The words fox, fox are the common part of fox-. Until now, in some places they use outdated expressions fox - yellowish, fox - turn yellow. That is, the beast was called a fox for its yellow wool.
IV. Working with deformed text.
1). Let's move on to the next task of Chanterelle.
(Fox mask)
-I am an unfortunate fox,
A wasp grabbed my tail.
I, poor thing, twirled around like that,
That shattered into pieces.
-We will help you, fox,
We will put you together again from letters.
SAIL
2). Working with a deformed proposal. (Work in pairs).
--Let's clean up the sentence. (Pairs make up a proposal, stick it on a strip of paper)
For the first row - three pairs
- The fox lives in the forest.
- The fox's house is a hole.

- But in winter the fox spends the night under a bush.
For the second row - three pairs
- The fox eats small animals and birds.
- The fox eats beetles and frogs.
- The fox can catch fish.
3). Compilation of text from sentences. (Group work)
--Now get into a group and see what happens in each group.
(Children unite in groups, make up text from sentences)
Distribution of roles: who will read the story.
Verification: texts are read.
1 group.
The fox lives in the forest. The house at the fox hole. But in winter, the fox spends the night under a bush.
-What conclusion can be drawn? The fox is what kind of animal?
Conclusion: The fox is a wild animal.
It turns out that foxes live everywhere: in the forest, and in the mountains, and in the steppes, and in the swamps.
2nd group.
The fox eats small animals and birds. The fox eats bugs and frogs. The fox can fish.
The fox eats bugs and frogs. The fox can fish.
-What conclusion can be drawn from this text?
Conclusion: The fox is a predator.
It turns out that the fox does not refuse juicy forest fruits: strawberries, blueberries, apples. But still, its main food is small animals.
4) Selection of a title for the text.
1. Fox.
2. The fox is a wild animal.
3. The fox is a predator.
--Which heading fits best with our text?
5) Work with an exhibition of books.
--Where can I read about the fox? (reference literature)
VI. Lesson summary
--What new did you learn at the lesson?
--Which task did you like the most?
--Clap your hands if you liked the lesson.
Extra-curricular reading in the first grade | Reading Article (Grade 1):
Extracurricular reading lessons in the first grade. Extracurricular reading in elementary school is a necessary and important link in the field of teaching younger students their native language. The purpose of these classes is to provide targeted guidance for students' independent reading of the various literature available to them in terms of content. Independent children's reading is an individual silent communication of a child with a range of available books and a book chosen for reading without the direct assistance of a teacher or other qualified reader. In the first year of study, work with a book, which I organize in extracurricular reading classes, is to a large extent propaedeutics of independent reading. The purpose of this work is to systematize the stock of knowledge and life observations that children have, to help them accumulate the minimum collective and individual reading experience and to prepare the minds and feelings of children in a timely manner for the independent choice and reading of small works of art: fairy tales, stories, poems. During the first half of the year, at the stage of learning to read and write, I suggest that the children themselves choose a book to read and present it in class on Monday.
The purpose of these classes is to provide targeted guidance for students' independent reading of the various literature available to them in terms of content. Independent children's reading is an individual silent communication of a child with a range of available books and a book chosen for reading without the direct assistance of a teacher or other qualified reader. In the first year of study, work with a book, which I organize in extracurricular reading classes, is to a large extent propaedeutics of independent reading. The purpose of this work is to systematize the stock of knowledge and life observations that children have, to help them accumulate the minimum collective and individual reading experience and to prepare the minds and feelings of children in a timely manner for the independent choice and reading of small works of art: fairy tales, stories, poems. During the first half of the year, at the stage of learning to read and write, I suggest that the children themselves choose a book to read and present it in class on Monday. The results of each child are recorded in "clouds".
The results of each child are recorded in "clouds".
Some children choose a book by length, others by illustrations, others by familiar names of writers and poets. In four months, many have time to get acquainted with the work of many famous children's writers. After completing the study of the period of literacy, we begin to study the subject "Literary reading" under the program "Perspective" and the lessons of extracurricular reading are logically built into the program, expanding and supplementing the material being studied. Children read the works written in the reader's diary.
In January I invite children to read Russian folk tales, after which it is easier for children to classify fairy tales, to formulate a theme and an idea.
After Russian folk tales, we read the tales of foreign writers, compare them, fill in the table and use the theoretical data in each lesson.
The organization of extracurricular reading already in the first year of study is impossible without children's books, which should be in every class. In addition, for the successful conduct of extracurricular reading lessons in the second half of the year, the school selects in advance, by the end of the first half of the year, "baby books" available to first graders (14 - 16 sets).
In addition, for the successful conduct of extracurricular reading lessons in the second half of the year, the school selects in advance, by the end of the first half of the year, "baby books" available to first graders (14 - 16 sets).
The library created in the classroom should be kept in a strict generally accepted order and actively used by first-graders in the learning process for children to gain personal reading experience.
Fairy tales by K.I. Chukovsky, I usually devote several lessons to this, including moments of fantasizing and writing in the lessons ...
they were excited, evaluate what they read, referring to the text. Most often, this succeeds in the case when, at the very beginning of the conversation, some opinion is revealed that requires discussion, since it is not indisputable ... ..
In the process of reading, discussing, examining a children's book, the teacher, at an opportunity, makes recommendations that encourage first-graders to independent work available to them in connection with the lesson during the week.