Social skills curriculum for elementary students
Social Skills Lessons & SEL Curriculum For Elementary School
Students in Pre-K through 2nd grade are at a crucial developmental milestone to begin social emotional skill development for early elementary students with Move This World. With their big imaginations, young students take naturally to our unique interactive videos. By inviting them to play, Move This World seamlessly introduces SEL concepts into their daily routine.
SEL Social Skills Build Communication
While children in this age group love to laugh, sing, and move, they also have very big feelings and emotions. They are still developing an awareness of how they relate to their peers, and they are learning to regulate their bodies. Their brains are doing hard work, and they don’t always know how to ask for a break or for help.
Teachers are under pressure to give individual attention to students without falling behind in a given day’s lesson plan. Administrators are aware that each classroom has complex dynamics, and it’s difficult to know if teachers have the tools they need to fully serve the students. Family members need the support and tools to help them bridge the gap for their children, whether learning is happening remotely or in the classroom.
Now imagine a radically different learning environment. Students have words for their emotions. When those emotions run high, you know how to help your students breathe their way to calm. Everyone starts the day with exercises that encourage focus and listening skills. Students pay attention to peers and family members and apply social skills that help them support each other. This is all possible, and this is how we Move This World.
Request a demo
Watch How Little Learners
Move This World
Activity: Emogometer
SEL Competency: Self Awareness
Skills: Identifying emotions, Expressing emotions
Objectives: Recognize that emotions vary in intensity. Recognize and label the intensity of an emotion we are experiencing and describe what causes our basic emotions.
Sign up for a demo
Age Appropriate Approach to Emotional Intelligence
Move This World’s early elementary program is designed to work in cooperation with the cognitive abilities of each grade level. Our program provides a grade-level specific SEL curriculum for Elementary Schools and doesn’t ask these students to be anyone other than who they already are.
Through short interactive social emotional videos for elementary students the incorporation of movement and creative expression, early elementary-aged students will open the day with guided exercises that help them prepare for learning in a safe environment. These exercises build sequentially over the course of the year, allowing students to build SEL skills at the right pace for their grade level.
Are you ready to watch your students Move This World? Contact us today to learn how Move This World can work in your school.
Fill out our form below to access the SEL Curriculum For Elementary School Guide exclusively from Move This World.
Research-Based Social Skills Curriculum and Program
Aug 25 2020
Positive Action Staff
•
SEL Articles
Early childhood education is necessary for healthy development. The initial years are the basis for children’s future education, helping them become lifelong learners and perceptive individuals.
Positive Actions offers a social skills curriculum for students, preschool through high school, to develop the positive habits they need for long term success.
What is a social skills curriculum?
Social skills are an essential part of everyday life. Fostering young student’s social abilities prepares them for a lifetime of productive interactions and meaningful relationships. The curriculum gives students the education they need to handle everything from non-verbal cues to uncomfortable situations.
The curriculum provides a supportive SEL framework in a formal setting. We draw on decades of history and research to instill students with the most advanced social skills program available. According to researchers, students in the program see a 19% improvement in pro-social behavior and an 85% reduction in disciplinary action.
Positive Action: The only program that you need
Positive Action has assisted students, teachers, and counselors across the country since 1982. Our social and emotional learning curriculum a social skills group curriculum with academic material. The combination gives participants the robust instruction they need to have long and healthy relationships.
Schools across the country, from Tallahassee, FL to Compton, CA, already experience the benefits of Positive Action. The supportive system fits with any existing educational programming and on any budget. Learn more about Positive Action results by checking out the success stories.
Program Structure
Our curriculum contains seven units that provide students with strong core knowledge and skills.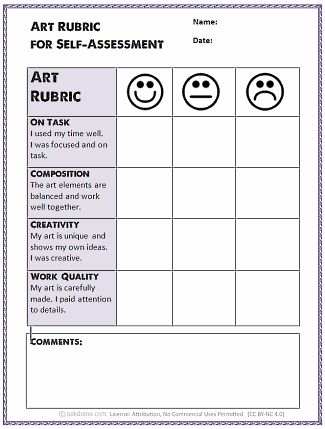 Each section focuses on different areas of self-improvement and helps students make meaningful changes. These seven units apply at all levels, whether teaching preschoolers or high schoolers.
Each section focuses on different areas of self-improvement and helps students make meaningful changes. These seven units apply at all levels, whether teaching preschoolers or high schoolers.
- Self – Concept
- Positive actions for your body and mind
- Managing yourself responsibly
- Treating others the way you like to be treated
- Telling yourself the truth
- Improving yourself
- Review
The stable baseline prepares students for specialized instruction. Positive Action offers supplement kits that let educators systematically explore particular topics in depth. Some of the additional packages cover community involvement, substance abuse, and bullying prevention.
Available for Multiple Grades
Preschool
Our materials help preschoolers transition from acting out to talking about their feelings. The extra support provides an essential building block for future well-being.
Elementary
The social skill curriculum for elementary students makes learning fun and interactive. Students engage with short scripted lessons that teach the importance of positive interactions. This evidence-based unit keeps students on schedule and communicative with teachers.
Students engage with short scripted lessons that teach the importance of positive interactions. This evidence-based unit keeps students on schedule and communicative with teachers.
Middle School
Students have a dynamic social network by the time they reach adolescence. The social skills curriculum for middle school pivots to emotional intelligence and self-management. The lessons encourage students to utilize appropriate social skills at school and in their personal lives.
High School
Social and emotional learning never stops. The high school curriculum prepares students for adulthood. The evidence-based lessons include the essential skills and insights people need to succeed as an independent and productive member of their community.
How to implement our Social Skills Program?
Implementing the Social Skills Program requires a collaborative effort. Positive Action believes in identifying leaders for each lesson and establishing ground rules and channels for clear communication. Teachers that introduce the programming in the morning can reinforce their concepts throughout the day.
Teachers that introduce the programming in the morning can reinforce their concepts throughout the day.
Further reading: Planning Positive Action Implementation
Research Outcomes
Positive Action doesn’t rely on gut feelings. The social skills curriculum comes with scientifically backed research from leading research institutions, including the Board of Education. Learn more about the science behind Positive Action by checking out various randomized-controlled trials.
Unlock the full potential of your students
Unlock students’ full potential today with our social skill program. The comprehensive Positive Action social skills curriculum guides teachers and educators step-by-step to foster more socially and emotionally in-tune students. You can make a difference in a child’s life with only 15 minutes a day.
Make a positive impact in your community by calling us at (208) 733-1328 or emailing us today.
Development of communication skills of junior schoolchildren with disabilities by means of a multisensory environment
Relevance
Childhood is a period when the fundamental qualities of a person are laid down, which provide psychological stability, positive moral guidelines, form vitality and purposefulness.
This period of life is especially significant for children with disabilities. These children are most often socially isolated from their peers due to existing problems in physical, mental or mental development, their communication with peers is episodic.
A child with disabilities is not a passive object of social assistance, but an actively developing person who has the right to meet versatile social needs in cognition, communication, and creativity. He is talented, like his peers who do not have health problems, but to discover his talents, develop them, he is prevented by inequality of opportunity.
The problem of the formation of communication skills in children with disabilities, in our opinion, is quite relevant, because. the degree of formation of the ability to actively interact with others affects not only the effectiveness of children's education, but also the process of their socialization and personality development as a whole.
In order for a child with disabilities to acquire social experience, it is necessary to create special conditions that facilitate his involvement in the surrounding reality. One of these conditions may be the organization of a multifunctional multisensory environment. An enriched multisensory environment creates a feeling of safety and security, reduces anxiety, nervous excitement and anxiety, and activates brain activity. During classes, younger students with disabilities master various methods of self-regulation, learn to overcome barriers in communication, better understand themselves and others.
One of these conditions may be the organization of a multifunctional multisensory environment. An enriched multisensory environment creates a feeling of safety and security, reduces anxiety, nervous excitement and anxiety, and activates brain activity. During classes, younger students with disabilities master various methods of self-regulation, learn to overcome barriers in communication, better understand themselves and others.
Purpose of the program
Development of communication skills and correction of the emotional-volitional sphere in younger schoolchildren with disabilities by means of a multi-sensory environment.
Program objectives
- Formation of a positive image of "I" and self-confidence.
- Correction of the emotional sphere, development of self-discipline, self-organization and self-control.
- Reducing the level of personal and situational anxiety, the formation of adequate self-esteem.
- Development of conflict-free interaction skills in a peer group and the ability to accept mutual assistance.
Program structure
The structure of the program includes the following sections:
Section 1. Development of the personal sphere, the formation of positive motivation for learning.
Section 2. Development of the emotional-volitional sphere.
Section 3. Development of communication skills.
Form of classes: group for 5-6 people.
Methods and techniques used in the implementation of the program:
- Communication games.
- Functional exercises aimed at developing attention, perception, ability to work collectively, etc.
- Art therapy: drawing therapy and fairy tale therapy.
- Psychogymnastics.
Terms and stages of the program implementation
This program is implemented during the academic year and consists of 16 lessons. The cycle is designed for 4 months with 1 lesson per week.
The duration of one lesson is from 30 to 45 minutes, depending on the individual characteristics of the students.
Expected results
- Reducing anxiety, increasing self-esteem and self-confidence.
- Development of skills of self-organization, self-regulation and management of one's emotions and behavior.
- Acquisition of experience of conflict-free communication and interaction with others.
Development of communication skills of junior schoolchildren in extracurricular activities
Author : Borzykh Galina Alexandrovna
Supervisor : Korlyakova Svetlana Georgievna
Heading : Pedagogy
Posted by V young scientist #21 (363) May 2021
Publication date : 16. 05.2021 2021-05-16
05.2021 2021-05-16
Article viewed: 509 times
Download electronic version
Download Part 6 (pdf)
References:
Borzykh, G. A. Development of communication skills of younger schoolchildren in extracurricular activities / G. A. Borzykh. - Text: direct // Young scientist. - 2021. - No. 21 (363). - S. 383-385. — URL: https://moluch.ru/archive/363/81123/ (date of access: 19.02.2023).
IN The article deals with the problem of developing communicative abilities in children of primary school age in extracurricular activities. The results of testing the psychological and pedagogical program for the development of children's communicative abilities, based on their inclusion in gaming activities, are presented and analyzed.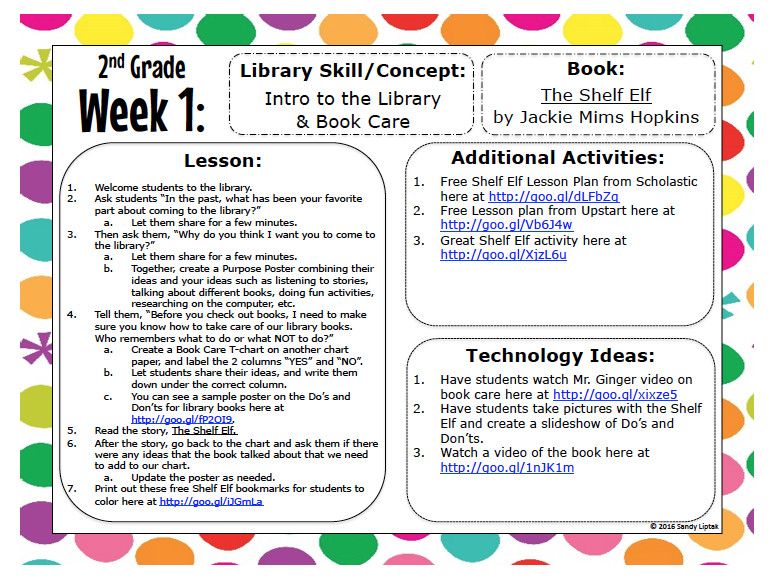
Keywords: communication skills, junior schoolchildren, extracurricular activities.
The article deals with the problem of the development of communication skills in children of primary school age in extracurricular activities. The article presents and analyzes the results of approbation of the psychological and pedagogical program for the development of children's communicative abilities, based on their inclusion in play activities.
keywords: communication skills, younger students, extracurricular activities.
The problem of communicative development of students is an important task of modern education. Communicative development is of particular importance at primary school age, as modern society expects from the younger generation the ability to communicate, distinguish between certain situations of communication, understand the state of other people in various situations and, on the basis of this, adequately build their behavior, be able to show respect for others, sympathy and empathy.
A number of scientific works were analyzed. So, I. M. Mikhailova considers communication skills as the abilities of a person, ensuring the effectiveness of her communication with other personalities and psychological compatibility in joint activities [4]; K. K. Platonov defines communication skills as the ability to form interpersonal relationships, ensuring successful collective activity and finding a place for each individual in it, as well as team building, the ability to attract people [cit. by 1]; F. B. Lomov divides communicative abilities into three groups: perceptual, information-communicative and interactive abilities [3].
On the one hand, communication skills are universal, because they are relevant to the development of any person, on the other hand, they are individual for each age group, since for their successful formation and development they must take into account various specific features (psychological, age, individual, etc.). Further).
Primary school age is an important period in the formation of communication skills, since it is this time that determines the solution of a number of communication and social problems:
- there is a restructuring of the child's relationship with the people around him;
- the child discovers a new place in the social space of human relationships;
- the active formation of important communication skills, abilities, skills and social qualities of the child's personality begins;
it is at school that new requirements are made regarding the speech development of the child;
there is an active development of reflexive abilities, on the correct formation of which many important aspects of the life of the child's personality directly depend;
social adaptation takes place;
the child still does not lose interest in play activities, which makes this period optimal in the effective use of the game for the development of communication skills and social behavior abilities [2].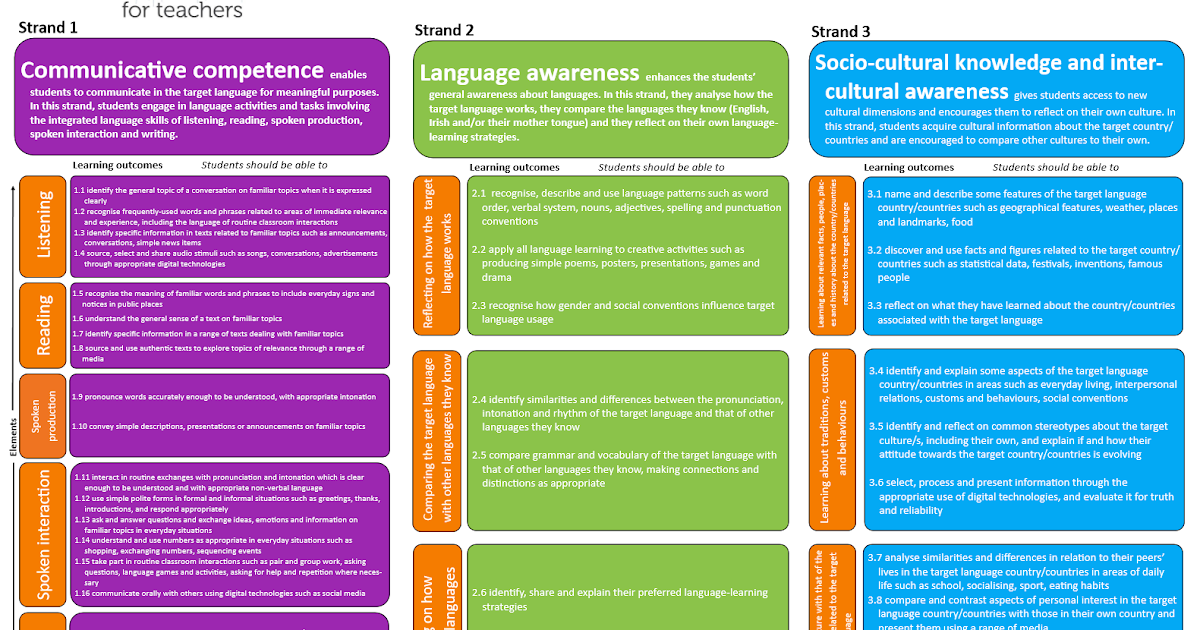
The effectiveness of the process of developing communicative abilities largely depends on the correct choice by the teacher of the appropriate forms of work with students of primary school age.
In the experimental work carried out with primary school students, we set a goal - to develop and test a psychological and pedagogical program for the development of communicative abilities of younger students in extracurricular activities.
Within the framework of the Federal State Educational Standard, extracurricular activities are understood as educational activities carried out in forms other than classroom and aimed at achieving personal, meta-subject and subject results by schoolchildren.
E. V. Sovetova defines extracurricular activities as a concept that unites all types of schoolchildren's activities (except educational), in which it is possible and expedient to solve the problems of their socialization and education. Extracurricular activities are an integral part of the educational process and one of the forms of organization of students' free time [5].
The existing experience of using game methods in domestic and foreign schools proves that it is advisable to develop communication skills and social behavior in the process of playing as the most accurate and accessible model of communication for younger students.
The game involves the creation of imaginary (conditional) situations and their beating. The creation of images and their playback (living) are the components of a communicative game, which is used to train the skills and abilities to communicate and can be carried out in a pair (dialogue) or group (polylogue) form, followed by an analysis of the actions of the game participants. The plots of such games represent real and fictional situations of communication.
The developed developmental program of the experiment was aimed at developing the perceptual, information-communicative and interactive components of children's abilities.
At the formative stage of the experiment, 20 group extracurricular activities were held, each of which was organized using gaming technologies.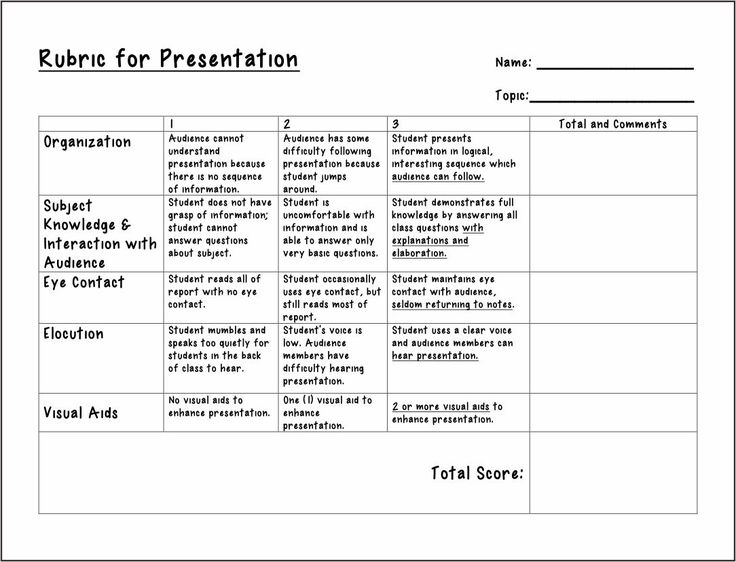
Role-playing, creative games, dramatization games, exercise games, outdoor games, games - situations were held with the children.
At the end of the complex of classes, positive results were obtained. Of particular note are the positive results in the development of the interactive component of communication skills: the absence of conflict situations; partnership; ability to navigate in a situation of communication; satisfaction in communication. 11 people out of 24 have a high level of interactive abilities, 11 people have an average level, and 2 people have a low level.
The group form of work allows you to include all participants who, in the course of performing the tasks set, go towards a common goal, have a common work plan and learn to interact with each other to obtain a successful result of the activity.
Literature:
- Bragutsa A.V. Development of communicative competence of students in elementary school // Primary school.
 — 2010.
— 2010. - Volkov, B.S., Volkova, N.V. Developmental psychology. In 2 parts. Part 2: From primary school age to youth: Textbook for university students / B. S. Volkov, N. V. Volkova. — M.: VLADOS, 2005.
- Lomov FB The problem of communication in psychology: a reader in psychology. - M., 1987. - S. 108-117.
- Mikhailova, I. M. Formation of communicative abilities of younger schoolchildren using visualization. / I. M. Mikhailova. — M.: Pskov, PGPU, 2005.
- Sovetova E. V. School of the new generation. Administrative work. - Rostov-on-Don: Phoenix, 2012.
Basic terms (automatically generated) : ability, extracurricular activities, primary school age, game, game activity, psychological and pedagogical development program, communication situation, social behavior.
Keywords
younger students, extracurricular activities, communication skillscommunication skills, younger students, extracurricular activities
Similar items
The value of
gaming activities for development and socialization. ..
.. game value in development junior schoolchildren Game is a kind of activity of a child or an adult in artificially simulating real situations in which a person reproduces. With the help of games , the child learns to work and continue the work of the elder ...
Psychological - pedagogical features of children junior ...
Junior school age age – stage of the development of child, which corresponds to the period of education in elementary school. The chronological boundaries of this age are different in different countries and in different historical conditions. These boundaries can be conditionally defined in...
Extracurricular activities junior schoolchildren 1
Extracurricular Activities schoolchildren - this is a set of all types of activities students , in which, in accordance with the main educational , the educational institution is solved by the tasks of education and socialization, development
9010 Formation of cognitive universal educational activities. ..
.. The leading type of activity of junior schoolchildren is learning, but the most optimal and acceptable for productive activity in this educational institution is game . Game is a type of activity in situations ...
Social - psychological development of children in junior ...
1. Educational Activities in Junior School Age Public Public
Self -
The ability to children understand situations and
Thus, School School School School School this is the period of the development of children in age from 6 to 11. ..
..
The role of extracurricular activities
junior schoolchildrenJunior school age age starts at the age of seven, when the child starts school, and lasts until about ten years. At the stage of junior school age the child is going through a crisis of seven years, social the situation of his development is changing.
Development skills communication in children younger age through...
Development creative abilities and imagination in the process of gaming communication . Development skills communication in various life
Younger age - the most important period in the development of preschoolers, which is characterized by a high intensity of physical and. ..
..
Similar articles
The value of
gaming activities for development and socialization...game value in development junior schoolchildren Game is a kind of activity of a child or an adult in artificially simulating real situations in which a person reproduces. With the help of games , the child learns to work and continue the work of the elder ...
Psychological - pedagogical features of children junior ...
Junior school age age – stage of the development of child, which corresponds to the period of education in elementary school. The chronological boundaries of this age are different in different countries and in different historical conditions. These boundaries can be conditionally defined in...
These boundaries can be conditionally defined in...
Extracurricular activities junior schoolchildren 1
Extracurricular Activities schoolchildren - this is a set of all types of activities students , in which, in accordance with the main educational , the educational institution is solved by the tasks of education and socialization, development
9010 Formation of cognitive universal educational activities... The leading type of activity of junior schoolchildren is learning, but the most optimal and acceptable for productive activity in this educational institution is game . Game is a type of activity in situations . ..
..
Social - psychological development of children in junior ...
1. Educational Activities in Junior School Age Public Public
Self -
The ability to children understand situations and
Thus,
School School School School School this is the period of the development of children in age from 6 to 11...The role of extracurricular activities
junior schoolchildren Junior school age age starts at the age of seven, when the child starts school, and lasts until about ten years. At the stage of junior school age the child is going through a crisis of seven years, social the situation of his development is changing.