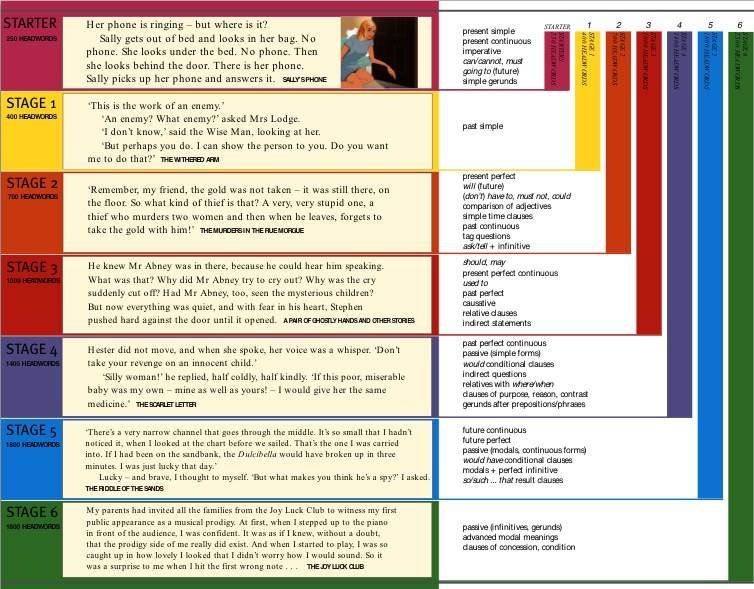
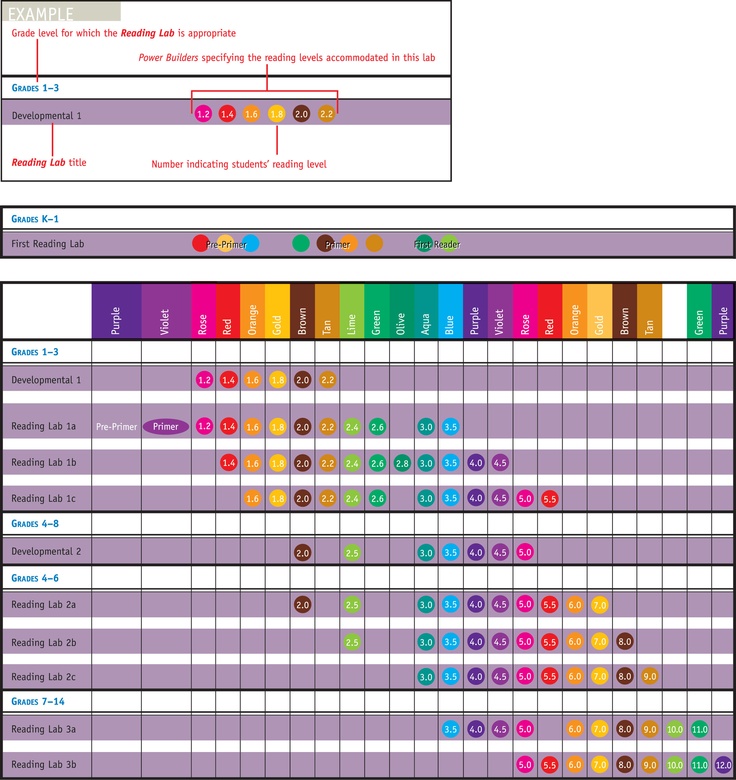
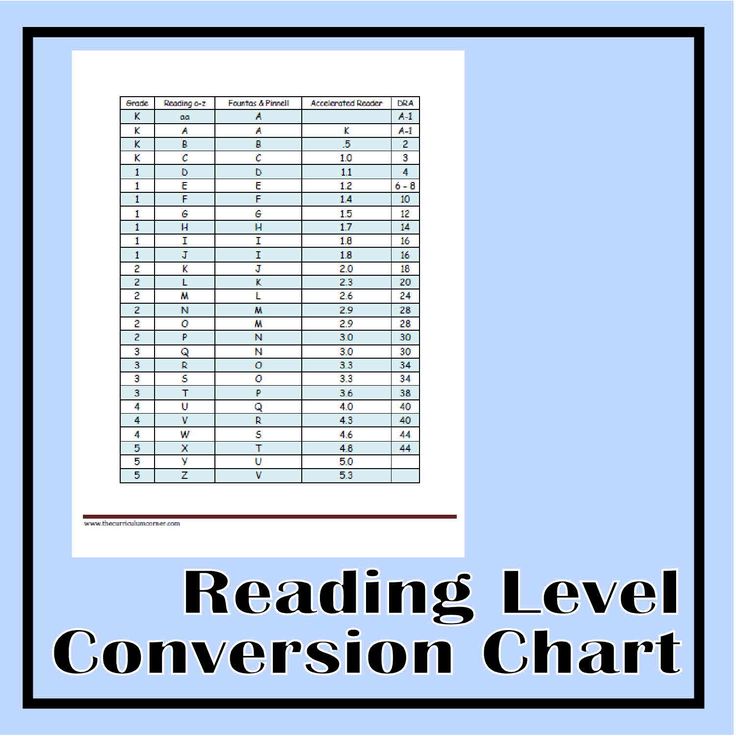
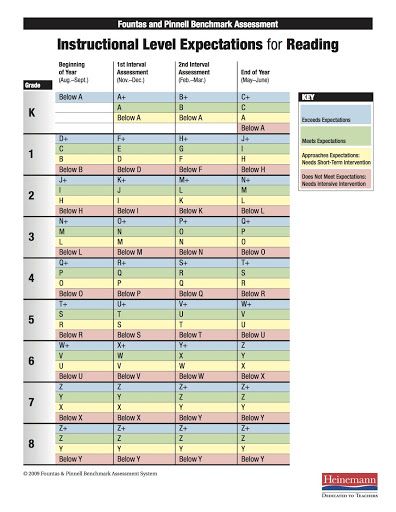
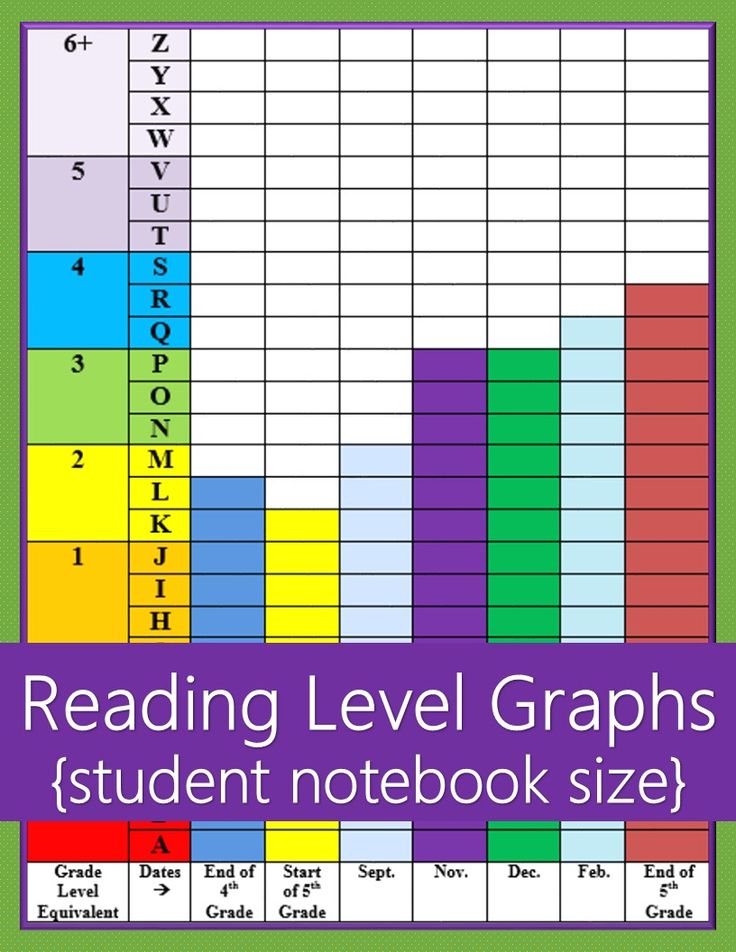
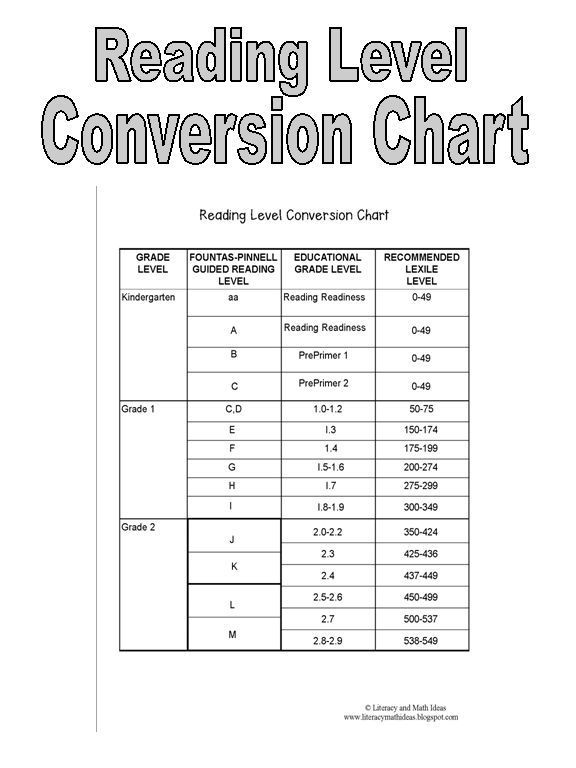
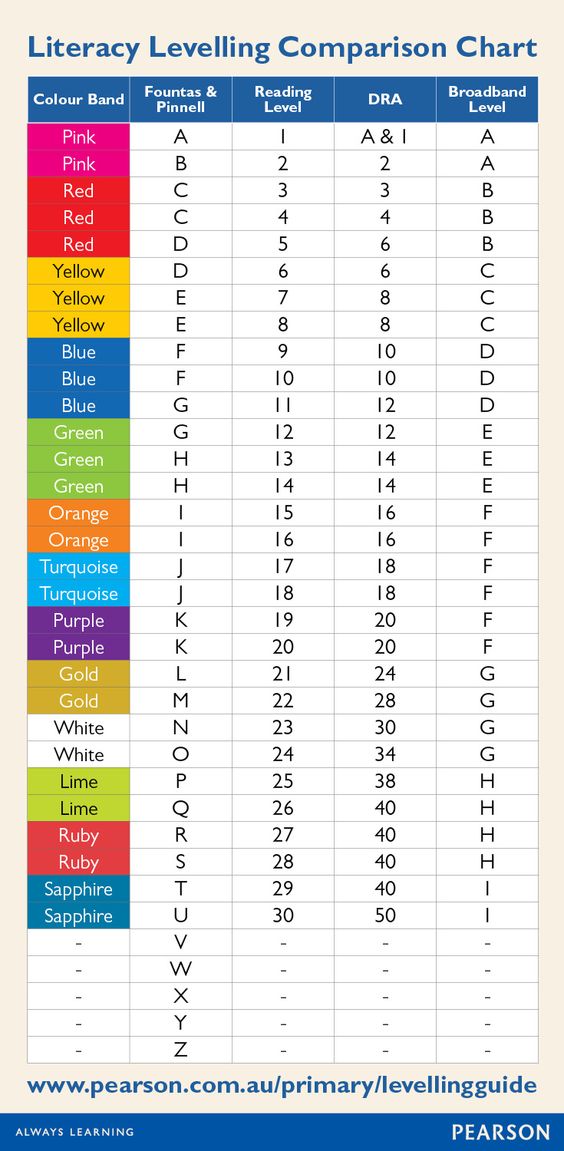
Step reading level chart
Leveling Chart | Scholastic Guided Reading Program for the Classroom
Use the grid below to shop by Guided Reading, Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA), and Lexile® Levels. This chart includes Lexile level recommendations and may also be used as a general leveling guide.
Click on links to shop the Teacher Store!
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels |
|---|
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kindergarten |
| Beginning Reader | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 |
|
| 190L-530L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
|
| 420L-650L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
|
| 520L-820L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
|
| 740L-940L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5 |
|
| 830L-1010L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 6 |
|
| 925L–1070L |
Back to Top
STEP | UChicago Impact
STEP provides districts and networks a meaningful, developmental literacy assessment that offers schools, leaders, and teachers rich, reliable student data. With STEP data, educators are equipped to increase the number of students on track to reading proficiency. In addition, STEP's team of Managers of Professional Learning empowers teachers to interpret and act on STEP data to improve and/or modify literacy practices to boost student achievement.
According to STEP’s validation report, students who reach STEP 12 by the end of third grade have an 86% chance of meeting or exceeding state standards.
The STEP Assessment
The STEP Assessment is an online, formative literacy assessment that provides educators with the insight needed to tailor instruction to meet the literacy needs of their students. When using STEP, teachers assess students at multiple points throughout the year to determine current achievement and instructional needs. Students progress across 19 distinct developmental steps toward the level of reading proficiency expected for grades Kindergarten through 5th grade. STEP offers two distinct assessment series, “Construct & Stabilize” and “Strengthen & Expand.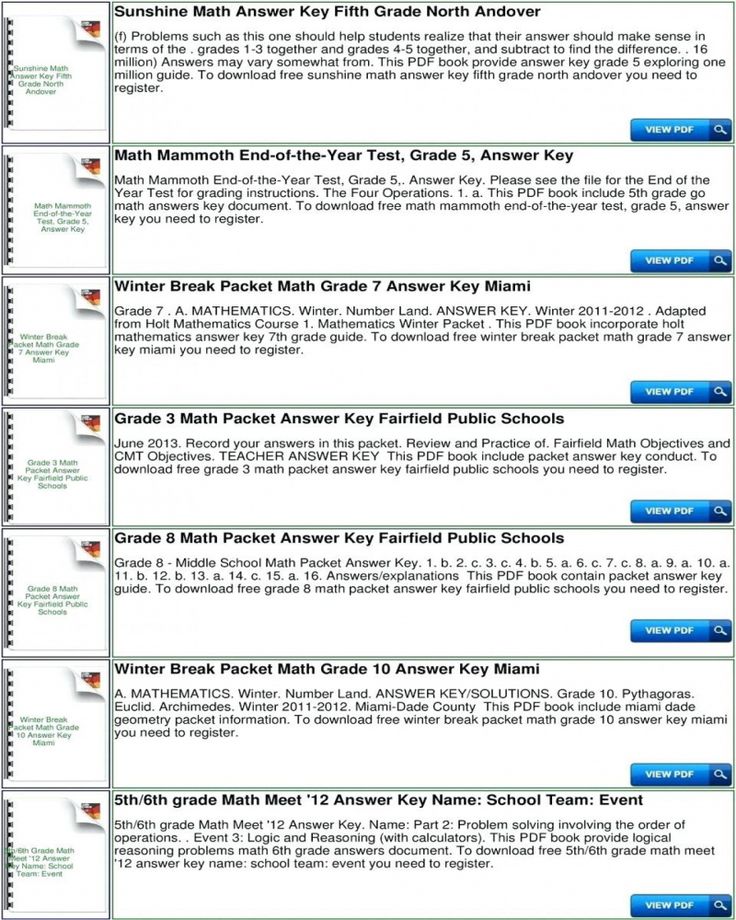 ”
”
STEP: Construct & Stabilize Series
The Construct & Stabilize series supports students with reading levels equivalent to the Kindergarten through 3rd grade levels and is designed to inform teachers about student progression against primary literacy skills necessary to build a strong foundation for later literacy development. The series is available in two equally leveled fiction texts, as well as one nonfiction text, and assesses the following reading skills:
- Phonemic Awareness
- Concepts about Print
- Letter/Word Knowledge
- Reading Accuracy and Use of Word Solving Strategies
- Fluency and Reading Rate
- Comprehension Conversation
- Retelling
- Developmental Spelling
STEP: Strengthen and Expand Series
The Strengthen & Expand series is designed to support students with reading levels equivalent to the 3rd through 5th grades. The series builds upon the foundational literacy skills established in the Construct & Stabilize series to deepen comprehension skills.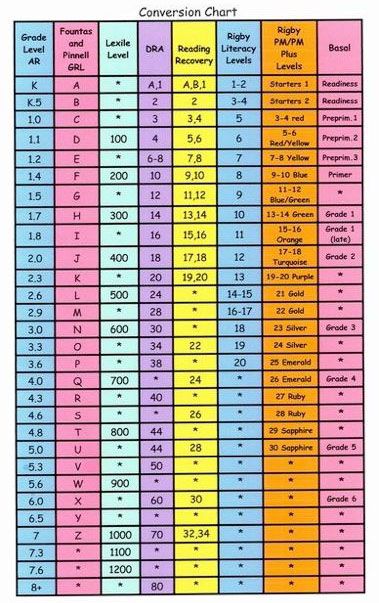 It features nonfiction text with an emphasis on Science and Social Studies. The series assesses the following reading skills:
It features nonfiction text with an emphasis on Science and Social Studies. The series assesses the following reading skills:
- Vocabulary
- Author’s Craft and Purpose
- Text Analysis and Features
- Comprehension
- Written Response
- Independent Compare and Contrast
Online Progress Monitoring
Online Progress Monitoring allows teachers to isolate and monitor a singular reading skill or set of skills aligned to each student’s assessed needs. All associated materials and resources for Online Progress Monitoring are available electronically through the Data Management System.
This new system enables teachers to continue virtually collecting and using formative reading data while facilitating virtual instruction—allowing them to differentiate their instructional practices just as they would when teaching in the classroom. All data captured for interactive, online progress monitoring is housed within the STEP Data Management System, thus enabling a clear picture of each student’s ongoing needs and progress.
The STEP Data Management System
The STEP Data Management System supports educators in using data to inform literacy instruction for all students, including those struggling to read proficiently as well as those reading at or above grade level. Teachers use the system to individually administer the STEP Assessment to students and results are viewed in real-time. As a student works through the various components of the assessment, the teacher captures student responses and that information is immediately available for scoring and analysis—enabling teachers to quickly make data-informed adjustments to their literacy instruction. STEP Assessment results can be filtered to highlight student achievement and progress toward reading goals and viewed at the network/district, school, grade, classroom, group, and individual student levels.
STEP Data Displays
The STEP Data Management System provides comprehensive insight into students’ reading abilities through historical, descriptive student data. The system generates a range of data displays, negating the need for educators to create charts.
The system generates a range of data displays, negating the need for educators to create charts.
The Network/District Wall
This Network/District Wall is a display of aggregate STEP achievement levels and growth for all schools within a network or district. Administrators can use this display to determine if assessment results have been entered, scored, and completed, as well as quickly identify high-level achievement trends across their schools.
The School Wall
The School Wall display provides a high-level view that indicates achievement and growth across and within grades represented in a school. School administrators and reading coaches use this display to identify achievement trends to determine and prioritize instructional supports for students and teachers.
The Classroom Wall
The Classroom Wall display provides teachers a snapshot of achievement for students in their classroom. Teachers use this display to track progress and growth within the term.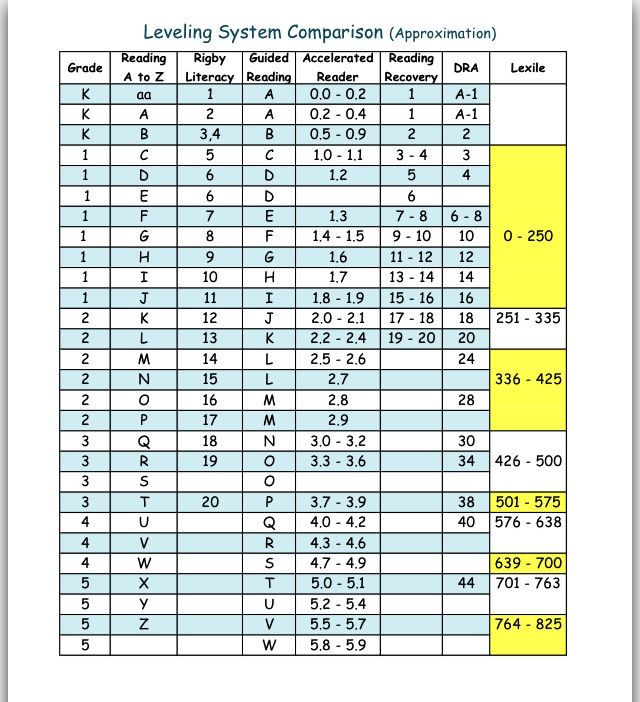 This information should then be utilized to create groups and inform instructional planning.
This information should then be utilized to create groups and inform instructional planning.
Student Displays
Student level displays offer access to a cumulative record of each student’s performance that depicts the rate and dates of progress. This helpful display indicates if a student is progressing consistently or has hit a plateau at a particular developmental level.
Component Level Display
This display provides teachers with details of achievement across the components of the assessment, such as rate, fluency, and comprehension. Users are also able to view target levels and student results for each item within the assessment.
Assessment Scoring Deep Dive
Rather than scoring each assessment individually, the Assessment Scoring display allows teachers to score all student responses for the same question at one time. Here, teachers can quickly compare and score each response against the STEP target response and indicate if the student provided adequate text evidence.
STEP Professional Learning
STEP Professional Learning (SPL) is designed to develop the knowledge base of teachers and support staff in developing the necessary skills for achieving reliable assessment data. The combination of the STEP Assessment data and comprehensive professional learning build staff capacity to provide instruction that promotes strong reading outcomes. Educators also gain a deep understanding of literacy best practices that enhance their overall instruction. Through STEP Professional Learning support, staff learn how to:
- Interpret and respond instructionally to assessment data
- Qualify which literacy skills should be progress monitored for each student and develop a process for doing so
- Create and implement robust, effective reading lessons informed by STEP data
SPL occurs in whole group, differentiated, and small group settings and is customized to align with school goals, teacher, and student needs. The SPL experience is unlike other professional development sessions. It is highly interactive and supports teachers in transforming concepts into actionable practice.
The SPL experience is unlike other professional development sessions. It is highly interactive and supports teachers in transforming concepts into actionable practice.
The outcome of SPL is the use of school-wide, systematic, and consistent approaches to instruction, scoring, and collaborative planning practices. Teachers will feel supported and empowered to continue this work independently and effectively after receiving ample STEP support over multiple years.
Why STEP Professional Learning Works
In 2017, The Learning Policy Institute, a non-partisan research institute based in Palo Alto, California, sought to identify the most effective components of professional development. Their research resulted in seven key features for effective professional development sessions, all of which SPL exemplifies.
Action diagram | AnyLogic Documentation
- Features
- Call action diagram
- Action diagram arguments
- Convert action diagram to function
Visual definition of algorithms using action diagramsEditing action diagram blocksCreating an action diagram.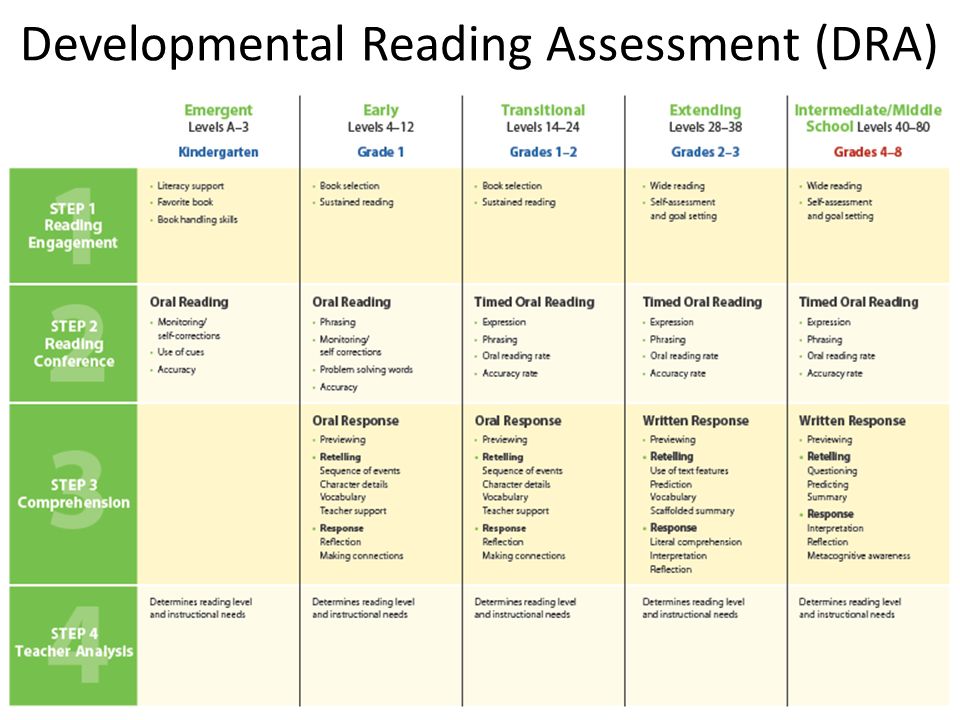 Tutorial.
Tutorial.
The activity diagram element defines the main properties of the diagram - its return type, arguments, access level, etc.
To access the elements you need to create an activity diagram, activate the palette Activity diagram .
To create a new activity diagram
- Drag element Action diagram from palette Action diagram to the agent type diagram.
- A simple action diagram will be drawn, consisting of a starting point (specified by the "action diagram" block) and a "return value" block.
- Change the name of the action diagram (directly in the text editor, which is activated in the graphical editor when adding a new element). This name will be used for calling the function defined by this action diagram.
- To set the activity chart properties, go to the panel Properties .
- If the function defined by your action diagram only performs some actions, but does not return any result of the calculations performed, indicate that this function does not return anything by selecting 9 in the button group0019 Action (does not return anything) .
- If you want the action chart to return the result of the calculations it performs, then you will need to specify what type the return value will be. The action diagram can return either the value of one of the most commonly used types (int, double, boolean, String) or the value of any other Java class (in this case, you will need to select option Other and enter the type name in the field on the right) .
- The activity diagram can be declared as static . A static activity diagram does not require instantiation of the agent type in which it is defined. The static activity diagram myFunction declared in the agent type MyClass will be accessible from anywhere in the model as MyClass.myFunction(). To make the activity diagram static, check the Static checkbox in the Specific property section.
- You have now completed the creation of a simple activity diagram. Now you will need to add other action diagram blocks to the created structure according to the algorithm you specify.
Features
- Basic
-
- The name of the activity chart. This name will be used to call the function defined by this activity diagram.
- If the option is selected, then the action diagram name will be displayed in the graphical editor.
- If this option is selected, then the activity diagram will be excluded from the model.
- If this option is selected, then the activity diagram will be displayed on the presentation while the model is running.
- If the option is selected, then the function specified by the action diagram will not return values as a result of its execution.
- If the option is selected, then the function specified by the action diagram will return the result of the calculations performed by it.
— The type of value returned by the action chart. The function can return either a value of one of the most commonly used types (int, double, boolean, String) or an object of any Java class (in this case, you will need to select option Other and enter the type name in the field on the right).
- Here you can set the function arguments, with which you can pass the data necessary for calculations to the function. Each argument is specified in a separate line of the table.
- Specific
-
- Sets the block fill color. Click inside the control and select the desired color from the list of commonly used colors, or select any other color using the Colors dialog.
- [Option only available in Library Developer Mode] If this option is selected, then the function defined by this activity diagram will be static. A static function does not require instantiation of the agent type in which it is defined. The static activity diagram myFunction declared in the agent type MyClass will be accessible from anywhere in the model as MyClass.myFunction().
- The level of access to the function specified by the action diagram. There are four access levels:
private - the function is available only from this agent type
protected - the function is available from this agent type and its subclasses
default - the function is available from anywhere in the model- If this option is selected, then you can set the units of measure for the value returned by the activity chart.
Call action diagram
To call a function defined using an activity diagram, the same syntax is used as for the functions themselves. You must specify the name of the activity diagram, followed by parentheses that contain a comma-separated list of the argument values passed to the diagram (if any), for example:
myFunction()
move(15, 35)
Action diagram arguments
If you need to pass some data necessary to perform calculations to the function specified using the action diagram, you can use arguments for this.
To set the action diagram arguments
- Select the element Activity diagram in the graphical editor or in the panel Projects .
- Set the arguments in table Arguments in panel Properties . Each argument is specified in a separate line of the table.
- Enter the name of the argument in cell Name .
- Specify the type of the argument in cell Type .
 Click in the cell and select the type you need from the drop-down list, or enter it yourself.
Click in the cell and select the type you need from the drop-down list, or enter it yourself.
If you specify arguments, then every time you call the action diagram, you will need to pass the values of these arguments to it (in the same order as they are specified in table Arguments ).
AnyLogic allows you to change the order of arguments in the table using the and buttons.
To delete an argument, select the corresponding line in the table and click the button.
Converting an activity diagram to a function
0019 Code is significant enough, it may be more convenient for you to continue working on this algorithm not as an action diagram, but as a regular AnyLogic function (in text form). For such cases, AnyLogic offers the possibility of converting an action diagram into a function (reverse conversion is not possible).
To convert an action diagram into a function
- Right-click on an element in the graphical editor.

- Select team Convert to function from context menu. You will see the function icon appear next to the action diagram in the graphics editor. The name of the created function will differ from the name of the activity diagram by the last digit.
- If you are sure you want to continue working on the algorithm as a function, delete your activity diagram.
- Change the function name to match the name of the remote activity chart.
- Continue working on the algorithm in the code editor located in the properties section Function body of the created function.
-
How can we improve this article?
Everything about creating a chart in Excel. Step by step guide with screenshots
Author Amina S. Reading 9 min Published
Reading 9 min Published
Excel is an amazing program that allows you to process not only numerical data. With its help, you can visually represent any information by building diagrams of varying degrees of complexity. It is enough just to specify the data in the cells, and the program will automatically build a chart based on them. Say it's amazing!
In this case, the user can customize the appearance of the diagram, which he likes. Today we will analyze in detail the available charting tools in Excel and other similar programs. After all, the basic principle is not limited to only the office suite from Microsoft, right? Therefore, the principles described here may well be used when working with other spreadsheet programs such as LibreOffice, WPS Office, or Google Sheets.
Contents
- How to create a chart based on Excel spreadsheet data
- How to work with charts in Excel
- How to set up a chart with percentages?
- How to change the font size in an Excel chart
- Pareto chart - definition and construction principle in Excel
Building a chart based on Excel table data
Before proceeding directly to building Excel charts, you need to understand what it is and what are they needed for. There are several ways to present information:
There are several ways to present information:
- Auditory.
- Text.
- Visual.
- Interactive.
The most familiar to an ordinary person is the auditory and textual way of transmitting information. The first involves the use of voice in order to present certain data, facts and figures. A very unreliable method that is not able to deliver information perfectly. The only thing it can be used for during presentations is to evoke certain emotions in the audience. Text can convey text, but has a much lower ability to evoke certain emotions. The interactive method involves the involvement of the audience (for example, investors). But if we talk about business data, then you can’t play much here.
The visual way of presenting information offers a huge number of advantages. It helps to combine all the advantages of the remaining methods. It transmits information very accurately, since it contains all the numbers, and a person can analyze the data based on the graph.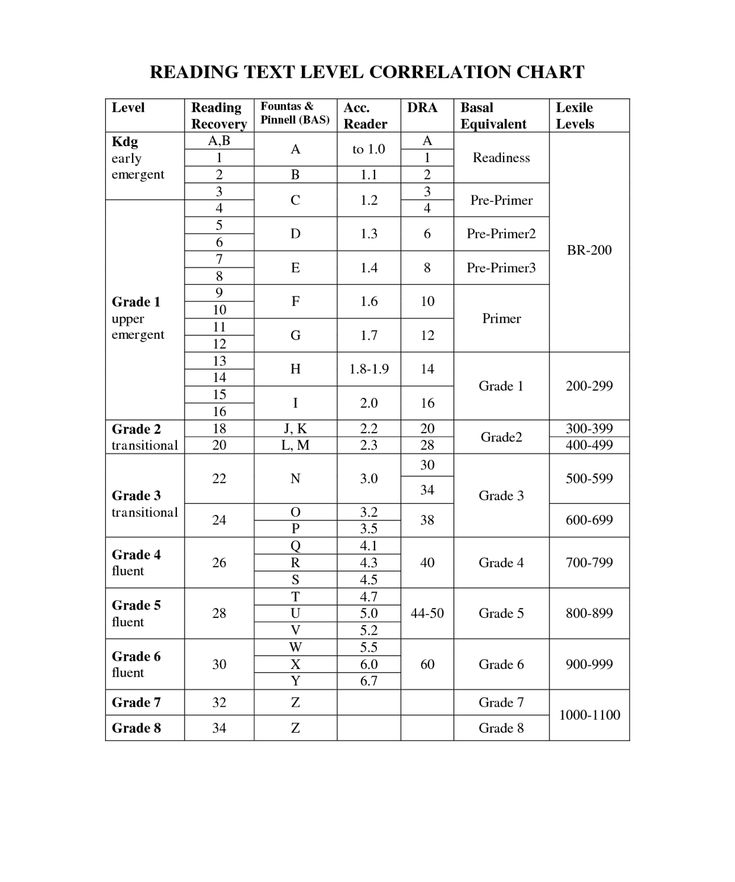 He is able to evoke emotions. For example, just look at the graph of the spread of coronavirus infection in recent times, and it immediately becomes clear how the graph can easily affect the emotional part of the brain.
He is able to evoke emotions. For example, just look at the graph of the spread of coronavirus infection in recent times, and it immediately becomes clear how the graph can easily affect the emotional part of the brain.
And what is important, it is able to involve a person who can selectively look at one or another part of the graph and analyze the information that he really needs. This is why charts have become so widespread around the world. They are used in various fields of human activity:
- During the presentation of research results of various levels. This is a universal point for both students and scientists defending a dissertation. This type of presentation of information, like a diagram, makes it possible to pack a large amount of information into a very convenient form and present all this data to a wide audience so that it immediately becomes clear. The diagram allows you to inspire confidence in what an applicant for a master's or doctoral degree says.
- During business presentations. Especially the creation of diagrams is necessary if it is necessary to present the project to the investor or report on the progress of its work.
This will make it clear that the authors of the project themselves take it seriously. Among other things, investors will be able to analyze all the necessary information on their own. Well, the point about the fact that the presence of diagrams in itself inspires confidence, because it is associated with the accuracy of the presentation of information, remains both for this area and all the following ones. - For reporting to superiors. Management loves the language of numbers. Moreover, the higher it is in rank, the more important it is for him. The owner of any business needs to understand how much this or that investment pays off, which sectors of production are unprofitable and which are profitable, and understand many other important aspects.
There are many other areas in which charts can be used.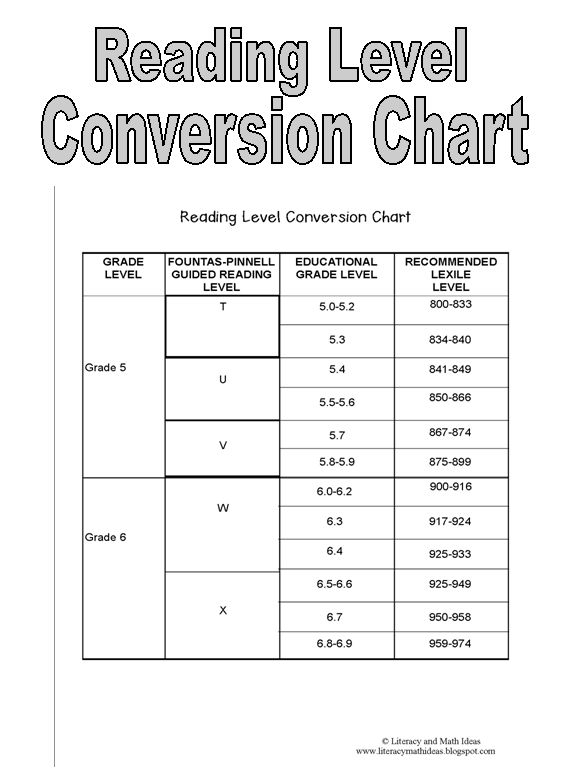 For example, in education. But no matter for what specific purposes they are compiled, if they are done in the Excel program, then in fact almost nothing needs to be done. The program will do everything for the person himself. In fact, building charts in Excel is not fundamentally different from creating regular tables. Therefore, anyone can create them very simply. But for clarity, let's describe the basic principle in the form of instructions. Follow these steps:
For example, in education. But no matter for what specific purposes they are compiled, if they are done in the Excel program, then in fact almost nothing needs to be done. The program will do everything for the person himself. In fact, building charts in Excel is not fundamentally different from creating regular tables. Therefore, anyone can create them very simply. But for clarity, let's describe the basic principle in the form of instructions. Follow these steps:
- Before creating a graph or chart, you must first create a table with the information that will be used for this. Let's also create such a table.
- After creating the table, you need to find the area that will be used for the basis of the diagram, and then click on the "Insert" tab with the left mouse button once. After that, the user will be able to choose the type of chart that he likes. This is a graph, and a pie chart, and a histogram. There is room to expand.
Attention! Programs vary in the number of chart types that can be created.
- Many other chart types can be used. They just aren't that popular. To view the entire list of available types, go to the "Diagram" menu and select a specific type there. We see that there is a slightly different menu here. There is nothing strange about this, since the buttons themselves may differ not only depending on the version of the office suite, but also on the very variety of the program and operating system. Here it is important to understand the logic first, and everything else should become intuitive.
- After selecting the appropriate chart type, click on it. You will then be presented with a list of subtypes, and you will need to select the one that best suits your situation. For example, if a histogram was selected, then you can select regular, bar, volume, and so on. The list of types with pictures, by which you can understand how the final diagram will look, is located directly in this menu.
- We click on the subtype that we are interested in, after which the program will do everything automatically.
 The resulting chart will appear on the screen.
The resulting chart will appear on the screen. - In our case, the picture turned out as follows.
- If we chose the "Chart" type, then our diagram would look like this.
- The pie chart has the following form.
As you can see, the instructions are not complicated at all. It is enough to enter a little data, and the computer will do the rest for you.
How to work with charts in Excel
After we have made a chart, we can already customize it. To do this, you need to find the "Designer" tab at the top of the program. This panel has the ability to set various properties of the chart we created earlier. For example, the user can change the color of the columns, as well as make more fundamental changes. For example, change the type or subtype. So, to do this, you need to go to the "Change chart type" item, and in the list that appears, you can select the desired type. Here you can also see all available types and subtypes.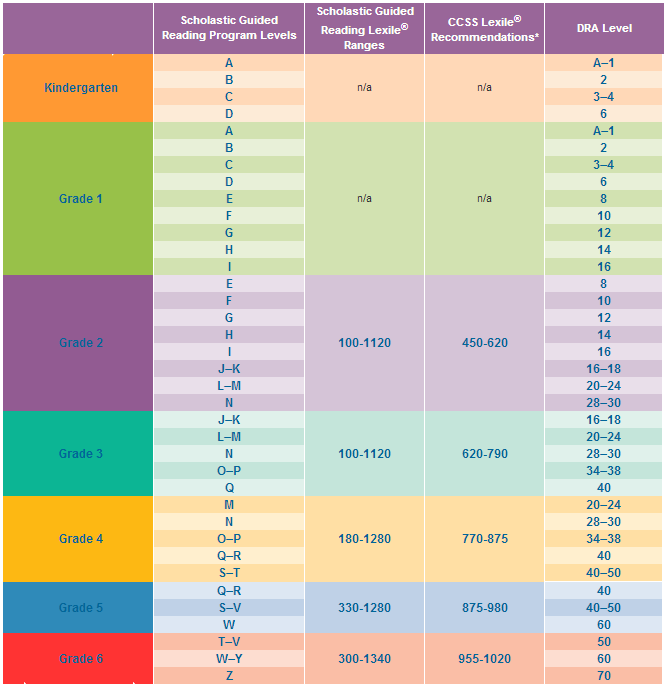
We can also add some element to the created graph. To do this, click on the appropriate button, which is located immediately on the left side of the panel.
It is also possible to carry out a quick setting. There is a special tool for this. The button corresponding to it can be found to the right of the "Add Chart Element" menu. Here you can choose almost any design option that fits the current task.
It is also quite useful if there is a designation of each of them next to the columns. To do this, you need to add captions through the "Add Chart Element" menu. After clicking on this button, a list will open in which we are interested in the corresponding item. Then we choose how the caption will be displayed. In our example, it is indicated in the screenshot.
Now this chart not only shows the information visually, but you can also understand exactly what each column means.
How do I set up a percentage chart?
Now let's move on to specific examples. If we need to create a chart in which we work with percentages, then we need to select a circular type. The instruction itself is as follows:
If we need to create a chart in which we work with percentages, then we need to select a circular type. The instruction itself is as follows:
- According to the mechanism described above, it is necessary to create a table with data and select a range with data that will be used to build a chart. After that, go to the "Insert" tab and select the appropriate type.
- After the previous step is completed, the program will open the Design tab automatically. Next, the user needs to analyze the available options and find the one where the percent icons are displayed.
- Further work with a pie chart will be carried out in a similar way.
How to change the font size in an Excel chart
Setting chart fonts allows you to make it much more flexible and informative. It is also useful if it needs to be shown on a big screen. Often the standard size is not enough to be visible to people from the back row. To set the chart font sizes, you need to right-click on the appropriate label and click on the font item in the list that appears.
After that, you need to make all the necessary adjustments and click on the "OK" button to save them.
Pareto chart - definition and construction principle in Excel
Many people know the Pareto principle, which says that 20% of effort gives 80% of the result and vice versa. Using this principle, you can draw a diagram that will allow you to find the most effective actions from which the result was the largest. And to build a chart of this type, the built-in tools of Microsoft Excel are enough. To build such an infographic, you must select the "Histogram" type. The sequence of our actions is as follows:
- Let's generate a table that describes the names of the products. We will have multiple columns. The first column will describe the total amount of the purchase of goods in money. The second column records the profit from the sale of these goods.
- We make the most ordinary histogram. To do this, you need to find the "Insert" tab, and then select the appropriate chart type.
- We now have a chart that has 2 columns of different colors, each representing a specific column. Below you can see the legend of the chart, according to which we understand where which column is.
- The next step that we need to perform is editing the column that is responsible for profit. We are faced with the task of seeing its change in dynamics. Therefore, we need a "Graph" chart type. Therefore, in the "Designer" tab, we need to find the "Change Chart Type" button and click on it. Then select a schedule from the list. It is important not to forget to select the corresponding column before doing this.
The Pareto chart is now ready. You can analyze the effectiveness and determine what can be sacrificed without fear. Editing this chart is done in exactly the same way as before. For example, you can add labels to bars and points on a chart, change the color of lines, columns, and so on.
Thus, Excel has a huge toolkit for creating charts and customizing them.