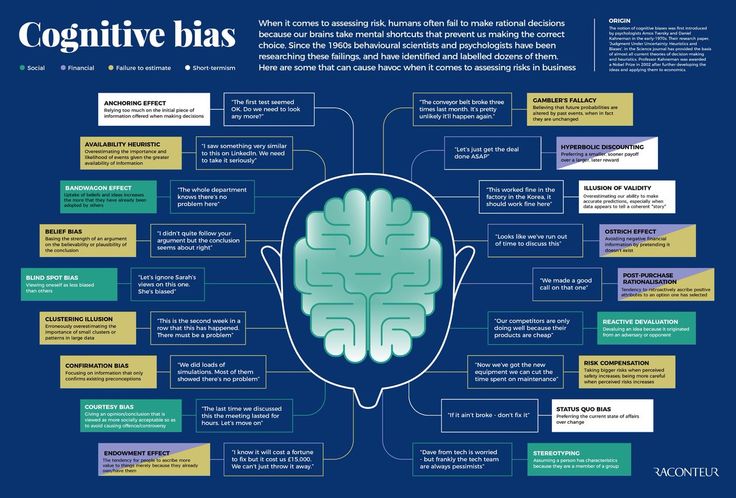
What is sight words means
What Are Sight Words? Get the Definition Plus Teaching Resources
When you’re a new teacher, the number of buzzwords that you have to master seems overwhelming at times. You’ve probably heard about many concepts, but you may not be entirely sure what they are or how to use them in your classroom. For example, new teacher Katy B. asks, “This seems like a really basic question, but what are sight words, and where do I find them?” No worries, Katy. We have you covered!
What’s the difference between sight words and high-frequency words?
Oftentimes we use the terms sight words and high-frequency words interchangeably. Opinions differ, but our research shows that there is a difference. High-frequency words are words that are most commonly found in written language. Although some fit standard phonetic patterns, some do not. Sight words are a subset of high-frequency words that do not fit standard phonetic patterns and are therefore not easily decoded.
We use both types of words consistently in spoken and written language, and they also appear in books, including textbooks, and stories. Once students learn to quickly recognize these words, reading comes more easily.
What are sight words and how can I teach my students to memorize them?
Sight words are words like come, does, or who that do not follow the rules of spelling or the six types of syllables. Decoding these words can be very difficult for young learners. The common practice has been to teach students to memorize these words as a whole, by sight, so that they can recognize them immediately (within three seconds) and read them without having to use decoding skills.
Can I teach sight words using the science of reading?
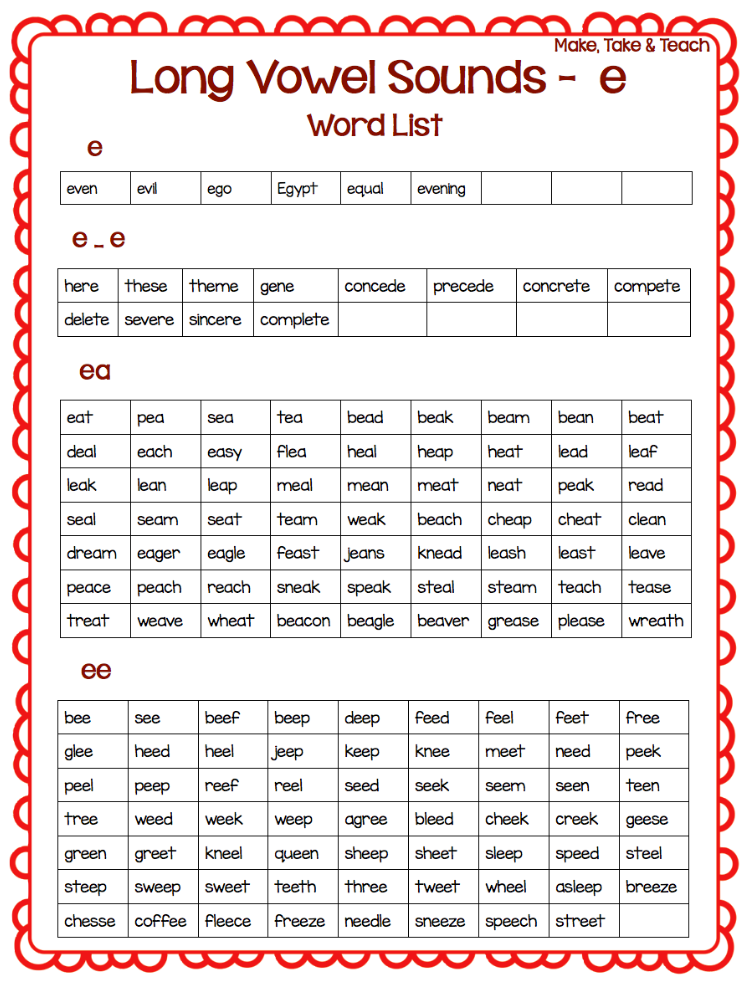
On the other hand, recent findings based on the science of reading suggests we can use strategies beyond rote memorization. According to the the science of reading, it is possible to sound out many sight words because they have recognizable patterns. Literacy specialist Susan Jones, a proponent of using the science of reading to teach sight words, recommends a method called phoneme-grapheme mapping where students first map out the sounds they hear in a word and then add graphemes (letters) they hear for each sound.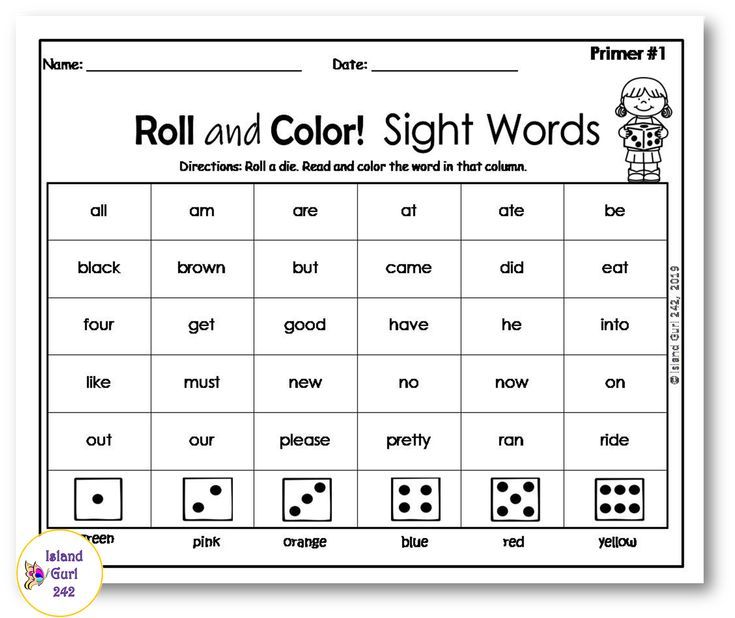
How else can I teach sight words?
There are many fun and engaging ways to teach sight words. Dozens of books on the subject have been published, including the much-revered Comprehensive Phonics, Spelling, and Word Study Guide by Fountas & Pinnell. Also, resources like games, manipulatives, and flash cards are readily available online and in stores. To help get you started, check out these Creative and Simple Sight Word Activities for the Classroom. Also, check out Susan Jones Teaching for three science-of-reading-based ideas and more.
ADVERTISEMENT
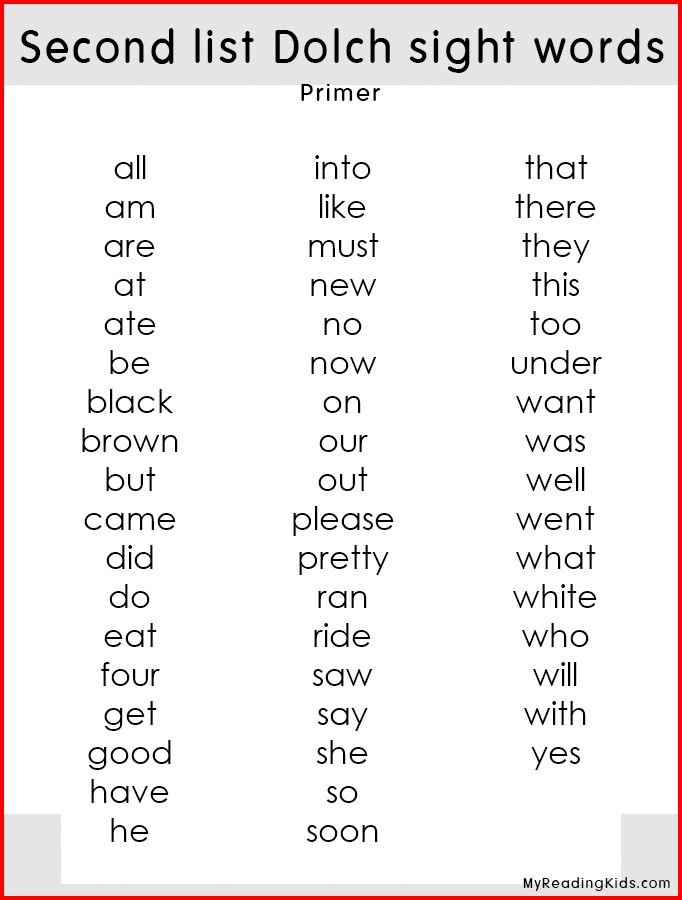
Where do I find sight word lists?
Two of the most popular sources are the Dolch High Frequency Words list and the Fry High Frequency Words list.
During the 1930s and 1940s, Dr. Edward Dolch developed his word list, used for pre-K through third grade, by studying the most frequently occurring words in the children’s books of that era. The list has 200 “service words” and also 95 high-frequency nouns. The Dolch word list comprises 80 percent of the words you would find in a typical children’s book and 50 percent of the words found in writing for adults.
The Dolch word list comprises 80 percent of the words you would find in a typical children’s book and 50 percent of the words found in writing for adults.
Dr. Edward Fry developed an expanded word list for grades 1–10 in the 1950s (updated in 1980), based on the most common words that appear in reading materials used in grades 3–9. The Fry list contains the most common 1,000 words in the English language. The Fry words include 90 percent of the words found in a typical book, newspaper, or website.
Looking for more sight word activities? Check out 20 Fun Phonics Activities and Games for Early Readers.
Want more articles like this? Be sure to sign up for our newsletters.
Sight words vs. High frequency words: What's the difference?
This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Sight words vs. high frequency words. What’s the difference? This is the beginning of our blog series all about sight words.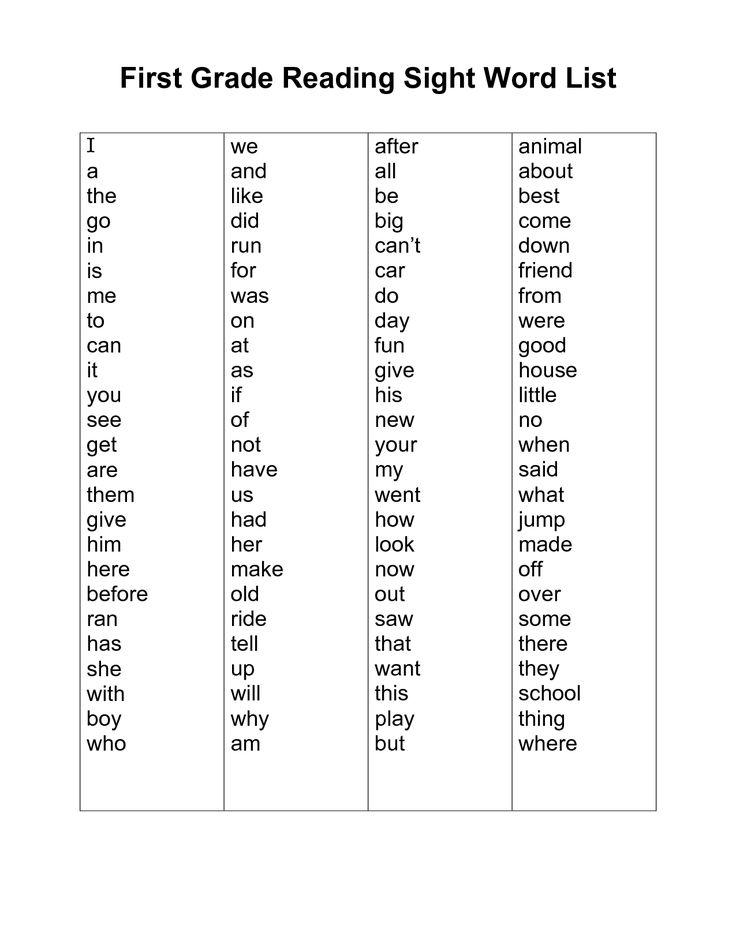
Traditionally, when teachers say “sight words,” they are referring to high frequency words that children should know by sight.
We often define sight words as words that kids can’t sound out – words like the, for example.
But this definition is not correct. While sight words may be irregular, the definition of sight words is NOT words that kids can’t sound out.
Reading researchers have a different definition of sight words.
A sight word is a word that is instantly and effortlessly recalled from memory, regardless of whether it is phonically regular or irregular. A sight-word vocabulary refers to the pool of words a student can effortlessly recognize.
David A. Kilpatrick, PhD
As an adult, most of the words you encounter are sight words, because unless you’re reading from a challenging textbook or a technical manual, you know the words automatically. You don’t need to sound them out.
You don’t need to sound them out.
High frequency words are the words that are most commonly used in the English language. These words may be regular (as in and) or irregular (as in the).
It’s essential that students develop automaticity as they read, and one way to do this is to help them read many high frequency words by sight.
Our goal is to make high frequency words SIGHT WORDS.We want our students to recognize high frequency words instantly. But the way we do this isn’t by giving them stacks of words to memorize.
Will students memorize some high frequency words?
Yes, at first.
They’ll memorize their names and a few other words like Dad and Mom.
And there’s nothing wrong with teaching pre-readers a small set of sight words before they begin reading. In their article, A New Model for Teaching High Frequency Words, Linda Farrell, Tina Osenga, and Michael Hunter recommend teaching the following sight words to new readers:
- the
- a
- I
- to
- and
- was
- for
- you
- is
- of
We can teach these words to students after they know letter names but before they’ve begun phonics instruction.
However.
This is just to get them started.
There’s a problem with the common practice of sending home lists of words for students to memorize. “While this method works for many students, it is an abysmal failure with others.” (A New Model for Teaching High Frequency Words, by Farrell, Osenga and Hunter).
Rather, we should integrate high frequency word instruction into phonics lessons whenever possible.
More on that in a minute. First …
What are flash words and heart words?Some educators refer to decodable high frequency words as “flash words.” These words appear so frequently that students should be able to read them in a flash.
Irregular high frequency words are sometimes called “heart words” because there are parts of the word that can’t be sounded out; students must learn those parts “by heart.”
Teach both flash words and heart words using phonicsBe leery of any reading program that says students need to “just memorize” irregular words.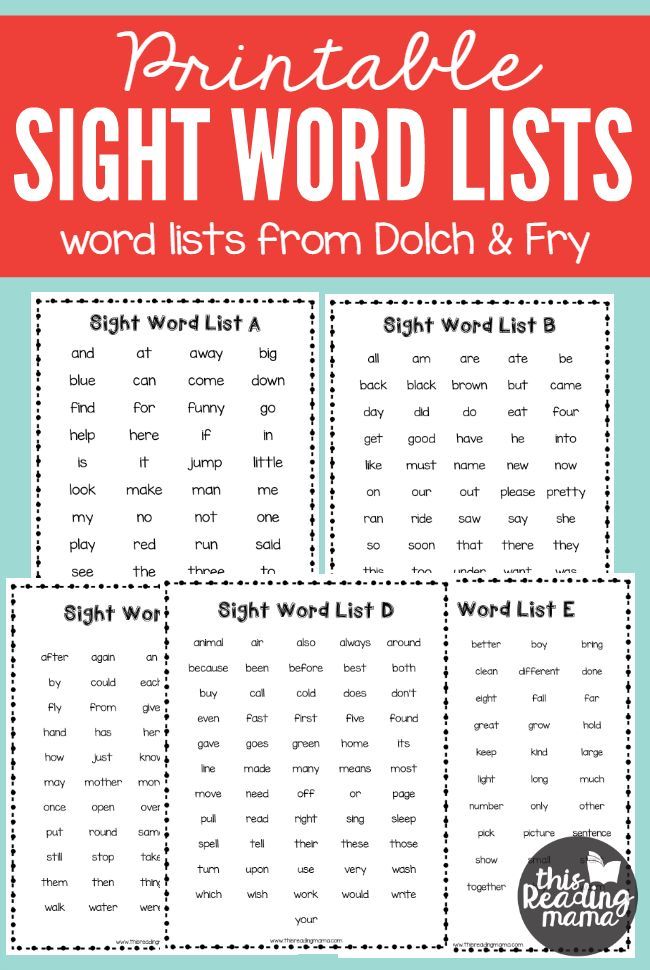
Rather, look for a program that organizes high frequency words to fit phonics lessons wherever possible.
In other words, teach the word can when students know the sounds of c, a, and n.
Even with irregular words (“heart words”) we can all attention to the part of the word that IS regular.
Really Great Reading has some excellent instructional videos to help you teach those tricky heart words.
Find all of Really Great Reading’s “heart word magic” videos here.
Will we just ask students to memorize SOME sight words?Yes. High frequency words are the glue that hold decodable sentences together. We want students to know some of these words so the decodable books they read make sense.
Because of that, we’ll teach a small number of sight words to pre-readers, and additional words as needed so our students can read their decodable books.
But let’s let go of this idea that students need to memorize lists and lists of sight words.
Turn high frequency words into sight words with these engaging mats!
High Frequency Word Practice Mats – 240 words!
$24.00
Students will count the sounds in words, spell them, read them in context, and more! What a meaningful, multi-sensory way to master high frequency words!
Buy Now
Stay tuned for the rest of this series!
Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9
Subscribing to our email newsletter is completely free. And when you do, you'll get access to our library of subscriber freebies! Sign up below to get access to a wonderful variety of math and literacy resources.
VISION - What is VISION?
The word consists of 6 letters: first h, second p, third e, fourth n, fifth and, last e,
The word vision in English letters (transliteration) - zrenie
- The letter from occurs 1 time.
 Words with 1 letter z
Words with 1 letter z - The letter r occurs 1 time. Words with 1 letter r
- The letter e occurs 2 times. Words with 2 letters e
- The letter n occurs 1 time. Words with 1 letter n
- The letter and occurs 1 time. Words with 1 letter and
Meanings of the word vision. What is vision?
Vision
Vision I Vision (visio, visus) is the physiological process of perceiving the size, shape and color of objects, as well as their relative position and distance between them; the source of visual perception is light ...
Medical Ecyclopedia
VISION (visio, visus) - the physiological process of perceiving the size, shape and color of objects, as well as their relative position and distance between them; the source of visual perceptions is light ...
Brief medical encyclopedia.- M., 1989
VISION (English vision) - the ability to receive and extract information about the world from the energy of electromagnetic radiation in the light range; a complex set of processes in the visual system…
Large psychological dictionary. - 2004
Field of view
Field of view I Field of view is the space simultaneously perceived by the eye with a fixed gaze and a fixed position of the head. It has certain boundaries corresponding to the transition of the optically active part of the retina to the optically blind.
Medical Ecyclopedia
nine0002 The field of view is the entire space from which the eye, when stationary, is able to receive light impressions. The eye perceives light as a yellow spot of the retina, and almost the entire surface of it ... F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron. - 1890-1907
FIELD OF VISION - a section of space perceived by the eye with a fixed gaze and a fixed position of the head. Allocate peripheral departments of P. z., characterizing peripheral vision, and central, related to central vision. nine0003 Brief medical encyclopedia. - M., 1989
Visual acuity
Visual acuity I Visual acuity is the ability of the eye to perceive separately two points located at a certain, usually small distance from each other.
Medical Ecyclopedia
VISUAL ACUITY - the ability of the eye to perceive separately two points located at a certain distance from each other; one of the most important characteristics of the organ of vision.
nine0003 Brief medical encyclopedia. - M., 1989
Visual acuity The main function of the visual analyzer. It is checked for each eye separately. Normal visual acuity is conditionally recognized as the ability to see separately two points at an angle of 1 minute.
Neurology. Complete explanatory dictionary. - 2010
Color vision
nine0002 Color vision, color vision, color perception, the ability of the human eye and many species of animals with daytime activity to distinguish colors, that is, to perceive differences in the spectral composition of visible radiation and in the color of objects. TSB. — 1969—1978
Color vision The visual experience of most vertebrates is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation intensity within their native visible wavelength range, from about 380 to 760 nm.
nine0003 Corsini R. Psychological Encyclopedia
COLOR VISION - visual ability associated with the analysis of electromagnetic radiation (in the spectral range of 400-700 nm) by a specialized sensory mechanism - a color analyzer.
Large psychological dictionary. - 2004
Binocular vision
nine0002 Binocular vision We usually get an idea of the location of a visible object in space with the help of vision with both eyes, or the so-called binocular vision. F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron. - 1890-1907
BINOCULAR VISION (from lat. bini - two oculus - eye; literally, "vision with 2 eyes") - vision with 2 eyes; provides perception of depth and volume of objects. nine0003 Large psychological dictionary.
- 2004
Binocular vision (from lat. bini - "two" and lat. oculus - "eye") - the ability to simultaneously clearly see the image of an object with both eyes; in this case, the animal or person sees one image of the object they are looking at...
en.wikipedia.org
Monocular
nine0002 Monocular vision is characterized by the fact that objects and moving objects that fall into the field of view of the looking subject are perceived predominantly with only one eye. Under normal conditions, a person who does not have any visual impairment... en.wikipedia.org
MONOCULAR VISION (English monocular vision) - vision with one eye. At M. h. the relative location of objects and distances to them are estimated by such indirect signs as a comparison of the apparent size of objects with their usual sizes .
Large psychological dictionary. - 2004..
Monocular vision - vision with one eye, characterized by - a relative narrowing of the boundaries of the field of view compared to binocular vision; and - the ability to evaluate the spatial characteristics of objects in perspective ...
glossary.ru
Photopic vision
Day vision is a mechanism for the perception of light by the human visual system, operating in conditions of relatively high illumination. It is carried out with the help of cones with a background brightness exceeding 10 cd/m2...
en.wikipedia.org
PHOTOPIC VISION Normal daytime vision; vision in conditions of sufficiently high illumination, when the cones of the retina are functioning.
Oxford Dictionary of Psychology. - 2002Photopic vision has the following general characteristics: (a) tones are perceived; (b) visual threshold…
Photopic vision is normal daytime vision when the retinal cones are functioning (as opposed to scotopic, "twilight" vision with retinal rod activation). nine0003 vocabulary.ru
Scotopic vision
Night vision is a mechanism for the perception of light by the human visual system, operating in relatively low light conditions. It is carried out using sticks with a background brightness of less than 0.01 cd / m2, which corresponds to night lighting conditions.
en.wikipedia.org
Scotopic vision (Greek skotos opsis - vision) - "twilight vision", vision in low light conditions, in which optical sensations are provided by retinal rods.
nine0003 vocabulary.ru
SCOTOPIC VISION Night vision, vision in low light conditions, in which visual sensations are provided by retinal rods. Scotopic vision has the following general characteristics (a) does not distinguish shades ...
Oxford Dictionary of Psychology. - 2002
Visually impaired children
nine0002 Visually Impaired Children Blind children are completely blind or have residual vision (from light perception to visual acuity of 0.04 in the better seeing eye with normal spectacle correction). Russian Pedagogical Encyclopedia / Ed. V.G. Panov. - 1993
VISUALLY IMPAIRED CHILDREN - Blind children are completely blind or have residual vision (from light perception to visual acuity of 0.
04 in the better seeing eye with normal spectacle correction). nine0003 Dictionary for parents of children with disabilities
Russian
Vision, -I.
Spelling dictionary. — 2004
Zr/eni/e [y/e].
Morphemic spelling dictionary. — 2002
Examples of the use of the word vision
Exploding, the firecracker damaged the goalkeeper's eyesight and caused temporary hearing loss.
Scientists from the University of Liverpool studied the vision of 185 people aged 18 to 75 years.
The fact is that in ordinary life I have excellent eyesight: I do not wear glasses or lenses.
The area around the eyes, nose, jaw and palate was restored to the patient, vision was preserved.
This is not the first time that Dominguez has come to the attention of the competent authorities.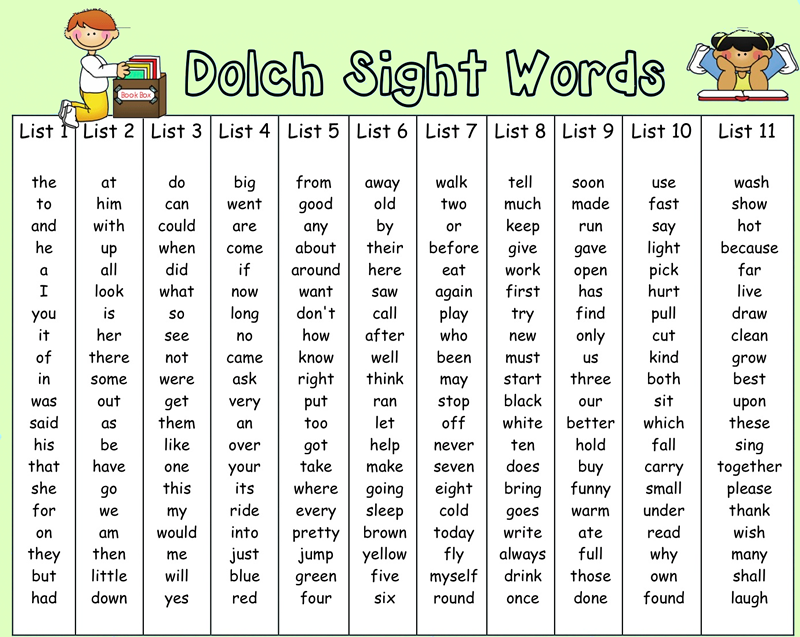
After removing the pencil, the pain in the head subsided, and vision began to recover. nine0003
- Words from the word "vision"
- Words starting with "z"
- Words starting with "zr"
- Words ending in "e"
- Words with "ie" at the end
- Words that start with "zre"
- Words that start with zren
- Words ending with "nie"
- Words ending with "enie"
- mature
- zipper
- spring nine0007 vision
- mature
- maturing
- visibility
Human vision concept, functions and visual impairment, organ of vision
What is human vision, or simply about the complex.
Vision is a unique gift given to us from birth. The value of which you begin to understand only when you start to lose it.
First of all, it must be said that sight is one of the five senses. Thanks to him we get up to 98% of information about the world around us. Visual impairment leads to loss of information and a decrease in the quality of life.
We often use this word. From childhood, we hear: “Vision must be protected”, passing the commission we always hear: “What is your vision?”. And as the years go by, we ourselves often begin to say: “My eyesight has begun to fail, I have a visual impairment”
But what is a person’s vision, what should it be in the norm in reality and what does it depend on?
Vision is an extremely complex functional mechanism that begins with the passage of a stream of light from objects through our eyes, with the transformation of the energy of light quanta into a nerve impulse that carries information to the brain. More precisely, to his occipital lobe. The visual process ends with the formation of an image of an object in our brain. nine0009
Visual impairment can occur at any stage of visual perception. Therefore, with a decrease in vision, it is very important to contact an experienced specialist in order to accurately diagnose and solve the problem that has arisen.
Therefore, with a decrease in vision, it is very important to contact an experienced specialist in order to accurately diagnose and solve the problem that has arisen.
The first and very important stage in the work of the organ of vision is the passage of the light flux through the transparent optical structures of the eye: the cornea, the anterior chamber filled with intraocular fluid, the lens of the eye, the vitreous body.
All must remain clear and undamaged. nine0003
Only in this case, the light can reach the retina of the eye, where the mysterious process of the transition of light energy into a nerve impulse takes place, in which all the smallest details of the object that emits or reflects the light flux are transmitted.
Of course, in order to fully transmit information further, the retina, optic nerve and visual pathways of the brain must be in perfect condition. Degenerative processes in the retina, tumor and head injury significantly reduce a person's vision. nine0003
nine0003
And the last stage on which vision depends is the cerebral cortex. It also determines the quality of vision, and in principle the ability to see. The human brain begins to learn to see from the moment of birth. But if a violation occurs on the path of the light flux, then the brain does not learn to perceive visual images and this causes a decrease in vision. This condition is called amblyopia. It also applies to visual impairment. The severity of amblyopia depends on the degree of damage to the anatomical structures in the path of the light stream. nine0003
The complexity of the organ of vision leads to the fact that vision has several functions, or rather five:
1. Central vision
2. Fields of view
3. Light perception
4. Color perception
5. Binocular vision.
It is the totality of all these functions that defines the concept - VISION of a person.
Violation of at least one of the functions leads to visual impairment and a decrease in the quality of life.