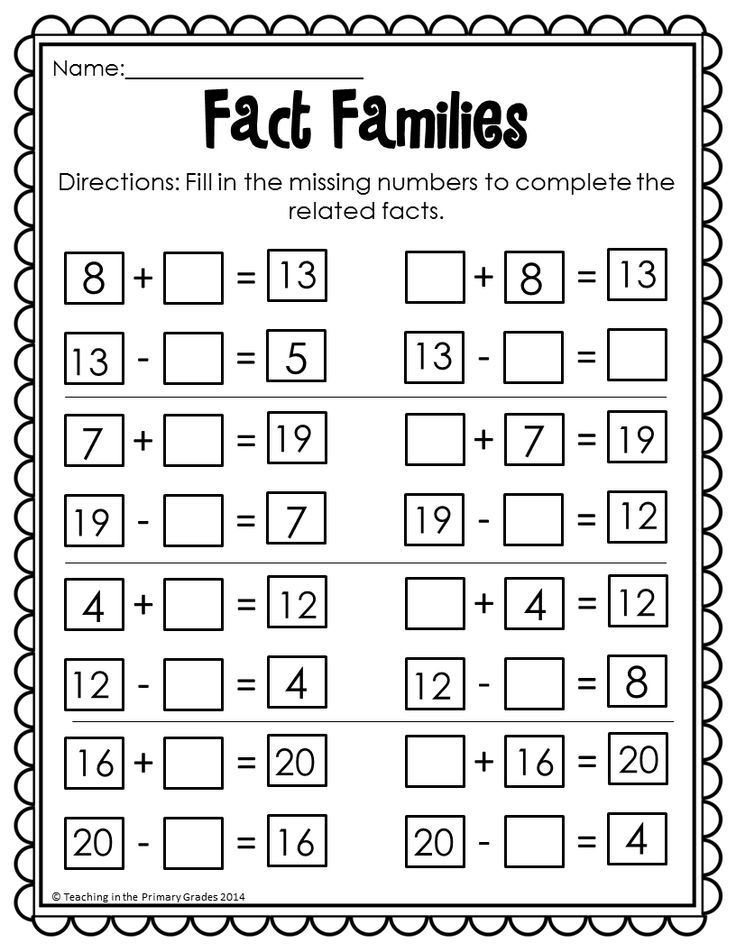
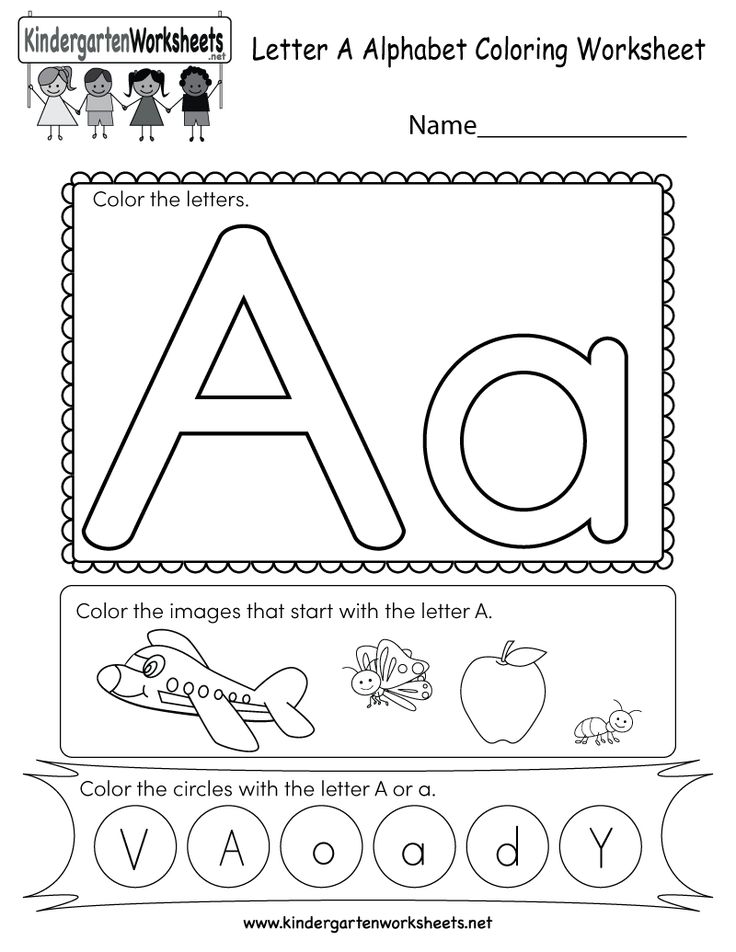
When should a child learn their abc's
FAQ: Your Reading Child
Q: How old should a child be when he or she learns to recognize letters?
A: Most children learn to recognize letters between ages 3 and 4. Typically, children will recognize the letters in their name first. By age 5, most kindergarteners begin to make sound-letter associations, such as knowing that “book” starts with the letter B.
Q: How old should a child be when he or she learns to read?
A: By age 6, most 1st graders can read some words aloud with ease. Typically, children recognize their names and some sight words. At this age most children can sound out some letter combinations. By 2nd grade, most children are able to sound out a simple book.
Q: What is phonics?
A: Phonics is simply the method of teaching someone to read by sounding out letters and letter groups. Phonics practice can involve reading books with only simple words, many of which rhyme or have similar letter patterns.
Q: How do you read with a child who is just learning letters and sounds?
A: To introduce the concept of letters and sounds, start by showing your child the letters in her name. Name each letter and sound out each sound. You can do this with other words that interest her (mom, dad, baby, etc.). Once your child knows most of the letters in the alphabet, point to letters in the books you read with her, and ask her what they are. Show her how you sound out simple words:
This word starts with “D” which is the “duh” sound. Then there’s an “o” and a “g”. The “g” makes a “guh” sound. “Duh”-o-“guh”. Do you think that word is dog?
As your child learns to read, try alternating pages in a simple book — you read one page, she tries to read the next.
Q: What are appropriate books for my child’s age and/or level?
A: Using Lexile Measures or Leveled Reading, your child’s school has probably determined the level at which your child is reading. Your goal is to help your child pick books that are challenging, but not too hard to enjoy. Librarians, teachers, and online databases like those at www.lexile.com can help.
Q: What is leveled reading?
A:Leveled reading is a way to match a reader to a book that is at the just-right level for him. An emerging reader needs to be challenged to read more difficult books, but the books can’t be too hard for him to attempt on his own. When entering a leveled reading program, a student first takes a test to determine his level.
An emerging reader needs to be challenged to read more difficult books, but the books can’t be too hard for him to attempt on his own. When entering a leveled reading program, a student first takes a test to determine his level.
Q: What is a Lexile Measure?
A: Both books and readers can be measured using the Lexile Framework. If your student has taken a test at school and received a Lexile Measure, you can visit www.Lexile.com to learn how to best use this information, including ways to find the perfect level book for your child.
Q: My child isn’t reading at his grade level and he says she “hates” reading. What should I do?
A: If your child falls behind even in early elementary school, you may want to have her evaluated for a learning disability. Even if the result is inconclusive, it’s best to know if your child has any special issues, as there are methods to teaching reading to children with special needs that work better than some traditional reading programs. Alternately, your child might just need more engaging books. There are many books available, such as the Captain Underpants series, as well as comic books, which “reluctant readers” love. Keep your child engaged with reading by encouraging her to read what she enjoys.
Alternately, your child might just need more engaging books. There are many books available, such as the Captain Underpants series, as well as comic books, which “reluctant readers” love. Keep your child engaged with reading by encouraging her to read what she enjoys.
Q: Where can I find lists of quality children's books?
A: The Association for Library Service to Children grants book and media awards to the best offerings for children. This is where you can find information on recent Newbery Award winners (most distinguished contribution to American literature for children) and Caldecott Medal winners (most distinguished American picture books), among others. This site also houses multiple book lists for children
Q: How can I encourage my child to read despite all the other distractions?
A: The best way to show that reading books can be fun and rewarding is to model the behavior you want from your children After dinner or on a lazy weekend afternoon, instead of turning on a movie or the TV, curl up with your own book, and encourage your child to do the same. Young children also love being read to, and if you are tired of the books in your house, a trip to the library can give you a new stack to read. Even if this only happens once a week, it may become a cherished family tradition.
Young children also love being read to, and if you are tired of the books in your house, a trip to the library can give you a new stack to read. Even if this only happens once a week, it may become a cherished family tradition.
Maximize Your Preschooler's Alphabet Recognition with These Expert Tips
Letter recognition is a crucial skill for toddlers and preschoolers to learn, and it serves as the foundation of reading and writing. This post explores the typical developmental curve for alphabet recognition and provides fun, age-appropriate, low-cost ways for your child to master this skill.
What is Letter Recognition?
Letter recognition is generally accepted as the ability to identify letters, both uppercase and lowercase. Being able to name a specific letter when surrounded by other letters is also an accepted definition. In this article, we share expert tips on how toddlers and preschoolers can learn to recognize the alphabet.
Toddler Letter Recognition
If your child is 2 to 3 years old, he or she may sing the alphabet song — but can’t yet identify letters. About 20 percent of children can recognize a few letters by age 3, often the letter that starts his or her own first name as well as other letters contained within the name. You may also notice that some of your child’s scribbles are starting to look like letters, especially the first letter of his or her name.
About 20 percent of children can recognize a few letters by age 3, often the letter that starts his or her own first name as well as other letters contained within the name. You may also notice that some of your child’s scribbles are starting to look like letters, especially the first letter of his or her name.
To help your child gain competency, encourage the singing of the alphabet song and look through books together that share information about letters. Consider providing your child with magnetic letters and other play materials that encourage learning of the alphabet. PBS.org provides more information about child development in this arena, while Teaching2and3YearOlds.com provides suggestions for fun ways to encourage toddlers to learn the alphabet.
Preschoolers Letter Recognition Tips
By the time children are older (4 years old and up), 60 percent know more than half of the uppercase letters and five to 10 lowercase ones. About 30 percent can recognize all letters, both upper and lower. Preschoolers often notice letters in their environment and understand that letters are related to sounds, which is an insight known as the “alphabetic principle.” They also recognize that numbers and letters are distinctively different in purpose, while letters that are similar in shape (p/q and b/d) are still often confusing. You can find more developmental information at PBS.org.
Preschoolers often notice letters in their environment and understand that letters are related to sounds, which is an insight known as the “alphabetic principle.” They also recognize that numbers and letters are distinctively different in purpose, while letters that are similar in shape (p/q and b/d) are still often confusing. You can find more developmental information at PBS.org.
HandsOnAsWeGrow.com provides 50 alphabet activities for your preschooler to enjoy, including Squirt the Letter. In this game, parents write random letters on the chalkboard. Also, have on hand alphabet blocks and ask your child to match what he or she sees on the chalkboard with what appears on a block. When your child makes a good match, then he or she can squirt the chalkboard with water in a spray bottle to make the letter disappear.
Another recommended game is Trash Can Alphabet Review. You simply take scraps of paper and write a letter on each one, using a marker (or you could use crayons or whatever else you have on hand). Point to a letter and ask your child to identify it; when the correct answer is given, your youngster can crumple up the paper and toss it into the waste can. Once the game is over, you can smooth out the scraps and play again when desired. You can also check out the other 48 suggestions given in the article.
Point to a letter and ask your child to identify it; when the correct answer is given, your youngster can crumple up the paper and toss it into the waste can. Once the game is over, you can smooth out the scraps and play again when desired. You can also check out the other 48 suggestions given in the article.
Alphabet Recognition Worksheets
One of the great things about the internet is finding free activities for your children. One of the things you can do is search for free, downloadable alphabet recognition worksheets. They're made up of different games, or sometimes coloring sheets that will help your child learn the alphabet. Megaworkbook has a lot of great suggestions to pick from.
Easy Outdoor Activities for Alphabet Recognition
When the weather is nice, it’s only natural to want your children to play outside. On those days, here is a simple game from ICanTeachMyChild.com that can help to teach your pre-K children the alphabet. Take sidewalk chalk and create a pathway of letters on your sidewalk or driveway. Let your child ride his or her bike over this path, singing the alphabet song as he or she rides over each letter. Do the same thing as your child walks along the path (skips, jumps, or whatever else works).
Let your child ride his or her bike over this path, singing the alphabet song as he or she rides over each letter. Do the same thing as your child walks along the path (skips, jumps, or whatever else works).
And, here’s a game you can play outdoors (or move indoors). Take masking tape and create letters. Then, let your child actively play with the letters. This writer’s child loves to take toy cars and use the masking tape as letter-shaped roads — and you can casually work the name of the letter into the conversation as your child is playing on it.
How to learn the alphabet with a child. Learning letters together
Letters are all around us. Signs, announcements, books and magazines - all this the child sees from a very early age. But it doesn’t immediately become clear that these “squiggles” are not just incomprehensible meaningless icons, but a way to convey information in the form of text. Therefore, with the study of the alphabet, a completely new world opens up for the baby, in which letters are folded into syllables, and syllables into words that can be read and later written. In our article, we will tell you when to start learning the alphabet, how to make the process interesting for a child, and what methods are best for children of different ages.
In our article, we will tell you when to start learning the alphabet, how to make the process interesting for a child, and what methods are best for children of different ages.
Why learn the alphabet?
It seems that the answer to this question is quite obvious - that the child can read. However, it's worth digging a little deeper. Often, parents do not fully realize what caused their desire for the child to quickly master the letters. If the kid is already 5-6 years old, and the first grade is just around the corner, then the desire to learn the basics so that further study is easier, understandable and logical. Or maybe your child is only three years old, but you want him to show off his knowledge at a family evening? Or do all the acquaintances vying with each other say that their children have not only learned the alphabet, but also read freely? Give yourself an honest answer to these questions, and consider whether it is necessary to postpone training until a more appropriate moment.
The most important thing is whether your child is ready. Curiosity, interest in new things, the ability to memorize previously unknown information are all signs that you can start learning the alphabet. But you should always remember that there is no point in teaching against the child’s desire, all classes should be held in an unobtrusive playful way. Questions “how to read?”, “What kind of letter?” Are pouring in on you, the baby is interested in not only pictures in books, but also captions to them, or are you going to school soon? Well, then feel free to start your acquaintance with the alphabet.
Basic tips for learning the alphabet with a child
The alphabet is not just a certain sequence of letters. This is the foundation from which the child's learning to read begins. Therefore, it is important to understand that simply learning the alphabet as a rhyme or a counting rhyme is possible, but practically useless if there is no practical application of the information received. If you do not start trying to teach your child to read immediately, but after a long break, there is a high probability that your baby will simply forget the letters by this point, and you will have to start all over again.
If you do not start trying to teach your child to read immediately, but after a long break, there is a high probability that your baby will simply forget the letters by this point, and you will have to start all over again.
There are a few general rules to follow when you start learning the alphabet with children:
1. Learn the sounds, not the letters
It's easy for us adults to figure out what the name of the letter is and what sound it is means may not match. For a small child, on the contrary, such a concept may be too complicated. Do not confuse the baby, he will eventually learn that the letters are called “be”, “el” or even “and short”, better demonstrate what sounds are indicated by the corresponding signs - “b”, “l”, “y”, give examples of words with these sounds. In this way, the child, with less effort, will be able to understand how syllables are read, and later whole words.
2. Do not learn the alphabet in order
Remembering a clear sequence is, of course, useful for the development of a child's memory, but it does not make it obvious to him what he actually learned and why. If, however, the alphabet is disassembled gradually, according to a clear and logical system, without overloading the child's perception excessively, there will be much more benefit, since knowledge will not be superficial, but based on a deeper understanding of the structure of the language.
If, however, the alphabet is disassembled gradually, according to a clear and logical system, without overloading the child's perception excessively, there will be much more benefit, since knowledge will not be superficial, but based on a deeper understanding of the structure of the language.
3. Do not mix vowels and consonants
Learning letters mixed up is no less a mistake than memorizing the alphabet strictly in order. Vowels and consonants must be studied separately, otherwise the child will be completely confused. Always remember that things that seem clear and simple to us, small children learn for the first time, so even the main sign by which sounds are divided (vowel-consonant) is not immediately comprehended. The situation when the studied letters do not have any common feature is confusing and slows down the assimilation of the material.
4. Vowels first
There are only 10 vowels in the Russian alphabet, so the child will have to remember a little at first. In addition, vowels require only a long “singing” and slight changes in the articulation of the lips, neither the tongue nor the teeth need to be connected, so it will be easier for the baby to understand how the written sign correlates with the sound being pronounced. When all the vowels are firmly learned, it will be possible to add consonants.
In addition, vowels require only a long “singing” and slight changes in the articulation of the lips, neither the tongue nor the teeth need to be connected, so it will be easier for the baby to understand how the written sign correlates with the sound being pronounced. When all the vowels are firmly learned, it will be possible to add consonants.
5. Don't force learning
Of course, you really want your child to learn all the letters and start reading as soon as possible, but you still shouldn't rush. Learn one or two letters, repeat what you have learned more often, do not move on to a new one without waiting for the consolidation of what has already been studied. Start with very simple and clear things. Show the young student the letter "A", tell how it is pronounced, what it looks like, what words begin with it. Fold it together with the baby from sticks, draw or mold it from plasticine - tactile sensations will help the child better remember the image of the letter and associate it with sound. Apply theory to practice, for example, ask while walking to look for the letter "A" on signs, in advertisements, and so on. Only when the child has learned the letter and the corresponding sound, proceed to the next, all the same one at a time, methodically and slowly.
Apply theory to practice, for example, ask while walking to look for the letter "A" on signs, in advertisements, and so on. Only when the child has learned the letter and the corresponding sound, proceed to the next, all the same one at a time, methodically and slowly.
Age-appropriate alphabet learning
3-4 years old
If you think your child is ready to learn letters at 3 years old, here are some tips and tricks to help you get great results.
First of all, in no case do not force or coerce the child into classes, they should take place exclusively at the request of the child, in a fun way, and end as soon as you see signs of fatigue and weakening of concentration. The optimal lesson time for a three-year-old is 5-7 minutes.
Do not set a goal to learn the entire alphabet in a short time, it is at best pointless, and in some cases it can even be harmful - up to a certain point the child's brain may simply not be ready for this or that knowledge. Do not try to outwit nature, at three years old your task is more to interest, captivate the child, show him the basics.
Do not try to outwit nature, at three years old your task is more to interest, captivate the child, show him the basics.
Do not overload your child with a lot of information - let your “lessons” take place no more than twice a week, and take the rest of the time to consolidate and repeat the studied material. At the same time, the regularity of classes is very important, conducting them from time to time is not the best idea, the child will get confused and forget what you went through with him.
Start with vowels. Move on to consonants only when you are sure that the child has firmly learned all 10 vowels and brought the skill to automatism. Vowels are best taught in pairs: A - Z, O - E, U - Yu, E - E, S - I. So it will be easier for the baby to remember. Later, this will also help with the assimilation of the principle of hardness-softness of consonants.
Use books with bright, large pictures. Closer to the age of four, the child will also be interested in blocks with letters, coloring books and stickers, posters with and without voice acting; but be careful with the posters - remember that we need to learn the sounds, not the names of the letters, so look for posters that pronounce exactly the sounds. Magnetic letters will also help - they can be placed on a magnetic board or simply on the refrigerator. You can learn rhymes and songs with the mention of the sounds that you are studying, play with letters cut out of paper.
Magnetic letters will also help - they can be placed on a magnetic board or simply on the refrigerator. You can learn rhymes and songs with the mention of the sounds that you are studying, play with letters cut out of paper.
Let the child represent the letter in different ways - by drawing, modeling with plasticine, folding with sticks or drawing lines in the sand or grits. Such activities are also useful for fine motor skills, and this is a very important skill for the baby, which affects, among other things, the development of speech.
There are more consonants in the Russian language, so it will take a longer time to study them, and if you consider that most consonants have both hard and soft variants, the task becomes even more complicated. But with the right approach, there should not be any particular difficulties. If the child has already mastered all the vowels and understands the difference between, for example, “A” and “I”, then it will not be difficult for him with your help to figure out how “ma” and “me” differ.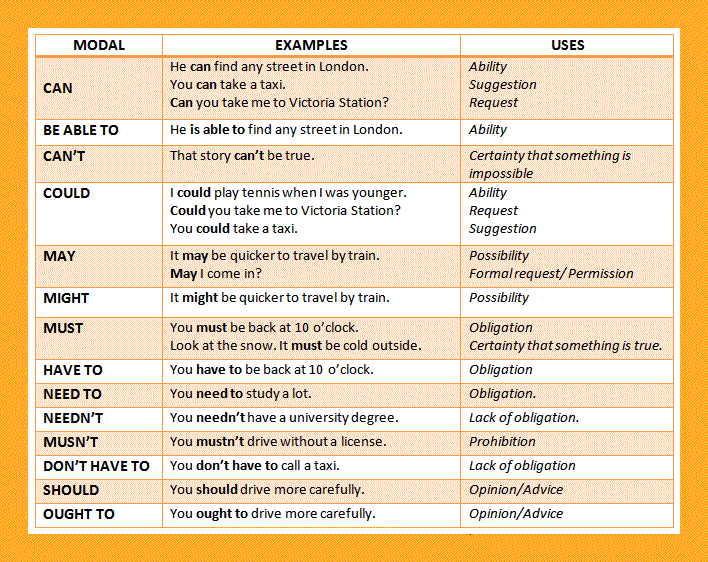 You can make a table where such pairs of syllables will be shown clearly. The main thing is to always clearly pronounce the sound yourself and achieve the same pronunciation in the child. Correct articulation is the key to both good diction and correct reading in the future.
You can make a table where such pairs of syllables will be shown clearly. The main thing is to always clearly pronounce the sound yourself and achieve the same pronunciation in the child. Correct articulation is the key to both good diction and correct reading in the future.
5-6 years old
For all our commitment to early development, many experts agree that the optimal age for learning the alphabet is 5-6 years old. The child will soon go to school, which means that his brain is already quite ready to memorize all the letters and gradually learn to read. At this age, it is especially important that your preschooler speaks clearly and correctly, so pay maximum attention to his speech, whether all sounds are pronounced without problems, whether some of them need to be corrected independently or with the help of a speech therapist.
If at three years the emphasis is on the play component of classes, then by the age of 5-6 it can be slightly shifted towards the child's consciousness. Tell us about how great it will be to read books yourself, how knowledge of the alphabet will come in handy at school. Keep the elements of the game, use the same methods that are suitable for four-year-olds, but increase the lesson time, introduce more printed materials. You will need special recipes for preschoolers, books and manuals with creative tasks, various sets of cards.
Tell us about how great it will be to read books yourself, how knowledge of the alphabet will come in handy at school. Keep the elements of the game, use the same methods that are suitable for four-year-olds, but increase the lesson time, introduce more printed materials. You will need special recipes for preschoolers, books and manuals with creative tasks, various sets of cards.
Introduce your child to syllables. Use single letter flashcards to show how a syllable is built - for example, say that a consonant and a vowel run or are attracted to each other and demonstrate their convergence by saying the syllable at the same time. Later, use cards with a ready-made printed or hand-drawn syllable in the lessons. Do not forget about the regularity of classes and the constant repetition of the material covered.
Primer learning
By the age of six, a good primer will be clear and easy to learn. For example, the “Primer” by N. Zhukova is considered one of the best, although for younger children it may seem boring - it focuses on learning without providing entertainment materials. But in this primer much attention is paid to speech therapy moments.
But in this primer much attention is paid to speech therapy moments.
“My primer: a book for teaching preschoolers to read” N.V. Nishchevoi - a manual also with a speech therapy bias, but the author adheres to his own methodology for studying letters and sounds. The path from simple sounds to complex ones will help the child develop both reading skills and good articulation.
In order for a child to develop a love for reading from a very early age, VV Shakirova's Journey to the Sound Book is a good choice. There is more entertainment material here that will interest and captivate the child. In addition, Shakirova paid a lot of attention to the development of motivation, and this will definitely come in handy in the future, in the process of further study.
Games for learning the alphabet
In this section, we will give examples of games that will make learning more interesting and at the same time more effective. Entertaining elements will not only diversify classes, but also provide a fairly wide field for applying the acquired knowledge in practice.
"Find the letter" . On a sheet of paper, arrange different letters in a random order. Let them be bright and large. You name the letter, and the child must find it and show it. A mobile version of this game is to hang sheets with large letters around the room, let the child find and tear off the desired sheet.
Memo . Prepare a set of cards, each letter must be represented in duplicate to get a certain number of pairs. Cards are laid out in several rows face down. Have the child turn over one card and name the sound that the letter on it represents. Then you need to find a pair for her by opening other cards. It didn’t work the first time - the cards are turned back face down and you have to look again. A pair was found - the player takes both cards for himself, and so on until the moment when all the cards run out.
“What letter does it begin with?” . Arrange several animals in a row - these can be drawings on paper, cards or small toys. Select the letters with which their names begin, and give them mixed to the child. The task is to correlate which letter refers to whom, and put it next to the desired animal.
Select the letters with which their names begin, and give them mixed to the child. The task is to correlate which letter refers to whom, and put it next to the desired animal.
Collect the letter . Draw a letter the size of the entire sheet of paper. Cut into several parts, let the kid assemble the resulting puzzle and name which letter is depicted on it.
Dice game . Surely you have cubes with letters, and if not, they are easy to make yourself out of paper. You roll a die and see which letter comes up on top. The child needs to remember an animal (or even an object!), The name of which begins with this letter and show it, for example, if the letter “B” fell out, then you can depict a crow - wave your hands like wings and croak.
Edible Letters . The alphabet is not only useful, but also delicious! Your child will have even more fun learning if he can not only name the letter, but also eat it. You can buy ready-made cookies in the form of letters, or bake them yourself, so the baby will even be more interesting, especially if you decorate the finished cookies together. You can also cut out letters from fruits and vegetables.
You can also cut out letters from fruits and vegetables.
No matter how your activities progress, be patient with your child, don't demand too much from him or scold him if something doesn't work out. If you follow the basic principles and recommendations, creatively approach the lessons and give the baby positive emotions, your child will definitely learn the alphabet easily and with pleasure.
At what age and how to learn the alphabet with a child
Is it good to know letters at two years old and is it so bad not to know them at four? What is the best way to learn the alphabet with a child?
When to start learning letters
Many parents want to teach their children to read and write as soon as possible and worry when the baby begins to memorize letters later than others. But modern experts believe that the rule “the sooner the better” does not apply here.
For example, according to neuropsychologist Anna Semenovich, learning letters and numbers from 2. 5-3 years is extremely harmful. The specialist explains that there are certain neurophysiological laws of brain development. At this age, the sensorimotor and emotional sphere of the baby is formed, the time has not yet come for cognitive processes. If you start to actively load him with learning, that is, untimely development of one of the mental functions, the child's brain will perform the assigned tasks, but the development of other structures of the psyche will suffer. This is fraught with a violation of emotional processes, the appearance of diseases is possible.
5-3 years is extremely harmful. The specialist explains that there are certain neurophysiological laws of brain development. At this age, the sensorimotor and emotional sphere of the baby is formed, the time has not yet come for cognitive processes. If you start to actively load him with learning, that is, untimely development of one of the mental functions, the child's brain will perform the assigned tasks, but the development of other structures of the psyche will suffer. This is fraught with a violation of emotional processes, the appearance of diseases is possible.
Anna draws attention to the fact that at first the child develops visual-figurative thinking, and then abstract-logical thinking. And teaching a child to write letters reverses this process, violating the law of psychology.
In her opinion, at the age of 3–4, a child should be taught everyday knowledge, teach routine, help to study the world around him, and you can also give him to creative circles. And the letters should be left for 4-5 years.
However, she admits that there are exceptions to the general rule: all children are different, some babies learn to read on their own at an early age.
How do you know when exactly to start the alphabet? Excellent advice on this matter is given by the psychologist Olga Melnitskaya. In her opinion, the main indicator is the child's sudden interest in letters. And there is nothing wrong with that, even if it happens at the age of 6, when he realizes that in order to receive information from the world, you need to be able to read.
It's time for the alphabet if the baby:
- imitates adults, pretending to read;
- asks what is written in the book or on the advertisement;
- pronounces almost all sounds;
- builds phrases;
- perceives well by ear - he can tell what his parents read to him from a book.
How to teach your child the alphabet
It is best to start learning with sounds, not letters: talk to your child as they are pronounced. Also, Dr. Komarovsky advises to learn vowels first - it is easier for children to memorize them.
Also, Dr. Komarovsky advises to learn vowels first - it is easier for children to memorize them.
Soft cubes, cards and magnets with objects whose names begin with different letters, coloring pages will help in learning. And many more benefits, ranging from the usual primer to modern toys like the musical alphabet.
Make the lessons playful, learn songs and rhymes together that will help you remember the letters. But most importantly - do not force the child to learn them. It is better to deal with him briefly, for 10 minutes or less, and if the baby gets bored, stop the lesson so as not to discourage interest.
Important: do not get annoyed if the child does not remember a letter that you have repeated many times, or pronounces it incorrectly. Continue to learn it for as long as you need for your crumbs.
Starting at the right time, with regular practice and patience, you will achieve an excellent result: the child will master the alphabet in a couple of months.