Basic preschool concepts
Basic Concepts to Teach Your Preschooler
“What should my preschooler know?”
This question often gets asked by parents. Many want to know what basic concepts their 4-year-old should know in order to be prepared for Kindergarten.
Academically speaking, it’s not a lot. It’s more valuable for your youngster to be able to listen to and follow directions than it is for him to recite the alphabet. While exposing him to the letters of the alphabet through fun activities like songs and puzzles is good practice at this age, expecting him to identify all 26 letters in upper and lower case isn’t really necessary. If you have a child who is advanced in Language Arts and is ready and interested in learning letters and reading, go ahead and do so. Otherwise, exposure to the written word through fun activities like I previously mentioned and read aloud time is usually enough.
I have compiled a list of basic concepts that are generally good for preschoolers to know. This is different from skills that they should be able to do which is found in this post: Preschool Skills Checklist. Both lists are just guidelines to help you out. Every child is unique and learns at a different rate so it’s fine if your child doesn’t know all of these by the time he starts doing Kindergarten level work. You can always cover the basic concepts that he didn’t learn as a preschooler then.
- ❑ Colors
- ❑ Shapes
- ❑ Numbers 1-10 (mainly counting from 1-10 although identifying at least 1-5 is helpful)
- ❑ Same and different
- ❑ Does not belong
- ❑ One-to-one correspondence
- ❑ Pattern recognition
- ❑ What comes next in a sequence of events
- ❑ Up and down
- ❑ Above, below, and beside (next to)
- ❑ Front and back
- ❑ Over, under, and in the middle
- ❑ In front of and behind
- ❑ Closed and open
- ❑ First, next, and last
- ❑ Inside and outside (in and out)
- ❑ Backward and forward
- ❑ Top and bottom
- ❑ Before and after
- ❑ High and low
- ❑ Big and little
- ❑ Largest and smallest
- ❑ Tall and short
- ❑ Wide and narrow (fat and skinny)
- ❑ Medium sized
- ❑ Long and short
- ❑ Same size
- ❑ Fast and slow
- ❑ Basic feelings such as happy, sad, mad, and glad
- ❑ Empty and full
- ❑ More and less (fewer)
- ❑ Many and few
- ❑ Part and whole
- ❑ Night and day
- ❑ On and off
- ❑ Loud and soft
- ❑ Hot and cold
- ❑ Hard and soft
- ❑ New and old
- ❑ Early and late
- ❑ Times of the day such as morning, afternoon, and evening
- ❑ Weather
- ❑ Seasons
- ❑ Simple categories such as food, clothes, animals, and toys
- ❑ Family members
- ❑ Parts of the body
- ❑ Stranger safety
- ❑ Full name
- ❑ Parents’ names
- ❑ Home phone number
- ❑ Birthday
- ❑ God
- ❑ Jesus
- ❑ Heaven
- ❑ Earth
- ❑ Angels
I have some preschool printables that teach some of these concepts here. I think your youngster will like them!
I think your youngster will like them!
Many blessings,
P.S. If you need some inspiration, you can find a list of more than 250 preschool themes to teach your child here: The Ultimate List of Preschool Themes
Concepts to teach for 2 to 5 year old toddlers and preschoolers!
A simple list of concepts that can be taught to the age group 2.5 to 5 years children at home. So here I am, listing a few Ideas about the concepts and topics that can be taught to our children.
CONCEPTS / TOPICS :
1. PHONICS/LANGUAGE
– Alphabet (Uppercase & Lowercase)
– Letter names and sounds
– Beginning sounds
– CVC words / Word Families
– Rhyming Words
– Sight Words(List 1)
– Opposites
– Naming Objects and People
– Using 2 to 3 words that goes together (like eating a banana etc.)
– Speaking in full sentences by the time they turn 3.5/4 years
– Narrating a situation
– Retelling a simple story
– Describing what they feel
– Describing what happens in school / playdate / outing etc.
– Recalling details about any incident that happened to them
– Knowing all the Family member’s names and faces and the relations between each other(like brother-sister, husband-wife, uncle-aunty, mother-father etc.)
2. MATHS / CONCEPTS
– Numbers 1 to 50/100, depending on child’s ability to grasp and remember
– Number Names 1 to 10
– Counting objects/ in a picture 1 to 20
– Big/small
– Long/short
– Tall/short
– Thick/ thin
– Heavy / light
– Empty/Full
– More/less
– Wide/narrow
– What goes together? (like a pencil and eraser or glass and water etc.)
– Small/medium/large
– First/next/then/last
– First/last
– Similar/Different
– Sequencing of objects
– Time
– Calendar
– Shapes (2D&3D)
– Colors (Primary/ Secondary)
– Odd one out
– Grouping/Categorizing
– Graphing
– Sorting Letters and Numbers
3. EVS / SCIENCE / GENERAL KNOWLEDGE
– Seasons
– Weather
– Parts of the body
– Sense organs
– Days of the week
– Months of the year
– Myself and My Family
– My school
– My classroom
– Fruits
– Vegetables
– Animals/Birds/Insects – Domestic/Wild/Young ones/ Homes of animals/Sounds of animals/Water animals/Reptiles etc.
– Flowers
– Vehicles
– Food and Nutrition
– Meals (Breakfast / Lunch /Dinner / Snacks)
– Community Helpers
– Cleanliness (Self/Home/Environment)
– Good Habits
– Good Manners
– Indoor Games
– Outdoor Games
– Sources of Water
– Uses of Water
– Living Beings/Non-Living Beings
– Plants and their types
– Festivals
– Places of worship (like Gurudwara, Temple, Mosque, Church etc.)
– Toys
– Actions
– Gender
– Birthday Party
– Hospital
– Railway station
– In a Village
These are the topics that are at the top of my mind. Please feel free to share and add more ideas/concepts if you have in mind, for the age group 2.5 to 5 year olds, in this thread. So it can be easy for everyone to refer back.
***Also keep in mind, that every child is Unique and has different grasping power. So please don’t compare your child to anyone else’s in the group, not even mine. This is just to motivate you and give a direction to your learnings at home. These should be done alongwith good, everyday Outdoor play and gross motor activities. Also, encourage your child’s interests and hobbies, so they can develop on their skills. Let it be drawing, coloring, painting, dancing, singing, or whatever, encourage them to develop their hobbies & interests.
These should be done alongwith good, everyday Outdoor play and gross motor activities. Also, encourage your child’s interests and hobbies, so they can develop on their skills. Let it be drawing, coloring, painting, dancing, singing, or whatever, encourage them to develop their hobbies & interests.
It’s much more important to “FOLLOW THEIR HEART” than just Academic Excellence. ***
Hope this helps You all !
Love
Deevyanka Pawar
Basic concepts of preschool pedagogy
Definition 1
Preschool pedagogy is an independent science that studies the patterns of upbringing, development and education of a child from the moment of his birth and before entering school.
A brief history of the formation and development of preschool pedagogy
The emergence of preschool pedagogy as an independent science is associated with the name of the Czech philosopher and teacher Ya.A. Comenius, who created the first system of preschool education. It was Comenius who first pointed out that in the process of education an important role is played by taking into account age characteristics. To this end, he developed an age periodization, which includes four age periods: childhood, adolescence, youth, and manhood.
It was Comenius who first pointed out that in the process of education an important role is played by taking into account age characteristics. To this end, he developed an age periodization, which includes four age periods: childhood, adolescence, youth, and manhood.
I.A. Comenius developed and proposed a special program to prepare children for systematic schooling. This program included basic knowledge from all fields of science, which are the foundation of subsequent training. The acquisition of knowledge within the framework of the program was carried out “from simple to complex”.
The continuation of the development of preschool pedagogy as a science is reflected in the works of Ya.A. Comenius: J.J. Russo, I.G. Pestalotsii, J. Locke, etc. In their works, they significantly advanced the solution of theoretical and practical issues of education and training.
L.N. Tolstoy, K.D. Ushinsky, V.G. Belinsky, A.I. Herzen, N.G. Chernyshevsky, etc.
World fame of Russian pedagogy is due to unique ideas, concepts and theories developed by KD Ushinsky. It was he who developed the psychological and pedagogical concept of personality development, and on its basis the theory of education and training was proposed. The greatest importance in the upbringing and development of preschoolers K.D. Ushinsky saw in the development of speech in children and their mental development. Such works by Ushinsky as "Native Word" and "Children's World" are relevant and in demand at the present time.
It was he who developed the psychological and pedagogical concept of personality development, and on its basis the theory of education and training was proposed. The greatest importance in the upbringing and development of preschoolers K.D. Ushinsky saw in the development of speech in children and their mental development. Such works by Ushinsky as "Native Word" and "Children's World" are relevant and in demand at the present time.
In the 19th century, preschool pedagogy continued to develop successfully as an independent discipline. In the twentieth century, preschool pedagogy deals with a wide range of issues related to the upbringing and development of preschool children. A great contribution to the study of these issues was made by such teachers and scientists as N.K. Krupskaya, A.S. Makarenko, S.T. Shatsky, P.P. Blonsky and V.A. Sukhomlinsky.
A.S. Makarenko developed and tested in practice a unique theory of raising a child in a team, and also considered the importance of family education in the development of the personality of children.
Methodological aspects of preschool pedagogy
Preschool pedagogy is aimed at studying:
The process of upbringing and education, its main goals and objectives, filling content, basic forms, methods and means of implementation. The influence of the upbringing process on the development of the child and the quality of the formation of his personality.
The basic concepts of preschool pedagogy "follow" from the functions assigned to it:
- Descriptive and applied function - aimed at the scientific description of the most promising and successful programs, technologies and models of the pedagogical process.
- Prognostic function - carries out a scientific forecast for the further development and improvement of the educational process in preschool educational institutions.
- Creative and transformative function - provides for mandatory accounting and reliance on scientific research conducted in the field of educating preschool children.

The object of preschool pedagogy is phenomena that directly affect the development of a child's personality.
The subject of preschool pedagogy is education, which is a holistic pedagogical process organized purposefully within a particular institution (family, preschool, etc.).
Tasks of preschool pedagogy:
- Solving the theoretical problems of educating preschool children.
- Implementation of the upbringing process in accordance with the age patterns of development.
- Implementation of research and generalization of pedagogical practice and experience of realized pedagogical activity.
- Forecasting the further development of preschool pedagogy as an independent science.
Note 1
Preschool pedagogy operates with a fairly wide range of concepts, which are based on: upbringing, training, development, pedagogical process, childhood, education.
Some basic concepts of preschool pedagogy
Education is a purposefully organized pedagogical process aimed at the implementation of vigorous activity that stimulates the comprehensive and full-fledged formation of the personality and the mastery of its social experience.
Development is an individual process of qualitative and quantitative changes in personality, carried out on the basis of properties inherited or acquired in the process of life.
Education is a purposeful and organized two-way process for the transfer and assimilation of specific knowledge, skills and abilities, as well as the development of children's cognitive activity.
Formation is a process of personality development, carried out under the influence of certain external influences, such as upbringing, training, social environment, etc.
Pedagogical process is a specially organized interaction of a teacher with students, which is implemented within a specific time frame and under the conditions of a specific educational system, aimed at achieving an educational goal and designed to lead to personal changes in an individual.
Subject-developing environment is a certain set of socio-cultural, natural and subject means aimed at meeting the needs of the immediate, future and actual development of the child.
Subject-developing environment provides for the formation and subsequent development of children's creative abilities through a variety of activities. In addition to the developing influence, the subject-developing environment is designed to have a relaxing effect on the child.
Knowledge is scientific facts, concepts, etc., which the child learns in the form of certain information.
Skills are actions formed and developed by the teacher, aimed at applying the acquired knowledge directly in practical activities.
Skills are certain actions brought to automatism through repeated performance of special exercises (reading, writing, etc.).
subject, basic concepts and functions.
Preschool pedagogy is a science that studies the patterns of upbringing, development, training and education of a child from birth to school.
The subject of is the education and development of preschool children. age.
age.
Functions of preschool pedagogy:
1. Descriptive - applied. It consists in the scientific description of promising programs, models, technologies of the educational process.
2.Prognostic. It implies a scientific forecast of ways to improve, update and modernize the educational process of DU.
3. Creative - transformative. It involves taking into account scientific research, forecasting when creating design and construction technologies.
Basic concepts of preschool pedagogy.
Upbringing is a purposeful pedagogical process of organizing and stimulating the active work of a formed personality to master the totality of social experience.
Development is a process of quantitative and qualitative changes in the inherited and acquired properties of an individual.
Learning is a two-way process of transferring and assimilating knowledge, skills, abilities, and developing children's cognitive activity.
Formation - the process of personality development under the influence of external influences: education, training, the social environment as a whole.
Pedagogy as an independent branch of theoretical knowledge began to take shape in the 17th century. By this time, there was an urgent need for science, designed to improve the existing pedagogical practice, to expand the boundaries and opportunities for upbringing and education.
Formation and development of preschool pedagogy. The emergence of preschool pedagogy is associated with the name of the Czech teacher and philosopher of the 17th century. Ya.A.Komensky (1592-1670), who created the first system of preschool education. He pointed out the need to take into account the age and individual characteristics of children; developed age periodization, including four age periods: childhood, adolescence, youth, and manhood. He proposed a knowledge program that prepared the child for systematic schooling, which contained the rudiments of knowledge from all fields of science. Knowledge and skills were arranged according to the principle of sequential transition from simple to complex, from easy to difficult.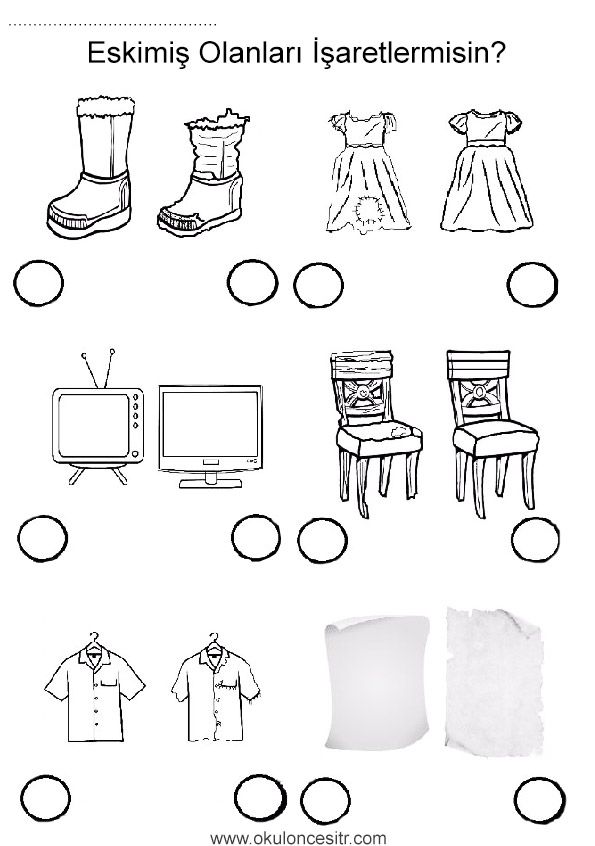
A turbulent period in the development of classical pedagogical theory begins with the scientific works of Ya. A. Komensky. A brilliant galaxy of subsequent classical teachers (J. Locke, J. J. Rousseau, I. G. Pestalozzi and others) significantly advanced the development of theoretical problems of education and training.
A worthy contribution to the creation of classical pedagogy was made by our compatriots Belinsky, Herzen, Chernyshevsky, Tolstoy. The world fame of Russian pedagogy was brought by K.D.Ushinsky. Ushinsky believed that "pedagogy is an art." He created the psychological and pedagogical concept of personality development and, on its basis, the theory of education and training. I saw the goal of teaching preschoolers in the mental development and development of speech. His works "Children's World", "Native Word" have not lost their significance at the present time.
The 19th century, marked by outstanding achievements, primarily in the field of natural science, physics, mathematics, was also favorable for the development of pedagogical science. During this period, it is intensively developing as an independent scientific discipline, rising from the description of facts and phenomena to comprehending the laws of the process of education and training. Within pedagogy, differentiation of knowledge is observed, its individual parts are singled out and isolated, such as, for example, preschool pedagogy.
During this period, it is intensively developing as an independent scientific discipline, rising from the description of facts and phenomena to comprehending the laws of the process of education and training. Within pedagogy, differentiation of knowledge is observed, its individual parts are singled out and isolated, such as, for example, preschool pedagogy.
Attention!
If you need help writing a paper, we recommend that you contact professionals. Over 70,000 authors are ready to help you right now. Free corrections and improvements. Find out the value of your work.
Calculation costGuaranteesReviews
XX c. with its turbulent socio-political changes in many countries, he posed the problem of educating a person in a new society for pedagogy. It was studied by S.T. Shatsky, P.P. Blonsky. Theoretical works of N.K. Krupskaya (1869-1939) cover a wide range of pedagogical problems, including those directly related to the upbringing of preschool children.