Basic shapes for preschoolers
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
| 5. | Conclusion |
| 6. | About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
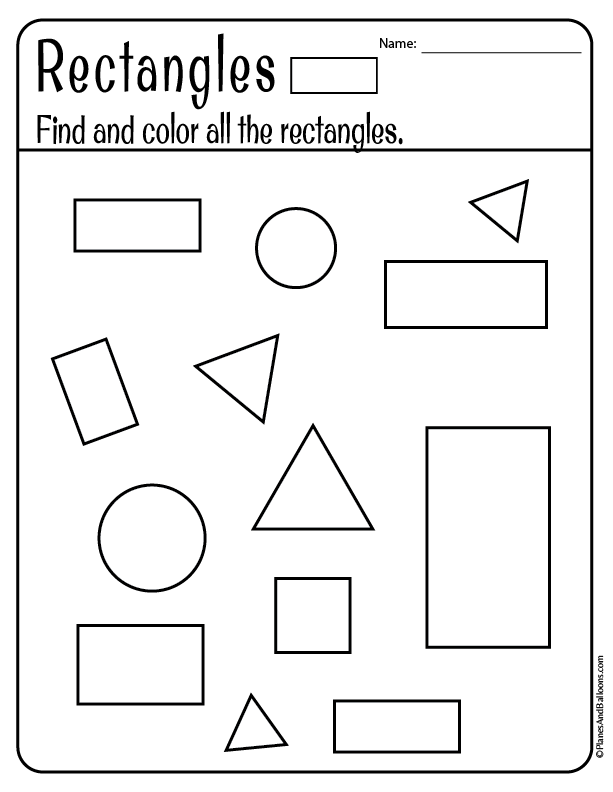
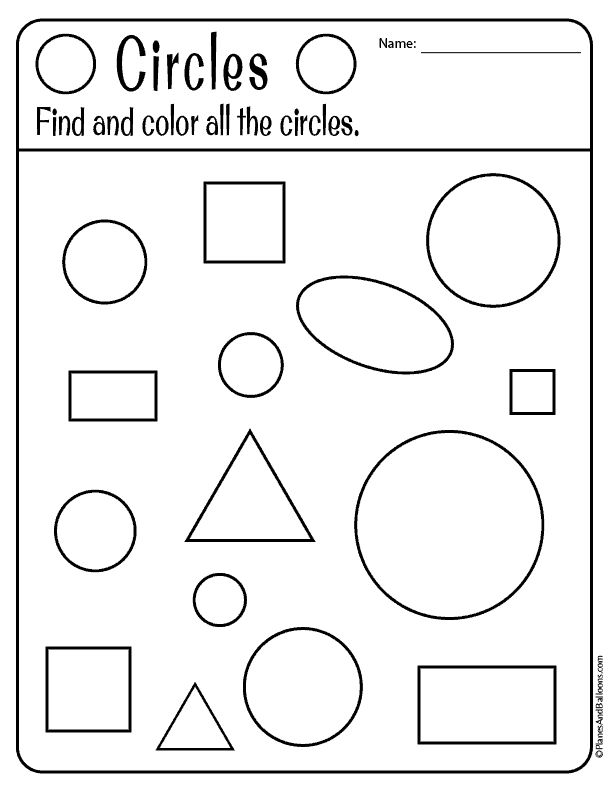
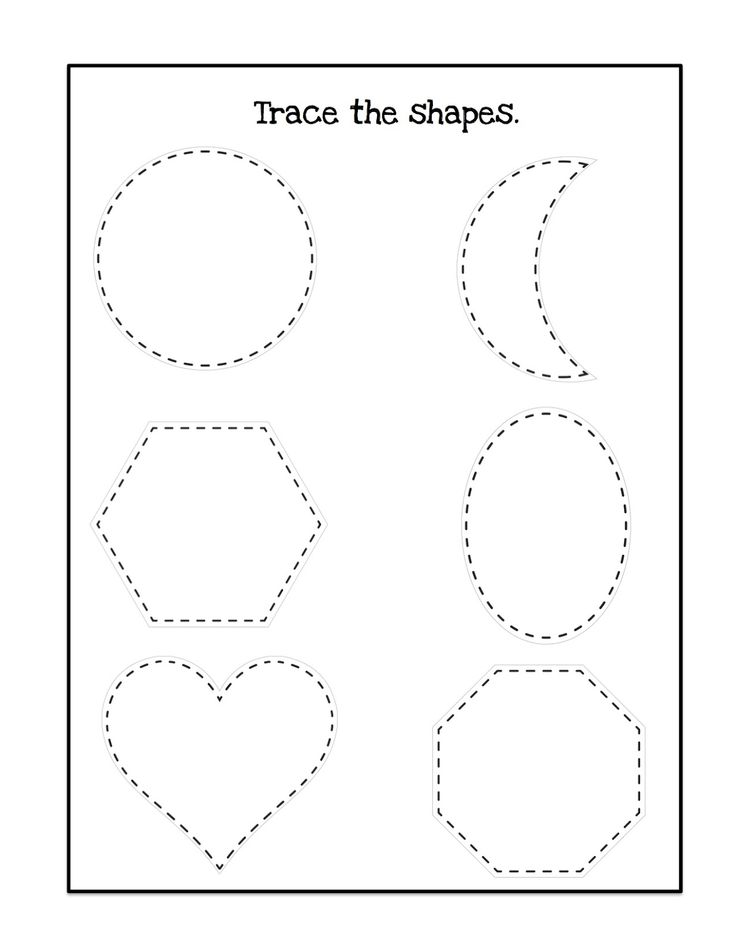
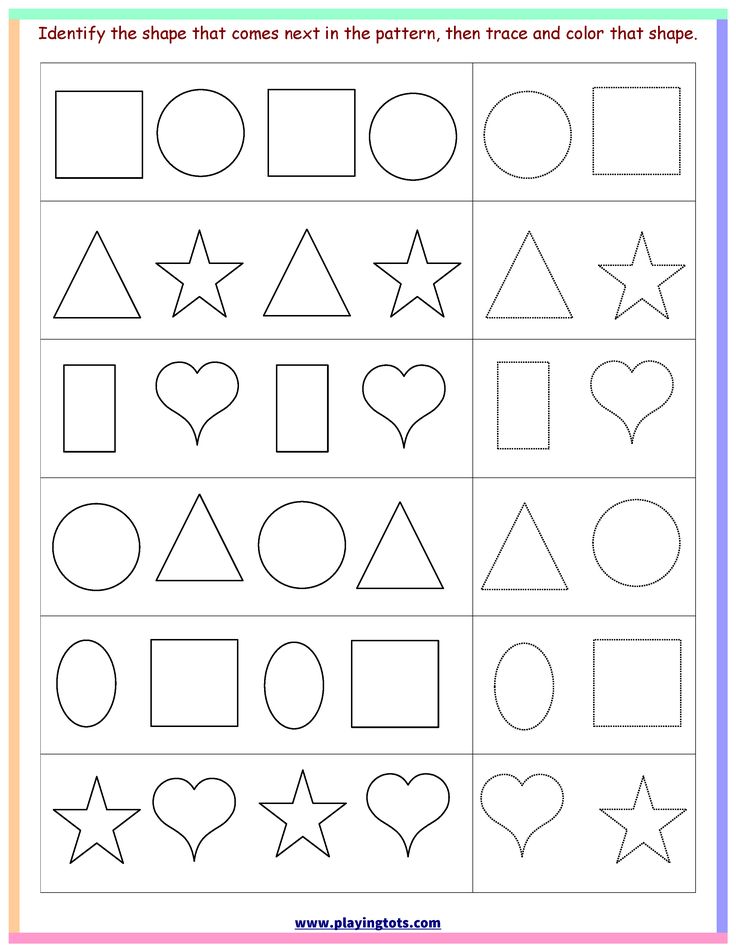
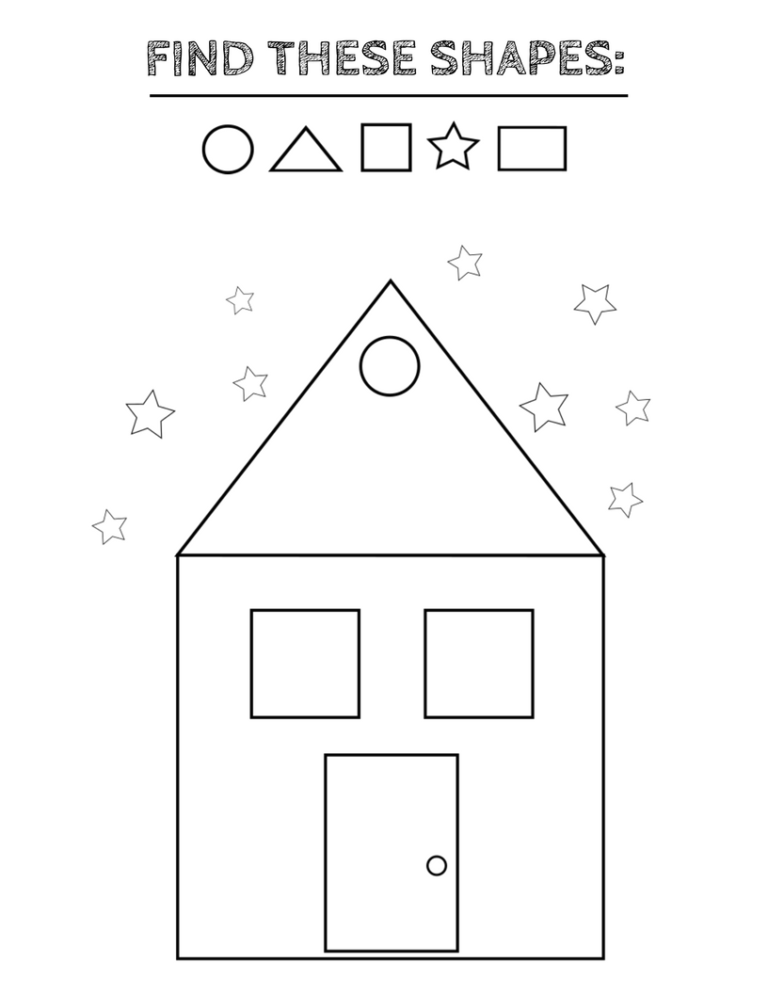
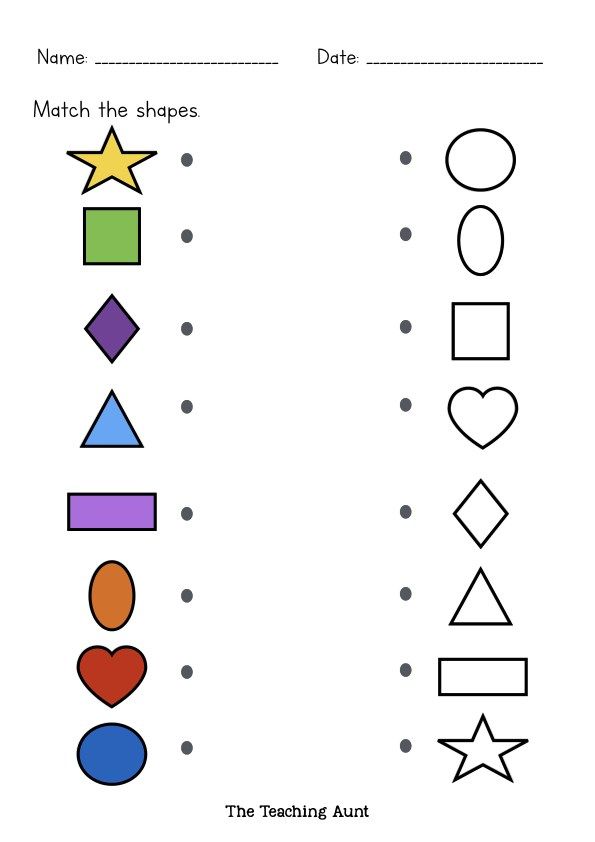
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
- Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction. Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten. Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids.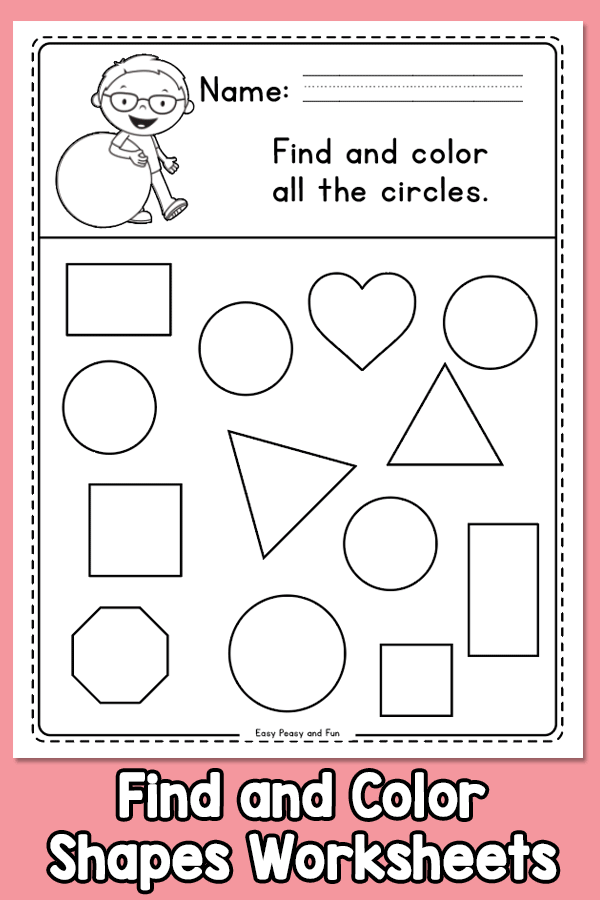 This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
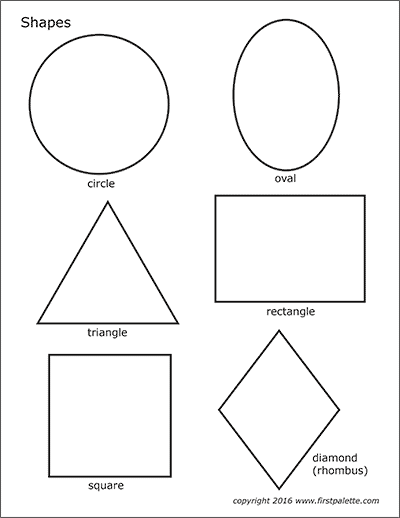
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
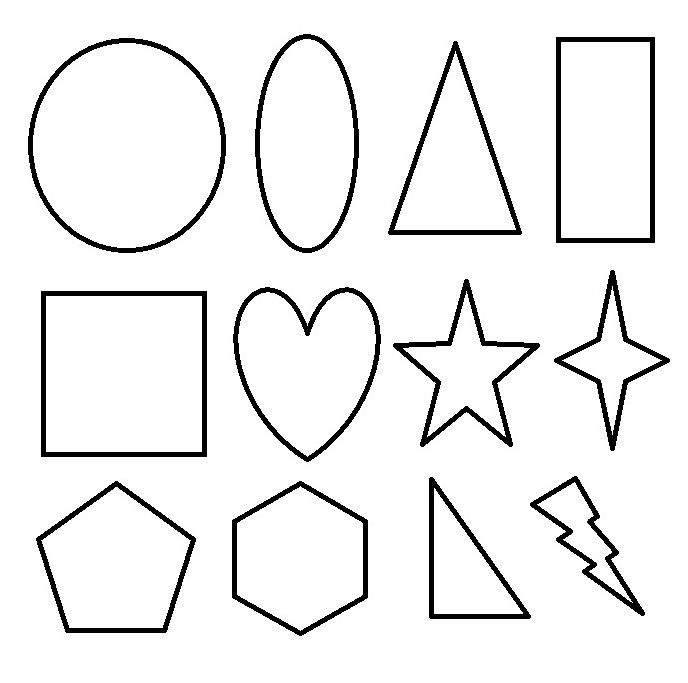
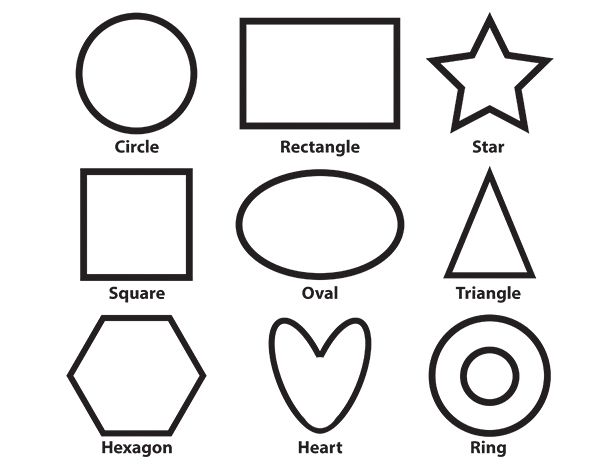
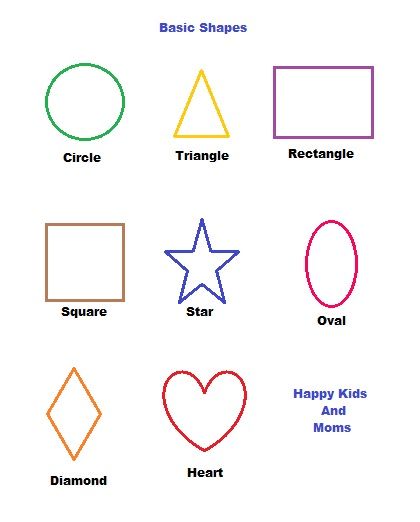
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc. Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them. Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card. Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus. Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Live Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
| 5. | Conclusion |
6. |
About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
- Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction. Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten. Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc.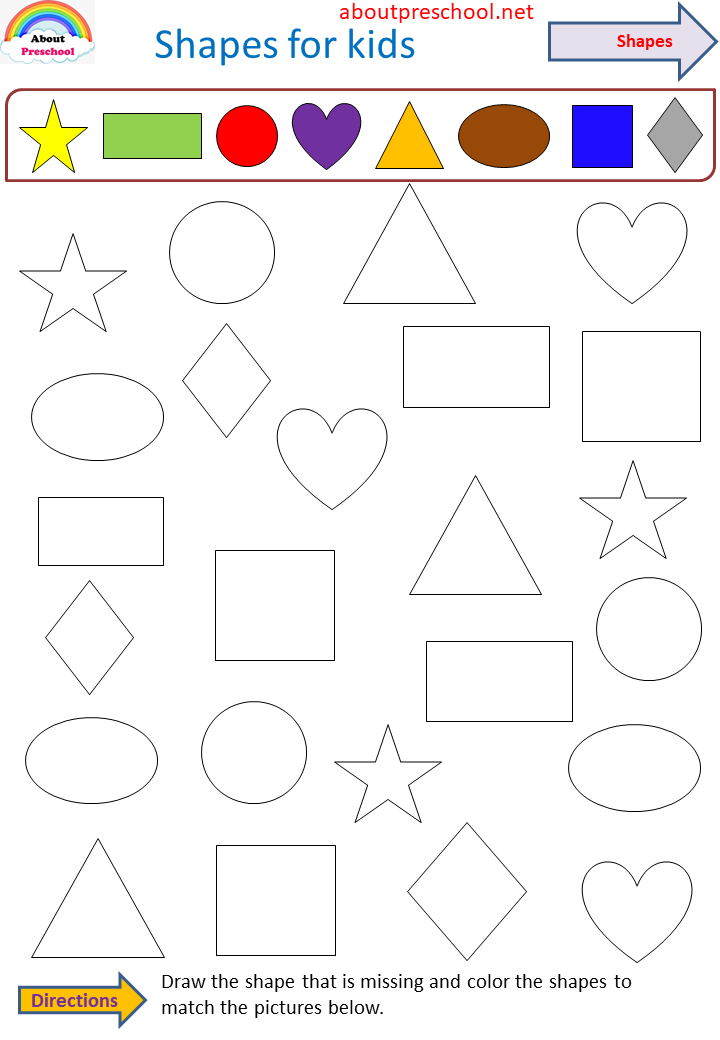 Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them. Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card.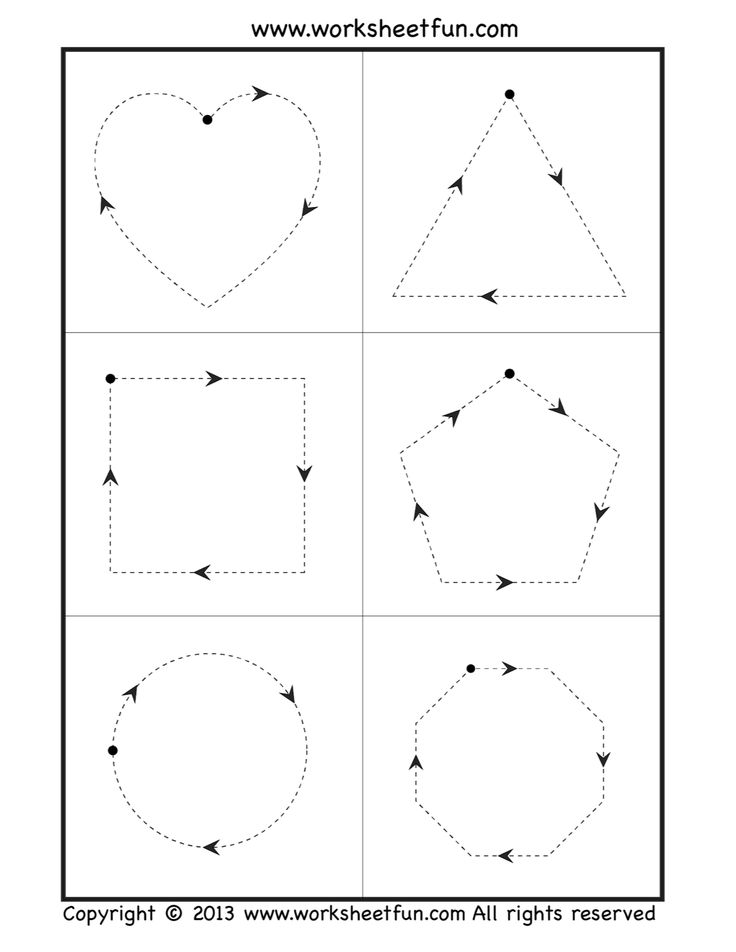 Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus. Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Live Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
MAIN FORMS OF JOINT ACTIVITIES OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN | Article on the topic:
MAIN FORMS OF JOINT ACTIVITIES OF ADULTS AND CHILDREN
Story game
Purpose: mastery of the child with a double system of means for constructing play activities.
Objectives: to gradually transfer to children gradually more complex ways of building a game.
The specificity of play activity (its "substitute" nature) requires the child to simultaneously master the dual system of means for its construction. The child must learn not only to perform a conditional play action, but also to designate an imaginary phenomenon or event.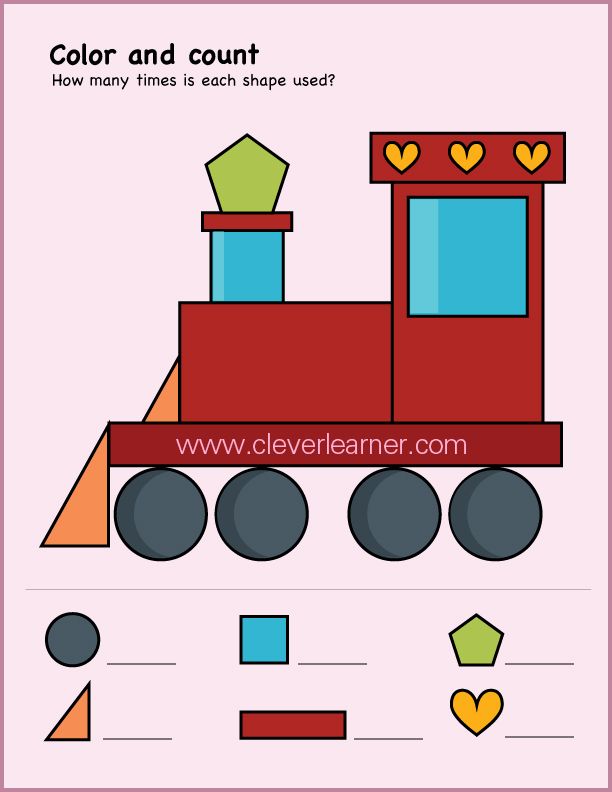 The formation of play activity involves the phased transfer to children of gradually more complex ways of building a game. At a younger preschool age, this is role-playing behavior, and at an older one, plot structure. The transfer to children of ways to build a game is carried out in their joint game with an adult, where the latter acts as a partner, a living carrier of the formed method in its entirety.
The formation of play activity involves the phased transfer to children of gradually more complex ways of building a game. At a younger preschool age, this is role-playing behavior, and at an older one, plot structure. The transfer to children of ways to build a game is carried out in their joint game with an adult, where the latter acts as a partner, a living carrier of the formed method in its entirety.
The process of play does not represent a continuous movement of the child in a conditional plan. The construction of the plot of the game is a constant transition from performing conditional game actions to designating the meaning of these actions and vice versa. Such explanatory actions organically enter the process of play, performing the functions of planning by the child an individual plan for unfolding the plot and coordinating them with the intentions of other players. These methods gradually change (become more complicated) throughout preschool childhood.
At the present time, for the full development of a story game, it needs formative influences from an adult.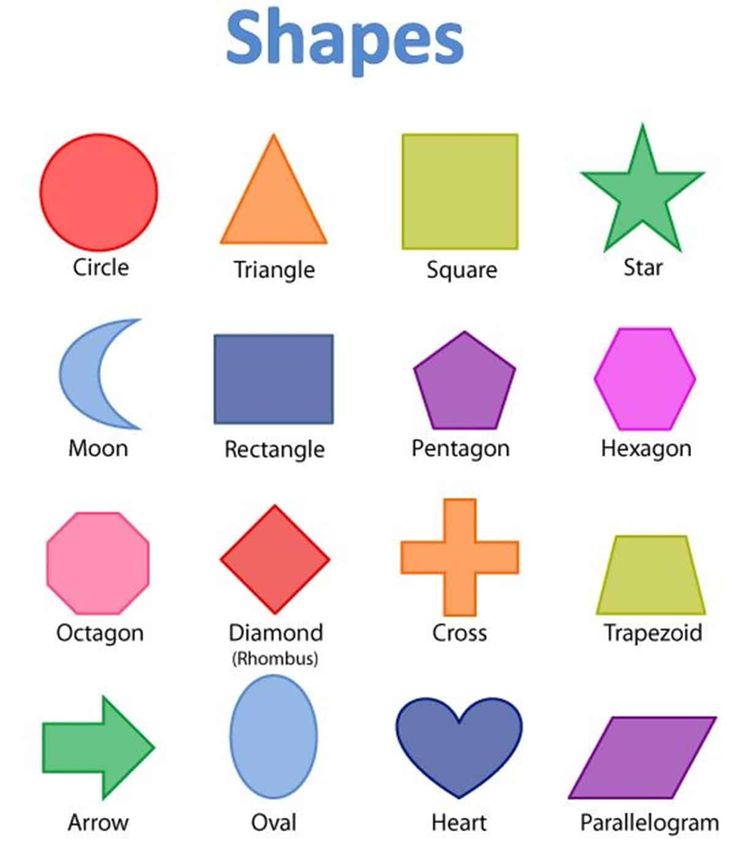 Being a special subculture of childhood, patterns of plot construction methods were passed from older generations of children to younger ones in the natural process of their joint game.
Being a special subculture of childhood, patterns of plot construction methods were passed from older generations of children to younger ones in the natural process of their joint game.
Playing with the rules
Purpose: to master the system of means for constructing play activities by the child.
Objectives: to gradually transfer to children gradually more complex ways of building a game.
Just like a story game, a game with rules in its entirety (observance of formalized rules, focus on winning) develops in a child not immediately, but gradually, throughout preschool childhood. At the age of 2-4 years, the child begins to master actions according to the rule, then, at the age of 4-5 years, he has ideas about winning within the framework of a game built on ready-made rules, and at the age of 6-7 years, the child acquires the ability to modify the rules according to preliminary agreements with other players. The implementation of all these stages is possible only if the adult introduces the child in a timely manner to the cultural forms of games with rules that are characteristic of preschool childhood. First, these should be the simplest outdoor games and games of skill, then games of luck that help the child to win, and, at the end of preschool childhood, games for mental competence.
First, these should be the simplest outdoor games and games of skill, then games of luck that help the child to win, and, at the end of preschool childhood, games for mental competence.
Productive activity
Purpose: mastering the child with representative (modeling) activities.
Tasks: creative work aimed at obtaining a substantive result that corresponds to one degree or another to the initial idea of the game.
Productive activities in preschool pedagogy mean representative (modeling) activities available to a preschooler. These are drawing, designing, modeling, appliqué and various synthetic, complex forms. In many ways, productive activities in preschool childhood are intertwined with story play. But, at the same time, productive activities have a significant difference from the story game. The content offered to an adult child for the implementation of pedagogically purposeful productive activities can be divided into four types: work on samples, work with unfinished products, work on graphic diagrams, and work on a verbal description of the goal [1] .
Cognitive and research activities
Purpose: to expand children's ideas about the world around them.
Tasks: mastery of children in characteristic ways of ordering experience.
Cognitive research activity in preschool childhood is an activity aimed at comprehending the world around. Only by the older preschool age does cognitive research activity begin to be purposeful, with its own motives and goals. In general, throughout preschool childhood, cognitive research activity accompanies play, productive activity, woven into them in the form of orienting actions, testing the possibilities of various materials, thinking and reasoning about surrounding things and phenomena.
As the child's psychophysiological functions develop, cognitive and research activities become more and more difficult. The development of perception, thinking, speech enables the child to shift from the study of things directly surrounding him to more abstract objects. The natural forms of cognitive research activity of a preschooler are direct actions with objects and verbal forms of research. Starting from the early preschool age, in cognitive research activity, the child not only expands his ideas about the environment, but also masters the methods of streamlining experience characteristic of a given culture, which allows him to have fairly holistic ideas about the world around him at an older preschool age.
Starting from the early preschool age, in cognitive research activity, the child not only expands his ideas about the environment, but also masters the methods of streamlining experience characteristic of a given culture, which allows him to have fairly holistic ideas about the world around him at an older preschool age.
Reading fiction
Purpose: activating the child's imagination, expanding awareness of the world, of phenomena that are not given in direct observation and practical experience. Tasks: mastering by children models of human behavior, intuitively and emotionally grasping a holistic picture of the world.
Fiction is a universal developmental educational tool, thanks to which the child goes beyond the directly perceived reality. Thanks to reading fiction, a child masters models of human behavior, intuitively and emotionally grasps a holistic picture of the world, and masters a rich language environment. Conventionally, the functions of fiction can be divided into two large classes: cognitive-moral and aesthetic functions.
The content of the cognitive and moral function consists in activating the child's imagination, expanding awareness of the world, especially about phenomena that are not given in direct observation and practical experience; mastering such methods of ordering information as causal and temporal relationships between events; mastering models of human behavior in various situations; the formation of value attitudes towards various phenomena of reality.
The aesthetic function includes the acquaintance and familiarization of the child with verbal art, and the development of good conversational speech through acquaintance with the literary language, the orientation of the child to individual verbal creativity through the samples given in literary texts, the upbringing of a culture of experiences and feelings.
The principle of the selection of literary texts is that they are a semantic background and a significant incentive for the implementation of productive, cognitive, research and gaming activities.
Toy library
Purpose: to introduce the child to play interaction, develop curiosity and initiative, provide conditions for individualization in the process of cognitive development.
Tasks:
- enrich the mathematical concepts of preschool children,
- to develop the thinking of children in the process of cognitive activity,
- to expand the scope of mathematical representations in situations of cognitive and gaming communication,
- to update communication skills Once a week in the evening, an "Open Day at the Game Library" is announced, to which two or three parents are invited. They are given the opportunity to take part in games as an equal partner, to get acquainted with the achievements of children, to see the features of educational and gaming communication with preschoolers.
The Game Library is updated thanks to an established tradition - “games to visit us”: every Thursday, on the day when the Toy Library is held, one of the children brings their favorite board game from home for a week and puts it in the Game Library introduces her to her comrades.
 For a whole week, the game "stays" in the group, and everyone can play it in their free time, after which it is returned to the owner.
For a whole week, the game "stays" in the group, and everyone can play it in their free time, after which it is returned to the owner. So each pupil is given the opportunity to "present" their favorite game, which causes emotionally significant experiences in preschoolers, and as a result, the children of the group during the school year have the opportunity to significantly expand their gaming experience.
Search and Research Laboratory
Purpose: to create conditions for the development of curiosity, initiative and independence in the process of cognitive activity, to enrich partner and independent search activities.
Objectives:
- develop the perception and observation of preschool children,
- stimulate the development of analytical skills, (establish cause-and-effect relationships),
- expand the scope of application of methods of search activity in solving problem situations,
- develop heuristic ways of understanding the environment,
- enrich cognitive and research communication with peers
Invaluable help in mastering cultural and scientific values and ways of cognition is provided by children's acquaintance with the discoveries of mankind.
 A number of such discoveries then become the subject of a special study of scientists - mathematicians, astronomers, geographers and others.
A number of such discoveries then become the subject of a special study of scientists - mathematicians, astronomers, geographers and others. The first touch of priceless inventions takes place in the course of preschool mathematics. Preschoolers are interested in how people learned to count, calculate, who invented numbers, who invented clocks, abacus, calculators, computers, how the calendar was made, devices for measuring tissues, areas, liquids, bulk substances appeared, what tasks were solved in the old days.
Each of these questions is a "chain" of reasoning, conversations, observations. Reflecting on the advantages and disadvantages of each new idea, together with the children we analyze why it was necessary to improve it. And, of course, it is not a specific answer that is important, but the developing effect achieved as a result of communication - the emergence of cognitive interest, the development of heuristic thinking, speech, ingenuity, the expansion of conceptual experience and independence.
Project activities
Purpose: formation of social and communication skills and attitudes of tolerant communication of children with peers and adults in the course of MINI and MEGA projects.
Tasks:
- organization of upbringing and educational work to develop preschoolers' skills of communicative culture in the course of organizing project activities using fairy tales and performing creative tasks for them;
- development of a universal model of upbringing and educational work of an educational organization in the course of training for teachers on the formation of preschoolers' social and communication skills and attitudes of tolerant communication with peers and adults;
- organizing and holding creative meetings in the parents' club in order to create conditions for the active participation of parents in MINI and MEGA projects aimed at shaping children's attitudes of positive communication with peers and adults through family education.
Consider various options for modern forms of education that are built on the basis of children's activities:
» interesting material for them, to learn new things, reflecting on what has already entered into their experience. In the game, children learn to express their attitude to what is happening, immerse themselves in a situation organized by adults: they turn into “travelers”, “Indians”, “inhabitants of the underwater kingdom”, etc.
2. Children's experimentation, as an active transforming activity of children, significantly changing the objects under study, allows children to successfully develop curiosity, activity, and the desire to independently find solutions to problems. Children are interested in different types of experiments. A thought experiment involves doing things in the mind. But the most interesting experiments are real experiments with real objects and their properties (water, ice, snow, air, etc.), which helps the child to master the essential features of inanimate nature, the plant world.
3. Collecting is one of the most effective forms of non-traditional education for preschoolers, it allows to deepen the cognitive interests of children. You can collect anything: candy wrappers, themed pictures or postcards, stones, sounds, smells, etc. Preschoolers are very interested in collecting photographs taken on their own and the subsequent design of thematic albums. When organizing such work with preschoolers, the discussion of the meaning and rules of gathering is accompanied by the organization of a variety of children's activities based on the use of the collection. The creation of joint collections for children and adults contributes to resolving the contradiction between the dominance of play and the insufficient development of cognitive motives in preschoolers. This goal can be realized on the condition that methods and techniques will be used in joint activities with an adult to ensure an increase in awareness in cognition: discussion of issues that allow children to identify the target and content characteristics of cognition (What do we want to know? Why? For what? How can we find out "With what? What needs to be done?").

4 . Fairy tale lessons. The child lives in a world of fantasy, fairy tales. For most children, a metaphor is a familiar reality, as childhood is filled with fairy tales, animated films, and fairy tale characters. Imagination is the inner world of children, an innate natural process by which they learn to understand the world around them, to interpret its meaning. Contact with the deep level of a fairy tale is not easy. The images in fairy tales affect the consciousness and the subconscious at the same time, which provides additional opportunities during communication. This is especially important for psychological and correctional work, when it is necessary to create an effective communication situation in a difficult emotional situation. Preschool education is filled with fairy tales, but also a fairy tale holiday in kindergarten is an excellent tool for relieving psycho-emotional stress and mental hygiene of a child.
5. Surprise activities. The content of this type of lesson includes information mastered by children in the process of educational work and updated by the introduction of unexpected conditions, unusual benefits and methods of organization.
 Thus, we can conclude that the use of non-traditional forms of teaching preschoolers will contribute to the formation of intellectual competence, creativity and independence of preschoolers, the development of integrative personality traits.
Thus, we can conclude that the use of non-traditional forms of teaching preschoolers will contribute to the formation of intellectual competence, creativity and independence of preschoolers, the development of integrative personality traits. The main feature of the organization of educational activities in preschool educational institutions at the present stage is the departure from educational activities (classes), raising the status of the game as the main activity of preschool children; inclusion in the process of effective forms of work with children: ICT, project activities, game, problem-learning situations within the framework of the integration of educational areas.
Thus, the "lesson" as a specially organized form of learning activity in kindergarten is cancelled. The occupation should be a specific children's activity that is interesting for children, specially organized by the educator, which implies their activity, business interaction and communication, the accumulation of certain information by children about the world around them, the formation of certain knowledge, skills and abilities.
 But the learning process remains. Teachers continue to "engage" with children.
But the learning process remains. Teachers continue to "engage" with children. Forms of organization of the educational process are changing - ensuring activity, initiative, independence and creativity. Knowledge, skills and abilities in the context of GEF DO become secondary - a framework approach to the content of education. The model of the educational process assumes a comprehensive approach, ensuring the development of children in all five complementary educational areas.
In accordance with the requirements of modern regulatory documents in the field of the content of preschool education, it is necessary for each educational organization to determine the strategic principles for describing the model of the educational process, specific guidelines that determine the tactics of the educational process in the context of the directions of the GEF DO. The main goal of each preschool educational organization is aimed at finding forms and methods of organizing the educational process, allowing to realize the main task of preschool education to create conditions for "the possibility of positive socialization of the child, his comprehensive personal development, the development of initiative and creative abilities through cooperation with adults and peers and activities corresponding to preschool age.
 "
" CONCLUSION: In a modern kindergarten, the educational process should not be limited to directly educational activities, it is extended throughout the day.
Forms of organization of children's activities | Material:
Educator
"MADOU Malinovsky kindergarten"
Kukuzova E.S.
Forms of organizing children's activities
Any preschool institution has a PEP, which is implemented during the entire period of the child's stay in kindergarten. What form does it take? These are not only classes, because they take very little time in the daily routine. Therefore, other forms of organization of children are also needed. The main form is, of course, a game. Learning can take place during the game and it is necessary to make sure that during the game the child does not even guess that he is being taught. But besides the game, there are other forms that allow you to make the life of a child in kindergarten interesting and eventful.
Consider these forms:
1.
 Workshop
Workshop 2. Experimentation and research
3. Design activity
4. Collecting
Workshop is a form of organization
These are not just classes, joint activities prevail here, collective forms of work that have a certain social motivation (decorating a group for a holiday, making souvenirs, crafts as a gift). Here it is very important for the child to independently make a choice of activities. He can draw, sculpt, make appliqué, that's his choice. He has the right to ask for help from the teacher, and the teacher should provide it only when the child really needs it. The child works at their own pace. The main thing is that the work is completed and has a result. This is the pedagogical support. Also, the child can choose his own partner. This is the difference from traditional classes.Experimentation and research is a form of cognitive research activity. It aims to broaden the horizons of children.
At what age is it supposed to start experimenting in kindergarten?
· From the 1st junior group (2–3 years old), children begin to take part in joint experimental activities with the teacher.
 While they are the simplest studies that help kids examine objects, noting their color, size or shape.
While they are the simplest studies that help kids examine objects, noting their color, size or shape. In the younger group (3-4 years old), cognitive research activities become more complicated. Together with the teacher, children learn to conduct experiments on the example of sensory standards. Thanks to experiments, they become aware of the previously hidden properties of the objects under study.
Experimentation in the middle group (4–5 years old) aims to develop in children the ability to independently obtain information about a new object. All senses are actively used for experiments.
· Using experimentation in the older group (5–6 years old), children should be encouraged to independently conduct experimental actions and reveal the hidden properties of phenomena and objects.
In the group preparatory to school (6-7 years old), cognitive and research activities are being improved. Not only independent work is welcomed, but also the choice of the optimal way of its implementation.
Experimentation in organized activities
In accordance with the educational program, experimental activities are planned in all age groups of the kindergarten, starting with the youngest in the area of "Introduction to the natural world."
It is planned to study with the help of experiments:
properties of sand, clay and stone;
properties of water in its various states;
temperature.
weighing heavy and light materials;
length measurement with yardsticks;
Observation of plant growth and the dependence of this process on lighting, temperature and watering;
study of color mixing.
Experimentation in free activity
In order for children to be able to do experiments on their own, a special subject environment and space for its development should be organized in the kindergarten.
The group has a free access to a special area - the corner of experimentation, which contains:
sets for experiments with picture instructions;
exploration toys - balls, cubes, small objects of various materials;
various natural materials - sand, water, clay, shells, wool;
measuring instruments - scales, measuring containers, hourglasses, rulers;
Instruments - pipettes, spatulas, measuring spoons, toothpicks, clear and colored glasses;
other saturated object medium - mirror, magnifying glass, salt, magnets;
Writing utensils for recording results.
Over time, each educator who supports the method of experimentation accumulates a lot of experience in using it in various activities. From the notes, a file cabinet will be formed, which contains natural science experiments for children on various topics. Below are examples of such topics.
Ecology:
structure of plants;
Conditions necessary for plant life;
plant propagation;
experiments in the vegetable garden and flower garden;
Experimental activities by season;
Animal research.
Research activities about man:
structure of man;
physiology;
Hygiene.
Physical experiments in kindergarten:
movement;
measurement;
magnetism.
substances and materials;
light and color;
sound.
Project activity is also a form of joint activity aimed at expanding the horizons of children, at educating the cognitive activity of a preschooler.
 Conditions are being created that allow children to independently or jointly with an adult acquire new experience, acquire knowledge through experimental, search methods.
Conditions are being created that allow children to independently or jointly with an adult acquire new experience, acquire knowledge through experimental, search methods. It follows that the chosen topic is "projected" onto all educational areas through various types of children's activities. Thus, it turns out a holistic, and not broken into parts, educational process. This will allow the child to “live through” the topic in different activities, without experiencing the difficulty of moving from subject to subject, to assimilate a larger amount of information, to comprehend the connections between objects and phenomena.
The project is a set of actions specially organized by adults and performed by children, culminating in the creation of creative works.
The project method describes a set of actions of the child and the ways (techniques) of organizing these actions by the teacher, that is, it is a pedagogical technology.
The main thesis of the modern understanding of the project method, which attracts many educational systems, is the understanding of children why they need the knowledge they receive, where and how they will use it in their lives.
Learn more