Kids things that start with y
Learn Vocabulary Words That Start With Y
Vocabulary Words That Start With Y
With this lesson, you can teach your child vocabulary words that start with Y. Positive nature comes from the positive vocabulary. Therefore, positive vocabulary will help your child communicate positively. So, in this lesson, we tried to add as many positive vocabulary words that start with Y as we could. With this lesson, you will be skilful to teach your child some helpful Y words for kids. Vocabulary words are the most crucial part of your child’s early childhood education. Therefore, we keep working on it. Through this platform, “The Soft Roots,” your child will learn primary education, including alphabets, words, numbers, shapes, colors, and grammar hassle-free.
What Words I Can Make With The Letter Y
Two Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yo: This word is used to greet someone in a cool way or to call someone. Teach this word to your child in a conversation and call him “Yo” with a smile, then tell him its meaning.
Three Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yak: This is a domestic cattle with long hair. Yaks are kept as domestic cattle for milk in Tibet and have very long horns. Teach this word to your child by showing pictures of yak.
Yam: Yam is a vegetable, and its root is widely consumed all over the world. Yams are packed with nutrition. Its root is consumed just like a potato. Teach this word to your child by showing him yam.
You: This word is used to address a second person by the first person. Teach this word to your child in a lesson of 1st, 2nd and 3rd persons.
Teach this word to your child in a lesson of 1st, 2nd and 3rd persons.
Yen: This word describes the currency of Japan. The symbol for the yen is ¥. Teach this word to your child in a lesson on popular currency names.
Yes: This word describes the authentication of someone or is used to approve something right. Teach this word to your child by telling him the meaning of yes and no and their uses.
Four Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yurt: Yurt is a circular tent that is held by a wooden structure. The fun part about yurt is that it is portable, as the wooden structure below the wool is collapsible. Yurt is widely used in central Asia, especially Mongolia. Teach this word to your child in a lesson on different types of tents or camps.
Yarn: Yarn is a long interlocked thread or fiber. This long fiber is spun and used for knitting and weaving.
Teach this word to your child by showing him a yarn and telling him what it is used for.
Yolk: The yellow section of an egg is called yolk. The yolk is full of protein and fats. Teach this word to your child by showing him the egg yolk and egg white.
Yard: This word describes a grassy area outside of the house. Teach this word to your child by showing him the yard in your house.
Yeah: This word is used as an alternative to the word yes. But to continue talking and complete a sentence after this word. Teach this word to your child by telling its meaning.
Yawn: Yawn is an involuntary action in which a person opens full mouth, and the lungs suck more air than usual. Then the lungs push out air slowly. Teach this word to your kid when he yawns.
Four Letter Words For Kids
Yell: The word yell describes shouting or making a loud noise in sorrow or excitement. Teach this word to your child by telling him its meaning and giving an example of someone who is yelling or shouting.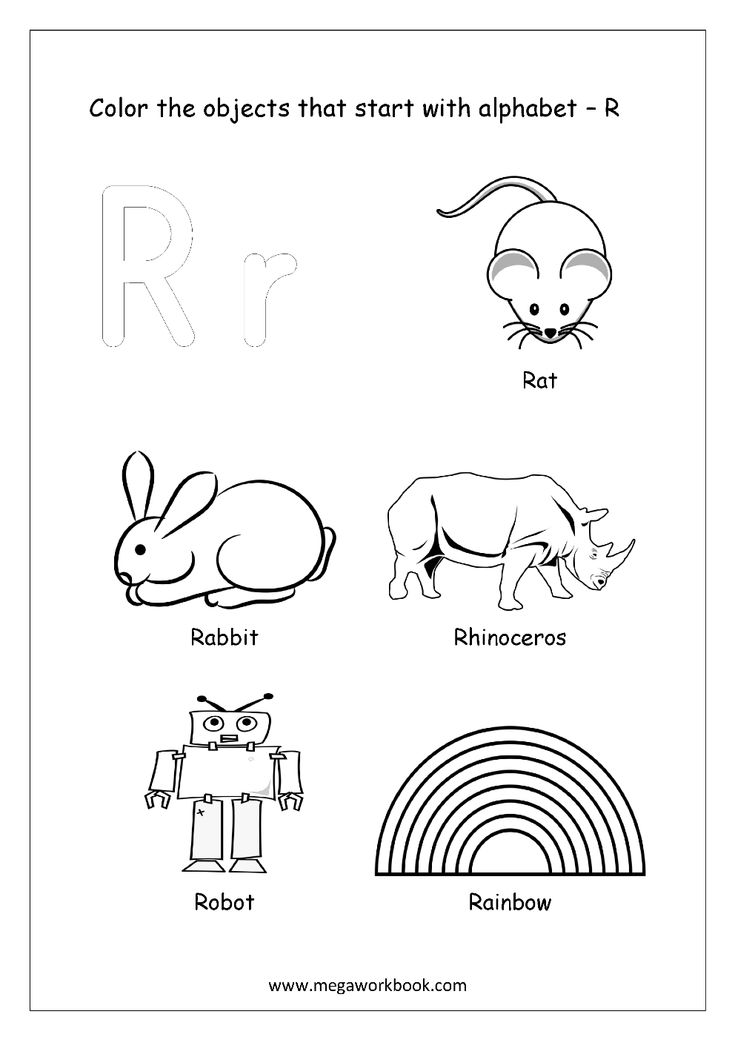
Yowl: This word is the synonym of yell. So teach this word to your child in a lesson on similar words.
Yoga: This word describes a set of mental, physical and spiritual exercises that originates from India. Yoga also includes meditation. Teach this word to your child in a lesson on different exercise names.
Yoke: A yoke is a wooden beam that connects two oxen or other animals so that they may pull together on a burden while working in pairs. Occasionally, yokes are attached to individual animals. Teach this word to your child by showing him pictures of the yoke.
Year: A year is a time in which a planet completes its one circle around the sun. The earth completes its circle around the sun in 365 days.
Yo-yo: Yo-Yo is a toy made from two plates around an axle, and a string or thread is looped around the axle. The tread is used to spin up or down. Teach this word to your child by showing him a yo-yo.
Five Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Young: This word describes a person who has spent less than half the time after birth. Anyone below 25-30 is considered young. Teach this word to your kid in a lesson on words describing different age groups.
Yucca: Yucca is a plant with long pointy leaves. Its starchy roots are like potatoes and consumed. Yucca is primarily found in warm regions of the USA and Mexico. Teach this word to your child by showing him the yucca plant’s pictures or its dish.
Yacht: A yacht is a medium-sized luxurious boat that is used for trips, cruises and parties. Teach this word to your child by showing him a yacht.
Yeast: The yeast is a unicellular fungus used widely in bakery items and the fermentation process. Yeasts are used to make bread and wines. Teach this word to your child by showing him yeast if you have some to show and tell him its uses.
Youth: The part of life when someone is young, it’s called his youth. Teach this word to your child in a lesson of different age and lifetime group names.
Teach this word to your child in a lesson of different age and lifetime group names.
Yummy: The word yummy describes something tasty. Teach this word to your child by explaining the meaning of this word. Then, tell him to use this word to describe anything he finds tasty.
Yucky: The word yucky is used to describe something gross or unpleasant. It creates an unpleasant feeling in the stomach. Teach your child the meaning of this word and how to use it in his communication.
What Words I Make With The Letter Y
Six Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yankee: This word describes a person who is an American. Teach this word to your child by telling him its meaning.
Yellow: This word describes a color. The lemon is yellow. Teach this word to your child in a lesson on colors.
Yip yip: The Yip Yips are characters from Sesame Street, an American educational children’s television show. Yip yips are puppets who represent aliens. Teach this word to your child by showing him this tv show.
Yip yips are puppets who represent aliens. Teach this word to your child by showing him this tv show.
Seven Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Youtube: Youtube is a social media platform for videos. People worldwide create, upload or share the videos on their channels with the whole world. Teach this word to your child by showing him youtube.
Yogurt: Yogurt is a semi-solid type of milk and a dairy product. It is prepared by putting some bacterias in the milk. Teach this word to your child by serving him sweet yoghurt.
Yule log: Yule log is a cake that is served during Christmas. Teach this word to your child by serving him with a yule log cake.
Eight Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yearbook: A yearbook is published once a year and highlights all the important events that happened in a year. Teach this word to your kid by showing him a yearbook.
Yogi Bear: Yogi Bear is a cartoon character that is like a bear and wear a cap and a tie around its neck. Yogi Bear cartoon is fun to watch. Teach this word to your child by showing him this fun cartoon.
Yogi Bear cartoon is fun to watch. Teach this word to your child by showing him this fun cartoon.
Yali Pear: A yali pear is an Asian or Chinese pear that is very delicious. Now it is also cultivated in the USA. Teach this word to your child by showing him a yali pear.
Nine Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yesterday: This word describes the past day. Teach the word to your child in a basic lesson of tenses and the present, past and future.
Yachtsman: A person who drives or sails a yacht is called a yachtsman. Teach this word to your child by explaining its relevance with a yacht.
Yardstick: This is a wooden stick of a yard or meter length used to measure objects’ length is called a yardstick. Teach this word to your child by showing him a yardstick.
Yuzu fruit: Yuzu is the most popular citrus fruit in Japan. Teach this word to your kid by showing him a yuzu fruit.
Yap island: This is an island in the pacific ocean. It is popular for its stone money. Teach this word to your kid while teaching him different country names on a world map.
Ten Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Youngberry: Youngberry is a hybrid berry between three other types of berries. Its color is purple and is very delicious. Teach this word to your child in a lesson on different berry types.
Youngster: A person at a young age is called a youngster. Teach this word to your kid in a lesson about people living different parts of their lives.
Yellowcake: This word represents the solid form of uranium oxide that is mined and enriched afterwards. Teach this word to your child by showing him pictures of yellowcake.
Twelve Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yellow baboon: This is a species of baboon that is yellow and found in American national parks. Teach this word to your child by showing him pictures of a yellow baboon.
Teach this word to your child by showing him pictures of a yellow baboon.
Yangmei Fruit: This is the name of wax berry or Chinese berry. This fruit is widely used in desserts. Teach this word to your child by serving him with a dessert of yangmei fruit, and he will love it.
Thirteen Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yellowfin Tuna: Yellowfin tuna is a species of medium-sized tuna and found in tropical oceans. It has yellowfins. Teach this word to your child by showing him pictures of yellowfin tuna.
Sixteen Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yellow Watermelon: This is just like a normal watermelon, and the only difference is that it has yellow flesh. Teach this word to your kid by showing him a yellow watermelon.
Seventeen Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yellow-Eyed Penguin: A penguin with yellow color around its eye is referred to as a yellow-eyed penguin. Teach this word to your kid in a lesson on different types of penguins.
Eighteen Letter Words That Start With Letter Y
Yellow Passion Fruit: Yellow passion fruit is like a big yellow lemon, with an edible pulp inside. Its found in South America. Teach this word to your child by showing him a yellow passion fruit.
Five most commonly used Y words
- You
- Your
- Yours
- Yes
- Yup
The longest word that starts with Y
Yangochiropteran: means a microbat
The common English verbs starting with Y
- Yield
- Yuck
- Yelp
- Yard
- yap
Five most commonly used positive words that start with the letter Y
- Yahoo
- Yahweh
- Yare
- Yay
- Yeah
Words that start with Y for Toddlers
- yes
- you
- year
- yummy
- yahoo
Words that start with Y for Kindergarten kids
- Your
- Year
- Yarn
- Yeti
- Young
Words that start with Y for Preschool kids
- Yo-yo
- Yarn
- Yes
- You
- Young
Conclusion
We are glad that your child is learning these vocabulary words quickly. That is why keep coming back with new words. Please come back for the words that start with z in the next lesson.
That is why keep coming back with new words. Please come back for the words that start with z in the next lesson.
You May Also Like:
Words That Start With Z
Words That Start With X
Learn Vocabulary Words That Start With Letter "Y" For Kids
- Learn “Y” Words With The Help Of This List For Kids
- List Of Words Starting With ‘Y’ Words For Kids
- Commonly Used Words That Begin With ‘Y’ For Kids
- ‘Y’ Words For Preschool And Kindergarten Kids
- Names Of Things That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
- Positive Words That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
- Cool Words That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
- How You Can Teach ‘Y’ Words To Kids?
Learning new words not only improves your child’s vocabulary but also helps them express themselves better. Learning words that start with Y for kindergarten will build up your child’s word bank for effective communication. Your preschooler learns to read and write simple sentences by observing others around him. As the kid advances academically, it becomes imperative to improve their lexicon to aid in their writing skills and improve their knowledge. Teach your child these Y words for grades 1, 2 and 3 and help them develop their language.
Learning words that start with Y for kindergarten will build up your child’s word bank for effective communication. Your preschooler learns to read and write simple sentences by observing others around him. As the kid advances academically, it becomes imperative to improve their lexicon to aid in their writing skills and improve their knowledge. Teach your child these Y words for grades 1, 2 and 3 and help them develop their language.
Y is an alphabet that is commonly used in the words that express various emotions; you will say ‘yummy’ for a tasty food item, shout ‘yay’ in excitement, and many more.
Learn “Y” Words With The Help Of This List For Kids
As your child moves up the academic grades, you must teach them more and more words to expand their knowledge base. Improving their word bank provides them with access to new information, which is crucial to enhancing their language skills. Reading skills can be taught to your child by making them learn words beginning with different alphabets. This article includes many Y words to help you to teach your kindergarten children. Words beginning with the letter Y are limited and a bit difficult to learn. You have to find out some words that are easy to understand and which your child can relate to from their daily life objects. It will make learning these words easy for them.
This article includes many Y words to help you to teach your kindergarten children. Words beginning with the letter Y are limited and a bit difficult to learn. You have to find out some words that are easy to understand and which your child can relate to from their daily life objects. It will make learning these words easy for them.
List Of Words Starting With ‘Y’ Words For Kids
By now, you must have realised the significance of teaching your child words beginning with different alphabets and how they increase their vocabulary. But, you may be a bit unclear on how to go about it. Teaching methods have come a long way since generations, and much has changed about the way kids are taught today. Lately, the teaching methods have evolved, and kids are educated using shapes, numbers, lists, colours, and other techniques that make learning interesting and fun. Learning words alphabetically is simpler and easier for children. In this article, we have listed Y words for grades 1, 2 and 3 to aid you in teaching your kids some new words.
Commonly Used Words That Begin With ‘Y’ For Kids
To begin with, here are some simple words that start with ‘Y’. Read these words out to your kids and give them some time to learn these. Also, make them repeat these words after you. You can ask them some of these words after a few days as this will help them refresh their memory and comprehend these words perfectly.
Common ‘Y’ Words:
| Yak | Yahoo | Yacht |
| Yarn | Yam | Yeast |
| Yawn | Yard | Yearn |
| Year | Yeah | Yemen |
| Yell | Yellow | Yelp |
| Yes | Yoga | Yesterday |
| Yet | Yo-Yo | Yoke |
| Yolk | Young | Yours |
| Your | Youth | Yuck |
| You | Yule | Yummy |
‘Y’ Words For Preschool And Kindergarten Kids
The vocabulary acquired in preschool and kindergarten enables children to learn to read and write and influences their further scholastic growth. Go through this list of words starts with Y for kindergarten kids and preschoolers to teach them some easy words beginning with ‘Y’. The list generally comprises simple two-letter to five-letter Y words to make it easy for your preschoolers and kindergarten kids to grasp it comfortably.
Go through this list of words starts with Y for kindergarten kids and preschoolers to teach them some easy words beginning with ‘Y’. The list generally comprises simple two-letter to five-letter Y words to make it easy for your preschoolers and kindergarten kids to grasp it comfortably.
2 Letter ‘Y’ Words
| Ya | Yi |
| Ye | Yo |
| Yu |
3 Letter ‘Y’ Words
| Yak | Yam |
| Yet | Yes |
| Yen | You |
4 Letter ‘Y’ Words
| Yarn | Yell |
| Year | Yawn |
| Yolk | Yeti |
| Your | Yuck |
5 Letter ‘Y’ Words
| Yacht | Yahoo |
| Young | Yeast |
| Yours | Yearn |
| Yummy | Youth |
Words That Start With Y For Classes 1, 2 and 3
As you dive deeper and deeper to find “Y” words for class 1 children, you will know that the words that begin with ‘Y’ only constitute 0. 03% of the English dictionary! But, you need to find out more and more Y words if you want to improve your kiddos’ vocabulary as they move from class 1 to class 2. Following are some 6-letter and 7-letter Y words that your first, second, and third graders need to learn as they upgrade to higher classes.
03% of the English dictionary! But, you need to find out more and more Y words if you want to improve your kiddos’ vocabulary as they move from class 1 to class 2. Following are some 6-letter and 7-letter Y words that your first, second, and third graders need to learn as they upgrade to higher classes.
6 Letter Y Words
| Yankee | Yearly |
| Yellow | Yeoman |
| Yonder | Yippie |
7 Letter Y Words
| Yelping | Yodling |
| Yoghurt | Yearned |
| Yonkers | Younger |
Names Of Things That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
Teaching methods that involve visuals are easy to comprehend and understand. Try showing your children things that start with the letter ‘Y’. Teaching them nondescript words will not increase their knowledge the same way that showing them some particular object would. Show them pictures of the things beginning with the letter ‘Y’ as these be a great conversation starter. The following table lists the names of things beginning with ‘Y’.
Show them pictures of the things beginning with the letter ‘Y’ as these be a great conversation starter. The following table lists the names of things beginning with ‘Y’.
| Yacht | Yarn | Yearbook |
| Yard | Yam | Yen |
| Yeast | Yak | Yeti |
| Yolk | Yoghurt | Yucca |
Animal Names That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
Childhood is a great time to start your kids on a reading journey when they soak up information like sponges. Kids are exposed to animals like bears, dogs, etc, from a tender age and are well-acquainted with them. You can develop their vocabulary and learning skills using various animal names, beginning with the letter ‘Y’. The list below displays animal names that start with ‘Y’.
| Yak | Yellowjacket |
| Yellowhammer | Yellow-headed caracara |
Places Names That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
Conversation with kids is a great way to build their language. Talking to them while you are out shopping, vacationing, or just walking in the garden, showing them places, and familiarising their names are some of the activities that introduce them to different words. Showing them places with ‘Y’ words is a good way to make them remember these. Below are some of the examples of places beginning with ‘Y’.
Talking to them while you are out shopping, vacationing, or just walking in the garden, showing them places, and familiarising their names are some of the activities that introduce them to different words. Showing them places with ‘Y’ words is a good way to make them remember these. Below are some of the examples of places beginning with ‘Y’.
| Yemen | Yorkshire |
| Yugoslavia | Yosemite National Park |
Food Names That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
Make your child’s learning a ‘yummy’ process. Try connecting language to their favourite foods, and they will surely surprise you with how swiftly they learn new words. Here is the list that shows some foods that begin with the letter ‘Y’.
| Yeast | Yam |
| Yorkshire pudding | Yoghurt |
Positive Words That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
Making your child learn some positive vocabulary helps him communicate his emotions effectively. It also develops a positive attitude in your child and a positive frame of mind early in life that greatly affects their academics, social interaction, and relationships. Following are some of the positive words that start with the letter ‘Y’.
It also develops a positive attitude in your child and a positive frame of mind early in life that greatly affects their academics, social interaction, and relationships. Following are some of the positive words that start with the letter ‘Y’.
| Yahoo | Yield | Yum |
| Yay | Yo | Yummy |
| Yeah | Young | Yummylicious |
| Yep | Yours | Yup |
| Yes | Youth | Yuppie |
Cool Words That Start With ‘Y’ Letter
Your kids’ enhanced vocabulary is directly linked to their academic achievements and mastery over language. The alphabet ‘Y’ has some cool words that are rarely used and making your child learn these will directly impact his vocabulary growth. Go through the list below:
| Yahoo | Yesteryear | Yo-Yo |
| Yawped | Yo | Yum |
| Yay | Yodeler | Yummy |
| Yeah | Yoohoo | Yuppie |
| Yard | Younglings | Yus |
How You Can Teach ‘Y’ Words To Kids?
Whatever you teach your child, it must be fun and interesting to him. No one likes reading to be a chore. Keep reading stories or poems, but keep these sessions short and simple. Here are some ideas to teach your little one ‘Y’ words without being too monotonous and dry.
No one likes reading to be a chore. Keep reading stories or poems, but keep these sessions short and simple. Here are some ideas to teach your little one ‘Y’ words without being too monotonous and dry.
- Phonics: Phonics refers to using letter sounds that help you read words. It helps little ones recognise the sound corresponding to a particular letter. Children begin developing their listening skills early and understand different sounds in words. The letter ‘Y’ is a vowel as well as a consonant. Making them understand different sounds associated with the letter ‘Y’ will enable them to decipher the words easily.
- Narrating stories: Storytelling has been associated with learning for ages. It stimulates young minds and fires their imagination, and proves to be more effective than teaching with facts and figures. Making animal sounds while reading animal stories aids in building their language.
- Rhymes: List some Y rhymes that you can recite for your young ones, and make a point that they sing along with you.
 When they try to sing rhymes along with you, they try to listen to you carefully and repeat it. This builds up their vocabulary.
When they try to sing rhymes along with you, they try to listen to you carefully and repeat it. This builds up their vocabulary.
- Worksheets: Using worksheets that display the letter ‘Y’ to enable them to learn to identify and write. It is a great way to begin their journey with ‘Y’. Make them practice and write it using different spreadsheets and handouts.
- Crafts and activities: Using ‘Y’ craft activities will train your young ones to recognise this letter. These fun and exciting activities will aid them in focusing and analyzing. Make use of crossword puzzles, word puzzles, and scribbles for ‘Y’ words to help them learn them quickly.
Vocabulary is the basis of any language. Having a strong vocabulary improves reading, writing, speaking, and all other areas of communication. Expanding a child’s vocabulary helps him express his thoughts efficiently and gives him access to more information. It is the foundation of any language. Teach your child more and more words starting with various vowels and consonants, including the letter ‘Y’.
Teach your child more and more words starting with various vowels and consonants, including the letter ‘Y’.
Adolescence crisis in girls and boys
Article content
- Physiological causes
- Psychology of the Teenage Crisis
- Phases of a Teen Crisis
- Manifestations in adolescence
- Features of the course in girls and boys
- Advice to parents on overcoming the crisis
Adolescence or pubertal crisis is a stage of mental development that develops during the transition from childhood to adulthood. It is expressed in the desire for self-affirmation, independence, independence.
According to Russian psychology, adolescence occurs at 11-17 years of age, when the pace of psychological, cognitive, social and physiological development is as high as possible. At the same time, an early period is distinguished from 10 to 14 years and a late one - from 15 to 17 years. However, the World Health Organization defines adolescence as a longer period, from 10 to 20 years of age.
In the case of successful overcoming of this stage, the child develops a new level of awareness, self-perception, develops the ability to evaluate and develop their qualities, abilities, work on shortcomings. The child is separated from the parents, but at the same time maintains a good relationship with them. In order to successfully pass the transitional age and avoid complications, parents need to be flexible, work on trusting relationships and recognize the right to independence, independent choice and making important decisions in time.
Physiological causes
Puberty is the age when the growth of the body occurs most actively. Development is in leaps and bounds. In a year, a child can grow by 7-10 centimeters and increase body weight by 5-9 kilograms. The skeleton becomes stronger, the muscles are improved. The heart muscle is rapidly growing in length and width, blood pressure and the rhythm of the heart are changing.
Along with the intensive growth of the body, the shape of the body also changes. Gender signs develop, the hormonal background changes, the endocrine system is rebuilt, the endocrine glands are activated. Moreover, puberty in girls begins earlier by 1-2 years and ends by the age of 15-16. At the age of 10-12 years, they overtake boys in growth. However, by the age of 15-16, boys are already significantly taller than girls and at the same time continue to grow until the age of 18-20.
Gender signs develop, the hormonal background changes, the endocrine system is rebuilt, the endocrine glands are activated. Moreover, puberty in girls begins earlier by 1-2 years and ends by the age of 15-16. At the age of 10-12 years, they overtake boys in growth. However, by the age of 15-16, boys are already significantly taller than girls and at the same time continue to grow until the age of 18-20.
It is very difficult for the nervous system to adapt to changes, as it simply does not have time to adapt to active growth. Therefore, often the psyche is in a state of excessive excitement or, on the contrary, tries to slow down the processes and goes into pronounced inhibition.
Due to all physiological changes, temporary disturbances develop in the child's body:
- jumps in blood pressure - hypertension is often observed, but hypotension is also a variant of the norm;
- dizziness, headaches;
- poor concentration, distracted attention;
- palpitations (tachycardia), a feeling of constriction in the region of the heart;
- dyspnea;
- fainting states;
- fast fatiguability;
- irritability, sleep disorders.

Physiological processes directly affect the health and behavior of a teenager. In order for the body to fully develop and the jump of maturation to be successful, it is necessary to provide high-quality support for the processes: proper nutrition, saturation of the diet with vitamins and microelements, adequate physical activity.
It is important to consider that there are significant individual characteristics in physical development and puberty. The age at which active changes begin in the child's body may deviate from group norms, and this should not cause concern.
Psychology of adolescence crisis
The main reason for the development of the crisis in adolescence is a significant gap between the physiological and social, emotional maturation of the individual. As we have already said, physiological growth during this period maximally outstrips the pace of development of the psyche.
Physiologically, a teenager in a short stage becomes an adult, a mature person. Outwardly, yesterday's child looks like an adult, begins to feel like that, but is not yet fully ready for independence and responsibility. Social maturation takes much longer.
Outwardly, yesterday's child looks like an adult, begins to feel like that, but is not yet fully ready for independence and responsibility. Social maturation takes much longer.
As a result of this gap, conflicts arise with adults. The child wants to feel free and independent, but in fact he still cannot cope with serious responsibility. On this basis, conflicts and misunderstandings arise. The personality of a teenager changes so much that sometimes it seems that the child has simply been replaced.
The pubertal period is expressed not only on the physiological, but also on the mental level. Moreover, the mental aspects of puberty can occur much earlier than physical maturation. Adolescents go through gender identification and orientation, begin to perceive themselves and others according to gender. Scientists agree that gender identification occurs to a greater extent under the influence of sociocultural factors than biological ones. The patterns and stereotypes that operate in society play a decisive role.
In the same period, romanticism develops - the desire for emotional intimacy. Teenagers form relationships that involve spending time together and having heartfelt conversations. The first love appears. In this case, physical intimacy is not mandatory, the platonic context comes to the fore, and only then the sexual one.
Given all the psychological changes taking place in a teenager, a crisis is necessary to solve a number of problems. As a result of successfully overcoming this developmental leap, a teenager:
- undergoes gender identification, assumes a male or female role;
- accepts his appearance with all the changes;
- changes the form of communication with others: parents, peers, etc.;
- adopts a new style of relations, turns from a child into an equal responsible member of society with mature behavior;
- develops interests, finds directions for the development of his abilities, subsequent professional orientation.

Phases of adolescence crisis
Psychologist Lev Semenovich Vygotsky identified three basic phases in the adolescent crisis:
- Negative, or pre-crisis . The earliest stage, which can show the first signs as early as 9-10 years. It is characterized by the beginning of the transition to a new type of interaction with others. The child begins to abandon the old system of values, breaks stereotypes, changes his attitude towards himself and others. Childish relationships with parents no longer suit him, but he is not yet ready for an adult system of interaction. The child has new interests, different views, the environment begins to change.
- Direct crisis stage . Often this stage reaches a peak at 13-15 years. It can manifest itself in different ways: from maximum protest, conflict and irritability in all areas of life, to a gradual transition to new roles, relationships and self-perception. New ways of thinking develop, new opportunities and interests appear.
 The teenager defends his opinion and the ability to make decisions independently, is separated from parental influence, control.
The teenager defends his opinion and the ability to make decisions independently, is separated from parental influence, control. - Positive, or post-crisis . It is considered the final stage of the puberty crisis. In this period, a teenager already forms values and priorities, determines the vector of further development, interests. Puberty is almost over, the place in society among peers is determined. A teenager strengthens the core of interests and continues to develop it in the future.
It is impossible to say exactly how long each phase lasts. In many ways, the duration of the stages depends not only on the teenager, but also on the correct reaction of parents to the manifestations of the crisis.
Manifestations of a crisis in adolescence
The severity of the crisis can be different. At the initial stage, psychologists identify two main features that are present in almost every child:
- Decline in school performance, performance .
 Physiological and mental changes, a change in the type of thinking directly affect the child's learning. He does not cope well with creative tasks, loses concentration, interest in learning. Even minor criticism can discourage the desire to delve into a particular area or topic.
Physiological and mental changes, a change in the type of thinking directly affect the child's learning. He does not cope well with creative tasks, loses concentration, interest in learning. Even minor criticism can discourage the desire to delve into a particular area or topic. - Adverse reactions . Even the most accommodating children tend to separate from their parents, and therefore they often show quick-tempered reactions even in familiar situations. Natural manifestations of negativism are pessimistic moods, increased irritability, dissatisfaction with oneself, whims, and nervousness.
As we move from one phase of the crisis to another, the manifestation of reactions also increases, which can be divided into three large groups :
- Emancipation reactions . The child wants independence, and this reaction is expressed in the avoidance of parental control, the denial of familiar values, and the withdrawal to communication with peers.
 The teenager demonstrates independence and autonomy, demands to recognize his equality and reckon with his opinion.
The teenager demonstrates independence and autonomy, demands to recognize his equality and reckon with his opinion. - Self-affirmation reactions . It is mainly expressed in communication with peers and showing interest in the opposite sex. During this period, friends become the main authority, there is an interest in romantic relationships.
- New Interest Search Reactions . In adolescence, the interests of a teenager are scattered in many directions: searching for oneself, striving for the unknown and novelty, immersion in informative and communicative spheres. A teenager is deeply interested in any intellectual and aesthetic direction (music, cinema, philosophy, etc.), looking for bodily-manual practices (taking care of his body, increasing endurance, strength), developing leadership skills (trying to take a worthy position among peers), immersing in the information field (spends a lot of time on the Internet, social networks).

Features of the course of the crisis in girls and boys
Puberty is different for girls and boys. In girls, as a rule, the symptoms of the transition period begin to appear from 10-11 years. At the same time, the signs of a crisis are rather weakly expressed in them. Boys enter the transitional age later - from about 12-13 years old. But the course of the crisis period is much more pronounced. This is mainly due to the fact that society traditionally has stricter requirements for boys and men than for girls and women.
In adolescent boys, the following features are most pronounced:
- Aggression, anger . The manner of behavior changes in relations both with peers and with adults - parents, teachers. This is mainly due to an increase in the production of testosterone in the body.
- Sudden bursts of emotion . Mood swings, like unreasonable aggression, are due to hormonal changes.

- A dull sense of fear . Teenagers often go in for extreme sports and decide on rash acts. The reason is also a change in testosterone levels.
- Striving for independence . Boys want to be perceived as grown men. To do this, they need to solve problems on their own, which is far from always within the power of a teenager. The inability to independently cope with troubles becomes the cause of a violation of mental balance.
- Desire to lead a lifestyle inherent in adult men . Teenagers want to do high-profile deeds and even feats. However, they do not always realize the consequences of rash actions.
- Interest in intimate aspects of life . Manifested in a strong attraction to the opposite sex.
- Preoccupation with appearance . It is wrong to assume that boys are less worried about their appearance than girls. Changes in appearance make adolescents vulnerable, and dissatisfaction with their own appearance leads to isolation, insecurity, and low self-esteem.
 They do not tolerate criticism in their address, and any reckless comment is perceived as negatively as possible.
They do not tolerate criticism in their address, and any reckless comment is perceived as negatively as possible.
In girls, adolescence is accompanied by the following signs:
- Concerned about appearance . Girls acutely perceive their discrepancy with the generally accepted canons of beauty. This is especially evident against the backdrop of the popularization of social networks. They want to be like beautiful girlfriends, artists, influencers. They start to follow fashion, they want to dress in trendy things.
- Desire to attract attention . Teenagers strive to show how interesting their inner world is and how unusual their views on life are. To attract attention, they use provocative behavior, dress in too catchy outfits, apply expressive makeup, dye their hair in bright colors.
- Mood swings . In girls, as in boys, hormonal surges cause mood swings, irritability, outbursts of anger and aggression.
- Interest in the opposite sex . Unlike boys, girls are more interested in platonic love. Often at this age they fall in love. If the first love turns out to be unrequited, this can lead to serious complications of the crisis - isolation, depression, suicidal tendencies.
Various distortions of manifestations depend on upbringing, environment, standards established in society.
Advice for parents on coping with the crisis
Despite the difficulties in communicating with parents and an active desire to separate, during a crisis period, a teenager needs the right support and protection from adults. At the same time, parents need to abandon the previous forms of control and give the child the necessary share of freedom.
Each child is unique, and parents will have to find an approach on their own. But a few simple recommendations will help to understand a teenager and help him overcome the crisis:
- Gently enter the environment.
 A friendly, calm approach will help overcome misunderstanding and aggression. Participation in life situations, common interests will allow you to unobtrusively help the child solve problems as needed.
A friendly, calm approach will help overcome misunderstanding and aggression. Participation in life situations, common interests will allow you to unobtrusively help the child solve problems as needed. - Interested in hobbies . It will not be superfluous to share the interests of the child, discuss his hobbies with him, talk about his thoughts and find out the point of view on various issues.
- Be patient with emotional swings . A violent reaction should not cause an explosion of emotions in response.
- Give freedom . It is important to provide the child with his own space, if possible - a private room. You should restrain your desire to control his actions, hobbies, emotions.
In conversations with a teenager, you should also adhere to a number of rules :
- Reject notations. Even small children do not like moralizing, and in a teenager they will only cause protest and aggression.
 After a few minutes, his attention will switch to something else.
After a few minutes, his attention will switch to something else. - Do not blame, do not criticize. Any comments should be made in an environmentally friendly way, without accusations, moralizing and imposing.
- Discuss in passing. Teenagers are not always ready for serious face-to-face conversations. Increased attention to the problems of the child will make him think that his independence is doubted. But careful conversation during joint activities will bring results.
- Do not raise your tone. Calm conversations are more effective than screams and scandals.
- Praise. Due to insecurity, teenagers are in great need of praise and approval.
- Communicate with the child in instant messengers, social networks. Children spend a lot of time on smartphones and tablets. Correspondence in messengers is familiar to them. Communication in such an environment will allow you to conduct conversations in a way that is comfortable for the child.

Even the correct behavior on the part of parents does not exclude the possibility of manifestation of conflict, aggression and disobedience of a teenager. However, a respectful attitude towards the individual and an appropriate manner of communication between adults can reduce the severity of crisis symptoms and their intensity.
Make an appointment
Registration through the site is preliminary.
Our employee will contact you to confirm the appointment with a specialist.
Set time
Time9:009:3010:0010:3011:0011:3012:0012:3013:0013:3014:0014:3015:0015:3016:0016:3017:0017:3018:0018:3019:0019:3020: 0020:3021:0021:30
I don’t know the specialist
-I don’t know-a pediatrician, allergists of the gynecologist of the Dermatologist of the Library of the Lorde, nephrology of the Orthodox, proctable of the Passimonologist, Pulmonathetic Deribided End (0019
More about the quality assurance of medical services
The strength and weakness of the “generation of change”: who are the children of the 90s and how do they differ from others
More and more is being said about the generation that grew up in the “dashing 90s”. Today, its representatives have entered the age of maturity, are building careers, occupying influential positions. But Western experts are perplexed: why the first post-Soviet generation, who grew up on liberal values and successfully blended into modern Russia, protests less than today's youth.
Today, its representatives have entered the age of maturity, are building careers, occupying influential positions. But Western experts are perplexed: why the first post-Soviet generation, who grew up on liberal values and successfully blended into modern Russia, protests less than today's youth.
Disadvantages of classifications
In the Western classification, children of the 90s fall into the category of millennials, that is, people born between 1980 and 2000. In general, this generation is characterized as calm, non-conflict, individualistic, accustomed to comfort and well-being. They are favored by their parents, so they see no reason to conflict with them and rebel; non-aggressive and cautious, since from childhood they were protected from any kind of danger; accustomed to approval and convenience; selfish and unaccustomed to responsibility.
However, it is obvious to Russians that this description is more suitable for those who grew up in the zero years and later, but clearly not for people whose childhood fell on the last decade of the last century. By the way, Russian sources explicitly state that “the upheavals of the late 80s and early 90s made their own adjustments to the upbringing of children born then, so many sociologists believe that our “millenniums” begin around the year 1989.”
By the way, Russian sources explicitly state that “the upheavals of the late 80s and early 90s made their own adjustments to the upbringing of children born then, so many sociologists believe that our “millenniums” begin around the year 1989.”
According to another classification focused on Russia, generation X includes children born in 1965-1985, and to generation Y (millennials) - born in 1985-2000. At the same time, the former are characterized as individualistic, materialistic and career-oriented and disillusioned with Soviet values, while the latter are characterized as an even more individualistic, but at the same time tolerant generation, striving for travel, self-development and freedom. This generation is called fearless, having grown up in conditions of stability, that is, close to the Western idea of millennials.
It is obvious that even such a classification does not single out children 90-x into a separate category, moreover, rather schematically “sorts” them into different age groups. The children of the 90s are also very different, and the similarities between them are observed rather not in life priorities, but in unconscious attitudes . Let's try to describe some of the features of those whose childhood fell on the "dashing decade" and explain why the next generation did not live up to the hopes of the West.
The children of the 90s are also very different, and the similarities between them are observed rather not in life priorities, but in unconscious attitudes . Let's try to describe some of the features of those whose childhood fell on the "dashing decade" and explain why the next generation did not live up to the hopes of the West.
Freedom and conformism
0 years as children, did not experience disappointment in Soviet values simply because they were not found. Vague memories of the last years of the USSR were most often associated with pictures of long lines and rare joys in the form of long-awaited treats and toys, but not with ideological battles [communists and democrats]. And Western values like freedom, respect for the law and the dignity of the individual, actively proclaimed in the new Russia, for most children, due to their age, went unnoticed.
Adults plunged into the whirlpool of freedom with irrepressible greed, a slave who broke free, fearing in the depths of his soul that everything could end tomorrow, so you need to have time to live here and now, forgetting about norms and restrictions, and children of the 90s followed their example. With the exception of children from well-to-do families, the bulk of schoolchildren of that time learned to survive quite well, showing remarkable courage, independence and initiative. However, it was precisely these qualities that led to the fact that in adulthood, many of these people, fearful of losing stability, became conformists: in the end, this was just the most convenient survival strategy.
With the exception of children from well-to-do families, the bulk of schoolchildren of that time learned to survive quite well, showing remarkable courage, independence and initiative. However, it was precisely these qualities that led to the fact that in adulthood, many of these people, fearful of losing stability, became conformists: in the end, this was just the most convenient survival strategy.
Yes, children of the 90s were not forced to pretend, say the “right” things and say formal oaths. They were not driven in formation, they were not scolded at general meetings, they did not interfere in their personal lives, they were not interested in the views of their parents. The next generation, which grew up without established ideas and obvious authorities, is used to making decisions on its own, not relying on elders and not trusting the collapsed past. For many children, the completely primitive slogan “Take everything from life!” has become the main value of the new era!
Hyperresponsibility
At the same time, the children of the 90s were really used to coping with difficulties alone, they learned well that in this world everyone is responsible for himself. Often this sad truth was taken straight from the family. In those years, parents did not yet know the rules of caring for the child and the importance of his unconditional acceptance, known in modern society. Many of the children who grew up in the 90s inherited all the costs of a harsh Soviet upbringing: humiliation, beatings, shouting, severe punishments and phrases like "I gave birth to you in vain" or "I'm tired of you." In the post-Soviet period, this set was supplemented with maxims like “you are nobody here”, “you have not earned anything yet”, and so on.
Often this sad truth was taken straight from the family. In those years, parents did not yet know the rules of caring for the child and the importance of his unconditional acceptance, known in modern society. Many of the children who grew up in the 90s inherited all the costs of a harsh Soviet upbringing: humiliation, beatings, shouting, severe punishments and phrases like "I gave birth to you in vain" or "I'm tired of you." In the post-Soviet period, this set was supplemented with maxims like “you are nobody here”, “you have not earned anything yet”, and so on.
The depreciation of the child's real feelings and the constant opposition of what one wants to what is "right" is in principle characteristic of the Spartan Soviet tradition. As the 90s showed, the attitudes that “men don’t cry”, and in case of any problems, you need to “clench your teeth and endure”, successfully survived the Soviet era and survived in society even without a touch of ideology.
However, a significant difference with the Soviet era is that in the USSR, with all the costs and inhumanity of such upbringing, children understood that they were being brought up after all. Parents 90's often simply had no time to take care of children, since they were forced to earn money. As a result, the feeling that you are really not needed and that no one will really help you was quite common .
Parents 90's often simply had no time to take care of children, since they were forced to earn money. As a result, the feeling that you are really not needed and that no one will really help you was quite common .
Moreover, children from poor families quickly realized that the harsh conditions in which they were placed were not educational, but real. They knew that the consequences of their mistakes could be not only parental punishment, but the inability to break through in life, earn money and support a family. "Severity" and the habit of not paying attention to their own feelings for such children seemed to be a real life necessity - moreover, the only way to survive.
Such children matured early and even earlier began to feel their responsibility for their parents, often without experiencing real closeness with them. Many from a young age seriously believed that “if I don’t go to university, there will be nothing to eat at home,” because they knew from their own experience that there really can be nothing to eat at home. And this is the main paradox of the next generation: at a time when some of its representatives allowed themselves anything, not paying attention to others, many children, on the contrary, treated themselves excessively strict and felt their personal responsibility and guilt for their adult parents, and for future children, and even for their own orphan deprivation.
And this is the main paradox of the next generation: at a time when some of its representatives allowed themselves anything, not paying attention to others, many children, on the contrary, treated themselves excessively strict and felt their personal responsibility and guilt for their adult parents, and for future children, and even for their own orphan deprivation.
Fear of the future
The instability of the changing world, wars and banditry, poverty and financial crises, combined with the lack of parental care and hyper-responsibility, inevitably gave rise to anxiety. The illusion of basic security collapsed early, and the children of the 90s rushed to live, catching every minute as if the future would never come. Fear of war and devastation crept into them when barricades appeared on Moscow and then Leningrad streets during the State Emergency Committee. It strengthened itself when the parliament was shot at 93m. The children did not yet understand who was right and who was wrong, and they simply saw that some were shooting at others, and were afraid that they would then shoot at them too.
Children of the 90s heard shots not from the TV, but under the windows, at night, when the "redistribution of property" was still being carried out and in the morning it was possible to find burned kiosks. And they saw the real war itself - the first Chechen war - mostly not in films, but in the news.
And that is why the fear of losing the shaky stability in many people of this generation turned out to be stronger than the most sincere desire for change.
The generation of the 90s turned out to be too divided to change the country, and for the most part they were not used to hatching any long-term strategies and images of the future for the whole nation. Unlike the perestroika generation, which knew the attractiveness of ideas, the next generation from childhood got used to the fact that tomorrow everything could collapse, so you need to live quickly, not thinking for a long time and trying to achieve the maximum while it is still possible.
People of the first post-Soviet generation are less likely to make one choice for life than their Soviet predecessors. The point is not only in a lower level of selflessness (paradoxically, the hyper-responsible part of this generation is sometimes characterized by excessive selflessness), but in the fact that children 90's don't see the future as their asset - something they can be sure of and have control over. They are used to thinking in more concrete terms, which can be expressed by the formula from Alexander Gorodnitsky's song: "Only what you take in your coat, only what you carry in your hands."
The point is not only in a lower level of selflessness (paradoxically, the hyper-responsible part of this generation is sometimes characterized by excessive selflessness), but in the fact that children 90's don't see the future as their asset - something they can be sure of and have control over. They are used to thinking in more concrete terms, which can be expressed by the formula from Alexander Gorodnitsky's song: "Only what you take in your coat, only what you carry in your hands."
These people perfectly withstand short-term and medium-term distances, but they are not used to thinking about the global fate of the country and making too long-term plans. This is quite logical, because if the future is unstable and scary, then it is simply impossible to predict, let alone change it and manage it.
Disappointment
Like their predecessors who were disillusioned with Soviet ideals, many children of the 90s also broke with the values of their early youth — even though not all of them understood exactly what values were at stake. Nevertheless, today, many Russians, largely under the influence of propaganda, have a stable association of rampant crime, banditry, anecdotal “new Russians” and mafia squabbles (which were in many ways a specific phenomenon of the CIS space) exclusively with reforms, democracy and the West.
Nevertheless, today, many Russians, largely under the influence of propaganda, have a stable association of rampant crime, banditry, anecdotal “new Russians” and mafia squabbles (which were in many ways a specific phenomenon of the CIS space) exclusively with reforms, democracy and the West.
Interestingly, even formally renouncing freedom as a value, the children of the 90s emphasized that they freely make their choice and do not go with the flow. It is most difficult for them to return to rejected ideas, since their disappointment is perceived by them as something very personal and suffered. It is really difficult to oppose this feeling, because disappointment, unlike ideology, is a feeling that appeals to personal experience, which for any person is perceived more sharply and more important than any logical system of views. In addition, one can argue with a system of views, but it is impossible to argue with experience in principle.
These features help to understand at least a little the paradoxical nature of the Russian next generation: who grew up in conditions of "wild" freedom and at the same time inclined to conformism - cynical and individualistic, but often too harsh on himself, anxious and uncertain about tomorrow.