Math art projects kindergarten
21 Math Art Projects for Kids
You are here: Home / Learn / Math Activities / 21 Math Art Projects for Kids
25694 shares
Math art projects are a unique way to combine right and left brain learning. Both my boys enjoy math, but they often balk when I suggest, "let's do an art project!" It's sort of depressing for me, since I'd much rather get out the paints than perform calculations. My solution has been to make math learning creative with math art projects and activities.
I need to get better about taking photos of our math art sessions. Perhaps now that I have a new camera I can get some decent pictures. But I digress. Anyway... I thought it would be fun to round up some math art ideas that we've tried, plus a few I've found on the internet that are in my virtual "to try" pile.
The best thing about all of these math art projects is that they will get math kids thinking about art and art kids thinking about math!
Math Art Projects and Ideas
Tessellations. We've done this several times, and somehow it never gets boring.
- See our how to make tessellations post.
- Three ways to make heart tessellations.
- Check out this fish tessellation idea at Art Projects for Kids.
Explore Symmetry.
- This is great for younger kids. You're probably familiar with the ol' fold the paper in half and smoosh trick. You can make symmetry art free style, like we did.
- Create gorgeous math art with parabolic curves. My son designed his own eyeball!!
- Create gorgeous objects like these butterflies from Buggy and Buddy.
- These symmetry art aliens make me smile.
Turn number sequences into art.
- We did this when we turned pi into a cityscape
- Spirolaterals will help your kids practice their multiplication tables.
- Create Fibonacci art with circles.
- This Fibonacci valentine from Math Four could be adapted for any time of the year.

Use math tools to create art. This is one of my favorite ideas!
- It can be really simple, like simply giving your kids a ruler, compass and protractor and see what they come up with. If using a compass is tricky, see my tip for drawing with a compass.
- I love this protractor art project that evokes Frank Stella's artwork.
- Use a ruler to create sunburst paintings, like these at Art Bar.
Explore math art with shapes.
- The boys love to play around with our homemade Montessori triangles. They don't even think about the fact that they are creating artistic designs!
- Explore Möbius strips.
- Make your own peek-a-boo shape book - free printable template.
- Paint a Mondrian window.
- We also had a great time with these Hexi cards to print out from Picklebums.
- E is for Explore has a few ways kids can use Kandinsky inspired art to think about about circles and relative size.

- Make mandalas. like this idea at NurtureStore. I've always wanted to do this.
- Use a geoboard. We were gifted a cheesy plastic geoboard, but Crayon Box Chronicles has instructions so you can make your own.
What do your kids prefer, math or art? Do you ever do math art projects with the kids?
Need more ideas?
25 Playful and Creative Math Ideas.
Math art activity and picture books
25694 shares
Reader Interactions
Super Cool Math Art with Parabolic Curves
You are here: Home / Learn / Math Activities / Super Cool Math Art with Parabolic Curves
3549 shares
We adore math art projects. I've been eyeing the idea of using parabolic curves in a creative endeavor with my math-loving kid for a while. I was experimenting in my own art journal with the groovy way you can fool the eye into thinking a group of straight lines is actually a curve when my 10 year old leaned over and said, "That is so cool!!"
That's when I knew I had a great math art activity for us to do together. Since my sons are naturally drawn to S.T.E.M. - themed activities, I do try and find ways to sneak in the "A" to make it S.T.E.A.M., in which the "A" stands for Art and Design. Last week I shared our Fibonacci Art Project, and like that lesson, our exploration of parabolic curves is just that: a process-based exploration.
Since my sons are naturally drawn to S.T.E.M. - themed activities, I do try and find ways to sneak in the "A" to make it S.T.E.A.M., in which the "A" stands for Art and Design. Last week I shared our Fibonacci Art Project, and like that lesson, our exploration of parabolic curves is just that: a process-based exploration.
I'll give you the basic instructions for how to make parabolic curves and then let you and your kids explore math art on your own! (Note: this post contains affiliate links)
What you need:
- Pencil (believe me, you do not want to start with ink!)
- Eraser (see above!)
- Pens. We've switched from Sharpies to Flair pens. You only have to smell them to find out why.
- Rulers or straight edges. It's easier to create squares if you have a triangle or t-square. I think it's well worth having a math set. They aren't very expensive and they are loads of fun, not to mention being handy for school projects.
- Protractor.
 Optional, but a must if you want to do a circle design. We get a lot of use from our 360 degrees protractor
Optional, but a must if you want to do a circle design. We get a lot of use from our 360 degrees protractor - Paper. We made ours in our art journal. The mixed media visual art journal is our absolute favorite, which regular readers (waving hello!) know that I frequently sing the praises of. Alternatively, you can use graph paper.
- Sharpener. You want sharp, sharp pencils for this project!
- Colored pencils. Optional, but fun.
Instructions:
1. Create a set of crossed lines, preferably at a 90 degree angle. (Kids can experiment with different angles once they've learned the basics.) For ease, make sure each line is an even measurement. We used 1 cm and 5mm increments
2. Divide the lines into equal divisions. In my example I've uses 5 millimeter increments.
3. Draw angled lines. Start on the bottom line in the left hand corner at the furthest mark. (See photo above. ) Draw a line from the mark to the first mark on the adjacent line. Draw a second line from the second furthest mark and connect it to the second mark on the adjacent line. (See photo below.)
) Draw a line from the mark to the first mark on the adjacent line. Draw a second line from the second furthest mark and connect it to the second mark on the adjacent line. (See photo below.)
4. Continue until all the lines have been drawn.
TIP: The starting/ending points of the first and last few lines can get "lost". To make it easier, number the marks. (See photo below)
Voila! A "curved" line appears.
5. Optional: go over pencil lines with marker and/or use colored pencils to create colorful designs.
TIP: For kids just starting out, divide the lines with wider marks. My example above is 5 mm, but Kiddo preferred to work with 1 cm sections.
Variations:
1. A single parabolic curve, while cool, is just the beginning. Encourage your kids to create boxes, triangles, and interlocking shapes as a basis to create elaborate math art designs!
2. Connect the dots in a circle! My son created a "parabolic eyeball".
Connect the dots in a circle! My son created a "parabolic eyeball".
For inspiration, here are some of our experiments, straight from our art journals. (You can see I need to work on my photo editing skills, ha ha ha.)
Watch more of our math art ideas in action:
MORE: Tessellations and the Pi Skyline are two of our favorite math drawing projects. Little kids can practice connecting the dots, too, with a giant dot to dot. Or check out more fantastic patterns in these math art books.
3549 shares
Project "Entertaining Mathematics in Kindergarten" | Project (senior group):
Project in the senior group on the topic:
"Entertaining mathematics in kindergarten"
In addition to interesting forms of work with children, the project offers a description of the products of creative activity and criteria for assessing the level of development of the child in the process of implementing the tasks. The work on the project made it possible to integrate various educational areas in order to achieve the most effective results in the development of the child, thereby providing preschoolers with the opportunity to organize their own independent activities using the knowledge gained about mathematical concepts.
The work on the project made it possible to integrate various educational areas in order to achieve the most effective results in the development of the child, thereby providing preschoolers with the opportunity to organize their own independent activities using the knowledge gained about mathematical concepts.
Justification of the need for the project:
Modern society needs people who are intellectually courageous, independent, thinking in an original way, creative, able to make non-standard decisions. All these personality traits in preschool age can be formed with the help of a variety of games through project activities.
Through project activities:
It is possible not only to transfer to children the amount of certain knowledge, but also to teach them to acquire this knowledge on their own, to be able to use the acquired knowledge in solving new cognitive and practical problems.
Based on the main natural activity of the child - the game - to form his communication skills and the ability to work in various groups, playing different social roles (leader, performer, mediator, etc. ) research methods: collect the necessary information, facts, be able to analyze them from different points of view, put forward hypotheses, draw conclusions and conclusions.
) research methods: collect the necessary information, facts, be able to analyze them from different points of view, put forward hypotheses, draw conclusions and conclusions.
A project is a system of progressively more difficult practical tasks. Thus, the child accumulates his own experience, deepens his knowledge and improves his skills. A preschooler develops such personality traits as independence, initiative, curiosity, interaction experience, etc., which is prescribed in the Federal State Requirements
for a kindergarten graduate.
The project is intended for classes with older children.
Project participants: children of senior preschool age, group teachers, parents of pupils.
Project goal: Increasing interest in mathematics among preschool children by creating conditions for research activities to study geometric shapes, numbers and lines in conjunction with the surrounding life, with objects of the immediate environment.
Tasks:
1. To form in preschoolers elementary ideas about geometric shapes and bodies; numbers from 0-10; various lines.
To form in preschoolers elementary ideas about geometric shapes and bodies; numbers from 0-10; various lines.
2. To develop the ability of children to independently use the acquired knowledge in various activities, to involve peers in extended games.
3. Maintain interest in learning, creating something new, unusual.
4. Form parents' interest in the achievements of their children in joint activities with them.
Classification of the project on the following grounds:
Dominant activity in the project:
Development of mathematical abilities.
Subject area:
interdisciplinary project (several sections of the program are involved: FEMP, cognitive development, speech development, artistic and aesthetic development, familiarization with fiction, physical development, game activity.) Work with parents is included.
Nature of contacts:
children, teachers, parents of the same group.
Number of project participants:
collective.
Duration of the project:
short-term (3 months - senior group)
The main theoretical positions of project-based learning:
The focus is on the child.
The educational process is built in the logic of activities that have a personal meaning for the child, which increases his motivation for learning.
The individual pace of work on the project ensures that each child reaches their own level of development.
Deeply conscious assimilation of basic knowledge is ensured through the universal use of this knowledge in different situations, in independent activities.
Positions of a teacher:
From a carrier of ready-made knowledge, he turns into a partner, consultant, organizer of an educational environment that meets the interests, capabilities and needs of children, providing situations of interaction with the world of people (peers, educator, parents, etc.).
Project implementation plan:
1. Choice of the project topic, its type, number of participants.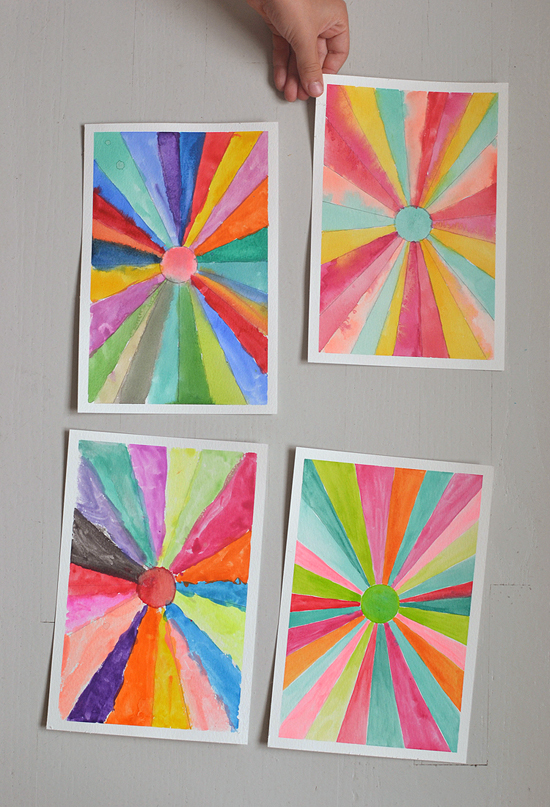
2. Statement of the problem.
3. Goal setting.
4. Considering steps to achieve the goal, forms and methods of work, distribution of roles.
5. Independent work of the project participants.
Children's independent activities within the framework of the project are encouraged and supported by teachers and parents in play and household activities in their free time.
Information about the project is disseminated through the design of the project, reports on the work done and presentation at the teachers' councils.
The content of the project stages:
The project includes three stages - preparatory, research and final (generalizing).
Project schedule:
Objectives: to expand children's knowledge; the ability to find given objects in the surrounding reality, in objects of the immediate environment, in nature.
- Introduce geometric shapes, solids, numbers, various lines.
- Joint organized activities.
- Didactic games.
- Cognitive development
- Observations.
- Guessing riddles.
- Inventing riddles
- Conversations.
- Looking at pictures and illustrations.
Speech development:
Learn to describe geometric figures and bodies, write stories and fairy tales about figures, numbers, lines.
Compilation of descriptive stories about figures, objects of a given shape.
Acquaintance with art. literature:
To consolidate mathematical concepts through acquaintance with works of art; the ability to notice in the texts of fairy tales objects of given forms, numbers, creative transformation of individual artistic images.
Artistic and aesthetic development:
To consolidate mathematical concepts through drawing various objects, modeling.
Turning figures, numbers and lines into objects.
"What the numbers look like"; making collages.
Playing activities:
Consolidate acquired knowledge through a variety of play activities; to form the ability of children to play different games, organize them.
- Didactic games.
- Outdoor games.
- Role-playing games.
- Theatrical games.
- Word games.
- Construction games.
Productive activity:
Develop an emotionally holistic attitude towards objects and images; children's creativity. To form the ability to create something new, interesting and unusual; rejoice in the results of your work.
- Collages
- Friezes
- Albums of children's activities
- Handicrafts
- Buildings made of constructor, builder, sand.
Independent activity:
To develop the ability of children to independently organize their activities in various activities, to involve peers in their activities.
- Various games.
- Research activities.
- Drawing drawings.
- Productive activity.
Working with parents:
Introduce parents to the topic of the project, get them interested. Turn parents to their children, make them want to play with them, spend more time, create something new together.
Consultation for parents on the topic: "The development of mathematical abilities in preschoolers."
Preparatory stage - October
Talks, classes were held, parents were involved in the project. Through FEMP, children were introduced to geometric shapes and bodies, they were taught to give a description, they were introduced to numbers and various lines. Through research activities, figures, bodies, numbers and lines were found in the surrounding reality, in objects of the immediate environment, in nature. Through the development of speech, descriptive stories were composed, fairy tales were composed. Through familiarization with fiction, they were introduced to works in which there are round objects “Gingerbread Man”, “Flower-seven-colored”, etc., there are certain figures “Three Bears”, “Wolf and Seven Kids”, etc. Through physical education, they were fixed in mobile games and games-competitions geometric shapes, bodies, numbers and lines. The knowledge of children was consolidated through a variety of playful, productive activities.
Working with children:
Before starting the project, we talked with the children about geometric shapes, solids, numbers and lines. Clarified their ideas about them. They offered the children a scheme of acquaintance:
What is the name of a geometric figure (body, figure, line)?
Description of a geometric figure (solids, numbers, lines).
What do they look like?
Where does it occur in the surrounding reality?
Research phase - November
Select a geometric figure, body, number or line. Explore it, give a description, find it in the surrounding reality and in the objects of the immediate environment.
In independent artistic and aesthetic activities, children draw geometric shapes, bodies, numbers, lines; turn them into objects; find pictures with these concepts in the surrounding reality, cut and paste them; molded from plasticine.
In the course of the work on educating preschoolers about geometric shapes, bodies, numbers, various lines, we widely used the game: in independent activities, children play individually or unite with peers in a variety of games with these mathematical concepts.
November 26 - children took part in an open lesson on FEMP and musical development: "Visiting a fairy tale - Cinderella"
Final, generalizing stage - December
The final stage is based on a variety of independent activities of children, products of children's activities: crafts , collages, friezes, albums, fairy tales.
Outcome of the project:
Generalization of the results of the work. The project will allow children to expand mathematical knowledge about geometric shapes, solids, numbers and various lines, to form the ability to use this knowledge in independent activities. Project activities will stimulate the development of logical thinking, imagination in children, increase motivation for research activities. Parents will develop a strong interest in creativity, together with their children.
Results-products and results-effects:
1. Participation of children in an open lesson on the development of mathematical and musical abilities.
2. Thematic collage "Turning figures into objects"
3. "Turning numbers into objects", "Drawing with figures"
References:
Yaroslavl, "Academy of Development", 1996.
Voronova V.Ya. "Creative games for preschoolers".
Venger L.A., Yachenko O.M., Govorova R.I., Tsekhanskaya R.I. "Games and exercises for the development of mental abilities in preschool children." M., "Enlightenment", 1998g.
Glagoleva V.G. "Logical alphabet for children 4-6 years old." S.-Pb., "Childhood-press", 1998
Ekhevich N. "Developing games for children." M., 1990
Usova AP "The role of play in the development of children." M., "Enlightenment", 1976.
Entertaining mathematics project | Mathematics project (senior group):
Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution Beryozka kindergarten
Cognitive project on the topic:
"Entertaining mathematics"
in the senior group
Project manager:
teacher Sitdikova Z. N.
Igrim, 2017
Relevance.
Mathematics is one of the most difficult subjects in the school cycle, therefore, in order to successfully teach a child at school already in kindergarten, it is necessary to promote the mathematical development of a preschooler, expand their mathematical horizons, and improve the quality of mathematical preparation for school. This will allow children to more confidently navigate the simplest patterns of the reality around them and actively use mathematical knowledge in everyday life.
Mathematical representations should be mastered by a preschooler consistently, evenly and systematically. To this end, it is necessary to organize educational activities carried out both in the process of organizing various types of activities (game, communication, labor, cognitive research, productive, musical and artistic, reading fiction), and during regime moments; as well as independent activities of children using a variety of gaming tools. Also, the mathematical development of children will be more effective when interacting with the families of children.
Didactic game and game exercises using visual material (using diagrams, cards, models, objects) arouse interest in children, facilitate and speed up the process of memorization, form techniques for working with memory and thinking, which in a visual and accessible form help children remember complex material.
Entertaining mathematical material is given by game elements contained in each task, logical exercise, entertainment, be it checkers or the most elementary puzzle. The inclusion of entertaining material in the GCD for FEMP allows you to keep children's interest in the lesson, and this creates the conditions for increasing the emotional attitude to the content of the educational material, ensures its accessibility and awareness. The mathematical techniques used, the combination of practical and gaming activities, the solution of problem-playing and search situations contribute to the development of elementary mathematical concepts in children.
In order to teach preschool children to love mathematics, to maintain interest in intellectual activity, to encourage them to solve search problems, it is necessary to approach the organization of the learning process creatively and with interest, use the variety and variability of educational games with mathematical content.
Type of project: cognitive-playing.
Implementation period: short-term (1 month).
Composition of participants: group (teacher, children of the senior group, parents).
The purpose of the project: the formation of elementary mathematical concepts in children of senior preschool age through entertaining material in the organized and independent activities of children.
Tasks:
- To create conditions for the assimilation of mathematical concepts by preschoolers, to ensure the successful development of children's abilities and thinking.
- To promote the development of the ability to count within 10 in direct and reverse order, to use ordinal and cardinal numbers correctly.
- Help to consolidate the ability to recognize and name geometric shapes.
- To help improve the ability to identify sets of objects or figures that have a common property.
- To promote the development of mental operations: logical thinking, ingenuity, visual memory, imagination, the ability to compare and analyze.
- Promote the development of interest in games that require mental effort, intellectual effort.
- To promote the development of independence, the ability to understand the learning task and perform it independently.
- Help improve the readiness of preschool children for schooling.
- Encourage parents to participate in the project and work with children at home.
Expected results:
- Raising the level of mathematical concepts in children of senior preschool age.
- Children have developed an interest in the very process of learning mathematics.
- Children independently find ways to solve cognitive problems, strive to achieve the goal, overcome difficulties, and are able to transfer the acquired experience to new situations.
- Activating parents' interest in using math games and exercises.
- Parents' awareness of the importance of forming elementary mathematical concepts in children with the help of entertaining material, expanding parents' knowledge of entertaining material.
Preparatory stage:
- Definition of the project topic.
- Setting goals and objectives of the project.
- Selection of methodological and fiction literature on the topic of the project.
- Selection of didactic, outdoor games, physical education sessions on the topic of the project.
- Production of educational games in mathematics.
- Drawing up a plan for the main stage of the project.
- Development of summaries of proposed educational activities, quizzes.
- Involving parents in joint work on the project:
- creative task: pick up mathematical riddles, tasks, rebuses and colorfully arrange this material;
- help of parents in making didactic games on FEMP.
- Parent survey.
- Making a folder - shifter "Mathematics for preschoolers".
- Conversation with parents "How to organize games for children at home using entertaining material"
Main stage:
- GCD according to the calendar-forward planning in the senior group:
- GCD for FEMP "Letters of the Queen of Mathematics", "Cities of the Queen of Mathematics" mathematics";
- GCD for fine arts: drawing "Funny Figures", pea appliqué "Magic Numbers", modeling "Funny Figures".
- Reading mathematical fairy tales, fairy tales with counting elements: "Three Bears", "Two Bear Cubs", "Twelve Months" by S. Marshak, "Flower - Seven-Colored" by V. Kataev; K. Ushinsky's story "Four Desires".
- Learning poems about numbers, counting rhymes, riddles about geometric shapes and numbers.
- Viewing computer presentation "Flight to the planet Mathematics", "Funny figures".
- Mathematical coloring, number drawing.
- Design.
- Working with counting sticks.
- Drawing geometric figures on a semolina
- Didactic games with mathematical content: "Tic-tac-toe", "Mathematical loto", "Ladybugs and daisies", "Labyrinths", "What numbers are lost", "Funny numbers", "Mathematical houses”, “Mosaic from caps”, “Tangram”, “Mathematical tablet “Geometric”, “Magic circles”, “Domino”, “Wonderful bag”, “simulator “Ladybugs”.
- Guessing riddles, entertaining questions, comic puzzles, puzzles.
- Outdoor games: "Make a figure", "The sea is worried."
- Finger exercises.
- Physical education minutes "Exercising", "Make a figure".
Final stage:
- Exhibition of educational games made together with children and parents.
- Conversation "Why I'm interested in mathematical games."
- Exhibition of baby books with mathematical tasks.
- Independent activity of children in the mathematical corner.
- The use of didactic games on FEMP at GCD.
- The final event - the quiz "Clever and clever".
- Processing and design of project materials.
Project progress.
The work on the project took place in several stages. At the preparatory stage, a plan for the implementation of the main stage of the project was drawn up, methodological and fiction literature, illustrative material, computer presentations "Flight to the Planet Mathematics", "Funny Figures", didactic games, physical exercises, finger gymnastics were selected. Developing games of mathematical content were made.
Parents were involved in the preparation of the project implementation: a survey was conducted with them, a folder was made for them - the “Mathematics for Preschoolers” movement. Parents also helped in the production of educational games in mathematics. Parents were given a task: to pick up entertaining mathematical material (problems, riddles, puzzles, rebuses) and colorfully arrange it.
At the main stage of the project, many lessons were related to the topic of the project. In the classes on the development of speech and reading fiction, we with children:
- read mathematical stories and fairy tales with mathematical content: "Three Bears", "Two Bear Cubs", "Twelve Months" by S. Marshak, "Flower - Seven-Flower" by V. Kataev; K. Ushinsky's story "Four Desires";
- memorized poems about numbers, counting rhymes, mathematical riddles.
During the art classes, children created drawings using geometric shapes, made “magic” numbers from peas and plasticine.
During math classes and during free activities, children worked with mathematical prescriptions - coloring pages, made constructions from construction kits, mosaics, Gyönysh blocks. The children also worked with counting sticks: they assembled figures according to the model and according to the plan. The children really enjoyed drawing geometric shapes on the semolina.
We played a lot of homemade didactic games of mathematical content:
- Tic Tac Toe. Tasks: to promote the development of attention, memory, the ability to focus on a particular subject for a long time, to promote the development of the ability to distinguish between concepts such as "diagonally", "vertically", "horizontally".
- "Mathematical Lotto". Tasks: to promote the assimilation of the sequence of numbers from 1 to 9; consolidate knowledge of geometric shapes.
- Ladybugs and Daisies. Purpose: the formation of the ability to compare, compare numbers and figures, arrange them in forward and reverse order.
- "Labyrinths". Tasks: to promote the development of logical and spatial thinking, multivariance, the ability to achieve goals, to promote the development of perseverance and patience.
- "What numbers are missing?". Purpose: development of the ability to determine the place of a particular number in a series and the relationship to the previous and subsequent number.
- Math Houses. Purpose: the formation of knowledge about the composition of the number of two smaller ones.
- Tangram puzzle. Purpose: to develop the ability of children to analyze images, to highlight geometric shapes in them, to break the whole object into parts, and vice versa - to compose a given model from elements.
- "Mathematical tablet "Geometric". Purpose: formation of the ability to create images, development of imaginative thinking, concentration,
- "Magic Circles". Purpose: development of counting skills and consolidation of the composition of the number.
- Ladybug trainer. Purpose: formation of the ability to navigate the playing field with cells, move the ladybug in the indicated direction, determine the spatial arrangement of objects: “above”, “below”, “right - left”, “left - right”.
- "Funny numbers". Purpose: the formation of the ability to lay out numbers from various materials at hand, the development of fine motor skills.
solved jokes, puzzles, guessed mathematical riddles. In this work, we used baby books made by parents. Together with the children, we learned and mastered new outdoor games, physical exercises and finger gymnastics of mathematical content.
At the final stage of the project, the following were arranged: a corner of entertaining mathematics, an exhibition of joint creative works of parents and children.