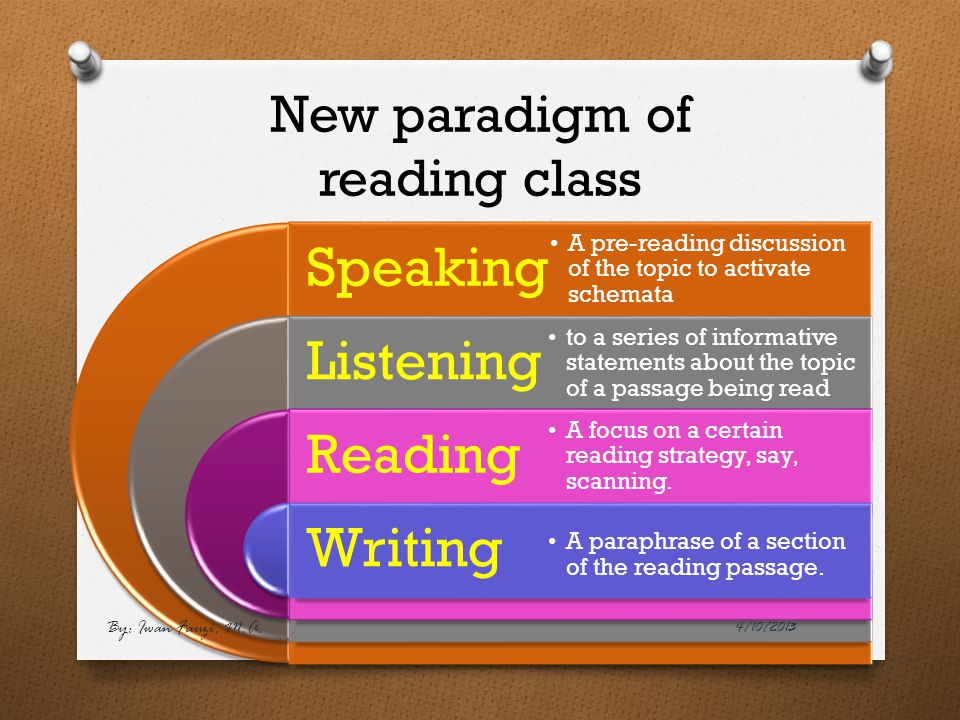
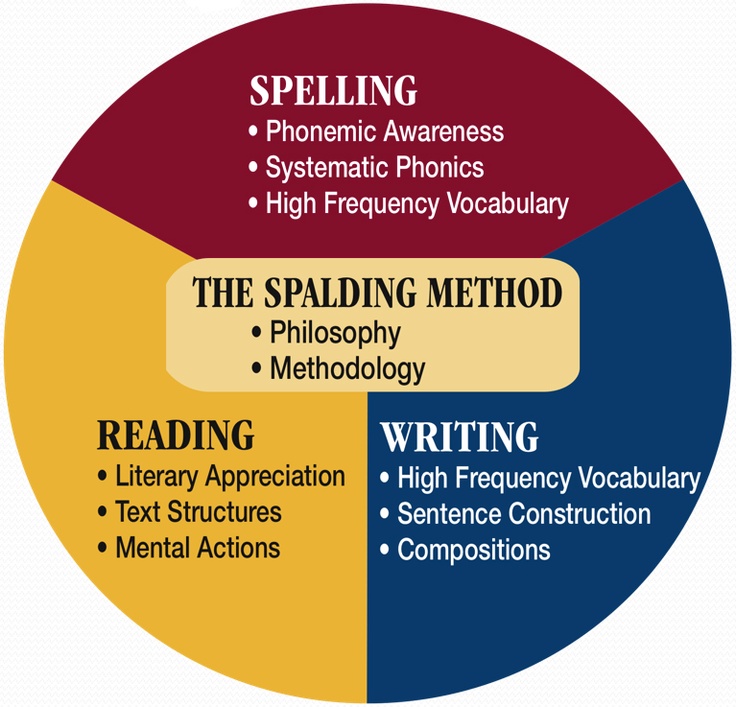
Methods in teaching reading
Teaching Reading: Strategies & Methods
Various studies show that promoting reading can have a major impact on children and their future. In this article, we’ll look at strategies and methods to support the teaching of reading and comprehension in early elementary school and beyond.
There’s more than one way to teach children to read. So, it’s important to have a range of different strategies and methods to encourage learning in different students.
Teaching reading: strategies & methods
- Read aloud to students
- Provide opportunities for students to read, write and talk about texts
- Read texts repeatedly to support fluency
- Teach children the tools to figure out words they don’t know
- Provide time for studying spoken language, including vocabulary and spelling
- Use prior knowledge to make connections
- Predict
- Visualize
- Summarize
- Teach critical thinking skills
The early years: strategies for teaching reading
Literacy teaching and learning are core responsibilities of teachers and schools. Yet teaching reading and writing is a complex and highly skilled professional activity. Many young learners start school with little knowledge about how to read and write. Teachers are tasked with helping children to bridge the significant gap between linking their written and spoken language. Learning to read is critical, with research showing that reading for pleasure can:
- Promote improved health and wellbeing
- Help build social connections and relationships
- Increase the chances of social mobility.
Literacy development is an evolving and non-linear process that encompasses foundational skills (phonemic awareness), word recognition, reading fluency, vocabulary, and reading comprehension (Simms & Marzano, 2018).
For a student’s ultimate success, teachers must:
- Understand how students learn these skills, and
- Implement best practices when teaching these skills.
Learning to read should include exposure to a wide variety of exciting books from different genres. Students should also experience reading through different mediums, such as interactive apps and web content.
Students should also experience reading through different mediums, such as interactive apps and web content.
Here are 10 strategies you can use to support your students in developing their reading skills and boosting comprehension.
1. Read aloud to students
Read-aloud regularly in the classroom and encourage parents to do the same at home. Reading aloud has many benefits for students, including improving comprehension, building listening skills, and broadening their vocabulary development.
2. Provide opportunities for students to read, write, and talk about texts
Regularly giving students time to read, write, and talk about texts can enhance their skill development across multiple areas. For instance, reading more helps you become a better writer. By talking about texts and hearing the perspectives of classmates, young children also have the opportunity to deepen their comprehension. Encourage parents to further engage young readers by asking them to help their child attack difficult words and ask questions about the text that will promote discussions.
3. Read texts repeatedly to support fluency
Allow students to read the same texts multiple times. By doing this, they not only build fluency but also build confidence. The more confident they become in their reading skills, the more likely they will enjoy reading.
4. Teach children the tools to figure out words they don’t know
Teaching students to read for the ultimate goal of producing independent readers begins by explicitly teaching the code we use to decode words. That starts with teaching phonemic awareness.
Here are some other strategies that support phonics instruction:
- For beginning readers, target words that are decodable. These are regular spellings with regular sounds. (Ex. such – /s/ /u/ /ch/ not gone)
- Sound out each phoneme and blend as you go by going back to the first sound everytime a sound is added. Hold the sound (sing) then add the next sound. Ex. /g/, /r/, gr—, /ow/, grow.
Note: Students may want to look at pictures for context, but this does not help them decode words. As we encourage students to read more difficult texts, they won’t have pictures to rely on, so encourage them not to use the pictures to decode difficult words.
As we encourage students to read more difficult texts, they won’t have pictures to rely on, so encourage them not to use the pictures to decode difficult words.
This might involve combining strategies, such as:
- Sounding out a word using phonics knowledge
- Looking at the pictures
- Skipping the word and coming back to it after reading the rest of the sentence
- Thinking about what would make sense.
As an elementary teacher, you can support the families of your young students by sharing phonics resources. By providing parents with practical resources, you are setting them up for a productive and positive reading experience with their child.
5. Provide time for studying spoken language, including vocabulary and spelling
A comprehensive approach to teaching reading also includes providing time to develop complementary skills, such as:
- Spoken language, including through conversation or oral presentations
- Vocabulary, such as building class lists while reading texts
- Spelling
- Grammar, such as through bite-sized video content like the Grammar Miniclips series.
6. Use prior knowledge to make connections
Each student brings unique prior knowledge to their reading education. This knowledge is the sum of all experiences they bring to the reading or viewing of a text. This could include personal experiences, cultural or religious experiences and concept knowledge. Prior knowledge helps young readers infer meaning from text, a skill recognized as a predictor of reading comprehension at various developmental stages and one of the drivers of sophisticated reading ability. An early reader can activate prior knowledge and make connections at each stage.
- Before reading, they could ask ‘What do I already know about this topic?’
- During reading, they could reflect ‘This part of the text is just like…’
- After reading, they could offer ‘I know more about this topic now.’
7. Predict
Prediction is about anticipation and working out the actions and ideas coming next. An early reader can use prediction at each stage of reading.
- Before reading, they could suggest ‘From the cover, I think this book will be about…’
- During reading, they could predict which word comes next in a sentence.
- After reading, they could comment on whether their predictions were correct.
8. Visualize
Visualizing combines using your senses and activating prior knowledge to create a mental picture. Ask students to create a “mind movie.” Young readers, especially with a teacher or parent prompting, can draw on their senses to imagine smells, sounds, tastes, and images that go with the story they are reading – like a show or movie in their mind.
9. Summarize
Teaching students to recall the main points or ideas of a story is not easy. First, they need to be able to put the story in order, then put it in their own words before they can articulate a ‘summing up’ of the author’s main ideas. To start to learn to summarize, young students can practice:
- Selecting the key words from a paragraph
- Locating the topic sentence (often found at the start or end of a paragraph)
- Responding to general questions about a story
- Talking through the story in their own words
10.
 Teach critical thinking skills
Teach critical thinking skillsCritical thinking gets readers to think about why an author creates a text in a particular way (author’s purpose). You can encourage young readers to ask some of the following questions to get them thinking critically about what they are reading:
- Why did the author write this story?
- What did the author leave out of the story?
- How do I feel about this story?
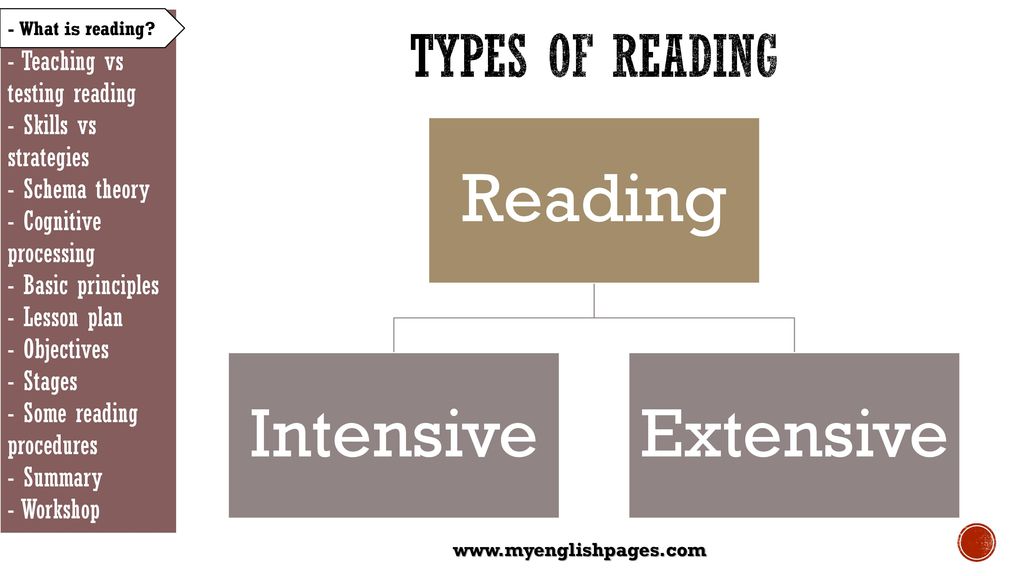
Reading comprehension strategies
Opportunities for teaching reading comprehension occur at all levels throughout the curriculum. Good comprehension draws from both linguistic knowledge and knowledge of the world we live in. Students develop skills in comprehension though high-quality discussion with teachers, and from regularly reading and discussing a range of texts across genres. Therefore, the reading strategies discussed earlier in the article should be practiced, consolidated and expanded on as a student progresses through school.
Growing readers must learn to read on the lines, between the lines, and beyond the lines. Reading will involve literal, interpretive, and inferential comprehension as it deepens in complexity. As students get more advanced, they’ll learn concepts such as transferring knowledge to new contexts and understanding an author’s viewpoint, purpose, and intended audience. And when they acquire those skills, they’ll be able to critically analyze messages and information in a range of literacy modes for various purposes.
Reading will involve literal, interpretive, and inferential comprehension as it deepens in complexity. As students get more advanced, they’ll learn concepts such as transferring knowledge to new contexts and understanding an author’s viewpoint, purpose, and intended audience. And when they acquire those skills, they’ll be able to critically analyze messages and information in a range of literacy modes for various purposes.
Recommendations for teachers to support the progression of reading comprehension:
- Make sure your students spend significant amounts of time reading engaging texts.
- Select texts for students which support authentic learning. These could include topic-based or interest-based texts.
- Give students access to a range of texts in various genres (multimodal, print-based, images, animations, graphic representations, video, audio, diagrams/charts, newspapers/magazines, fiction, non-fiction).
- Identify and discuss vocabulary from rich texts with your students.

- Give your students time to talk to each other about the texts they have read and listened to.
- Give students time to write and reflect on their reading.
Bring English language arts classes to life for your students
ClickView offers a huge range of educational videos for use in your ELA classes for elementary, middle and high school students. We regularly produce high-quality, curriculum-aligned videos and add these to the collection.
Browse English Language Arts Resources
3 Methods of teaching reading to children
Learning how to read is one of the most important things a child will do before the age of 10. That’s because everything from vocabulary growth to performance across all major subjects at school is linked to reading ability. The Phonics Method teaches children to pair sounds with letters and blend them together to master the skill of decoding.
The Whole-word Approach teaches kids to read by sight and relies upon memorization via repeat exposure to the written form of a word paired with an image and an audio. The goal of the Language Experience Method is to teach children to read words that are meaningful to them. Vocabulary can then be combined to create stories that the child relates to. Yet while there are various approaches to reading instruction, some work better than others for children who struggle with learning difficulties.
The goal of the Language Experience Method is to teach children to read words that are meaningful to them. Vocabulary can then be combined to create stories that the child relates to. Yet while there are various approaches to reading instruction, some work better than others for children who struggle with learning difficulties.
The most common kind of dyslexia, phonological dyslexia, causes individuals to have trouble hearing the sounds that make up words. This makes it difficult for them to sound out words in reading and to spell correctly. Dyslexic learners may therefore benefit from a method that teaches whole-word reading and de-emphasizes the decoding process.
Orton Gillingham is a multi-sensory approach that has been particularly effective for dyslexic children. It combines visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and tactile learning to teach a program of English phonics, allowing children to proceed at a pace that suits them and their ability.
No two students will learn to read in exactly the same way, thus remaining flexible in your approach is key. It can be useful to combine methods, teach strategies and provide the right classroom accommodations, particularly for students who have specific learning differences. Remember that motivation is key and try to be patient so as to avoid introducing any negative associations with school and learning.
It can be useful to combine methods, teach strategies and provide the right classroom accommodations, particularly for students who have specific learning differences. Remember that motivation is key and try to be patient so as to avoid introducing any negative associations with school and learning.
Learn more about motivating children to read, different kinds of dyslexia, identifying dyslexia, the Orton-Gillingham approach to reading, and strategies to help children with dyslexia in these posts.
Pre-literacy skills
Children begin acquiring the skills they need to master reading from the moment they are born. In fact, an infant as young as six months old can already distinguish between the sounds of his or her mother tongue and a foreign language and by the age of 2 has mastered enough native phonemes to regularly produce 50+ words. Between the ages of 2-3 many children learn to recognize a handful of letters.
They may enjoy singing the alphabet song and reciting nursery rhymes, which helps them develop an awareness of the different sounds that make-up English words.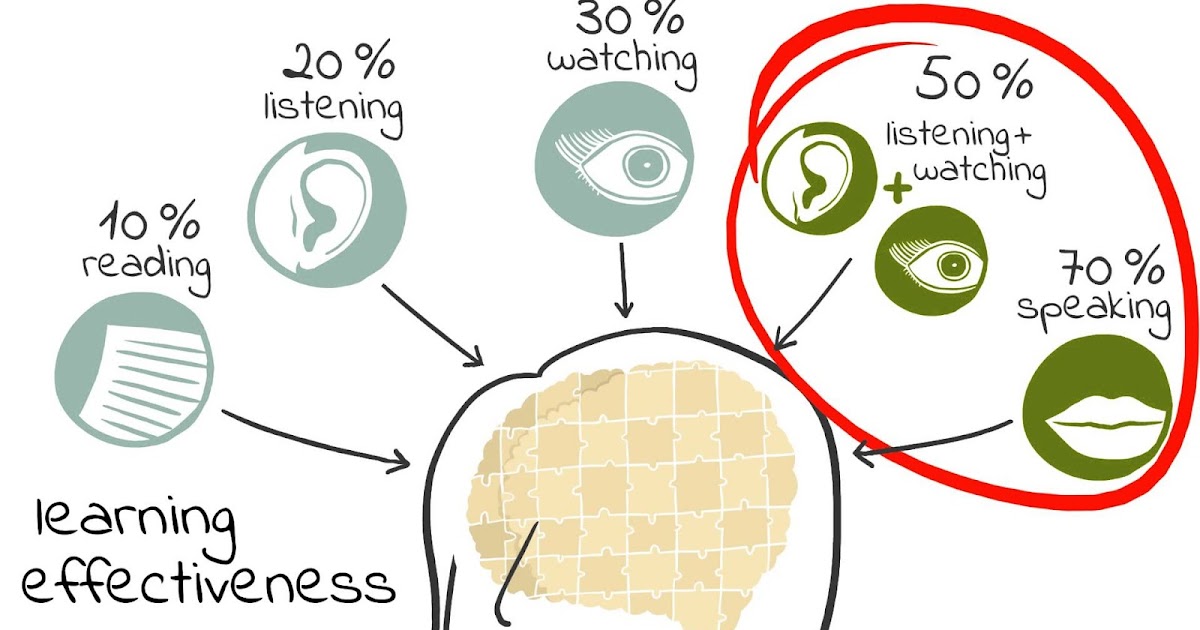 As fine motor skills advance, so does the ability to write, draw and copy shapes, which eventually can be combined to form letters.
As fine motor skills advance, so does the ability to write, draw and copy shapes, which eventually can be combined to form letters.
There are plenty of ways parents can encourage pre-literacy skills in children, including pointing out letters, providing ample opportunities for playing with language, and fostering an interest in books. It can be helpful to ask a child about their day and talk through routines to assist with the development of narrative skills.
Visit your local library and bookstore as often as possible. The more kids read with their parents, teachers and caregivers, the more books become a familiar and favorite pastime. Young children should be encouraged to participate in reading by identifying the pictures they recognize and turning the pages.
Discover more about fostering pre-literacy skills.
1. The Phonics Method
The smallest word-part that carries meaning is a phoneme. While we typically think of letters as the building blocks of language, phonemes are the basic units of spoken language. In an alphabetic language like English, sounds are translated into letters and letter combinations in order to represent words on the page. Reading thus relies on an individual’s ability to decode words into a series of sounds. Encoding is the opposite process and is how we spell.
In an alphabetic language like English, sounds are translated into letters and letter combinations in order to represent words on the page. Reading thus relies on an individual’s ability to decode words into a series of sounds. Encoding is the opposite process and is how we spell.
The Phonics Method is concerned with helping a child learn how to break words down into sounds, translate sounds into letters and combine letters to form new words. Phonemes and their corresponding letters may be taught based on their frequency in English words. Overall there are 40 English phonemes to master and different programs take different approaches to teaching them. Some materials introduce word families with rhyming words grouped together. It’s also possible to teach similarly shaped letters or similar sounding letters together.
The Phonics Method is one of the most popular and commonly used methods. In the beginning progress may be slow and reading out loud halting, but eventually the cognitive processes involved in translating between letters and sounds are automatized and become more fluent. However, English is not always spelled the way it sounds. This means some words can’t be sounded out and need to be learned through memorization.
However, English is not always spelled the way it sounds. This means some words can’t be sounded out and need to be learned through memorization.
2. The Whole-word Approach
This method teaches reading at the word level. Because it skips the decoding process, students are not sounding out words but rather learning to say the word by recognizing its written form. Context is important and providing images can help. Familiar words may initially be presented on their own, then in short sentences and eventually in longer sentences. As their vocabulary grows, children begin to extract rules and patterns that they can use to read new words.
Reading via this method is an automatic process and is sometimes called sight-reading. After many exposures to a word children will sight-read the majority of the vocabulary they encounter, only sounding out unfamiliar terms.
Sight-reading is faster and facilitates reading comprehension because it frees up cognitive attention for processing new words. That’s why it is often recommended that children learn to read high frequency English vocabulary in this way. The Dolch word list is a set of terms that make-up 50-75% of the vocabulary in English children’s books.
That’s why it is often recommended that children learn to read high frequency English vocabulary in this way. The Dolch word list is a set of terms that make-up 50-75% of the vocabulary in English children’s books.
Learn more about teaching sight-reading and the Dolch List.
3. The Language Experience Method
Learning to read nonsense words in a black-and-white activity book is not always the most effective approach. The Language Experience Method of teaching reading is grounded in personalized learning where the words taught are different for every child. The idea is that learning words that the child is already familiar with will be easier.
Teachers and parents can then create unique stories that use a child’s preferred words in different configurations. Children can draw pictures that go with them and put them together in a folder to create a special reading book. You can look for these words in regular children’s fiction and use them to guess at the meaning of unknown words met in a context – an important comprehension strategy that will serve kids in later grades.
8 Tips for parents
No matter which method or methods you use, keep these tips in mind:
-
Read as often as possible. Develop a routine where you read a book together in the morning or in the evening. You may start by reading aloud but have the child participate by running a finger along the text. Make reading fun, include older children and reserve some family reading time where everyone sits together with their own book to read for half an hour—adults included!
-
Begin with reading material that the child is interested in. If he or she has a favorite subject, find a book full of related vocabulary to boost motivation.
-
Let the child choose his or her own book. When an individual has agency and can determine how the learning process goes, he or she is more likely to participate. Take children to libraries or bookstores and encourage them to explore books and decide what they would like to read.
-
Consider graded readers. As a child develops his or her reading ability, you will want to increase the challenge of books moving from materials that present one word per page to longer and longer sentences, and eventually, paragraph level text. If you’re not sure a book is at the right level for your child, try counting how many unfamiliar words it contains per page. You can also take the opposite approach and check to see how many Dolch words are present.
-
Talk about what you see on the page. Use books as a way to spur conversation around a topic and boost vocabulary by learning to read words that are pictured but not written. You can keep a special journal where you keep a record of the new words. They will be easier to remember because they are connected through the story.
-
Avoid comparisons with peers. Every child learns to read at his or her own pace. Reading is a personal and individual experience where a child makes meaning and learns more about how narrative works as he or she develops stronger skills.

-
Don’t put too much pressure. Forcing a child into reading when he or she is not ready can result in negative reactions and cause more harm than good.
-
Do speak with your child’s teacher. If your child doesn’t enjoy reading and struggles with decoding and/or sight reading, it may be due to a specific learning difficulty. It’s advised you first discuss it with your child’s teacher who may recommend an assessment by a specialist.
Learning difficulties
If reading is particularly challenging and your child isn’t making progress there could be a specific learning difficulty such as dyslexia or ADHD that is causing the problem. Conditions like dyslexia are hereditary and it’s not unlikely that another family member will also have a hard time with reading. Visual processing, visual impairment and hearing impairment can also cause reading difficulties.
In the case of the latter, if you can’t hear the words it’s hard to identify the sounds inside them and develop an understanding of phonics. Hearing impairment based reading difficulties are a common issue in teaching children with Down syndrome to read.
Hearing impairment based reading difficulties are a common issue in teaching children with Down syndrome to read.
Orton-Gillingham
Orton-Gillingham is an approach designed to help struggling readers. It’s based on the work of Dr. Samuel Orton and Dr. Anna Gillingham and has been in use for the past 80+ years. Orton-Gillingham allows every child to proceed at a pace that is right for him or her and introduces English phonics in a multi-sensory way.
For example, children may see a letter combination, say it aloud and trace it in the air with their finger. Rich sensory experiences help to enhance learning and can be provided using different materials like drawing in sand, dirt, shaving cream or chocolate pudding. Children may form letters using their hands or move in a rhythmic way that mimics the syllables in a word. Singing, dancing, art activities and plenty of repetition develop reading skills.
Learn more in this post on taking a multi-sensory approach to reading.
Touch-typing and multi-sensory reading
TTRS is a touch-typing program that follows the Orton-Gillingham approach and teaches reading in a multi-sensory way. Children see a word on the screen, hear it read aloud and type it. They use muscle memory in the fingers to remember spelling – which is particularly important for children who have dyslexia-- and practice with high frequency words that build English phonics knowledge and decoding skills. Learning happens via bite-size modules that can be repeated as often as is needed. Progress is shown through automatized feedback and result graphs build confidence and motivation.
Learn more
Children as young as 6-7 can begin learning to type as soon as their hands are big enough to rest comfortably on the keyboard. Discover more about teaching kids to type and the benefits of typing in these posts.
How to teach reading, or a brief overview of methods of teaching reading
How to teach a child to read? How to make this process fun and interesting? What is the best age to start learning to read? These and many other similar questions concern modern parents.
I am glad that the question “How to get a child to read?” is a thing of the past.
Modern society is inclined to ensure that any "learning" becomes voluntary, the task of the teacher and parent is to motivate for some new action, to make the learning process such that the child himself wants to learn.
Teaching reading is an important topic for parents of preschool children. So how do you make this process fun and literate?
Many parents begin to teach reading “on a whim”, which sometimes leads to sad results: either the child loses the desire to learn to read, or when entering grade 1, a small student has problems in mastering some topics related to spelling and pronunciation of words. Sometimes the two problems go hand in hand.
You might be interested in the online conference “Reading. Motivation. Children”
So, in order to avoid mistakes, here are some of the most common methods of teaching reading.
It is worth considering that when writing an article I rely on a purely personal perception of methods and on personal experience as a primary school teacher.
Many are familiar from the school curriculum.
Based on phonetics - teaching the pronunciation of letters and sounds. This is a sound, or otherwise, phonetic method that develops a child's phonemic hearing, allows you to hear and highlight sounds in words. This technique does not require a lot of expensive teaching didactic material in the form of cards, diagrams, notebooks.
There are plenty of games and exercises to help your child learn to isolate sounds from speech while playing on the go.
The basis of the traditional way of teaching reading is, first of all, acquaintance with sound, learning to distinguish it at the beginning, middle, end of a word, and only then acquaintance with its lettering in writing.
Parents often make a common mistake: they buy bright cubes that speak alphabets, manuals, where a certain image is assigned to a specific letter (A-Watermelon, H-Teapot, etc. ) The child remembers the image-letter, but it is difficult for him to read the word , because it is necessary to carry out analytical work, which is still beyond the strength of a preschooler.
) The child remembers the image-letter, but it is difficult for him to read the word , because it is necessary to carry out analytical work, which is still beyond the strength of a preschooler.
It's good when parents comment on learning and teach a child to single out individual sounds in words, they conduct a syllable-sound analysis of words. Let's summarize: the sound method of teaching reading begins with an acquaintance with the sound, proceeds to the image of this sound in writing, and as a fixation, the correct correlation of sounds and letters. Teaching involves learning to read on the basis of warehouses. A warehouse is a pair of a consonant and a vowel, or a consonant and a hard or soft sign. Or one letter. With the help of this technique, reading and the logic of building words are quickly assimilated, there are many fun and outdoor games, there is no binding to a specific age The only negative that can “emerge” in elementary school is that it is difficult to study the composition of a word later on. are not learned, their style is remembered in the game. All cubes differ in size, color and sound that they make so that the child in the learning process can feel the difference between a consonant and a vowel, hard and deaf, voiced and soft. So, a wonderful technique for teaching reading to individuals or in small groups. And, it is worth noting, a parent who has decided to deal with a child using this method should still understand well that learning should take place through a game, and not through the usual connection of cubes. It is clear that at home it is difficult to do, as it requires certain financial costs and laborious work on the production of didactic material, but for those who wish to send their child to Montessori groups, a few words about teaching reading according to this program This is probably the only method in which the material is distributed for kinesthetics, auditory and visual learners separately, since the principle of learning is based on the "two-hemispheric" work of the brain. The associative method of memorizing both individual letters and rules, exercises is used - everything is learned jokingly, playing. For example, at the initial stage, a letter can be laid out from buttons, molded - an excellent job for kinesthetics; with a letter, you can make a small couplet - why not a memory for audials? Н and in my opinion, this system of education is perfect for creative children and parents, teachers, but it will be meaningless for those who prefer a strict structure, logic. It is based on the traditional method, but added with original features. Of course, these are not all methods of teaching reading, one could also mention the system of Doman and Sergey Polyakov, do not forget the method of Pavel Tyulenev, however, all the principles of teaching come down to single rules, which, let me combine into the following code: You might be interested in the webinar “Functional reading in working with foreign and bilingual children” Lastly, the interest of the trainee himself to the basic rules of a particular technique should be taken into account. To the question "When is it time for a child to be able to read? » there is no ready-made answer, but we want to immediately warn against two misconceptions: “It is not necessary to teach a child to read at home, they will teach you at school anyway. "There is no time to waste - the sooner the baby begins to read, the better." All children are different and develop at their own pace. Therefore, you should not impose teaching reading to a preschooler as soon as he is 4-5 years old, if the student himself does not yet show interest in this activity. Instead, you can begin to develop an interest in reading through bright and engaging books. A good option would also be games that involve letters. The indicator to be guided by is not the age of a preschooler, but his speech skills. It's time to learn to read if… If the speech development of a preschooler proceeds without gross violations. Let's figure out what criteria will help you find out if a child is ready to learn to read: Understanding addressed speech. The kid must understand sentences, phrases, individual words that others around him turn to. Vocabulary. The more words a child knows, the better he will understand what he read. It will also help him communicate with adults and other children. Grammar. The ability to correctly build sentences, select and change words is important for children who are learning to read. Pronunciation. Remember: at preschool age, a child may have minor flaws in grammar and pronunciation - this is normal. Over time, these violations will be corrected, and they should not be considered an obstacle to reading. But if the baby is not yet very confident in speaking, do not rush him to read - this will not help develop speech, but only demotivate. Skysmart Study Box Download the box to make studying easier and more fun. Learn about life hacks and games that will keep your child interested in learning. Close knowledge gaps with games and comics It's hard for us adults to imagine how difficult it really is for a baby to learn from scratch such a complex skill as reading. If parents take the child's progress for granted and express dissatisfaction when the child does not understand something, this will not push the future student to development, but will only complicate the process. Therefore, it is important to praise for small victories: I learned the letter that was passed last time - great, I coped without my father's help with the word as much as two syllables - clever. Do not take failures as a result of the negligence of the little student. When a child does not understand the first time, this is an occasion to look for another explanation or give more time to practice. If you feel tired and irritated, you should stop the activity and return to it in a good mood. Do not expect perseverance and a desire to spend hours figuring out unfamiliar letters from your baby. But regular practice is important - much more important than the duration of the session. And it doesn’t have to be just lessons: you can look for familiar letters on signs during a walk, on a door plate in a children’s clinic, on a package of your favorite corn flakes. In a series of studies conducted by Dr. Victoria Purcell-Gates among five-year-olds who could not yet read, those children to whom their parents regularly read aloud for two years expressed their thoughts in more literary language, built longer phrases and used more complex syntax. In addition, reading aloud with adults contributed to the expansion of children's vocabulary, as parents explained the meanings of new words that children did not encounter in everyday life. Expert Opinion According to neuroscientist Marianne Wolfe, book evenings with parents help develop a love of reading because the child develops a connection between reading aloud and feelings of love and warmth. The role of communication in teaching literacy cannot be overestimated. At first, it is important to ask if the future student is interested, if he is tired, what was remembered from the lesson. When a preschooler learns to read coherent texts, be sure to ask questions about their content. It's great if the child reads on his own and without the prompting of the parents, but even in this case, do not deprive him of the opportunity to discuss what he read with you. Which of the characters do you like? Do you think this character is like you? Would you like to be like her? What would you do if you were a hero? Why did the described event happen? How are these two events related? How did what you read make you feel? What do you remember most from what you read? What do you think the author wanted to teach? Why did he write this? Do you agree with the author? It is important to select questions individually, based on the age of the child. With younger children, discuss everything together, ask simple questions, direct their attention to some facts. From the correspondence between sounds and letters to syllables, from short words to longer and more complex words. It would seem that this is obvious, but no: sometimes parents are so happy with the success of the child at first that they push him to study more complex topics than he is ready to accept. Of course, the program should adapt to the future student, but you should not skip steps, even if the child is making progress. There are methods that offer to teach a child to read by memorizing whole words. Alas, experiments show that such techniques generally work worse. For example, a group of scientists from the United States came up with an artificial alphabet and offered subjects to learn it, and then read the words written using this alphabet. Therefore, we advise you to choose those teaching methods that involve clear instructions about the relationship between sound and letter - and this is especially important for those children who have difficulty reading. Below we have compiled a few of these techniques that you can use to teach your preschooler at home. The way to teach a child to read through warehouses was actually used in Rus', but for modern parents this technique is associated with the name of the philologist Nikolai Alexandrovich Zaitsev. Zaitsev suggests not focusing on the study of individual letters, as it can be difficult for students to understand how letters can merge into syllables and words. Teaching a child to read by syllables is also not always easy: one syllable can be quite long ( shine, ruble ), and the boundaries of syllables are not obvious ( Lun-tik or Lu-ntik ?). Therefore, in Zaitsev's methodology, a warehouse is used as the main unit. Warehouse can be a combination of a consonant and a vowel (pa-pa, ma-ma), a single consonant or vowel (de- d , i-s -li, A -le-sha), as well as a combination of a consonant with a hard or soft sign (ma- l -chi-k, use d -yem). In order for a preschooler to understand the differences between the recording of voiced and soft, vowels and consonants, different types of warehouses have their own cube size, color and content, thanks to which the cubes sound when they are shaken. One of the advantages of the technique is that children willingly play with blocks themselves, and the process of learning to read becomes active, mobile. This technique, according to some sources, was developed by the Romans. Later, Nadezhda Sergeevna Zhukova, a Soviet and Russian speech therapist, created a primer based on it. In it, she built her own system in which sounds and letters are sequentially introduced into speech. Due to the fact that the concept of a syllable is introduced at an early stage, it is faster and easier to teach a child to read syllables together. By the way, as in Zaitsev's technique, it is proposed to sing syllables, and not just pronounce them. Based on the syllabic method, Zhukova developed a set of teaching aids - copybooks, copybooks and a book for reading. Benefits will help teach children to read correctly 6 and 7 years old at home. Both techniques for teaching preschoolers to read are used in the Skysmart Ready for School course. The course consists of two stages: first, children get acquainted with letters and warehouses, which allows them to quickly start reading simple words, and then they learn what a syllable is. Gradually, we introduce more complex syllabic constructions, move on to reading phrases and sentences. This method originated in the USSR and is still considered the main one in Russian schools and kindergartens. It was developed by the Soviet teacher and Russian language methodologist Voskresenskaya Alexandra Ilyinichna. Like N.S. Zhukova, Voskresenskaya proposed her own order in which children should learn letters and sounds. Two-letter syllables (including one consonant): am, ma, ra, etc. and simple words from them: ra-ma, ma-sha, Pa-sha, etc. Three-letter syllables with a central vowel: poppy, lat, etc. The combination of the first two stages into words: sa-lat, earth-la, etc. Words of three syllables and six letters: az-bu-ka, ve-se-lo, etc. Words of two syllables and six letters: question-ros, tea-nick, etc. Words with a combination of vowels at the beginning and at the end of the word: chair, March, etc. In this way, children simultaneously prepare for more complex syllables at each stage and reinforce what they have learned earlier. Learning to read, as a rule, takes place in several stages. First, the child listens to the sound, visually remembers the letters. Different games will help with this, where you need to look for letters, invent words, etc. When this stage is over, you can move on to syllables and games to work them out. And only after that it will be possible to proceed to words, and then to sentences and texts. The first step is to teach your child to recognize letters. To do this, you can use pictures with hidden letters. We use such exercises in the preparation for school lessons in Skysmart. Ask your child to identify what letter a word begins with, or name as many words as possible that begin with a certain letter. Next, we train to distinguish correctly written letters from incorrect ones. This is also important for learning to write: preschoolers often mirror letters or distort individual elements. To learn how to distinguish between vowels and consonants, tasks will help you determine the sound with which a word begins. It will also help to remember the difference between vowels and consonants and search for an extra letter. When your child can read short words, ask him to make a word out of letters on his own. Composing words from syllables is convenient if you have cubes at hand, but you can also try on paper. Another good exercise is to fill in the missing letter in the word.
Sometimes I hear the opinion that this technique is boring, requires rote memorization, and evokes boredom. Ready to argue.
There are a lot of tricks when boring reading columns of syllables "pro, pra, pru" turns into an exciting game: 

As in most methods, this one is based on the game.
Due to the associative series, vocabulary is expanding, imagination and logic are developing.
And what about turning a letter into a fantastic image - this visual technique will surely appreciate it.
Many teaching methods in teaching reading in the classroom, of course, many teachers impose on the traditional methodology to develop cognitive interest.  For this system, only a textbook developed by a teacher is needed, which makes the learning process accessible to everyone.
For this system, only a textbook developed by a teacher is needed, which makes the learning process accessible to everyone.
The main task of the primer is to teach the child to merge letters into syllables, and to form words from syllables. Sufficiently the same type of work throughout the entire training, which can cause denial in the child, since the sign system is still poorly perceived for him. According to the author, in speech activity, it is easier for a child to single out a syllable than a sound in a spoken word - this is what training is built on.

Related articles
How to easily teach a child of 4-6 years old to read - the best methods and exercises
How to understand that it's time
 ” Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child.
” Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child. 
 For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors. Making reading easier for preschoolers
Praise more and never scold
 After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text.
After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text. Exercise little but regularly
 It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games.
It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games. Read books aloud
Discuss read
 For example, you can ask:
For example, you can ask:
 The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences.
The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences. Go from simple to complex
 At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second.
At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second. Methods of teaching preschoolers to read
Warehouse reading
 Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective.
Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective. Syllabic reading
Sound analytical-synthetic teaching method
 The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:

Exercises for learning to read
Letter memory exercises
Exercises for vowels and consonants
Word Building Exercises