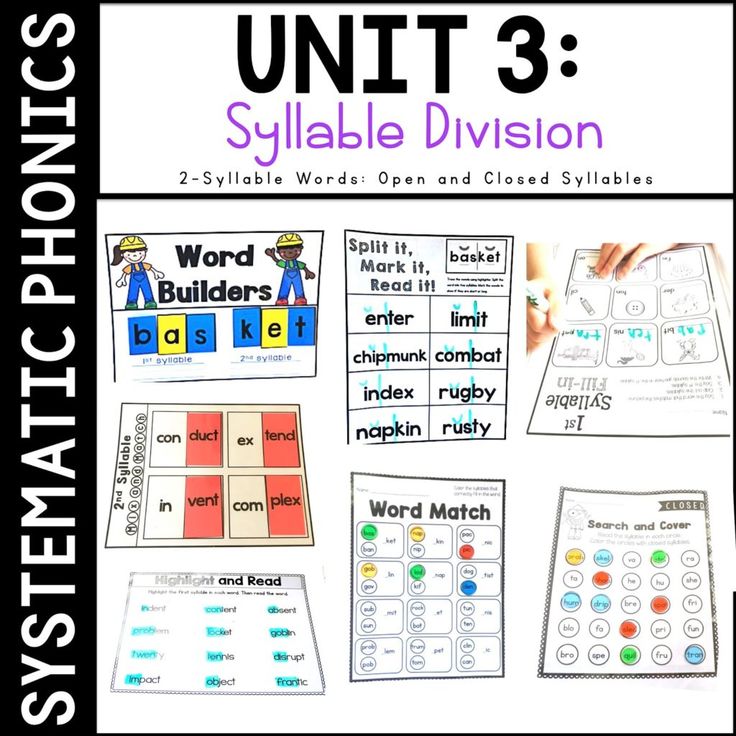
Reading leveling systems
A Guide to Reading Levels and Leveled Reading Systems
Leveled reading systems are significant because students must read certain materials at their appropriate level in school. Assessing reading levels is key, if they are not at their proper reading level, they will have difficulty in the classroom. This can affect the child’s interest in a topic or text, which can either help or hinder their comprehension. Reading levels are used to determine if a child is struggling with their reading. Reading scores are significant for parents and teachers of children from kindergarten through grades 2-3. These formative years are vital to developing essential literacy skills. Many studies have shown the relationship between poor reading scores in early grades and poor performance in later grades.
These levels are not just important to teachers during the school year, but parents must be aware Reading levels are significant to help determine if a child is reading below grade level or above grade level. Reading levels are also used to assist in determining appropriate classroom placement. Reading scores are often used for educational interventions, which can benefit struggling readers.
What is the Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
The Developmental Reading Assessment(DRA) is a standardized reading test used to determine a student’s instructional level in reading. The DRA is administered individually to students by teachers or reading specialists. Students read aloud a selection (or selections) to the proctor. As the levels increase, so does the difficulty.
You can assess reading comprehension, fluency, and accuracy using the DRA numerical scale. Students are described as being near, at, or significantly below grade level. Once you’ve obtained the student’s DRA score, you can compare it to books at the correct level.
The DRA has the students read a passage aloud to the proctor. The teacher/proctor is looking for several things while the student is reading the passage:
Prosody, Pronunciation, Expression, Word accuracy, Miscues, substitutions, self-corrections, re-reading, sounding out
Once the student has five errors in a passage, the assessment, and the previous passage is used for scoring.
Reading passages correlate to their corresponding grade level. Reading levels on the DRA have standard scores ranging from 0-44. Examples of reading levels, an average first-grade reading level ranges from 4-16. We would expect the student in the higher ranges at the end of the school year. The Reading levels ranges are:
- Reading Level 4-28 (First and second grades combined)
- Reading Level 20-38 (Second and third grades combined)
- Reading Level 30-44 (Third and fourth grades combined)
You can see the standard ranges in the correlation chart at the end of the article.
What is the Fountas and Pinnell Guided Reading Assessment
Fountas and Pinnell Reading Levels Grade Equivalents is another prevalent reading assessment tool in many elementary schools. Fountas and Pinnell(sometimes referred to as the guided reading level system) is the publisher and creator of this reading assessment. The administration of the Fountas-Pinnell is very similar to the DRA, and the scores are cross-referenceable to the DRA.
The Fountas and Pinnell Benchmark Assessment System is also conducted by having students read selections in increasing difficulty. The teacher will have the student read the passage and count miscues, errors, self-corrections. These miscues are what the teacher will score as Reading Errors.
What is the Lexile Framework for Reading?
The Lexile Framework was developed in 2000 by MetaMetrics, a company that created the SAT I exam. Since then, it has been used widely with 100 companies and publishers in the United States using it.
Your youngster receives a Lexile reading level from a school or state test, not a “Lexile” assessment. The range of the Lexile measure ranges from less than 0L for early readers to more than 2000L for advanced readers. If a reader’s score is less than 0L, they are labeled as a beginning reader. If you’re not sure what your child’s Lexile reading score is, ask their teacher.
The Lexile Framework for Reading is a measure that gives a rigorous, comprehensive description of text complexity based on sentence length and word difficulty. This Framework makes it possible to match readers with targeted text that builds their vocabulary, comprehension, and fluency–the essential elements of reading success. The
This Framework makes it possible to match readers with targeted text that builds their vocabulary, comprehension, and fluency–the essential elements of reading success. The
The Lexile Framework, a more stringent numerical filtering, analyzes a book’s difficulty and matches the reader’s skill to the text’s Lexile level. This system from MetaMetrics, a UK-based educational measurement firm, targets books at the correct reading level for the child’s skill. It’s comprised of an algorithm that analyzes both words and sentence length at the same time.
Only prose is included in the Lexile database. NP and Non-Prose are two words used to categorize poems, plays, and songs. A book is classified as an Adult Directed, or AD, work if shared as a read-aloud. A book is a Nonconforming Text, or NC if its words and sentence length are more complicated than the subject matter. An NC book is appropriate for older readers who require age-appropriate material. BR(beginning readers) is the term used to describe books with a Lexile score of zero or less.
An Overview of Leveled Reading Systems
Spread the love
Looking for information about leveled reading systems? Well, we have you covered. In this article, we will provide you will a brief overview of leveled reading systems.
Grade Level Equivalent
The Grade Level Equivalent denotes the readability of the text by grade. It is a manifestation of the grade level at which a learner reading on-grade could read the book independently. For instance, a learner who is in the first month of 4th grade and reading on-grade would be matched to a book with a Reading Level of 4.1. Each grade level has a .1 to .9 range.
Guided Reading Level
The guided reading level system gives a precise literacy level for books. This alphabetic system has many levels within each grade level. For example, grade 2 is equivalent to guided literacy levels J through M. This allows you to tailor your reading program accurately to a wide range of reading capabilities. Each book is carefully assessed before being leveled, and educator input is considered in the leveling process.
Each book is carefully assessed before being leveled, and educator input is considered in the leveling process.
The Lexile Framework® for Reading
The Lexile Framework, a better numerical filter, assesses a book’s difficulty and matches reader ability and content difficulty based on the numeric Lexile scale. This system from education assessment company MetaMetrics targets books on the right literacy level for the kid’s ability. It is predicated on an algorithm that measures vocabulary and sentence length.
DRA
Developmental Reading Assessment is a reading assessment tool that identifies students’ independent literacy levels in grades K–8. Using the DRA numerical scale, you can assess reading accuracy, fluency, and comprehension. Learners are near, at, or above grade level, below grade level, or significantly below grade level. Once you know the learner’s DRA score, you can match that score with books appropriately.
Grade Level
Filtering books by grade level is a coherent system. If you utilize a basal series to teach reading, you probably utilize this system. If you’re looking for science books for a unit of study, a grade level search is precise enough.
If you utilize a basal series to teach reading, you probably utilize this system. If you’re looking for science books for a unit of study, a grade level search is precise enough.
Reading Recovery
Reading Recovery is a one-on-one remediation program designed to supplement reading instruction for learners in grades K–2 who are slow to read. You can compare Reading Recovery and guided literacy levels; Reading Recovery levels have limited usefulness when used by themselves.
Unleveled books
If you can’t identify a level for a book, compare it to similar leveled books. Remember, you will need to assess whether a book is developmentally appropriate for a given learner or group. For example, just because a young learner can read a book about the Holocaust does not mean the subject is appropriate for that learner. Another example is a book written in slang may be difficult for learners to comprehend.
Concluding thoughts
Observe your unique learners, the subject matter, your colleagues, and your learners’ parents. Be flexible and trust your judgment. A well-informed educator who understands leveling systems and knows their learners will make wise choices about books.
Be flexible and trust your judgment. A well-informed educator who understands leveling systems and knows their learners will make wise choices about books.
Immersive Reader - Immersive Reading Tools
Favorites
Featured
Explore the most popular Azure products
AI + machine learning
AI + Machine Learning
Build the next generation of AI applications for any developer, any scenario.
Analytics
Analytics
Get the benefits of collecting, storing, processing, analyzing, and visualizing data of any type, size, and speed.
Computing environment
Computing
Take advantage of cloud computing and scale on demand. At the same time, you pay only for the resources that you use.
Containers
Containers
Develop and manage containerized applications faster with built-in tools
Database
Databases
Continue to grow rapidly and innovate quickly with secure, fully managed, enterprise-grade database services.
Devops
DevOps
Innovate quickly with simple, reliable tools for continuous delivery
Developer Tools
Developer Tools
Build, continuously deliver and manage cloud applications using any platform and any language
Hybrid and multi-cloud environment
Hybrid and multi-cloud
Get the latest from Azure anywhere - add cloud computing agility and innovation to your on-premises workloads
certificate
Identity
Manage user identities and access to protect devices, data, applications, and infrastructure from advanced threats
Integration
Integration
Effortlessly integrate on-premises and cloud applications, data and processes across the enterprise.
Internet of Things
IoT
Connect resources or environments, discover analytics and take smart actions to transform your organization
Control
Control
Simplify, automate, and streamline cloud resource management and compliance
Multimedia
Multimedia
High quality video delivery anywhere, anytime, to any device
Migration
Migration
Simplify and accelerate cloud migration with our guides, tools and resources
mixed reality
Mixed Reality
Connect the real and digital worlds in immersive and interactive solutions
Mobile applications
Mobile apps
Build and deploy cross-platform and native apps for any mobile device
Networking
Networking
Connect cloud and on-premises services and infrastructure to deliver the best experience for your customers and users.
Safety
Security
Enterprise Threat Protection for Hybrid Cloud Workloads
storage
Storage
Get highly scalable, secure cloud storage for your data, applications, and workloads.
Internet
Internet
Quickly and efficiently build, deploy and scale powerful web applications
Windows Virtual Desktop
Windows Virtual Desktop
The best virtual desktop experience provided by Azure
What is Tile Alignment System (TSL) video
Author Admin Read 5 min. Views 62 Such work is within the power of real masters of facing. When laying, most of the time is spent on leveling the tiles with each other, so that they form a strictly flat surface and have the same thickness of the joints between them. To do this, the craftsmen use rules, building levels and plastic crosses that fix the distance between the tiles.
To do this, the craftsmen use rules, building levels and plastic crosses that fix the distance between the tiles.
But if you use a special device called a tile leveling system (SVP), then the productivity of an experienced tiler can double. Those who want to revet the bathroom with their own hands, even in the absence of certain skills, can do a good job with this type of work using such simple and very original devices. Learn more about what SVP is and how to use it in this informational material.
Contents
- The principle of the tile leveling system
- Which SVP manufacturers offer
- What is included in the SVP
- Video
The principle of the tile leveling system
The SVP tile leveling system consists of two small plastic parts. One of them is made in the form of a wedge with teeth, and the second is in the form of a key with a round or polygonal base and is called a clamp. On the laid tile, two clamps are inserted on each side, under its base. The wall thickness of this part controls the thickness of the seam. Next, the next one is installed close to the leg of the clamp, into which a wedge is inserted and pressed against both tiles with a light tap. Thus, they are aligned in one plane.
The wall thickness of this part controls the thickness of the seam. Next, the next one is installed close to the leg of the clamp, into which a wedge is inserted and pressed against both tiles with a light tap. Thus, they are aligned in one plane.
Inserting two devices into each seam, cover the entire surface. In this case, the clamps are installed at a distance of 5 cm from the edge of the tile. Some masters additionally insert plastic crosses in the corners to ensure a perfectly even seam. All clamps and inserted wedges remain in the coating until the adhesive is completely dry. The wedges are then removed and the top of the clamp is broken with a light blow from a rubber mallet. In this case, the base remains under the tiles.
It is important to consider one condition. The first tile must be laid perfectly evenly or with the planned slope. The adhesive that is used for cladding exhibits shrinkage, and it can move the tiles out of place. This phenomenon often occurs if the thickness of the adhesive is more than 5 mm.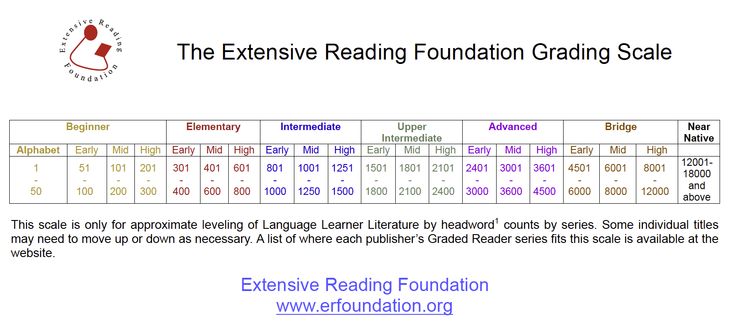 If the SVP do-it-yourself tile leveling system is used, then such an undesirable defect can be completely avoided.
If the SVP do-it-yourself tile leveling system is used, then such an undesirable defect can be completely avoided.
Which SVPs are offered by manufacturers
There are a large number of different types of SVPs on the market, both from domestic manufacturers and from foreign ones. Russian manufacturers offer the market two types of such devices. These are SVP and DLS (DLS). The main difference between SVP and DLS is as follows: if SVP suggests installing two clips on each side of the tile and crosses in the corners, then DLS recommends installing one at a time, moreover, plastic crosses can be omitted. The DLS kit includes a special device that ensures the alignment of four tiles at once.
The Belarusian company "Farton" has developed a similar device, vaguely reminiscent of the Russian SVP, but has different dimensions, which allows it to be used for laying tiles and porcelain stoneware with a thickness of 6 to 14 mm.
Rubi hovercraft from a European manufacturer has appeared on the market. They are made of high quality plastic. Flexible petals of the supporting area securely fix tiles with a thickness of 3 to 20 cm. The screeds are pre-soaked in water, which provides them with a break in one place, and they are removed with special pliers. Such products have some disadvantages. There is an insufficient number of clamping caps in the kit, besides, they exert a small clamping force.
They are made of high quality plastic. Flexible petals of the supporting area securely fix tiles with a thickness of 3 to 20 cm. The screeds are pre-soaked in water, which provides them with a break in one place, and they are removed with special pliers. Such products have some disadvantages. There is an insufficient number of clamping caps in the kit, besides, they exert a small clamping force.
Compared to other models of the Russian manufacturer, the SVP has a simple and at the same time quite robust design. Provides reliable fixation, while the ties are practically not torn. However, to remove the ties, the blow must be directed perpendicular to the seam, otherwise the tie may break in the wrong place.
What is included in the SVP kit
The consumption of accessory clamps depends on the dimensions of the tile. The smaller the tile, the more clamps are used. For example, if the tile has a size of 300x300 mm, then 44 pieces will be used per 1 m2 of the lined surface.